Pancreatic Comorbidities in Pediatric Celiac Disease: Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency, Pancreatitis, and Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
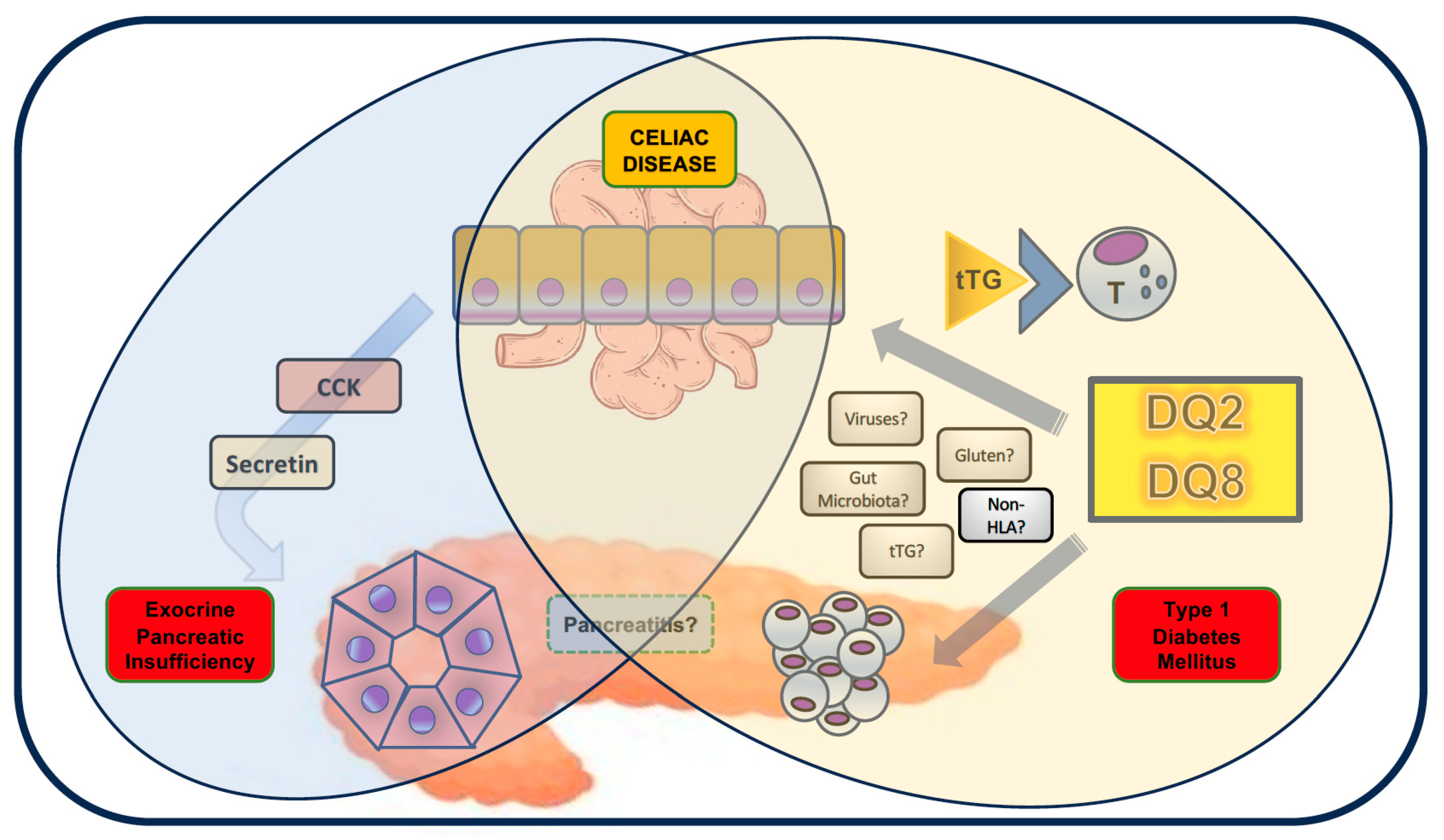
1. Introduction
2. Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency
3. Pancreatitis
4. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
5. Other Potential Pancreatic Comorbidities?
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindfors, K.; Ciacci, C.; Kurppa, K.; Lundin, K.E.A.; Makharia, G.K.; Mearin, M.L.; Murray, J.A.; Verdu, E.F.; Kaukinen, K. Coeliac disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catassi, C.; Verdu, E.F.; Bai, J.C.; Lionetti, E. Coeliac disease. Lancet 2022, 399, 2413–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therrien, A.; Kelly, C.P.; Silvester, J.A. Celiac Disease: Extraintestinal Manifestations and Associated Conditions. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2020, 54, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanacci, V.; Vanoli, A.; Leoncini, G.; Arpa, G.; Salviato, T.; Bonetti, L.R.; Baronchelli, C.; Saragoni, L.; Parente, P. Celiac disease: Histology-differential diagnosis-complications. A practical approach. Pathologica 2020, 112, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Arora, A.; Strand, T.A.; Leffler, D.A.; Catassi, C.; Green, P.H.; Kelly, C.P.; Ahuja, V.; Makharia, G.K. Global prevalence of celiac disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.A.; Jeong, J.; Underwood, F.E.; Quan, J.; Panaccione, N.; Windsor, J.W.; Coward, S.; deBruyn, J.; Ronksley, P.E.; Shaheen, A.A.; et al. Incidence of celiac disease is increasing over time: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 507–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poddighe, D.; Abdukhakimova, D. Celiac Disease in Asia beyond the Middle East and Indian subcontinent: Epidemiological burden and diagnostic barriers. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 2251–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, E.; Pjetraj, D.; Gatti, S.; Catassi, G.; Bellantoni, A.; Boffardi, M.; Cananzi, M.; Cinquetti, M.; Francavilla, R.; Malamisura, B.; et al. Prevalence and detection rate of celiac disease in Italy: Results of a SIGENP multicenter screening in school-age children. Dig. Liver Dis. 2023, 55, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddighe, D.; Rakhimzhanova, M.; Marchenko, Y.; Catassi, C. Pediatric Celiac Disease in Central and East Asia: Current Knowledge and Prevalence. Medicina 2019, 55, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonicola, A.; Wieser, H.; Gizzi, C.; Soldaini, C.; Ciacci, C. Associations between celiac disease, extra-gastrointestinal manifestations, and gluten-free diet: A narrative overview. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpińska, M.; Czauderna, M. Pancreas—Its functions, disorders, and physiological impact on the mammal’s organism. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 807632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Pan, A.; Fu, Y.; Dai, Y. Chapter 1—Anatomy and Physiology of the Pancreas. In Integrative Pancreatic Intervention Therapy A Holistic Approach; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Fusco, J.; El-Gohary, Y.; Gittes, G.K. Chapter 90—Anatomy, Physiology, and Embryology of the Pancreas. In Shackelford’s Surgery of the Alimentary Tract, 8th ed.; Yeo, C.J., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1062–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Heaton, E.S.; Jin, S. Importance of multiple endocrine cell types in islet organoids for type 1 diabetes treatment. Transl. Res. 2022, 250, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capurso, G.; Traini, M.; Piciucchi, M.; Signoretti, M.; Arcidiacono, P.G. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency: Prevalence, diagnosis, and management. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcomb, D.C.; Buchner, A.M.; Forsmark, C.E. AGA Clinical Practice Update on the Epidemiology, Evaluation, and Management of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Barkin, J.A.; Barkin, J.S. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is common in celiac disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 3421–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regan, P.T.; DiMagno, E.P. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in celiac sprue: A cause of treatment failure. Gastroenterology 1980, 78, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansaldi, N.; Oderda, G. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in celiac sprue. Gastroenterology 1981, 80, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroccio, A.; Iacono, G.; Montalto, G.; Cavataio, F.; Di Marco, C.; Balsamo, V.; Notarbartolo, A. Exocrine pancreatic function in children with celiac disease before and after a gluten-free diet. Gut 1991, 32, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroccio, A.; Iacono, G.; Montalto, G.; Cavataio, F.; Lorello, D.; Soresi, M.; Di Martino, D.; Notarbartolo, A. Pancreatic insufficiency in celiac disease is not dependent on nutritional status. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1994, 39, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroccio, A.; Iacono, G.; Ippolito, S.; Verghi, F.; Cavataio, F.; Soresi, M.; Giannitrapani, L.; Notarbartolo, A.; Montalto, G. Usefulness of faecal elastase-1 assay in monitoring pancreatic function in childhood celiac disease. Ital. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1998, 30, 500–504. [Google Scholar]
- Carroccio, A.; Verghi, F.; Santini, B.; Lucidi, V.; Iacono, G.; Cavataio, F.; Soresi, M.; Ansaldi, N.; Castro, M.; Montalto, G. Diagnostic accuracy of fecal elastase 1 assay in patients with pancreatic maldigestion or intestinal malabsorption: A collaborative study of the Italian Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Hepatology. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2001, 46, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkowiak, J.; Herzig, K.H. Fecal elastase-1 is decreased in villous atrophy regardless of the underlying disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 31, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.C.; Morán, C.E.; Mauriño, E.C.; Bai, J.C. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuluce, M.E.; Barutcu, A.; Yavuz, S.; Agin, M.; Cetiner, S.; Tumgor, G. Evaluation of pancreatic functions in cases of primary and secondary malnutrition. Minerva Pediatr. 2022, 74, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamilova, A.T.; Azizova, G.K.; Poddighe, D.; Umarnazarova, Z.E.; Abdullaeva, D.A.; Geller, S.I.; Azimova, N.D. Celiac Disease in Uzbek Children: Insights into Disease Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics in Symptomatic Pediatric Patients. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nousia-Arvanitakis, S.; Karagiozoglou-Lamboudes, T.; Aggouridaki, C.; Malaka-Lambrellis, E.; Galli-Tsinopoulou, A.; Xefteri, M. Influence of jejunal morphology changes on exocrine pancreatic function in celiac disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1999, 29, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Nousia-Arvanitakis, S.; Fotoulaki, M.; Tendzidou, K.; Vassilaki, C.; Agguridaki, C.; Karamouzis, M. Subclinical exocrine pancreatic dysfunction resulting from decreased cholecystokinin secretion in the presence of intestinal villous atrophy. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 43, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroccio, A.; Iacono, G.; Montalto, G.; Cavataio, F.; Lorello, D.; Greco, L.; Soresi, M.; Notarbartolo, A. Pancreatic enzyme therapy in childhood celiac disease: A double-blind prospective randomized study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1995, 40, 2555–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoosuf, S.; Makharia, G.K. Evolving therapy for celiac disease. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoosuf, S.; Barrett, C.G.; Papamichael, K.; Madoff, S.E.; Kurada, S.; Hansen, J.; Silvester, J.A.; Therrien, A.; Singh, P.; Dennis, M.; et al. Pancreatic enzyme supplementation versus placebo for improvement of gastrointestinal symptoms in non-responsive celiac disease: A cross-over randomized controlled trial. Front. Med. 2023, 9, 1001879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.S.; Dambalkar, A.; Chhabra, P.; Sharma, R.; Nada, R.; Sharma, V.; Rana, S.; Bhasin, D.K. Is pancreatic exocrine insufficiency in celiac disease related to structural alterations in pancreatic parenchyma? Ann. Gastroenterol. 2016, 29, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti Bellocchi, M.C.; Crinò, S.F.; De Marchi, G.; De Pretis, N.; Ofosu, A.; Caldart, F.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Frulloni, L. A clinical and pathophysiological overview of intestinal and systemic diseases associated with pancreatic disorders: Causality or casualty? Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, H.; Ciacci, C.; Soldaini, C.; Gizzi, C.; Santonicola, A. Gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary manifestations associated with untreated celiac disease in adults and children: A narrative overview. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddighe, D.; Dossybayeva, K.; Abdukhakimova, D.; Akhmaltdinova, L.; Ibrayeva, A. Celiac disease and gallbladder: Pathophysiological aspects and clinical issues. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, R.Z.; Freeman, A.J. Pancreatitis in Children. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 68, 1273–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morinville, V.D.; Barmada, M.M.; Lowe, M.E. Increasing incidence of acute pancreatitis at an American pediatric tertiary care center: Is greater awareness among physicians responsible? Pancreas 2010, 39, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nydegger, A.; Heine, R.G.; Ranuh, R.; Gegati-Levy, R.; Crameri, J.; Oliver, M.R. Changing incidence of acute pancreatitis: 10-year experience at the Royal Children’s Hospital, Melbourne. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morinville, V.D.; Husain, S.Z.; Bai, H.; Barth, B.; Alhosh, R.; Durie, P.R.; Freedman, S.D.; Himes, R.; Lowe, M.E.; Pohl, J.; et al. Definitions of pediatric pancreatitis and survey of present clinical practices. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 55, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejczyk, E.; Wejnarska, K.; Dadalski, M.; Kierkus, J.; Ryzko, J.; Oracz, G. The nutritional status and factors contributing to malnutrition in children with chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2014, 14, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, S.N.; Smyth, N.D.; O’Sullivan, M.; Feehan, S.; Ridgway, P.F.; Conlon, K.C. The prevalence of malnutrition and fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies in chronic pancreatitis. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2014, 29, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhani, K.; Farrell, J.J. Autoimmune pancreatitis: An update on diagnosis and management. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 45, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheers, I.; Palermo, J.J.; Freedman, S.; Wilschanski, M.; Shah, U.; Abu-El-Haija, M.; Barth, B.; Fishman, D.S.; Gariepy, C.; Giefer, M.J.; et al. Recommendations for diagnosis and management of autoimmune pancreatitis in childhood: Consensus from INSPPIRE. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 67, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.M.; Deheragoda, M.; Harrison, P.; Devlin, J.; Sellars, M.; Hadzic, N.; Dhawan, A.; Grammatikopoulos, T. Autoimmune pancreatitis in children: A single-centre experience in diagnosis, management, and long-term follow-up. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pretis, N.; Frulloni, L. Autoimmune pancreatitis type 2. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2020, 36, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroccio, A.; Di Prima, L.; Scalici, C.; Soresi, M.; Cefalù, A.B.; Noto, D.; Averna, M.R.; Montalto, G.; Iacono, G. Unexplained elevated serum pancreatic enzymes: A reason to suspect celiac disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliori, M.; Galassi, E.; Gullo, L. Search for celiac disease in subjects with asymptomatic pancreatic hyperenzymemia. Pancreas 2011, 40, 979–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Montgomery, S.M.; Ekbom, A. Risk of pancreatitis in 14,000 individuals with celiac disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadr-Azodi, O.; Sanders, D.S.; Murray, J.A.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Patients with celiac disease have an increased risk for pancreatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1136–1142.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhayyat, M.; Saleh, M.A.; Abureesh, M.; Khoudari, G.; Qapaja, T.; Mansoor, E.; Simons-Linares, C.R.; Vargo, J.; Stevens, T.; Rubio-Tapia, A.; et al. The risk of acute and chronic pancreatitis in celiac disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 2691–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osagiede, O.; Lukens, F.J.; Wijarnpreecha, K.; Corral, J.E.; Raimondo, M.; Krönert, P.T. Acute pancreatitis in celiac disease: Has the inpatient prevalence changed and is it associated with worse outcomes? Pancreas 2020, 49, 1202–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultron, G.; Latif, U.; Park, A.; Phatak, U.; Pashankar, D.; Husain, S.Z. Acute pancreatitis in a child with celiac disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 49, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halabi, I.M. Coeliac disease presenting as acute pancreatitis in a 3-year-old. Ann. Trop. Paediatr. 2010, 30, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, B.J.; Cantor, M.; Retrosi, G.; Gheorghe, R.; Wrogemann, J.; Mujawar, Q. Autoimmune pancreatitis masquerading as celiac disease. Pancreas 2019, 48, e53–e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, M.; Shahrour, M.; Haleem, R.A.; Ciecierega, T. Celiac disease presenting as acute pancreatitis: A case report and review of the literature. J. Gastrointest. Dig. Syst. 2015, 5, 344. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, M.M.; McDaniels, S.; Kyle, K.; Michael, M.; Giacopuzzi, J.; Brown, L.A. Pancreatitis in pre-adolescent children: A 10-year experience in the pediatric emergency department. BMC Emerg. Med. 2019, 19, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uc, A.; Husain, S.Z. Pancreatitis in children. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilian, M.; Jalali, R. Prevalence of celiac disease in children with type 1 diabetes: A review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2021, 15, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, M.; Norström, F.; Persson, M.; Elding Larsson, H.; Forsander, G.; Åkesson, K.; Samuelsson, U.; Ludvigsson, J.; Carlsson, A. Prevalence and Predictive Factors for Celiac Disease in Children With Type 1 Diabetes: Whom and When to Screen? A Nationwide Longitudinal Cohort Study of Swedish Children. Diabetes Care. 2024, 47, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker-Smith, J.A.; Grigor, W. Coeliac disease in a diabetic child. Lancet 1969, 1, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooft, C.; Devos, E.; Kriekemans, J.; Van Damme, J. Malabsorption and diabetes mellitus in children. Helv. Paediatr. Acta 1968, 23, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walker-Smith, J.A. Diabetes and coeliac disease. Lancet 1969, 2, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komrower, G.M. Coeliac disease in a diabetic child. Lancet 1969, 1, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooft, C.; Devos, E.; Van Damme, J. Coeliac disease in a diabetic child. Lancet 1969, 2, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkbeck, J.A. Coeliac disease in a diabetic child. Lancet 1969, 2, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooft, C.; Roels, H.; Devos, E. Diabetes and coeliac disease. Lancet 1969, 2, 1192. [Google Scholar]
- Thain, M.E.; Hamilton, J.R.; Ehrlich, R.M. Coexistence of diabetes mellitus and celiac disease. J. Pediatr. 1974, 85, 527–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savilahti, E.; Simell, O.; Koskimies, S.; Rilva, A.; Akerblom, H.K. Celiac disease in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J. Pediatr. 1986, 108, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivisto, V.A.; Kuitunen, P.; Tiilikainen, A.; Akerblom, H.K. HLA antigens in patients with juvenile diabetes mellitus, coeliac disease, and both of the diseases. Diabete Metab. 1977, 3, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Barta, L.; Kősai, I.; Molnár, M.; Körner, A.; Gyödi, E. Simultaneous occurrence of diabetes mellitus and coeliac disease. Acta Paediatr. Hung. 1985, 26, 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Kurppa, K.; Laitinen, A.; Agardh, D. Coeliac disease in children with type 1 diabetes. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2018, 2, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.; Loveridge-Lenza, B.; Horvath, K. Celiac Disease in Children. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 68, 1205–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poddighe, D.; Rebuffi, C.; De Silvestri, A.; Capittini, C. Carrier frequency of HLA-DQB1*02 allele in patients affected with celiac disease: A systematic review assessing the potential rationale of a targeted allelic genotyping as a first-line screening. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 1365–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía-León, M.E.; Ruiz-Dyck, K.M.; Calderón de la Barca, A.M. HLA-DQ genetic risk gradient for type 1 diabetes and celiac disease in northwestern Mexico. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2015, 80, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smigoc Schweiger, D.; Mendez, A.; Kunilo Jamnik, S.; Bratanic, N.; Bratina, N.; Battelino, T.; Brecelj, J.; Vidan-Jeras, B. High-risk genotypes HLA-DR3-DQ2/DR3-DQ2 and DR3-DQ2/DR4-DQ8 in co-occurrence of type 1 diabetes and celiac disease. Autoimmunity 2016, 49, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.T.; Sun, A.; Mayo, A.; Forgan, M.; Comrie, A.; Gillett, P.M. Coeliac screening in a Scottish cohort of children with type 1 diabetes mellitus: Is DQ typing the way forward? Arch. Dis. Child. 2016, 101, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, J.A. Immunogenetics of type 1 diabetes: A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 64, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silvestri, A.; Capittini, C.; Poddighe, D.; Valsecchi, C.; Marseglia, G.; Tagliacarne, S.C.; Scotti, V.; Rebuffi, C.; Pasi, A.; Martinetti, M.; et al. HLA-DQ genetics in children with celiac disease: A meta-analysis suggesting a two-step genetic screen4ng procedure starting with HLA-DQ β chains. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 83, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Størdal, K.; Tapia, G.; Lund-Blix, N.A.; Stene, L.C. Genotypes predisposing for celiac disease and autoimmune diabetes and risk of infections in early childhood. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2024, 78, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuja-Halkola, R.; Lebwohl, B.; Halfvarson, J.; Wijmenga, C.; Magnusson, P.K.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Heritability of non-HLA genetics in coeliac disease: A population-based study in 107,000 twins. Gut 2016, 65, 1793–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, D.J.; Plagnol, V.; Walker, N.M.; Cooper, J.D.; Downes, K.; Yang, J.H.; Howson, J.M.; Stevens, H.; McManus, R.; Wijmenga, C.; et al. Shared and distinct genetic variants in type 1 diabetes and celiac disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2767–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkkola, A.; Laine, A.P.; Karhunen, M.; Härkönen, T.; Ryhänen, S.J.; Ilonen, J.; Knip, M. HLA and non-HLA genes and familial predisposition to autoimmune diseases in families with a child affected by type 1 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Liu, X.; Hadley, D.; Hagopian, W.; Liu, E.; Chen, W.M.; Onengut-Gumuscu, S.; Simell, V.; Rewers, M.; Ziegler, A.G.; et al. Identification of non-HLA genes associated with celiac disease and country-specific differences in a large, international pediatric cohort. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Singh, J.; Minz, R.W.; Anand, S.; Saikia, B.; Bhadada, S.K.; Dayal, D.; Kumar, M.; Dhanda, S.K. Shared and distinct genetics of pure type 1 diabetes and type 1 diabetes with celiac disease, homology in their auto-antigens and immune dysregulation states: A study from North India. Acta Diabetol. 2024, 61, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahaly, G.J.; Hansen, M.P. Type 1 diabetes associated autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giersiepen, K.; Lelgemann, M.; Stuhldreher, N.; Ronfani, L.; Husby, S.; Koletzko, S.; Korponay-Szabó, I.R.; ESPGHAN Working Group on Coeliac Disease Diagnosis. Accuracy of diagnostic antibody tests for coeliac disease in children: Summary of an evidence report. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 54, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, M.A.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Michels, A.W. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2014, 383, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Jeong, J.; Jeong, E.M.; Cho, S.-Y.; Kang, J.W.; Lim, J.; Heo, J.; Kang, H.; Kim, I.-G.; Shin, D.-M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress activates transglutaminase 2 leading to protein aggregation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marre, M.; Profozich, J.; Coneybeer, J.; Geng, X.; Bertera, S.; Trucco, M.; Piganelli, J. Disruption of tolerance by ER stress in type 1 diabetes (BA8P.128). J. Immunol. 2014, 192 (Suppl. 1), 113.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turley, S.J.; Lee, J.W.; Dutton-Swain, N.; Mathis, D.; Benoist, C. Endocrine self and gut non-self intersect in the pancreatic lymph nodes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17729–17733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagopian, W.; Lee, H.S.; Liu, E.; Rewers, M.; She, J.X.; Ziegler, A.G.; Lernmark, B.; Toppari, J.; Rich, S.S.; Krischer, J.P.; et al. Co-occurrence of Type 1 Diabetes and Celiac Disease Autoimmunity. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20171305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, G. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Celiac Disease: Distinct Autoimmune Disorders That Share Common Pathogenic Mechanisms. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2019, 92, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.T.; Davis-Richardson, A.G.; Giongo, A.; Gano, K.A.; Crabb, D.B.; Mukherjee, N.; Casella, G.; Drew, J.C.; Ilonen, J.; Knip, M.; et al. Gut microbiome metagenomics analysis suggests a functional model for the development of autoimmunity for type 1 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Goffau, M.C.; Fuentes, S.; van den Bogert, B.; Honkanen, H.; de Vos, W.M.; Welling, G.W.; Hyoty, H.; Harmsen, H.J. Aberrant gut microbiota composition at the onset of type 1 diabetes in young children. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdukhakimova, D.; Dossybayeva, K.; Poddighe, D. Fecal and duodenal microbiota in pediatric celiac disease. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 652208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Rawat, A.; Al-Jarrah, B.; Saraswathi, S.; Gad, H.; Elawad, M.; Hussain, K.; Hendaus, M.A.; Al-Masri, W.; Malik, R.A.; et al. Distinctive microbial signatures and gut-brain crosstalk in pediatric patients with celiac disease and type 1 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguayo-Patrón, S.V.; Trujillo-Rivera, O.A.; Cornejo-Granados, F.; Ochoa-Leyva, A.; Calderón de la Barca, A.M. HLA-Haplotypes Influence Microbiota Structure in Northwestern Mexican Schoolchildren Predisposed for Celiac Disease or Type 1 Diabetes. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddighe, D.; Capittini, C. The role of HLA in the association between IgA deficiency and celiac disease. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 8632861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt-Jorgensen, M.; Holm, L.J.; Josefsen, K.; Buschard, K. Possible prevention of diabetes with a gluten-free diet. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.H.F.; Larsen, C.S.; Zachariassen, L.F.; Mentzel, C.M.J.; Laigaard, A.; Krych, L.; Nielsen, D.S.; Gobbi, A.; Haupt-Jorgensen, M.; Buschard, K.; et al. Gluten-free diet reduces autoimmune diabetes mellitus in mice across multiple generations in a microbiota-independent manner. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 127, 102795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, V.B.I.; Förø, D.; Buschard, K.; Kristiansen, K.; Pociot, F.; Kiilerich, P.; Josefsen, K.; Haupt-Jorgensen, M.; Antvorskov, J.C. A gluten-free diet during pregnancy and early life increases short chain fatty acid-producing bacteria and regulatory T cells in prediabetic NOD mice. Cells 2023, 12, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funsten, M.C.; Yurkovetskiy, L.A.; Kuznetsov, A.; Reiman, D.; Hansen, C.H.F.; Senter, K.I.; Lee, J.; Ratiu, J.; Dahal-Koirala, S.; Antonopoulos, D.A.; et al. Microbiota-dependent proteolysis of gluten subverts diet-mediated protection against type 1 diabetes. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 213–227.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marietta, E.V.; Gomez, A.M.; Yeoman, C.; Tilahun, A.Y.; Clark, C.R.; Luckey, D.H.; Murray, J.A.; White, B.A.; Kudva, Y.C.; Rajagopalan, G. Low incidence of spontaneous type 1 diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice raised on gluten-free diets is associated with changes in the intestinal microbiome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdu, E.F.; Danska, J.S. Common ground: Shared risk factors for type 1 diabetes and celiac disease. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, J.; Singh, K.B.; Nnadozie, M.C.; Abdal, M.; Shrestha, N.; Abe, R.A.M.; Masroor, A.; Khorochkov, A.; Mohammed, L. New evidence in the pathogenesis of celiac disease and type 1 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Cureus 2021, 13, e16721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lernmark, B.; Agardh, D.; Akolkar, B.; Gesualdo, P.; Hagopian, W.A.; Haller, M.J.; Hyöty, H.; Johnson, S.B.; Elding Larsson, H.; Liu, E.; et al. Looking back at the TEDDY study: Lessons and future directions. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2025, 21, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemppainen, K.M.; Ardissone, A.N.; Davis-Richardson, A.G.; Fagen, J.R.; Gano, K.A.; León-Novelo, L.G.; Vehik, K.; Casella, G.; Simell, O.; Ziegler, A.G.; et al. Early childhood gut microbiomes show strong geographic differences among subjects at high risk for type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honeyman, M.C.; Coulson, B.S.; Stone, N.L.; Gellert, S.A.; Goldwater, P.N.; Steele, C.E.; Couper, J.J.; Tait, B.D.; Colman, P.G.; Harrison, L.C. Association between rotavirus infection and pancreatic islet autoimmunity in children at risk of developing type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stene, L.C.; Honeyman, M.C.; Hoffenberg, E.J.; Haas, J.E.; Sokol, R.J.; Emery, L.; Taki, I.; Norris, J.M.; Erlich, H.A.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; et al. Rotavirus infection frequency and risk of celiac disease autoimmunity in early childhood: A longitudinal study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemppainen, K.M.; Lynch, K.F.; Liu, E.; Lönnrot, M.; Simell, V.; Briese, T.; Koletzko, S.; Hagopian, W.; Rewers, M.; She, J.X.; et al. Factors That Increase Risk of Celiac Disease Autoimmunity After a Gastrointestinal Infection in Early Life. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 694–702.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaarala, O.; Jokinen, J.; Lahdenkari, M.; Leino, T. Rotavirus Vaccination and the Risk of Celiac Disease or Type 1 Diabetes in Finnish Children at Early Life. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 674–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Yin, Z.; Kamdar, N.; Lee, G.J. Rotavirus vaccination is not associated with incident celiac disease or autoimmune thyroid disease in a national cohort of privately insured children. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanz, J.M.; Clarke, C.L.; Xu, S.; Daley, M.F.; Shoup, J.A.; Schroeder, E.B.; Lewin, B.J.; McClure, D.L.; Kharbanda, E.; Klein, N.P.; et al. Association Between Rotavirus Vaccination and Type 1 Diabetes in Children. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inns, T.; Fleming, K.M.; Iturriza-Gomara, M.; Hungerford, D. Paediatric rotavirus vaccination, coeliac disease and type 1 diabetes in children: A population-based cohort study. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, V.L.; Estrada, D.E.; Lerer, T.; Balarezo, F.; Sylvester, F.A. Effect of gluten-free diet on growth and glycemic control in children with type 1 diabetes and asymptomatic celiac disease. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 23, 1169–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Puttha, R.; Ghezaiel, S.; Skae, M.; Cooper, C.; Amin, R.; North West England Paediatric Diabetes Network. The effect of biopsy-positive silent coeliac disease and treatment with a gluten-free diet on growth and glycaemic control in children with Type 1 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2009, 26, 1250–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderström, H.; Cervin, M.; Dereke, J.; Hillman, M.; Tiberg, I.; Norström, C.; Carlsson, A. Does a gluten-free diet lead to better glycemic control in children with type 1 diabetes? Results from a feasibility study and recommendations for future trials. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2022, 26, 100893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Agarwala, A.; Makharia, G.; Bhatnagar, S.; Tandon, N. Effect of Gluten-Free Diet on Metabolic Control and Anthropometric Parameters in Type 1 Diabetes with Subclinical Celiac Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Endocr. Pract. 2020, 26, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, F.H.; Clarke, A.B.; Joachim, K.C.; Assor, E.; McDonald, C.; Saibil, F.; Lochnan, H.A.; Punthakee, Z.; Parikh, A.; Advani, A.; et al. Screening and Treatment Outcomes in Adults and Children with Type 1 Diabetes and Asymptomatic Celiac Disease: The CD-DIET Study. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1553–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saneifard, H.; Sheikhy, A.; Fallahzadeh, A.; Shakiba, M.; Kazemi Aghdam, M.; Mosallanejad, A. Role of Gluten-Free Diet on HbA1c Level in Children with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Celiac Disease. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 22, e144736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozzillo, E.; Franceschi, R.; Di Candia, F.; Rosanio, F.M.; Leonardi, L.; Fedi, L.; Rosé, V.; Cauvin, V.; Franzese, A.; Marcovecchio, M.L. The impact of gluten-free diet on growth, metabolic control and quality of life in youth with type 1 diabetes and celiac disease: A systematic review. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 191, 110032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eland, I.; Klieverik, L.; Mansour, A.A.; Al-Toma, A. Gluten-Free Diet in Co-Existent Celiac Disease and Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Is It Detrimental or Beneficial to Glycemic Control, Vascular Complications, and Quality of Life? Nutrients 2022, 15, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozzillo, E.; Marigliano, M.; Cuccurullo, I.; Berchielli, F.; Auricchio, R.; Maffeis, C.; Maria Rosanio, F.; Iafusco, D.; Pedrolli, C.; Pertile, R.; et al. Maintaining the gluten-free diet: The key to improve glycemic metrics in youths with type 1 diabetes and celiac disease. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 207, 111074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taczanowska, A.; Schwandt, A.; Amed, S.; Tóth-Heyn, P.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C.; Volsky, S.K.; Svensson, J.; Szypowska, A. Celiac disease in children with type 1 diabetes varies around the world: An international, cross-sectional study of 57,375 patients from the SWEET registry. J. Diabetes 2021, 13, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, J.; Sildorf, S.M.; Pipper, C.B.; Kyvsgaard, J.N.; Bøjstrup, J.; Pociot, F.M.; Mortensen, H.B.; Buschard, K. Potential beneficial effects of a gluten-free diet in newly diagnosed children with type 1 diabetes: A pilot study. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, V.; Pruhova, S.; Kulich, M.; Kolouskova, S.; Vosahlo, J.; Romanova, M.; Petruzelkova, L.; Obermannova, B.; Funda, D.P.; Cinek, O.; et al. Gluten-free diet in children with recent-onset type 1 diabetes: A 12-month intervention trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderström, H.; Rehn, J.; Cervin, M.; Ahlstermark, C.; Bybrant, M.C.; Carlsson, A. Compliance to a Gluten-Free Diet in Swedish Children with Type 1 Diabetes and Celiac Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Rani, S.; Verma, S.; Khanna, A. Adherence to gluten free diet and problems faced by children with celiac disease and type 1 diabetes mellitus. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2024, 13, 4252–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, L.; Catarino, M.; Festas, C.; Alves, P. Vulnerability in Children with Celiac Disease: Findings from a Scoping Review. Children 2024, 11, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pes, L.; La Salvia, A.; Pes, G.M.; Dore, M.P.; Fanciulli, G. Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms and celiac disease: Rare or neglected association? J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, S.; Bjarnason, I.; Swinson, C.M.; Polak, J.M.; Murray, W.; Levi, A.J. Malignant pancreatic somatostatinoma in a patient with dermatitis herpetiformis and coeliac disease. Digestion 1988, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundling, F.; Nerlich, A.; Heitland, W.; Schepp, W. Neuroendocrine pancreatic carcinoma after initial diagnosis of acute postpartal coeliac disease in a 37-year old woman—Fatal coincidence or result of a neglected disease? Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 2449–2454. [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon, H.; Dowling, D.; Alexander, S. A neuroendocrine cause for refractory symptoms in coeliac disease. JGH Open 2021, 5, 1314–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, İ. Childhood neuroendocrine tumors of the digestive system: A single center experience. Medicine 2022, 101, e28795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koca, T.; Dereci, S.; Karahan, N.; Akcam, M. Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors in two children. Indian Pediatr. 2016, 53, 70–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gaiani, F.; de’Angelis, N.; Minelli, R.; Kayali, S.; Carra, M.C.; de’Angelis, G.L. Pediatric gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor: A case report and review of the literature. Medicine 2019, 98, e17154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, M.B.; Al Sbihi, A.; Reddy, S.N.; Green, P. Prevalence of malignant neoplasms in celiac disease patients—A nationwide United States population-based study. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 15, 1048–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromny, I.; Neubauer, K. Pancreatic cancer in celiac disease patients—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebwohl, B.; Green, P.H.R.; Emilsson, L.; Mårild, K.; Söderling, J.; Roelstraete, B.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Cancer risk in 47,241 individuals with celiac disease: A nationwide cohort study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, e111–e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujasinovic, M.; Lindgren, F.; Kartalis, N.; Pozzi Mucelli, R.; Rutkowski, D.; Waldthaler, A.; Ghorbani, P.; Moro, C.F.; Casswall, T.; Löhr, J.M. Pediatric autoimmune pancreatitis: Clinical findings and outcomes in Sweden. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2025, epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddighe, D. Autoimmune pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer: Epidemiological aspects and immunological considerations. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3825–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macinga, P.; Bajer, L.; Del Chiaro, M.; Chari, S.T.; Dite, P.; Frulloni, L.; Ikeura, T.; Kamisawa, T.; Kubota, K.; Naitoh, I.; et al. Pancreatic cancer in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis: A scoping review. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasher, O.; Hall, N.J.; Sebire, N.J.; de Coppi, P.; Pierro, A. Pancreatic tumours in children: Diagnosis, treatment and outcome. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2015, 31, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Article | Age Sex | Acute Symptoms | Timing (vs. CD Onset) | Amylase (U/L) | Lipase (U/L) | Anti-tTG IgA (U/mL) | Duodenal Biopsy | Follow-Up | Relapse | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Year) | ||||||||||
| [Country] | ||||||||||
| Bultron (2009) [USA] | 9 yrs. M | Emesis Abdominal Pain | diagnosis | 351 | 1657 | 31 | n/a | 6 mo | N | - |
| Halabi (2010) [USA] | 3 yrs. M | Emesis Abdominal Pain | diagnosis | 4513 | 2343 | 3 | TVA | 6 mo | N | CD |
| serology negative | ||||||||||
| Sultan (2015) [Palestine] | 12 yrs. F | Emesis Abdominal Pain | diagnosis | 470 | n/a | 55 | TVA (Marsh III) | n/a | N | - |
| Patel (2019) [Canada] | 4 yrs. F | Abdominal Pain Jaundice | 6–12 mo | n/a | H | 19.4 | n/a | 18 mo | N | AIP |
| Type 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poddighe, D. Pancreatic Comorbidities in Pediatric Celiac Disease: Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency, Pancreatitis, and Diabetes Mellitus. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101243
Poddighe D. Pancreatic Comorbidities in Pediatric Celiac Disease: Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency, Pancreatitis, and Diabetes Mellitus. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(10):1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101243
Chicago/Turabian StylePoddighe, Dimitri. 2025. "Pancreatic Comorbidities in Pediatric Celiac Disease: Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency, Pancreatitis, and Diabetes Mellitus" Diagnostics 15, no. 10: 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101243
APA StylePoddighe, D. (2025). Pancreatic Comorbidities in Pediatric Celiac Disease: Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency, Pancreatitis, and Diabetes Mellitus. Diagnostics, 15(10), 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101243






