Indications for and Outcomes of Three Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Approaches for the Decompression of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.2. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
3. Results
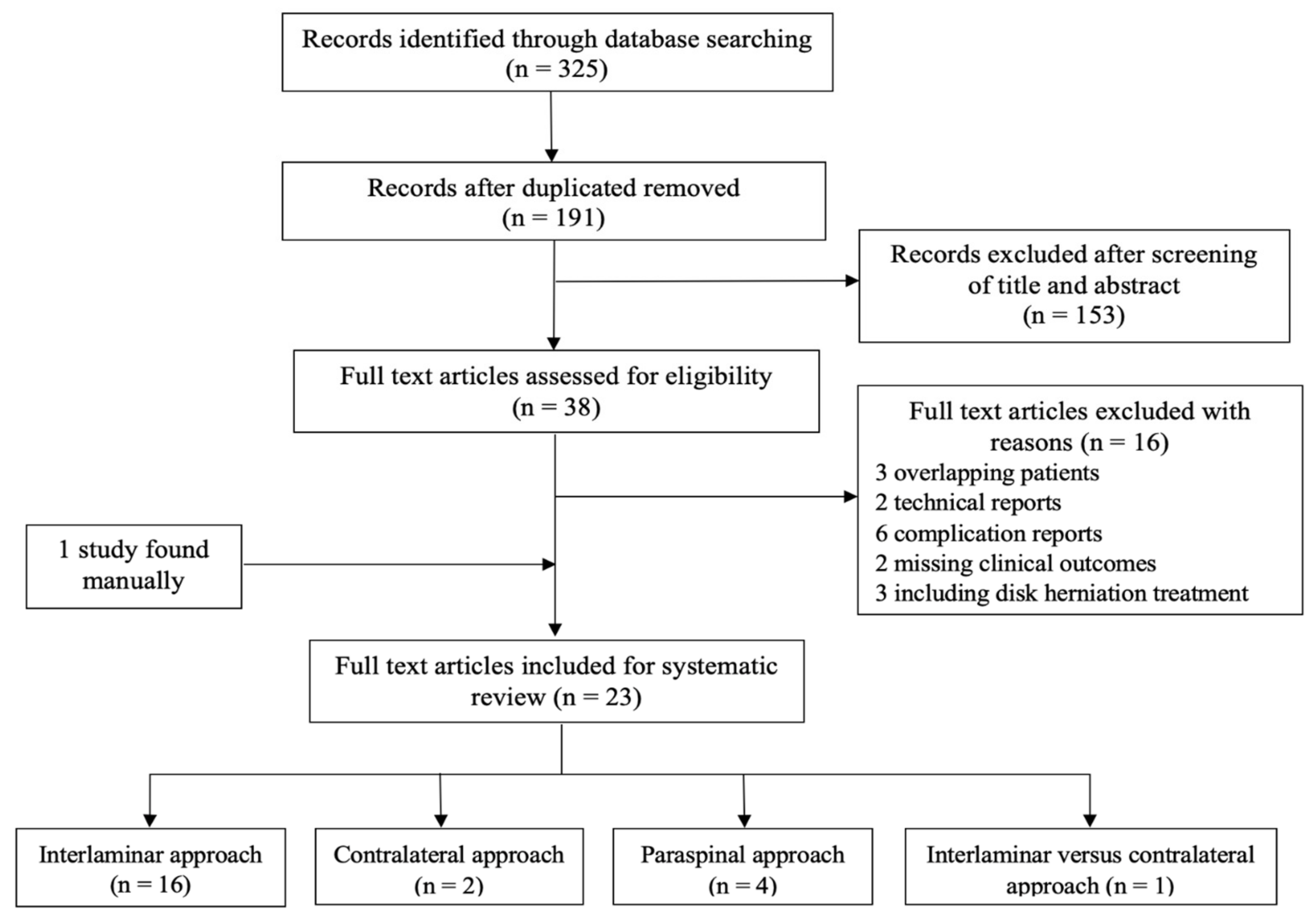
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Surgical and Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalichman, L.; Cole, R.; Kim, D.H.; Li, L.; Suri, P.; Guermazi, A.; Hunter, D.J. Spinal stenosis prevalence and association with symptoms: The Framingham Study. Spine J. 2009, 9, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, G.C.; Ferreira, P.H.; Yoo, R.I.; Harris, I.A.; Pinheiro, M.B.; Koes, B.W.; van Tulder, M.W.; Rzewuska, M.; Maher, C.G.; Ferreira, M.L. Surgical options for lumbar spinal stenosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 11, CD012421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobbs, R.J.; Li, J.; Sivabalan, P.; Raley, D.; Rao, P.J. Outcomes after decompressive laminectomy for lumbar spinal stenosis: Comparison between minimally invasive unilateral laminectomy for bilateral decompression and open laminectomy: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2014, 21, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truumees, E. Spinal stenosis: Pathophysiology, clinical and radiologic classification. Instr. Course Lect. 2005, 54, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guiot, B.H.; Khoo, L.T.; Fessler, R.G. A minimally invasive technique for decompression of the lumbar spine. Spine 2002, 27, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbary, K.; Kim, J.S.; Park, C.W.; Jun, S.G.; Hwang, J.H. Biportal Endoscopic Decompression of Exiting and Traversing Nerve Roots Through a Single Interlaminar Window Using a Contralateral Approach: Technical Feasibilities and Morphometric Changes of the Lumbar Canal and Foramen. World Neurosurg. 2018, 117, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltse, L.L.; Spencer, C.W. New uses and refinements of the paraspinal approach to the lumbar spine. Spine 1988, 13, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.C.; Kim, J.S.; Ryu, K.S.; Kang, B.U.; Ahn, Y.; Lee, S.H. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for L5-S1 disc herniation: Transforaminal versus interlaminar approach. Pain Phys. 2013, 16, 547–556. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar]
- Wewers, M.E.; Lowe, N.K. A critical review of visual analogue scales in the measurement of clinical phenomena. Res. Nurs. Health 1990, 13, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbank, J.C.; Couper, J.; Davies, J.B.; O’Brien, J.P. The Oswestry low back pain disability questionnaire. Physiotherapy 1980, 66, 271–273. [Google Scholar]
- Macnab, I. Negative disc exploration. An analysis of the causes of nerve-root involvement in sixty-eight patients. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1971, 53, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, H.M. Irrigation endoscopic decompressive laminotomy. A new endoscopic approach for spinal stenosis decompression. Spine J. 2015, 15, 2282–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, Y.K.; Park, C.W.; Jun, S.G.; Park, J.H.; Tse, A.C. Comparative Cohort Study for Expansion of Lateral Recess and Facet Joint Injury after Biportal Endoscopic Ipsilateral Decompression and Contralateral Decompression. Asian Spine J. 2022, 16, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, W.; Liao, Z.; Chen, C.; Feng, X.; Ke, W.; Wang, B.; Li, S.; Wang, K.; Zeng, X.; Wu, X.; et al. Clinical Outcomes of Uniportal and Biportal Lumbar Endoscopic Unilateral Laminotomy for Bilateral Decompression in Patients with Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Retrospective Pair-Matched Case-Control Study. World Neurosurg. 2022, 161, e134–e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Z.; Shibayama, M.; Nakamura, S.; Yamada, M.; Kawai, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Yoshimatsu, H.; Kuraishi, K.; Hoshi, N.; Miura, Y.; et al. Clinical Comparison of Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Laminectomy versus Microendoscopic Laminectomy for Single-Level Laminectomy: A Single-Center, Retrospective Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2021, 148, e581–e588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aygun, H.; Abdulshafi, K. Unilateral Biportal Endoscopy Versus Tubular Microendoscopy in Management of Single Level Degenerative Lumbar Canal Stenosis: A Prospective Study. Clin. Spine Surg. 2021, 34, E323–E328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Park, J.; Jang, H.S.; Heo, Y.W.; Han, H.; Kim, H.J.; Chang, B.S.; Lee, C.K.; Yeom, J.S. Biportal endoscopic versus microscopic lumbar decompressive laminectomy in patients with spinal stenosis: A randomized controlled trial. Spine J. 2020, 20, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pao, J.L.; Lin, S.M.; Chen, W.C.; Chang, C.H. Unilateral biportal endoscopic decompression for degenerative lumbar canal stenosis. J. Spine Surg. 2020, 6, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, W.K.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, D.J.; Park, E.J.; Heo, J. Clinical and radiological outcomes between biportal endoscopic decompression and microscopic decompression in lumbar spinal stenosis. J. Orthop. Sci. 2020, 25, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Choi, S.H.; Shim, D.M.; Lee, I.S.; Oh, Y.K.; Woo, Y.H. Advantages of New Endoscopic Unilateral Laminectomy for Bilateral Decompression (ULBD) over Conventional Microscopic ULBD. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 12, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Jung, S.B. Percutaneous Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Spine Surgery Using a 30-Degree Arthroscope in Patients With Severe Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Technical Note. Clin. Spine Surg. 2019, 32, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.; Park, S.Y.; Kang, C.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Suh, S.W. Is biportal technique/endoscopic spinal surgery satisfactory for lumbar spinal stenosis patients?: A prospective randomized comparative study. Medicine 2019, 98, e15451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, D.H.; Lee, D.C.; Park, C.K. Comparative analysis of three types of minimally invasive decompressive surgery for lumbar central stenosis: Biportal endoscopy, uniportal endoscopy, and microsurgery. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 46, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.J.; Kim, J.E. Efficacy of Biportal Endoscopic Spine Surgery for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2019, 11, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Choi, D.J. Unilateral biportal endoscopic decompression by 30° endoscopy in lumbar spinal stenosis: Technical note and preliminary report. J. Orthop. 2018, 15, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, D.H.; Quillo-Olvera, J.; Park, C.K. Can Percutaneous Biportal Endoscopic Surgery Achieve Enough Canal Decompression for Degenerative Lumbar Stenosis? Prospective Case-Control Study. World Neurosurg. 2018, 120, e684–e689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torudom, Y.; Dilokhuttakarn, T. Two Portal Percutaneous Endoscopic Decompression for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Preliminary Study. Asian Spine J. 2016, 10, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eum, J.H.; Heo, D.H.; Son, S.K.; Park, C.K. Percutaneous biportal endoscopic decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: A technical note and preliminary clinical results. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 24, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, D.H.; Kim, J.S.; Park, C.W.; Quillo-Olvera, J.; Park, C.K. Contralateral Sublaminar Endoscopic Approach for Removal of Lumbar Juxtafacet Cysts Using Percutaneous Biportal Endoscopic Surgery: Technical Report and Preliminary Results. World Neurosurg. 2019, 122, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.K.; Son, S.K.; Park, W.W.; Choi, S.H.; Jung, D.Y.; Kim, D.H. Unilateral Biportal Endoscopy for Decompression of Extraforaminal Stenosis at the Lumbosacral Junction: Surgical Techniques and Clinical Outcomes. Neurospine 2021, 18, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, D.H.; Sharma, S.; Park, C.K. Endoscopic Treatment of Extraforaminal Entrapment of L5 Nerve Root (Far Out Syndrome) by Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Approach: Technical Report and Preliminary Clinical Results. Neurospine 2019, 16, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Choi, D.J.; Park, E.J. Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Foraminal Decompression Using Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Spine Surgery for Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2018, 10, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, D.J.; Lee, K.Y.; Hwang, S.J. Extraforaminal approach of biportal endoscopic spinal surgery: A new endoscopic technique for transforaminal decompression and discectomy. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2018, 28, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Choi, D.J.; Park, E.J.J.; Lee, H.J.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, M.C.; Oh, J.S. Biportal Endoscopic Spinal Surgery for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. Asian Spine J. 2019, 13, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Choi, D.J. Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Decompression by 30° Arthroscopy in Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Minimum 2-Year Follow-up. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2018, 10, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abumi, K.; Panjabi, M.M.; Kramer, K.M.; Duranceau, J.; Oxland, T.; Crisco, J.J. Biomechanical evaluation of lumbar spinal stability after graded facetectomies. Spine 1990, 15, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenis, L.G.; An, H.S. Spine update. Lumbar foraminal stenosis. Spine 2000, 25, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavin, D.; Casha, S.; Wiebe, S.; Feasby, T.E.; Clark, C.; Isaacs, A.; Holroyd-Leduc, J.; Hurlbert, R.J.; Quan, H.; Nataraj, A.; et al. Lumbar Fusion for Degenerative Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosurgery 2017, 80, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourtaheri, S.; Issa, K.; Lord, E.; Ajiboye, R.; Drysch, A.; Hwang, K.; Faloon, M.; Sinha, K.; Emami, A. Paraspinal Muscle Atrophy After Lumbar Spine Surgery. Orthopedics 2016, 39, e209–e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Jeong, J.H.; Cho, H.G.; Chang, B.S.; Lee, C.K.; Yeom, J.S. Comparative observational study of surgical outcomes of lumbar foraminal stenosis using minimally invasive microsurgical extraforaminal decompression alone versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion: A prospective cohort study. Eur. Spine J. 2015, 24, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.B.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, Y.; Kim, J.M. Risk factor for unsatisfactory outcome after lumbar foraminal and far lateral microdecompression. Spine 2006, 31, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, M.; Iesato, N.; Terashima, Y.; Tanimoto, K.; Oshigiri, T.; Emori, M.; Teramoto, A.; Yamashita, T. Mid-term Clinical Results of Microendoscopic Decompression for Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis. Spine Surg. Relat. Res. 2019, 3, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kang, J.H.; Srikantha, U.; Jang, I.T.; Oh, S.H. Extraforaminal compression of the L-5 nerve root at the lumbosacral junction: Clinical analysis, decompression technique, and outcome. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2014, 20, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, L.T.; Fessler, R.G. Microendoscopic decompressive laminotomy for the treatment of lumbar stenosis. Neurosurgery 2002, 51, S146–S154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pao, J.L.; Chen, W.C.; Chen, P.Q. Clinical outcomes of microendoscopic decompressive laminotomy for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur. Spine J. 2009, 18, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Menéndez, M.; Bravo-Ricoy, J.A.; Casal-Moro, R.; Hernández-Blanco, M.; Jorge-Barreiro, F.J. Midterm outcome after microendoscopic decompressive laminotomy for lumbar spinal stenosis: 4-year prospective study. Neurosurgery 2009, 65, 100–110; discussion 110; quiz A112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.; Kang, H.Y.; Modi, H.N.; Prada, N.; Nicolau, R.J.; Joh, J.Y.; Pan, W.J.; Lee, S.H. Risk of developing seizure after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy. J. Spinal. Disord. Tech. 2011, 24, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.H.; Kim, S.K.; Suh, D.W.; Lee, S.C. Novel Instruments for Percutaneous Biportal Endoscopic Spine Surgery for Full Decompression and Dural Management: A Comparative Analysis. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Choi, D.J.; Park, E.J. Risk Factors and Options of Management for an Incidental Dural Tear in Biportal Endoscopic Spine Surgery. Asian Spine J. 2020, 14, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Study | Year | Study Design | Number of Patients/Levels Operated | Male/Female | Age (Years) | Indication | Lumbar Segment | Follow-Up (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hua et al. [16] | 2022 | Retrospective comparative study | 36/36 | 15/21 | 57.3 ± 10.9 | Single-level lumbar spinal canal stenosis | L2-3:1 L3-4:1 L4-5:27 L5-S1:7 | 12 |
| Ito et al. [17] | 2021 | Retrospective comparative study | 42/42 | 16/28 | 66.3 ± 12.3 | Single-level lumbar spinal canal stenosis | L3-4:13 L4-5:24 L5-S1:5 | 6 |
| Aygun et al. [18] | 2021 | Prospective comparative study | 77/77 | 44/33 | 64.64 ± 10.9 | Single-level lumbar spinal canal stenosis | N/A | 24 |
| Park et al. [19] | 2020 | Randomized controlled trial | 32/32 | 13/19 | 66.2 | Single-level lumbar spinal stenosis | L2-3:2 L3-4:5 L4-5:25 | 12 |
| Pao et al. [20] | 2020 | Retrospective case series | 81/ 105 | 38/43 | 70.2 ± 10.8 | Lumbar spinal canal stenosis | T11-12:1 L1-2:1 L2-3:4 L3-4:28 L4-5:67 L5-S1:4 | 8.6 |
| Min et al. [21] | 2020 | Retrospective comparative study | 54/54 | 27/27 | 65.74 ± 10.52 | Lumbar central stenosis or lateral recess stenosis without foraminal stenosis | L2-3:1 L3-4:7 L4-5:43 L5-S1:2 | 27.2 ± 5.4 |
| Kim et al. [22] | 2020 | Retrospective comparative study | 30/30 | 13/17 | 64.23 ± 5.26 | Lumbar central canal stenosis | L2-3:2 L3-4:8 L4-5:18 L5-S1:2 | 12 |
| Kim et al. [23] | 2019 | Retrospective case series | 58/58 | 25/33 | 63.1 ± 11.8 | Severe and focal lumbar spinal canal stenosis | L3-4:10 L4-5:46 L5-S1:2 | 18 |
| Kang et al. [24] | 2019 | Randomized controlled trial | 32/32 | 13/19 | 65.1 ± 8.6 | Single-level lumbar spinal canal stenosis | L3-4:4 L4-5:16 L5-S1:12 | 6 |
| Heo et al. [25] | 2019 | Retrospective comparative study | 37/37 | 15/22 | 66.7 ± 9.4 | Single-level lumbar central and lateral recess stenosis at L4-L5 | L4-5:37 | 12.5 ± 3.3 |
| Choi et al. [26] | 2019 | Retrospective comparative study | 35/35 | 14/21 | 65.4 ± 11.8 | Lumbar spinal canal stenosis | N/A | 6 |
| Kim et al. [27] | 2018 | Retrospective case series | 105/ (N/A) | 46/59 | 71.2 ± 8.9 | Lumbar spinal canal stenosis | N/A | 14 |
| Heo et al. [28] | 2018 | Prospective comparative study | 46/ 46 | 18/28 | 65.8 ± 8.9 | Single-level lumbar central stenosis | L2-3:1 L3-4:8 L4-5:33 L5-S1:4 | 14.5 ± 2.3 |
| Torudom et al. [29] | 2016 | Retrospective case series | 30/35 | 11/19 | 56 ± 6.2 | Lumbar spinal stenosis | L4-5:21 Others: N/A | 24 |
| Eum et al. [30] | 2016 | Retrospective case series | 58/58 | 18/40 | 63.4 ± 7.4 | Single-level lumbar spinal stenosis | L3-4:9 L4-5:44 L5-S1:5 | 13.8 ± 3.3 |
| Soliman [14] | 2015 | Retrospective case series | 94/214 | 38/56 | 52 | Lumbar spinal stenosis | L2-3:28 L3-4:72 L4-5:90 L5-S1:24 | 28 |
| Study | Year | Study Design | Number of Patients/Levels Operated | Male/Female | Age (Years) | Indication | Lumbar Segment | Follow-Up (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heo et al. [31] | 2019 | Retrospective case series | 10/10 | 5/5 | 57.3 ± 14.7 | Lumbar juxtafacet cyst | L3-4:4 L4-5:6 | 10.1 ± 5.2 |
| Akbary et al. [6] | 2018 | Retrospective case series | 30/30 | 15/15 | 61 | Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis at two contiguous levels and unilateral radiculopathy | L2-3:2 L3-4:7 L4-5:12 L5-S1:9 | 5.67 ± 3.5 |
| Study | Year | Study Design | Number of Patients/Levels Operated | Male/Female | Age (Years) | Indication | Lumbar Segment | Follow-Up (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Park et al. [32] | 2021 | Retrospective case series | 35/35 | 16/19 | 68.4 ± 6.6 | Extraforaminal stenosis at L5-S1 | L5-S1:35 | 14.9 ± 4.2 |
| Heo et al. [33] | 2019 | Retrospective case series | 16/16 | 4/10 | 59.5 ± 7.2 | Unilateral extraforaminal entrapment of the L5 nerve root (far out syndrome) | L5-S1:16 | 11 ± 5.0 |
| Kim et al. [34] | 2018 | Retrospective case series | 31/31 | 14/17 | 70.5 ± 8.9 | Lumbar foraminal stenosis | L2-3:3 L3-4:1 L3-4-5:2 L4-5:12 L4-5-S1:2 L5-S1:11 | 14.8 ± 1.6 |
| Ahn et al. [35] | 2018 | Retrospective case series | 21/27 | 10/11 | 64.2 ± 10.7 | Lumbar foraminal stenosis | L1-2:1 L2-3:4 L3-4:9 L4-5:6 L5-S1:7 | 14.8 ± 2.96 |
| Study | Approach | Operation Time per Level (min) | Preoperative | Final Follow-Up | Macnab * (%) | Complications | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS Leg Pain | VAS Back Pain | ODI | VAS Leg Pain | VAS Back Pain | ODI | |||||
| Hua et al. [16] | Interlaminar | 69.4 ± 18.5 | 7.0 | 5.4 | 51.4 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 19.8 | 94.4 | Dural injury:2 |
| Ito et al. [17] | 57 ± 10.3 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 23.5 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 11.3 | N/A | Dural injury: 2 | |
| Aygun et al. [18] | 57.74 | N/A | N/A | 53.18 | N/A | N/A | 8.26 | 92 | N/A | |
| Park et al. [19] | 67.2 ± 19.8 | 6.5 | 6.1 | 46.2 | 2.61 | 2.75 | 19.79 | N/A | Dura injury: 2 Postoperative hematoma: 1 | |
| Pao et al. [20] | 89 ± 56.9 | 7.3 | 4.3 | 54.6 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 14.6 | 93.8 | Dura injury: 4 Transient weakness: 1 Epidural hematoma: 1 Inadequate decompression: 1 | |
| Min et al. [21] | 53.6 ± 6.7 | 7.38 | 5.27 | 60.4 | 1.48 | 1.64 | 15.4 | 83 | Dural injury: 2 Epidural hematoma: 1 | |
| Kim et al. [22] | 58.1 ± 6.04 | N/A | 7.13 | 71.2 | N/A | 1.23 | 23.53 | 76.66 | Dural injury: 1 | |
| Kim et al. [23] | N/A | 7.9 | 7.1 | N/A | 1.6 | 1.9 | N/A | 93.1 | Dural injury: 2 | |
| Kang et al. [24] | 36 ± 11 | N/A | 6.3 | 55 | N/A | 1.6 | 5 | N/A | Postoperative hematoma: 1 | |
| Heo et al. [25] | 62.4 ± 5.7 | 8.05 | 7.02 | 58.68 | 2.16 | 1.95 | 23.14 | N/A | Dural injury: 1 Postoperative hematoma: 1 | |
| Choi et al. [26] | N/A | 6.3 | 6.8 | N/A | 2.2 | 2.8 | N/A | N/A | Dural injury: 2 Root injury: 1 | |
| Kim et al. [27] | 53 ± 13.5 | 7.7 | N/A | 67.4 | 2.4 | N/A | 22.9 | 88 | Dural injury: 2 Postoperative hematoma: 1 | |
| Heo et al. [28] | 61.1 ± 5.2 | 7.96 | 7.04 | 57.98 | 2.07 | 1.98 | 21.98 | N/A | Dural injury: 1 Postoperative hematoma: 1 | |
| Torudom et al. [29] | 98.3 ± 14.3 | 8.3 | 7.2 | 65.2 | 2.3 | 2.4 | 24 | 83 | Transient paresthesia: 2 | |
| Eum et al. [30] | 68.9 ± 16.1 | 8.3 | N/A | 67.2 | 2.4 | N/A | 24.3 | 81 | Postoperative headache: 3 Dural injury: 2 Transient leg numbness: 2 Postoperative hematoma: 1 | |
| Soliman [14] | 62.8 | N/A | N/A | 64.2 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 87 | Dural injury: 6 | |
| Heo et al. [31] | Contralateral | 60.1 ± 23.4 | N/A | 7.64 | 45.35 | N/A | 1.63 | 15.82 | NA | Transient hypoesthesia: 1; Postoperative epidural hematoma: 1 |
| Akbary et al. [6] | 102.5 ± 43.66 | N/A | N/A | 67.9 | N/A | N/A | 15.7 | N/A | 0 | |
| Park et al. [32] | Paraspinal | 63.5 ± 14.4 | 7.23 | 3.71 | 61.5 | 2.26 | 2.34 | 28.6 | 80 | 0 |
| Heo et al. [33] | 72.8 ± 15.5 | 8.4 | N/A | 60.2 | 2.8 | N/A | 22.1 | 71.4 | Perirenal fluid collection (abdominal pain): 1 | |
| Kim et al. [34] | 48.7 ± 13.9 | 7.87 | 5.13 | 66.81 | 1.45 | 1.52 | 17.39 | 80.6 | 0 | |
| Ahn et al. [35] | 96.7 ± 25.9 | 7.5 | N/A | N/A | 2.5 | N/A | N/A | 80.9 | Dural injury: 1 | |
| Yeung et al. [15] | Interlaminar | 69 ± 25.1 | Improvement in VAS scores for leg pain: 69.3% | N/A | 0 | |||||
| Contralateral | 69.2 ± 35.6 | Improvement in VAS scores for leg pain: 63.6% | N/A | Persistent right leg pain: 1 | ||||||
| Interlaminar | Contralateral | Paraspinal | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of studies | 17 | 3 | 4 |
| Total number of patients | 884 | 74 | 103 |
| Mean age (years) | 64.11 (range, 52–71.2) | 61.37 (range, 57.3–65.8) | 65.65 (range, 59.5–70.5) |
| Most frequently operated level | L4-5 (45.7%) | L4-5 (45%) | L5-S1 (56.9%) |
| Mean operation time (min) | 64.24 (range, 36–98.3) | 77.27 (range, 60.1–102.5) | 70.43 (range, 48.7–96.7) |
| Complications | 5.7% | 4.05% | 1.94% |
| Improvement in VAS scores for leg pain | 73.46% | 63.6% | 70.9% |
| Improvement in VAS scores for back pain | 68.96% | 78.66% | 53.65% |
| Improvement in ODI scores | 67.41% | 71% | 67.17% |
| Macnab (%) * | 87.22 | N/A | 78.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bui, A.T.; Trinh, G.M.; Wu, M.-H.; Hoang, T.T.; Hu, M.-H.; Pao, J.-L. Indications for and Outcomes of Three Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Approaches for the Decompression of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061092
Bui AT, Trinh GM, Wu M-H, Hoang TT, Hu M-H, Pao J-L. Indications for and Outcomes of Three Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Approaches for the Decompression of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(6):1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061092
Chicago/Turabian StyleBui, Anh Tuan, Giam Minh Trinh, Meng-Huang Wu, Tung Thanh Hoang, Ming-Hsiao Hu, and Jwo-Luen Pao. 2023. "Indications for and Outcomes of Three Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Approaches for the Decompression of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Systematic Review" Diagnostics 13, no. 6: 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061092
APA StyleBui, A. T., Trinh, G. M., Wu, M.-H., Hoang, T. T., Hu, M.-H., & Pao, J.-L. (2023). Indications for and Outcomes of Three Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Approaches for the Decompression of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics, 13(6), 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061092







