The Microsurgical Resection of an Arteriovenous Malformation in a Patient with Thrombophilia: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
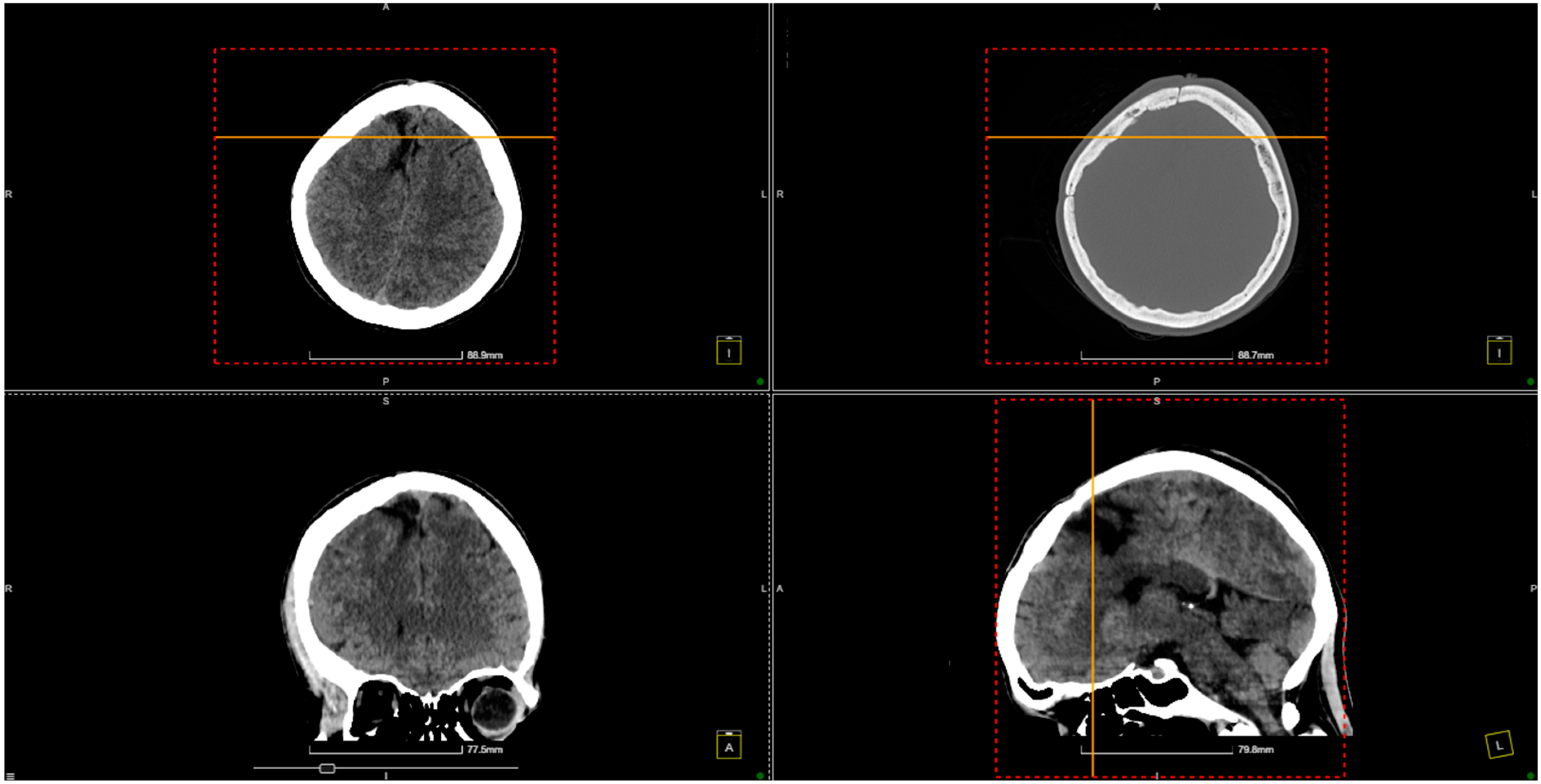
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Chen, P.; Li, R.; Han, H.; Li, Z.; Ma, L.; Yan, D.; Zhang, H.; Lin, F.; Li, R.; et al. Rupture-related quantitative hemodynamics of the supratentorial arteriovenous malformation nidus. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 138, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyemang, K.; Rose, A.; Olukoya, O.; Brown, J.; George, E.J.S. Spontaneous obliteration of brain arteriovenous malformations: Illustrative cases. J. Neurosurg. Case Lessons 2022, 4, CASE22309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Han, H.; Meng, X.; Jin, H.; Gao, D.; Ma, L.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Yan, D.; Zhang, H.; et al. Development and Validation of a Scoring System for Hemorrhage Risk in Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e231070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, D.; Li, Z.; Ma, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Ye, X.; Meng, X.; Jin, H.; Li, Y.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Elderly Brain Arteriovenous Malformations After Different Management Modalities: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 609588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.G.; Oliveira, R.; Vilela, P.; Oliveira, S.N. Spontaneous thrombosis of cerebral arteriovenous malformation post COVID-19. Neurol. Sci 2021, 42, 4909–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-S.; Lin, T.-M.; Wu, H.-M.; Lee, C.-C.; Yang, H.-C.; Luo, C.-B.; Guo, W.-Y.; Chung, W.-Y.; Lin, C.-J. Stagnant venous outflow in ruptured arteriovenous malformations revealed by delayed quantitative digital subtraction angiography. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 134, 109455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, E.A.; Birk, H.; Burkhardt, J.-K.; Chen, X.; Yue, J.K.; Guo, D.; Rutledge, W.C.; Lasker, G.F.; Partow, C.; Tihan, T.; et al. Reductions in brain pericytes are associated with arteriovenous malformation vascular instability. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rooij, W.; Jacobs, S.; Sluzewski, M.; van der Pol, B.; Beute, G.; Sprengers, M. Curative Embolization of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations with Onyx: Patient Selection, Embolization Technique, and Results. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Yan, F.; Xu, W.; Gao, L.; Zheng, J.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Yan, F.; et al. Spontaneous thrombosis in main draining veins of unruptured cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Medicine 2019, 98, e15588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.; Patel, U.; Wharton, S.B.; Cooper, P.C.; Makris, M. Fatal spontaneous thrombosis of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation in a young patient with a rare heterozygous prothrombin gene mutation. Case report. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 106, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulumuddin, M.I.; Sani, A.F.; Kurniawan, D. Spontaneous thrombosis of deep brain arteriovenous malformation in a patient with intraventricular and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Radiol. Case Rep. 2023, 18, 3620–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krapf, H.; Siekmann, R.; Freudenstein, D.; Küker, W.; Skalej, M. Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous maformation: Angiography and MR imaging follow-up and review of the literature. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2001, 22, 1556–1560. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fry, D.L. Acute vascular endothelial changes associated with increased blood velocity gradients. Circ. Res. 1968, 22, 165–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viñuela, F.; Nombela, L.; Roach, M.R.; Fox, A.J.; Pelz, D.M. Stenotic and occlusive disease of the venous drainage system of deep brain AVM’s. J. Neurosurg. 1985, 63, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quisling, R.; Mickle, J. Venous pressure measurements in vein of Galen aneurysms. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1989, 10, 411–417. [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist, K.; Wang, X.; Svensson, P.J.; Sundquist, J.; Hedelius, A.; Lönn, S.L.; Zöller, B.; Memon, A.A. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 4G/5G polymorphism, factor V Leiden, prothrombin mutations and the risk of VTE recurrence. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 114, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, E.J. Genetic Testing for Thrombophilia-Related Genes: Observations of Testing Patterns for Factor V Leiden (G1691A) and Prothrombin Gene ‘Mutation’ (G20210A). Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2019, 45, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiori, A.; Mosena, L.; Prins, M.H.; Prandoni, P. The risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism among heterozygous carriers of factor V Leiden or prothrombin G20210A mutation. A systematic review of prospective studies. Haematologica 2007, 92, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; He, M.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Xu, J. Microsurgery for intracranial arteriovenous malformation: Long-term outcomes in 445 patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonchev, N.; Pinchuk, A.; Dumitru, C.A.; Neyazi, B.; Swiatek, V.M.; Stein, K.P.; Sandalcioglu, I.E.; Rashidi, A. Postoperative Acute Intracranial Hemorrhage and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Brain Metastases Receiving Acetylsalicylic Acid Perioperatively. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 4599–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.M.; Yang, H.C.; Lee, C.C.; Wu, H.M.; Hu, Y.S.; Luo, C.B.; Guo, W.Y.; Kao, Y.H.; Chung, W.Y.; Lin, C.J. Stasis index from hemodynamic analysis using quantitative DSA correlates with hemorrhage of supratentorial arteriovenous malformation: A cross-sectional study. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 132, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, J.K.; Hu, Y.-S.; Lin, T.-M.; Lin, C.-J.; Lirng, J.-F.; Wu, H.-M.; Yang, H.-C.; Lee, C.-C.; Luo, C.-B.; Guo, W.-Y. Shortened cerebral circulation time correlates with seizures in brain arteriovenous malformation: A cross-sectional quantitative digital subtraction angiography study. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 5402–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.; Rämö, J.T.; Jurgens, S.J.; Niiranen, T.; Sanna-Cherchi, S.; Bauer, K.A.; Haj, A.; Choi, S.H.; Palotie, A.; Daly, M.; et al. Thrombosis risk in single- and double-heterozygous carriers of factor V Leiden and prothrombin G20210A in FinnGen and the UK Biobank. Blood 2024, 143, 2425–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, J.; Bauer, K.A. Managing thromboembolic risk in patients with hereditary and acquired thrombophilias. Blood 2020, 135, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci, M.; Binetti, B.M.; Tripodi, A.; Chantarangkul, V.; Semeraro, N. Hyperprothrombinemia associated with prothrombin G20210A mutation inhibits plasma fibrinolysis through a TAFI-mediated mechanism. Blood 2004, 103, 2157–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
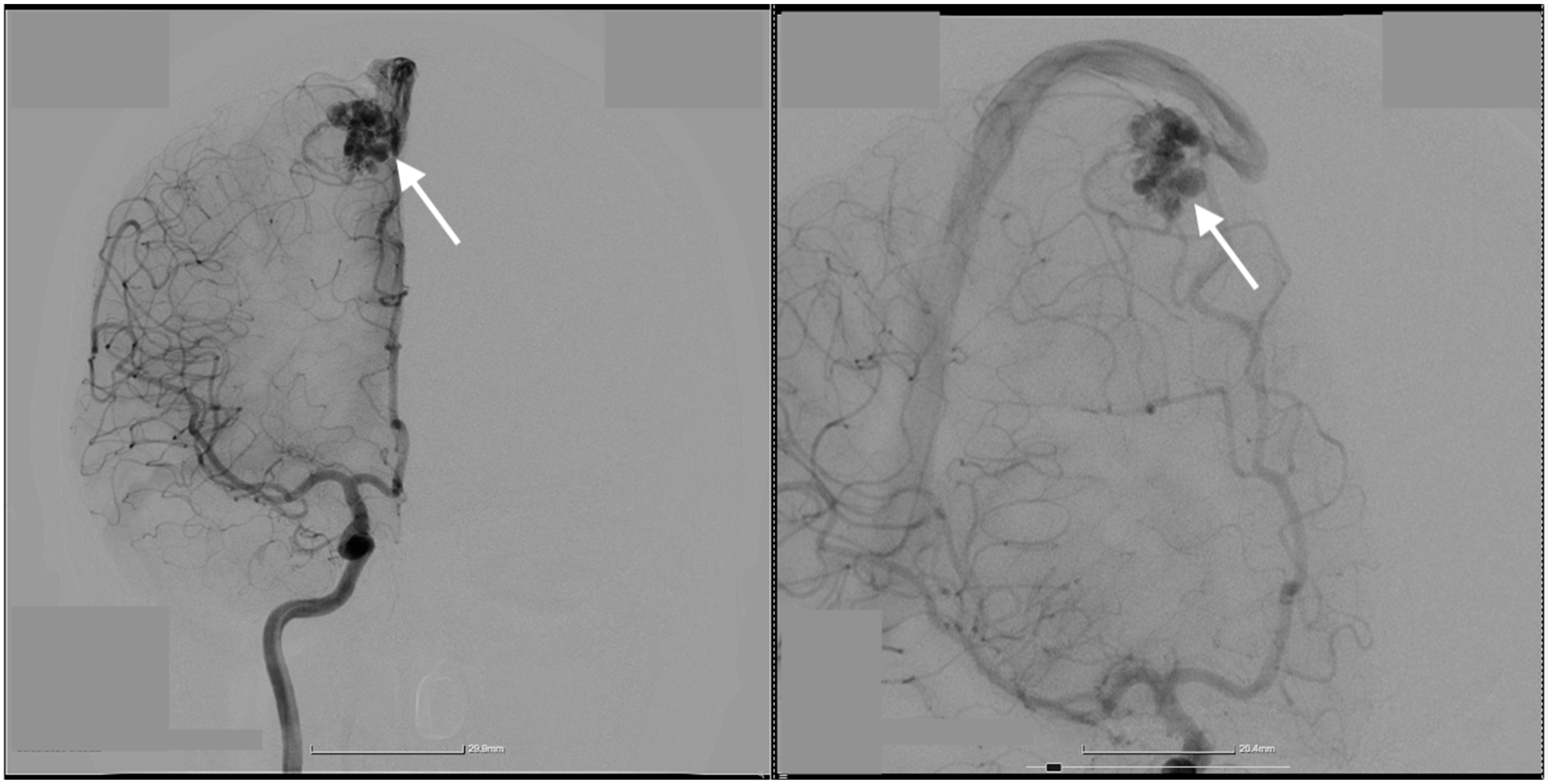
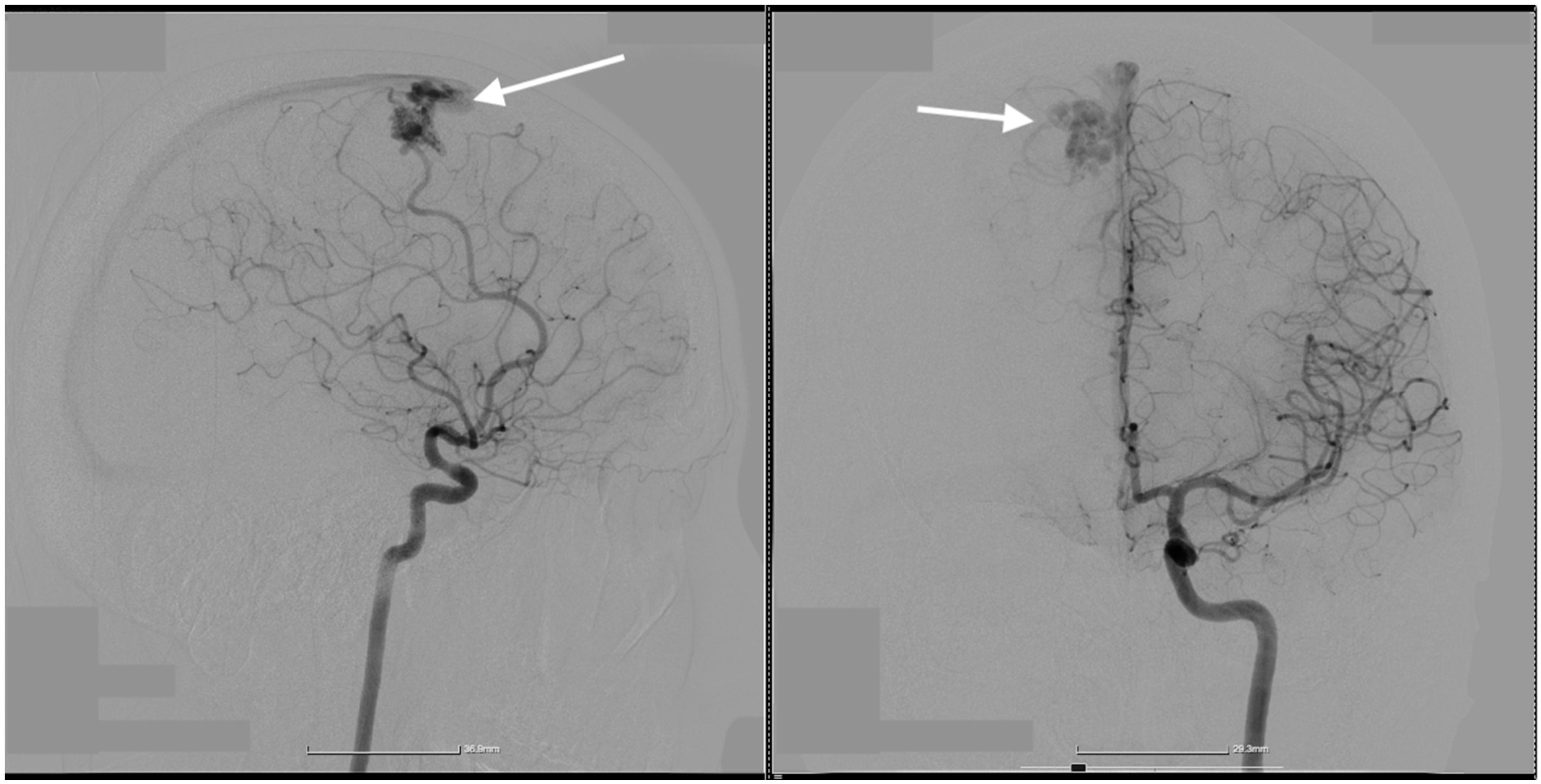
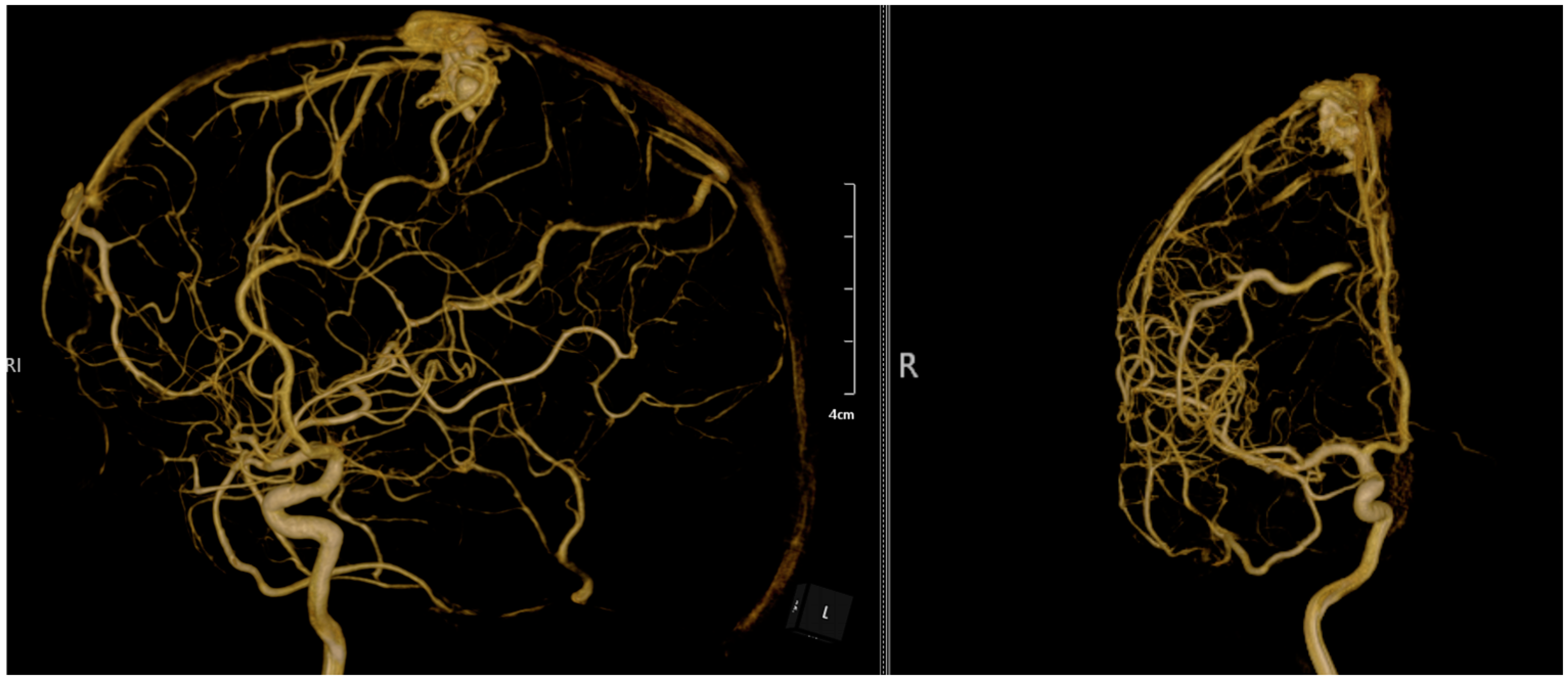
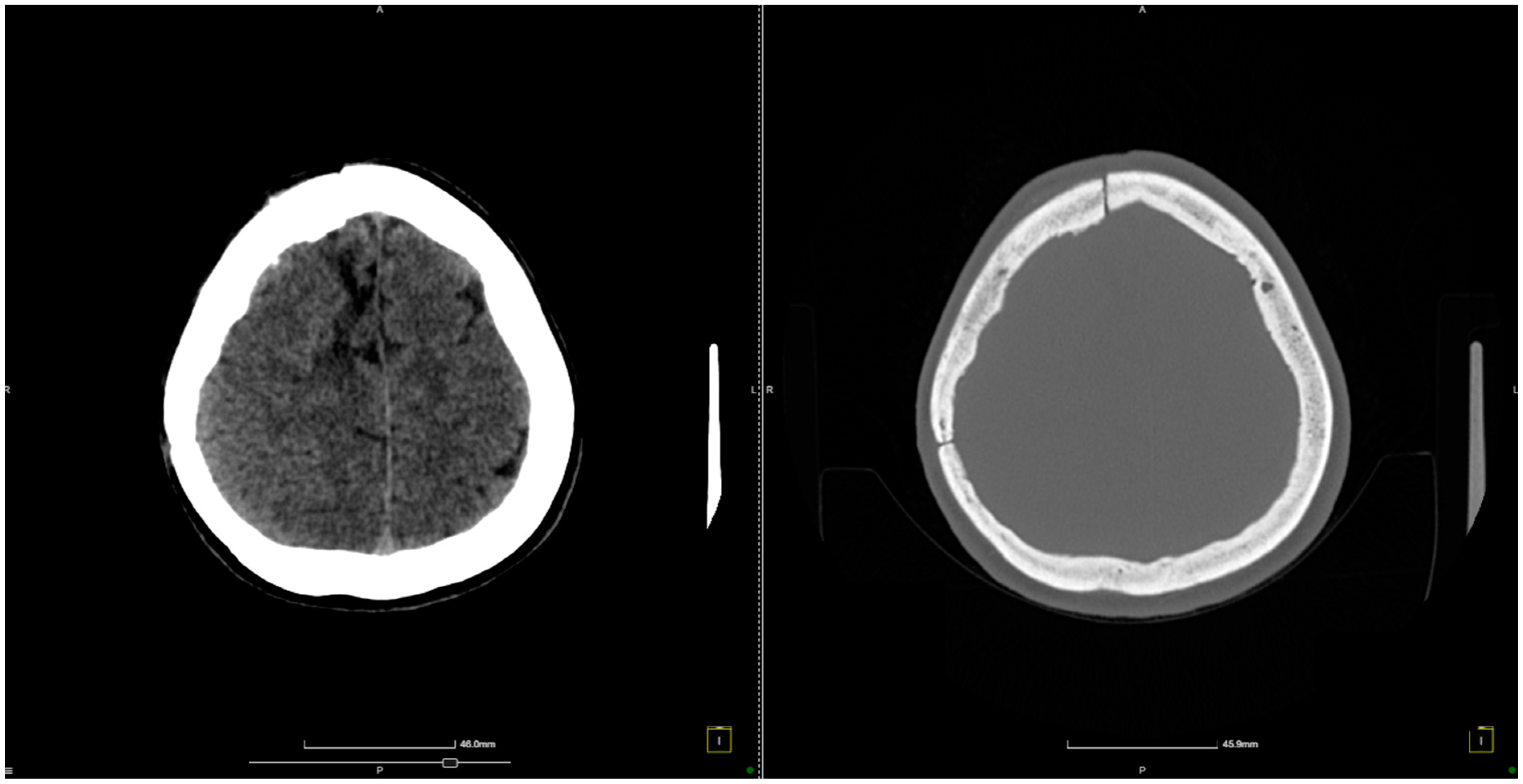
| Study | Number of Patients | Sex Ratio | AVM Localization | Rupture Status | AVM Diameter | Associated Complications | Arterial Feeder(s) | Venous Outflow(s) | Size of Nidus (cm) | Surgical Approach | Treatment Method | Characteristics of Thrombophilia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al. (2023) [20] | 4 | Mixed | Deep brain regions | All ruptured | 0.79–2.56 cm | Hemorrhage, neurological deficits | Tiny arterial branches | Single draining vein | 0.79–2.56 | Transvenous embolization | Onyx embolization | Thrombophilia not detailed, but hemorrhage risks increased in hypercoagulable states |
| Massoud et al. (2022) [1] | 4 | Mixed | Supratentorial | Ruptured | 0.79–2.56 cm | Hemorrhage, embolization-induced rupture | Small feeders with tortuous paths | Single draining vein | 0.79–2.56 | Transvenous embolization | Onyx-based TVE | TVE management helped control complications associated with thrombosis risks |
| Chen et al. (2021) [4] | 5 | Mixed | Deep brain | Ruptured | Variable | Neurological deficits, hemorrhage | Variable deep feeders | Single draining vein | Variable | Transvenous embolization | Combined approach (arterial and venous) | No direct thrombophilia analysis, but TVE showed good outcomes in hemorrhage control |
| Rodrigues et al. (2020) [5] | 1 | Male | Parieto-temporal | Thrombosed (spontaneous) | Not specified | Seizures, focal neurological deficits | Anterior cerebral artery | Parieto-temporal cortical vein | Not specified | Conservative management | Anticoagulation, dexamethasone | Thrombosis linked to hypercoagulable state induced by COVID-19, leading to spontaneous AVM thrombosis |
| Lin et al. (2019) [21] | 45 | Mixed | Supratentorial | 36% ruptured | 1.8–6.2 cm | Hemorrhage, seizures | MCA feeders | Multiple venous drainers | 3.2 | Superselective catheterization | Endovascular embolization | Thrombophilia not directly associated with but implicated in hemorrhage risk |
| Burkhardt et al. (2018) [7] | 24 | Mixed | Supratentorial | Mixed | Variable | Venous drainage issues | Small arterial feeders | Single draining vein | Variable | Transvenous embolization | Combined transarterial and transvenous embolization | No thrombophilia data, but complications noted with venous thrombosis |
| Rooij et al. (2011) [8] | 24 | Mixed | Frontal, occipital, parietal, temporal | Mixed | 1–3 cm | Hemorrhage, seizures | MCA and ACA feeders | Single superficial draining vein | 1–3 | Curative embolization | Onyx embolization | Thrombophilia not directly analyzed, but embolization was complicated by venous reflux |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toader, C.; Brehar, F.-M.; Radoi, M.P.; Serban, M.; Covache-Busuioc, R.-A.; Glavan, L.-A.; Ciurea, A.V.; Dobrin, N. The Microsurgical Resection of an Arteriovenous Malformation in a Patient with Thrombophilia: A Case Report and Literature Review. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14232613
Toader C, Brehar F-M, Radoi MP, Serban M, Covache-Busuioc R-A, Glavan L-A, Ciurea AV, Dobrin N. The Microsurgical Resection of an Arteriovenous Malformation in a Patient with Thrombophilia: A Case Report and Literature Review. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(23):2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14232613
Chicago/Turabian StyleToader, Corneliu, Felix-Mircea Brehar, Mugurel Petrinel Radoi, Matei Serban, Razvan-Adrian Covache-Busuioc, Luca-Andrei Glavan, Alexandru Vlad Ciurea, and Nicolaie Dobrin. 2024. "The Microsurgical Resection of an Arteriovenous Malformation in a Patient with Thrombophilia: A Case Report and Literature Review" Diagnostics 14, no. 23: 2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14232613
APA StyleToader, C., Brehar, F.-M., Radoi, M. P., Serban, M., Covache-Busuioc, R.-A., Glavan, L.-A., Ciurea, A. V., & Dobrin, N. (2024). The Microsurgical Resection of an Arteriovenous Malformation in a Patient with Thrombophilia: A Case Report and Literature Review. Diagnostics, 14(23), 2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14232613






