Polyarthritis in Sjögren’s Syndrome: Difficulties in Distinguishing Extraglandular Manifestation and Associated Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Age and Gender
3.2. Laboratory Parameters
3.3. Extraglandular Manifestations and Associated Diseases
3.4. Treatment
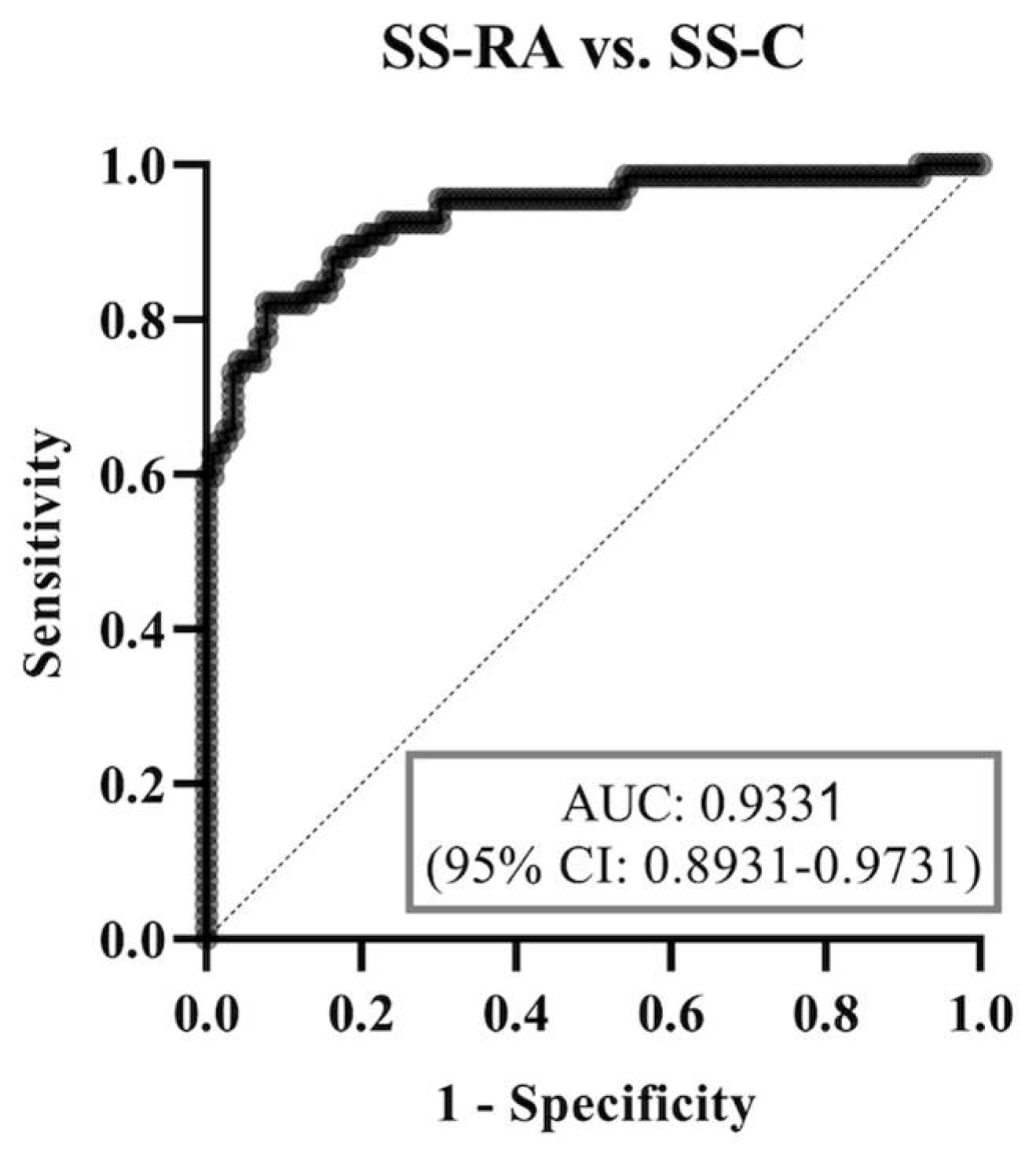
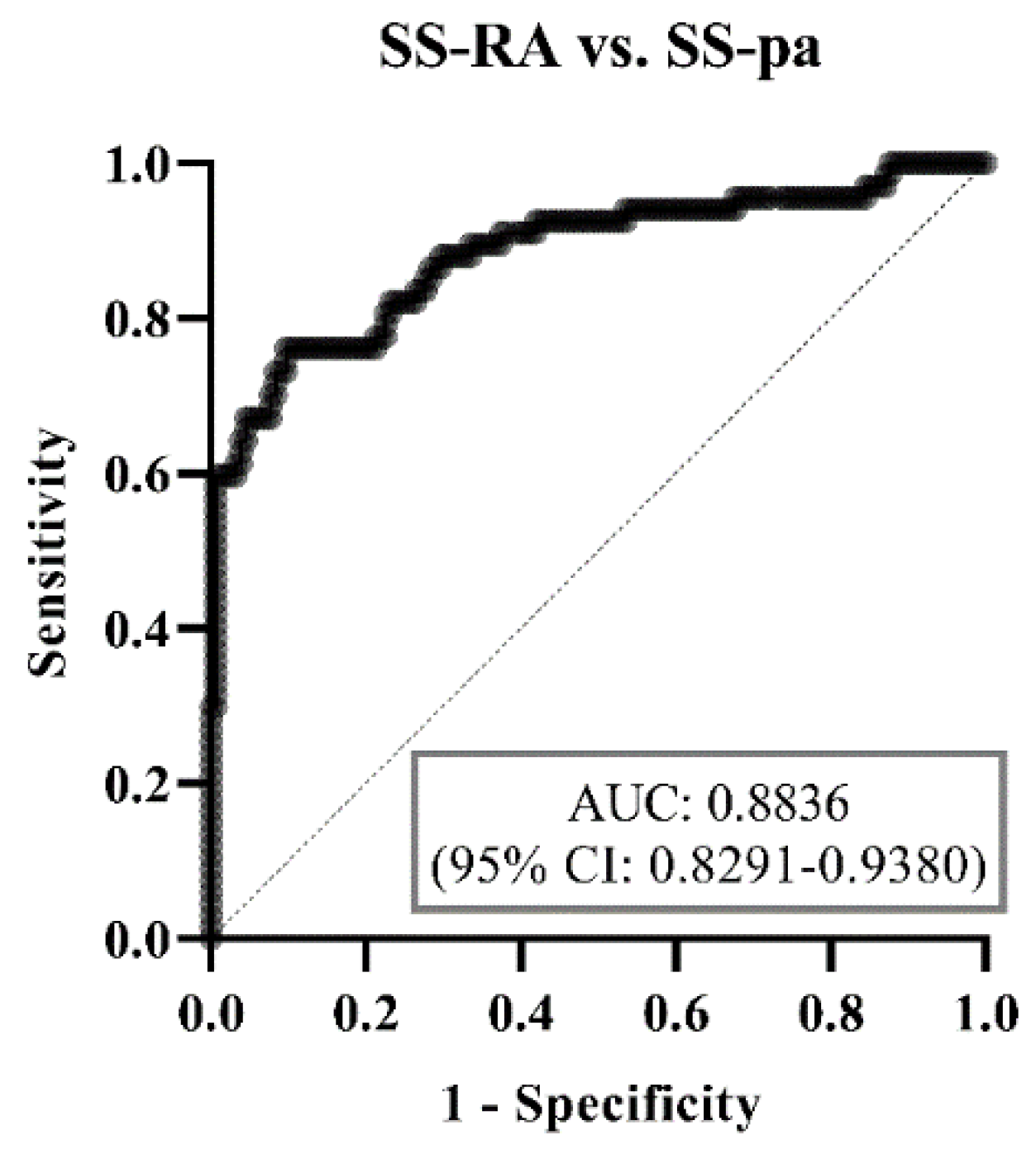
3.5. Binary Multiparametric Logistic Regression Model and ROC Curve Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tarn, J.R.; Howard-Tripp, N.; Lendrem, D.W.; Mariette, X.; Saraux, A.; Devauchelle-Pensec, V.; Seror, R.; Skelton, A.J.; James, K.; McMeekin, P.; et al. Symptom-based stratification of patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome: Multi-dimensional characterisation of international observational cohorts and reanalyses of randomised clinical trials. Lancet Rheumatol. 2019, 1, e85–e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Font, J. Primary Sjögren’s syndrome: New clinical and therapeutic concepts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocturne, G.; Mariette, X. B cells in the pathogenesis of primary Sjögren syndrome. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Yang, M.; Ma, N.; Huang, F.; Zhong, R. Epidemiology of primary Sjögren’s syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1983–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauchais, A.L.; Ouattara, B.; Gondran, G.; Lalloué, F.; Petit, D.; Ly, K.; Lambert, M.; Launay, D.; Loustaud-Ratti, V.; Bezanahari, H.; et al. Articular manifestations in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: Clinical signifcance and prognosis of 188 patients. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Pu, J.; Wu, Z.; Tang, J.; Wang, X. Osteoarthritis or arthritis? Toward understanding of primary Sjögren’s syndrome patients with arthralgia. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payet, J.; Belkhir, R.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Bergé, E.; Desmoulins, F.; Meyer, O.; Mariette, X.; Seror, R. ACPA-positive primary Sjögren’s syndrome: True primary or rheumatoid arthritis-associated Sjögren’s syndrome? RMD Open 2015, 1, e000066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Fleson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiboski, C.H.; Shiboski, S.C.; Seror, R.; Criswell, L.A.; Labetoulle, M.; Lietman, T.M.; Rasmussen, A.; Scofield, H.; Vitali, C.; Bowman, S.J.; et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Consensus and Data-driven Methodology Involving Three International Patient Cohorts. Arthritis Rheum. 2017, 69, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seror, R.; Bowman, S.; Brito-Zerón, P. EULAR Sjögren’s syndrome disease activity index (ESSDAI): A user guide. RMD Open 2015, 1, e000022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezcua-Guerra, L.; Hofmann, F.; Vargas, A.; Rodriguez-Henriquez, P.; Solano, C.; Hernández-Díaz, C.; Castillo-Martinez, D.; Ventura Ríos, L.; Gutiérrez, M.; Pineda, C. Joint Involvement in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: An Ultrasound “Target Area Approach to Arthritis”. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 640265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsampoulas, C.G.; Skopouli, F.N.; Sartoris, D.J. Hand radiographic changes in patients with primary and secondary Sjögren’s syndrome. Scan. J. Rheumatol. 1986, 15, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Poltronieri, A.; Alarcon-Segovia, D. Articular manifestatins of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Rheumatol. 1983, 10, 485–488. [Google Scholar]
- Barcelos, F.; Abreu, I.; Patto, J.V.; Trindade, H.; Teixeira, A. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid factor in Sjögren’s syndrome. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2009, 34, 608–612. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, Y.S.; Park, S.H.; Lee, J.; Kwok, S.K.; Ju, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Jeon, C.H. Follow-up of primary Sjogren’s syndrome patients presenting positive anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides antibody. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 1443–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassold, N.; Seror, R.; Mariette, X.; Nocturne, G. Characteristics of Sjögren’s syndrome associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Letter. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Ding, Y.; Feng, M.; Guo, J.; Sun, X.; Zhao, J.; Yu, D.; Li, Z. Characteristics of Sjögren’s syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszarny, A.; Majdan, M.; Dryglewska, M.; Tabarkiewicz, J. Prevalence of selected organ-specific autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis and primary Sjögren’s syndrome patients. Reumatologia 2015, 53, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biro, E.; Szekanecz, Z.; Czirják, L.; Dankó, K.; Kiss, E.; Szabó, N.A.; Szűcs, G.; Zeher, M.; Bodolay, E.; Szegedi, G.; et al. Association of systemic and thyroid autoimmune diseases. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 25, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, H.; Mariette, X. Renal involvement in primary Sjögren syndrome. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronbichler, A.; Mayer, G. Renal involvement in autoimmune connective tissue diseases. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, T.; Bathon, J. Renal Manifestations of Rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 44, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soy, M.; Piskin, S. Cutaneous findings in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 26, 1350–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Brito-Zerón, P.; Bombardieri, S.; Bootsma, H.; De Vita, S.; Dörner, T.; Fisher, B.A.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Hernandez-Molina, G.; Kocher, A.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of Sjögren’s syndrome with topical and systemic therapies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Bian, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, F. Clinical characteristics and risk factors for overlapping rheumatoid arthritis and Sjögren’s syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Cho, S.K.; Kim, H.W.; Han, J.; Kim, Y.; Hwang, K.G.; Sung, Y.K. The Prevalence of Sjögren’s Syndrome in Rheumatoid Artritis Patients and Their Clinical Features. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conforti, A.; Di Cola, I.; Pavlych, V.; Ruscitti, P.; Berardicurti, O.; Ursini, F.; Giacomelli, R.; Cipriani, P. Beyond the joints, the extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroche, M.; Degboe, Y.; Constantin, A. Sjögren’s syndrome associated with erosive rheumatoid arthritis alters its prognosis and long-term therapeutic response: A case-control study. Rheumatol. Int. 2023, 43, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.E.; Frits, M.L.; Iannaccone, C.K.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Shadick, N.A.; Liao, K.P. Clinical characteristics of RA patients with secondary SS and association with joint damage. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollert, F.; Fisher, B.A. Equal rights in autoimmunity: Is Sjögren’s syndrome ever “secondary”? Rheumatology 2020, 59, 121825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.C. Update on the diagnosis and management of early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Med. 2020, 20, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameter | SS-C n = 129 | SS-pa n = 159 | SS-RA n = 68 | SS-pa vs. SS-C | SS-RA vs. SS-C | SS-RA vs. SS-pa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male gender | 13 (10.2%) | 8 (5%) | 3 (4.4%) | 0.1133 | 0.2719 | 1.0000 |
| Age (median year) | 68.0 | 63.0 | 65.5 | 0.0140 | 1.0000 | 0.2273 |
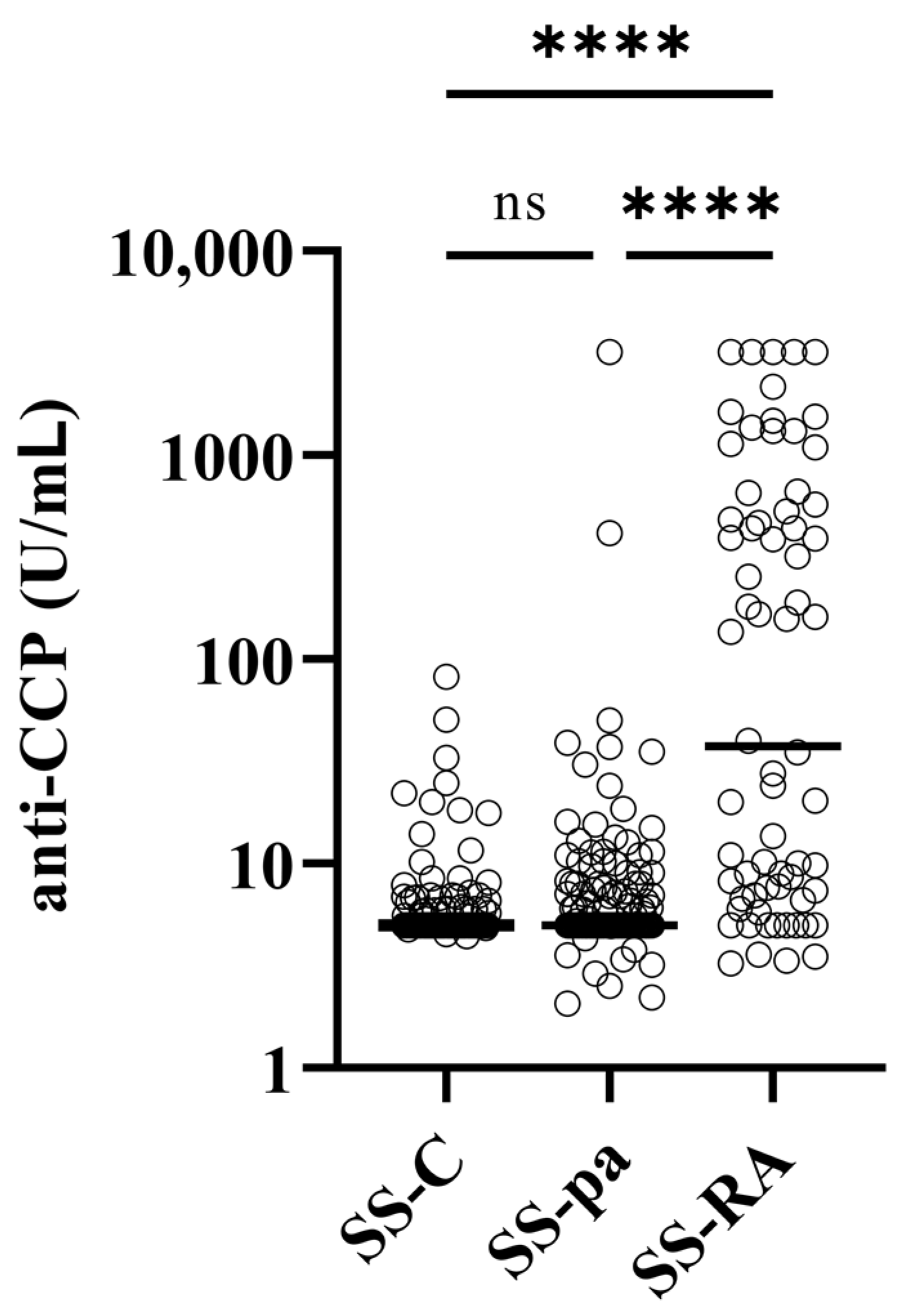
| Anti-CCP (U/mL) | 5 | 5 | 37.5 | 1.0000 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Anti-CCP positivity | 3 (2.3%) | 7 (4.4%) | 36 (52.9%) | 0.5223 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| RF (IU/mL) | 10 | 10 | 30.5 | 1.0000 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| RF positivity | 45 (35.4%) | 54 (34.2%) | 48 (70.6%) | 0.8248 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| ANA positivity | 70 (54.7%) | 94 (59.1%) | 40 (58.8%) | 0.4507 | 0.5786 | 0.9669 |
| Anti-Ro/SS-A (U/mL) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| Anti-Ro/SS-A positivity | 49 (38.3%) | 65 (40.9%) | 26 (38.2%) | 0.6546 | 0.9950 | 0.7095 |
| Anti-La/SS-B (U/mL) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 1.0000 | 0.3889 | 0.4855 |
| Anti-La/SS-B positivity | 34 (26.6%) | 44 (27.7%) | 12 (17.6%) | 0.8335 | 0.1610 | 0.1085 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 2.6 | 2.2 | 2.6 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| CRP positivity | 30 (23.4%) | 43 (27%) | 23 (33.8%) | 0.4990 | 0.1308 | 0.3395 |
| ESR (mm/h) | 20 | 18 | 22 | 1.0000 | 0.8268 | 0.3462 |
| ESR positivity | 70 (54.7%) | 79 (49.7%) | 41 (60.3%) | 0.4083 | 0.5450 | 0.1499 |
| WBC (G/L) | 6.15 | 6.25 | 6.15 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| WBC abnormal% | 25 (19.5%) | 34 (21.4%) | 16 (23.5%) | 0.6656 | 0.5677 | 0.9297 |
| IgG (g/L) | 10.7 | 10.7 | 10.3 | 1.0000 | 0.2748 | 0.7956 |
| IgG abnormal% | 32 (25%) | 31 (19.5%) | 12 (17.6%) | 0.4397 | 0.1305 | 0.3840 |
| Raynaud’s phenomenon | 27 (21.1%) | 52 (33.3%) | 19 (27.9%) | 0.0245 | 0.2929 | 0.4417 |
| Lung involvement | 10 (7.8%) | 25 (16.4%) | 15 (22.1%) | 0.0323 | 0.0065 | 0.3473 |
| Hashimoto’s thyroiditis | 28 (21.9%) | 22 (13.8%) | 11 (16.2%) | 0.0857 | 0.4524 | 0.6828 |
| Kidney involvement | 7 (5.5%) | 16 (10.1%) | 10 (14.9%) | 0.1914 | 0.0335 | 0.3611 |
| Lymphadenopathy | 4 (3.1%) | 9 (5.7%) | 4 (5.9%) | 0.3978 | 0.4531 | 1.0000 |
| Skin involvement | 33 (25.8%) | 52 (32.7%) | 25 (36.8%) | 0.2419 | 0.1388 | 0.6464 |
| Associated autoimmune diseases | 39 (30.5%) | 52 (33.3%) | 19 (27.9%) | 0.6137 | 0.7451 | 0.4417 |
| Associated non-autoimmune disease | 45 (35.2%) | 60 (38.4%) | 21 (30.9%) | 0.6233 | 0.6344 | 0.2959 |
| Parameter | SS-C n = 129 | SS-pa n = 159 | SS-RA n = 68 | SS-pa vs. SS-C | SS-RA vs. SS-C | SS-RA vs. SS-pa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucocorticoid | 35 (27.3%) | 51 (32.1%) | 50 (73.5%) | 0.4373 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Methotrexate | 4 (3.1%) | 20 (12.6%) | 25 (36.8%) | 0.0045 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Leflunomid | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 25 (36.8%) | - | - | - |
| Sulfasalazine | 3 (2.3%) | 14 (8.8%) | 3 (4.4%) | 0.0236 | 0.4198 | 0.4085 |
| Azathioprine | 8 (6.3%) | 17 (10.7%) | 2 (2.9%) | 0.2113 | 0.4986 | 0.0666 |
| Antimalarials | 24 (18.8%) | 49 (30.8%) | 17 (25%) | 0.0209 | 0.3571 | 0.4272 |
| SS-pa vs. SS-C | SS-RA vs. SS-C | SS-RA vs. SS-pa | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Odds Ratio | p Value | Odds Ratio | p Value | Odds Ratio | p Value |
| Age | 1 (0.99–1.01) | 0.5414 | 0.96 (0.94–0.98) | <0.0001 | 0.97 (0.95–0.98) | <0.0001 |
| Anti-CCP low positive | 2.04 (0.36–15.93) | 0.4387 | 9.49 (0.64–245.1) | 0.115 | 4.49 (0.63–30.02) | 0.1181 |
| Anti-CCP high positive | 1.73 (0.11–48.51) | 0.7043 | 419.3 (42.67–14,068) | <0.0001 | 164.6 (31.68–1461) | <0.0001 |
| RF low positive | 0.93 (0.43–2.03) | 0.8525 | 2.49 (0.59–10.69) | 0.211 | 2.06 (0.65–6.25) | 0.2057 |
| RF high positive | 1.27 (0.48–3.39) | 0.6283 | 18.73 (3.91–111.5) | 0.0005 | 13.5 (3.87–51.97) | <0.0001 |
| Anti-SS-A/Ro60 positive | 1.74 (0.73–4.3) | 0.2176 | 5.92 (1.27–30.72) | 0.0267 | 6.04 (1.74–22.73) | 0.0057 |
| Anti-SS-B/La positive | 0.73 (0.28–1.87) | 0.509 | 0.06 (0.01–0.36) | 0.0035 | 0.05 (0.01–0.2) | <0.0001 |
| Raynaud’s syndrome | 2.01 (1.12–3.68) | 0.0206 | 3.42 (1.13–11.06) | 0.0328 | 1.63 (0.65–4.19) | 0.2997 |
| Lung involvement | 3.02 (1.2–8.44) | 0.0246 | 11.55 (2.14–71.76) | 0.0057 | 1.36 (0.4–4.34) | 0.611 |
| Hashimoto’s thyreoditis | 0.61 (0.3–1.21) | 0.1574 | 0.77 (0.2–2.68) | 0.686 | 1.9 (0.59–5.75) | 0.2644 |
| Kidney involvement | 1.65 (0.59–4.93) | 0.3477 | 3.42 (0.63–18.89) | 0.1491 | 4.67 (1.07–20.06) | 0.037 |
| Lymphadenopathy | 1.86 (0.43–9.95) | 0.4251 | 0.18 (0–14.55) | 0.4396 | 0.14 (0.01–1.06) | 0.0697 |
| Skin involvement | 1.28 (0.7–2.35) | 0.4291 | 1.46 (0.44–4.59) | 0.5198 | 0.72 (0.28–1.76) | 0.4753 |
| Associated immune diseases | 1.05 (0.58–1.9) | 0.8693 | 0.73 (0.19–2.63) | 0.6361 | 0.68 (0.25–1.78) | 0.4446 |
| Associated non-immune diseases | 1.03 (0.59–1.82) | 0.9096 | 1.56 (0.47–5.23) | 0.4647 | 1.14 (0.45–2.86) | 0.7746 |
| Male gender | 0.53 (0.18–1.49) | 0.2351 | 0.07 (0–1.01) | 0.1148 | 0.28 (0.02–2.33) | 0.2953 |
| CRP positive | 0.84 (0.43–1.65) | 0.6141 | 1.03 (0.31–3.32) | 0.9647 | 1.12 (0.4–3.05) | 0.8207 |
| ESR positive | 0.79 (0.43–1.45) | 0.4556 | 1.21 (0.31–4.86) | 0.7792 | 1.03 (0.4–2.62) | 0.9594 |
| WBC low | 0.79 (0.36–1.72) | 0.5451 | 0.3 (0.05–1.34) | 0.1355 | 1.17 (0.32–4.07) | 0.8108 |
| WBC high | 2.41 (0.68–10.07) | 0.1903 | 1.21 (0.03–20.06) | 0.9015 | 0.31 (0.02–2.78) | 0.3548 |
| IgG low | 0.42 (0.16–1.08) | 0.0734 | 0.67 (0.08–4.09) | 0.6825 | 0.43 (0.06–2.23) | 0.3391 |
| IgG high | 0.83 (0.3–2.26) | 0.7093 | 0.03 (0–0.25) | 0.0028 | 0.23 (0.03–1.27) | 0.1091 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aradi, Z.; Nagy, G.; Horváth, I.F.; Antal-Szalmás, P.; Szántó, A. Polyarthritis in Sjögren’s Syndrome: Difficulties in Distinguishing Extraglandular Manifestation and Associated Rheumatoid Arthritis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141494
Aradi Z, Nagy G, Horváth IF, Antal-Szalmás P, Szántó A. Polyarthritis in Sjögren’s Syndrome: Difficulties in Distinguishing Extraglandular Manifestation and Associated Rheumatoid Arthritis. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(14):1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141494
Chicago/Turabian StyleAradi, Zsófia, Gábor Nagy, Ildikó Fanny Horváth, Péter Antal-Szalmás, and Antónia Szántó. 2024. "Polyarthritis in Sjögren’s Syndrome: Difficulties in Distinguishing Extraglandular Manifestation and Associated Rheumatoid Arthritis" Diagnostics 14, no. 14: 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141494
APA StyleAradi, Z., Nagy, G., Horváth, I. F., Antal-Szalmás, P., & Szántó, A. (2024). Polyarthritis in Sjögren’s Syndrome: Difficulties in Distinguishing Extraglandular Manifestation and Associated Rheumatoid Arthritis. Diagnostics, 14(14), 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141494






