Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for the Diagnosis of Skin Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Data Selection and Extraction
2.3. Quality Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
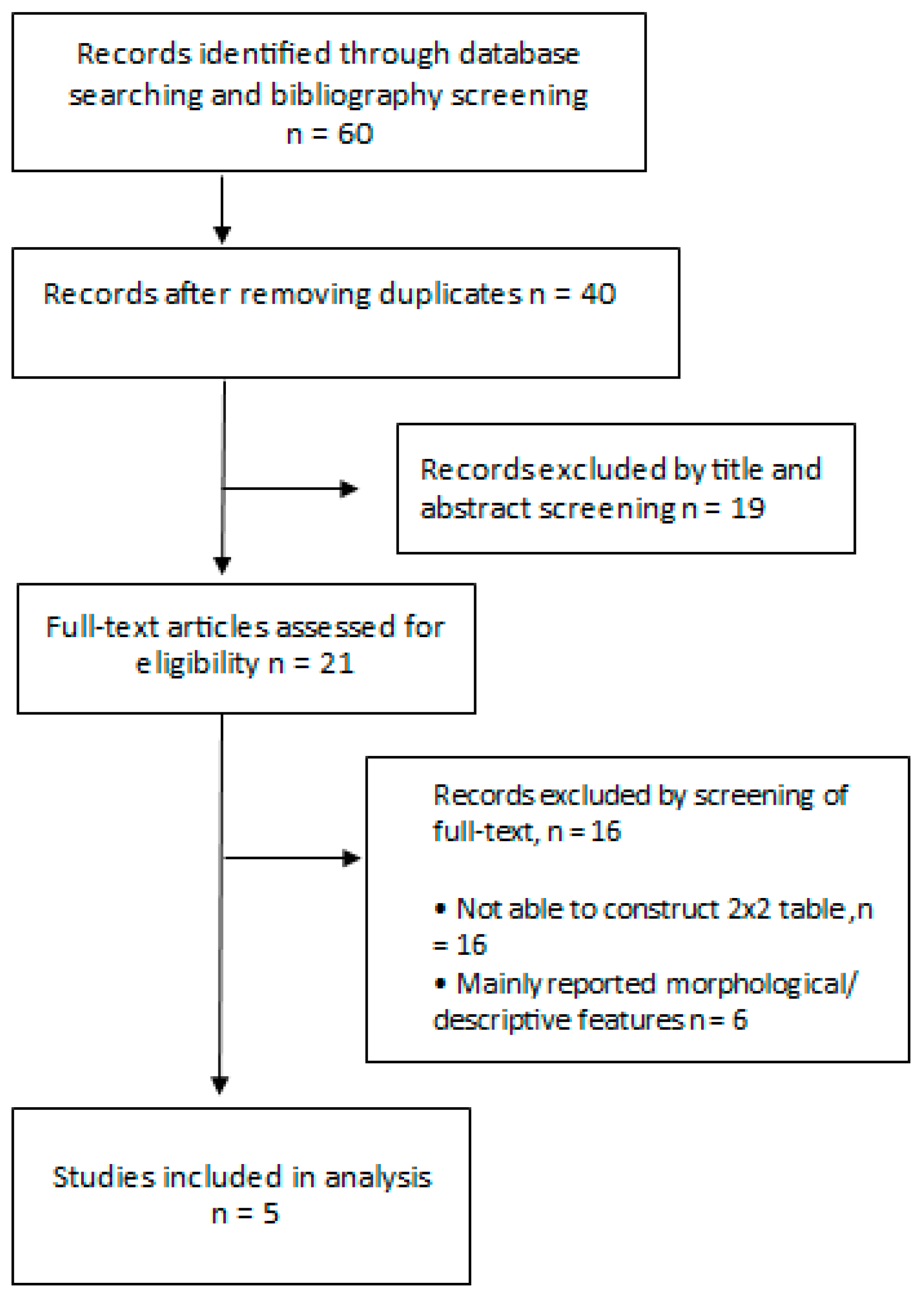
3.1. Description of Studies Included
3.2. Quality Assessment
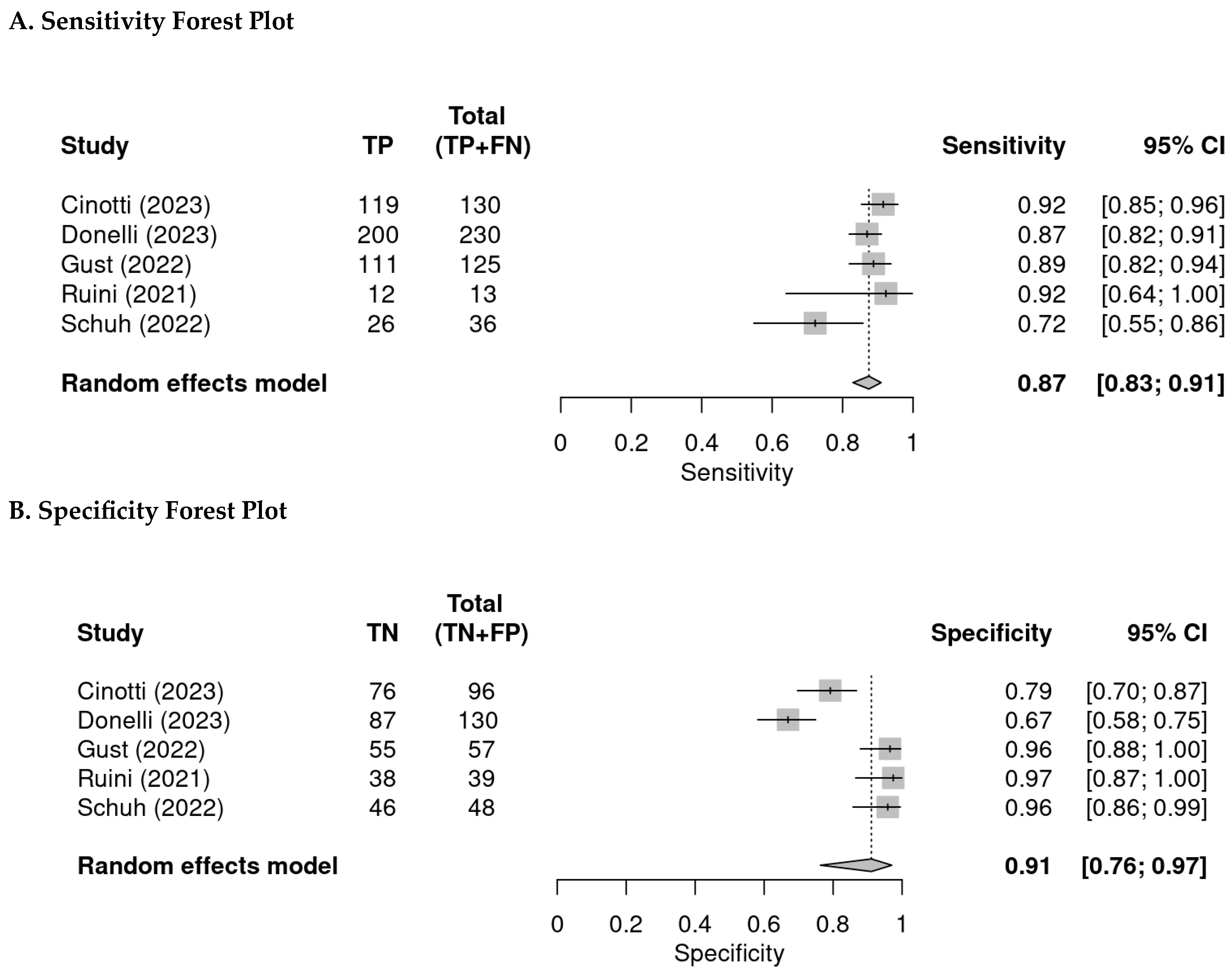
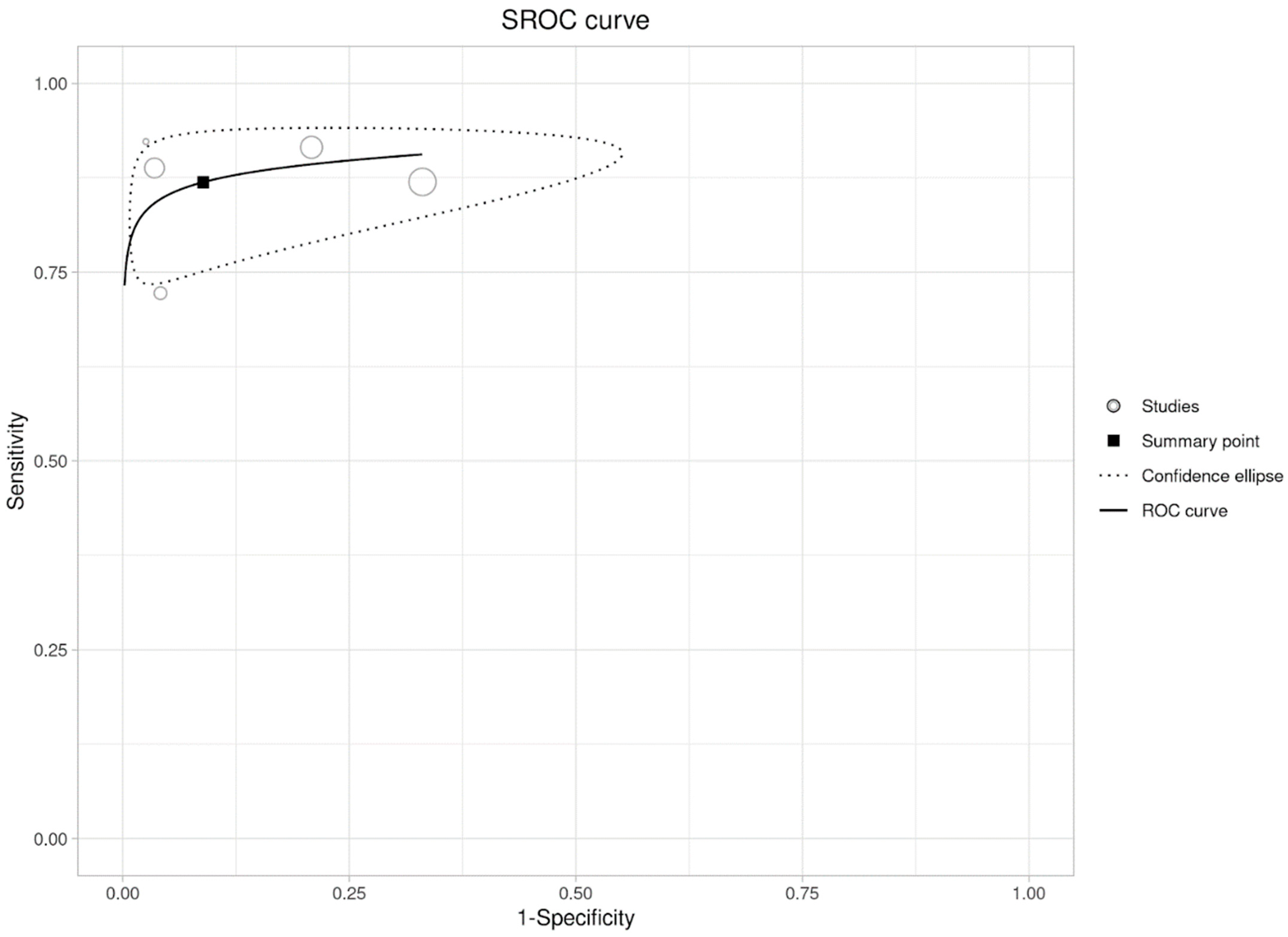
3.3. Per-Lesion Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Latriglia, F.; Ogien, J.; Tavernier, C.; Fischman, S.; Suppa, M.; Perrot, J.-L.; Dubois, A. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography (LC-OCT) for Skin Imaging in Dermatology. Life 2023, 13, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donelli, C.; Suppa, M.; Tognetti, L.; Perrot, J.L.; Calabrese, L.; Pérez-Anker, J.; Malvehy, J.; Rubegni, P.; Cinotti, E. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for the Diagnosis of Skin Carcinomas: Real-Life Data over Three Years. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 8853–8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.; Levine, A.; Markowitz, O. Optical coherence tomography in dermatology. Cutis 2017, 100, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.; Markowitz, O. Introduction to reflectance confocal microscopy and its use in clinical practice. JAAD Case Rep. 2018, 4, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Secrest, A.; Anderson, A.; Saul, M.I.; Ho, J.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Ferris, L.K. Estimating the cost of skin cancer detection by dermatology providers in a large health care system. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 701–709.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, R.S. Prevalence of a history of skin cancer in 2007: Results of an incidence-based model. Arch. Dermatol. 2010, 146, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apalla, Z.; Lallas, A.; Sotiriou, E.; Lazaridou, E.; Ioannides, D. Epidemiological trends in skin cancer. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2017, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, S.Z.; Ekwueme, D.U.; Holman, D.M.; Rim, S.H.; Thomas, C.C.; Saraiya, M. Economic burden of skin cancer treatment in the USA: An analysis of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey Data, 2012–2018. Cancer Causes Control 2023, 34, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R. Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Plana, M.N.; Arevalo-Rodriguez, I.; Fernandez-Garcia, S.; Soto, J.; Fabregate, M.; Pérez, T.; Roqué, M.; Zamora, J. Meta-DiSc 2.0: A web application for meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy data. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2022, 22, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, J.; Abraira, V.; Muriel, A.; Khan, K.; Coomarasamy, A. Meta-DiSc: A software for meta-analysis of test accuracy data. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2006, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinotti, E.; Brunetti, T.; Cartocci, A.; Tognetti, L.; Suppa, M.; Malvehy, J.; Perez-Anker, J.; Puig, S.; Perrot, J.L.; Rubegni, P. Diagnostic Accuracy of Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for the Diagnosis of Skin Carcinomas. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, C.; Schuh, S.; Welzel, J.; Daxenberger, F.; Hartmann, D.; French, L.E.; Ruini, C.; Sattler, E.C. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography Increases the Diagnostic Accuracy and Confidence for Basal Cell Carcinoma in Equivocal Lesions: A Prospective Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruini, C.; Schuh, S.; Gust, C.; Kendziora, B.; Frommherz, L.; French, L.E.; Hartmann, D.; Welzel, J.; Sattler, E. Line-field optical coherence tomography: In vivo diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma subtypes compared with histopathology. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 46, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuh, S.; Ruini, C.; Perwein, M.K.E.; Daxenberger, F.; Gust, C.; Sattler, E.C.; Welzel, J. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography: A New Tool for the Differentiation between Nevi and Melanomas? Cancers 2022, 14, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinnes, J.; Deeks, J.J.; Chuchu, N.; di Ruffano, L.F.; Matin, R.N.; Thomson, D.R.; Wong, K.Y.; Aldridge, R.B.; Abbott, R.; Fawzy, M.; et al. Dermoscopy, with and without visual inspection, for diagnosing melanoma in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 12, Cd011902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carli, P.; De Giorgi, V.; Crocetti, E.; Mannone, F.; Massi, D.; Chiarugi, A.; Giannotti, B. Improvement of malignant/benign ratio in excised melanocytic lesions in the ‘dermoscopy era’: A retrospective study 1997–2001. Br. J. Dermatol. 2004, 150, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carli, P.; de Giorgi, V.; Chiarugi, A.; Nardini, P.; Weinstock, M.A.; Crocetti, E.; Stante, M.; Giannotti, B. Addition of dermoscopy to conventional naked-eye examination in melanoma screening: A randomized study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 50, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, O.; Mimouni, I.; Gdalevich, M.; Marghoob, A.A.; Levi, A.; Hodak, E.; Leshem, Y.A. The diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy for basal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamińska-Winciorek, G.; Placek, W. The most common mistakes on dermatoscopy of melanocytic lesions. Postep. Dermatol. Alergol. 2015, 32, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, J.G.; Barnhill, R.L.; Elder, D.E.; Longton, G.M.; Pepe, M.S.; Reisch, L.M.; Carney, P.A.; Titus, L.J.; Nelson, H.D.; Onega, T.; et al. Pathologists’ diagnosis of invasive melanoma and melanocytic proliferations: Observer accuracy and reproducibility study. BMJ 2017, 357, j2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.Q.; Ma, S.J.; Mo, Y.; Huo, S.T.; Wen, Y.Q.; Chen, Q. Comparison of dermoscopy and reflectance confocal microscopy for the diagnosis of malignant skin tumours: A meta-analysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.D.; Ma, S.; Li, X.; Zhong, X.; Duan, C.; Chen, Q. A meta-analysis of reflectance confocal microscopy for the diagnosis of malignant skin tumours. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnes, J.; Deeks, J.J.; Chuchu, N.; Saleh, D.; Bayliss, S.E.; Takwoingi, Y.; Davenport, C.; Patel, L.; Matin, R.N.; O’Sullivan, C.; et al. Reflectance confocal microscopy for diagnosing keratinocyte skin cancers in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 12, Cd013191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante di Ruffano, L.; Dinnes, J.; Deeks, J.J.; Chuchu, N.; Bayliss, S.E.; Davenport, C.; Takwoingi, Y.; Godfrey, K.; O’Sullivan, C.; Matin, R.N.; et al. Optical coherence tomography for diagnosing skin cancer in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 12, Cd013189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsea, A.M.; Carstea, E.M.; Ghervase, L.; Giurcaneanu, C.; Pavelescu, G. Clinical application of optical coherence tomography for the imaging of non-melanocytic cutaneous tumors: A pilot multi-modal study. J. Med. Life 2010, 3, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.Q.; Mo, Y.; Wen, Y.Q.; Cheng, M.-J.; Huo, S.-T.; Chen, X.-J.; Chen, Q. Optical coherence tomography for the diagnosis of malignant skin tumors: A meta-analysis. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 020902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.M.; Cho, J.Y.; Lee, W.J.; Chang, S.E.; Lee, M.W.; Won, C.H. Emerging Minimally Invasive Technologies for the Detection of Skin Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, E.S.; Berkowitz, E.Z.; Fuchs, B.S.; Singer, G.K.; Yoo, J.Y. Use of high-frequency, high-resolution ultrasound before Mohs surgery. Dermatol. Surg. 2010, 36, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zeng, H.; Kalia, S.; Lui, H. Using Raman Spectroscopy to Detect and Diagnose Skin Cancer In Vivo. Dermatol. Clin. 2017, 35, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarac, E.; Meiwes, A.; Eigentler, T.; Forchhammer, S.; Kofler, L.; Häfner, H.; Garbe, C. Diagnostic Accuracy of Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy in Non-melanoma Skin Cancer. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvehy, J.; Hauschild, A.; Curiel-Lewandrowski, C.; Mohr, P.; Hofmann-Wellenhof, R.; Motley, R.; Berking, C.; Grossman, D.; Paoli, J.; Loquai, C.; et al. Clinical performance of the Nevisense system in cutaneous melanoma detection: An international, multicentre, prospective and blinded clinical trial on efficacy and safety. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 171, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstockt, J.; Verspeek, S.; Thiessen, F.; Tjalma, W.A.; Brochez, L.; Steenackers, G. Skin Cancer Detection Using Infrared Thermography: Measurement Setup, Procedure and Equipment. Sensors 2022, 22, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerami, P.; Yao, Z.; Polsky, D.; Jansen, B.; Busam, K.; Ho, J.; Martini, M.; Ferris, L.K. Development and validation of a noninvasive 2-gene molecular assay for cutaneous melanoma. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 76, 114–120.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischman, S.; Perez-Anker, J.; Tognetti, L.; Di Naro, A.; Suppa, M.; Cinotti, E.; Viel, T.; Monnier, J.; Rubegni, P.; del Marmol, V.; et al. Non-invasive scoring of cellular atypia in keratinocyte cancers in 3D LC-OCT images using Deep Learning. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnier, F.; Pedrazzani, M.; Fischman, S.; Viel, T.; Lavoix, A.; Pegoud, D.; Nili, M.; Jimenez, Y.; Ralambondrainy, S.; Cauchard, J.-H.; et al. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography coupled with artificial intelligence algorithms to identify quantitative biomarkers of facial skin ageing. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verzi, A.E.; Broggi, G.; Micali, G.; Sorci, F.; Caltabiano, R.; Lacarrubba, F. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography of psoriasis, eczema and lichen planus: A case series with histopathological correlation. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1884–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, C.; Taddeucci, P.; Bertello, M.; Cinotti, E.; Cortonesi, G.; Rubegni, P.; Russo, F. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography for the diagnosis of nodular scabies mimicking breast cancer skin metastasis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2023, 62, e195–e196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacarrubba, F.; Verzi, A.E.; Puglisi, D.F.; Micali, G. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography: A novel, non-invasive imaging technique for a rapid, in-vivo diagnosis of herpes infection of the skin. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, e404–e406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verzi, A.E.; Micali, G.; Lacarrubba, F. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography in molluscum contagiosum: A case series. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, e934–e936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcinelli, F.; Lazzeri, L.; Rubegni, P.; Russo, F. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography (LC-OCT) in bullous striae distensae. Ital. J. Dermatol. Venerol. 2023, 159, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefani, A.; Fionda, B.; Cappilli, S.; Tagliaferri, L.; Peris, K. Extramammary Paget disease imaged by LC-OCT and treated with radiotherapy. Int. J. Dermatol. 2023, 62, e503–e505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefani, A.; Cappilli, S.; Ricci, C.; Costantini, A.; Paradisi, A.; Peris, K. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography (LC-OCT) in Hailey-Hailey disease: Another brick in the wall. Int. J. Dermatol. Mar. 2023, 62, e178–e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, T.M.; Pathak, G.N.; Rao, B.K. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography imaging findings of scalp psoriasis. JAAD Case Rep. 2023, 39, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, G.N.; Truong, T.M.; Rao, B.K. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography assessment of pityriasis rosea. JAAD Case Rep. 2023, 39, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maione, V.; Bighetti, S.; Bettolini, L.; Zambelli, C.; Calzavara-Pinton, P. The role of line-field confocal optical coherence tomography (LC-OCT) in the diagnosis of eccrine poroma: A case report. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2023, 64, e216–e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woliner-van der Weg, W.; Peppelman, M.; Elshot, Y.S.; Visch, M.B.; Crijns, M.B.; Alkemade, H.A.C.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Adang, E.; Amir, A.; Gerritsen, M.J.P.; et al. Biopsy outperforms reflectance confocal microscopy in diagnosing and subtyping basal cell carcinoma: Results and experiences from a randomized controlled multicentre trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hieken, T.J.; Hernández-Irizarry, R.; Boll, J.M.; Jones Coleman, J.E. Accuracy of diagnostic biopsy for cutaneous melanoma: Implications for surgical oncologists. Int. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 2013, 196493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westers-Attema, A.; Joosten, V.M.; Roozeboom, M.H.; Nelemans, P.; Lohman, B.; Botterweck, A.; Steijlen, P.; Marion, A.; Kelleners-Smeets, N. Correlation between histological findings on punch biopsy specimens and subsequent excision specimens in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2015, 95, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsini, C.; Trovato, E.; Cortonesi, G.; Pedrazzani, M.; Suppa, M.; Rubegni, P.; Tognetti, L.; Cinotti, E. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography: New insights for psoriasis treatment monitoring. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Garfinkel, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; de Haan, K.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Bai, B.; Rivenson, Y.; et al. Biopsy-free in vivo virtual histology of skin using deep learning. Light. Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnes, J.; Deeks, J.J.; Saleh, D.; Chuchu, N.; Bayliss, S.E.; Patel, L.; Davenport, C.; Takwoingi, Y.; Godfrey, K.; Matin, R.N.; et al. Reflectance confocal microscopy for diagnosing cutaneous melanoma in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 12, Cd013190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzumdar, S.; Wu, R.; Rothe, M.J.; Grant-Kels, J.M. Reflectance confocal microscopy decreases the cost of skin lesion diagnosis: A single institution retrospective chart review. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellacani, G.; Witkowski, A.; Cesinaro, A.M.; Losi, A.; Colombo, G.; Campagna, A.; Longo, C.; Piana, S.; De Carvalho, N.; Giusti, F.; et al. Cost-benefit of reflectance confocal microscopy in the diagnostic performance of melanoma. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
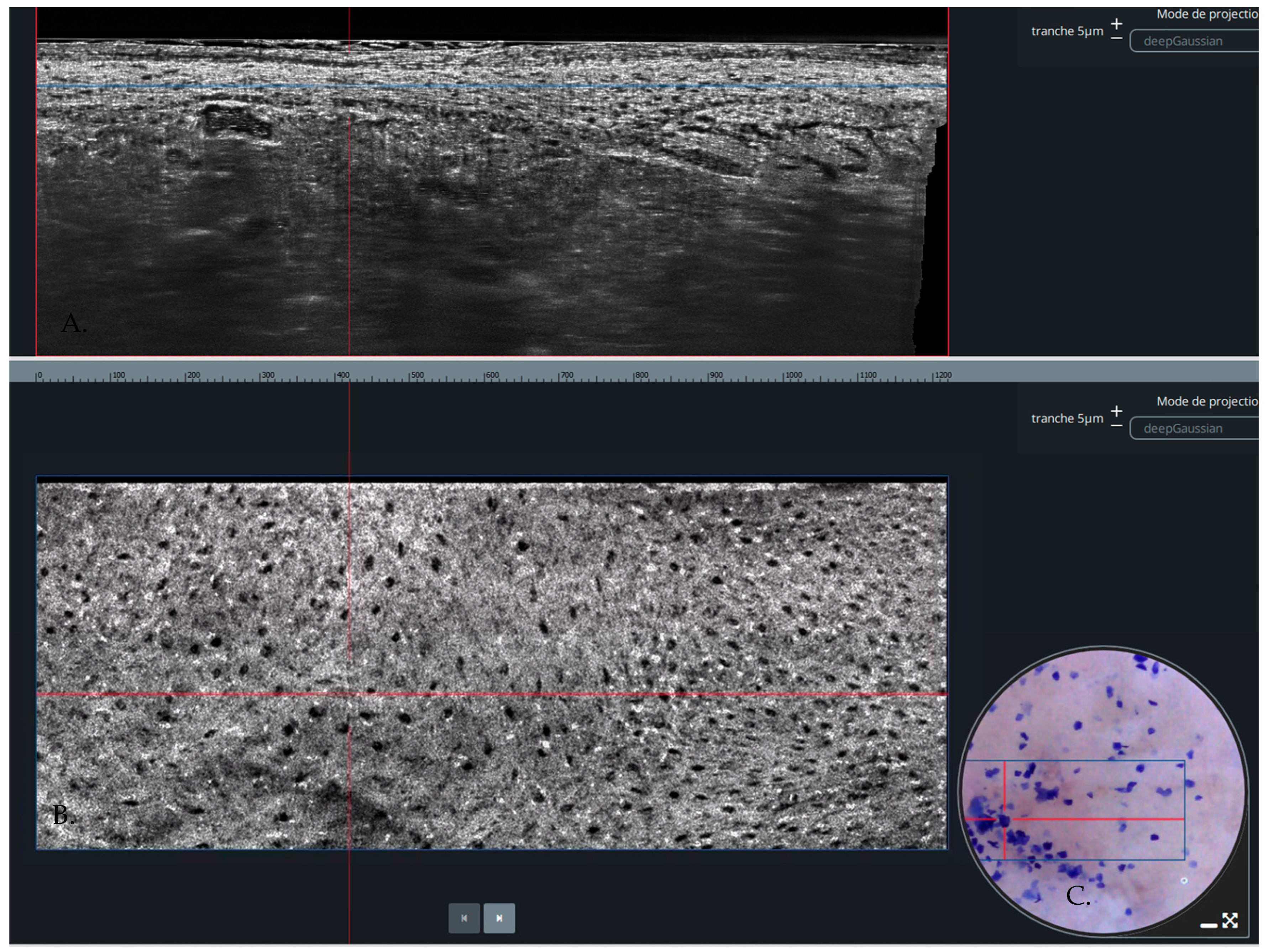
| Author | Year (Published) | Country | Centre | Type of Cancer | Patients (n) | Age (Mean or Median) | Males | Females | Lesions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cinotti et al. [12] | 2023 | Italy | One | BCC, SCC, melanomas | 196 | 64.45 | 115 | 81 | 226 |
| Donelli et al. [2] | 2023 | Italy | One | BCC, SCC, melanomas, AK | NA | NA | NA | NA | 360 |
| Gust et al. [13] | 2022 | Germany | Two | BCC, SCC, AK | 154 | 70.8 | 102 | 52 | 182 |
| Ruini et al. [14] | 2021 | Germany | One | BCC | 52 | 71 | 35 | 17 | 52 |
| Schuh et al. [15] | 2022 | Germany | Two | Melanomas | 75 | 51 | NA | NA | 84 |
| Risk of Bias | Applicability Concerns | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Year | Patient Selection | Index Test | Reference Standard | Flow and Timing | Patient Selection | Index Test | Reference Standard |
| Cinotti et al. [12] | 2023 | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Donelli et al. [2] | 2023 | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Gust et al. [13] | 2022 | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Ruini et al. [14] | 2021 | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Schuh et al. [15] | 2022 | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Razi, S.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Pathak, G.; Agarwal, P.; Horgan, A.; Parikh, P.; Deshmukh, F.; Rao, B.K. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for the Diagnosis of Skin Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141522
Razi S, Kuo Y-H, Pathak G, Agarwal P, Horgan A, Parikh P, Deshmukh F, Rao BK. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for the Diagnosis of Skin Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(14):1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141522
Chicago/Turabian StyleRazi, Shazli, Yen-Hong Kuo, Gaurav Pathak, Priya Agarwal, Arianna Horgan, Prachi Parikh, Farah Deshmukh, and Babar K. Rao. 2024. "Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for the Diagnosis of Skin Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Diagnostics 14, no. 14: 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141522
APA StyleRazi, S., Kuo, Y.-H., Pathak, G., Agarwal, P., Horgan, A., Parikh, P., Deshmukh, F., & Rao, B. K. (2024). Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for the Diagnosis of Skin Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics, 14(14), 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141522






