Ultrasound Assessment of Sarcopenia in Alcoholic Liver Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Inclusion Criteria
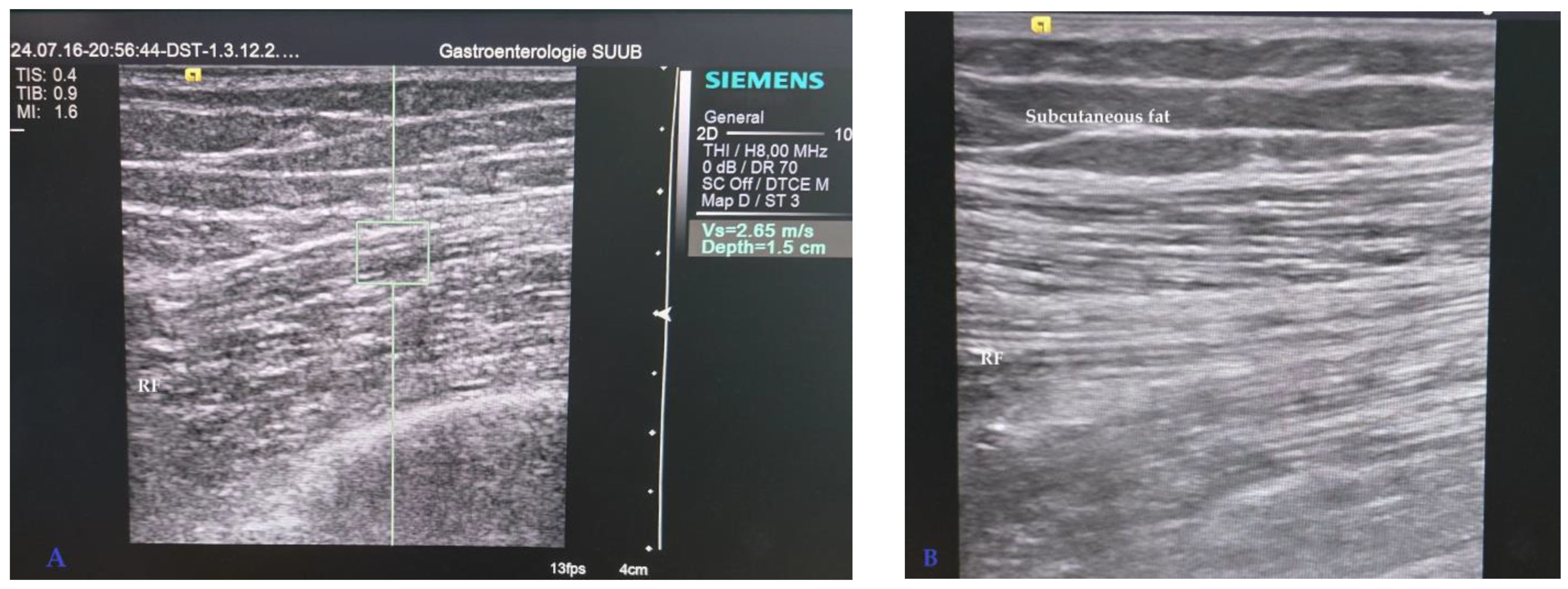
2.2. Ultrasound Assessment of Rectus Femoris
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of Study Population
3.2. Clinical and Biological Results
3.3. Rectus Femoris Ultrasound Measurement Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tadokoro, T.; Morishita, A.; Himoto, T.; Masaki, T. Nutritional Support for Alcoholic Liver Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tandon, P.; Low, G.; Mourtzakis, M.; Zenith, L.; Myers, R.P.; Abraldes, J.G.; Shaheen, A.A.M.; Qamar, H.; Mansoor, N.; Carbonneau, M.; et al. A Model to Identify Sarcopenia in Patients with Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 1473–1480.e3, Erratum in Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, L.; Jolley, S.E.; Molina, P.E. Alcoholic Myopathy: Pathophysiologic Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Alcohol. Res. 2017, 38, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roberts, H.C.; Denison, H.J.; Martin, H.J.; Patel, H.P.; Syddall, H.; Cooper, C.; Sayer, A.A. A review of the measurement of grip strength in clinical and epidemiological studies: Towards a standardised approach. Age Ageing 2011, 40, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, A.J.; Wallen, M.P.; Ryan, J.; Ward, L.C.; Coombes, J.S.; Macdonald, G.A. Evaluation of techniques used to assess skeletal muscle quantity in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 44, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hari, A. Muscular abnormalities in liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 4862–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Writing Group for the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People 2 (EWGSOP2), and the Extended Group for EWGSOP2. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, E.J.; Lai, J.C.; Wang, C.W.; Dasarathy, S.; Lobach, I.; Montano-Loza, A.J.; Dunn, M.A. Fitness, Life Enhancement, and Exercise in Liver Transplantation Consortium A multicenter study to define sarcopenia in patients with end-stage liver disease. Liver Transpl. 2017, 23, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address: easloffice@easloffice.eu; European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on nutrition in chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 172–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirón Mombiela, R.; Vucetic, J.; Rossi, F.; Tagliafico, A.S. Ultrasound Biomarkers for Sarcopenia: What Can We Tell So Far? Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2020, 24, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticinesi, A.; Meschi, T.; Narici, M.V.; Lauretani, F.; Maggio, M. Muscle ultrasound and sarcopenia in older individuals: A clinical perspective. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toptas, M.; Yalcin, M.; Akkoc, İ.; Demir, E.; Metin, C.; Savas, Y.; Kalyoncuoglu, M.; Can, M.M. The relation between sarcopenia and mortality in patients at intensive care unit. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 20185263208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkisas, S.; Bastijns, S.; Baudry, S.; Bauer, J.; Beaudart, C.; Beckwée, D.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Gasowski, J.; Hobbelen, H.; Jager-Wittenaar, H.; et al. Application of ultrasound for muscle assessment in sarcopenia: 2020 SARCUS update. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2021, 12, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, J.E.; Anker, S.D.; von Haehling, S. Prevalence, incidence, and clinical impact of sarcopenia: Facts, numbers, and epidemiology-update 2014. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2014, 5, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, T.; Wythe, S.; O’Beirne, J.; Martin, D.; Gilbert-Kawai, E. Review article: The role of the microcirculation in liver cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cola, S.; D’amico, G.; Caraceni, P.; Schepis, F.; Loredana, S.; Lampertico, P.; Toniutto, P.; Martini, S.; Maimone, S.; Colecchia, A.; et al. Myosteatosis is closely associated with sarcopenia and significantly worse outcomes in patients with cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2024. epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, W.K.; Phillips, B.E.; Williams, J.P.; Rankin, D.; Smith, K.; Lund, J.N.; Atherton, P.J. Development of a new Sonovue contrast-enhanced ultrasound approach reveals temporal and age-related features of muscle microvascular responses to feeding. Physiol Rep. 2013, 1, e00119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendur, H.N.; Cindil, E.; Cerit, M.N.; Kilic, P.; Gultekin, I.I.; Oktar, S.O. Evaluation of effects of aging on skeletal muscle elasticity using shear wave elastography. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 128, 109038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfuraih, A.M.; Tan, A.L.; O’Connor, P.; Emery, P.; Wakefield, R.J. The effect of ageing on shear wave elastography muscle stiffness in adults. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becchetti, C.; Lange, N.F.; Delgado, M.G.; Brönnimann, M.P.; Maurer, M.H.; Dufour, J.F.; Berzigotti, A. 2D shear wave elastography of the rectus femoris muscle in patients with cirrhosis: Feasibility and clinical findings. A pilot study. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2023, 47, 102080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreta, M.C.; Fleet, A.; Reebye, R.; McKernan, G.; Berger, M.; Farag, J.; Munin, M.C. Reliability and Validity of the Modified Heckmatt Scale in Evaluating Muscle Changes with Ultrasound in Spasticity. Arch. Rehabil. Res. Clin. Transl. 2020, 2, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich-Rust, M.; Nierhoff, J.; Lupsor, M.; Sporea, I.; Fierbinteanu-Braticevici, C.; Strobel, D.; Takahashi, H.; Yoneda, M.; Suda, T.; Zeuzem, S.; et al. Performance of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse imaging for the staging of liver fibrosis: A pooled meta-analysis. J. Viral Hepat. 2011, 19, e212–e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, C.; Minniti, S.; Bucci, A.; Mucelli, R.P. ARFI: From basic principles to clinical applications in diffuse chronic disease—A review. Insights Imaging 2016, 7, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Koya, S.; Hirota, K.; Matsuse, H.; Torimura, T. Subcutaneous Fat Thickness of the Lower Limb is Associated with Trunk Muscle Mass in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Simple Assessment for Sarcopenia Using Conventional Ultrasonography. Kurume Med. J. 2022, 67, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhariwal, S.M.; Roy, A.M.; Taneja, S.M.; Bansal, A.M.; Gorsi, U.M.; Singh, S.M.; De, A.M.; Verma, N.M.; Premkumar, M.M.; Duseja, A.M.; et al. Assessment of Sarcopenia Using Muscle Ultrasound in Patients with Cirrhosis and Sarcopenic Obesity (AMUSE STUDY). J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2023, 57, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daphnee, D.K.; John, S.; Vaidya, A.; Khakhar, A.; Bhuvaneshwari, S.; Ramamurthy, A. Hand grip strength: A reliable, reproducible, cost-effective tool to assess the nutritional status and outcomes of cirrhotics awaiting liver transplant. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2017, 19, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocîrlan, M.; Mănuc, M.; Diculescu, M.; Ciocîrlan, M. Is rectus abdominis thickness associated with survival among patients with liver cirrhosis? A prospective cohort study. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2019, 137, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pita, A.; Ziogas, I.A.; Ye, F.P.; Chen, Y.; Rauf, M.A.; Matsuoka, L.K.M.; Kaur, N.M.; Whang, G.; Zielsdorf, S.M.; Bastas, G.; et al. Feasibility of Serial Ultrasound Measurements of the Rectus Femoris Muscle Area to Assess Muscle Loss in Patients Awaiting Liver Transplantation in the Intensive Care Unit. Transplant. Direct 2020, 6, e618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kan, G.A.; Chumlea, W.C.; Gillette-Guyonet, S.; Houles, M.; Dupuy, C.; Rolland, Y.; Vellas, B. Clinical trials on sarcopenia: Methodological issues regarding phase 3 trials. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2011, 27, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano-Loza, A.J.; Angulo, P.; Meza-Junco, J.; Prado, C.M.M.; Sawyer, M.B.; Beaumont, C.; Esfandiari, N.; Ma, M.; Baracos, V.E. Sarcopenic obesity and myosteatosis are associated with higher mortality in patients with cirrhosis. J. Cachex-Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalafateli, M.; Karatzas, A.; Tsiaoussis, G.; Koutroumpakis, E.; Tselekouni, P.; Koukias, N.; Konstantakis, C.; Assimakopoulos, S.; Gogos, C.; Thomopoulos, K.; et al. Muscle fat infiltration assessed by total psoas density on computed tomography predicts mortality in cirrhosis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2018, 31, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.W.; Yu, K.; Shyh-Chang, N.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, T.; Ma, S.; Luo, L.; Guang, L.; Liang, K.; Ma, W.; et al. Pathogenesis of sarcopenia and the relationship with fat mass: Descriptive review. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapaliya, S.; Runkana, A.; McMullen, M.R.; E Nagy, L.; McDonald, C.; Prasad, S.V.N.; Dasarathy, S. Alcohol-induced autophagy contributes to loss in skeletal muscle mass. Autophagy 2014, 10, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebadi, M.; Tsien, C.; Bhanji, R.A.; Dunichand-Hoedl, A.R.; Rider, E.; Motamedrad, M.; Mazurak, V.C.; Baracos, V.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Myosteatosis in Cirrhosis: A Review of Diagnosis, Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Potential Interventions. Cells 2022, 11, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | Alcoholic Hepatitis | Alcoholic Cirrhosis | Method | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 28 | 15 | - | - |
| Sex (M/F) | 20 M/8 F | 10 M/5 F | Chi Square | 0.746 |
| Age (years) | 53.89 (± 9.2) | 50.13 (±8.4) | ANOVA | 0.196 |
| Ascites (0/1) | 12 (43%) | 0 | Chi Square | 0.003 * |
| Encephalopathy (0/1) | 7 (25%) | 0 | Chi Square | 0.034 * |
| Esophageal Varices (0/1) | 7 (25%) | 4 (26%) | Chi Square | 0.905 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.42 (±4.2) | 22.36 (±3.5) | T test | 0.440 |
| WBC (×103 cells/uL) | 9.88 (±5) | 9.86 (±3.3) | T test | 0.988 |
| PLT (×103 cells/uL) | 127.61 (±83) | 164.6 (±53) | T test | 0.126 |
| INR | 1.7 (±0.3) | 1.53 (±0.3) | T test | 0.006 * |
| ALT (U/L) | 49.86 (±29.3) | 58.33 (±22.7) | T test | 0.336 |
| AST (U/L) | 134.11 (±71.4) | 66.6 (±24.9) | T test | 0.001 * |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.59 (0.51–1.09) | 0.87(0.7–1.1) | M-W U | 0.161 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 26 (17–55) | 45 (41–54) | M-W U | 0.044 * |
| Albumin (mg/dL) | 2.75 (±0.77) | 3.02 (±0.48) | T test | 0.380 |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 6.15 (4.67–12) | 1.8 (1.4–2.1) | M-W U | 0.001 * |
| ALP (mg/dL) | 121 (94–169.5) | 42 (41–55) | M-W U | 0.001 * |
| GGT (U/L) | 378 (122–768.75) | 60 (55–110) | M-W U | 0.001 * |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 10.45 (3.15–26.5) | 0.7 (0.6–2.5) | M-W U | 0.001 * |
| LDH (U/L) | 203 (170–250) | 80 (77–89) | M-W U | 0.001 * |
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 131.43 (±7.32) | 135.2 (±2.95) | T test | 0.235 |
| RFM (cm) | 1.34 (1.12–1.61) | 1.24 (1.03–1.65) | M-W U | 0.760 |
| RFMS (m/s) | 1.78 (1.45–2.49) | 1.35 (1.22–1.45) | M-W U | 0.001 * |
| RFE (0/1) | 22 (78.6%) | 8 (55.3%) | Chi Square | 0.086 |
| 30sCST (n) | 10.8 (±2.1) | 11.47(±2.23) | T test | 0.380 |
| MELD | 17.07 (±7.24) | 11.41 (±3.45) | T test | 0.007 * |
| MDF | 28.45 (25.2–58.44) | - | - | - |
| Child–Pugh | - | A—6 (40%) B—9 (60%) | - | - |
| Variable, r (p-Value) | RFM | RFMS |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | −0.178 (0.221) | 0.021 (0.887) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.320 (0.090) | −0.025 (0.620) |
| PLT (×103) | 0.512 (<0.001) * | −0.034 (0.817) |
| INR | −0.571 (<0.001) * | 0.309 (0.031) * |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.217 (0.135) | 0.135 (0.355) |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 0.549 (p < 0.001) * | −0.80 (0.585) |
| RFM | - | 0.067 (0.647) |
| RFMS | 0.067 (0.647) | - |
| 30sCST | 0.786 (p < 0.001) * | −0.444 (0.002) |
| MDF | −0.514 (p < 0.001) * | 0.480 (<0.001) * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Enciu, V.-T.; Ologeanu, P.M.; Fierbinteanu-Braticevici, C. Ultrasound Assessment of Sarcopenia in Alcoholic Liver Disease. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171891
Enciu V-T, Ologeanu PM, Fierbinteanu-Braticevici C. Ultrasound Assessment of Sarcopenia in Alcoholic Liver Disease. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(17):1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171891
Chicago/Turabian StyleEnciu, Vlad-Teodor, Priscila Madalina Ologeanu, and Carmen Fierbinteanu-Braticevici. 2024. "Ultrasound Assessment of Sarcopenia in Alcoholic Liver Disease" Diagnostics 14, no. 17: 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171891
APA StyleEnciu, V.-T., Ologeanu, P. M., & Fierbinteanu-Braticevici, C. (2024). Ultrasound Assessment of Sarcopenia in Alcoholic Liver Disease. Diagnostics, 14(17), 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171891






