Topotecan in a Real-World Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cohort: Prognostic Biomarkers Improve Selection of Patients for Second-Line Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Survival Analysis of the Whole Cohort
3.2. Toxicity
3.3. Prediction of Response
3.4. Prognostic Value of Different Markers and Scores
3.5. Multivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Gümüş, Z.H.; Colarossi, C.; Memeo, L.; Wang, X.; Kong, C.Y.; Boffetta, P. SCLC: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Genetic Susceptibility, Molecular Pathology, Screening, and Early Detection. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahnert, K.; Kauffmann-Guerrero, D.; Huber, R.M. SCLC-State of the Art and What Does the Future Have in Store? Clin. Lung Cancer 2016, 17, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saida, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Kikuchi, T. Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Current Landscape and Future Prospects. OncoTargets Ther. 2023, 16, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Pawel, J.; Schiller, J.H.; Shepherd, F.A.; Fields, S.Z.; Kleisbauer, J.P.; Chrysson, N.G.; Stewart, D.J.; Clark, P.I.; Palmer, M.C.; Depierre, A.; et al. Topotecan versus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and vincristine for the treatment of recurrent small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, M.E.R.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.; Tsekov, H.; Shparyk, Y.; Čučeviá, B.; Juhasz, G.; Thatcher, N.; Ross, G.A.; Dane, G.C.; Crofts, T. Phase III Trial Comparing Supportive Care Alone With Supportive Care With Oral Topotecan in Patients With Relapsed Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5441–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horita, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Sato, T.; Tsukahara, T.; Nagakura, H.; Tashiro, K.; Shibata, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Nagai, K.; Inoue, M.; et al. Topotecan for Relapsed Small-cell Lung Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 1347 Patients. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffmann-Guerrero, D.; Kahnert, K.; Kiefl, R.; Sellmer, L.; Walter, J.; Behr, J.; Tufman, A. Systemic inflammation and pro-inflammatory cytokine profile predict response to checkpoint inhibitor treatment in NSCLC: A prospective study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffmann-Guerrero, D.; Kahnert, K.; Syunyaeva, Z.; Tufman, A.; Huber, R.M. Pretherapeutic Inflammation Predicts Febrile Neutropenia and Reduced Progression-Free Survival after First-Line Chemotherapy in SCLC. Oncol. Res. Treat 2018, 41, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Soler, R.; Glisson, B.S.; Lee, J.S.; Fossella, F.V.; Murphy, W.K.; Shin, D.M.; Hong, W.K. Treatment of patients with small-cell lung cancer refractory to etoposide and cisplatin with the topoisomerase I poison topotecan. J. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 14, 2785–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzoni, A.; Hansen, H.; Dombernowsky, P.; Gamucci, T.; Kaplan, S.; Postmus, P.; Giaccone, G.; Schaefer, B.; Wanders, J.; Verweij, J. Topotecan, a new active drug in the second-line treatment of small-cell lung cancer: A phase II study in patients with refractory and sensitive disease. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Early Clinical Studies Group and New Drug Development Office, and the Lung Cancer Cooperative Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 1997, 15, 2090–2096. [Google Scholar]
- Takeda, K.; Negoro, S.; Sawa, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Kawahara, M.; Isobe, T.; Kudoh, S.; Masuda, N.; Niitani, H.; Fukuoka, M. A phase II study of topotecan in patients with relapsed small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2003, 4, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Pawel, J.; Gatzemeier, U.; Pujol, J.-L.; Moreau, L.; Bildat, S.; Ranson, M.; Richardson, G.; Steppert, C.; Rivière, A.; Camlett, I.; et al. Phase II Comparator Study of Oral Versus Intravenous Topotecan in Patients With Chemosensitive Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, J.R.; von Pawel, J.; Pujol, J.-L.; Papai, Z.; Quoix, E.; Ardizzoni, A.; Poulin, R.; Preston, A.J.; Dane, G.; Ross, G. Phase III study of oral compared with intravenous topotecan as second-line therapy in small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2086–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, H.; Yamada, Y.; Minemura, H.; Sugiyama, T.; Kotake, M.; Kaira, K.; Kanazawa, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Kasai, T.; Shibata, Y.; et al. Topotecan monotherapy for the treatment of relapsed small cell lung cancer in elderly patients: A retrospective analysis. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treat, J.; Huang, C.H.; Lane, S.R.; Levin, J. Topotecan in the treatment of relapsed small cell lung cancer patients with poor performance status. Oncologist 2004, 9, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilenbaum, R.C.; Huber, R.M.; Treat, J.; Masters, G.; Kaubitzsch, S.; Lane, S.; Wissel, P. Topotecan therapy in patients with relapsed small-cell lung cancer and poor performance status. Clin. Lung Cancer 2006, 8, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korfel, A.; Oehm, C.; von Pawel, J.; Keppler, U.; Deppermann, M.; Kaubitsch, S.; Thiel, E. Response to topotecan of symptomatic brain metastases of small-cell lung cancer also after whole-brain irradiation. a multicentre phase II study. Eur. J. Cancer 2002, 38, 1724–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorusso, V.; Galetta, D.; Giotta, F.; Rinaldi, A.; Romito, S.; Brunetti, C.; Silvestris, N.; Colucci, G. Topotecan in the treatment of brain metastases. A phase II study of GOIM (Gruppo Oncologico dell’Italia Meridionale). Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 2259–2263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ardizzoni, A.; Manegold, C.; Debruyne, C.; Gaafar, R.; Buchholz, E.; Smit, E.F.; Lianes, P.; ten Velde, G.; Bosquee, L.; Legrand, C.; et al. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) 08957 phase II study of topotecan in combination with cisplatin as second-line treatment of refractory and sensitive small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 143. [Google Scholar]
- Stathopoulos, G.P.; Christodoulou, C.; Stathopoulos, J.; Skarlos, D.; Rigatos, S.K.; Giannakakis, T.; Armenaki, O.; Antoniou, D.; Athanasiadis, A.; Giamboudakis, P.; et al. Second-line chemotherapy in small cell lung cancer in a modified administration of topotecan combined with paclitaxel: A phase II study. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 57, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.J.; Cho, B.C.; Shin, S.J.; Cheon, S.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Chang, J.; Kim, S.K.; Sohn, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Combination of topotecan and etoposide as a salvage treatment for patients with recurrent small cell lung cancer following irinotecan and platinum first-line chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2007, 61, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurata, T.; Kashii, T.; Takeda, K.; Seki, N.; Tsuboi, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Satoh, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Fukuoka, M. A Phase I Study of Topotecan Plus Carboplatin for Relapsed SCLC: WJTOG Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, T.L.; Cho, B.C.; Udud, K.; Fischer, J.R.; Shepherd, F.A.; Martinez, P.; Ramlau, R.; Syrigos, K.N.; Shen, L.; Chadjaa, M.; et al. Cabazitaxel Versus Topotecan in Patients with Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Progressive Disease During or After First-Line Platinum-Based Chemotherapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulou, C.; Kalofonos, H.P.; Briasoulis, E.; Bafaloukos, D.; Makatsoris, T.; Koutras, A.; Skarlos, D.V.; Samantas, E. Combination of topotecan and cisplatin in relapsed patients with small cell lung cancer: A phase II study of the hellenic cooperative oncology group (HeCOG). Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 57, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suk Heist, R.; Fain, J.; Chinnasami, B.; Khan, W.; Molina, J.R.; Sequist, L.V.; Temel, J.S.; Fidias, P.; Brainerd, V.; Leopold, L.; et al. Phase I/II Study of AT-101 with Topotecan in Relapsed and Refractory Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, P.K.; Rudin, C.M.; Pietanza, M.C.; Brown, A.; Rizvi, N.A.; Takebe, N.; Travis, W.; James, L.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Juergens, R.; et al. A phase II study of obatoclax mesylate, a Bcl-2 antagonist, plus topotecan in relapsed small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2011, 74, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spigel, D.R.; Waterhouse, D.M.; Lane, S.; Legenne, P.; Bhatt, K. Efficacy and safety of oral topotecan and bevacizumab combination as second-line treatment for relapsed small-cell lung cancer: An open-label multicenter single-arm phase II study. Clin. Lung Cancer 2013, 14, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, A.; Sugawara, S.; Yamazaki, K.; Maemondo, M.; Suzuki, T.; Gomi, K.; Takanashi, S.; Inoue, C.; Inage, M.; Yokouchi, H.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial Comparing Amrubicin With Topotecan in Patients With Previously Treated Small-Cell Lung Cancer: North Japan Lung Cancer Study Group Trial 0402. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 5401–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jotte, R.; Conkling, P.; Reynolds, C.; Galsky, M.D.; Klein, L.; Fitzgibbons, J.F.; McNally, R.; Renschler, M.F.; Oliver, J.W. Randomized Phase II Trial of Single-Agent Amrubicin or Topotecan as Second-Line Treatment in Patients With Small-Cell Lung Cancer Sensitive to First-Line Platinum-Based Chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Pawel, J.; Jotte, R.; Spigel, D.R.; O’Brien, M.E.R.; Socinski, M.A.; Mezger, J.; Steins, M.; Bosquée, L.; Bubis, J.; Nackaerts, K.; et al. Randomized Phase III Trial of Amrubicin Versus Topotecan As Second-Line Treatment for Patients With Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 4012–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogami, N.; Hotta, K.; Kuyama, S.; Kiura, K.; Takigawa, N.; Chikamori, K.; Shibayama, T.; Kishino, D.; Hosokawa, S.; Tamaoki, A.; et al. A phase II study of amrubicin and topotecan combination therapy in patients with relapsed or extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer: Okayama Lung Cancer Study Group Trial 0401. Lung Cancer 2011, 74, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| n = 44 | |
|---|---|
| Male (n (%)) | 25 (56.8%) |
| Female (n (%)) | 19 (43.2%) |
| Age (mean ± Sdev) | 64.3 ± 9.9 |
| Males | 65.52 ± 10.4 |
| Females | 62.6 ± 9.2 |
| ECOG-PS | |
| 0 | 6 (13.6%) |
| 1 | 19 (43.2%) |
| 2 | 14 (31.8%) |
| 3 | 5 (11.4%) |
| Smoking status (n (%)) | |
| Current smoker | 9 (20.5%) |
| Former smoker | 35 (79.5%) |
| Pharmaceutical form (n (%)) | |
| Intravenous | 40 (90.9%) |
| Oral | 4 (9.1%) |
| Median of applied cycles [range] | 3 (1–17) |
| Mean applied dosage [range] | 1.22 mg/m2 [0.625–2.4 mg/m2] |
| Median time from first diagnosis until topotecan | 8.3 months |
| Median time from last treatment until topotecant (treatment free intervall, TFI) | 1.7 months |
| <3 months (n (%)) | 32 (72.7) |
| ≥3 months | 12 (27.3) |
| Prior IO treatment (n (%)) | |
| Yes | 15 (34.1%) |
| No | 29 (65.9%) |
| Active brain metastases (n (%)) | |
| Yes | 15 (34.1%) |
| No | 29 (64.9%) |
| WBRT before topotecan (n (%)) | |
| Yes | 20 (45.5%) |
| No | 24 (54.5%) |
| 1st-line treatment (n (%)) | |
| Chemo(-immuno) therapy | 31 (70.5%) |
| Radiochemotherapy | 13 (29.5%) |
| Best response to topotecan treatment (n (%)) | |
| PR | 6 (13.6%) |
| SD | 8 (18.2%) |
| PD | 23 (52.3%) |
| Death | 7 (15.9%) |
| Median PFS [CI 95%] | HR [CI 95%] | p-Value [Log Rank] | Median OS [CI 95%] | HR [CI 95%] | p-Value [Log Rank] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
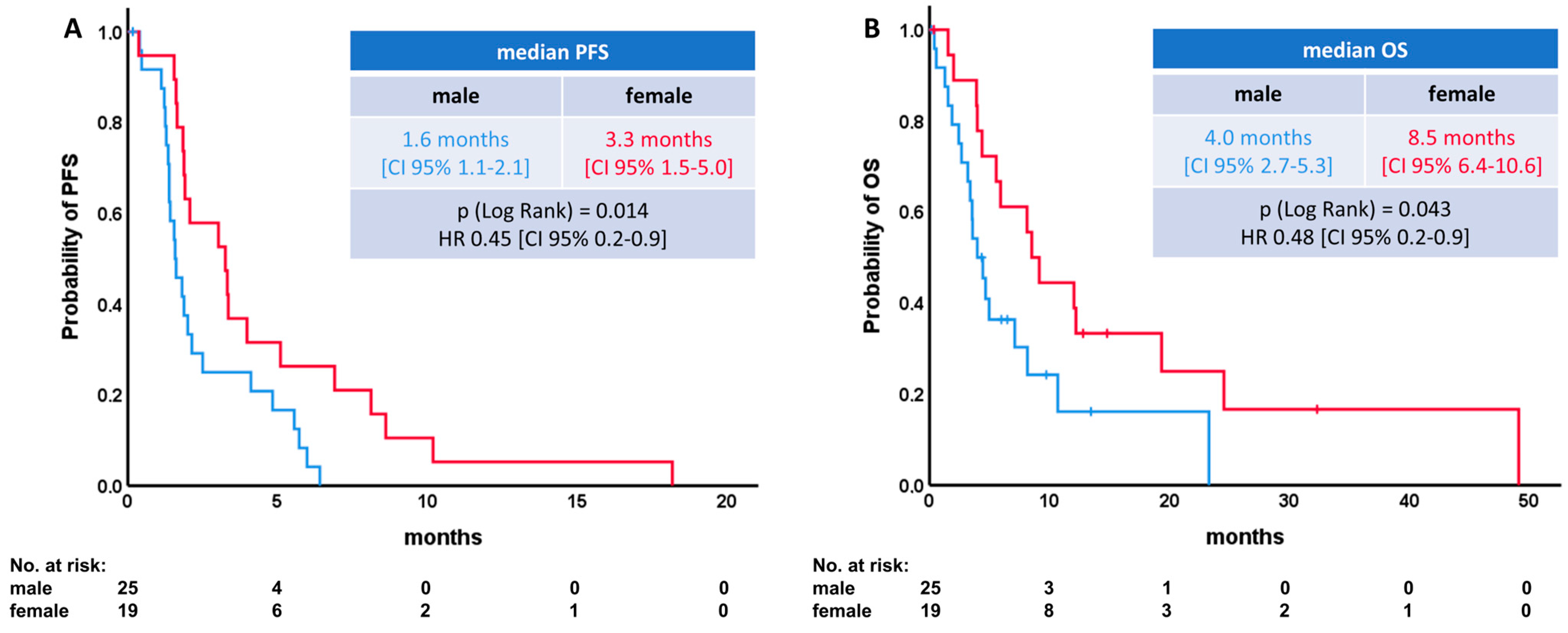
| Gender | ||||||
| Male | 1.6 [1.1–2.1] | p = 0.014 | 4.0 [2.7–5.3] | p = 0.043 | ||
| Female | 3.3 [1.5–5.0] | 0.45 [0.2–0.9] | 8.5 [6.4–10.6] | 0.48 [0.2–0.9] | ||
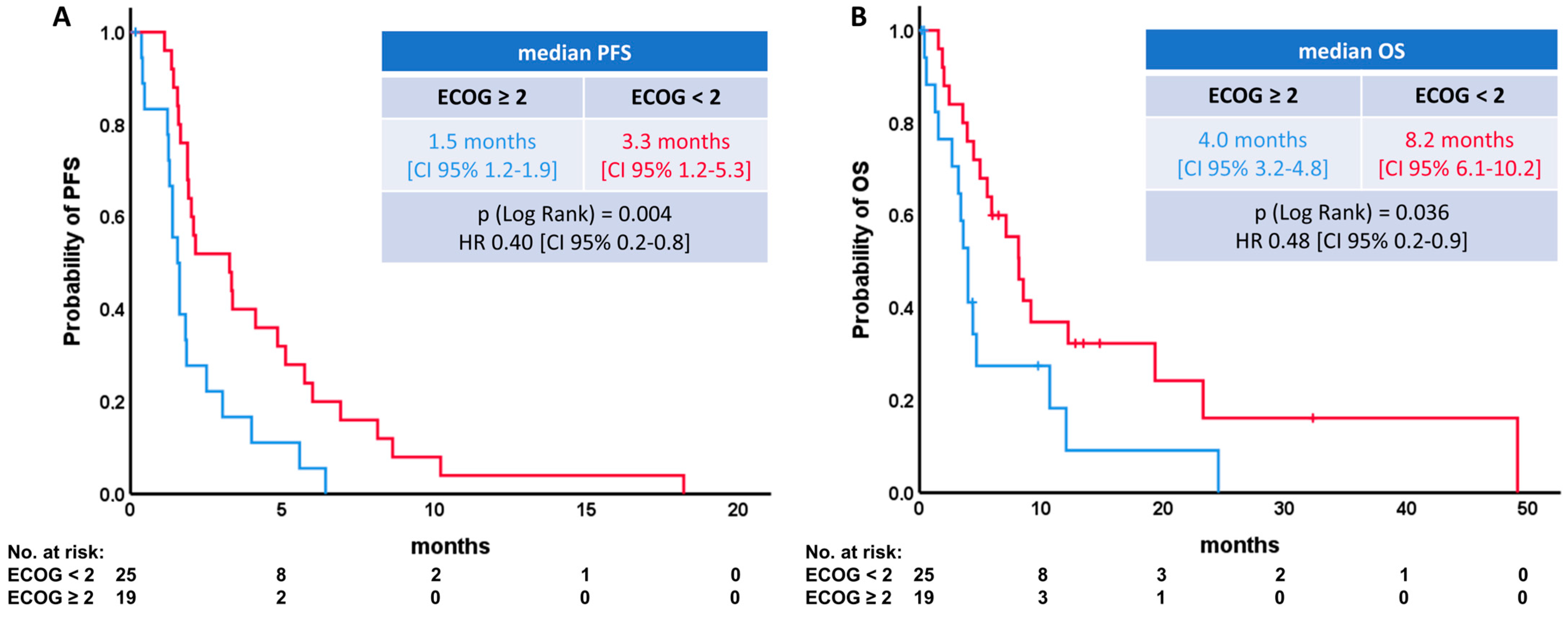
| ECOG | ||||||
| <2 | 3.3 [1.2–5.3] | 0.40 [0.2–0.8] | p = 0.004 | 8.2 [6.1–10.2] | 0.48 [0.2–0.9] | p = 0.036 |
| ≥2 | 1.5 [1.2–1.9] | 4.0 [3.2–4.8] | ||||
| Age | ||||||
| <70 years | 1.9 [0.4–3.5] | p = 0.433 | 5.9 [2.0–9.8] | p = 0.713 | ||
| ≥70 years | 1.9 [1.5–2.3] | 1.2 [0.6–2.6] | 4.0 [3.4–4.6] | 1.1 [0.5–2.6] | ||
| Time until topotecan | ||||||
| ≤8.3 months | 1.9 [1.5–2.3] | p = 0.719 | 4.4 [3.6–5.1] | p = 0.484 | ||
| >8.3 months | 1.9 [0.3–3.5] | 0.66 [0.3–1.3] | 8.6 [4.4–12.7] | 0.78 [0.4–1.6] | ||
| Median time from last treatment until topotecant (treatment free interval, TFI) | ||||||
| <3 months (n (%)) | 1.9 [1.6–2.2] | 1.9 [0.6–5.8] | p = 0.205 | 5.0 [3.4–6.5] | 1.5 [0.1–2.5] | p = 0.711 |
| ≥3 months | 1.9 [0.0–5.8] | 9.1 [1.7–16.6] | ||||
| Mean topotecan dosage | ||||||
| <1.25 mg/m2 | 3.3 [1.2–5.3] | p = 0.547 | 8.1 [3.9–12.3] | p = 0.111 | ||
| ≥1.25 mg/m2 | 1.6 [1.2–2.0] | 1.4 [0.8–2.7] | 4.3 [3.1–5.7] | 1,7 [0.9–3.5] | ||
| Prior IO treatment | ||||||
| Yes | 1.8 [1.2–2.4] | p = 0.903 | 5.0 [0.8–9.1] | p = 0.855 | ||
| No | 2.1 [0.4–3.9] | 0.9 [0.5–1.6] | 5.9 [0.5–11.4] | 2.1 [0.5–8.8] | ||
| Active brain metastases | ||||||
| No | 3.0 [1.5–4.6] | p = 0.028 | 7.1 [2.5–11.7] | p = 0.633 | ||
| Yes | 1.6 [1.3–1.9] | 1.9 [1.0–3.6] | 4.7 [3.7–5.7] | 1.2 [0.6–2.6] | ||
| WBRT before topotecan | ||||||
| No | 2.1 [0.0–4.4] | p = 0.475 | 7.1 [2.5–11.7] | p = 0.571 | ||
| Yes | 1.8 [1.7–2.0] | 1.1 [0.6–2.0] | 5.0 [2.7–7.2] | 0.8 [0.4–1.6] | ||
| 1st-line treatment | ||||||
| Chemo(-immuno) therapy | 1.8 [0.9–2.8] | p = 0.638 | 4.4 [3.6–5.2] | p = 0.089 | ||
| Radiochemotherapy | 1.9 [1.5–2.4] | 0.7 [0.3–1.4] | 12.0 [6.8–17.2] | 0.5 [0.2–1.1] |
| Categorial Variables | |||
| Variable | p-Value | Variable | p-Value |
| Gender (male vs. women) | p = 0.054 | Active brain metastases (yes vs. no) | p = 0.598 |
| ECOG (0 vs. 1 vs. 2 vs. 3) | p = 0.085 | WBRT (yes vs. no) | p = 0.813 |
| Application (p.o. vs. i.v.) | p = 0.152 | 1st-line treatment (CX vs. RCT) | p = 0.420 |
| GPS (0 vs. 1 vs. 2) | p = 0.207 | Age (<70 vs. ≥70) | p = 0.709 |
| Prior IO treatment (yes vs. no) | p = 0.128 | Time till Topotecan (≤8.3 vs. >8.3 months) | p = 0.195 |
| Dosage (<1.25 mg/m2 vs. ≥1.25 mg/m2) | p = 0.010 | LDH (≤250 vs. >250 U/l) | p = 0.195 |
| CRP (≤0.5 vs. >0.5 mg/dL | p = 0.32 | NLR (≤6 vs. >6) | p = 0.598 |
| Sodium (<135 vs. ≥135 mmol/L) | p =0.092 | TLR (≤200 vs. >200) | p = 1 |
| PNI (<40 vs. ≥40) | p = 0.262 | SII (<1500 vs. ≥1500) | p = 0.349 |
| PI (1 + 2 vs. 3 + 4) | p = 0.287 | ||
| Continuous Variables | |||
| Variable | p-Value | Variable | p-Value |
| Age | p = 0.830 | NLR | p = 0.257 |
| Mean topotecan dosage | p = 0.009 | TLR | p = 0.860 |
| LDH | p = 0.059 | PNI | p = 0.174 |
| CRP | p = 0.007 | SII | p = 0.166 |
| Sodium | p = 0.419 | ||
| Median PFS [CI 95%] | HR [CI 95%] | p-Value [Log Rank] | Median OS [CI 95%] | HR [CI 95%] | p-Value [Log Rank] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDH | ||||||
| ≤250 U/L | 3.0 [0.9–5.1] | p = 0.006 | 8.5 [4.0–13.1] | p = 0.370 | ||
| >250 U/L | 1.6 [1.2–2.1] | 2.2 [1.2–4.3] | 3.6 [1.8–5.4] | 1.4 [0.7–2.8] | ||
| CRP | ||||||
| ≤0.5 mg/dL | 3.4 [0.7–6.0] | p = 0.089 | 9.1 [5.7–12.6] | p = 0.102 | ||
| >0.5 mg/dL | 1.6 [1.3–2.0] | 1.6 [0.8–3.1] | 4.4 [2.7–6.0] | 1.6. [0.8–3.1] | ||
| NLR | ||||||
| ≤6 | 3.0 [0.9–5.1] | p = 0.002 | 8.2 [4.1–12.2] | p = 0.01 | ||
| >6 | 1.3 [1.1–1.6] | 2.5 [1.3–4.9] | 4.4 [1.8–7.1] | 2.6 [1.2–5.5] | ||
| Sodium | ||||||
| <135 mmol/L | 1.6 [1.5–1.7] | p = 0.066 | 4.4 [2.9–5.8] | p = 0.029 | ||
| ≥135 mmol/L | 3.0 [1.6–4.4] | 0.5 [0.3–1.1] | 8.1 [4.1–12.2] | 0.4 [0.2–0.9] | ||
| TLR | ||||||
| ≤200 | 3.0 [0.4–5.7] | p = 0.020 | 8.1 [3.0–13.2] | p = 0.734 | ||
| >200 | 1.9 [1.5–2.3] | 1.9 [1.0–3.7] | 4.7 [3.5–5.8] | 1.1 [0.6–2.2] | ||
| GPS | ||||||
| 0 | 3.0 [0.4–5.6] | p = 0.011 | 9.1 [5.6–12.66] | p = 0.008 | ||
| ≥1 | 1.6 [1.2–2.1] | 2.3 [1.2–4.6] | 4.0 [2.2–5.7] | 2.6 [1.3–5.4] | ||
| PNI | ||||||
| <40 | 1.4 [1.2–1.7] | p = 0.015 | 2.4 [1.2–3.6] | p < 0.001 | ||
| ≥40 | 2.5 [0.9–4.1] | 0.4 [0.2–0.9] | 8.6 [2.4–8.8] | 0.2 [0.1–0.4] | ||
| SII | ||||||
| <1500 | 3.0 [0.9–5.1] | p = 0.014 | 8.1 [3.0–13.3] | p = 0.431 | ||
| ≥1500 | 1.6 [1.3–1.8] | 2.1 [1.1–3.9] | 4.7 [2.9–6.5] | 1.3 [0.7–2.7] | ||
| PI | ||||||
| 1–2 | 3.3 [2.6–4.0] | p = 0.003 | 9.1 [2.4–15.9] | p = 0.001 | ||
| 3–4 | 1.6 [1.3–1.9] | 2.4 [1.3–4.7] | 3.6 [2.9–4.2] | 3.2 [1.5–6.6] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lambrecht, L.; Arnold, P.; Behr, J.; Mertsch, P.; Tufman, A.; Kauffmann-Guerrero, D. Topotecan in a Real-World Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cohort: Prognostic Biomarkers Improve Selection of Patients for Second-Line Treatment. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141572
Lambrecht L, Arnold P, Behr J, Mertsch P, Tufman A, Kauffmann-Guerrero D. Topotecan in a Real-World Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cohort: Prognostic Biomarkers Improve Selection of Patients for Second-Line Treatment. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(14):1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141572
Chicago/Turabian StyleLambrecht, Laura, Paola Arnold, Jürgen Behr, Pontus Mertsch, Amanda Tufman, and Diego Kauffmann-Guerrero. 2024. "Topotecan in a Real-World Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cohort: Prognostic Biomarkers Improve Selection of Patients for Second-Line Treatment" Diagnostics 14, no. 14: 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141572
APA StyleLambrecht, L., Arnold, P., Behr, J., Mertsch, P., Tufman, A., & Kauffmann-Guerrero, D. (2024). Topotecan in a Real-World Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cohort: Prognostic Biomarkers Improve Selection of Patients for Second-Line Treatment. Diagnostics, 14(14), 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141572






