Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay Using Gold Nanoparticles for Detecting Treponema pallidum subspp. pallidum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Primers and DNA Probe Design
2.4. Optimization of PCR Reaction Conditions
2.5. Optimization of LAMP Reaction Conditions
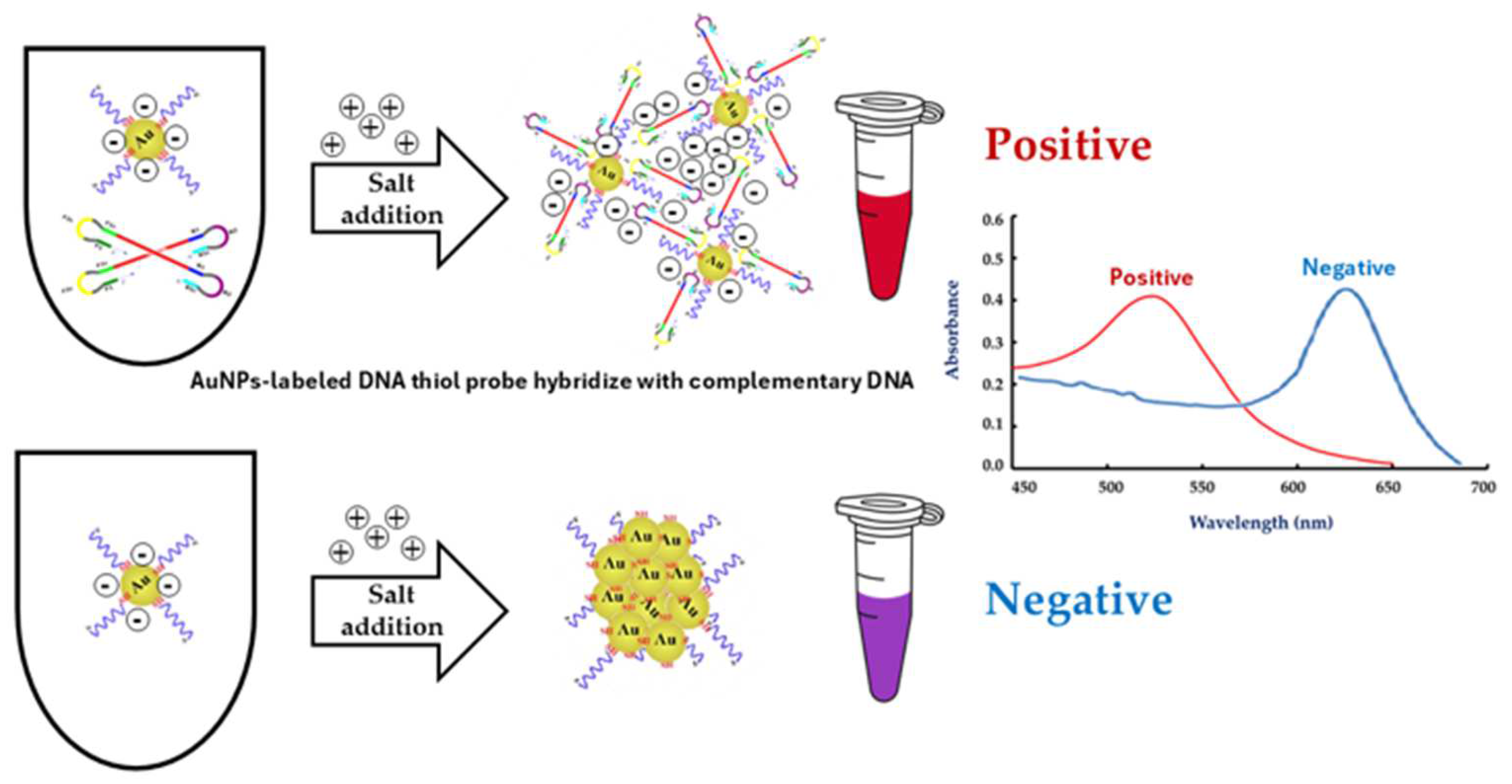
2.6. Preparation of the AuNPs-Labeled DNA Thiol Probe
2.7. Optimization of LAMP-AuNPs Reaction Conditions
2.8. Analytical Sensitivity and Specificity Tests
2.9. The Diagnostic Testing Accuracy
3. Results and Discussion
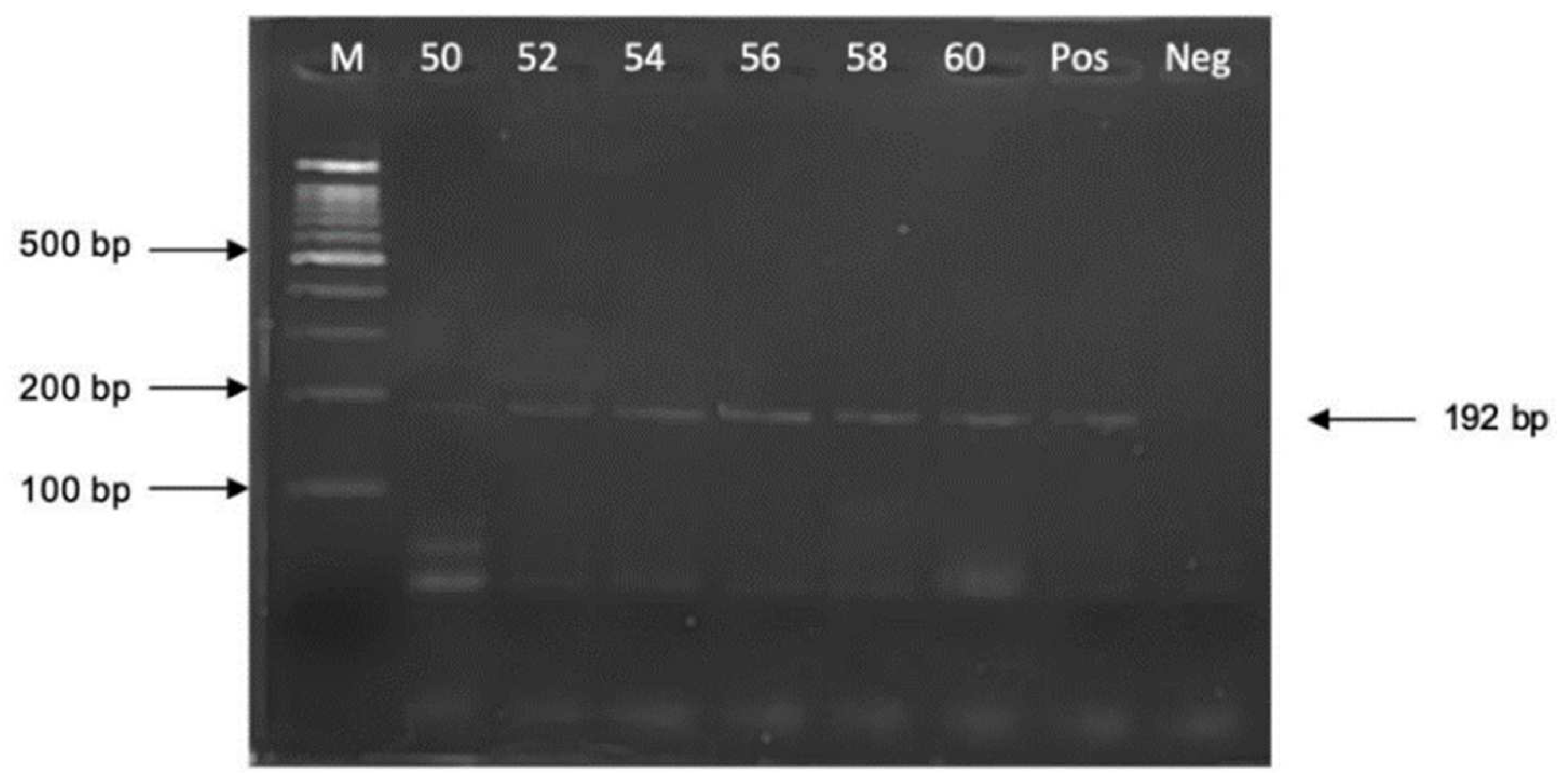
3.1. Optimization of PCR Amplification
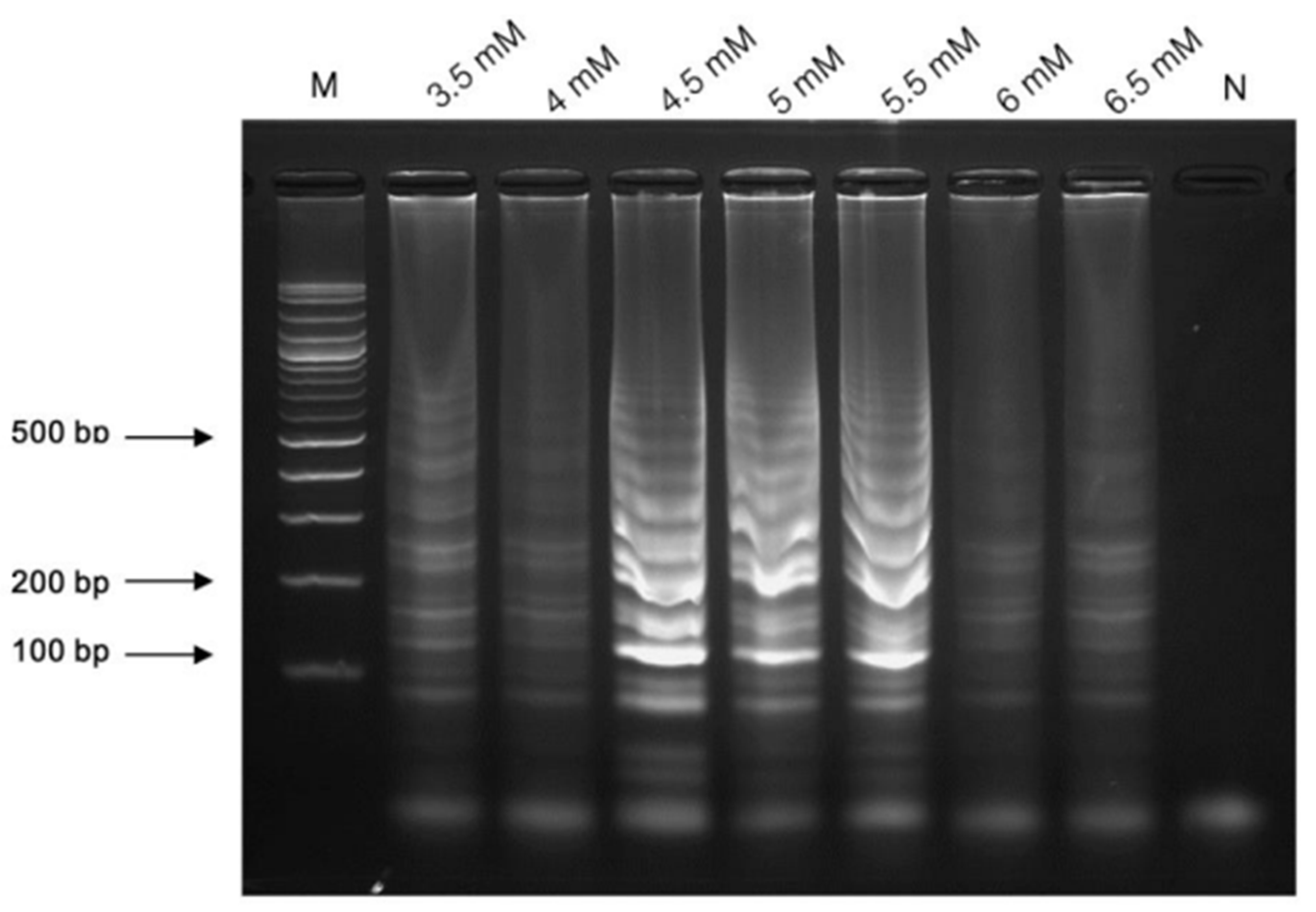
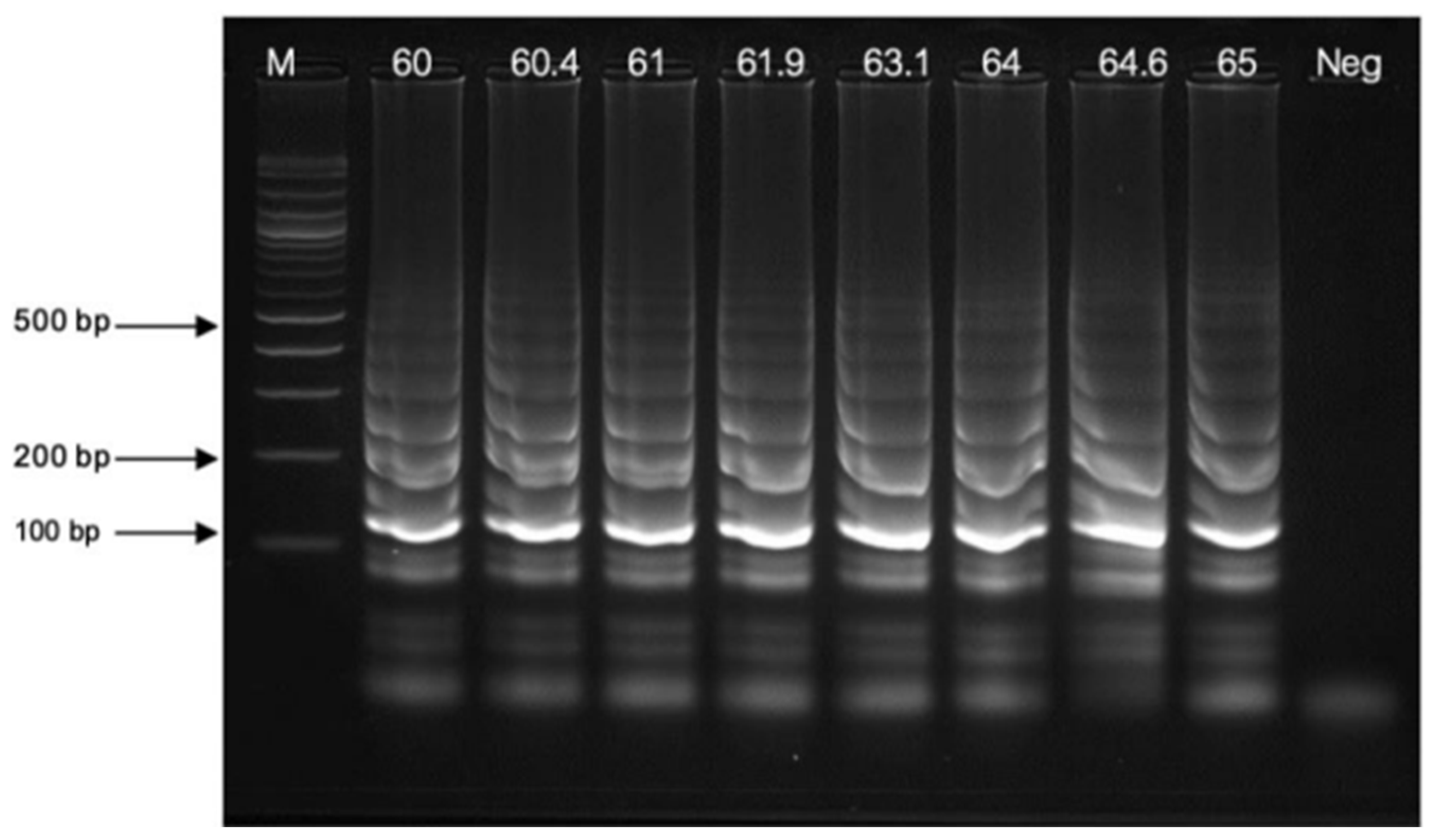
3.2. Optimization of LAMP Amplification
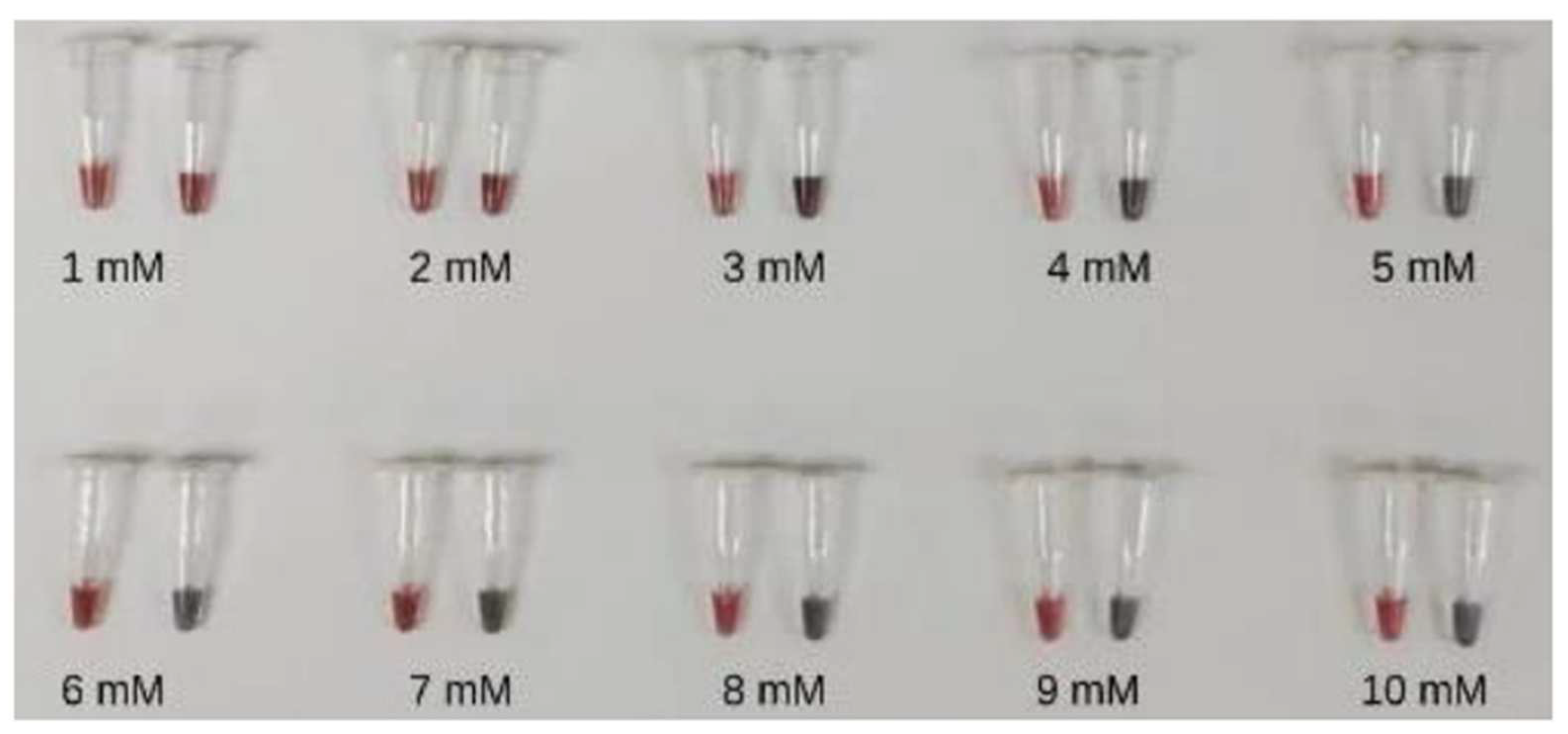
3.2.1. The Concentration of MgSO4
3.2.2. Temperature Variations
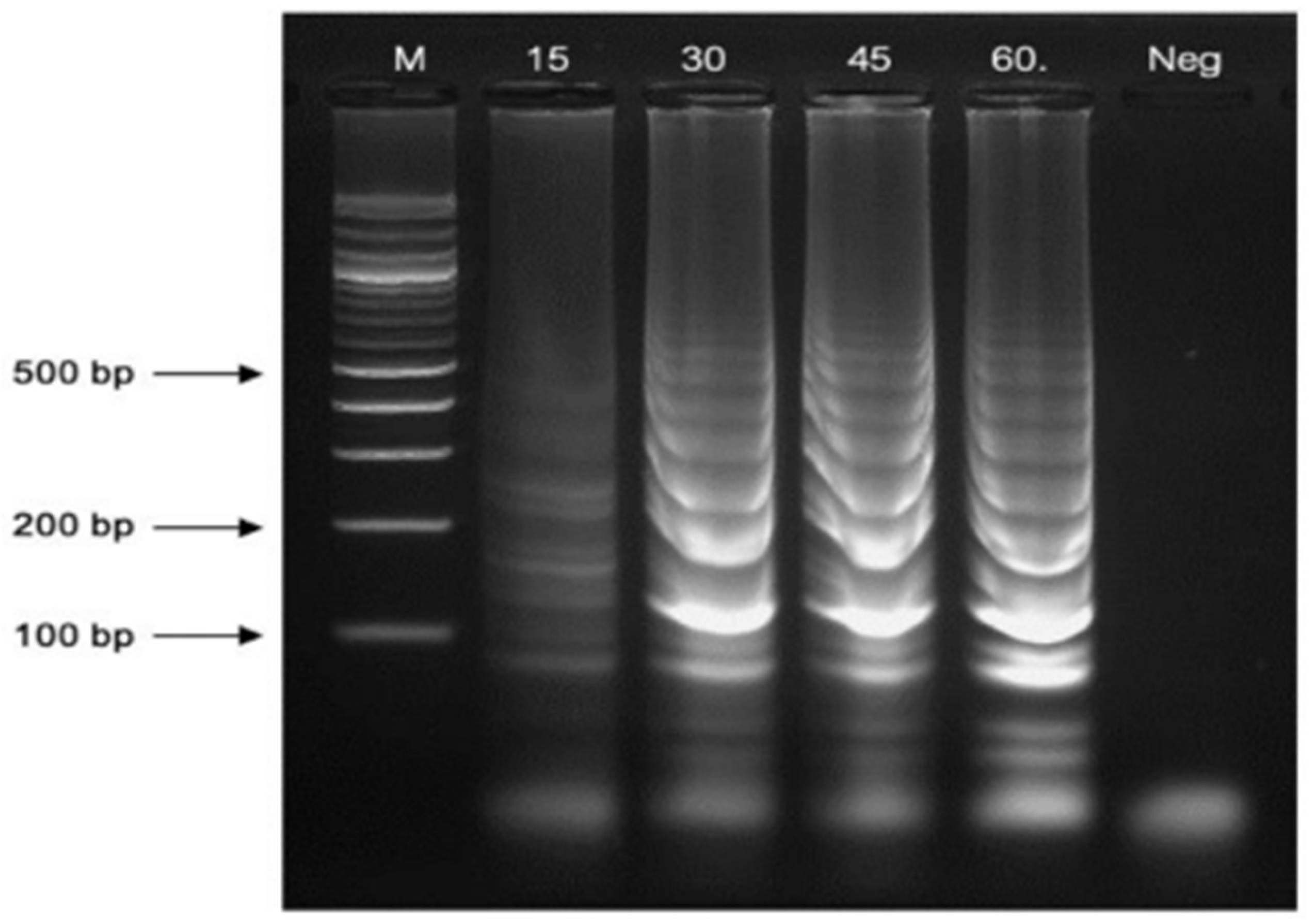
3.2.3. Reaction Time Variations
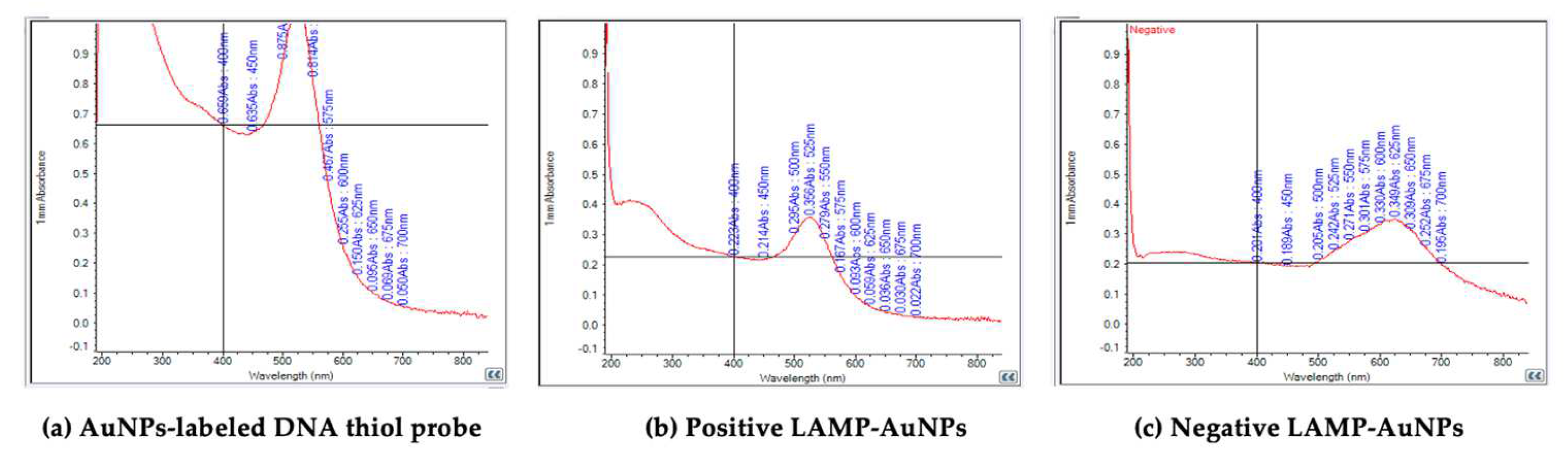
3.3. The Optimal Conditions for LAMP-AuNPs
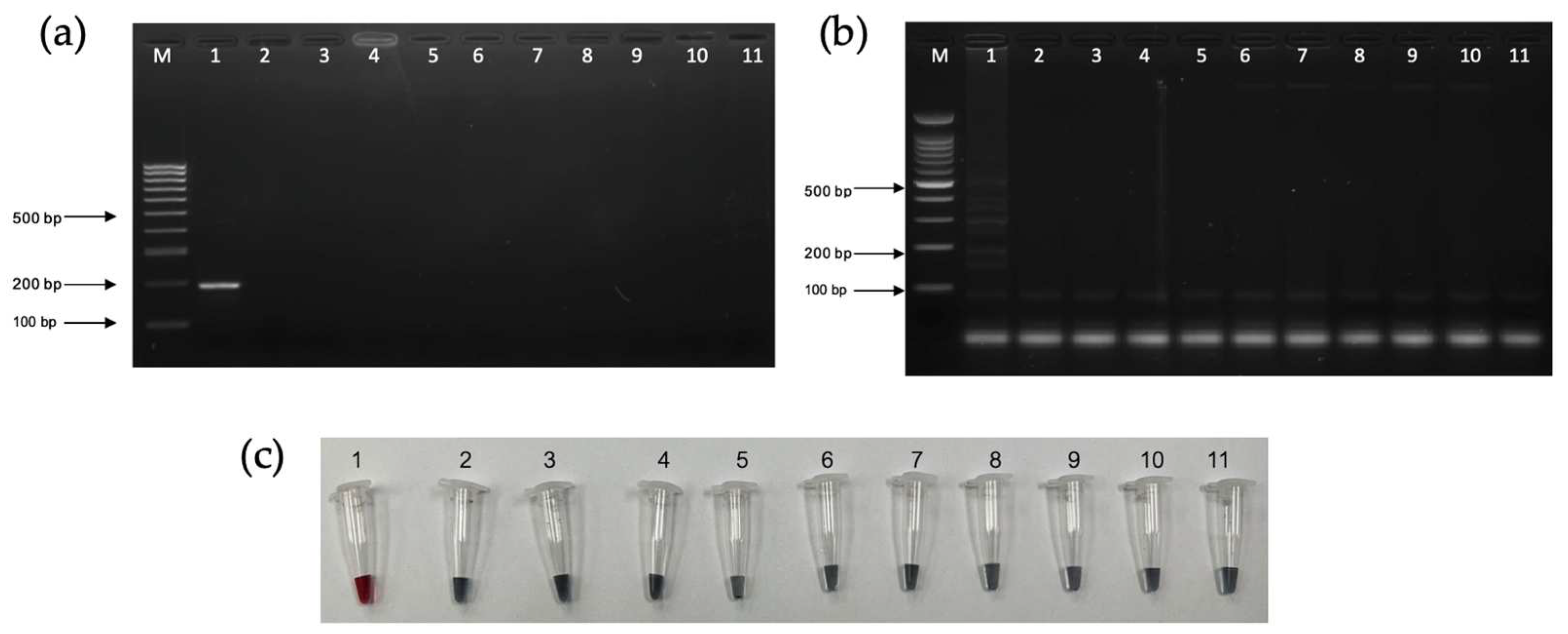
3.4. Analytical Sensitivity and Specificity Tests
3.5. The Diagnostic Testing Accuracy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaisongkram, N. Epidemiological characteristics among patients with syphilis in Thailand. Dis. Control J. 2023, 49, 54–56. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Y.-T.; Gao, T.-Y.; Li, H.-Y.; Ma, Y.-T.; Li, H.-J.; Xian-Yu, C.-Y.; Deng, N.-J.; Zhang, C. Global, regional, and national trends of syphilis from 1990 to 2019: The 2019 global burden of disease study. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguero-Seña, A.C.; Pillay, A.; Cox, D.L.; Radolf, J.D. Treponema and Brachyspira, Human Host-Associated Spirochetes. In Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 12th ed.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 1083–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Procop, G.W.; Church, D.L.; Hall, G.S.; Janda, W.M.; Koneman, E.W.; Schreckenberger, P.C. Koneman’s Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Peeling, R.W.; David, M.; Kamb, M.L.; Chen, X.-S.; Radolf, J.D.; Benzaken, A.S. Syphilis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soreng, K.; Levy, R.; Fakile, Y. Serologic testing for syphilis: Benefits and challenges of a reverse algorithm. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2014, 36, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarese, G.; Facciorusso, A.; Mastrolonardo, M.; Herzum, A.; Parodi, A.; Drago, F. Atypical Manifestations of Syphilis: A 10-Year Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, Y. Laboratory Diagnostic Tools for Syphilis: Current Status and Future Prospects. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 574806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, S.; Akinlusi, I.; Shi, T.; Cervantes, J. Secondary Syphilis: Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Diagnostic Testing. Venereology 2023, 2, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, C.; Schwartzman, G.; Khachemoune, A. Syphilis in Dermatology: Recognition and Management. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2023, 24, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, E.; Tognetti, L.; Campoli, M.; Cinotti, E.; Rubegni, P. Syphilis Diagnosis and Treatment: State of The Art. Dermatology 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyaputra, F.; Hendry, S.; Braddick, M.; Sivabalan, P.; Norton, R. The Laboratory Diagnosis of Syphilis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e00100-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffet, M.; Grange, P.A.; Gerhardt, P.; Carlotti, A.; Calvez, V.; Bianchi, A.; Dupin, N. Diagnosing Treponema pallidum in Secondary Syphilis by PCR and Immunohistochemistry. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2345–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, Y.; Nagamine, K.; Tomita, N.; Notomi, T. Detection of loop mediated isothermal amplification reaction by turbidity derived from magnesium pyrophosphate formation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 289, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamine, K.; Hase, T.; Notomi, T. Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers. Mol. Cell. Probes 2002, 16, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, H.T.C.; Le, M.Q.; Vuong, C.D.; Parida, M.; Minekawa, H.; Notomi, T.; Hasebe, F.; Morita, K. Development and evaluation of a novel loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for rapid detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1956–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, M.; Horioke, K.; Ishida, H.; Dash, P.K.; Saxena, P.; Jana, A.M.; Islam, M.A.; Inoue, S.; Hosaka, N.; Morita, K. Rapid detection and differentiation of dengue virus serotypes by real-time reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2895–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstain, J.M.; Grimprel, E.; Lukehart, S.A.; Norgard, M.V.; Radolf, J.D. Sensitive Detection of Treponema pallidum by Using the Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fohn, M.J.; Wignall, F.S.; Baker-Zander, S.A.; Lukehart, S.A. Specificity of antibodies from patients with pinta for antigens of Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum. J. Infect. Dis. 1988, 157, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornburg, R.W.; Baseman, J.B. Comparison of major protein antigens and protein profiles of Treponema pallidum and Treponema pertenue. Infect. Immun. 1983, 42, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, E.W., 3rd; Roddy, R.E.; Lukehart, S.A.; Hom, J.; Holmes, K.K.; Tam, M.R. Detection of Treponema pallidum in lesion exudate with a pathogen-specific monoclonal. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1985, 2, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchitto, K.S.; Jones, S.A.; Schell, R.F.; Holmans, P.L.; Norgard, M.V. Monoclonal antibody analysis of specific antigenic similarities among pathogenic Treponema pallidum subspecies. Infect. Immun. 1984, 45, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchitto, K.S.; Selland-Grossling, C.K.; Norgard, M.V. Molecular specificities of monoclonal antibodies directed against virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect. Immun. 1986, 51, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norgard, M.V.; Chamberlain, N.R.; Swancutt, M.A.; Goldberg, M.S. Cloning and expression of the major 47-kilodaltosurface immunogen of Treponema pallidum in Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1986, 54, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radolf, J.D.; Norgard, M.V. Pathogen specificity of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum integral membrane proteins identified by phase parti-tioning with Triton X-114. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 1825–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storhoff, J.J.; Elghania, R.; Mucic, R.C.; Mirkin, C.A.; Letsinger, R.L. One-Pot Colorimetric Differentiation of Polynucleotides with Single Base Imperfections Using Gold Nanoparticle Probes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetang-Nun, Y.; Jaroenram, W.; Sriurairatana, S.; Suebsing, R.; Kiatpathomchai, W. Visual detection of white spot syndrome virus using DNA-functionalized gold nanoparticles as probes combined with loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Mol. Cell. Probes 2013, 27, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruang-areerate, T.; Sukphattanaudomchoke, C.; Thita, T.; Leelayoova, S.; Piyaraj, P.; Mungthin, M.; Suwannin, P.; Polpanich, D.; Tangchaikeeree, T.; Jangpatarapongsa, K.; et al. Development of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay using SYBR safe and gold—nanoparticle probe for detection of Leishmania in HIV patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, F.F.; Veigas, B.; Matias, A.S.; Doria, G.; Flores, O.; Baptista, P.V. Allele specific LAMP-gold nanoparticle for characterization of single nucleotide polymorphisms. Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 16, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangrak STI Center. National Guideline for Syphilis Testing: Laboratory Manual for Diagnosis and Monitoring; Aksorn Graphic and Design Publishing House LP; Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Public Health: Nonthaburee, Thailand, 2021.
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Duan, J.; Zhao, F. PCR detection for syphilis diagnosis: Status and prospects. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, M.; Guy, R.J.; Jeoffreys, N.J.; Finlayson, R.J.; Donovan, B. A longitudinal evaluation of Treponema pallidum PCR testing in early syphilis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.J.; Gunson, R.N.; Carman, W.F.; Winter, A.J. A new multiplex real-time PCR test for HSV1/2 and syphilis: An evaluation of its impact in the laboratory and clinical setting. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2010, 86, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tipple, C.; Hanna, M.O.F.; Hill, S.; Daniel, J.; Goldmeier, D.; McClure, M.O.; Taylor, G.P. Getting the measure of syphilis: qPCR to better understand early infection. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2011, 87, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grange, P.A.; Gressier, L.; Dion, P.L.; Farhi, D.; Benhaddou, N.; Gerhardt, P.; Morini, J.P.; Deleuze, J.; Pantoja, C.; Bianchi, A.; et al. Evaluation of a PCR test for detection of Treponema pallidum in swabs and blood. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.-S.; Qiang, D.J.; Wu, S.-Q.; Zhang, Q.-G.; Yin, Y.-H. Evaluation of nPCR for detection of Treponema pallidum in primary syphilis. Prog. Mod. Biomed. 2013, 13, 4529–4531. [Google Scholar]
- Dumaresq, J.; Langevin, S.; Gagnon, S.; Serhir, B.; Deligne, B.; Tremblay, C.; Tsang, R.S.W.; Fortin, C.; Coutlée, F.; Roger, M. Clinical prediction and diagnosis of neurosyphilis in HIV-infected patients with early syphilis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 4060–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.; Águas, M.J.; Batista, T.; Araújo, C.; Mansinho, K.; Da Luz Martins Pereira, F. Detection of Treponema pallidum Sp. Pallidum DNA in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) by two PCR techniques. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2016, 30, 628–632. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhaecke, C.; Grange, P.; Benhaddou, N.; Blanche, P.; Salmon, D.; Parize, P.; Lortholary, O.; Caumes, E.; Pelloux, I.; Epaulard, O.; et al. Clinical and biological characteristics of 40 patients with neurosyphilis and evaluation of Treponema pallidum nested polymerase chain reaction in cerebrospinal fluid samples. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Gong, W.; Qian, Y.; Guan, Z.; Lu, H.; Gu, X.; Shi, M.; et al. Sensitive detection of Treponema pallidum DNA from the whole blood of patients with syphilis by the nested PCR assay. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Diagnostic Test | Gold Standard | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Disease | No Disease | ||
| Positive | True positive (TP) | False positive (FP) | PPV = TP/(TP + FP) |
| Negative | False negative (FN) | True negative (TN) | NPV = TN/(FN + TN) |
| Sensitivity = TP/(TP + FN) | Specificity = TN/(FP + TN) | ||
| The Diagnostic Testing Accuracy | PCR-AGE | LAMP-AGE | LAMP-AuNPs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic sensitivity | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Diagnostic specificity | 94.5% | 91% | 91% |
| Accuracy | 97.25% | 95.5% | 95.5% |
| Positive predictive value (PPV) | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Negative predictive value (NPV) | 94.5% | 91% | 91% |
| Positive likelihood ratio (LR+) | 18.18 | 11.11 | 11.11 |
| Negative likelihood ratio (LR−) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Methods | Sample Size | Specimens | Target | Sensitivity % | Specificity % | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Routine PCR | 288 | Swab | Tpp47 | 89.1 | 99.1 | 33 |
| Multiplex real-time PCR | 15 | Swab | Tpp47 Taqman-LNA | 100 | 100 | 34 |
| Real-time PCR | 99 | Ulcer lesion | Tpp47 | 100 | 97.14 | 35 |
| Nested PCR | 329 | Swab | Tpp47 | 92.0 | 95.0 | 36 |
| Nested PCR | 315 | Blood | Tpp47 | 90.3 | 100 | 37 |
| Real-time PCR | 122 | CSF | Tpp47 | 58.0 | 67.0 | 38 |
| Routine PCR | 124 | CSF | Tpp47 | 75.8 | 86.8 | 39 |
| Nested PCR | 40 | CSF | Tpp47 | 42.5 | 97.0 | 40 |
| Nested PCR | 262 | Whole blood | Tpp47 | 53.6 | - | 41 |
| LAMP-AuNPs | 400 | Serum | Tpp47 | 100 | 91.0 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phurijaruyangkun, S.; Tangjitrungrot, P.; Jaratsing, P.; Augkarawaritsawong, S.; Pongparit, S.; Veeramano, R.; Tanomnuch, K.; Areekit, S.; Chansiri, K.; Santiwatanakul, S. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay Using Gold Nanoparticles for Detecting Treponema pallidum subspp. pallidum. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14202323
Phurijaruyangkun S, Tangjitrungrot P, Jaratsing P, Augkarawaritsawong S, Pongparit S, Veeramano R, Tanomnuch K, Areekit S, Chansiri K, Santiwatanakul S. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay Using Gold Nanoparticles for Detecting Treponema pallidum subspp. pallidum. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(20):2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14202323
Chicago/Turabian StylePhurijaruyangkun, Saranthum, Pongbun Tangjitrungrot, Pornpun Jaratsing, Suphitcha Augkarawaritsawong, Sawanya Pongparit, Rungnapa Veeramano, Kularb Tanomnuch, Supatra Areekit, Kosum Chansiri, and Somchai Santiwatanakul. 2024. "Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay Using Gold Nanoparticles for Detecting Treponema pallidum subspp. pallidum" Diagnostics 14, no. 20: 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14202323
APA StylePhurijaruyangkun, S., Tangjitrungrot, P., Jaratsing, P., Augkarawaritsawong, S., Pongparit, S., Veeramano, R., Tanomnuch, K., Areekit, S., Chansiri, K., & Santiwatanakul, S. (2024). Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay Using Gold Nanoparticles for Detecting Treponema pallidum subspp. pallidum. Diagnostics, 14(20), 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14202323





