Ten Questions on Using Lung Ultrasonography to Diagnose and Manage Pneumonia in Hospital-at-Home Model: Part II—Confounders and Mimickers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Question 4: Do Pulmonary Comorbidities Affect the Accuracy of Ultrasound Diagnosis for Pneumonia?
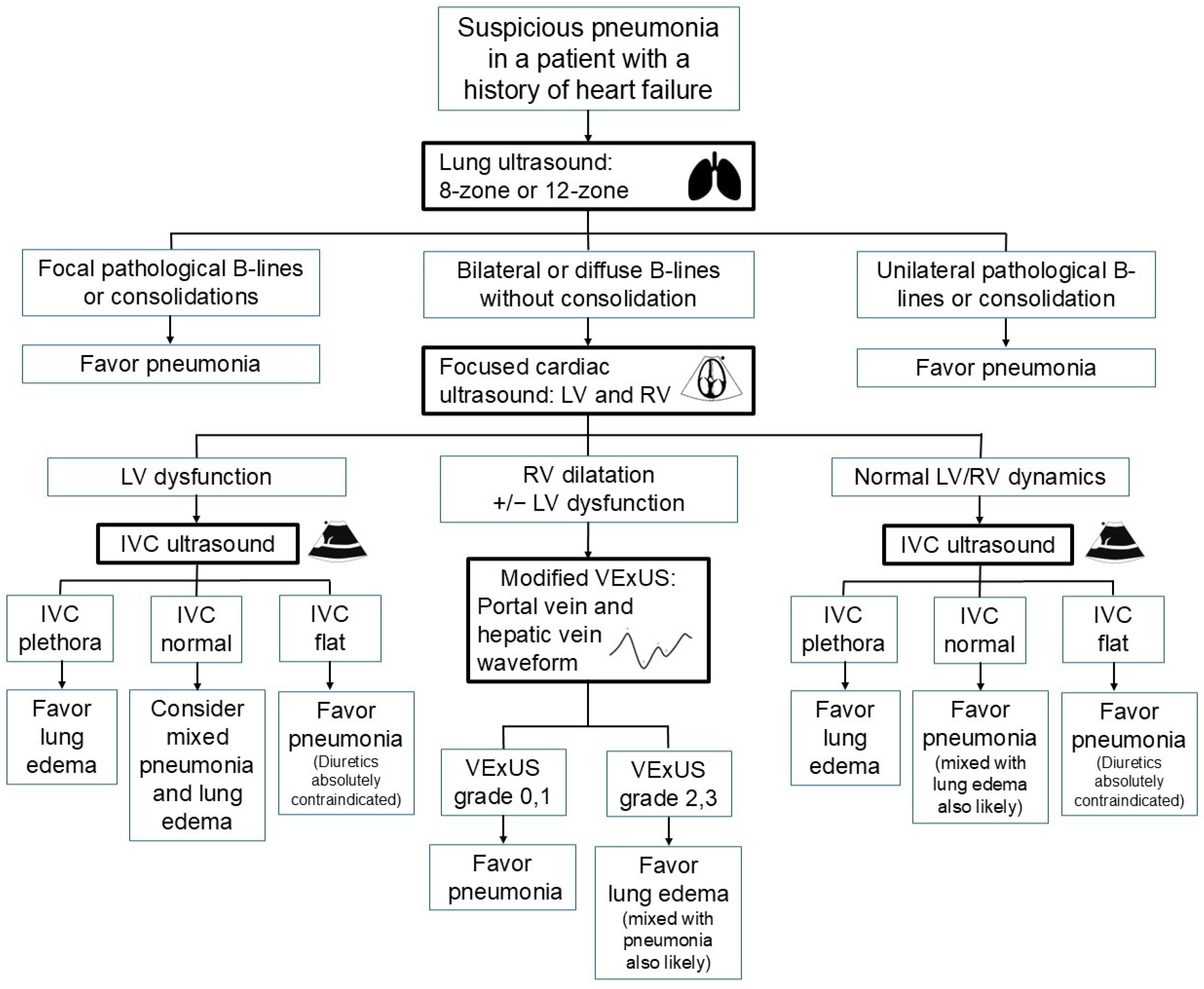
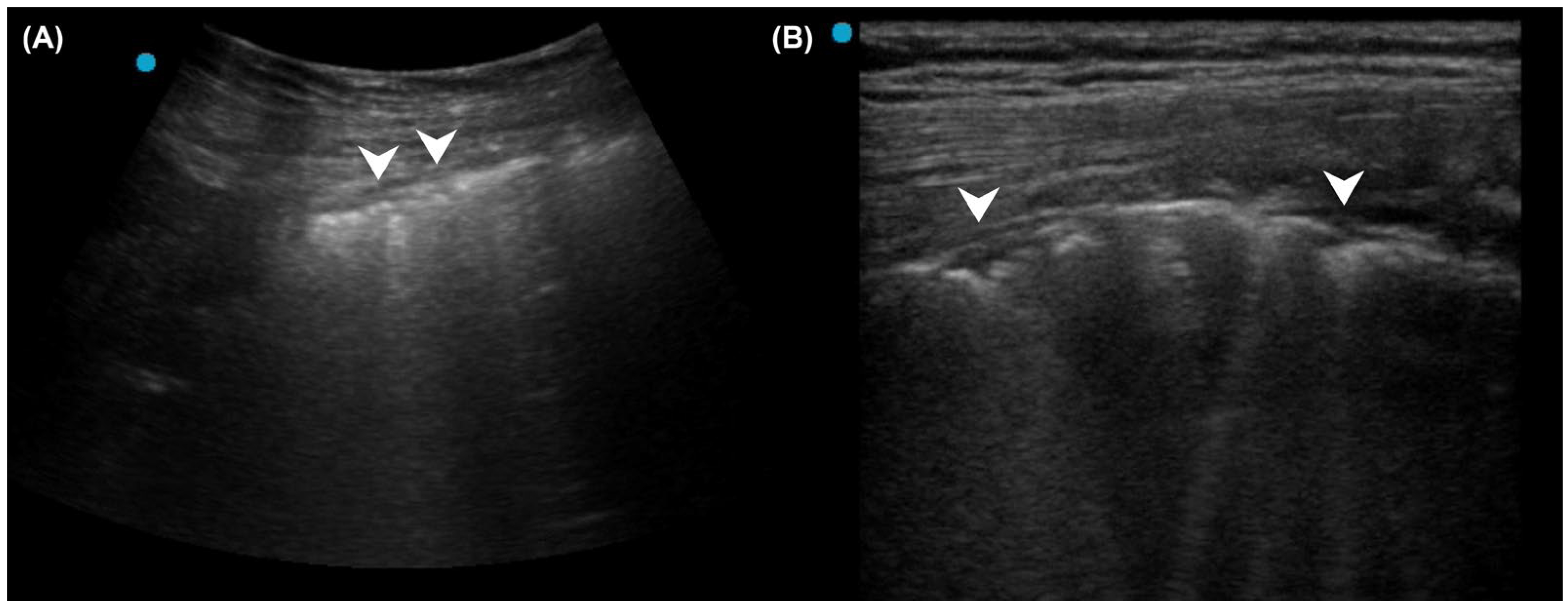
2.1. Pneumonia Diagnosis in Patients with Heart Failure
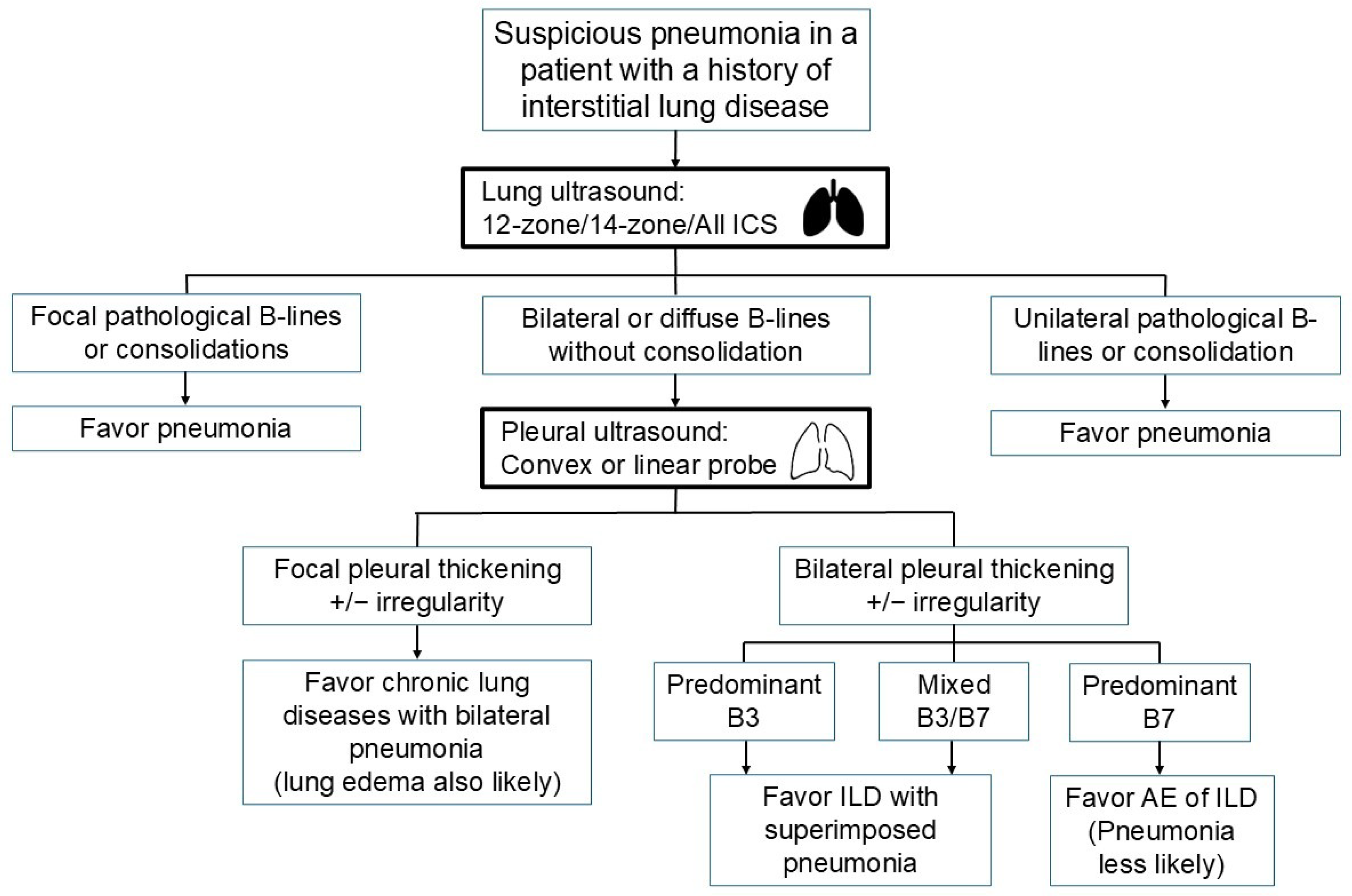
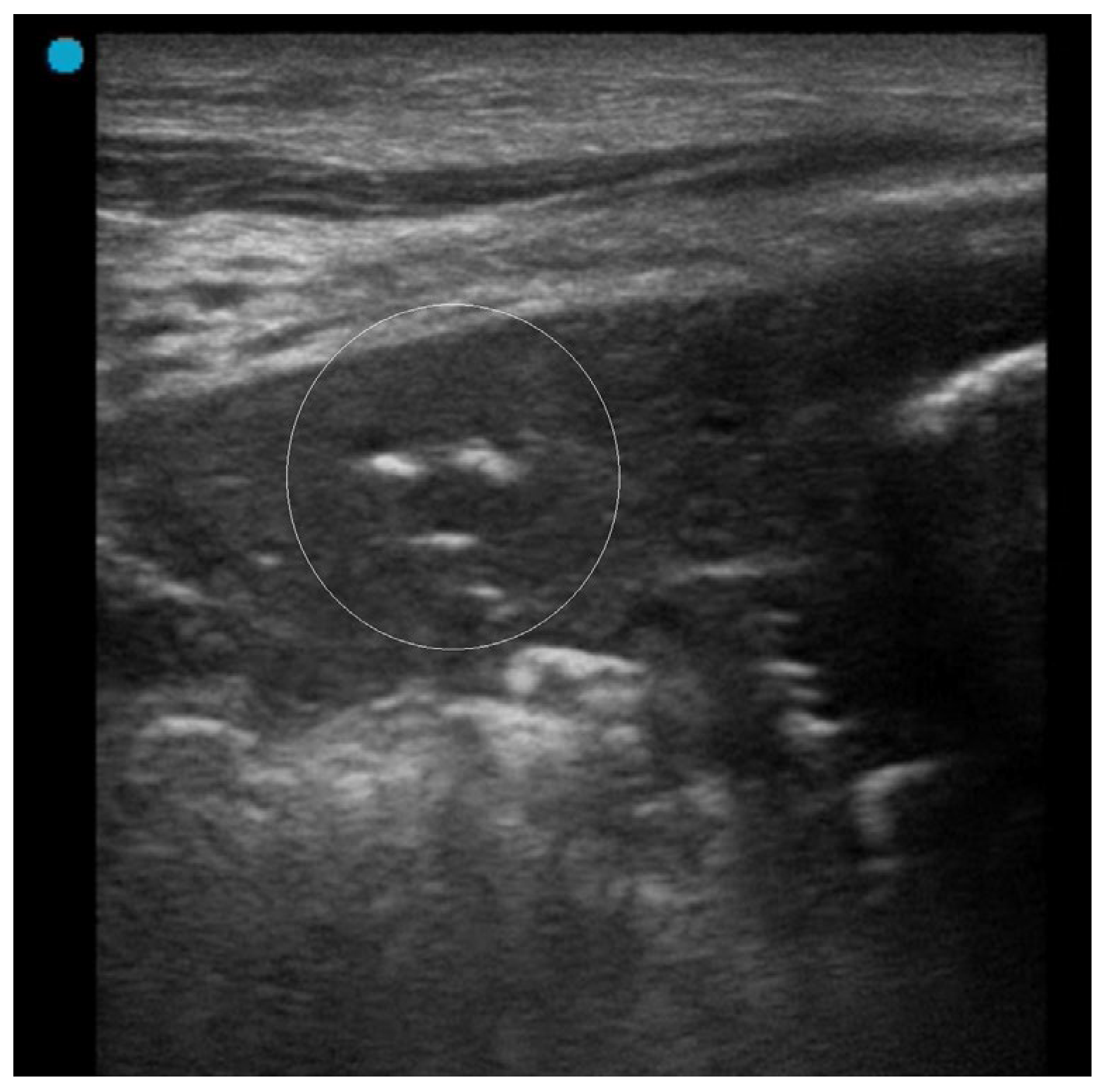
2.2. Pneumonia Diagnosis in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease
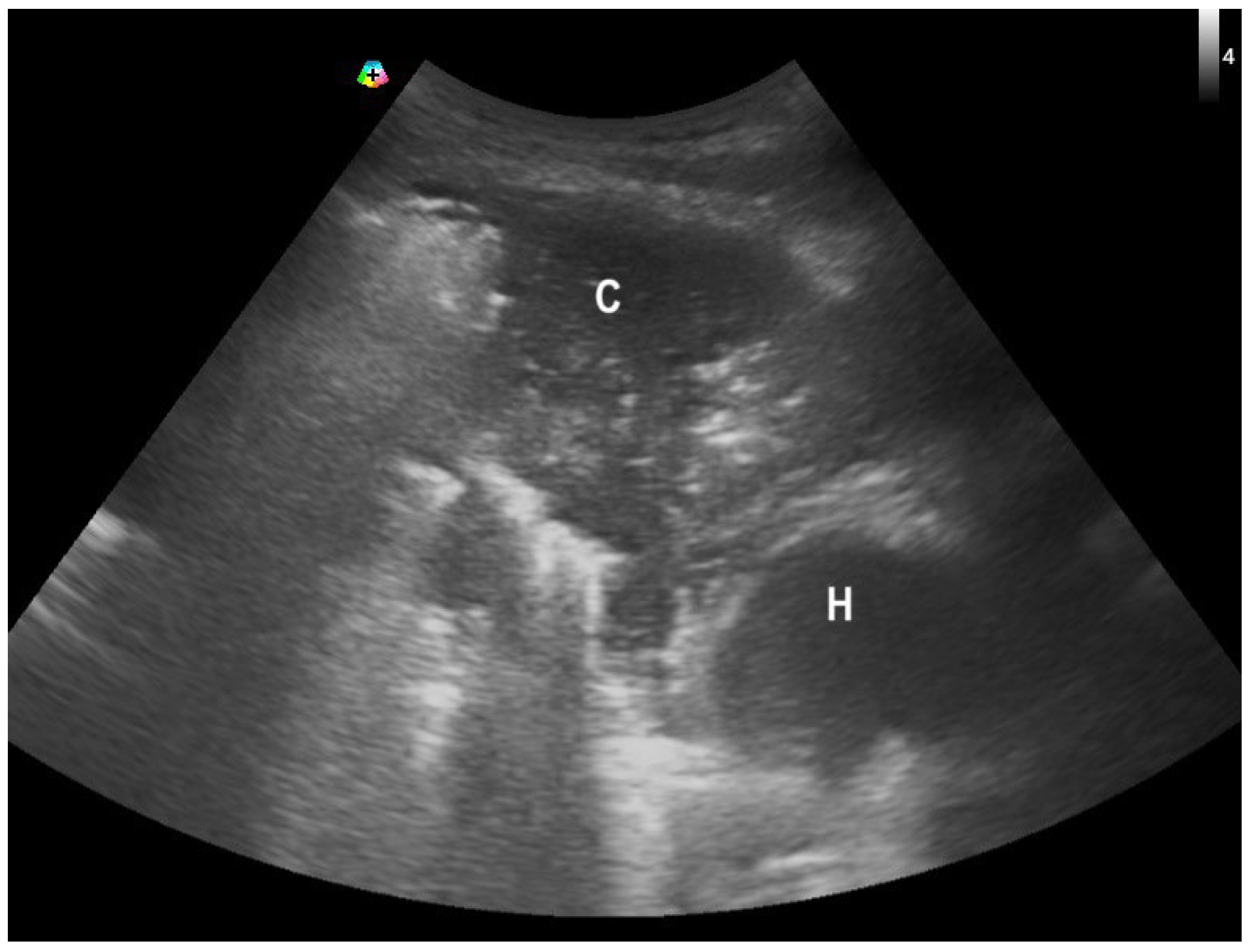
2.3. Pneumonia Diagnosis in the Presence of Pleural Effusion
3. Question 5: Do Other Differential Diagnoses Mimic the Ultrasound Patterns of Pneumonia?
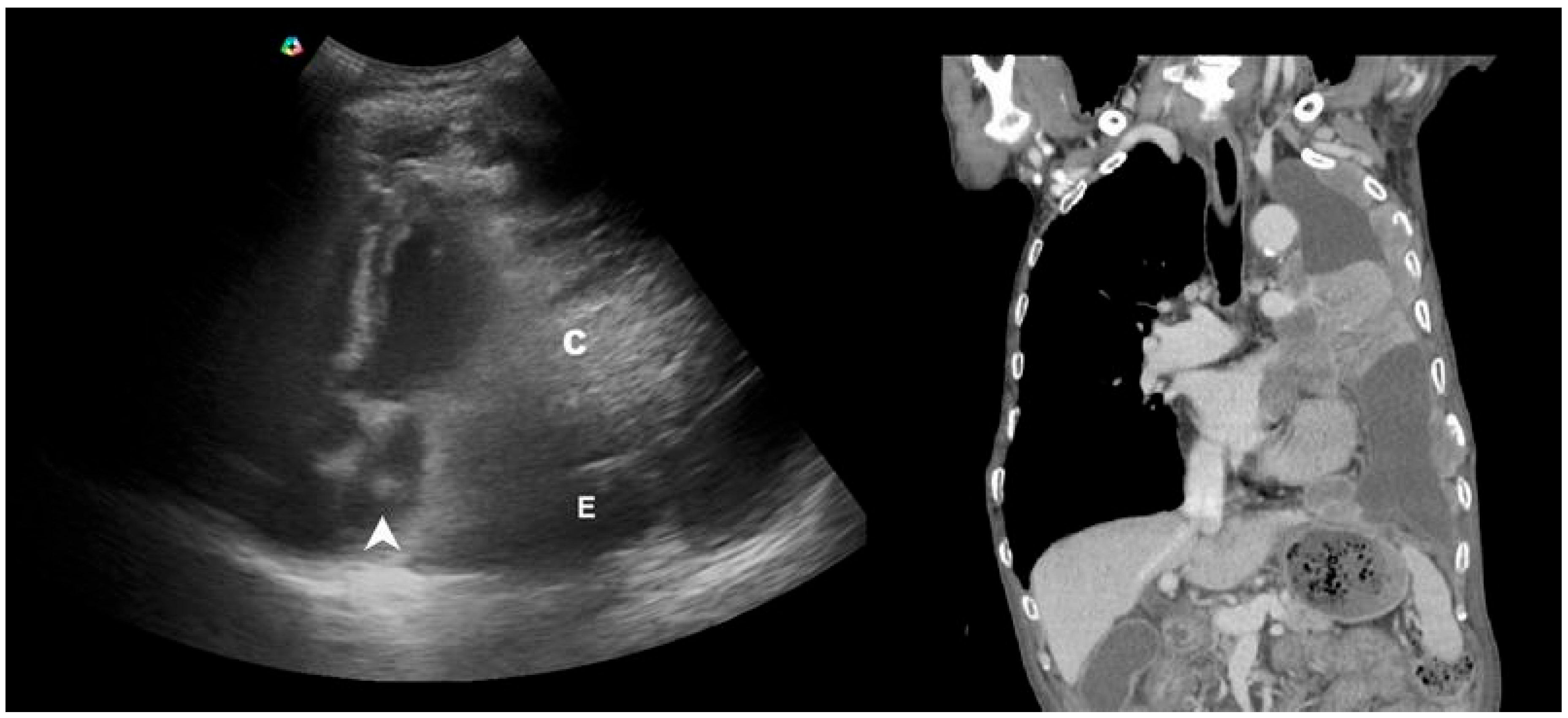
3.1. Atelectasis
3.2. Lung Contusion
3.3. Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia or Eosinophilic Pneumonia
3.4. Neoplastic Lesions
4. Question 6: Do Ultrasound Findings Correlate with Pneumonia Severity?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Federman, A.D.; Soones, T.; DeCherrie, L.V.; Leff, B.; Siu, A.L. Association of a Bundled Hospital-at-Home and 30-Day Postacute Transitional Care Program With Clinical Outcomes and Patient Experiences. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Goor, H.M.R.; de Hond, T.A.P.; van Loon, K.; Breteler, M.J.M.; Kalkman, C.J.; Kaasjager, K.A.H. Designing a Virtual Hospital-at-Home Intervention for Patients with Infectious Diseases: A Data-Driven Approach. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salton, F.; Kette, S.; Confalonieri, P.; Fonda, S.; Lerda, S.; Hughes, M.; Confalonieri, M.; Ruaro, B. Clinical Evaluation of the ButterfLife Device for Simultaneous Multiparameter Telemonitoring in Hospital and Home Settings. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouvenne, A.; Ticinesi, A.; Siniscalchi, C.; Rendo, M.; Cerundolo, N.; Parise, A.; Castaldo, G.; Chiussi, G.; Carrassi, R.; Guerra, A.; et al. The Multidisciplinary Mobile Unit (MMU) Program Bringing Hospital Specialist Geriatric Competencies at Home: A Feasible Alternative to Admission in Older Patients with Urgent Complaints. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zychlinski, N.; Fluss, R.; Goldberg, Y.; Zubli, D.; Barkai, G.; Zimlichman, E.; Segal, G. Tele-medicine controlled hospital at home is associated with better outcomes than hospital stay. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0309077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magor, D.; Berkov, E.; Siomin, D.; Karniel, E.; Lasman, N.; Waldman, L.R.; Gringauz, I.; Stern, S.; Kassif, R.L.; Barkai, G.; et al. Interpretation of Heart and Lungs Sounds Acquired via Remote, Digital Auscultation Reached Fair-to-Substantial Levels of Consensus among Specialist Physicians. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, A.W.; McKee, J.L.; Couperus, K.; Colombo, C.J. Patient Self-Performed Point-of-Care Ultrasound: Using Communication Technologies to Empower Patient Self-Care. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xirouchaki, N.; Bolaki, M.; Psarologakis, C.; Pediaditis, E.; Proklou, A.; Papadakis, E.; Kondili, E.; Georgopoulos, D. Thoracic ultrasound use in hospitalized and ambulatory adult patients: A quantitative picture. Ultrasound J. 2024, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, N.M.; Jowkar, N.; Ma, I.W.Y.; Schulwolf, S.; Selame, L.A.; Fischetti, C.E.; Kapur, T.; Goldsmith, A.J. Novice-performed point-of-care ultrasound for home-based imaging. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Bellinger, R.; Shedd, A.; Wolfshohl, J.; Walker, J.; Healy, J.; Taylor, J.; Chao, K.; Yen, Y.H.; Tzeng, C.T.; et al. Point-of-Care Ultrasound in Airway Evaluation and Management: A Comprehensive Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganchi, F.A.; Hardcastle, T.C. Role of Point-of-Care Diagnostics in Lower- and Middle-Income Countries and Austere Environments. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Aquila, P.; Raimondo, P.; Racanelli, V.; De Luca, P.; De Matteis, S.; Pistone, A.; Melodia, R.; Crudele, L.; Lomazzo, D.; Solimando, A.G.; et al. Integrated lung ultrasound score for early clinical decision-making in patients with COVID-19: Results and implications. Ultrasound J. 2022, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabuel Ortega, P.; Almendros Lafuente, N.; Cánovas García, S.; Martínez Gálvez, L.; González-Vidal, A. The correlation between point-of-care ultrasound and digital tomosynthesis when used with suspected COVID-19 pneumonia patients in primary care. Ultrasound J. 2022, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, N.C.; Lin, Y.F.; Tsai, H.B.; Huang, T.Y.; Hsu, C.H. Ten Questions on Using Lung Ultrasonography to Diagnose and Manage Pneumonia in the Hospital-at-Home Model: Part I-Techniques and Patterns. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, D.A.; Mezière, G.A. Relevance of lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of acute respiratory failure: The BLUE protocol. Chest 2008, 134, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Msolli, M.A.; Sekma, A.; Marzouk, M.B.; Chaabane, W.; Bel Haj Ali, K.; Boukadida, L.; Bzeouich, N.; Gannoun, I.; Trabelssi, I.; Laaouiti, K.; et al. Bedside lung ultrasonography by emergency department residents as an aid for identifying heart failure in patients with acute dyspnea after a 2-h training course. Ultrasound J. 2021, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, F.M.; Ehrman, R.R.; Barton, A.; Sarmiento, E.; Ottenhoff, J.E.; Nti, B.K. B-line quantification: Comparing learners novice to lung ultrasound assisted by machine artificial intelligence technology to expert review. Ultrasound J. 2021, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, K.T.; Kimura, B.J.; Korcarz, C.E.; Pellikka, P.A.; Rahko, P.S.; Siegel, R.J. Focused cardiac ultrasound: Recommendations from the American Society of Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2013, 26, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waweru-Siika, W.; Plüddemann, A.; Heneghan, C. Focused Cardiac Ultrasound Training for Non-cardiologists: An Overview and Recommendations for a Lower Middle-Income Country. Crit. Care Clin. 2022, 38, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronshteyn, Y.S.; Hashmi, N.; Privratsky, J.R.; Barbeito, A. Blood or Fat? Differentiating Hemopericardium versus Epicardial Fat Using Focused Cardiac Ultrasound. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekambaram, K.; Hassan, K. Establishing a Novel Diagnostic Framework Using Handheld Point-of-Care Focused-Echocardiography (HoPE) for Acute Left-Sided Cardiac Valve Emergencies: A Bayesian Approach for Emergency Physicians in Resource-Limited Settings. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins Barros, I.M.; Barros, M.V.L.; Almeida Martins, L.N.; Ribeiro, A.L.P.; de Camargo, R.S.S.; Oliveira, C.D.L.; Ferreira, A.M.; de Oliveira, L.C.; Bierrenbach, A.L.; Haikal, D.S.A.; et al. Accuracy and reliability of focused echocardiography in patients with Chagas disease from endemic areas: SaMi-Trop cohort study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzuoli, A.; Evangelista, I.; Beltrami, M.; Pirrotta, F.; Tavera, M.C.; Gennari, L.; Ruocco, G. Clinical, Laboratory and Lung Ultrasound Assessment of Congestion in Patients with Acute Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Herrero, S.; Lorenzo-Villalba, N.; Urbano, E.; Sánchez-Sauce, B.; Aguilar-Rodríguez, F.; Bernabeu-Wittel, M.; Garcia-Alonso, R.; Soler-Rangel, L.; Trapiello-Valbuena, F.; Garcia-García, A.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Lung and Cava Vein Ultrasound in Elderly Patients Admitted for Acute Heart Failure: PROFUND-IC Registry Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmowihardjo, L.N.; Schippers, J.R.; Haaksma, M.E.; Smit, M.R.; Bogaard, H.J.; Heunks, L.; Juffermans, N.P.; Schultz, M.J.; Endeman, H.; van Velzen, P.; et al. The diagnostic accuracy of lung ultrasound to determine PiCCO-derived extravascular lung water in invasively ventilated patients with COVID-19 ARDS. Ultrasound J. 2023, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaubien-Souligny, W.; Rola, P.; Haycock, K.; Bouchard, J.; Lamarche, Y.; Spiegel, R.; Denault, A.Y. Quantifying systemic congestion with Point-Of-Care ultrasound: Development of the venous excess ultrasound grading system. Ultrasound J. 2020, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assavapokee, T.; Rola, P.; Assavapokee, N.; Koratala, A. Decoding VExUS: A practical guide for excelling in point-of-care ultrasound assessment of venous congestion. Ultrasound J. 2024, 16, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.C.; Gill, E.A.; Douglas, I.J.; Longino, A.A. Evaluation of a modified venous excess ultrasound (VExUS) protocol for estimation of venous congestion: A cohort study. Ultrasound J. 2025, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasiou, V.; Peteinidou, E.; Moysidis, D.V.; Daios, S.; Gogos, C.; Liatsos, A.C.; Didagelos, M.; Gossios, T.; Efthimiadis, G.K.; Karamitsos, T.; et al. Multiorgan Congestion Assessment by Venous Excess Ultrasound Score in Acute Heart Failure. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2024, 37, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longino, A.; Martin, K.; Leyba, K.; Siegel, G.; Thai, T.N.; Riscinti, M.; Douglas, I.S.; Gill, E.; Burke, J. Prospective Evaluation of Venous Excess Ultrasound for Estimation of Venous Congestion. Chest 2024, 165, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leote, J.; Judas, T.; Broa, A.L.; Lopes, M.; Abecasis, F.; Pintassilgo, I.; Gonçalves, A.; Gonzalez, F. Time course of lung ultrasound findings in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and cardiac dysfunction. Ultrasound J. 2022, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancusi, C.; Fucile, I.; Gargiulo, P.; Mosca, M.; Migliaccio, B.; Basile, C.; Gargiulo, G.; Santoro, C.; Morisco, C.; De Luca, N.; et al. Lung Ultrasound in Coronary Care Unit, an Important Diagnostic Tool for Concomitant Pneumonia. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepri, G.; Markovic, M.; Bellando-Randone, S.; Sebastiani, M.; Guiducci, S. The Burden of Interstitial Lung Involvement in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Could Lung Ultrasound Have a Role in Its Detection? A Literature Review. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasco, P.G.; de Luna Cardenal, G.; Garrido, I.M.; Pinilla, J.M.; Rodríguez, G.F.; Mateo, J.J.; Ruiz, D.C. Assessment of interstitial lung disease in Sjögren’s syndrome by lung ultrasound: A pilot study of correlation with high-resolution chest tomography. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2017, 12, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radić, M.; Đogaš, H.; Gelemanović, A.; Jurić Petričević, S.; Škopljanac, I.; Radić, J. Pulmonary Ultrasonography in Systemic Sclerosis-Induced Interstitial Lung Disease-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, C.; Busto, G.; Rella, V.; Barile, R.; Cacciapaglia, F.; Fornaro, M.; Iannone, F.; Lacedonia, D.; Quarato, C.M.I.; Trotta, A.; et al. Transthoracic Lung Ultrasound in Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: Capacity to Differentiate Chest Computed-Tomographic Characteristic Patterns. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofíudóttir, B.K.; Harders, S.; Laursen, C.B.; Lage-Hansen, P.R.; Nielsen, S.M.; Just, S.A.; Christensen, R.; Davidsen, J.R.; Ellingsen, T. Detection of Interstitial Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Thoracic Ultrasound: A Diagnostic Test Accuracy Study. Arthritis Care Res. 2024, 76, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Rabaneda, E.F.; Bong, D.A.; Castañeda, S.; Möller, I. Use of ultrasound to diagnose and monitor interstitial lung disease in rheumatic diseases. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 3547–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, C.; Mattolini, L.; Tofani, L.; Gargani, L.; Landini, N.; Roma, N.; Lepri, G.; Orlandi, M.; Guiducci, S.; Bellando-Randone, S.; et al. Lung Ultrasound B-Lines in the Evaluation of the Extent of Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, F.; La Rocca, G.; Elefante, E.; Sambataro, G.; Tripoli, A.; Governato, G.; Fulvio, G.; Moretti, M.; Bulleri, A.; Romei, C.; et al. Pleural Irregularities: A new ultrasound marker for lung involvement in primary Sjögren’s disease. Jt. Bone Spine 2025, 92, 105820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongodi, S.; Colombo, A.; Orlando, A.; Cavagna, L.; Bouhemad, B.; Iotti, G.A.; Mojoli, F. Combined ultrasound-CT approach to monitor acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease. Ultrasound J. 2020, 12, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanani, Z.; Gupta, R. The Management of Interstitial Lung Disease in the ICU: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, R.; Saraya, T.; Yamada, S.; Nakajima, K.; Doi, K.; Akizawa, T.; Ishikawa, N.; Kurokawa, N.; Kobayashi, F.; Nunokawa, H.; et al. Clinical Evaluation of Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease in a Single Tertiary Center: Perspectives before and after the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- On, R.; Matsumoto, T.; Kushima, H.; Hirano, R.; Fujita, M. Prevalence of viral infection in acute exacerbation of interstitial lung diseases in Japan. Respir. Investig. 2020, 58, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candel, F.J.; Salavert, M.; Basaras, M.; Borges, M.; Cantón, R.; Cercenado, E.; Cilloniz, C.; Estella, Á.; García-Lechuz, J.M.; Garnacho Montero, J.; et al. Ten Issues for Updating in Community-Acquired Pneumonia: An Expert Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.A.; Makhlouf, H.A. B-lines: Transthoracic chest ultrasound signs useful in assessment of interstitial lung diseases. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2014, 9, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Manandhar, S. Lung Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease. J. Nepal. Health Res. Counc. 2023, 20, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, C.B.; Sloth, E.; Lambrechtsen, J.; Lassen, A.T.; Madsen, P.H.; Henriksen, D.P.; Davidsen, J.R.; Rasmussen, F. Focused sonography of the heart, lungs, and deep veins identifies missed life-threatening conditions in admitted patients with acute respiratory symptoms. Chest 2013, 144, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, C.B.; Sloth, E.; Lassen, A.T.; Christensen, R.D.; Lambrechtsen, J.; Madsen, P.H.; Henriksen, D.P.; Davidsen, J.R.; Rasmussen, F. Point-of-care ultrasonography in patients admitted with respiratory symptoms: A single-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, B.P.; Gilman, M.D.; Humphrey, K.L.; Alkasab, T.K.; Gibbons, F.K.; Shepard, J.A.; Wu, C.C. Outcome of recommendations for radiographic follow-up of pneumonia on outpatient chest radiography. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musher, D.M.; Roig, I.L.; Cazares, G.; Stager, C.E.; Logan, N.; Safar, H. Can an etiologic agent be identified in adults who are hospitalized for community-acquired pneumonia: Results of a one-year study. J. Infect. 2013, 67, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves dos Santos, J.W.; Torres, A.; Michel, G.T.; de Figueiredo, C.W.C.; Mileto, J.N.; Foletto, V.G., Jr.; de Nóbrega Cavalcanti, M.A. Non-infectious and unusual infectious mimics of community-acquired pneumonia. Respir. Med. 2004, 98, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaksma, M.E.; Smit, J.M.; Heldeweg, M.L.A.; Nooitgedacht, J.S.; de Grooth, H.J.; Jonkman, A.H.; Girbes, A.R.J.; Heunks, L.; Tuinman, P.R. Extended Lung Ultrasound to Differentiate Between Pneumonia and Atelectasis in Critically Ill Patients: A Diagnostic Accuracy Study. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 50, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, D.; Mezière, G.; Seitz, J. The dynamic air bronchogram. A lung ultrasound sign of alveolar consolidation ruling out atelectasis. Chest 2009, 135, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, A.; Yang, P.C.; Lee, L.; Wu, H.D.; Kuo, S.H.; Luh, K.T.; Chen, W.J.; Lin, F.Y. Reactive pulmonary artery vasoconstriction in pulmonary consolidation evaluated by color Doppler ultrasonography. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2000, 26, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görg, C.; Bert, T. Transcutaneous colour Doppler sonography of lung consolidations: Review and pictorial essay. Part 2: Colour Doppler sonographic patterns of pulmonary consolidations. Ultraschall Med. 2004, 25, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, D.A.; Lascols, N.; Prin, S.; Mezière, G. The “lung pulse”: An early ultrasound sign of complete atelectasis. Intensive Care Med. 2003, 29, 2187–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, S.W.; Liu, F.; Li, Q.P.; Kong, X.Y.; Feng, Z.C. The diagnosis of neonatal pulmonary atelectasis using lung ultrasonography. Chest 2015, 147, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldati, G.; Testa, A.; Silva, F.R.; Carbone, L.; Portale, G.; Silveri, N.G. Chest ultrasonography in lung contusion. Chest 2006, 130, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovida, S.; Orso, D.; Naeem, S.; Vetrugno, L.; Volpicelli, G. Lung ultrasound in blunt chest trauma: A clinical review. Ultrasound 2022, 30, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, S.V.; Patel, D.; Machnicki, S.; Naidich, D.; Stover, D.; Travis, W.D.; Brown, K.K.; Naidich, J.J.; Mahajan, A.; Esposito, M.; et al. Algorithmic Approach to the Diagnosis of Organizing Pneumonia: A Correlation of Clinical, Radiologic, and Pathologic Features. Chest 2022, 162, 156–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, Y.; Kawamura, T.; Higashino, T.; Mimura, R.; Tsukamoto, H.; Sasaki, S. Clinical features of acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia: An early histologic pattern of various acute inflammatory lung diseases. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higo, H.; Ichikawa, H.; Arakawa, Y.; Mori, Y.; Tamura, T.; Kuyama, S.; Matsumoto, C.; Sugimoto, K.; Hamada, N.; Suwaki, T.; et al. The Clinical Significance of Interstitial Pneumonia with Autoimmune Features in Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia: A Prospective Multicenter Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.E.; Jhun, B.W. The utility of thoracic ultrasound in patients with acute eosinophilic pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperandeo, M.; Rea, G.; Grimaldi, M.A.; Trovato, F.; Dimitri, L.M.; Carnevale, V. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound does not discriminate between community acquired pneumonia and lung cancer. Thorax 2017, 72, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.W.; Chen, Y.L.; Wu, H.D.; Chien, Y.C.; Huang, C.K.; Wang, H.C. Application of transthoracic shear-wave ultrasound elastography in lung lesions. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2002347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarato, C.M.I.; Venuti, M.; Dimitri, L.; Lacedonia, D.; Simeone, A.; Mirijello, A.; De Cosmo, S.; Maiello, E.; Taurchini, M.; Scioscia, G.; et al. Transthoracic ultrasound shear wave elastography for the study of subpleural lung lesions. Ultrasonography 2022, 41, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankudavicius, V.; Miliauskas, S.; Poskiene, L.; Vajauskas, D.; Zemaitis, M. Diagnostic Yield of Transbronchial Cryobiopsy Guided by Radial Endobronchial Ultrasound and Fluoroscopy in the Radiologically Suspected Lung Cancer: A Single Institution Prospective Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caroli, G.; Dell’Amore, A.; Cassanelli, N.; Dolci, G.; Pipitone, E.; Asadi, N.; Stella, F.; Bini, A. Accuracy of transthoracic ultrasound for the prediction of chest wall infiltration by lung cancer and of lung infiltration by chest wall tumours. Heart Lung Circ. 2015, 24, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.; Tobino, K.; Yasuda, Y.; Sueyasu, T.; Nishizawa, S.; Yoshimine, K.; Munechika, M.; Asaji, M.; Yamaji, Y.; Tsuruno, K.; et al. A Community-acquired Lung Abscess Attributable to Streptococcus pneumoniae which Extended Directly into the Chest Wall. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bui, J.T.; Schranz, A.J.; Strassle, P.D.; Agala, C.B.; Mody, G.N.; Ikonomidis, J.S.; Long, J.M. Pulmonary complications observed in patients with infective endocarditis with and without injection drug use: An analysis of the National Inpatient Sample. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, N.C.; Tseng, C.L.; Yang, C.W.; Hsu, C.H. Man With Dyspnea. Ann Emerg Med. 2022, 79, e105–e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnikel, M.; Alig, A.H.S.; Anton, S.; Arenz, L.; Bendz, H.; Fraccaroli, A.; Götschke, J.; Vornhülz, M.; Plohmann, P.; Weiglein, T.; et al. Follow-up lung ultrasound to monitor lung failure in COVID-19 ICU patients. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, T.; Bulla, P.; Jödicke, L.; Klein, C.; Bott, S.M.; Keller, R.; Malek, N.; Fröhlich, E.; Göpel, S.; Blumenstock, G.; et al. Can follow up lung ultrasound in Coronavirus Disease-19 patients indicate clinical outcome? PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargent, A.; Chatelain, E.; Kreitmann, L.; Quenot, J.P.; Cour, M.; Argaud, L.; COVID-LUS study group. Lung ultrasound score to monitor COVID-19 pneumonia progression in patients with ARDS. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, H.; Ohya, A.; Yamagata, H.; Iwashita, M.; Abe, T.; Takeuchi, I. Prolonged mechanical ventilation in patients with severe COVID-19 is associated with serial modified-lung ultrasound scores: A single-centre cohort study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, L.; Galante, O.; Almog, Y.; Dayan, R.R.; Smoliakov, A.; Ullman, Y.; Shamia, D.; Ohayon, R.B.D.; Golbets, E.; El Haj, K.; et al. Point of Care Lung Ultrasound Injury Score-A simple and reliable assessment tool in COVID-19 patients (PLIS I): A retrospective study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosz, G.; Gyombolai, P.; Tóth, J.T.; Szabó, M. Reliability and clinical correlations of semi-quantitative lung ultrasound on BLUE points in COVID-19 mechanically ventilated patients: The ‘BLUE-LUSS’-A feasibility clinical study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reissig, A.; Copetti, R.; Mathis, G.; Mempel, C.; Schuler, A.; Zechner, P.; Aliberti, S.; Neumann, R.; Kroegel, C.; Hoyer, H. Lung ultrasound in the diagnosis and follow-up of community-acquired pneumonia: A prospective, multicenter, diagnostic accuracy study. Chest 2012, 142, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoicescu, E.R.; Manolescu, D.L.; Iacob, R.; Cerbu, S.; Dima, M.; Iacob, E.R.; Ciuca, I.M.; Oancea, C.; Iacob, D. The Assessment of COVID-19 Pneumonia in Neonates: Observed by Lung Ultrasound Technique and Correlated with Biomarkers and Symptoms. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1. What ultrasound techniques are essential for diagnosing pneumonia? |
| 2. What are the ultrasound patterns associated with pneumonia? |
| 3. Do different settings or etiologies of pneumonia influence the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography? |
| 4. Do pulmonary comorbidities affect the accuracy of ultrasound diagnosis for pneumonia? |
| 5. Do other differential diagnoses mimic the ultrasound patterns of pneumonia? |
| 6. Do ultrasound findings correlate with pneumonia severity? |
| 7. Do initial ultrasound findings associated with pneumonia hold prognostic value? |
| 8. Do the ultrasound patterns improve in accordance with pneumonia recovery? |
| 9. Is ultrasound superior to chest x-ray for diagnosing pneumonia? |
| 10. Does ultrasonography lead to overdiagnosis of pneumonia? |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, N.-C.; Lin, Y.-F.; Tsai, H.-B.; Liao, C.; Hsu, C.-H. Ten Questions on Using Lung Ultrasonography to Diagnose and Manage Pneumonia in Hospital-at-Home Model: Part II—Confounders and Mimickers. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101200
Hsu N-C, Lin Y-F, Tsai H-B, Liao C, Hsu C-H. Ten Questions on Using Lung Ultrasonography to Diagnose and Manage Pneumonia in Hospital-at-Home Model: Part II—Confounders and Mimickers. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(10):1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101200
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Nin-Chieh, Yu-Feng Lin, Hung-Bin Tsai, Charles Liao, and Chia-Hao Hsu. 2025. "Ten Questions on Using Lung Ultrasonography to Diagnose and Manage Pneumonia in Hospital-at-Home Model: Part II—Confounders and Mimickers" Diagnostics 15, no. 10: 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101200
APA StyleHsu, N.-C., Lin, Y.-F., Tsai, H.-B., Liao, C., & Hsu, C.-H. (2025). Ten Questions on Using Lung Ultrasonography to Diagnose and Manage Pneumonia in Hospital-at-Home Model: Part II—Confounders and Mimickers. Diagnostics, 15(10), 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101200






