Comparison of Precision, Agreement, and Accuracy of Two Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Biometers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
- Primary endpoint:
- Secondary or exploratory endpoints:
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mirzayev, I.; Gündüz, A.K.; Aydın Ellialtıoğlu, P.; Gündüz, Ö.Ö. Clinical Applications of Anterior Segment Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography: A Systematic Review. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2023, 42, 103334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, J.X.; Chang, D.F. Intraocular Lens Power Formulas, Biometry, and Intraoperative Aberrometry: A Review. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, e94–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshirfar, M.; Buckner, B.; Ronquillo, Y.C.; Hofstedt, D. Biometry in Cataract Surgery: A Review of the Current Literature. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2019, 30, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashiyama, T.; Mori, H.; Nakajima, F.; Ohji, M. Comparison of a New Biometer Using Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography and a Conventional Biometer Using Partial Coherence Interferometry. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galzignato, A.; Lupardi, E.; Hoffer, K.J.; Barboni, P.; Schiano-Lomoriello, D.; Savini, G. Repeatability of New Optical Biometer and Agreement with 2 Validated Optical Biometers, All Based on SS-OCT. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2023, 49, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, D.; Weikert, M.P.; Koch, D.D. Calculation of Axial Length Using a Single Group Refractive Index versus Using Different Refractive Indices for Each Ocular Segment: Theoretical Study and Refractive Outcomes. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gali, H.E.; Sella, R.; Afshari, N.A. Cataract Grading Systems: A Review of Past and Present. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2019, 30, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danjo, Y. Modification of the Barrett Universal II Formula by the Combination of the Actual Total Corneal Power and Virtual Axial Length. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2023, 261, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R.J. Cataract Surgery from 1918 to the Present and Future—Just Imagine! Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 185, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montés-Micó, R. Evaluation of 6 Biometers Based on Different Optical Technologies. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2022, 48, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montés-Micó, R.; Pastor-Pascual, F.; Ruiz-Mesa, R.; Tañá-Rivero, P. Ocular Biometry with Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2020, 47, 802–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, A.K.; Nayak, S.; Mahobia, A.; Anto, M.; Pandey, P. Accuracy of Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulae in Short Eyes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 70, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melles, R.B.; Holladay, J.T.; Chang, W.J. Accuracy of Intraocular Lens Calculation Formulas. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Shirayama, M.; Ma, X.J.; Kohnen, T.; Koch, D.D. Optimizing Intraocular Lens Power Calculations in Eyes with Axial Lengths above 25.0 Mm. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2011, 37, 2018–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLaren, R.E.; Sagoo, M.S.; Restori, M.; Allan, B.D.S. Biometry Accuracy Using Zero- and Negative-Powered Intraocular Lenses. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2005, 31, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gao, R.; Yu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, W.; McAlinden, C.; Wang, Q. Comprehensive Comparison of Axial Length Measurement with Three Swept-Source OCT-Based Biometers and Partial Coherence Interferometry. J. Refract. Surg. 2019, 35, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasavada, S.A.; Patel, P.; Vaishnav, V.R.; Ashena, Z.; Srivastava, S.; Vasavada, V.; Nanavaty, M.A. Comparison of Optical Low-Coherence Reflectometry and Swept-Source OCT-Based Biometry Devices in Dense Cataracts. J. Refract. Surg. 2020, 36, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaoki, A.; Kojima, T.; Hasegawa, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Kaga, T.; Tanaka, K.; Ichikawa, K. Evaluation of Axial Length Measurement Using Enhanced Retina Visualization Mode of the Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Biometer in Dense Cataract. Ophthalmic Res. 2021, 64, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Yu, Y.F.; Li, E.J.; Lv, N.X.; Liu, Z.C.; Zhou, H.G.; Song, X.D. Global, Regional, National Burden and Gender Disparity of Cataract: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tañá-Rivero, P.; Tañá-Sanz, S.; Pastor-Pascual, F.; Ruiz-Mesa, R.; Montés-Micó, R. Axial Length Measurement Failure Rates Using Optical Biometry Based on Swept-Source OCT in Cataractous Eyes. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2022, 19, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savini, G.; Di Maita, M.; Hoffer, K.J.; Næser, K.; Schiano-Lomoriello, D.; Vagge, A.; Di Cello, L.; Traverso, C.E. Comparison of 13 Formulas for IOL Power Calculation with Measurements from Partial Coherence Interferometry. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 105, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Liao, X. How to Choose the Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulas in Eyes with Extremely Long Axial Length? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0296771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Xiong, R.; Liu, Z.; Young, C.A.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, X.; Jin, G. Network Meta-Analysis of Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formula Accuracy in 1016 Eyes With Long Axial Length. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 257, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Multack, S.; Plummer, N.; Smits, G.; Hall, B. Randomized Trial Comparing Prediction Accuracy of Two Swept Source Optical Coherence Tomography Biometers. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2023, 17, 2423–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammas, H.J.; Shammas, M.C.; Jivrajka, R.V.; Cooke, D.L.; Potvin, R. Effects on IOL Power Calculation and Expected Clinical Outcomes of Axial Length Measurements Based on Multiple vs Single Refractive Indices. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 14, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Kang, E.K.; Kim, H.; Kang, M.J.; Byun, Y.S.; Joo, C.K. Accuracy of Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Based Biometry for Intraocular Lens Power Calculation: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019, 19, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorkin, N.; Achiron, A.; Abumanhal, M.; Abulafia, A.; Cohen, E.; Gutfreund, S.; Mandelblum, J.; Varssano, D.; Levinger, E. Comparison of Two New Integrated SS-OCT Tomography and Biometry Devices. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2022, 48, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blehm, C.H.B. Refractive Predictability of a Swept Source Optical Coherence Tomography Biometer in Long and Short Eyes Implanted with Extended Depth of Focus Intraocular Lenses. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2023, 17, 3525–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, W.; Lin, T.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, C.; Lin, H.; Chen, W. Accuracy of Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulas in Long Eyes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2018, 46, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammas, H.J.; Taroni, L.; Pellegrini, M.; Shammas, M.C.; Jivrajka, R.V. Accuracy of Newer Intraocular Lens Power Formulas in Short and Long Eyes Using Sum-of-Segments Biometry. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2022, 48, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitblat, O.; Khalili, S.; Ali, A.; Mireskandari, K.; Vega, Y.; Tuuminen, R.; Elbaz, U.; Sella, R. Evaluation of IOL Power Calculation with the Kane Formula for Pediatric Cataract Surgery. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2022, 260, 2877–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, H.; Gao, L.; Du, J.; Chen, W.; Gao, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, Z. Comparing the Accuracy of New Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulae in Short Eyes after Cataract Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. Ophthalmol. 2022, 42, 1939–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
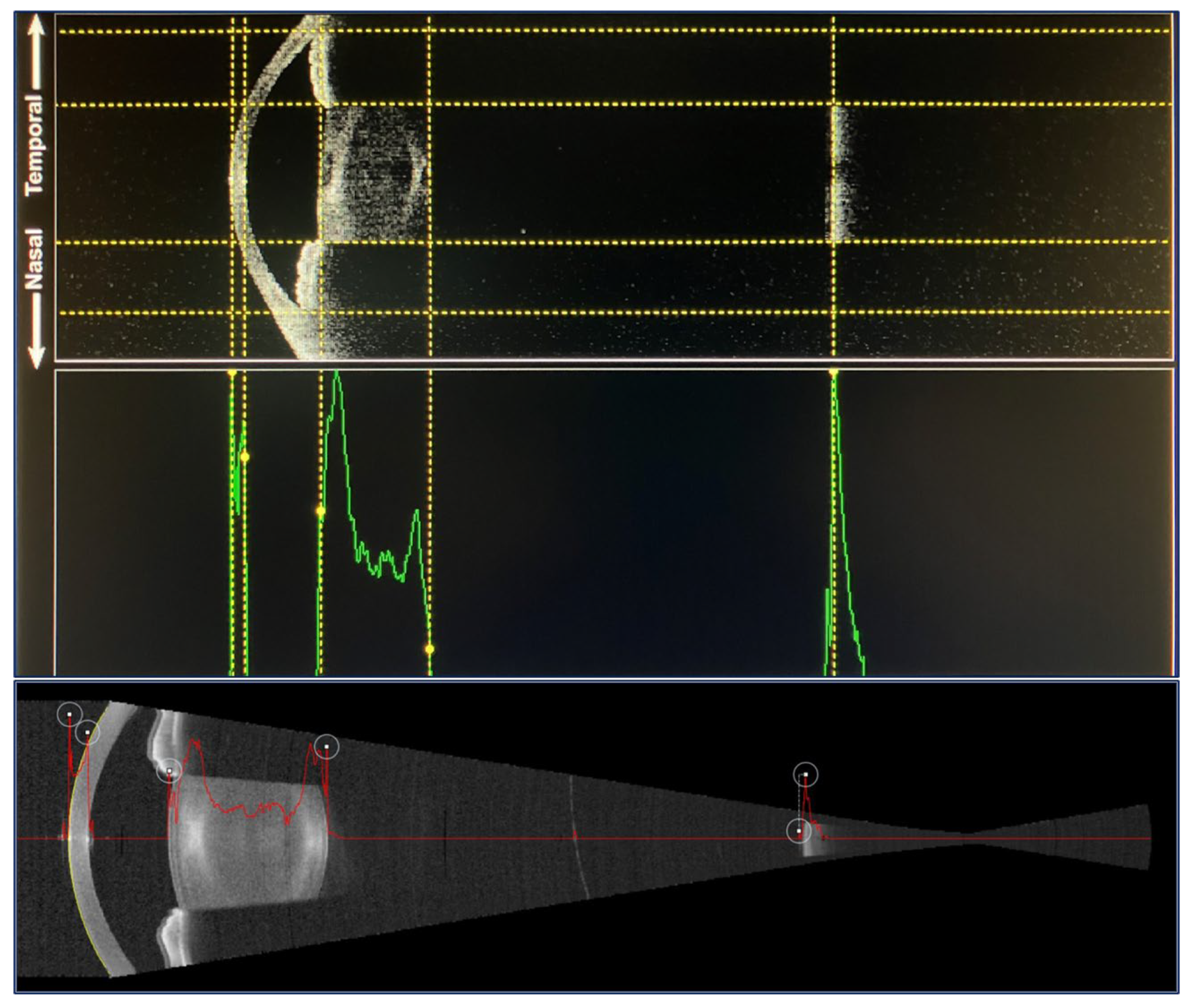
| Characteristics | Argos® | Eyestar 900® |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Alcon Healthcare | Haag-Streit |
| Method | SS-OCT | SS-OCT |
| Center wavelength | 1060 nm | 1060 nm |
| Scan speed | 3000 A-scans/s | 30,000 A-scans/s |
| B-scan axial resolution | 50 µm | N/R |
| Scan depth range | 50 mm | 14 to 38 mm |
| Last generation formulas available | Yes | Yes |
| AL measurement approach | Sum of segments | Group refractive index |
| Other | Enhanced Retina Visualization, integration with other devices | Quantification of lens tilting, vision simulator |
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| N, eyes | 107 |
| Age | 73.1 (7.8) years |
| Females | 65 (60.8%) |
| Right eyes | 51 (47.7%) |
| Parameter | Argos® | Eyestar 900® | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
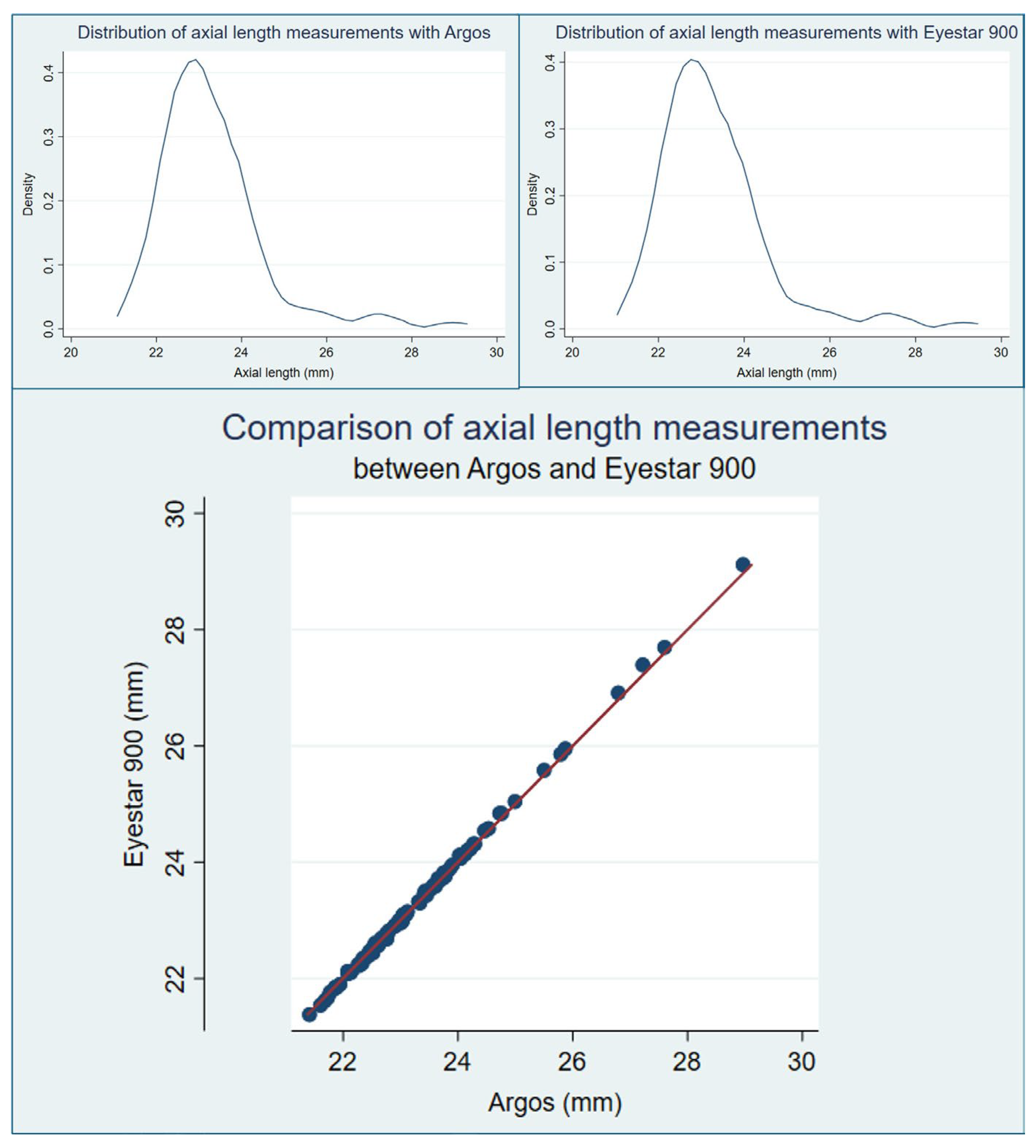
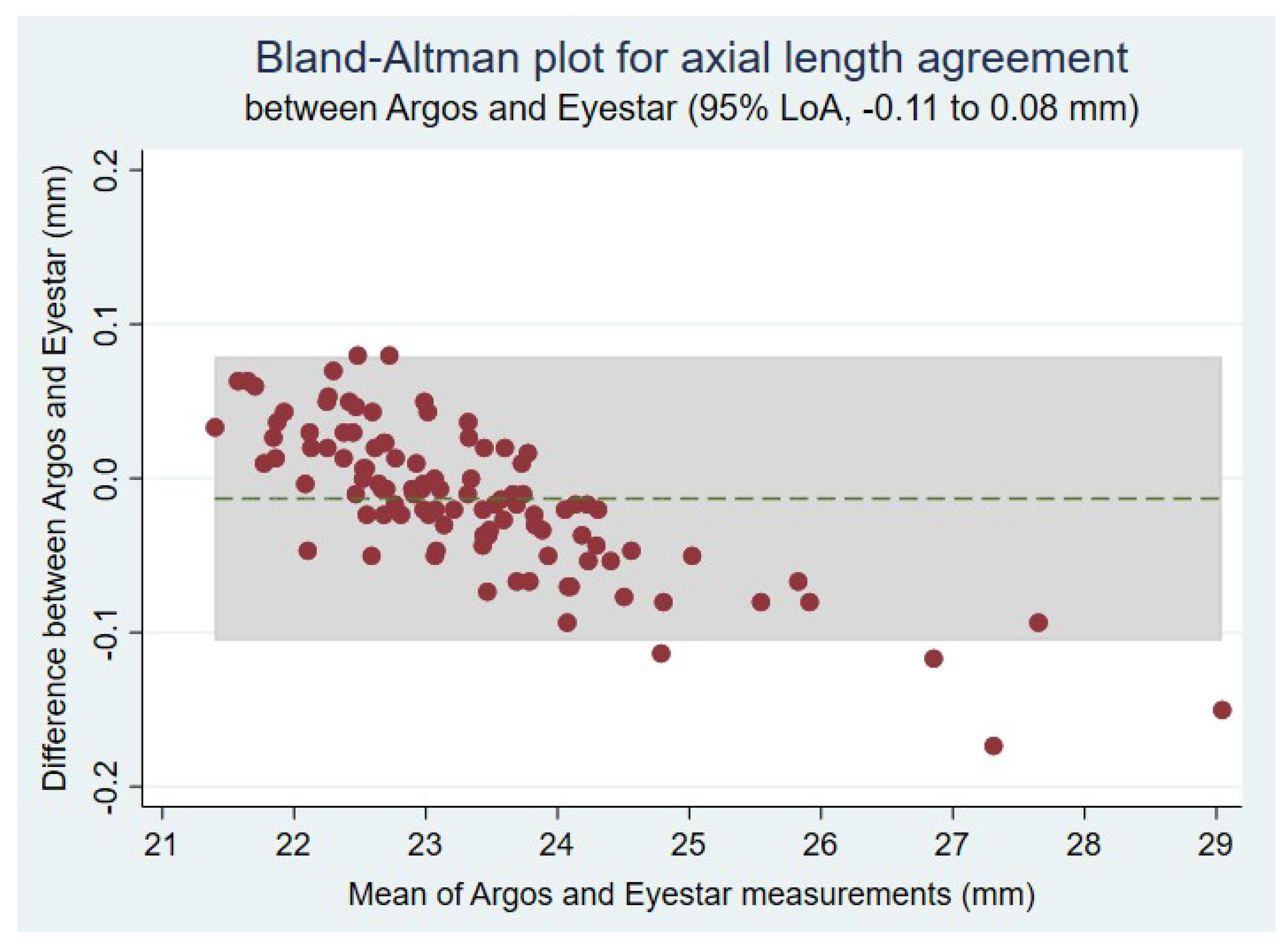
| AL * | 23.33 (1.24) mm | 23.35 (1.28) mm | <0.0001 |
| 95% LoA | −11 to 0.08 mm | N/A | |
| Pearson corr. coeff. | 0.99 | <0.0001 | |
| SW | 0.0058 (0.0058) | 0.0000 (0.0058) | <0.0001 |
| Failed AL measurements | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1.00 |
| Differences in pre-and post-AL | −0.01 (0.04) mm | −0.02 (0.05) mm | N/A |
| Prediction error | 0.04 (0.35) D | 0.03 (0.33) D | 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guarro, M.; Vázquez, M.; Díaz, J.C.; Ruiz, S.; Gimeno, M.; Rodríguez, L.; López, E.; Sararols, L.; Biarnés, M. Comparison of Precision, Agreement, and Accuracy of Two Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Biometers. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14212422
Guarro M, Vázquez M, Díaz JC, Ruiz S, Gimeno M, Rodríguez L, López E, Sararols L, Biarnés M. Comparison of Precision, Agreement, and Accuracy of Two Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Biometers. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(21):2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14212422
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuarro, Mercè, Meritxell Vázquez, Juan Carlos Díaz, Sergi Ruiz, Maties Gimeno, Lara Rodríguez, Elena López, Laura Sararols, and Marc Biarnés. 2024. "Comparison of Precision, Agreement, and Accuracy of Two Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Biometers" Diagnostics 14, no. 21: 2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14212422
APA StyleGuarro, M., Vázquez, M., Díaz, J. C., Ruiz, S., Gimeno, M., Rodríguez, L., López, E., Sararols, L., & Biarnés, M. (2024). Comparison of Precision, Agreement, and Accuracy of Two Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Biometers. Diagnostics, 14(21), 2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14212422







