Advanced MRI Techniques: Diagnosis and Follow-Up of Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
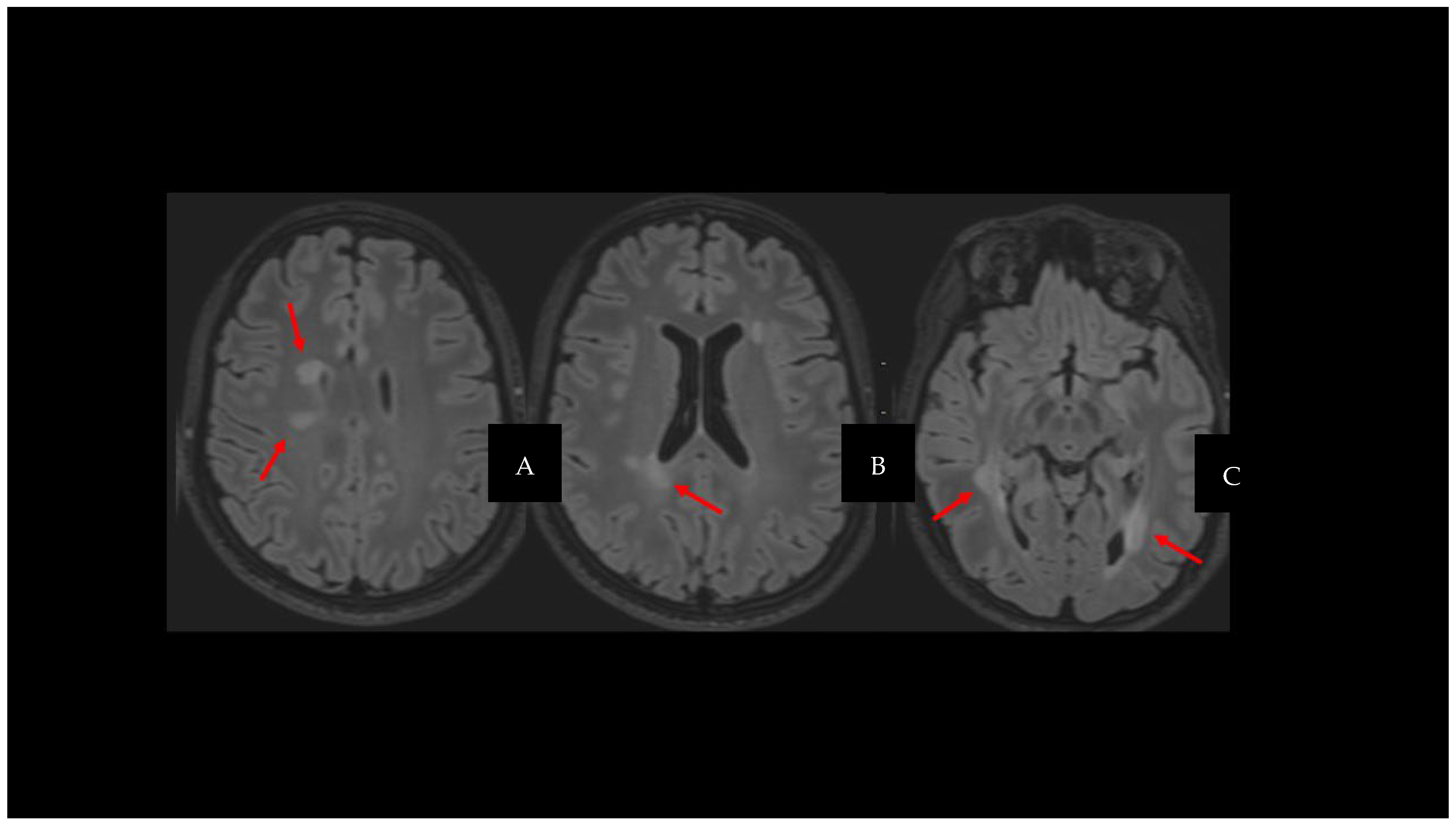
2. Cortical Lesions
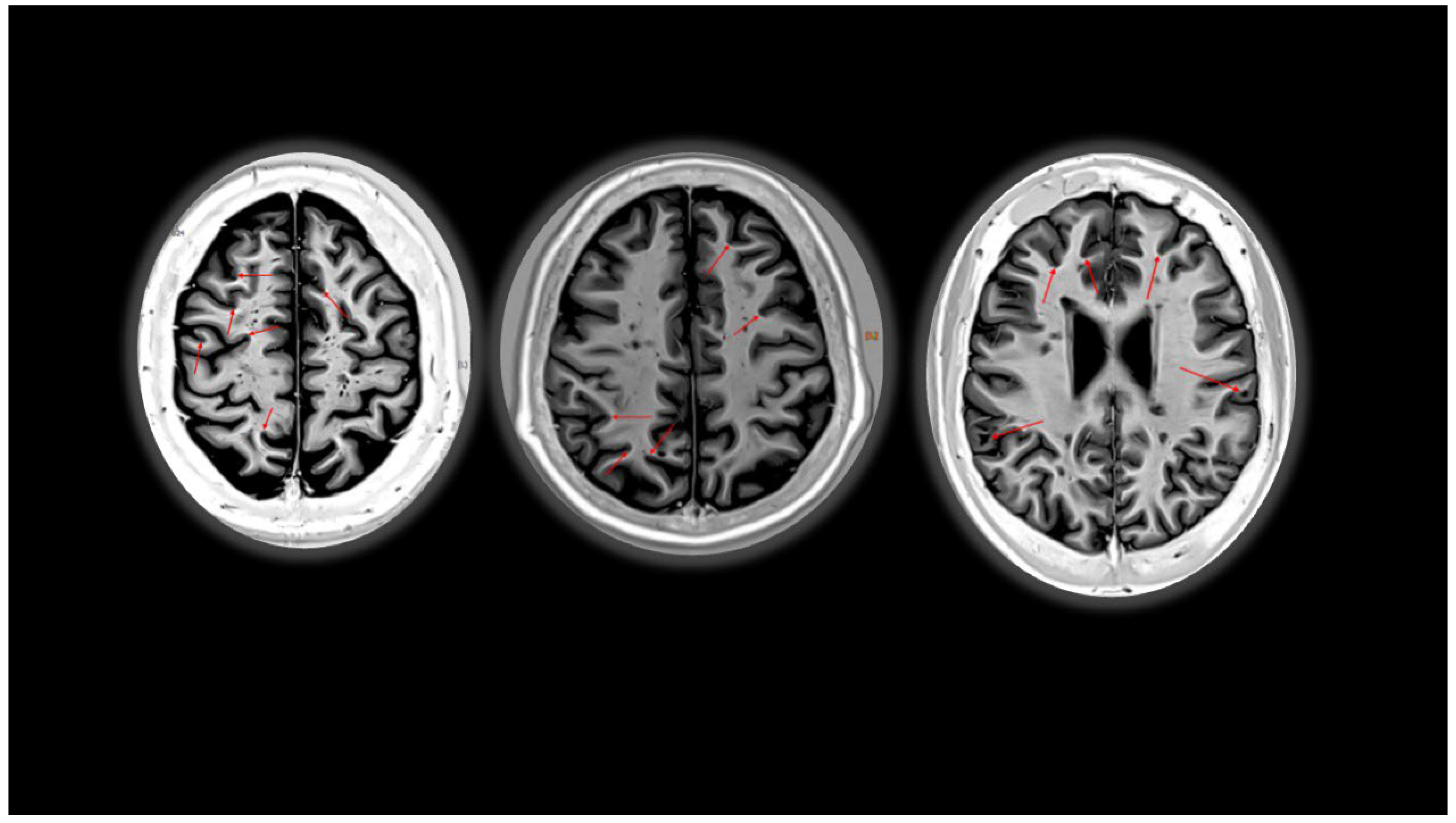
3. Iron-Derived Imaging and Chronic Inflammation
3.1. Central Vein Sign
3.2. Paramagnetic Rim Lesions
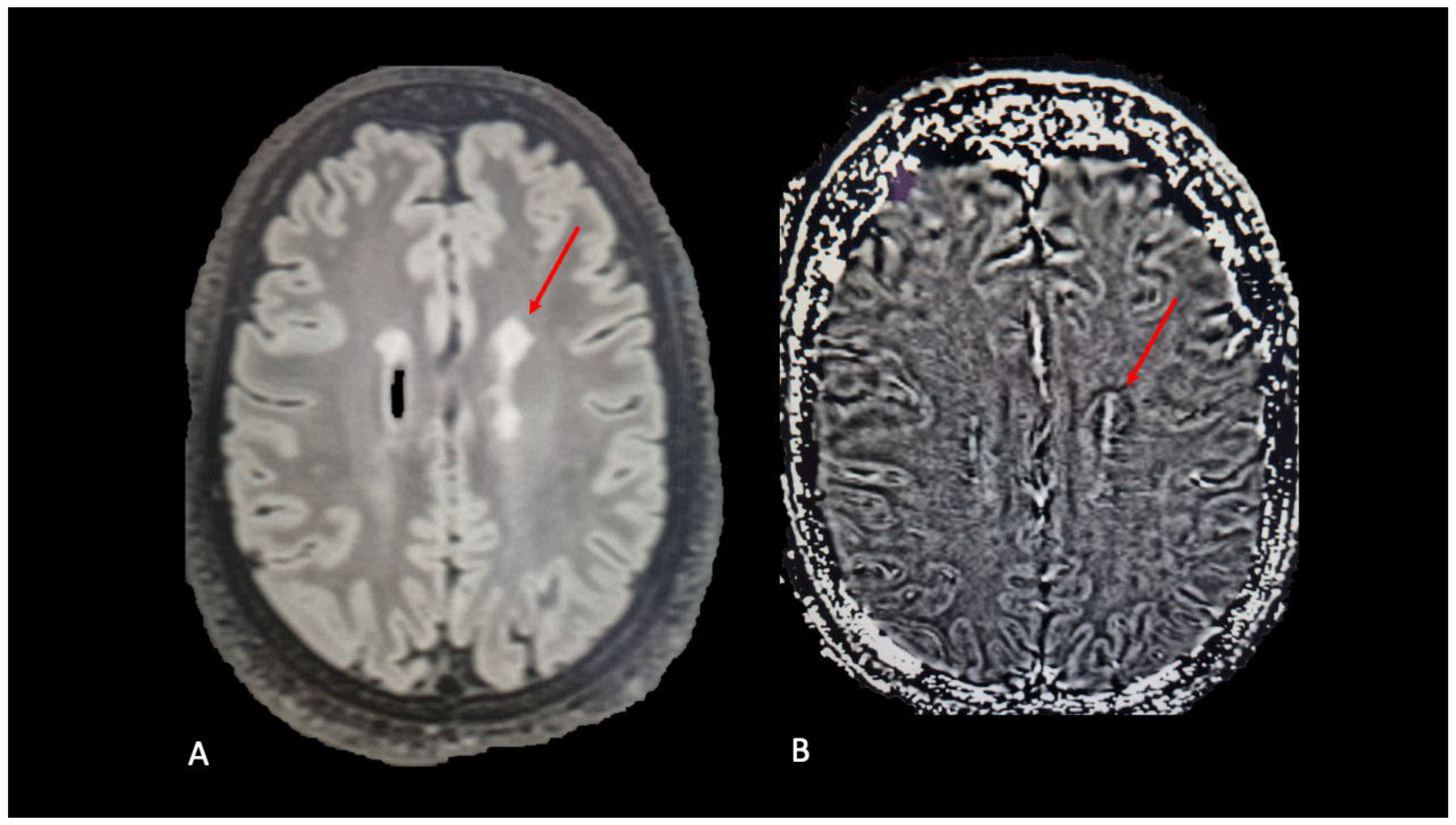
4. Slowly Expanding Lesions
5. Leptomeningeal Enhancement
6. Brain Atrophy
7. Choroid Plexus Enlargement
8. Diffusion Tensor Imaging
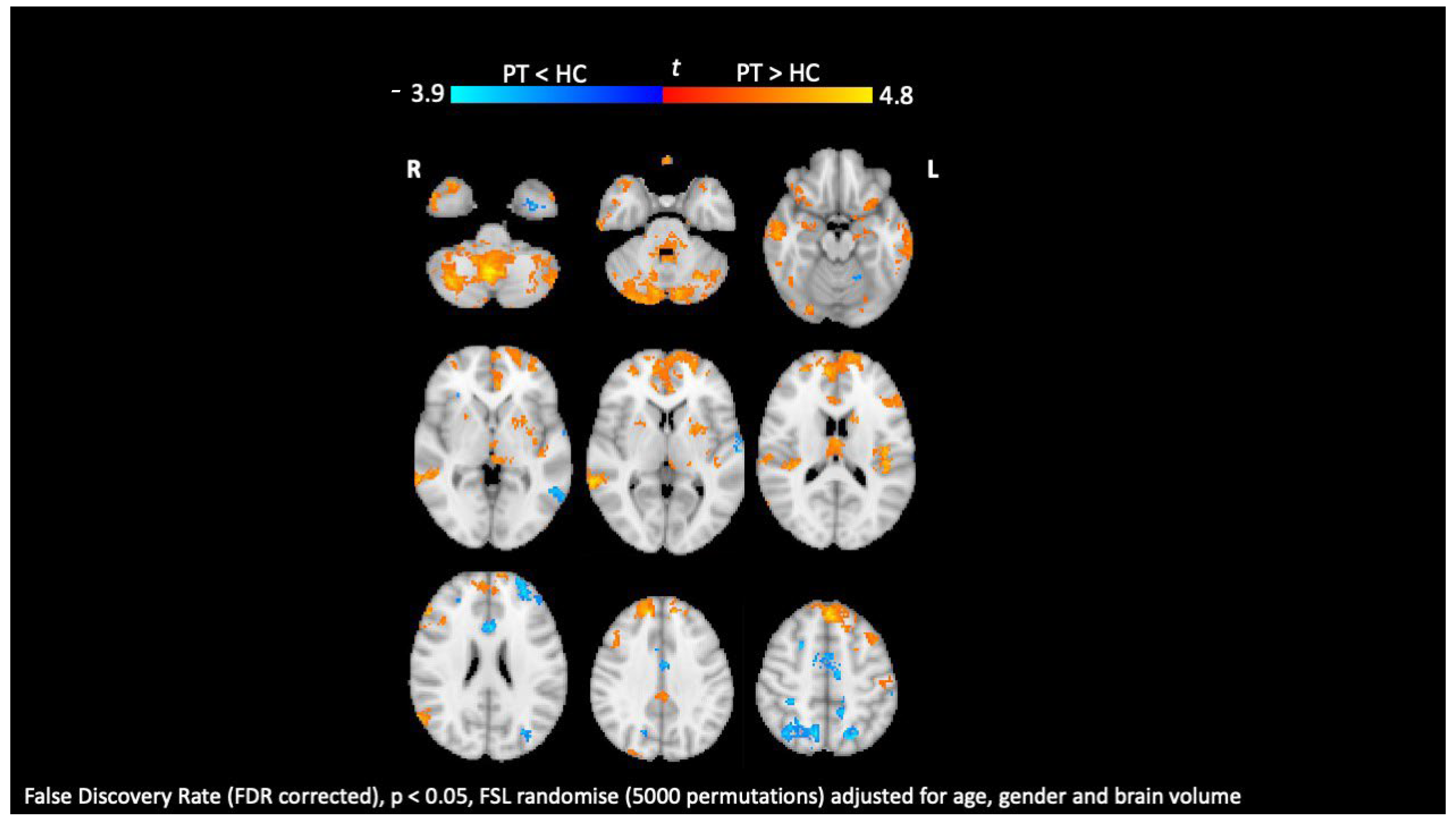
9. Functional MRI
10. Magnetization Transfer Imaging
11. Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
12. Positron Emission Tomography
13. Spinal Cord
14. Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting
15. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hernandez, A.L.; O’Connor, K.C.; Hafler, D.A. Multiple Sclerosis. In The Autoimmune Diseases: Fifth Edition; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 735–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, D.S.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Calabresi, P.A. Multiple Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, N.; Virgilio, E.; Covelli, A.; Giovannini, B.; Foschi, M.; Montini, F.; Nasello, M.; Nilo, A.; Prestipino, E.; Schirò, G.; et al. Aging in multiple sclerosis: From childhood to old age, etiopathogenesis, and unmet needs: A narrative review. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1207617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahn, K.; Slusher, B.; Kaplin, A. Cognitive Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis: A Forgotten Disability Remembered. Available online: http://www.dana.org/news/cerebrum/detail.aspx?id=39986 (accessed on 30 November 2012).
- Ghasemi, N.; Razavi, S.; Nikzad, E. Multiple Sclerosis: Pathogenesis, Symptoms, Diagnoses and Cell-Based Therapy. Cell J. Yakhteh 2017, 19, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Confavreux, C.; Compston, A. Section Two the Cause and Course of Multiple Sclerosis The Natural History of Multiple Sclerosis. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7173457/ (accessed on 30 November 2012).
- Wildner, P.; Stasiołek, M.; Matysiak, M. Differential diagnosis of multiple sclerosis and other inflammatory CNS diseases. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 37, 101452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.J.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Carroll, W.M.; Coetzee, T.; Comi, G.; Correale, J.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Freedman, M.S.; et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, M.; Rocca, M.A.; Ciccarelli, O.; De Stefano, N.; Evangelou, N.; Kappos, L.; Rovira, A.; Sastre-Garriga, J.; Tintorè, M.; Frederiksen, J.L.; et al. MRI criteria for the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: MAGNIMS consensus guidelines. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klineova, S.; Lublin, F.D. Clinical course of multiple sclerosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a028928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato-Abad, V.; Labiano-Fontcuberta, A.; Rodríguez-Yáñez, S.; García-Vázquez, R.; Munteanu, C.R.; Andrade-Garda, J.; Domingo-Santos, A.; Sánchez-Seco, V.G.; Aladro, Y.; Martínez-Ginés, M.L.; et al. Classification of radiologically isolated syndrome and clinically isolated syndrome with machine-learning techniques. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klawiter, E.C. Current and New Directions in MRI in Multiple Sclerosis. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2013, 19, 1058–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassini, V.; Sinclair, A.; Sawlani, V.; Overell, J.; Pearson, O.R.; Hall, J.; Guadagno, J. Diagnosis and management of multiple sclerosis: MRI in clinical practice. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 2917–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, G.; Jones, D.E. The sequence of disease-modifying therapies in relapsing multiple sclerosis: Safety and immunologic considerations. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 2351–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chylińska, M.; Komendziński, J.; Wyszomirski, A.; Karaszewski, B. Brain Atrophy as an Outcome of Disease-Modifying Therapy for Remitting-Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Int. 2023, 2023, 4130557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierhansl, L.; Hartung, H.-P.; Aktas, O.; Ruck, T.; Roden, M.; Meuth, S.G. Thinking outside the box: Non-canonical targets in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 578–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, L. No evidence of disease activity (NEDA) in multiple sclerosis—Shifting the goal posts. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2019, 22, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.; Hersh, C.M. Updates and advances in multiple sclerosis neurotherapeutics. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2023, 13, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocsis, K.; Szabó, N.; Tóth, E.; Király, A.; Faragó, P.; Kincses, B.; Veréb, D.; Bozsik, B.; Boross, K.; Katona, M.; et al. Two Classes of T1 Hypointense Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis with Different Clinical Relevance. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 619135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvi, A.; Tur, C.; Chard, D.; Stutters, J.; Ciccarelli, O.; Cortese, R.; Battaglini, M.; Pietroboni, A.; De Riz, M.; Galimberti, D.; et al. Slowly expanding lesions relate to persisting black-holes and clinical outcomes in relapse-onset multiple sclerosis. Neuroimage Clin. 2022, 35, 103048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, K.R.; Ontaneda, D. The Role of Advanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techniques in Multiple Sclerosis Clinical Trials. Neurotherapeutics 2017, 14, 905–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collorone, S.; Prados, F.; Kanber, B.; Cawley, N.M.; Tur, C.; Grussu, F.; Solanky, B.S.; Yiannakas, M.; Davagnanam, I.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.M.G.; et al. Brain microstructural and metabolic alterations detected in vivo at onset of the first demyelinating event. Brain 2021, 144, 1409–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, R.; Collorone, S.; Ciccarelli, O.; Toosy, A.T. Advances in brain imaging in multiple sclerosis. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2019, 12, 1756286419859722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, F.; Abdulkadir, A.; Fartaria, M.J.; Rahmanzadeh, R.; Lu, P.-J.; Galbusera, R.; Barakovic, M.; Thiran, J.-P.; Granziera, C.; Cuadra, M.B. Multiple sclerosis cortical and WM lesion segmentation at 3T MRI: A deep learning method based on FLAIR and MP2RAGE. Neuroimage Clin. 2020, 27, 102335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compston, A.; Coles, A. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet 2008, 372, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rosa, F.; Wynen, M.; Al-Louzi, O.; Beck, E.S.; Huelnhagen, T.; Maggi, P.; Thiran, J.-P.; Kober, T.; Shinohara, R.T.; Sati, P.; et al. Cortical lesions, central vein sign, and paramagnetic rim lesions in multiple sclerosis: Emerging machine learning techniques and future avenues. Neuroimage Clin. 2022, 36, 103205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, M.; Filippi, M.; Gallo, P. Cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, D.M.; Roy, S.; Oh, J.; Izbudak, I.; Pham, D.; Courtney, S.; Caffo, B.; Jones, C.K.; van Zijl, P.; Calabresi, P.A. Association of cortical lesion burden on 7-T magnetic resonance imaging with cognition and disability in multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maranzano, J.; Dadar, M.; Rudko, D.; De Nigris, D.; Elliott, C.; Gati, J.; Morrow, S.; Menon, R.; Collins, D.; Arnold, D.; et al. Comparison of multiple sclerosis cortical lesion types detected by multicontrast 3T and 7T MRI. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedaghat, S.; Jang, H.; Ma, Y.; Afsahi, A.M.; Reichardt, B.; Corey-Bloom, J.; Du, J. Clinical evaluation of white matter lesions on 3D inversion recovery ultrashort echo time MRI in multiple sclerosis. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 13, 4171–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, E.S.; Sati, P.; Sethi, V.; Kober, T.; Dewey, B.; Bhargava, P.; Nair, G.; Cortese, I.C.; Reich, D.S. Improved visualization of cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis using 7T MP2RAGE. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fartaria, M.J.; Sati, P.; Todea, A.; Radue, E.-W.; Rahmanzadeh, R.; O’Brien, K.; Reich, D.S.; Cuadra, M.B.; Kober, T.; Granziera, C. Automated Detection and Segmentation of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Using Ultra-High-Field MP2RAGE. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seewann, A.; Kooi, E.-J.; Roosendaal, S.; Pouwels, P.; Wattjes, M.; van der Valk, P.; Barkhof, F.; Polman, C.; Geurts, J. Postmortem Verification of MS Cortical Lesion Detection with 3D DIR. Neurology 2012, 78, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolber, P.; Montag, S.; Fleischer, V.; Luessi, F.; Wilting, J.; Gawehn, J.; Gröger, A.; Zipp, F. Identification of cortical lesions using DIR and FLAIR in early stages of multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, M.; Preziosa, P.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Ciccarelli, O.; De Stefano, N.; Geurts, J.J.G.; Paul, F.; Reich, D.S.; Toosy, A.T.; et al. Assessment of lesions on magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis: Practical guidelines. Brain 2019, 142, 1858–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ontaneda, D.; Chitnis, T.; Rammohan, K.; Obeidat, A.Z. Identification and management of subclinical disease activity in early multiple sclerosis: A review. J. Neurol. 2023, 271, 1497–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, L.; Prados, F.; Chung, K.; Goodkin, O.; Kanber, B.; Sudre, C.; Yiannakas, M.; Samson, R.S.; Mangesius, S.; Thompson, A.J.; et al. Cortical involvement determines impairment 30 years after a clinically isolated syndrome. Brain 2021, 144, 1384–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouman, P.M.; Noteboom, S.; Santos, F.A.N.; Beck, E.S.; Bliault, G.; Castellaro, M.; Calabrese, M.; Chard, D.T.; Eichinger, P.; Filippi, M.; et al. Multicenter Evaluation of AI-generated DIR and PSIR for Cortical and Juxtacortical Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Detection. Radiology 2023, 307, e221425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, E.S.; Maranzano, J.; Luciano, N.J.; Parvathaneni, P.; Filippini, S.; Morrison, M.; Suto, D.J.; Wu, T.; van Gelderen, P.; A de Zwart, J.; et al. Cortical lesion hotspots and association of subpial lesions with disability in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2022, 28, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, M.; Poretto, V.; Favaretto, A.; Alessio, S.; Bernardi, V.; Romualdi, C.; Rinaldi, F.; Perini, P.; Gallo, P. Cortical lesion load associates with progression of disability in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2012, 135, 2952–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stüber, C.; Pitt, D.; Wang, Y. Iron in multiple sclerosis and its noninvasive imaging with quantitative susceptibility mapping. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hametner, S.; Dal Bianco, A.; Trattnig, S.; Lassmann, H. Iron related changes in MS lesions and their validity to characterize MS lesion types and dynamics with Ultra-high field magnetic resonance imaging. Brain Pathol. 2018, 28, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hametner, S.; Wimmer, I.; Haider, L.; Pfeifenbring, S.; Brück, W.; Lassmann, H. Iron and neurodegeneration in the multiple sclerosis brain. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 74, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassmann, H.; van Horssen, J. Oxidative stress and its impact on neurons and glia in multiple sclerosis lesions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2016, 1862, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvi, A.; Haider, L.; Prados, F.; Tur, C.; Chard, D.; Barkhof, F. In vivo imaging of chronic active lesions in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2022, 28, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, T.; Ludwin, S.; Prat, A.; Antel, J.; Brück, W.; Lassmann, H. An updated histological classification system for multiple sclerosis lesions. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Absinta, M.; Lassmann, H.; Trapp, B.D. Mechanisms underlying progression in multiple sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2020, 33, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patani, R.; Balaratnam, M.; Vora, A.; Reynolds, R. Remyelination can be extensive in multiple sclerosis despite a long disease course. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2007, 33, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrikios, P.; Stadelmann, C.; Kutzelnigg, A.; Rauschka, H.; Schmidbauer, M.; Laursen, H.; Sorensen, P.S.; Brück, W.; Lucchinetti, C.; Lassmann, H. Remyelination is extensive in a subset of multiple sclerosis patients. Brain 2006, 129, 3165–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Loughlin, E.; Madore, C.; Lassmann, H.; Butovsky, O. Microglial phenotypes and functions in multiple sclerosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a028993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassmann, H. Multiple sclerosis pathology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a028936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Absinta, M.; Sati, P.; Masuzzo, F.; Nair, G.; Sethi, V.; Kolb, H.; Ohayon, J.; Wu, T.; Cortese, I.C.M.; Reich, D.S. Association of Chronic Active Multiple Sclerosis Lesions with Disability in Vivo. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruetten, P.P.R.; Gillard, J.H.; Graves, M.J. Introduction to Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping and Susceptibility Weighted Imaging. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20181016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.; Kister, I.; Sinnecker, T.; Wuerfel, J.; Brisset, J.-C.; Paul, F.; Ge, Y. Longitudinal study of multiple sclerosis lesions using ultra-high field (7T) multiparametric MR imaging. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, W.; Tong, K.A.; Yeom, K.W.; Kuzminski, S. Susceptibility-weighted imaging and quantitative susceptibility mapping in the brain. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 42, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnato, F.; Sati, P.; Hemond, C.C.; Elliott, C.; Gauthier, S.A.; Harrison, D.M.; Mainero, C.; Oh, J.; Pitt, D.; Shinohara, R.T.; et al. Imaging chronic active lesions in multiple sclerosis: A 2 consensus statement 3 behalf of the NAIMS Cooperative. Brain 2024, 27, awae013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beynon, V.; George, I.C.; Elliott, C.; Arnold, D.L.; Ke, J.; Chen, H.; Zhu, L.; Ke, C.; Giovannoni, G.; Scaramozza, M.; et al. Chronic lesion activity and disability progression in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. BMJ Neurol. Open 2022, 4, e000240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, K.C.N.K.; Mollison, D.; Meijboom, R.; York, E.N.; Kampaite, A.; Thrippleton, M.J.; Chandran, S.; Waldman, A.D. The prevalence of paramagnetic rim lesions in multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, H.; McNeil, C.J.; Waiter, G.D. The impact of brain iron accumulation on cognition: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landes-Chateau, C.; Levraut, M.; Okuda, D.T.; Themelin, A.; Cohen, M.; Kantarci, O.H.; Siva, A.; Pelletier, D.; Mondot, L.; Lebrun-Frenay, C.; et al. The diagnostic value of the central vein sign in radiologically isolated syndrome. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2024, 11, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapucci, C.; Tazza, F.; Rebella, S.; Boffa, G.; Sbragia, E.; Bruschi, N.; Mancuso, E.; Mavilio, N.; Signori, A.; Roccatagliata, L.; et al. OPEN ACCESS EDITED BY Central Vein Sign and Diffusion MRI Diierentiate Microstructural Features within White Matter Lesions of Multiple Sclerosis Patients with Comorbidities. Available online: http://www.xinapse.com (accessed on 30 November 2012).
- Al-Louzi, O.; Letchuman, V.; Manukyan, S.; Beck, E.S.; Roy, S.; Ohayon, J.; Pham, D.L.; Cortese, I.; Sati, P.; Reich, D.S. Central Vein Sign Profile of Newly Developing Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis: A 3-Year Longitudinal Study. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 9, e1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellaro, M.; Tamanti, A.; Pisani, A.I.; Pizzini, F.B.; Crescenzo, F.; Calabrese, M. The use of the central vein sign in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagol, A.; Cortese, R.; Barakovic, M.; Schaedelin, S.; Ruberte, E.; Absinta, M.; Barkhof, F.; Calabrese, M.; Castellaro, M.; Ciccarelli, O.; et al. Diagnostic Performance of Cortical Lesions and the Central Vein Sign in Multiple Sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 2024, 81, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, P.; Absinta, M.; Grammatico, M.; Vuolo, L.; Emmi, G.; Carlucci, G.; Spagni, G.; Barilaro, A.; Repice, A.M.; Emmi, L.; et al. Central vein sign differentiates Multiple Sclerosis from central nervous system inflammatory vasculopathies. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saade, C.; Bou-Fakhredin, R.; Yousem, D.M.; Asmar, K.; Naffaa, L.; El-Merhi, F. Gadolinium and multiple sclerosis: Vessels, barriers of the brain, and glymphatics. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 2168–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassmann, H. Pathogenic mechanisms associated with different clinical courses of multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, R.J.M.; Simons, M. CNS remyelination and inflammation: From basic mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Neuron 2022, 110, 3549–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correale, J.; Gaitán, M.I.; Ysrraelit, M.C.; Fiol, M.P. Progressive multiple sclerosis: From pathogenic mechanisms to treatment. Brain 2017, 140, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meaton, I.; Altokhis, A.; Allen, C.M.; A Clarke, M.; Sinnecker, T.; Meier, D.; Enzinger, C.; Calabrese, M.; De Stefano, N.; Pitiot, A.; et al. Paramagnetic rims are a promising diagnostic imaging biomarker in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2022, 28, 2212–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, C.; Rudko, D.A.; Arnold, D.L.; Fetco, D.; Elkady, A.M.; Araujo, D.; Zhu, B.; Gafson, A.; Tian, Z.; Belachew, S.; et al. Lesion-level correspondence and longitudinal properties of paramagnetic rim and slowly expanding lesions in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2023, 29, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajnc, N.; Schmidbauer, V.; Leinkauf, J.; Haider, L.; Bsteh, G.; Kasprian, G.; Leutmezer, F.; Kornek, B.; Rommer, P.S.; Berger, T.; et al. Paramagnetic rim lesions lead to pronounced diffuse periplaque white matter damage in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2023, 29, 1406–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal-Bianco, A.; Grabner, G.; Kronnerwetter, C.; Weber, M.; Höftberger, R.; Berger, T.; Auff, E.; Leutmezer, F.; Trattnig, S.; Lassmann, H.; et al. Slow expansion of multiple sclerosis iron rim lesions: Pathology and 7 T magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Absinta, M.; Sati, P.; Schindler, M.; Leibovitch, E.C.; Ohayon, J.; Wu, T.; Meani, A.; Filippi, M.; Jacobson, S.; Cortese, I.C.; et al. Persistent 7-tesla phase rim predicts poor outcome in new multiple sclerosis patient lesions. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2597–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, E.K.; Song, C.J.; Sohn, E. Iron Rim Lesions as a Specific and Prognostic Biomarker of Multiple Sclerosis: 3T-Based Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.; Al-Louzi, O.; Beck, E.S.; Sati, P.; Absinta, M.; Reich, D.S. From pathology to MRI and back: Clinically relevant biomarkers of multiple sclerosis lesions. Neuroimage Clin. 2022, 36, 103194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, C.; Wolinsky, J.S.; Hauser, S.L.; Kappos, L.; Barkhof, F.; Bernasconi, C.; Wei, W.; Belachew, S.; Arnold, D.L. Slowly expanding/evolving lesions as a magnetic resonance imaging marker of chronic active multiple sclerosis lesions. Mult. Scler. J. 2019, 25, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, C.; Arnold, D.; Chen, H.; Ke, C.; Zhu, L.; Chang, I.; Cahir-McFarland, E.; Fisher, E.; Zhu, B.; Gheuens, S.; et al. Patterning chronic active demyelination in slowly expanding/evolving white matter MS lesions. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preziosa, P.; Pagani, E.; Meani, A.; Moiola, L.; Rodegher, M.; Filippi, M.; Rocca, M.A. Slowly Expanding Lesions Predict 9-Year Multiple Sclerosis Disease Progression. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 9, e1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvi, A.; Mendelsohn, Z.; Hamed, W.; Chard, D.; Tur, C.; Stutters, J.; MacManus, D.; Kanber, B.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.M.G.; Barkhof, F.; et al. Treatment reduces the incidence of newly appearing multiple sclerosis lesions evolving into chronic active, slowly expanding lesions: A retrospective analysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2024, 31, e16092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.L.; Elliott, C.; Martin, E.C.; Hyvert, Y.; Tomic, D.; Montalban, X. Effect of Evobrutinib on Slowly Expanding Lesion Volume in Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis: A Post Hoc Analysis of a Phase 2 Trial. Neurology 2024, 102, e208058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvi, A.; Clarke, M.A.; Prados, F.; Chard, D.; Ciccarelli, O.; Alberich, M.; Pareto, D.; Barranco, M.R.; Sastre-Garriga, J.; Tur, C.; et al. Relationship between paramagnetic rim lesions and slowly expanding lesions in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2023, 29, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ineichen, B.V.; Tsagkas, C.; Absinta, M.; Reich, D.S. Leptomeningeal enhancement in multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases: A systematic review and Meta-Analysis. Neuroimage Clin. 2022, 33, 102939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siger, M. Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis Patients: Review. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2022, 32, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ineichen, B.V.; Beck, E.S.; Piccirelli, M.; Reich, D.S. New Prospects for Ultra-High-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Multiple Sclerosis. Investig. Radiol. 2021, 56, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Absinta, M.; Cortese, I.C.; Vuolo, L.; Nair, G.; de Alwis, M.P.; Ohayon, J.; Meani, A.; Martinelli, V.; Scotti, R.; Falini, A.; et al. Leptomeningeal Gadolinium Enhancement across the Spectrum of Chronic Neuroinflammatory Diseases. Neurology 2017, 88, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andravizou, A.; Dardiotis, E.; Artemiadis, A.; Sokratous, M.; Siokas, V.; Tsouris, Z.; Aloizou, A.-M.; Nikolaidis, I.; Bakirtzis, C.; Tsivgoulis, G.; et al. Brain atrophy in multiple sclerosis: Mechanisms, clinical relevance and treatment options. Autoimmun. Highlights 2019, 10, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutzelnigg, A.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Stadelmann, C.; Brück, W.; Rauschka, H.; Bergmann, M.; Schmidbauer, M.; Parisi, J.E.; Lassmann, H. Cortical demyelination and diffuse white matter injury in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2005, 128, 2705–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moccia, M.; de Stefano, N.; Barkhof, F. Imaging outcome measures for progressive multiple sclerosis trials. Mult. Scler. 2017, 23, 1614–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.H.; Barkhof, F.; Frank, J.A.; Parker, G.J.M.; Thompson, A.J. Measurement of Atrophy in Multiple Sclerosis: Pathological Basis, Methodological Aspects and Clinical Relevance. Brain 2002, 125, 1676–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankoff, B.; Louapre, C. Can we use regional grey matter atrophy sequence to stage neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis? Brain 2018, 141, 1580–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tur, C.; Moccia, M.; Barkhof, F.; Chataway, J.; Sastre-Garriga, J.; Thompson, A.J.; Ciccarelli, O. Assessing treatment outcomes in multiple sclerosis trials and in the clinical setting. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riederer, F. Ocrelizumab versus placebo in primary progressive multiple sclerosis. J. Fur Neurol. Neurochir. Und Psychiatr. 2017, 18, 30–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshaghi, A.; Prados, F.; Brownlee, W.J.; Altmann, D.R.; Tur, C.; Cardoso, M.J.; De Angelis, F.; van de Pavert, S.H.; Cawley, N.; De Stefano, N.; et al. Deep gray matter volume loss drives disability worsening in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Lorenzo, S.; Konings, J.; van der Pol, S.; Kamermans, A.; Amor, S.; van Horssen, J.; Witte, M.E.; Kooij, G.; de Vries, H.E. Inflammation of the choroid plexus in progressive multiple sclerosis: Accumulation of granulocytes and T cells. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergsland, N.; Dwyer, M.G.; Jakimovski, D.; Tavazzi, E.; Benedict, R.H.B.; Weinstock-Guttman, B.; Zivadinov, R. Association of Choroid Plexus Inflammation on MRI with Clinical Disability Progression Over 5 Years in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Neurology 2023, 100, E911–E920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preziosa, P.; Pagani, E.; Meani, A.; Storelli, L.; Margoni, M.; Yudin, Y.; Tedone, N.; Biondi, D.; Rubin, M.; Rocca, M.A.; et al. Chronic Active Lesions and Larger Choroid Plexus Explain Cognition and Fatigue in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 11, e200205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricigliano, V.A.G.; Morena, E.; Colombi, A.; Tonietto, M.; Hamzaoui, M.; Poirion, E.; Bottlaender, M.; Gervais, P.; Louapre, C.; Bodini, B.; et al. Choroid plexus enlargement in inflammatory multiple sclerosis: 3.0-T MRI and translocator protein PET evaluation. Radiology 2021, 301, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricigliano, V.A.G.; Louapre, C.; Poirion, E.; Colombi, A.; Panah, A.Y.; Lazzarotto, A.; Morena, E.; Martin, E.; Bottlaender, M.; Bodini, B.; et al. Imaging Characteristics of Choroid Plexuses in Presymptomatic Multiple Sclerosis: A Retrospective Study. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 9, e200026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmierer, K.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.; Boulby, P.A.; Scaravilli, F.; Altmann, D.R.; Barker, G.J.; Tofts, P.S.; Miller, D.H. Diffusion tensor imaging of post mortem multiple sclerosis brain. Neuroimage 2007, 35, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werring, D.J.; Clark, C.A.; Barker, G.J.; Thompson, A.J.; Miller, D.H. Diffusion tensor imaging of lesions and normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 1999, 52, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, M.; Agosta, F. Diffusion tensor imaging and functional MRI. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 136, 1065–1087. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kolasa, M.; Hakulinen, U.; Helminen, M.; Hagman, S.; Raunio, M.; Rossi, M.; Brander, A.; Dastidar, P.; Elovaara, I. Longitudinal assessment of clinically isolated syndrome with diffusion tensor imaging and volumetric MRI. Clin. Imaging 2015, 39, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovaris, M.; Bozzali, M.; Iannucci, G.; Ghezzi, A.; Caputo, D.; Montanari, E.; Bertolotto, A.; Bergamaschi, R.; Capra, R.; Mancardi, G.L.; et al. Assessment of normal-appearing white and gray matter in patients with primary progressive multiple sclerosis: A diffusion-tensor magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolasa, M.; Hakulinen, U.; Brander, A.; Hagman, S.; Dastidar, P.; Elovaara, I.; Sumelahti, M. Diffusion tensor imaging and disability progression in multiple sclerosis: A 4-year follow-up study. Brain Behav. 2019, 9, e01194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Soley, E.; Martinez-Heras, E.; Solana, E.; Solanes, A.; Radua, J.; Vivo, F.; Prados, F.; Sepulveda, M.; Cabrera-Maqueda, J.M.; Fonseca, E.; et al. Diffusion tensor imaging metrics associated with future disability in multiple sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Højsgaard Chow, H.; Talbot, J.; Lundell, H.; Marstrand, L.; Madsen, C.G.; Søndergaard, H.B.; Hansen, M.B.; Sørensen, P.S.; Siebner, H.R.; Sellebjerg, F. Dimethyl fumarate treatment of primary progressive multiple sclerosis: Results of an open-label extension study. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2023, 70, 104458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivadinov, R.; Bergsland, N.; Hagemeier, J.; Carl, E.; Kolb, H.; Hojnacki, D.; Weinstock-Guttman, B. Effect of teriflunomide on gray and white matter brain pathology in multiple sclerosis using volumetric and diffusion-tensor imaging MRI measures. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 388, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, R.J.; Coffey, C.S.; Conwit, R.; Cudkowicz, M.E.; Gleason, T.; Goodman, A.; Klawiter, E.C.; Matsuda, K.; McGovern, M.; Naismith, R.T.; et al. Phase 2 Trial of Ibudilast in Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosperini, L.; Fanelli, F.; Petsas, N.; Sbardella, E.; Tona, F.; Raz, E.; Fortuna, D.; De Angelis, F.; Pozzilli, C.; Pantano, P. Multiple sclerosis: Changes in microarchitecture of white matter tracts after training with a video game balance board. Radiology 2014, 273, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, M.; Maekawa, T.; Kamiya, K.; Hagiwara, A.; Goto, M.; Takemura, M.Y.; Fujita, S.; Andica, C.; Kamagata, K.; Cohen-Adad, J.; et al. Advanced Diffusion MR Imaging for Multiple Sclerosis in the Brain and Spinal Cord. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2022, 21, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cortese, R.; De Stefano, N.; Giorgio, A. Structural and Functional Connectivity Substrates of Cognitive Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 671894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, S.; Samson, R.S.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.M.; Miller, D.H. Imaging outcomes for trials of remyelination in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, G.H. Overview of functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 22, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Yu, R. A window into the brain: Advances in psychiatric fMRI. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 542467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.E.; Glover, G.H. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Methods. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2015, 25, 289–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, R.B. The physics of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Rep. Prog. Phys. 2013, 76, 096601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocca, M.A.; Schoonheim, M.M.; Valsasina, P.; Geurts, J.J.G.; Filippi, M. Task- and resting-state fMRI studies in multiple sclerosis: From regions to systems and time-varying analysis. Current status and future perspective. Neuroimage Clin. 2022, 35, 103076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laura, D.G.; Silvia, T.; Nikolaos, P.; Patrizia, P. The role of fMRI in the assessment of neuroplasticity in MS: A systematic review. Neural Plast. 2018, 2018, 3419871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sbardella, E.; Petsas, N.; Tona, F.; Pantano, P. Resting-state fMRI in MS: General concepts and brief overview of its application. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 212693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cercignani, M.; Dipasquale, O.; Bogdan, I.; Carandini, T.; Scott, J.; Rashid, W.; Sabri, O.; Hesse, S.; Rullmann, M.; Lopiano, L.; et al. Cognitive fatigue in multiple sclerosis is associated with alterations in the functional connectivity of monoamine circuits. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Bhavsar, R.; Mao, T.; Mamikonyan, E.; Raizen, D.; Detre, J.A.; Weintraub, D.; Rao, H. Perfusion Imaging of Fatigue and Time-on-Task Effects in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 901203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolappan, M.; Henderson, A.P.D.; Jenkins, T.M.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.M.; Plant, G.T.; Thompson, A.J.; Miller, D.H. Assessing structure and function of the afferent visual pathway in multiple sclerosis and associated optic neuritis. J. Neurol. 2009, 256, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, E.N.; Thrippleton, M.J.; Meijboom, R.; Hunt, D.P.J.; Waldman, A.D. Quantitative magnetization transfer imaging in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Commun. 2022, 4, fcac088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Muircheartaigh, J.; Vavasour, I.; Ljungberg, E.; Li, D.K.B.; Rauscher, A.; Levesque, V.; Garren, H.; Clayton, D.; Tam, R.; Traboulsee, A.; et al. Quantitative neuroimaging measures of myelin in the healthy brain and in multiple sclerosis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 2104–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Grossman, R.I.; Udupa, J.K.; Babb, J.S.; Kolson, D.L.; McGowan, J.C. Magnetization transfer ratio histogram analysis of gray matter in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2001, 22, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.W.L.; Pardini, M.; Brownlee, W.J.; Fernando, K.; Samson, R.S.; Carrasco, F.P.; Ourselin, S.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.M.G.; Miller, D.H.; Chard, D.T. An abnormal periventricular magnetization transfer ratio gradient occurs early in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2017, 140, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granziera, C.; Wuerfel, J.; Barkhof, F.; Calabrese, M.; De Stefano, N.; Enzinger, C.; Evangelou, N.; Filippi, M.; Geurts, J.J.G.; Reich, D.S.; et al. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging towards clinical application in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2021, 144, 1296–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosta, F.; Rovaris, M.; Pagani, E.; Sormani, M.P.; Comi, G.; Filippi, M. Magnetization transfer MRI metrics predict the accumulation of disability 8 years later in patients with multiple sclerosis. Brain 2006, 129, 2620–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Elskamp, I.J.; Knol, D.; Vrenken, H.; Karas, G.; Meijerman, A.; Filippi, M.; Kappos, L.; Fazekas, F.; Wagner, K.; Pohl, C.; et al. Lesional magnetization transfer ratio: A feasible outcome for remyelinating treatment trials in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2010, 16, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, M.; Rocca, M.A.; Sormani, M.P.; Pereira, C.; Comi, G. Short-term evolution of individual enhancing MS lesions studied with magnetization transfer imaging. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1999, 17, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivadinov, R.; Dwyer, M.G.; Hussein, S.; Carl, E.; Kennedy, C.; Andrews, M.; Hojnacki, D.; Heininen-Brown, M.; Willis, L.; Cherneva, M.; et al. Voxel-wise magnetization transfer imaging study of effects of natalizumab and IFNβ-1a in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2012, 18, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.L.; Gold, R.; Kappos, L.; Bar-Or, A.; Giovannoni, G.; Selmaj, K.; Yang, M.; Zhang, R.; Stephan, M.; Sheikh, S.I.; et al. Magnetization transfer ratio in the delayed-release dimethyl fumarate DEFINE study. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 2429–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, H.-P.; Derfuss, T.; Cree, B.A.; Sormani, M.P.; Selmaj, K.; Stutters, J.; Prados, F.; MacManus, D.; Schneble, H.-M.; Lambert, E.; et al. Efficacy and safety of temelimab in multiple sclerosis: Results of a randomized phase 2b and extension study. Mult. Scler. 2022, 28, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.W.L.; Cunniffe, N.G.; Prados, F.; Kanber, B.; Jones, J.L.; Needham, E.; Georgieva, Z.; Rog, D.; Pearson, O.R.; Overell, J.; et al. Safety and efficacy of bexarotene in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (CCMR One): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, phase 2a study. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Zheng, Y.; Mahajan, K.R.; A Cohen, J.; Fox, R.J.; Ontaneda, D. Effect of ibudilast on thalamic magnetization transfer ratio and volume in progressive multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2023, 29, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, D.L.; Piani-Meier, D.; Bar-Or, A.; Benedict, R.H.; Cree, B.A.; Giovannoni, G.; Gold, R.; Vermersch, P.; Arnould, S.; Dahlke, F.; et al. Effect of siponimod on magnetic resonance imaging measures of neurodegeneration and myelination in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis: Gray matter atrophy and magnetization transfer ratio analyses from the EXPAND phase 3 trial. Mult. Scler. 2022, 28, 1526–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisel, A.A.; Naumova, A.V.; Yarnykh, V.L. Macromolecular Proton Fraction as a Myelin Biomarker: Principles, Validation, and Applications. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 819912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnato, F.; Hametner, S.; Franco, G.; Pawate, S.; Sriram, S.; Lassmann, H.; Gore, J.; Smith, S.E.; Dortch, R. Selective Inversion Recovery Quantitative Magnetization Transfer Brain MRI at 7T: Clinical and Postmortem Validation in Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neuroimaging 2018, 28, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gussew, A. Advances in Proton MR Spectroscopy for Quantifying Pain Associated Metabolic Changes in the Human Brain. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Ilmenau, Fakultät für Informatik und Automatisierung, Ilmenau, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stromillo, M.L.; Giorgio, A.; Rossi, F.; Battaglini, M.; Hakiki, B.; Malentacchi, G.; Santangelo, M.; Gasperini, C.; Bartolozzi, M.L.; Portaccio, E.; et al. Brain Metabolic Changes Suggestive of Axonal Damage in Radiologically Isolated Syndrome. Neurology 2013, 80, 2090–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecil, K.M. Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: Technique for the Neuroradiologist. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2013, 23, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yang, J.; Shen, J. Measuring N-acetylaspartate synthesis in vivo using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 172, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Schependom, J.; Guldolf, K.; D’Hooghe, M.B.; Nagels, G.; D’Haeseleer, M. Detecting neurodegenerative pathology in multiple sclerosis before irreversible brain tissue loss sets in. Transl. Neurodegener. 2019, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Munsaka, S.M.; Kraft-Terry, S.; Ernst, T. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy to assess neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013, 8, 576–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rispoli, M.G.; Valentinuzzi, S.; De Luca, G.; Del Boccio, P.; Federici, L.; Di Ioia, M.; Digiovanni, A.; Grasso, E.A.; Pozzilli, V.; Villani, A.; et al. Contribution of metabolomics to multiple sclerosis diagnosis, prognosis and treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huhn, K.; Mennecke, A.; Linz, P.; Tschunko, F.; Kästle, N.; Nagel, A.M.; Uder, M.; Dörfler, A.; Linker, R.A.; Engelhorn, T. 23Na MRI reveals persistent sodium accumulation in tumefactive MS lesions. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 379, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paula Faria, D. Myelin positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in multiple sclerosis. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1842–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankoff, B.; Poirion, E.; Tonietto, M.; Bodini, B. Exploring the heterogeneity of MS lesions using positron emission tomography: A reappraisal of their contribution to disability. Brain Pathol. 2018, 28, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airas, L.; Nylund, M.; Rissanen, E. Evaluation of microglial activation in multiple sclerosis patients using positron emission tomography. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rissanen, E.; Tuisku, J.; Rokka, J.; Paavilainen, T.; Parkkola, R.; Rinne, J.O.; Airas, L. In vivo detection of diffuse inflammation in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis using PET imaging and the radioligand11C-PK11195. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sucksdorff, M.; Matilainen, M.; Tuisku, J.; Polvinen, E.; Vuorimaa, A.; Rokka, J.; Nylund, M.; Rissanen, E.; Airas, L. Brain TSPO-PET predicts later disease progression independent of relapses in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2020, 143, 3318–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauckneht, M.; Capitanio, S.; Raffa, S.; Roccatagliata, L.; Pardini, M.; Lapucci, C.; Marini, C.; Sambuceti, G.; Inglese, M.; Gallo, P.; et al. Molecular imaging of multiple sclerosis: From the clinical demand to novel radiotracers. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2019, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Shalom, I.; Karni, A.; Kolb, H. The Role of Molecular Imaging as a Marker of Remyelination and Repair in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poutiainen, P.; Jaronen, M.; Quintana, F.J.; Brownell, A.L. Precision medicine in multiple sclerosis: Future of PET imaging of inflammation and reactive astrocytes. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodini, B.; Stankoff, B. PET is necessary to make the next step forward in understanding MS pathophysiology—Yes. Mult. Scler. J. 2019, 25, 1086–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaunzner, U.W.; Gauthier, S.A. MRI in the assessment and monitoring of multiple sclerosis: An update on best practice. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2017, 10, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, O.; Gold, R.; Meuth, S.G.; Linker, R.A.; Skripuletz, T.; Wiendl, H.; Wattjes, M.P. Prognostic relevance of MRI in early relapsing multiple sclerosis: Ready to guide treatment decision making? Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2024, 17, 17562864241229325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggieri, S.; Prosperini, L.; Petracca, M.; Logoteta, A.; Tinelli, E.; De Giglio, L.; Ciccarelli, O.; Gasperini, C.; Pozzilli, C. The added value of spinal cord lesions to disability accrual in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 4995–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroman, P.W.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.; Bacon, M.; Schwab, J.; Bosma, R.; Brooks, J.; Cadotte, D.; Carlstedt, T.; Ciccarelli, O.; Cohen-Adad, J.; et al. The current state-of-the-art of spinal cord imaging: Methods. NeuroImage 2014, 84, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, N.B.; Salah, R.; Huang, J.C.; Hathout, G.M. A comparison of sagittal short T1 inversion recovery and T2-weighted FSE sequences for detection of multiple sclerosis spinal cord lesions. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2014, 129, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moccia, M.; Ruggieri, S.; Ianniello, A.; Toosy, A.; Pozzilli, C.; Ciccarelli, O. Advances in spinal cord imaging in multiple sclerosis. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2019, 12, 1756286419840593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moccia, M. Improving Longitudinal Spinal Cord Atrophy Measurements for Clinical Trials in Multiple Sclerosis by Using the Generalised Boundary Shift Integral (GBSI). Ph.D. Thesis, University College London, London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Schlaeger, R.; Papinutto, N.; Panara, V.; Bevan, C.; Lobach, I.V.; Bucci, M.; Caverzasi, E.; Gelfand, J.M.; Green, A.J.; Jordan, K.M.; et al. Spinal cord gray matter atrophy correlates with multiple sclerosis disability. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischof, A.; Papinutto, N.; Keshavan, A.; Rajesh, A.; Kirkish, G.; Zhang, X.; Mallott, J.M.; Asteggiano, C.; Sacco, S.; Gundel, T.J.; et al. Spinal Cord Atrophy Predicts Progressive Disease in Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2022, 91, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, M.A.; Valsasina, P.; Meani, A.; Gobbi, C.; Zecca, C.; Barkhof, F.; Schoonheim, M.M.; Strijbis, E.M.; Vrenken, H.; Gallo, A.; et al. Spinal cord lesions and brain grey matter atrophy independently predict clinical worsening in definite multiple sclerosis: A 5-year, multicentre study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 94, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, A.J.E.; Clarke, M.A.; O’Grady, K.P.; Schilling, K.G.; Smith, S.A. Advanced spinal cord MRI in multiple sclerosis: Current techniques and future directions. Neuroimage Clin. 2022, 36, 103244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petracca Monica Margoni Giulia Bommarito, M. Monitoring Progressive Multiple Sclerosis with Novel Imaging Techniques. Neurol. Ther. 2018, 7, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Mehta, B.B.; Coppo, S.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, D.; Seiberlich, N.; Griswold, M.A.; Gulani, V. Magnetic resonance fingerprinting—An overview. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 3, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieger, B.; Akçakaya, M.; Pariente, J.C.; Llufriu, S.; Martinez-Heras, E.; Weingärtner, S.; Schad, L.R. Time efficient whole-brain coverage with MR Fingerprinting using slice-interleaved echo-planar-imaging. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badve, C.; Yu, A.; Dastmalchian, S.; Rogers, M.; Ma, D.; Jiang, Y.; Margevicius, S.; Pahwa, S.; Lu, Z.; Schluchter, M.; et al. MR fingerprinting of adult brain tumors: Initial experience. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Gulani, V.; Seiberlich, N.; Liu, K.; Sunshine, J.L.; Duerk, J.L.; Griswold, M.A. Magnetic resonance fingerprinting. Nature 2013, 495, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Imaging Techniques | Novel Finding | Clinical Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIR, PSIR, MP2RAGE | CLs | Marker of disability and cognitive impairment | Acquisition time, availability of 3T and 7T MRI for better resolution |
| SWI, T2*, QSM | CVS, PRLs | Differential diagnosis (CVS); disability and disease progression (PRLs) | Availability of 3T and 7T MRI for better resolution, acquisition time |
| DTI | Pre-lesion alteration in NAWM | Early detection of new lesions | Lack of specificity |
| fMRI | Functional changes, plasticity, functional reserve | Study of fatigue and functional reserve | Lack of standardized protocol with high inter-subject variability |
| MT imaging | Pre-lesion alteration | Predicting long term disability accumulation | Lack of specificity and lack of standardized protocol |
| MRS | Neural integrity and functionality | Differential diagnosis | Lack of reproducibility and lack of standardized protocol |
| PET | Quantification of neuroinflammation | Quantification of demyelination and remyelination | Radiations |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nistri, R.; Ianniello, A.; Pozzilli, V.; Giannì, C.; Pozzilli, C. Advanced MRI Techniques: Diagnosis and Follow-Up of Multiple Sclerosis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14111120
Nistri R, Ianniello A, Pozzilli V, Giannì C, Pozzilli C. Advanced MRI Techniques: Diagnosis and Follow-Up of Multiple Sclerosis. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(11):1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14111120
Chicago/Turabian StyleNistri, Riccardo, Antonio Ianniello, Valeria Pozzilli, Costanza Giannì, and Carlo Pozzilli. 2024. "Advanced MRI Techniques: Diagnosis and Follow-Up of Multiple Sclerosis" Diagnostics 14, no. 11: 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14111120
APA StyleNistri, R., Ianniello, A., Pozzilli, V., Giannì, C., & Pozzilli, C. (2024). Advanced MRI Techniques: Diagnosis and Follow-Up of Multiple Sclerosis. Diagnostics, 14(11), 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14111120







