The Clinical Courses and Prognosis of Cirrhotic Patients after First Acute Decompensation: Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Data Collection and Definitions of Clinical Parameters
2.3. Primary Outcomes and Follow-Up
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Study Population and Baseline Characteristics According to Clinical Courses after the First Acute Decompensation
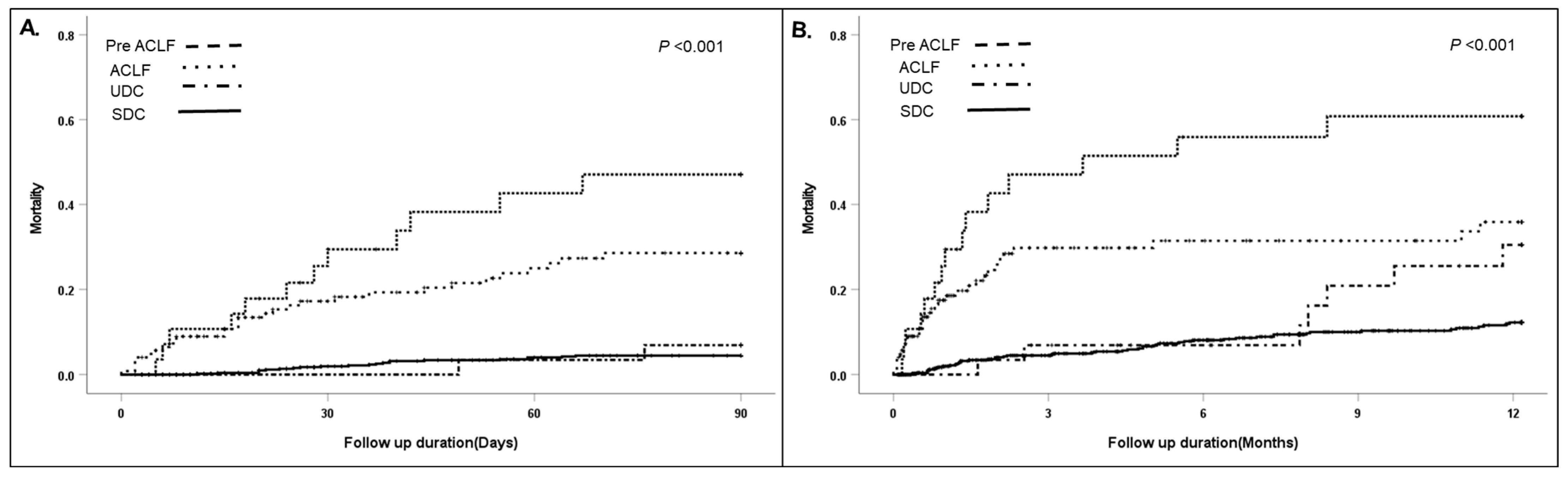
3.2. Short/Long-Term Mortality According to Clinical Course and the Factors Associated with Readmission in Patients after the First Acute Decompensation
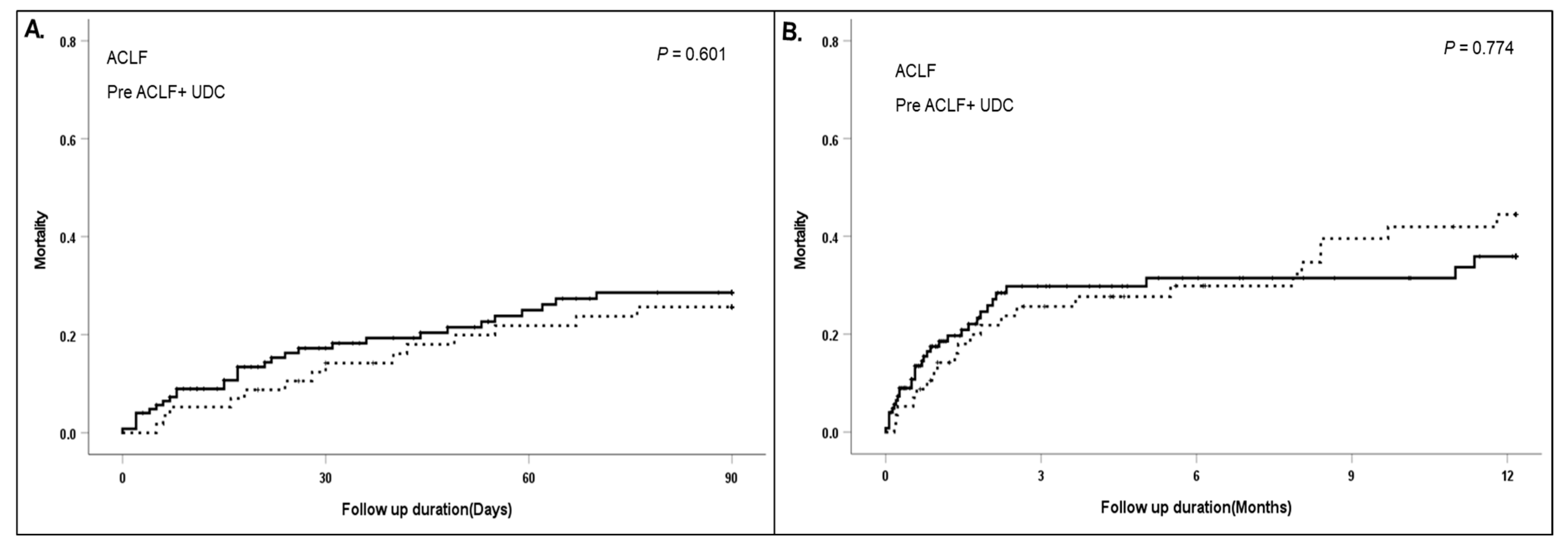
3.3. Clinical Difference between Initial ACLF at First AD and Newly Developed ACLF within 3 Months of First AD (Pre ACLF)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Gines, P.; Pavesi, M.; Angeli, P.; Cordoba, J.; Durand, F.; Gustot, T.; Saliba, F.; Domenicali, M.; et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a distinct syndrome that develops in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1426–1437.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, A.; Jindal, A.; Maiwall, R.; Sharma, M.K.; Sharma, B.C.; Pamecha, V.; Mahtab, M.; Rahman, S.; Chawla, Y.K.; Taneja, S.; et al. Liver failure determines the outcome in patients of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF): Comparison of APASL ACLF research consortium (AARC) and CLIF-SOFA models. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, V.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Gines, P.; EASL-CLIF Consortium CANONIC Study. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: A new syndrome that will re-classify cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S131–S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; O’Leary, J.G.; Reddy, K.R.; Wong, F.; Biggins, S.W.; Patton, H.; Fallon, M.B.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Maliakkal, B.; Malik, R.; et al. Survival in infection-related acute-on-chronic liver failure is defined by extrahepatic organ failures. Hepatology 2014, 60, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustot, T.; Stadlbauer, V.; Laleman, W.; Alessandria, C.; Thursz, M. Transition to decompensation and acute-on-chronic liver failure: Role of predisposing factors and precipitating events. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75 (Suppl. S1), S36–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, J.; Acevedo, J.; Wiest, R.; Gustot, T.; Amoros, A.; Deulofeu, C.; Reverter, E.; Martinez, J.; Saliba, F.; Jalan, R.; et al. Bacterial and fungal infections in acute-on-chronic liver failure: Prevalence, characteristics and impact on prognosis. Gut 2018, 67, 1870–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, K.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Lang, R.; Jiang, W. Disruption of the gut-liver axis in the pathogenesis of acute-on-chronic liver failure. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebicka, J.; Fernandez, J.; Papp, M.; Caraceni, P.; Laleman, W.; Gambino, C.; Giovo, I.; Uschner, F.E.; Jimenez, C.; Mookerjee, R.; et al. The PREDICT study uncovers three clinical courses of acutely decompensated cirrhosis that have distinct pathophysiology. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuppan, D.; Afdhal, N.H. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2008, 371, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Korean Association for the Study of the Liver. KASL clinical practice guidelines for management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2022, 28, 276–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Korean Association for the Study of the Liver. KASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatitis C. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2016, 22, 76–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, C.L.; Adams, D.; Assis, D.N.; Kerkar, N.; Manns, M.P.; Mayo, M.J.; Vierling, J.M.; Alsawas, M.; Murad, M.H.; Czaja, A.J. Diagnosis and Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis in Adults and Children: 2019 Practice Guidance and Guidelines from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2020, 72, 671–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Korean Association for the Study of the Liver. KASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of alcoholic liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2013, 19, 216–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.P.; Columbus, M. Assessing Alcohol Problems: A Guide for Clinicians and Researchers; NIAAA Treatment Handbook Series; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1995; Volume 9, 573p.
- Muckart, D.J.; Bhagwanjee, S. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference definitions of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome and allied disorders in relation to critically injured patients. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 25, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalan, R.; Pavesi, M.; Saliba, F.; Amorós, A.; Fernandez, J.; Holland-Fischer, P.; Sawhney, R.; Mookerjee, R.; Caraceni, P.; Moreau, R. The CLIF Consortium Acute Decompensation score (CLIF-C ADs) for prognosis of hospitalised cirrhotic patients without acute-on-chronic liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gitto, S.; Vitale, G.; Villa, E.; Andreone, P. Update on Alcohol and Viral Hepatitis. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2014, 2, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelena, J.; Altamirano, J.; Abraldes, J.G.; Affo, S.; Morales-Ibanez, O.; Sancho-Bru, P.; Dominguez, M.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Fernandez, J.; Arroyo, V.; et al. Systemic inflammatory response and serum lipopolysaccharide levels predict multiple organ failure and death in alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology 2015, 62, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burak, K.W.; Meeberg, G.A.; Myers, R.P.; Fick, G.H.; Swain, M.G.; Bain, V.G.; Kneteman, N.M.; Hilsden, R.J. Validation of the Model of End-Stage Liver Disease for Liver Transplant Allocation in Alberta: Implications for Future Directions in Canada. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 2016, 1329532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Godfrey, E.L.; Malik, T.H.; Lai, J.C.; Mindikoglu, A.L.; Galvan, N.T.N.; Cotton, R.T.; O’Mahony, C.A.; Goss, J.A.; Rana, A. The decreasing predictive power of MELD in an era of changing etiology of liver disease. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19, 3299–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, G.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Pagliaro, L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: A systematic review of 118 studies. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripoll, C.; Groszmann, R.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Grace, N.; Burroughs, A.; Planas, R.; Escorsell, A.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Makuch, R.; Patch, D.; et al. Hepatic venous pressure gradient predicts clinical decompensation in patients with compensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalafateli, M.; Triantos, C.K.; Nikolopoulou, V.; Burroughs, A. Non-variceal gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with liver cirrhosis: A review. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 2743–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Gonzalez, J.A.; Garcia-Compean, D.; Vazquez-Elizondo, G.; Garza-Galindo, A.; Jaquez-Quintana, J.O.; Maldonado-Garza, H. Nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clinical features, outcomes and predictors of in-hospital mortality. A prospective study. Ann. Hepatol. 2011, 10, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Fernandez, M.; Sanchez-Munoz, D.; Galan-Jurado, M.V.; Larraona, J.L.; Suarez, E.; Lamas, E.; Rodriguez-Hornillo, M.C.; Pabon, M. Influence of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs in gastrointestinal bleeding due to gastroduodenal ulcers or erosions in patients with liver cirrhosis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 29, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo-Espinoza, I.E.; Pérez-Hernández, J.L.; Lajud-Barquín, F.A.; López-Pérez, R.Y.; Santana-Montes, M.O.; Diego-Salazar, P.M.; Higuera de la Tijera, M.F. Variceal versus non-variceal etiology of gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis and related secondary complications. Ann. Hepatol. 2022, 27, 100591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjeorgjievski, M.; Cappell, M.S. Portal hypertensive gastropathy: A systematic review of the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, natural history and therapy. World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 231–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Gomez, M.; Montagnese, S.; Jalan, R. Hepatic encephalopathy in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcar, L.; Semmler, G.; Pomej, K.; Simbrunner, B.; Bauer, D.; Hartl, L.; Jachs, M.; Paternostro, R.; Bucsics, T.; Pinter, M.; et al. Patterns of acute decompensation in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis and course of acute-on-chronic liver failure. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2021, 9, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatitis C virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 392–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, J.; Shao, L.; Xin, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Shi, D.; Jiang, J.; Sun, S.; Jin, L.; et al. Development of diagnostic criteria and a prognostic score for hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Gut 2018, 67, 2181–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Total (n = 622) | SDC (n = 565) | Readmission within 3 Months at First AD | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UDC (n = 29) | Pre ACLF (n = 28) | ||||
| Baseline characteristics at first AD | |||||
| Age (years) | 54.9 11.6 | 54.7 11.3 | 58.9 14.0 | 54.7 13.0 | 0.258 |
| Male (%) | 449 (72.2) | 412 (72.9) | 19 (65.5) | 18 (64.3) | 0.199 |
| Aetiology | 0.197 | ||||
| Virus | 92 (12.3) | 77 (13.6) | 1 (3.4) | 9 (32.1) | |
| Alcohol | 513 (68.8) | 381 (67.4)) | 20 (69.0) | 13 (46.4) | |
| Virus and Alcohol | 75 (10.1) | 55 (9.7) | 2 (6.9) | 5 (17.9) | |
| AIH/PBC | 25 (3.4) | 22 (3.9) | 2 (6.9) | 0 | |
| Cryptogenic | 41 (6.5) | 30 (5.3) | 4 (13.8) | 1 (3.6) | |
| AD | |||||
| Ascites | 202 (32.5) | 185 (32.7) | 9 (31.0) | 8 (28.6) | 0.654 |
| Bacterial infection | 44 (7.1) | 37 (6.5) | 5 (17.2) | 2 (7.1) | 0.108 |
| Varix bleeding | 185 (29.7) | 172 (30.4) | 8 (27.6) | 5 (17.9) | 0.230 |
| Nonvariceal bleeding | 46 (7.4) | 37 (6.5) | 3 (10.3) | 6 (21.4) | 0.011 |
| HE | 49 (7.9) | 40 (7.1) | 5 (17.2) | 4 (14.3) | 0.020 |
| Jaundice | 229 (36.8) | 210 (37.2) | 8 (27.6) | 11 (39.3) | 0.568 |
| CKD | 6 (1.0) | 4 (0.7) | 1 (3.4) | 1 (3.6) | 1.000 |
| DM | 132 (21.2) | 120 (21.2) | 6 (20.7) | 6 (21.4) | 1.000 |
| HTN | 135 (21.7) | 120 (21.2) | 7 (24.1) | 8 (28.6) | 1.000 |
| PE | |||||
| Alcoholism | 322 (51.8) | 296 (52.4) | 11 (37.9) | 15 (53.6) | 0.330 |
| Bacterial infection | 30 (4.8) | 26 (4.6) | 3 (10.3) | 1 (3.6) | 0.418 |
| Varix bleeding | 127 (20.4) | 116 (20.5) | 8 (27.6) | 3 (10.7) | 0.826 |
| Non-variceal bleeding | 32 (5.1) | 25 (4.4) | 2 (6.9) | 5 (17.9) | 0.011 |
| Toxic | 12 (1.9) | 11 (1.9) | 0 | 1 (3.6) | 0.920 |
| Virus activation | 26 (4.2) | 21 (3.7) | 0 | 5 (17.9) | 0.069 |
| Others | 28 (4.5) | 25 (4.4) | 0 | 0 | 0.771 |
| Alcohol intake # | 428 (68.8) | 394 (69.7) | 18 (62.1) | 16 (57.1) | 0.108 |
| Alcohol amount (g/day) | 50.0 (0–100) | 50.0 (0–100) | 50 (0–100) | 19.2 (0–75.0) | 0.261 |
| SIRS, n (%) | 127 (25.2) | 142 (25.1) | 4 (13.8) | 11 (39.3) | 0.845 |
| Laboratory data | |||||
| WBCx103/L | 7.15 (5.00–10.26) | 7.20 (5.00–10.32) | 6.72 (5.10–9.14) | 6.85 (5.50–11.23) | 0.600 |
| Haemoglobin | 10.9 (8.7–12.5) | 10.9 (8.7–12.5) | 10.3 (7.3–12.4) | 10.7 (8.4–12.7) | 0.395 |
| Platelet, mg/L | 103 (70–151) | 105 (70–151) | 111 (76–155) | 76 (54–137) | 0.246 |
| Bilirubin, mg/dL | 3.3 (1.5–7.5) | 3.3 (1.5–7.3) | 3.2 (1.2–5.7) | 10.0 (2.3–15.9) | 0.071 |
| Albumin, g/dL | 2.9 (2.6–3.3) | 2.9 (2.6–3.3) | 2.8 (2.6–3.3) | 2.8 (2.3–3.1) | 0.159 |
| INR | 1.43 (1.25–1.71) | 1.42 (1.24–1.70) | 1.39 (1.25–1.59) | 1.76 (1.54–2.23) | 0.006 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.8 (0.6–1.0) | 0.8 (0.6–1.0) | 0.9 (0.6–1.2) | 0.7 (0.6–1.1) | 0.852 |
| Sodium, mEq/L | 137 (133–140) | 137 (133–140) | 136 (133–139) | 133 (130–137) | 0.021 |
| Child–Pugh score | 9.0 (7.0–10.0) | 9.0 (7.0–10.0) | 9.0 (7.5–11.0) | 10.0 (9.0–11.0) | 0.010 |
| MELD score | 15.6 (11.9–20.4) | 15.5 (11.7–20.2) | 15.0 (10.9–18.5) | 21.5 (15.0–25.5) | 0.017 |
| MELD-Na score | 17.9 (13.6–23.7) | 17.7 (13.3–23.3) | 17.3 (14.0–23.0) | 25.1 (18.5–28.5) | 0.007 |
| MELD-3 score | 14.2 (8.1–20.3) | 14.0 (7.8–19.7) | 14.8 (7.8–19.5) | 21.7 (16.4–25.0) | 0.003 |
| CLIF-C AD | 57.7 (52.3–63.6) | 57.2 (52.1–63.3) | 60.4 (23.0–64.9) | 62.8 (59.2–66.9) | 0.007 |
| Clinical course after first AD | |||||
| Hospitalisation < 3 month | |||||
| 1 | 53 (8.5) | 0 | 28 (96.6) | 25 (89.3) | |
| 2 | 4 (0.6) | 0 | 1 (3.4) | 3 (10.7) | |
| Adverse outcomes | |||||
| 90-day mortality | 36 (5.8) | 22 (3.9) | 2 (6.9) | 12 (42.9) | <0.001 |
| LT | 9 (1.4) | 8 (1.4) | 1 (3.4) | 0 | |
| 1-year mortality | 73 (11.7) | 51 (9.0) | 7 (24.1) | 15 (53.6) | <0.001 |
| LT | 12 (1.9) | 11 (1.9) | 1 (3.4) | 0 | |
| Overall mortality | 90 (14.5) | 65 (11.5) | 9 (31.0) | 16 (57.1) | <0.001 |
| LT | 12 (1.9) | 11 (1.9) | 1 (3.4) | 0 | |
| 90-Day Mortality (%) | p | 1-Year Mortality (%) | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDC | UDC | Pre ACLF | SDC | UDC | Pre ACLF | |||
| MELD, initial | ||||||||
| <15 (n = 282) | 2/262 (0.8) | 1/14 (7.1) | 1/6 (16.7) | 0.003 | 8/262 (3.1) | 2/14 (14.3) | 3/6 (50.0) | <0.001 |
| ≥15 (n = 339) | 23/302 (9.3) | 2/15 (13.3) | 11/22 (50.0) | <0.001 | 54/302 (17.9) | 6/15 (40) | 12/22 (54.5) | <0.001 |
| Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR (95% CI) p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | p-Value | Model 2 | p-Value | |||
| Age | 1.016 (0.992–1.039) | 0.192 | ||||
| Sex | 0.687 (0.387–1.221) | 0.200 | ||||
| Aetiology of LC | 1.095 (0.829–1.448) | 0.522 | ||||
| Ascites | 0.873 (0.482–1.581) | 0.654 | ||||
| Bacterial infection | 1.998 (0.847–4.713) | 0.114 | ||||
| Varix bleeding | 0.675 (0.354–1.286) | 0.232 | ||||
| Non-variceal bleeding | 2.676 (1.219–5.873) | 0.014 | 3.089 (1.376–6.935) | 0.006 | 2.747 (1.236–6.103) | 0.013 |
| HE | 2.461 (1.127–5.375) | 0.024 | 2.858 (1.273–6.388) | 0.011 | 2.532 (1.144–5.602) | 0.022 |
| Jaundice | 0.845 (0.475–1.504) | 0.568 | ||||
| Haemoglobin | 0.962 (0.874–1.058) | 0.422 | ||||
| Platelet | 0.999 (0.995–1.003) | 0.566 | ||||
| Total bilirubin | 1.039 (1.004–1.075) | 0.027 | ||||
| Albumin | 0.656 (0.411–1.048) | 0.078 | ||||
| INR | 1.971 (1.068–3.637) | 0.030 | ||||
| Na | 0.959 (0.918–1.002) | 0.060 | ||||
| Alcohol intake | 0.634 (0.363–1.109) | 0.110 | ||||
| Alcohol amount | 0.998 (0.994–1.002) | 0.277 | ||||
| SIRS | 1.064 (0.573–1.977) | 0.845 | ||||
| CLIF AD score | 1.058 (1.015–1.103) | 0.008 | 1.034 (1.002–1.067) | 0.035 | ||
| MELD-Na | 1.064 (1.019–1.112) | 0.005 | 1.075 (1.027–1.125) | 0.002 | ||
| Pre ACLF (n = 28) | ACLF (n = 124) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline characteristics at first AD | |||
| Age (years) | 54.7 13.0 | 53.6 10.2 | 0.676 |
| Male (%) | 18 (64.3) | 103 (83.1) | 0.026 |
| Aetiology | 0.042 | ||
| Virus | 4 (14.3) | 5 (4.0) | |
| Alcohol | 20 (71.4) | 99 (79.8) | |
| Virus and Alcohol | 3 (10.7) | 13 (1.5) | |
| AIH/PBC | 0 | 1 (0.8) | |
| Cryptogenic | 1 (3.6) | 6 (4.8) | |
| AD | |||
| Ascites | 8 (28.6) | 32 (25.8) | 0.765 |
| Bacterial infection | 2 (7.1) | 14 (11.3) | 0.520 |
| Varix bleeding | 5 (17.9) | 28 (22.6) | 0.585 |
| Non-variceal bleeding | 6 (21.4) | 8 (6.5) | 0.014 |
| HE | 4 (14.3) | 38 (30.6) | 0.081 |
| Jaundice | 11 (39.3) | 61 (49.2) | 0.345 |
| CKD | 1 (3.6) | 11 (8.9) | 1.000 |
| DM | 6 (21.4) | 28 (22.6) | 1.000 |
| HTN | 8 (28.6) | 27 (21.8) | 1.000 |
| PE | |||
| Alcoholism | 15 (53.6) | 84 (67.7) | 0.157 |
| Bacterial infection | 1 (3.6) | 13 (10.5) | 0.255 |
| Varix bleeding | 3 (10.7) | 19 (15.3) | 0.533 |
| Non-variceal bleeding | 5 (17.9) | 7 (5.6) | 0.031 |
| Toxic | 1 (3.6) | 1 (0.8) | 0.248 |
| Virus activation | 5 (17.9) | 1 (0.8) | <0.001 |
| Others | 0 | 2 (1.6) | 0.500 |
| Alcohol intake # | 16 (57.1) | 101 (81.5) | 0.006 |
| Alcohol amount (g/day) | 19.2 (0–75.0) | 75 (35.0–142.5) | 0.006 |
| SIRS, n (%) | 11 (39.3) | 47 (37.9) | 0.892 |
| Laboratory data | |||
| WBCx103/L | 6.85 (5.50–11.23) | 9.56 (6.84–13.12) | 0.029 |
| Haemoglobin | 10.7 (8.4–12.7) | 10.3 (8.1–12.2) | 0.275 |
| Platelet, mg/L | 76 (54–137) | 92 (59–142) | 0.358 |
| Bilirubin, mg/dL | 10.0 (2.3–15.9) | 7.8 (2.9–19.6) | 0.888 |
| Albumin, g/dL | 2.8 (2.3–3.1) | 2.7 (2.2–3.0) | 0.499 |
| INR | 1.76 (1.54–2.23) | 1.84 (1.36–2.76) | 0.408 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.7 (0.6–1.1) | 2.1 (1.2–3.0) | <0.001 |
| Sodium, mEq/L | 133 (130–137) | 133 (130–137) | 0.973 |
| Child–Pugh score | 10.0 (9.0–11.0) | 11.0 (9.0–12.0) | 0.083 |
| MELD score | 21.5 (15.0–25.5) | 28.0 (22.1–34.0) | <0.001 |
| MELD-Na score | 25.1 (18.5–28.5) | 30.4 (25.0–35.7) | <0.001 |
| ACLF grade | 0.461 | ||
| 1 | 9 (32.1) | 56 (45.2) | |
| 2 | 15 (53.6) | 45 (36.3) | |
| 3 | 4 (14.3) | 23 (18.5) | |
| Clinical course after first AD | |||
| Hospitalisation < 3 month | <0.001 | ||
| 1 | 25 (89.3) | 3 (2.4) | |
| 2 | 3 (10.7) | 1 (0.8) | |
| Adverse events | |||
| 90-day mortality | 12 (42.9) | 30 (24.2) | 0.047 |
| LT | 0 | 6 (4.8) | |
| 1-year mortality | 15 (53.6) | 33 (26.6) | 0.006 |
| LT | 0 | 6 (4.8) | |
| Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | p-Value | Model 2 | p-Value | |||
| Age | 0.998 (0.966–1.032) | 0.925 | ||||
| Sex | 0.681 (0.308–1.506 | 0.342 | ||||
| Aetiology of LC | 0.012 | 0.001 | 0.005 | |||
| Alcohol | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Virus and Alcohol | 2.706 (0.930–7.878) | 0.068 | 3.235 (1.056–9.970) | 0.040 | 2.964 (0.990–8.876) | 0.052 |
| Virus | 3.559 (1.471–8.614) | 0.005 | 5.535 (2.125–14.419) | <0.001 | 4.294 (1.719–10.724) | 0.002 |
| Ascites | 0.825 (0.327–1.906) | 0.652 | ||||
| Bacterial infection | 1.011 (0.232–4.406) | 1.011 | ||||
| Varix bleeding | 0.500 (0.187–1.336) | 0.167 | ||||
| Non-variceal bleeding | 3.777 (1.449–9.846) | 0.007 | 5.536 (1.763–17.380) | 0.003 | 3.420 (1.165–10.038) | 0.025 |
| HE | 2.033 (0.676–6.116) | 0.207 | ||||
| Jaundice | 1.116 (0.513–2.426) | 0.782 | ||||
| CKD | 4.363 (0.493–38.651) | 0.186 | ||||
| DM | 1.013 (0.402–2.552) | 0.978 | ||||
| HTN | 1.471 (0.633–3.417) | 0.370 | ||||
| Haemoglobin | 1.032 (0.900–1.183) | 0.652 | ||||
| Platelet | 0.996 (0.989–1.002) | 0.206 | ||||
| Total bilirubin | 1.087 (1.045–1.130) | <0.001 | ||||
| Albumin | 0.494 (0.250–0.975) | 0.042 | ||||
| INR | 4.459 (2.144–9.274) | <0.001 | ||||
| Cr | 0.867 (0.247–3.047) | 0.824 | ||||
| Na | 0.946 (0.893–1.002) | 0.058 | ||||
| Alcohol intake | 0.583 (0.270–1.256) | 0.168 | ||||
| Alcohol amount | 0.996 (0.990–1.002) | 0.230 | ||||
| SIRS | 1.985 (0.909–4.336) | 0.085 | ||||
| MELD-Na | 1.154 (0.179–1.234) | <0.001 | 1.198 (1.108–1.295) | <0.001 | ||
| CLIP AD score | 1.058 (1.015–1.103) | 0.008 | 1.072 (1.024–1.122) | 0.003 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.-E.; Song, D.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Yoon, E.L.; Kang, S.H.; Jung, Y.-K.; Kwon, J.H.; Lee, S.W.; Han, S.K.; et al. The Clinical Courses and Prognosis of Cirrhotic Patients after First Acute Decompensation: Prospective Cohort Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14010014
Kim JH, Kim S-E, Song DS, Kim HY, Yoon EL, Kang SH, Jung Y-K, Kwon JH, Lee SW, Han SK, et al. The Clinical Courses and Prognosis of Cirrhotic Patients after First Acute Decompensation: Prospective Cohort Study. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jung Hee, Sung-Eun Kim, Do Seon Song, Hee Yeon Kim, Eileen L. Yoon, Seong Hee Kang, Young-Kul Jung, Jung Hyun Kwon, Sung Won Lee, Seul Ki Han, and et al. 2024. "The Clinical Courses and Prognosis of Cirrhotic Patients after First Acute Decompensation: Prospective Cohort Study" Diagnostics 14, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14010014
APA StyleKim, J. H., Kim, S.-E., Song, D. S., Kim, H. Y., Yoon, E. L., Kang, S. H., Jung, Y.-K., Kwon, J. H., Lee, S. W., Han, S. K., Chang, Y., Jeong, S. W., Yoo, J. J., Jin, Y.-J., Cheon, G. J., Kim, B. S., Seo, Y. S., Kim, H., Park, J. W., ... Kim, D. J., on behalf of the Korean Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure (KACLiF) Study Group. (2024). The Clinical Courses and Prognosis of Cirrhotic Patients after First Acute Decompensation: Prospective Cohort Study. Diagnostics, 14(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14010014









