Evaluation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT-3) Protein Expression in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Cases in Hospital USM
Abstract
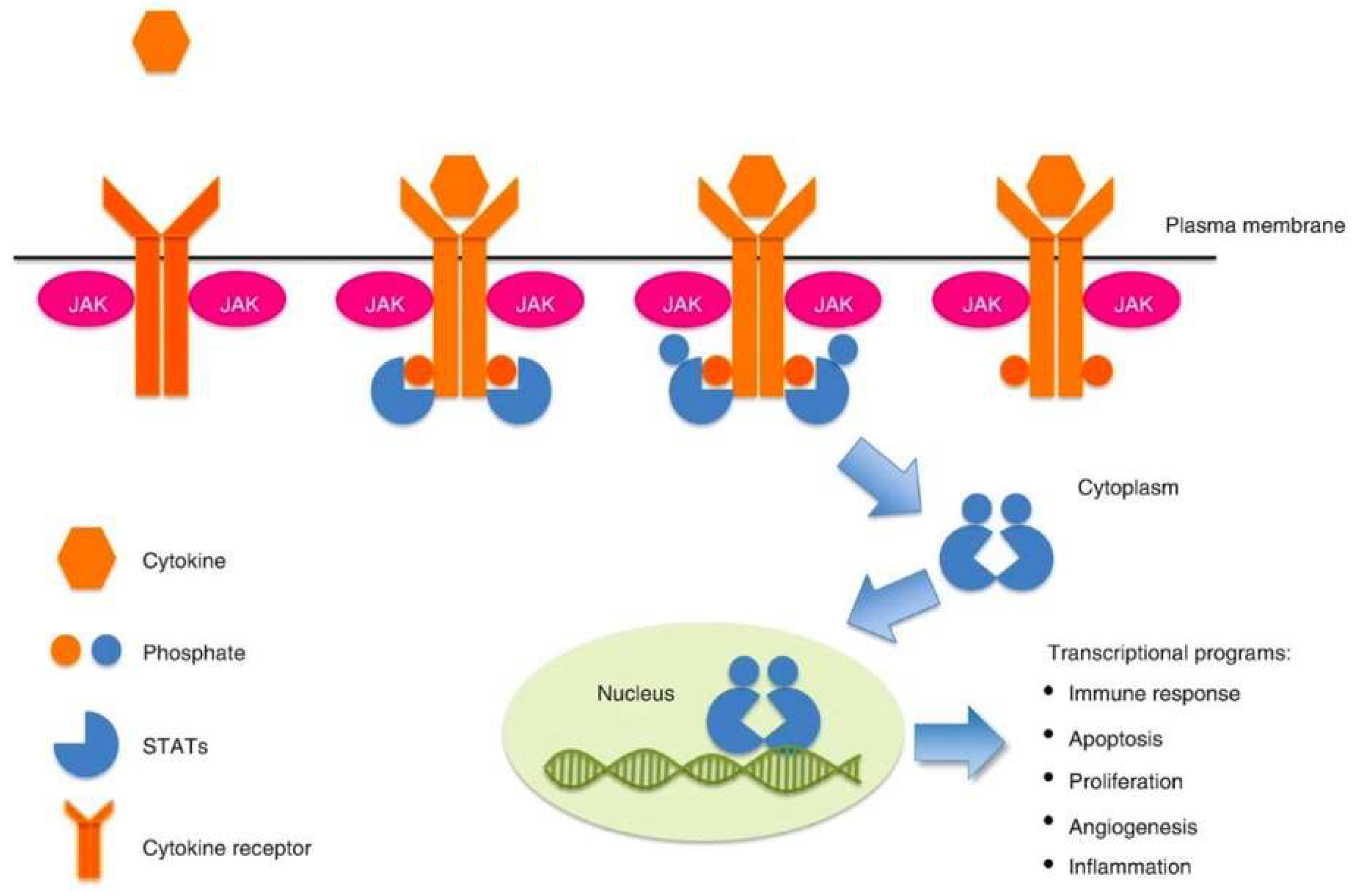
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Menet, C.J.; Van Rompaey, L.; Geney, R. Advances in the discovery of selective JAK inhibitors. Prog. Med. Chem. 2013, 52, 153–223. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Abbas, A.; Aster, J. Robbins Basic Pathology, 10th ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 463–474. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffbrand, A.V.; Moss, P.A.H. Hoffbrand’s Essential Haematology, 7th ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; p. 634. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, N.; Balko, M. Role of JAK-STAT Pathway in Cancer Signaling. Predict. Biomark. Oncol. Appl. Precis. Med. 2018, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, L.M.; Gandhi, M.K. Deregulated JAK/STAT signalling in lymphomagenesis, and its implications for the development of new targeted therapies. Blood Rev. 2015, 29, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.J.; Putoczki, T. Jak-stat signalling pathway in cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, K.B.; Rui, L. Stat3 activation and oncogenesis in lymphoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Man, Q.W.; Huo, F.Y.; Gao, X.; Lin, H.; Li, S.R.; Wang, J.; Su, F.C.; Cai, L.; Shi, Y.; et al. STAT3 pathway in cancers: Past, present, and future. MedComm 2022, 3, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rébé, C.; Végran, F.; Berger, H.; Ghiringhelli, F. STAT3 activation: A key factor in tumor immunoescape. Jak-Stat 2013, 2, e23010. [Google Scholar]
- Derenzini, E.; Younes, A. Targeting the JAK-STAT pathway in lymphoma: A focus on pacritinib. Drug Eval. 2013, 22, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harb, O.A.; Kaf, R.M.; Taha, H.F.; Ahmed, R.Z.; Mandour, D.; Al Attar, A.Z.; Fathy, A.; Almoregy, A.S.; Osman, G.; Gertallah, L.M. Prognostic values and clinical implications of programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), fork head transcription factor P-1 (FOXP-1) and signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT-3) expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL); an immu. Surg. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J.; Vardiman, J.W. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; Volume 108. [Google Scholar]
- Mozaheb, Z. Epidemiology of Lymphoid Malignancy in Asia. Epidemiol. Insights 2012, 16, 326–342. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda-Filho, A.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Marcos-Gragera, R.; Steliarova-Foucher, E.; Bray, F. Global patterns and trends in the incidence of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Causes Control. 2019, 30, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manan, A.A.; Basri, H.; Kaur, N.; Abd Rahman, S.Z.; Amir, P.N.; Ali, N.; Raman, S.; Bahtiar, B.; Mustafa Ramdzuan, N.S.; Syed Soffian, S.S.; et al. Malaysia National Cancer Registry Report (MNCRR) 2012–2016. Natl. Cancer Regist. 2019, 42–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ohgami, R.S.; Ma, L.; Monabati, A.; Zehnder, J.L.; Arber, D.A. STAT3 mutations are present in aggressive B-cell lymphomas including a subset of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas with CD30 expression. Haematologica 2014, 99, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Song, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, J. High nuclear expression of STAT3 is associated with unfavorable prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2011, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ok, C.Y.; Chen, J.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Tzankov, A.; Manyam, G.C.; Li, L.; Visco, C.; Montes, S.; Dybkaer, K.; Chiu, A.; et al. Clinical implications of phosphorylated STAT3 expression in de Novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5113–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.J.; Yang, J.M.; Lee, J.O.; Lee, J.S.; Paik, J.H. Clinicopathologic implication of PD-L1 and phosphorylated STAT3 expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seffens, A.; Herrera, A.; Tegla, C.; Buus, T.B.; Hymes, K.B.; Ødum, N.; Geskin, L.J.; Koralov, S.B. STAT3 dysregulation in mature T and NK cell lymphomas. Cancers 2019, 11, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crescenzo, R.; Abate, F.; Lasorsa, E.; Tabbo, F.; Gaudiano, M.; Chiesa, N.; Di Giacomo, F.; Spaccarotella, E.; Barbarossa, L.; Ercole, E.; et al. Convergent mutations and kinase fusions lead to oncogenic STAT3 activation in anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 516–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liang, L.; Li, D.; Nong, L.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhang, B.; Li, T. JAK3/STAT3 oncogenic pathway and PRDM1 expression stratify clinicopathologic features of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 3219–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, H.Y.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Hwang, J.; Lee, S.; Kwak, S.H.; Park, K.S.; Yoo, H.Y.; Kim, W.S.; et al. Genetic alterations of JAK/STAT cascade and histone modification in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma nasal type. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17764–17776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.L.; Nairismägi, M.L.; Laurensia, Y.; Lim, J.Q.; Tan, J.; Li, Z.M.; Pang, W.L.; Kizhakeyil, A.; Wijaya, G.C.; Huang, D.C.; et al. Oncogenic activation of the STAT3 pathway drives PD-L1 expression in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 1146–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Drennan, A.C.; Kimpara, S.; Rumball, I.; Selzer, C.; Cameron, H.; Kellicut, A.; et al. Gene regulation and suppression of type i interferon signaling by STAT3 in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E498–E505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Score | Extent of Markers Expression | Intensity of Positive Score |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No positive cells/HPF | Nil |
| 1 | <10% positive cells/HPF | Weak |
| 2 | 10–30% positive cells/HPF | Moderate |
| 3 | >30% positive cells/HPF | Strong |
| n | (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age Group (years) | ≤60 | 54 (mean) | 51 | (53.7) |
| >60 | 44 | (46.3) | ||
| Ethnic group | Malay | 86 | (90.5) | |
| Non-Malay | ||||
| - Chinese | 7 | (7.4) | ||
| - Indian | 1 | (1.1) | ||
| - Others | 1 | (1.1) | ||
| Gender | Female | 33 | (34.7) | |
| Male | 62 | (65.3) | ||
| Site | Nodal | 30 | (31.6) | |
| Extra nodal | 47 | (49.5) | ||
| Nodal and extra nodal | 18 | (18.9) | ||
| Tumour size (cm) | <10 | 7 (median) | 60 | (63.2) |
| ≥10 | 35 | (36.8) | ||
| B symptoms | Absent | 41 | (43.2) | |
| Present | 54 | (56.8) | ||
| LDH level (U/L) | <480 (Normal) | 720 (median) | 31 | (32.6) |
| ≥480 (Elevated) | 64 | (67.4) | ||
| Stage of disease | Stage I–II (Early) | 28 | (29.5) | |
| Stage III–IV (Advanced) | 67 | (70.5) | ||
| n | (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | T/Natural Killer cells | 7 | (7.4) |
| B cells | 88 | (92.6) | |
| Subtypes | Indolent B cell | 14 | (14.7) |
| Follicular lymphoma | 4 | (4.2) | |
| Mantle cell lymphoma | 3 | (3.2) | |
| Extra nodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma | 3 | (3.2) | |
| Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma | 1 | (1.1) | |
| Primary cutaneous follicular centre lymphoma | 1 | (1.1) | |
| SLL | 2 | (2.1) | |
| Aggressive B cell DLBCL group | 74 61 | (77.9) (64.3) | |
| - DLBCL-NGCB | 20 | (21.1) | |
| - DLBCL-GCB | 15 | (15.8) | |
| - DLBCL NOS | 17 | (17.9) | |
| - DLBCL double expressions | 7 | (7.4) | |
| - DLBCL triple expressions | 2 | (2.1) | |
| Others aggressive B cell | 13 | (14.0) | |
| - PMBL | 4 | (4.2) | |
| - Primary DLBCL of CNS | 3 | (3.2) | |
| - EBV-positive DLBCL, NOS | 1 | (1.1) | |
| - T cell/histiocyte- rich B cell lymphoma | 1 | (1.1) | |
| - B-cell lymphoma, unclassifiable, with features intermediate between diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and classic Hodgkin lymphoma | 1 | (1.1) | |
| - Plasmablastic lymphoma | 1 | (1.1) | |
| - B-lymphoblastic leukaemia/lymphoma | 1 | (1.1) | |
| - Burkitt Lymphoma | 1 | (1.1) | |
| T cell NHL | 7 | (7.4) | |
| T-lymphoblastic leukaemia/lymphoma | 3 | (3.2) | |
| ALCL, ALK-positive | 3 | (3.2) | |
| Extra nodal Natural Killer/T cell lymphoma, nasal type | 1 | (1.1) | |
| Subtypes | STAT-3 Protein Expression | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | ||
| n (%) | n (%) | ||
| B cell NHL | Indolent B cell | 5 (5.3) | 9 (9.5) |
| Follicular lymphoma | 2 (2.1) | 2 (2.1) | |
| Mantle cell lymphoma | 0 (0.0) | 3 (3.2) | |
| Extra nodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma | 1 (1.1) | 2 (2.1) | |
| Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma | 1 (1.1) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Primary cutaneous follicular centre lymphoma | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.1) | |
| SLL | 1 (1.1) | 1 (1.1) | |
| Aggressive B cell | 13 (13.7) | 61 (64.2) | |
| 1. DLBCL group | 9 (9.5) | 52 (54.7) | |
| - DLBCL-NGCB | 1 (1.1) | 19 (20.0) | |
| - DLBCL-GCB | 4 (4.2) | 11 (11.6) | |
| - DLBCL NOS | 2 (2.1) | 15 (15.8) | |
| - DLBCL double expressions | 2 (2.1) | 5 (5.3) | |
| - DLBCL triple expressions | 0 (0.0) | 2 (2.1) | |
| 2. Others aggressive B cell | 4 (4.2) | 9 (9.5) | |
| - PMBL | 1 (1.1) | 3 (3.2) | |
| - Primary DLBCL of CNS | 1 (1.1) | 2 (2.1) | |
| - EBV-positive DLBCL, NOS | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.1) | |
| - T cell/histiocyte- rich B cell lymphoma | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.1) | |
| - B-cell lymphoma, unclassifiable, with features intermediate between diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and classic Hodgkin lymphoma | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.1) | |
| - Plasmablastic lymphoma | 1 (1.1) | 0 (0.0) | |
| - B-lymphoblastic leukaemia/lymphoma | 1 (1.1) | 0 (0.0) | |
| - Burkitt Lymphoma | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.1) | |
| T cell NHL | T cell | 2 (2.1) | 5 (5.3) |
| T-lymphoblastic leukaemia/lymphoma | 0 (0.0) | 3 (3.2) | |
| ALCL, ALK-positive | 2 (2.1) | 1 (1.1) | |
| Extra nodal Natural Killer/T cell lymphoma, nasal type | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.1) | |
| Total | 95 (100.0) | 20 (21.1) | 75 (78.9) |
| STAT-3 Protein Expression | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | p Value | ||||
| n | (%) | n | (%) | |||
| Age group (years) | ≤60 | 11 | (55.0) | 40 | (53.3) | 0.894 a |
| >60 | 9 | (45.0) | 35 | (46.7) | ||
| Ethnic group | Malay | 18 | (90.0) | 68 | (90.7) | >0.950 b |
| Non-Malay | 2 | (10.0) | 7 | (9.3) | ||
| Gender | Female | 7 | (35.0) | 26 | (34.7) | 0.978 a |
| Male | 13 | (65.0) | 49 | (65.3) | ||
| Site | Nodal | 3 | (15.0) | 27 | (36.0) | 0.196 a |
| Extra nodal | 12 | (60.0) | 35 | (46.7) | ||
| Nodal and extra nodal | 5 | (25.0) | 13 | (17.3) | ||
| Tumour size (cm) | <10 | 10 | (50.0) | 50 | (66.7) | 0.170 a |
| ≥10 | 10 | (50.0) | 25 | (33.3) | ||
| B symptoms | Absent | 11 | (55.0) | 30 | (40.0) | 0.229 a |
| Present | 9 | (45.0) | 45 | (60.0) | ||
| LDH level (U/L) | <480 (Normal) | 6 | (30.0) | 25 | (33.3) | 0.778 a |
| ≥480 (Elevated) | 14 | (70.0) | 50 | (66.7) | ||
| Stage of disease | Stage I-II (Early) | 7 | (35.0) | 21 | (28.0) | 0.542 a |
| Stage III-IV (Advanced) | 13 | (65.0) | 54 | (72.0) | ||
| STAT-3 Protein Expression | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | p Value | ||||
| n | (%) | n | (%) | |||
| Type | T/Natural Killer cells | 2 | (10.0) | 5 | (6.7) | 0.636 b |
| B | 18 | (90.0) | 70 | (93.3) | ||
| Subtype | Indolent B cell | 5 | (25.0) | 9 | (12.0) | 0.214 b |
| Aggressive B cell | 13 | (65.0) | 61 | (81.3) | ||
| T/Natural Killer cells | 2 | (10.0) | 5 | (6.7) | ||
| B cell NHL | DLBCL group | 9 | (50) | 52 | (74.3) | 0.046 a |
| Others B cell NHL | 9 | (50) | 18 | (25.7) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muhamad, I.R.; Che Ibrahim, N.B.; Hussain, F.A. Evaluation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT-3) Protein Expression in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Cases in Hospital USM. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091649
Muhamad IR, Che Ibrahim NB, Hussain FA. Evaluation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT-3) Protein Expression in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Cases in Hospital USM. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(9):1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091649
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuhamad, Izyan Rifhana, Noorul Balqis Che Ibrahim, and Faezahtul Arbaeyah Hussain. 2023. "Evaluation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT-3) Protein Expression in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Cases in Hospital USM" Diagnostics 13, no. 9: 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091649
APA StyleMuhamad, I. R., Che Ibrahim, N. B., & Hussain, F. A. (2023). Evaluation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT-3) Protein Expression in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Cases in Hospital USM. Diagnostics, 13(9), 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091649





