Hemodynamic and Genetic Associations with the Risk of Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Development in an Ethnic Cohort of Kazakhs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results of the Study
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 38, 3618–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orriols, M.; Gomez-Puerto, M.C.; Ten Dijke, P. BMP type II receptor as a therapeutic target in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 16, 2979–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tielemans, B.; Delcroix, M.; Belge, C.; Quarck, R. TGFβ and BMPRII signalling pathways in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiè, N.; Palazzini, M.; Manes, A. Confirmation of survival prediction based on 2022 ESC/ERS pulmonary hypertension guidelines new haemodynamic thresholds. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 4692–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chazova, I.E.; Arkhipova, O.A.; Martynyuk, T.V. Legochnaya arterial naya gipertenziya v Rossii: Analiz shestiletnego nablyudeniya po dannym Natsional nogo registra. Ther. Arch. 2019, 1, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Morrell, N.W. Genetics and the molecular pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2013, 15, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Ma, Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, Q.; Li, W.; Xiong, C.; Zhou, Z. Genetic analyses in a cohort of 191 pulmonary arterial hypertension patients. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navas, P.; Tenorio, J.; Quezada, C.A.; Barrios, E.; Gordo, G.; Arias, P.; López Meseguer, M.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Palomino Doza, J.; Lapunzina, P.; et al. Molecular Analysis of BMPR2, TBX4, and KCNK3 and Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Spanish Patients and Families with Idiopathic and Hereditary Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2016, 69, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girerd, B.; Montani, D.; Jais, X.; Eyries, M.; Yaici, A.; Sztrymf, B.; Savale, L.; Parent, F.; Coulet, F.; Godinas, L.; et al. Genetic counselling in a national referral Centre for pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir. J. 2016, 47, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharmin, N.; Nganwuchu, C.C.; Nasim, M.T. Targeting the TGF-β signaling pathway for resolution of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 7, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrell, N.W.; Aldred, M.A.; Chung, W.K.; Elliott, C.G.; Nichols, W.C.; Soubrier, F.; Trembath, R.C.; Loyd, J.E. Genetics and genomics of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Pauciulo, M.W.; Welch, C.L.; Lutz, K.A.; Coleman, A.W.; Gonzaga-Jauregui, C.; Wang, J.; Grimes, J.M.; Martin, L.J.; He, H.; et al. Novel risk genes and mechanisms implicated by exome sequencing of 2572 individuals with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichstaedt, C.A.; Belge, C.; Chung, W.K.; Gräf, S.; Grünig, E.; Montani, D.; Quarck, R.; Tenorio-Castano, J.A.; Soubrier, F.; Trembath, R.C.; et al. Genetic counselling and testing in pulmonary arterial hypertension: A consensus statement on behalf of the International Consortium for Genetic Studies in PAH. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 2, 2201471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guignabert, C.; Bailly, S.; Humbert, M. Restoring BMPRII functions in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Opportunities, challenges and limitations. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 2, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, K.B.; Machado, R.D.; Pauciulo, M.W.; Thomson, J.R.; Phillips, J.A.; Loyd, J.E.; Nichols, W.C.; Trembath, R.C. Heterozygous germline mutations in BMPR2, encoding a TGF-beta receptor, cause familial primary pulmonary hypertension. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.D.; Girerd, B.; Montani, D.; Wang, X.J.; Galiè, N.; Austin, E.D.; Elliott, G.; Asano, K.; Grünig, E.; Yan, Y.; et al. BMPR2 mutations and survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: An individual participant data meta-analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfarr, N.; Fischer, C.; Ehlken, N.; Becker-Grünig, T.; López-González, V.; Gorenflo, M.; Hager, A.; Hinderhofer, K.; Miera, O.; Nagel, C.; et al. Hemodynamic and genetic analysis in children with idiopathic, heritable, and congenital heart disease associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gräf, S.; Haimel, M.; Bleda, M.; Hadinnapola, C.; Southgate, L.; Li, W.; Hodgson, J.; Liu, B.; Salmon, R.M.; Southwood, M.; et al. Identification of rare sequence variation underlying heritable pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nat. Commun. 2018, 1, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichstaedt, C.A.; Sassmannshausen, Z.; Shaukat, M.; Cao, D.; Xanthouli, P.; Gall, H.; Sommer, N.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Seyfarth, H.J.; Lerche, M.; et al. Gene panel diagnostics reveals new pathogenic variants in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respir. Res. 2022, 1, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, R.D.; Welch, C.L.; Haimel, M.; Bleda, M.; Colglazier, E.; Coulson, J.D.; Debeljak, M.; Ekstein, J.; Fineman, J.R.; Golden, W.C.; et al. Biallelic variants of ATP13A3 cause dose-dependent childhood-onset pulmonary arterial hypertension characterised by extreme morbidity and mortality. J. Med. Genet. 2022, 9, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montani, D.; Girerd, B.; Jaïs, X.; Laveneziana, P.; Lau, E.M.T.; Bouchachi, A.; Hascoët, S.; Günther, S.; Godinas, L.; Parent, F.; et al. Screening for pulmonary arterial hypertension in adults carrying a BMPR2 mutation. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 1, 2004229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badlam, J.B.; Badesch, D.B.; Austin, E.D.; Benza, R.L.; Chung, W.K.; Farber, H.W.; Feldkircher, K.; Frost, A.E.; Poms, A.D.; Lutz, K.A.; et al. United States Pulmonary Hypertension Scientific Registry: Baseline Characteristics. Chest 2021, 1, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southgate, L.; Machado, R.D.; Gräf, S.; Morrell, N.W. Molecular genetic framework underlying pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condon, D.F.; Nickel, N.P.; Anderson, R.; Mirza, S.; de Jesus Perez, V.A. The 6th world symposium on pulmonary hypertension: What’s old is new. F1000Research 2019, 8, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiè, N.; McLaughlin, V.V.; Rubin, L.J.; Simonneau, G. An overview of the 6th World Symposium on Pulmonary Hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 1, 1802148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, K.W.; Thenappan, T. World Health Organization Group I Pulmonary Hypertension: Epidemiology and Pathophysiology. Cardiol. Clin. 2016, 34, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andruska, A.; Spiekerkoetter, E. Consequences of BMPR2 deficiency in the pulmonary vasculature and beyond: Contributions to pulmonary arterial hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 9, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, A.Y.; Kim, B.G.; Kwon, S.; Seo, J.; Kim, H.K.; Chang, H.J.; Chang, S.A.; Cho, G.Y.; Rhee, S.J.; Jung, H.O.; et al. Prevalence and clinical features of bone morphogenetic protein receptor type 2 mutation in Korean idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension patients: The PILGRIM explorative cohort. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisaki, H.; Nakanishi, N.; Kyotani, S.; Takashima, A.; Tomoike, H.; Morisaki, T. BMPR2 mutations found in Japanese patients with familial and sporadic primary pulmonary hypertension. Hum. Mutat. 2004, 23, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.W.; Chang, S.K.; Chen, Y.W.; Lin, W.W.; Tsai, W.J.; Wang, K.Y. Whole Exome Sequencing of Patients with Heritable and Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Central Taiwan. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 911649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfarr, N.; Szamalek-Hoegel, J.; Fischer, C.; Hinderhofer, K.; Nagel, C.; Ehlken, N.; Tiede, H.; Olschewski, H.; Reichenberger, F.; Ghofrani, A.H.; et al. Hemodynamic and clinical onset in patients with hereditary pulmonary arterial hypertension and BMPR2 mutations. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, E.D.; Phillips, J.A.; Cogan, J.D.; Hamid, R.; Yu, C.; Stanton, K.C.; Phillips, C.A.; Wheeler, L.A.; Robbins, I.M.; Newman, J.H.; et al. Truncating and missense BMPR2 mutations differentially affect the severity of heritable pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respir. Res. 2009, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.T.; Weng, K.P.; Chang, S.K.; Huang, W.C.; Chen, L.W. Hemodynamic and Clinical Profiles of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patients with GDF2 and BMPR2 Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 5, 2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pousada, G.; Baloira, A.; Vilariño, C.; Cifrian, J.M.; Valverde, D. Novel mutations in BMPR2, ACVRL1 and KCNA5 genes and hemodynamic parameters in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Locus | Polymorphism | Primers | 5′-3′ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II (BMPR2) | p13 chr 2 | rs1061157 | rs1061157-F | CCGAACTAATTCCAATAAC |
| rs1061157-R | CTCCACTTACTCTGTATAC | |||
| FAM-rs1061157-G | FAM-AGAGCACAGAGGCCTAATTCTC-BHQ1 | |||
| ROX-rs1061157-A | ROX-AGAAGAGCACAGAGACCTAATTCTC-BHQ2 | |||
| BMPR2 | P2 chr 37 | rs2228545 | rs2228545-F | CTGCATTGATTGTATTCATC |
| rs2228545-R | TTCCCAAGAGACCTACTA | |||
| FAM-rs2228545-C | FAM-AAGTTTGATTTGTGCTTGCTGCC-BHQ1 | |||
| ROX-rs2228545-T | ROX-CAAGTTTGATTTGTGCTTGTTGCCA-BHQ2 | |||
| BMPR2 | P2 chr 38 | rs17199249 | rs17199249-F | CCACGTTTTGTGTTTTATTG |
| rs17199249-R | GGCAAGAGAACTAAGTGA | |||
| FAM-rs17199249-T | FAM-CCCTTTTCTTTATTCAGCCCCTTA-BHQ1 | |||
| ROX-rs17199249-G | ROX-CCCTTTTCTTGATTCAGCCCCTT-BHQ2 | |||
| BMPR2 | P2 chr 38 | rs113305949 | rs113305949-F | TGACCTAAAACACTGTGA |
| rs113305949-R | GTTGCTCACATATCAAAGA | |||
| FAM-rs113305949-C | FAM-CATGCCAAGTCCCTATGAAGGAA-BHQ1 | |||
| ROX-rs113305949-A | ROX-CATGCCAAGTACCTATGAAGGAA-BHQ2 |
| BMPR2 | Group | Genotype | Allele | MAF (Global1000G) | x2 | HWE p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G/G | G/A | A/A | ||||||
| rs1061157 (G > A) | IPAH (n = 51) | 34 (63.8%) | 10 (21.3%) | 7 (14.9%) | G = 83 (81.37%), A = 19 (18.63%), MAF—0.2353 | A = 0.11269/20,267 | 0.044 | 0.834 |
| Non-IPAH (n = 117) | 64 (54.7%) | 35 (29.9%) | 18 (15.4%) | |||||
| G/G | G/A | A/A | ||||||
| rs2228545 (G > A | IPAH (n = 52) | 3 (5.8%) | 30 (57.7%) | 19 (36.5%) | G = 51 (49.04%), A = 53(50.96%), MAF—0.6538 | A = 0.033121/8480 | 12.517 | <0.001 |
| Non-IPAH (n = 125) | 7 | 102 | 16 | |||||
| T/T | T/G | G/G | ||||||
| rs17199249 | IPAH (n = 53) | 30 (54.0%) | 15 (30.0%) | 8 (16.0%) | T = 75 (70.75%), G = 31 (29.24%), MAF—0.2925 | G = 0.125136/38,507 | 0.001 | 0.975 |
| Non-IPAH (n = 125) | 77 (61.6%) | 29 (23.2%) | 19 (15.2%) | |||||
| C/C | C/A | A/A | ||||||
| rs113305949 | IPAH (n = 51) | 39 (76.5%) | 10 (19.6%) | 2 (3.9%) | C = 88 (86.27), A = 14 (13.73) MAF—0.1375 | A = 0.027411/846 | 0.002 | 0.962 |
| Non-IPAH (n = 124) | 97 (78.2%) | 22 (17.7%) | 5 (4.1%) | |||||
| Variable | All Patients (n = 53) | Patients with BMPR2 Mutation (n = 17) | Patients Without BMPR2 Mutation (n = 36) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 45.0 (35.0–51.0) | 46.0 (39.0–51.5) | 44.0 (35.0–50.8) | 0.333 |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 46 (86.8%) | 14 (82.4%) | 32 (88.9%) | 0.040 * |
| Male | 7 (13.2%) | 3 (17.6%) | 4 (11.1%) | |
| Age at diagnosis IPAH, years | 40.0 (32.0–48.0) | 42.0 (35.5–49.5) | 40.0 (28.5–45.0) | 0.221 |
| Family history of PAH | ||||
| Yes | 47 (88.6%) | 15 (100.0%) | 32 (84.2%) | 0.263 |
| No | 3 (5.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (7.9%) | |
| Unknown | 3 (5.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (7.9%) | |
| 6 MWD (6 min walk distance), m | 328.26 (64.32) | 333.53 (53.27) | 326.18 (68.74) | 0.712 |
| NYHA | ||||
| I | 4 (7.6%) | 1 (6.7%) | 3 (7.9%) | 0.922 |
| II | 19 (35.8%) | 6 (40.0%) | 13 (34.2%) | |
| III | 30 (56.6%) | 8 (53.3%) | 22 (57.9%) | |
| sPO2, % | 95.0 (93.0–97.0) | 95.0 (93.5–97.0) | 95.0 (92.3–96.0) | 0.564 |
| Echocardiography | ||||
| LVEF, % | 58.7 (57.0–63.0) | 57.1 (56.0–58.2) | 60.4 (57.8–64.0) | 0.017 * |
| Pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP), mmHg | 78.0 (66.0–90.0) | 80.0 (63.5–92.0) | 77.5 (66.0–89.5) | 0.969 |
| Early diastolic pulmonary regurgitation velocity, m/s | 2.0 (1.9–2.7) | 2.0 (1.9–2.4) | 2.0 (1.8–2.8) | 0.968 |
| Fractional area contraction RV, (FAC), % | 33.0 (30.0–35.0) | 34.0 (31.5–35.5) | 33.0 (29.3–34.0) | 0.239 |
| Tricuspid annulus plane excursion (TAPSE), mm | 1.7 (1.6–1.9) | 1.7 (1.6–1.8) | 1.7 (1.6–1.9) | 0.765 |
| Right atrium area (end-systole), cm2 | 20.0 (17.0–26.0) | 19.0 (18.0–25.5) | 21.0 (17.0–26.0) | 0.968 |
| Pulmonary artery diameter, cm | 2.8 (2.3–3.1) | 2.6 (2.4–2.9) | 2.8 (2.3–3.3) | 0.313 |
| Pleural effusion | ||||
| Yes | 42 (79.2%) | 14 (93.3%) | 28 (73.7%) | 0.122 |
| No | 11 (20.8%) | 1 (6.7%) | 10 (26.3%) | |
| Hemodynamic at diagnosis | ||||
| mRAP, mmHg | 5.0 (4.0–6.0) | 5.0 (4.0–6.0) | 5.0 (4.0–6.0) | 0.703 |
| mPAP, mmHg | 44.0 (36.0–52.0) | 40.0 (37.0–51.0) | 44.0 (36.3–51.3) | 0.642 |
| Fick CI, L/min per m2 | 2.3 (1.9–2.7) | 2.2 (1.9–2.6) | 2.6 (2.3–3.1) | 0.027 * |
| PVR, WU | 8.9 (6.0–13.6) | 10.8 (8.7–14.9) | 8.6 (5.9–12.6) | 0.038 * |
| PVR I | 15.0 (9.6–22.1) | 16.2 (9.8–25.7) | 13.9 (9.7–21.1) | 0.413 |
| SVR I | 31.8 (25.6–36.4) | 29.7 (26.0–34.6) | 32.7 (24.2–36.6) | 0.867 |
| SvO2, % | 67.3 (62.5–69.3) | 66.3 (60.9–68.0) | 67.5 (63.0–70.2) | 0.291 |
| Vasodilator responder | ||||
| Positive | 27 (50.9%) | 9 (60.0%) | 18 (47.4%) | 0.176 |
| Negative | 6 (11.3%) | 3 (20.0%) | 3 (7.9%) | |
| Not performed | 20 (37.8%) | 3 (20.0%) | 17 (44.7%) | |
| Laboratories | ||||
| NT–proBNP, pg/mL | 670.0 (258.0–1214.0) | 670.0 (282.2–1031.0) | 665.5 (237.0–1341.3) | 0.992 |
| mRAP (mmHg) | mPAP (mmHg) | Fick CI (L/min per m2) | PVR (WU) | SVR (I) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1061157 | |||||
| Mutation | 4.0 (2.0; 5.0) | 43.14 (15.67) | 2.50 (2.30; 2.90) | 9,40 (5.20; 13.95) | 30.29 (8.28) |
| No mutation | 5.0 (4.0; 6.0) | 44.54 (11.54) | 2.20 (1.90; 2.68) | 8,85 (6.25; 13.01) | 31.41 (8.31) |
| p | 0.58 | 0.770 | 0.137 | 0.793 | 0.741 |
| rs17199249 | |||||
| Mutation | 4.50 (3.75; 5.25) | 38.25 (8.57) | 2.58 (0.78) | 5.90 (4.93; 9.33) | 31.43 (8.79) |
| No mutation | 5.0 (4.0; 6.0) | 45.55 (11.99) | 2.34 (0.53) | 10.04 (7.25; 14.3) | 31.60 (7.93) |
| p | 0.470 | 0.107 | 0.277 | 0.035 | 0.956 |
| rs113305949 | |||||
| Mutation | 5.0 (4.0; 6.0) | 46.0 (2.83) | 2.30 (2.05; 2.55) | 6.60 (6.0; 7.20) | 24.70 (19.65; 29.75) |
| No mutation | 4.0 (4.0; 4.0) | 44.36 (11.99) | 2.30 (1.90; 2.68) | 9.25 (6.25; 13.80) | 32.15 (25.95; 36.64) |
| p | 0.440 | 0.849 | 0.853 | 0.478 | 0.437 |
| BMPR2 Mutation | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Carrier | Non-Carrier | ||
| Total | |||
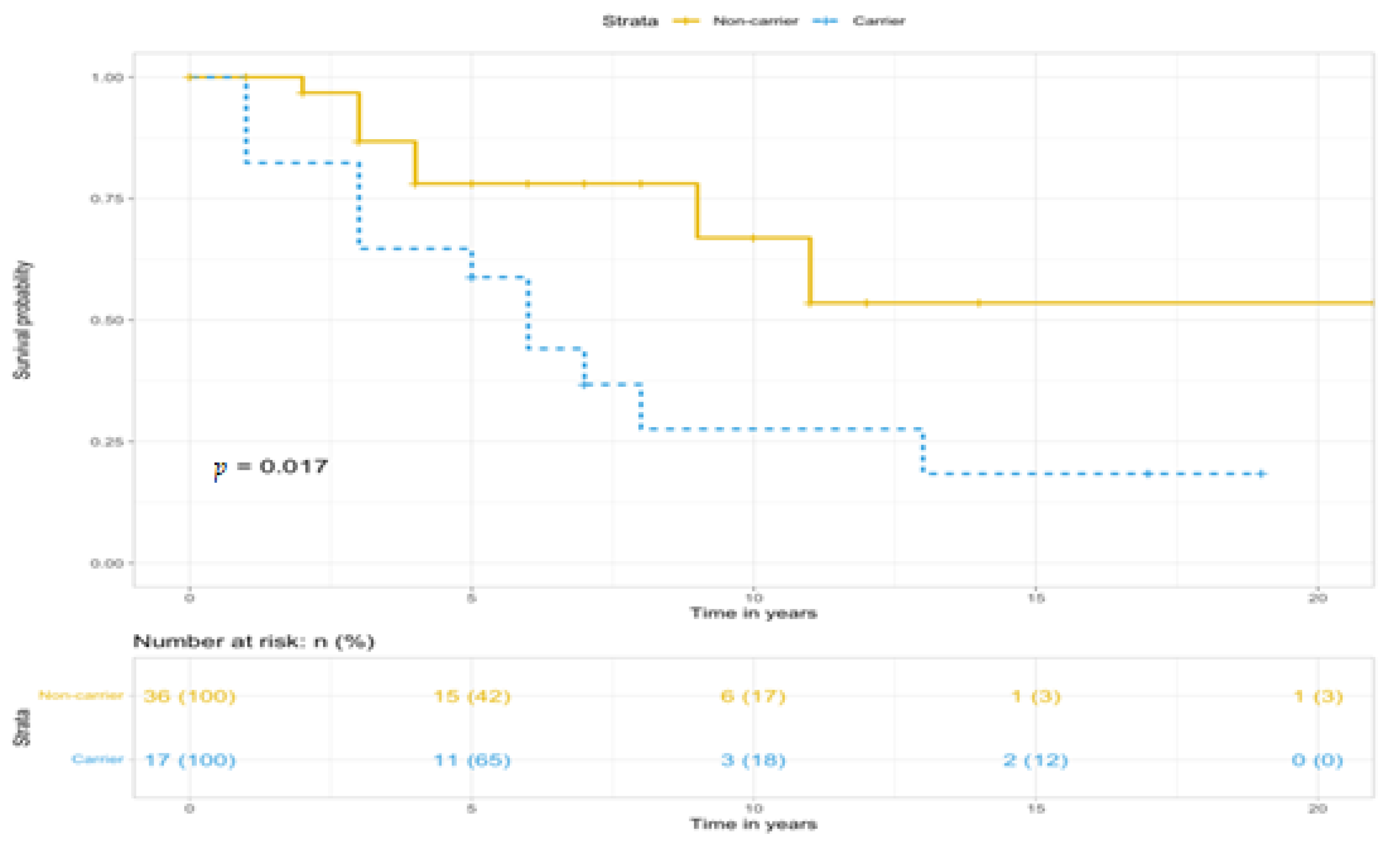
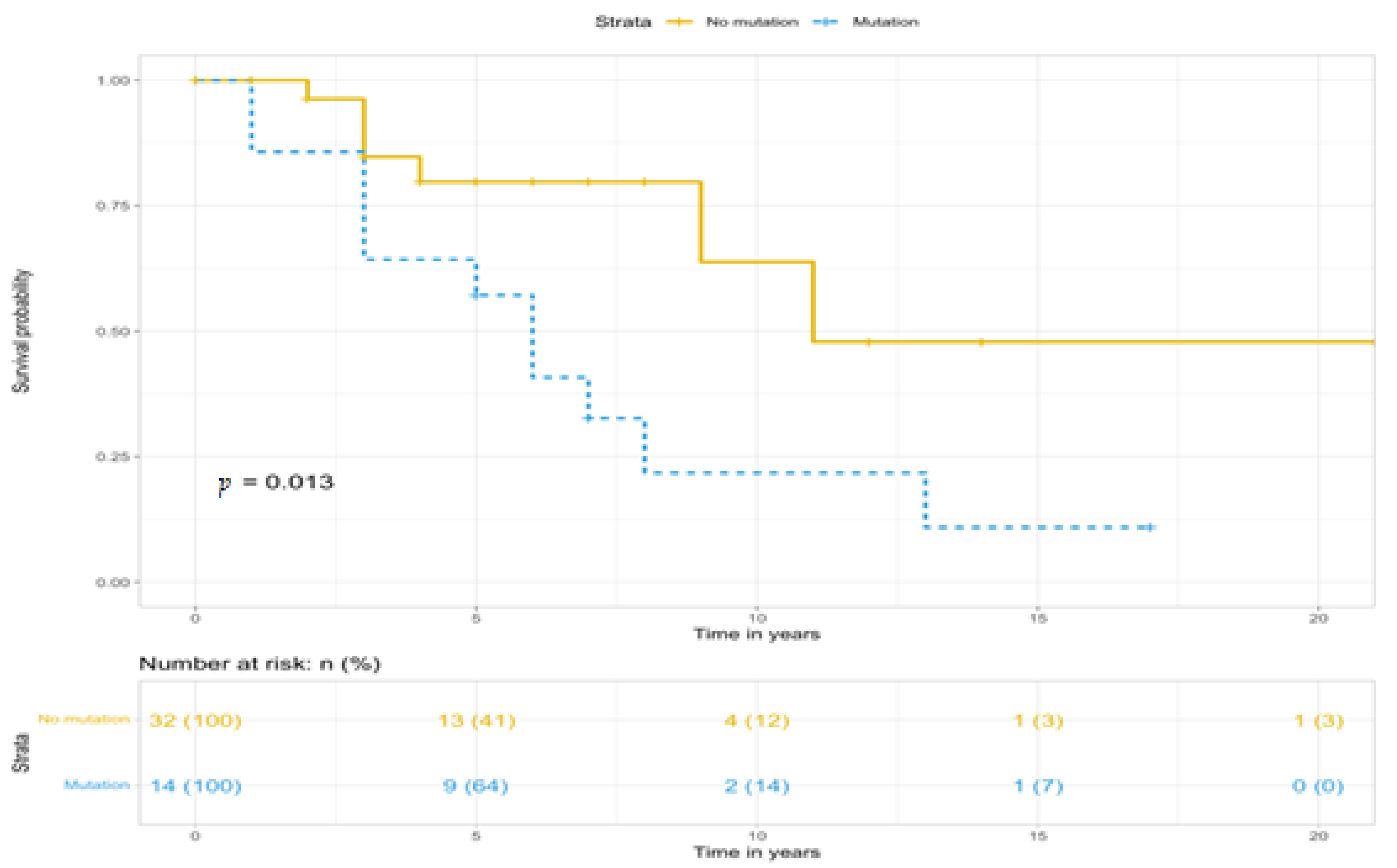
| n | 17 | 36 | 0.022 |
| Deaths, n (%) | 12 (70.6%) | 8 (22.2%) | |
| HR (95%CI) | 2.869 (1.165–7.065) | REF | |
| Female patients | |||
| n | 14 | 32 | 0.019 |
| Deaths (n, %) | 11 (78.6%) | 7 (21.9%) | |
| HR (95%CI) | 3.142 (1.212–8.143) | REF | |
| Male patients | |||
| n | 3 | 4 | 0.806 |
| Deaths (n, %) | 1 (33.3%) | 1 (25%) | |
| HR (95%CI) | 1.414 (0.088–22.64) | REF | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taizhanova, D.; Nurpissova, T.; Abildinova, G.; Martynyuk, T.; Kulmyrzayeva, N.; Zholdybayeva, E. Hemodynamic and Genetic Associations with the Risk of Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Development in an Ethnic Cohort of Kazakhs. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14232687
Taizhanova D, Nurpissova T, Abildinova G, Martynyuk T, Kulmyrzayeva N, Zholdybayeva E. Hemodynamic and Genetic Associations with the Risk of Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Development in an Ethnic Cohort of Kazakhs. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(23):2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14232687
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaizhanova, Dana, Togzhan Nurpissova, Gulshara Abildinova, Tamilla Martynyuk, Nazgul Kulmyrzayeva, and Elena Zholdybayeva. 2024. "Hemodynamic and Genetic Associations with the Risk of Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Development in an Ethnic Cohort of Kazakhs" Diagnostics 14, no. 23: 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14232687
APA StyleTaizhanova, D., Nurpissova, T., Abildinova, G., Martynyuk, T., Kulmyrzayeva, N., & Zholdybayeva, E. (2024). Hemodynamic and Genetic Associations with the Risk of Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Development in an Ethnic Cohort of Kazakhs. Diagnostics, 14(23), 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14232687





