The Association of Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference with Sepsis-Related Mortality in South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Statements
2.2. Data Source
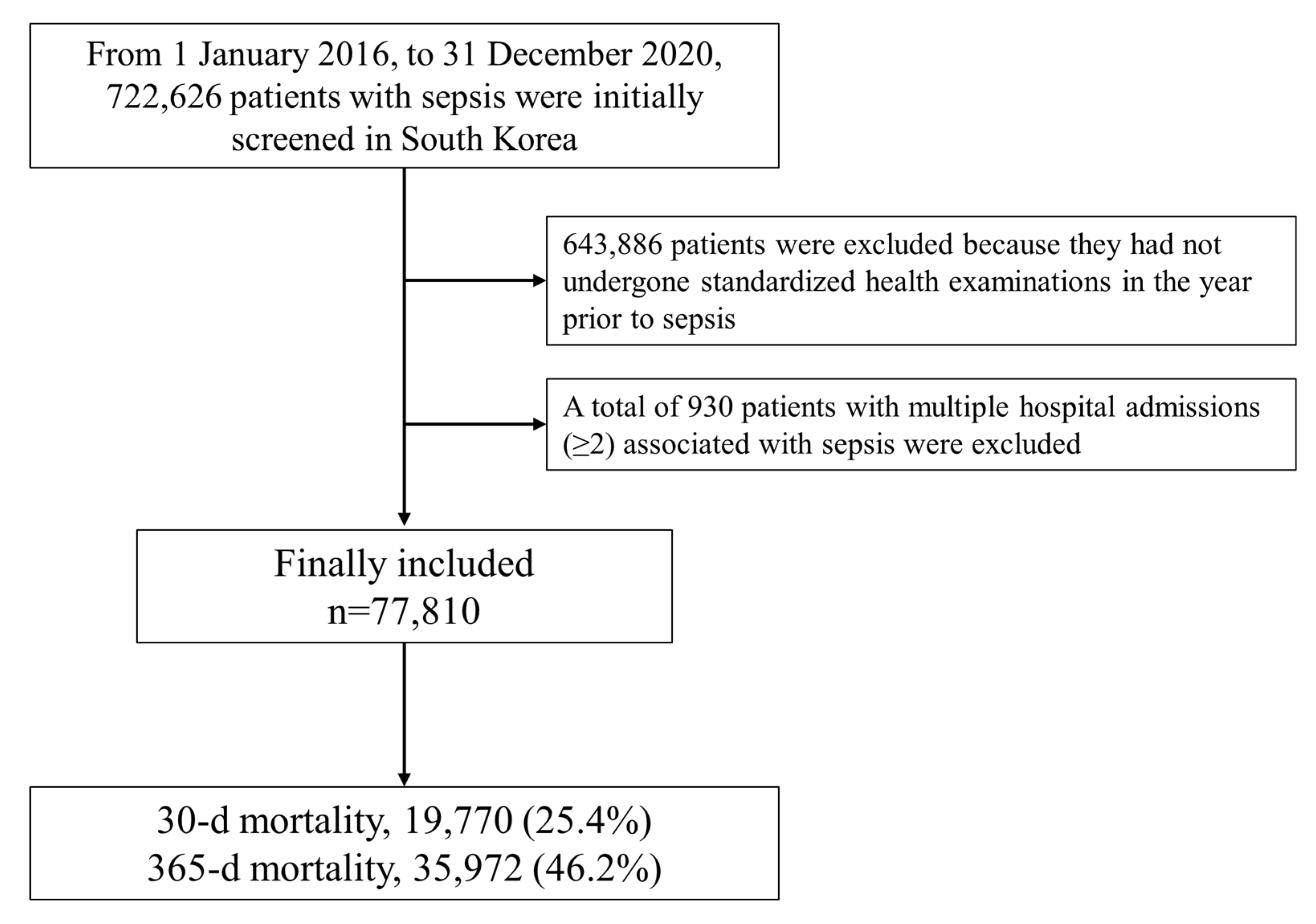
2.3. Study Population
2.4. BMI and WC (Independent Variable)
2.5. Endpoints
2.6. Variables Analyzed
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
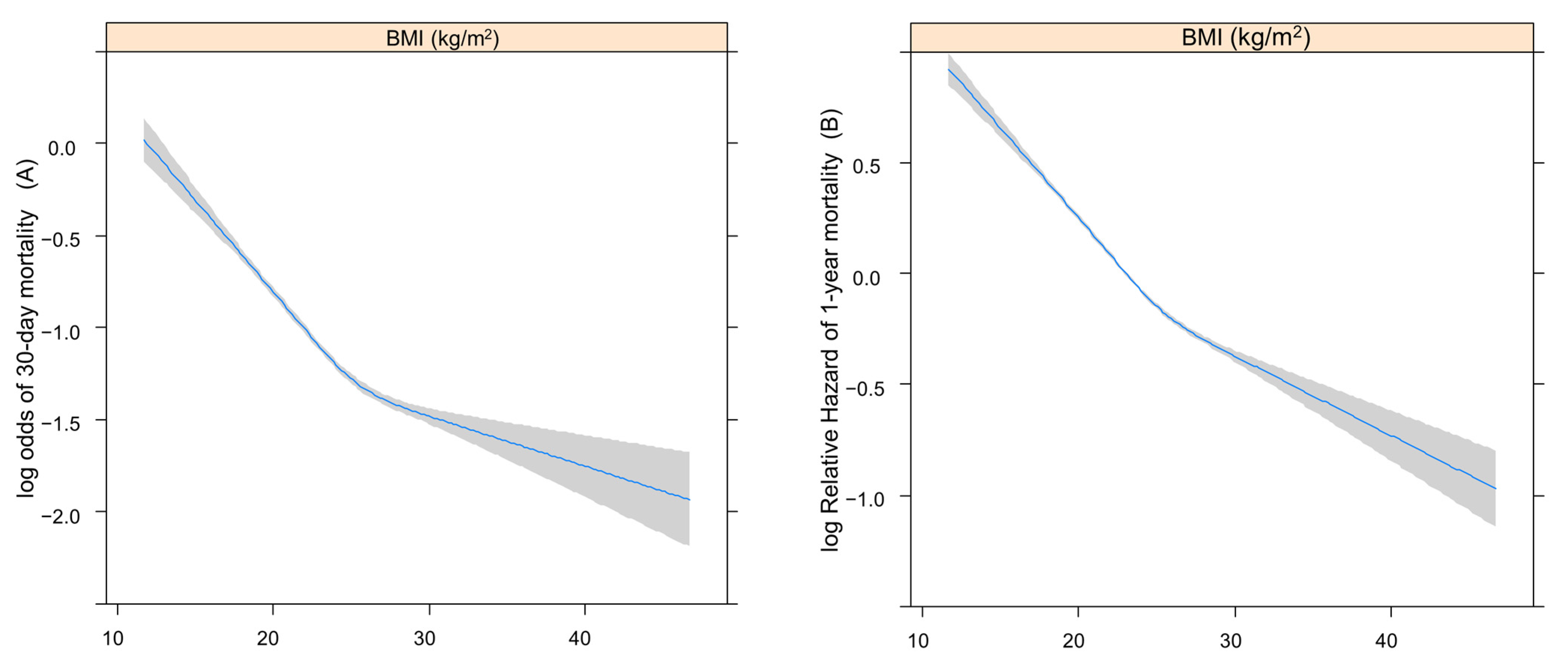
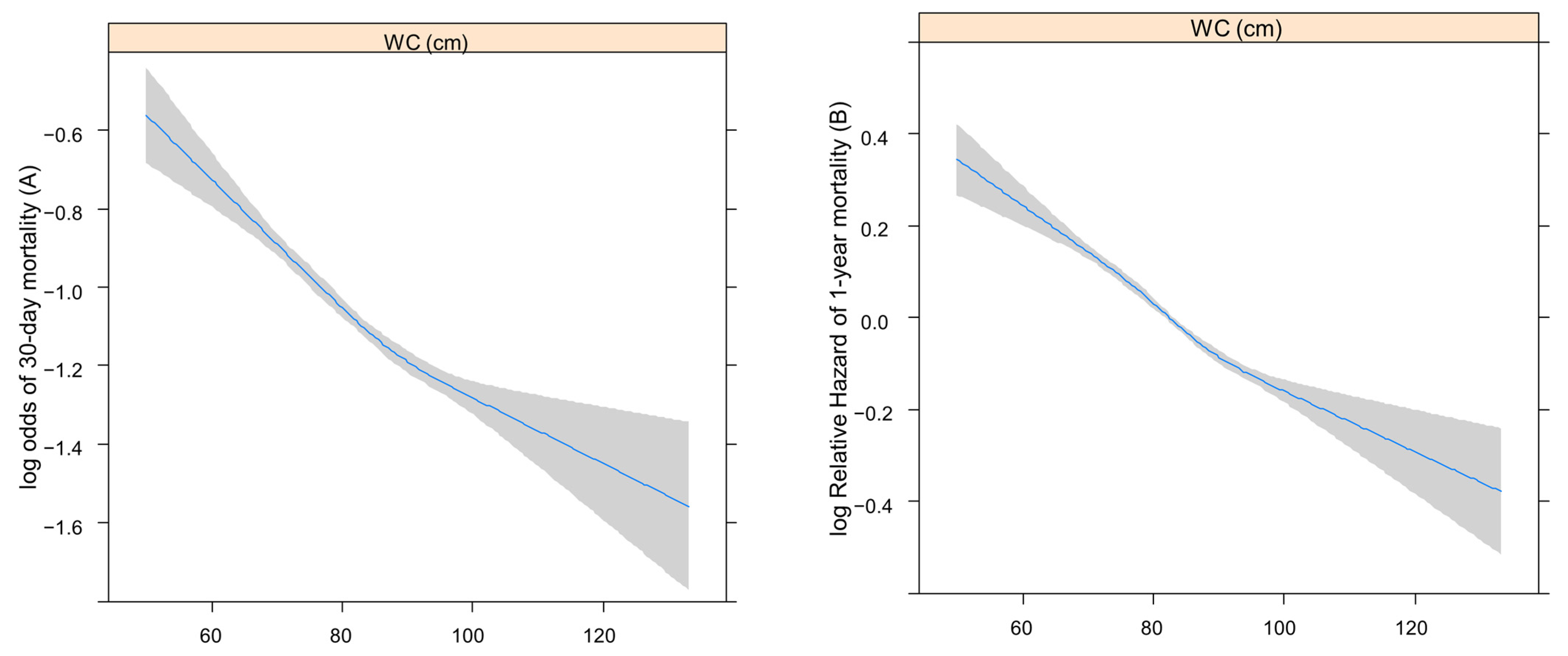
3.2. Restricted Cubic Splines
3.3. Survival Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oh, T.K.; Song, I.-A. Quality of life after sepsis and its association with mortality among sepsis survivors in South Korea: A population level cohort study. J. Crit. Care 2021, 64, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun-Buisson, C.; Doyon, F.; Carlet, J.; Dellamonica, P.; Gouin, F.; Lepoutre, A.; Mercier, J.-C.; Offenstadt, G.; Régnier, B. Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of severe sepsis and septic shock in adults: A multicenter prospective study in intensive care units. JAMA 1995, 274, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angus, D.C.; Linde-Zwirble, W.T.; Lidicker, J.; Clermont, G.; Carcillo, J.; Pinsky, M.R. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: Analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasabuchi, Y.; Yasunaga, H.; Matsui, H.; Lefor, A.T.; Horiguchi, H.; Fushimi, K.; Sanui, M. The dose-response relationship between body mass index and mortality in subjects admitted to the ICU with and without mechanical ventilation. Respir. Care 2015, 60, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Tsai, C.-L.; Hwang, L.-Y.; Lai, D.; Markham, C.; Patel, B. Obesity and mortality, length of stay and hospital cost among patients with sepsis: A nationwide inpatient retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalani, C.; Venigalla, T.; Bailey, J.; Udeani, G.; Surani, S. Sepsis patients in critical care units with obesity: Is obesity protective? Cureus 2020, 12, e6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinnusi, M.E.; Pineda, L.A.; El Solh, A.A. Effect of obesity on intensive care morbidity and mortality: A meta-analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, D.J.; Sun, J.; Welsh, J.; Cui, X.; Suffredini, A.F.; Eichacker, P.Q. Increased body mass index and adjusted mortality in ICU patients with sepsis or septic shock: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.; Fan, J.; Yu, C.; Guo, Y.; Bian, Z.; Wei, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Du, H.; Chang, L. Body-mass index and long-term risk of sepsis-related mortality: A population-based cohort study of 0.5 million Chinese adults. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulton, T.G.; Weiner, M.G.; Morales, K.H.; Gaieski, D.F.; Mehta, J.; Lautenbach, E. The effect of obesity on clinical outcomes in presumed sepsis: A retrospective cohort study. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2014, 9, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuperman, E.F.; Showalter, J.W.; Lehman, E.B.; Leib, A.E.; Kraschnewski, J.L. The impact of obesity on sepsis mortality: A retrospective review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wacharasint, P.; Boyd, J.H.; Russell, J.A.; Walley, K.R. One size does not fit all in severe infection: Obesity alters outcome, susceptibility, treatment, and inflammatory response. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurzinger, B.; Dünser, M.W.; Wohlmuth, C.; Deutinger, M.C.; Ulmer, H.; Torgersen, C.; Schmittinger, C.A.; Grander, W.; Hasibeder, W.R. The association between body-mass index and patient outcome in septic shock: A retrospective cohort study. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2010, 122, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, D.J.; Demirkale, C.Y.; Sun, J.; Rhee, C.; Fram, D.; Eichacker, P.; Klompas, M.; Suffredini, A.F.; Kadri, S.S. Does obesity protect against death in sepsis? A retrospective cohort study of 55,038 adult patients. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.E.; Szychowski, J.M.; Griffin, R.; Safford, M.M.; Shapiro, N.I.; Howard, G. Long-term mortality after community-acquired sepsis: A longitudinal population-based cohort study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e004283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ness-Abramof, R.; Apovian, C.M. Waist circumference measurement in clinical practice. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2008, 23, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, G.E.; Kim, Y.-H.; Han, K.; Jung, J.-H.; Rhee, E.-J.; Lee, S.-S.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, K.-W.; Lee, W.-Y. Obesity fact sheet in Korea, 2019: Prevalence of obesity and abdominal obesity from 2009 to 2018 and social factors. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 29, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.O.; Jung, C.H.; Song, Y.D.; Park, C.Y.; Kwon, H.S.; Cha, B.S.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, K.U.; Ko, K.S.; Lee, B.W. Background and data configuration process of a nationwide population-based study using the korean national health insurance system. Diabetes Metab. J. 2014, 38, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.W.; Cho, J.; Park, J.H.; Cho, B. National General Health Screening Program in Korea: History, current status, and future direction. Precis. Future Med. 2022, 6, 9–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. BMI Classification. World Health Organization 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/topic-details/GHO/body-mass-index (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Lean, M.; Han, T.; Morrison, C. Waist circumference as a measure for indicating need for weight management. Bmj 1995, 311, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHLBI Obesity Education Initiative Expert Panel on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Obesity in Adults (US); National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: The Evidence Report; National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Desquilbet, L.; Mariotti, F. Dose-response analyses using restricted cubic spline functions in public health research. Stat. Med. 2010, 29, 1037–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Liu, C.; Huang, C.; Fang, X. The role of increased body mass index in outcomes of sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. 2017, 17, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Q.; Ding, Y.; Ge, H.; Shen, N.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, Y. Impact of body mass index on survival of medical patients with sepsis: A prospective cohort study in a university hospital in China. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e021979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, M.K.; Choi, D.J.; Shin, T.G.; Jeon, K.; Suh, G.Y.; Sim, M.S.; Song, K.J.; Jeong, Y.K.; Jo, I.J. Body mass index and outcomes in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. Acute Crit. Care 2013, 28, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sato, T.; Kudo, D.; Kushimoto, S.; Hasegawa, M.; Ito, F.; Yamanouchi, S.; Honda, H.; Andoh, K.; Furukawa, H.; Yamada, Y. Associations between low body mass index and mortality in patients with sepsis: A retrospective analysis of a cohort study in Japan. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabi, Y.M.; Dara, S.I.; Tamim, H.M.; Rishu, A.H.; Bouchama, A.; Khedr, M.K.; Feinstein, D.; Parrillo, J.E.; Wood, K.E.; Keenan, S.P. Clinical characteristics, sepsis interventions and outcomes in the obese patients with septic shock: An international multicenter cohort study. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Niekerk, G.; Meaker, C.; Engelbrecht, A.-M. Nutritional support in sepsis: When less may be more. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preiser, J.C.; van Zanten, A.R.; Berger, M.M.; Biolo, G.; Casaer, M.P.; Doig, G.S.; Griffiths, R.D.; Heyland, D.K.; Hiesmayr, M.; Iapichino, G.; et al. Metabolic and nutritional support of critically ill patients: Consensus and controversies. Crit Care 2015, 19, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auiwattanakul, S.; Chittawatanarat, K.; Chaiwat, O.; Morakul, S.; Kongsayreepong, S.; Ungpinitpong, W.; Yutthakasemsunt, S.; Buranapin, S. Effects of nutrition factors on mortality and sepsis occurrence in a multicenter university-based surgical intensive care unit in Thailand (THAI-SICU study). Nutrition 2019, 58, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wischmeyer, P.E. Nutrition Therapy in Sepsis. Crit Care Clin 2018, 34, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koster, A.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Schatzkin, A.; Mouw, T.; Adams, K.F.; van Eijk, J.T.M.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Harris, T.B. Waist circumference and mortality. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 167, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, E.J.; Newton, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Patel, A.V.; McCullough, M.L.; Campbell, P.T.; Thun, M.J.; Gapstur, S.M. Waist circumference and all-cause mortality in a large US cohort. Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerhan, J.R.; Moore, S.C.; Jacobs, E.J.; Kitahara, C.M.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Adami, H.-O.; Ebbert, J.O.; English, D.R.; Gapstur, S.M.; Giles, G.G. A pooled analysis of waist circumference and mortality in 650,000 adults. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamdari, N.M.; Rahimi, F.S.; Afaghi, S.; Zarghi, A.; Qaderi, S.; Tarki, F.E.; Ghafouri, S.R.; Besharat, S. The impact of metabolic syndrome on morbidity and mortality among intensive care unit admitted COVID-19 patients. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 1979–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.T. Inadequate exercise as a risk factor for sepsis mortality. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.E.; Griffin, R.; Judd, S.; Shapiro, N.I.; Safford, M.M. Obesity and risk of sepsis: A population-based cohort study. Obesity 2013, 21, E762–E769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, I.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Ross, R. Waist circumference and not body mass index explains obesity-related health risk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, A.; Evans, L.E.; Alhazzani, W.; Levy, M.M.; Antonelli, M.; Ferrer, R.; Kumar, A.; Sevransky, J.E.; Sprung, C.L.; Nunnally, M.E. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 304–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.-K.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, E.-J.; Lee, E.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Song, I.-A. Effect of early nutritional support on clinical outcomes of critically ill patients with sepsis and septic shock: A single-center retrospective study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karampela, I.; Chrysanthopoulou, E.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Dalamaga, M. Is there an obesity paradox in critical illness? Epidemiologic and metabolic considerations. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichon, I.; Ortmann, W.; Santocki, M.; Opydo-Chanek, M.; Kolaczkowska, E. Scrutinizing Mechanisms of the ‘Obesity Paradox in Sepsis’: Obesity Is Accompanied by Diminished Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) Due to Restricted Neutrophil–Platelet Interactions. Cells 2021, 10, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Median [IQR, Range] or N (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age, year | 68.0 [60–78, 40–84] | |
| Male sex | 41,790 (53.7) | |
| Main diagnosis of sepsis | 27,197 (35.0) | |
| Having a job | 46,264 (59.5) | |
| Residence at sepsis | ||
| Urban area | 25,353 (32.6) | |
| Rural area | 52,457 (67.4) | |
| Household income level | ||
| Medical aid program | 4960 (6.4) | |
| Q1 (lowest) | 13,618 (17.5) | |
| Q2 | 11,852 (15.2) | |
| Q3 | 15,542 (20.0) | |
| Q4 (highest) | 24,787 (31.9) | |
| Unknown | 7051 (9.1) | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.4 [21.0–26.0, 10.0–54.5] | |
| <18.5 | 6386 (8.2) | |
| 18.5–24.9 | 46,254 (59.4) | |
| 25.0–29.9 | 21,419 (27.5) | |
| 30.0–34.9 | 3221 (4.1) | |
| >35.0 | 530 (0.7) | |
| Waist circumference | 90.5 [79.6–102.5, 58.1–131.3] | |
| Normal | 51,259 (65.9) | |
| High | 15,804 (20.3) | |
| Very high | 10,747 (13.8) | |
| CCI, point | 3.0 [1.0–4.0, 0–17] | |
| ICU admission | 24,413 (31.4) | |
| Ventilator support | 12,682 (16.3) | |
| ECMO support | 315 (0.4) | |
| CRRT use | 3522 (4.5) | |
| Type of hospital | ||
| General hospital | 55,873 (71.8) | |
| Hospital | 7324 (9.4) | |
| Long-term facility care hospital | 14,290 (18.4) | |
| Other | 323 (0.4) | |
| IM department | 52,304 (67.2) | |
| Surgery-associated hospital admission | 30,808 (39.6) | |
| Year | ||
| 2013 | 7213 (9.3) | |
| 2014 | 7277 (9.4) | |
| 2015 | 7923 (10.2) | |
| 2016 | 9271 (11.9) | |
| 2017 | 10,958 (14.1) | |
| 2018 | 11,415 (14.7) | |
| 2019 | 11,719 (15.1) | |
| 2020 | 12,034 (15.5) | |
| Variable | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, year | 1.04 (1.04, 1.04) | <0.001 | |
| Male sex | 1.38 (1.32, 1.44) | <0.001 | |
| Main diagnosis of sepsis | 1.03 (0.99, 1.07) | 0.193 | |
| Having a job | 0.93 (0.90, 0.97) | 0.001 | |
| Residence at sepsis | |||
| Urban area | 1 | ||
| Rural area | 1.06 (1.02, 1.10) | 0.007 | |
| Household income level | |||
| Medical aid program | 1.06 (0.98, 1.16) | 0.159 | |
| Q1 (lowest) | 1 | ||
| Q2 | 0.93 (0.87, 0.99) | 0.021 | |
| Q3 | 0.92 (0.86, 0.97) | 0.003 | |
| Q4 (highest) | 0.85 (0.80, 0.89) | <0.001 | |
| Unknown | 0.67 (0.62, 0.73) | <0.001 | |
| BMI | |||
| <18.5 | 1.45 (1.36, 1.54) | <0.001 | |
| 18.5–24.9 | 1 | ||
| 25.0–29.9 | 0.80 (0.77, 0.84) | <0.001 | |
| 30.0–34.9 | 0.85 (0.76, 0.95) | 0.004 | |
| >35.0 | 0.78 (0.59, 1.02) | 0.068 | |
| Waist circumference | |||
| Normal | 1 | ||
| High | 0.89 (0.84, 0.93) | <0.001 | |
| Very high | 0.87 (0.81, 0.94) | <0.001 | |
| CCI, point | 1.10 (1.08, 1.12) | <0.001 | |
| ICU admission | 0.93 (0.88, 0.98) | 0.008 | |
| Ventilator support | 6.49 (6.14, 6.86) | <0.001 | |
| ECMO support | 1.26 (0.99, 1.60) | 0.066 | |
| CRRT use | 2.65 (2.43, 2.88) | <0.001 | |
| Type of hospital | |||
| General hospital | 1 | ||
| Hospital | 1.74 (1.64, 1.86) | <0.001 | |
| Long-term facility care hospital | 1.59 (1.50, 1.68) | <0.001 | |
| Other hospital | 0.93 (0.65, 1.31) | 0.661 | |
| IM department | 1.27 (1.22, 1.33) | <0.001 | |
| Surgery-associated hospital admission | 1.01 (0.96, 1.06) | 0.695 | |
| Year | |||
| 2013 | 1 | ||
| 2014 | 0.96 (0.89, 1.04) | 0.337 | |
| 2015 | 0.91 (0.84, 0.99) | 0.019 | |
| 2016 | 0.85 (0.78, 0.91) | <0.001 | |
| 2017 | 0.75 (0.70, 0.81) | <0.001 | |
| 2018 | 0.71 (0.66, 0.76) | <0.001 | |
| 2019 | 0.70 (0.65, 0.80) | <0.001 | |
| 2020 | 0.75 (0.70, 0.80) | <0.001 | |
| Variable | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, year | 1.03 (1.03, 1.03) | <0.001 | |
| Male sex | 1.37 (1.33, 1.40) | <0.001 | |
| Main diagnosis of sepsis | 0.92 (0.90, 0.94) | <0.001 | |
| Having a job | 0.94 (0.92, 0.96) | <0.001 | |
| Residence at sepsis | |||
| Urban area | 1 | ||
| Rural area | 1.05 (1.03, 1.07) | <0.001 | |
| Household income level | |||
| Medical aid program | 1.08 (1.03, 1.14) | 0.002 | |
| Q1 (lowest) | 1 | ||
| Q2 | 0.96 (0.93, 0.99) | 0.040 | |
| Q3 | 0.96 (0.93, 0.99) | 0.017 | |
| Q4 (highest) | 0.91 (0.89, 0.94) | <0.001 | |
| Unknown | 0.87 (0.83, 0.91) | <0.001 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | |||
| <18.5 | 1.30 (1.26, 1.34) | <0.001 | |
| 18.5–24.9 | 1 | ||
| 25.0–29.9 | 0.82 (0.80, 0.85) | <0.001 | |
| 30.0–34.9 | 0.81 (0.76, 0.87) | <0.001 | |
| >35.0 | 0.93 (0.79, 1.09) | 0.357 | |
| Waist circumference | |||
| Normal | 1 | ||
| High | 0.92 (0.89, 0.95) | <0.001 | |
| Very high | 0.89 (0.85, 0.93) | <0.001 | |
| CCI, point | 1.08 (1.06, 1.09) | <0.001 | |
| ICU admission | 0.90 (0.87, 0.93) | <0.001 | |
| Ventilator support | 3.43 (3.32, 3.54) | <0.001 | |
| ECMO support | 1.18 (1.04, 1.35) | 0.010 | |
| CRRT support | 1.74 (1.67, 1.82) | <0.001 | |
| Type of hospital | |||
| General hospital | 1 | ||
| Hspital | 1.42 (1.37, 1.48) | <0.001 | |
| Long-term facility care hospital | 1.87 (0.81, 1.94) | <0.001 | |
| Other | 0.66 (0.52, 0.86) | 0.002 | |
| IM department | 1.23 (1.20, 1.26) | <0.001 | |
| Surgery-associated hospital admission | 1.17 (1.14, 1.21) | <0.001 | |
| Year | |||
| 2013 | 1 | ||
| 2014 | 1.00 (0.96, 1.05) | 0.888 | |
| 2015 | 0.93 (0.89, 0.97) | 0.001 | |
| 2016 | 0.89 (0.85, 0.93) | <0.001 | |
| 2017 | 0.83 (0.79, 0.87) | <0.001 | |
| 2018 | 0.80 (0.76, 0.83) | <0.001 | |
| 2019 | 0.79 (0.76, 0.83) | <0.001 | |
| 2020 | 0.81 (0.78, 0.84) | <0.001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, T.-K.; Song, I.-A. The Association of Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference with Sepsis-Related Mortality in South Korea. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060574
Oh T-K, Song I-A. The Association of Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference with Sepsis-Related Mortality in South Korea. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(6):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060574
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Tak-Kyu, and In-Ae Song. 2024. "The Association of Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference with Sepsis-Related Mortality in South Korea" Diagnostics 14, no. 6: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060574
APA StyleOh, T.-K., & Song, I.-A. (2024). The Association of Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference with Sepsis-Related Mortality in South Korea. Diagnostics, 14(6), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060574





