Diagnostic Accuracy of MMP-8 and IL-6-Based Point-of-Care Testing to Detect Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Peritonitis: A Single-Center Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Objectives
2.3. Institutional Review Board and Electronic Patient Data Software
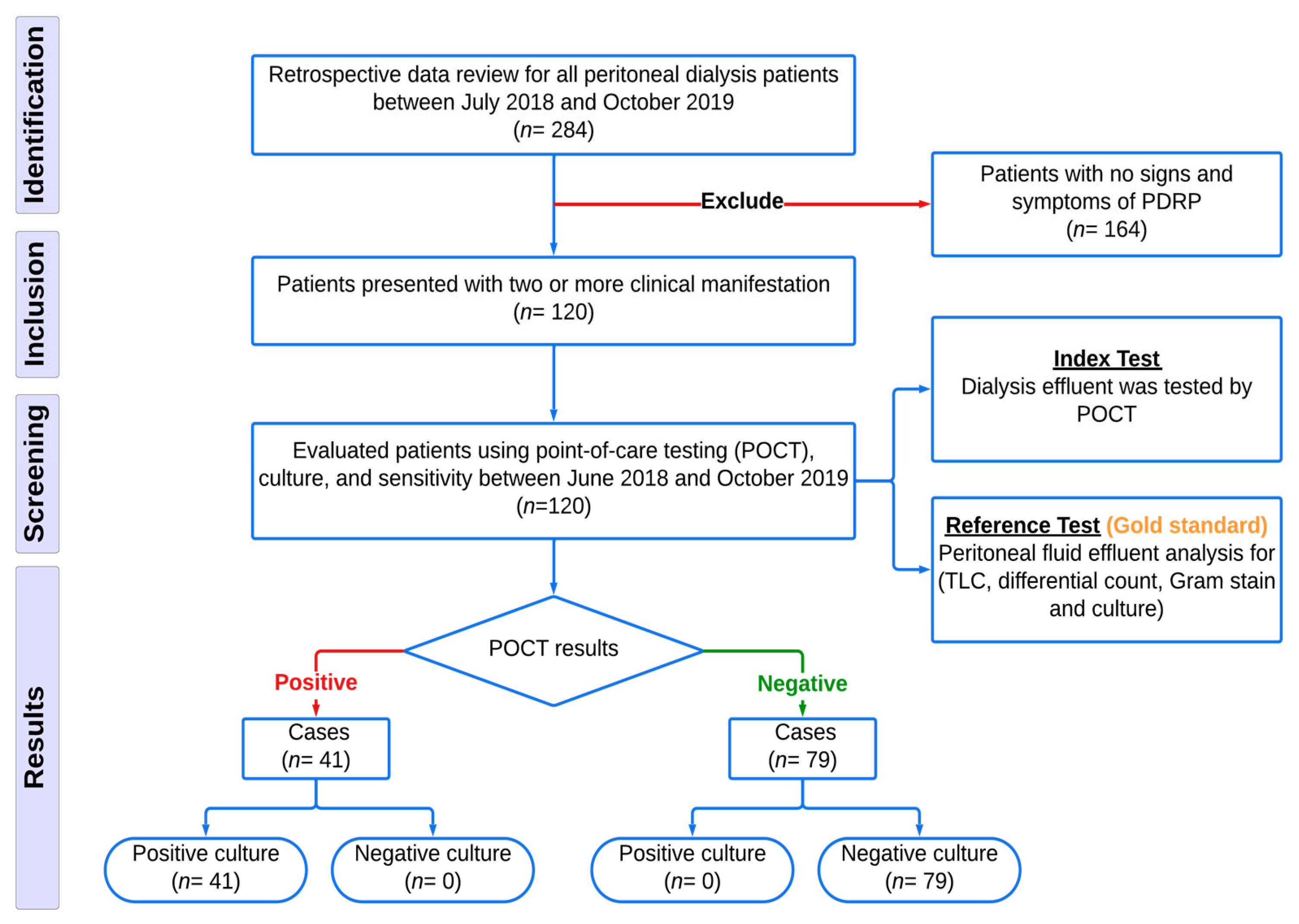
2.4. Study Population
2.4.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.4.2. Exclusion Criteria
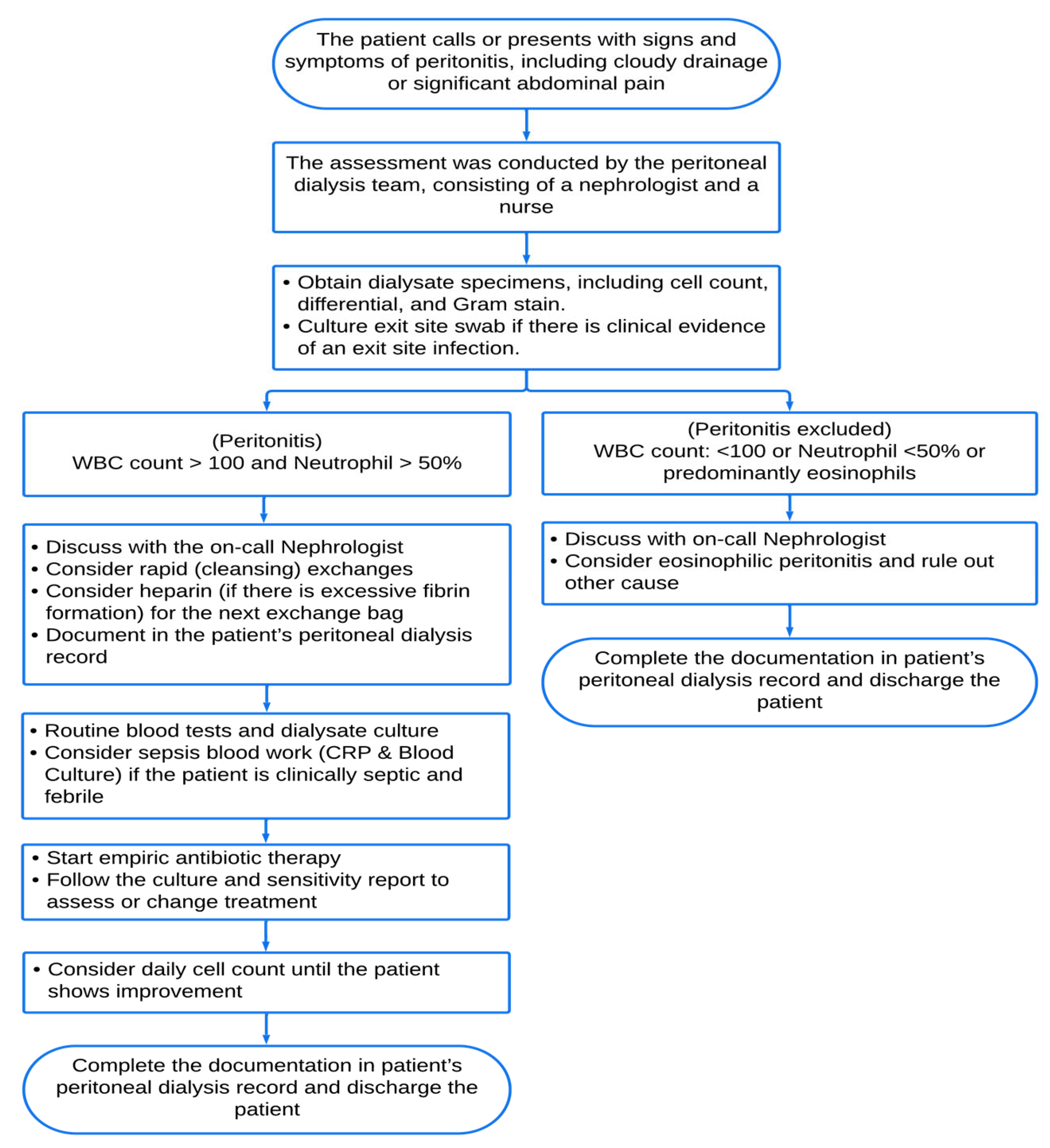
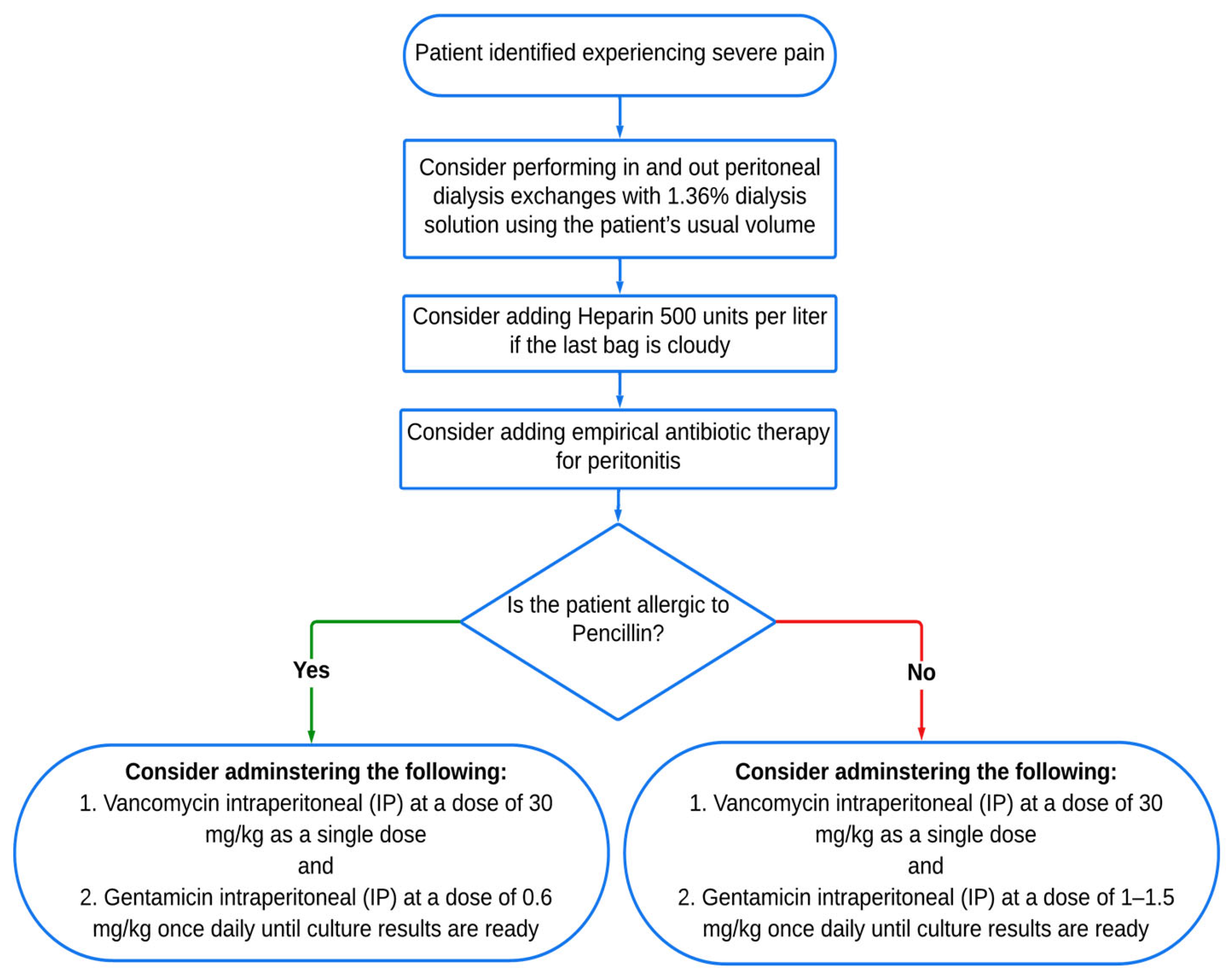
2.5. Case Definitions
2.6. Data Collection
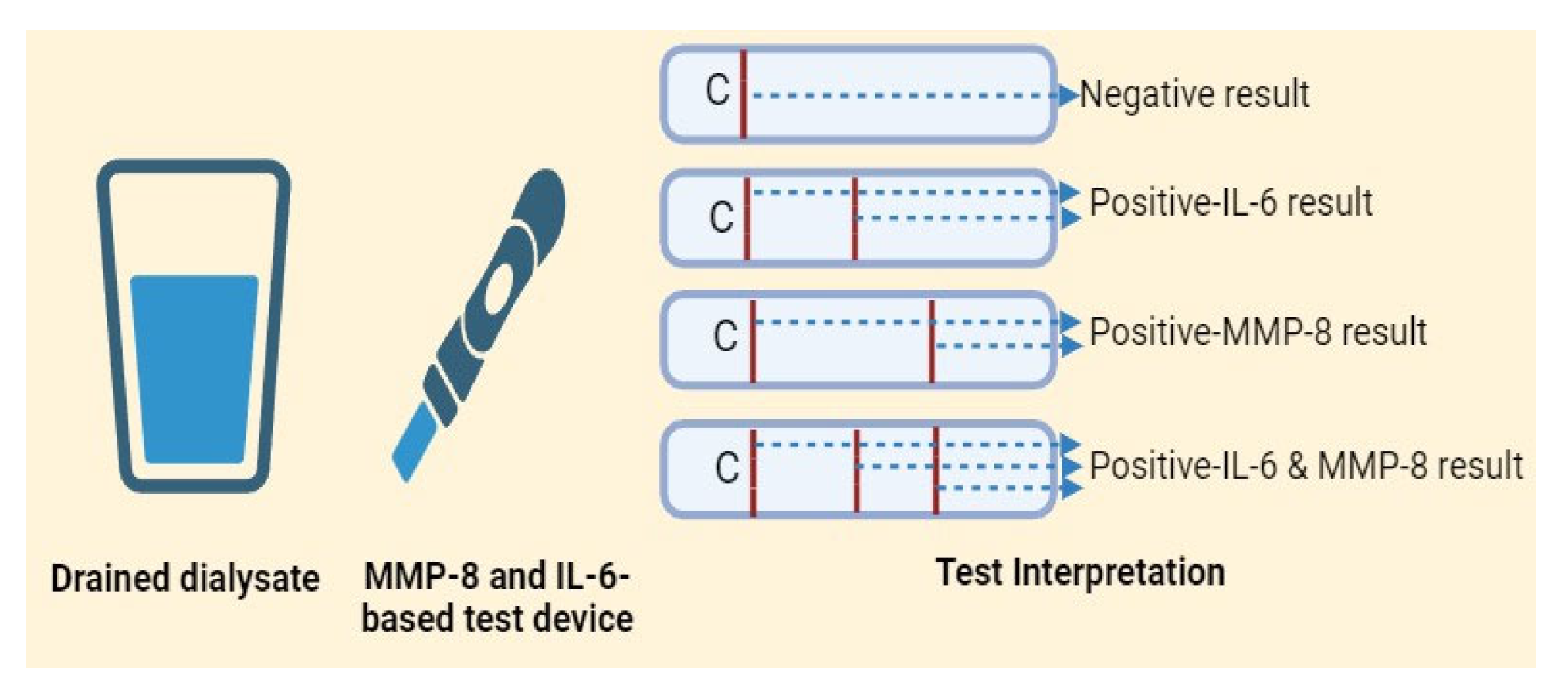
2.7. Study Procedure and Interpretation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
- Sensitivity = number of patients with true positive test/number of patients with true positive test + number of patients with false negative test.
- Specificity = number of patients with true negative test/number of patients with true negative test + number of patients with false positive test.
- Positive predictive value = number of patients with true positive test/number of patients with true positive test + number of patients with false positive test.
- Negative predictive value = number of patients with true negative test/number of patients with true negative test + number of patients with false negative test.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. POCT and Other Test Results in Comparison with the Reference Standard
4. Discussion
Limitations and Strengths of this Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- François, K.; Bargman, J.M. Evaluating the benefits of home-based peritoneal dialysis. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2014, 7, 447–455. [Google Scholar]
- Oreopoulos, D.G.; Thodis, E.; Passadakis, P.; Vargemezis, V. Home dialysis as a first option: A new paradigm. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2009, 41, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, Y.; Higuchi, C.; Io, H.; Wakabayashi, K.; Tsujimoto, H.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Yuasa, H.; Ryuzaki, M.; Ito, Y.; Nakamoto, H. Comparison of peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis as first renal replacement therapy in patients with end-stage renal disease and diabetes: A systematic review. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2019, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Malki, H.; Rashed, A.H.; Asim, M. Renal replacement therapy in Qatar—Past, present and future. Open J. Nephrol. 2018, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sahlawi, M.; AlRukhaimi, M.; Al-Ghamdi, S.M.; Al Salmi, I.; Al-Aradi, A.H.; Hamad, A.; AlSahow, A. Peritoneal dialysis in the Arabian Gulf countries: Challenges and opportunities. Perit. Dial. Int. 2023, 44, 08968608231204107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigidi, M.M.; Fituri, O.M.; Chandy, S.K.; Asim, M.; Al Malki, H.A.; Rashed, A.H. Microbial spectrum and outcome of peritoneal dialysis related peritonitis in Qatar. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2010, 21, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Trionfetti, F.; Marchant, V.; González-Mateo, G.T.; Kawka, E.; Márquez-Expósito, L.; Ortiz, A.; López-Cabrera, M.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Strippoli, R. Novel Aspects of the Immune Response Involved in the Peritoneal Damage in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients under Dialysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Biesen, W.; Vanholder, R.; Lameire, N. The role of peritoneal dialysis as the first-line renal replacement modality. Perit. Dial. Int. 2000, 20, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.K.-T.; Chow, K.M.; Cho, Y.; Fan, S.; Figueiredo, A.E.; Harris, T.; Kanjanabuch, T.; Kim, Y.-L.; Madero, M.; Malyszko, J. ISPD peritonitis guideline recommendations: 2022 update on prevention and treatment. Perit. Dial. Int. 2022, 42, 110–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, M.R. A systematic review of peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis rates over time from national or regional population-based registries and databases. Perit. Dial. Int. 2022, 42, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaar, B.G.; Plantinga, L.C.; Crews, D.C.; Fink, N.E.; Hebah, N.; Coresh, J.; Kliger, A.S.; Powe, N.R. Timing, causes, predictors and prognosis of switching from peritoneal dialysis to hemodialysis: A prospective study. BMC Nephrol. 2009, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perl, J.; Davies, S.J.; Lambie, M.; Pisoni, R.L.; McCullough, K.; Johnson, D.W.; Sloand, J.A.; Prichard, S.; Kawanishi, H.; Tentori, F. The Peritoneal Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (PDOPPS): Unifying efforts to inform practice and improve global outcomes in peritoneal dialysis. Perit. Dial. Int. 2016, 36, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redpath Mahon, A.C.; Richardson, T.; Neu, A.M.; Warady, B.A.; Investigators, S. Factors associated with high-cost hospitalization for peritonitis in children receiving chronic peritoneal dialysis in the United States. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotsanas, D.; Polkinghorne, K.R.; Korman, T.M.; Atkins, R.C.; Brown, F. Risk factors for peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis: Can we reduce the incidence and improve patient selection? Nephrology 2007, 12, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ye, H.; Huang, R.; Yi, C.; Wu, J.; Yu, X.; Yang, X. Incidence and risk factors of peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis in elderly patients: A retrospective clinical study. Perit. Dial. Int. 2020, 40, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzer, W.L. Peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis: Challenges and solutions. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2018, 11, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthucumarana, K.; Howson, P.; Crawford, D.; Burrows, S.; Swaminathan, R.; Irish, A. The relationship between presentation and the time of initial administration of antibiotics with outcomes of peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis patients: The PROMPT study. Kidney Int. Rep. 2016, 1, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oki, R.; Tsuji, S.; Hamasaki, Y.; Komaru, Y.; Miyamoto, Y.; Matsuura, R.; Yamada, D.; Doi, K.; Kume, H.; Nangaku, M. Time until treatment initiation is associated with catheter survival in peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudville, N.; Kemp, A.; Clayton, P.; Lim, W.; Badve, S.V.; Hawley, C.M.; McDonald, S.P.; Wiggins, K.J.; Bannister, K.M.; Brown, F.G. Recent peritonitis associates with mortality among patients treated with peritoneal dialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2012, 23, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-P.; Chang, C.-C.; Wen, Y.-K.; Chiu, P.-F.; Yang, Y. Predictors of peritonitis and the impact of peritonitis on clinical outcomes of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients in Taiwan—10 years’ experience in a single center. Perit. Dial. Int. 2014, 34, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, V.W.-K.; Li, P.K.-T. Peritoneal dialysis in Asia. Kidney Dis. 2015, 1, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichairuangthum, K.; Krairittichai, U. Rapid Diagnosis of Peritonitis in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients by Using Urine Reagent Strip. Bull. Dep. Med. Serv. 2010, 35, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Rathore, V.; Joshi, H.; Kimmatkar, P.D.; Malhotra, V.; Agarwal, D.; Beniwal, P.; Dawra, R.; Gupta, P. Leukocyte esterase reagent strip as a bedside tool to detect peritonitis in patients undergoing acute peritoneal dialysis. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2017, 28, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Tak, W.; Lee, J. Using reagent strips for rapid diagnosis of peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis patients. Adv. Perit. Dial. 2005, 21, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- AlSahow, A.; AlRukhaimi, M.; Al Wakeel, J.; Al-Ghamdi, S.M.; AlGhareeb, S.; AlAli, F.; Al Salmi, I.; AlHelal, B.; AlGhonaim, M.; Bieber, B.A. Demographics and key clinical characteristics of hemodialysis patients from the Gulf Cooperation Council countries enrolled in the dialysis outcomes and practice patterns study phase 5 (2012–2015). Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2016, 27, S12–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, K.M.; Li, P.K.-T.; Cho, Y.; Abu-Alfa, A.; Bavanandan, S.; Brown, E.A.; Cullis, B.; Edwards, D.; Ethier, I.; Hurst, H. ISPD catheter-related infection recommendations: 2023 update. Perit. Dial. Int. 2023, 43, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, C.-C.; Li, P.K.-T.; Johnson, D.W.; Bernardini, J.; Dong, J.; Figueiredo, A.E.; Ito, Y.; Kazancioglu, R.; Moraes, T.; Van Esch, S. ISPD catheter-related infection recommendations: 2017 update. Perit. Dial. Int. 2017, 37, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, W.W.-S.; Li, P.K.-T. Recent advances in novel diagnostic testing for peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 41, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodlad, C.; George, S.; Sandoval, S.; Mepham, S.; Parekh, G.; Eberl, M.; Topley, N.; Davenport, A. Measurement of innate immune response biomarkers in peritoneal dialysis effluent using a rapid diagnostic point-of-care device as a diagnostic indicator of peritonitis. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mologic Ltd. Available online: https://mologic.co.uk/our-core-markets/infection-and-infectious-disease/periplex/ (accessed on 9 January 2024).
- Shigidi, M.M.; Fituri, O.M.; Chandy, S.K.; Asim, M.; Al Malki, H.A.; Rashed, A.H. Peritoneal dialysis, an expanding mode of renal replacement therapy in Qatar. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2011, 22, 587–593. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.K.-T.; Szeto, C.C.; Piraino, B.; de Arteaga, J.; Fan, S.; Figueiredo, A.E.; Fish, D.N.; Goffin, E.; Kim, Y.-L.; Salzer, W. ISPD peritonitis recommendations: 2016 update on prevention and treatment. Perit. Dial. Int. 2016, 36, 481–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, A.; Man, A.; Voidăzan, S. Accuracy of diagnostic tests. J. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 7, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Lane, C.; Punzalan, S. Correlation of periscreen strip results and white cell count in peritoneal dialysis peritonitis. J. Ren. Care 2010, 36, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moral, M.N.; Martínez-Camblor, P.; González, A.M.; Suárez, C.R.; Álvarez, J.E.S. MUL+DO: A multicomponent index for the quick diagnosis of peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis patients. Nefrología 2018, 38, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cropper, E.; Coleclough, S.; Griffiths, S.; Saunders, S.; Williams, J.; Rutherford, P.A. Rapid diagnosis of peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis patients. J. Nephrol. 2003, 16, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Falda, A.; Doretto, P. Automated analysis for differentiating leukocytes in body fluids using the software “biological liquid application” on ADVIA 2120/2120i hematology analyzer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2018, 32, e22578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckup, M.; Kaneda, J.M.; Birk, A.M.; Glockner, E.; Venook, R.; Jain, A.; Sharma, S.; Wong, C.; Sutha, K. Utilising low-cost, easy-to-use microscopy techniques for early peritonitis infection screening in peritoneal dialysis patients. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Shi, R.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Pan, H.; Wang, D. Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting gram-negative bacterial infections in patients with peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, A.K.; Okpechi, I.G.; Osman, M.A.; Cho, Y.; Cullis, B.; Htay, H.; Jha, V.; Makusidi, M.A.; McCulloch, M.; Shah, N. Epidemiology of peritoneal dialysis outcomes. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 779–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, A.; Ismail, H.; Elsayed, M.; Kaddourah, A.; Ahmed, H.; Ibrahim, R.; Ali, A.; Alali, F. The epidemiology of acute peritonitis in end-stage renal disease patients on peritoneal dialysis in Qatar: An 8-year follow-up study. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2018, 29, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnakirouchenan, R.; Holley, J.L. Peritoneal dialysis versus hemodialysis: Risks, benefits, and access issues. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2011, 18, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerschbaum, J.; König, P.; Rudnicki, M. Risk factors associated with peritoneal-dialysis-related peritonitis. Int. J. Nephrol. 2012, 2012, 483250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, P.-Y.; Verger, C. Evaluation of a new rapid-diagnostic test for peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis: The PERIPLEX® device. Bull. Dial. Domic. 2020, 3, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, S.J.; Nolan, M.; Klingbeil, L.; Harmon, K.; Lahni, P.; Zingarelli, B.; Wong, H.R. Intestine-derived matrix metalloproteinase-8 is a critical mediator of polymicrobial peritonitis. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, e200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Friberg, I.M.; Kift-Morgan, A.; Parekh, G.; Morgan, M.P.; Liuzzi, A.R.; Lin, C.-Y.; Donovan, K.L.; Colmont, C.S.; Morgan, P.H. Machine-learning algorithms define pathogen-specific local immune fingerprints in peritoneal dialysis patients with bacterial infections. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spieth, P.M.; Kubasch, A.S.; Penzlin, A.I.; Illigens, B.M.-W.; Barlinn, K.; Siepmann, T. Randomized controlled trials—A matter of design. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2016, 12, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar]

| Characteristics | N (%)/(Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|
| Age (Mean ± SD) | 55.6 ± 15.6 (range: 23–90 years) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 52 (43.3) |
| Female | 68 (56.7) |
| Nationality | |
| Arab national (Qataris) | 25 (20.8) |
| Arab non-national (Arab non-Qataris) | 44 (36.7) |
| South Asian (Pakistani/Indian) | 30 (25) |
| Other mixed nationalities | 21 (17.4) |
| Comorbidities Diabetes mellitus | 56 (47.1) |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 48 (40.3) |
| Eye disease | |
| Retinopathy | 15 (12.5) |
| Blindness | 2 (1.7) |
| Others (Glaucoma, Cataracts) | 13 (10.8) |
| Neuropathy | 15 (12.6) |
| Hypertension | 110 (91.7) |
| Pulmonary disease | |
| Asthma | 8 (6.7) |
| Interstitial lung disease | 2 (1.7) |
| Others (IPF, COPD) | 9 (7.6) |
| Dyslipidemia | 46 (38.7) |
| Hypoparathyroidism (post-surgical) | 2 (1.7) |
| Hyperparathyroidism (secondary to renal failure) | 16 (13.4) |
| Hypothyroidism | 16 (13.4) |
| PD duration (Mean ± SD) | 38.5 ± 30.4 (range: 5–142 months) |
| Hyperthyroidism | 0 (0) |
| Oncology disease | |
| Breast cancer | 1 (0.8) |
| Gynecological malignancy | 1 (0.8) |
| Others (leukemia, lung cancer) | 5 (4.2) |
| Peripheral vascular disease | |
| Diabetic foot | 3 (2.5) |
| Others (Gangrene, Amputation) | 2 (1.7) |
| Cardiac disease | |
| Coronary artery disease | 25 (20.8) |
| Angina | 3 (2.5) |
| Cardiomyopathy | 4 (3.4) |
| Heart failure | 12 (10.1) |
| Arrhythmia | 3 (2.5) |
| Valvular heart disease | 3 (2.5) |
| Others (Angina, MI) | 13 (10.9) |
| Neurological diseases | |
| Ischemic stroke | 14 (11.8) |
| Intracranial/hematoma | 3 (2.5) |
| Epilepsy | 5 (4.2) |
| Others (MS, CVA, TIA) | 1 (0.8) |
| Clinical Characteristics | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Clinical presentation | |
| Abdominal pain | 67 (57.8) |
| Fever | 33 (28.4) |
| Vomiting | 14 (12.1) |
| Diarrhea | 5 (4.3) |
| Cloudy outflow | 19 (16.4) |
| Hazy outflow | 10 (8.6) |
| Low BP | 7 (5.8) |
| Peritoneal fluid effluent tests | |
| POCT results | 41 (34.2) |
| Culture results | 40 (33.3) |
| WBC (TLC) | |
| Less than 100 (No PDRP) | 78 (65.0) |
| Between 100 to 1000 (Mild) | 21 (17.5) |
| Between 1000 to 3000 (Moderate) | 6 (5.0) |
| More than 3000 (Severe) | 15 (12.6) |
| Neutrophil (PMN) (>50%) | 41 (34.2) |
| Confirmed PDRP | 41 (34.2) |
| Type of organisms | |
| Gram-positive | 21 (52.5) |
| Gram-negative | 12 (30) |
| TB | 1 (2.5) |
| Fungal | 1 (2.5) |
| No growth | 5 (12.5) |
| Treatment | 40 (33.3) |
| Admission | 26 (21.7) |
| Clinical Evaluation (n = 41) | TLC > 100/mL and PMN > 50% (n = 41) | Culture (n = 40) | MMP-8/IL-POCT Positive (n = 41) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDRP (n = 41) | 41 | 41 | 40 | 41 |
| No PDRP (n = 79) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sensitivity | 100% | 100% | 97.56% | 100% |
| Specificity | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| PPV | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| NPV | 100% | 100% | 98.75% | 100% |
| Accuracy | 100% | 100% | 99.16% | 100% |
| PDRP | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | |||
| MMP-8 and IL-6-based POCT test results | Positive | 41 | 0 | 41 |
| Negative | 0 | 79 | 79 | |
| Total | 41 | 79 | 120 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, R.; Hijazi, M.M.; AlAli, F.; Hamad, A.; Bushra, A.; Mirow, L.; Siepmann, T. Diagnostic Accuracy of MMP-8 and IL-6-Based Point-of-Care Testing to Detect Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Peritonitis: A Single-Center Experience. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14111113
Ibrahim R, Hijazi MM, AlAli F, Hamad A, Bushra A, Mirow L, Siepmann T. Diagnostic Accuracy of MMP-8 and IL-6-Based Point-of-Care Testing to Detect Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Peritonitis: A Single-Center Experience. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(11):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14111113
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Rania, Mido Max Hijazi, Fadwa AlAli, Abdullah Hamad, Ahlam Bushra, Lutz Mirow, and Timo Siepmann. 2024. "Diagnostic Accuracy of MMP-8 and IL-6-Based Point-of-Care Testing to Detect Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Peritonitis: A Single-Center Experience" Diagnostics 14, no. 11: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14111113
APA StyleIbrahim, R., Hijazi, M. M., AlAli, F., Hamad, A., Bushra, A., Mirow, L., & Siepmann, T. (2024). Diagnostic Accuracy of MMP-8 and IL-6-Based Point-of-Care Testing to Detect Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Peritonitis: A Single-Center Experience. Diagnostics, 14(11), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14111113








