Identification of Genetic Alterations in Rapid Progressive Glioblastoma by Use of Whole Exome Sequencing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Sample
2.2. DNA Isolation
2.3. Whole Exome Sequencing
2.4. Variant Calling and Variant Annotation
3. Results
3.1. Patients
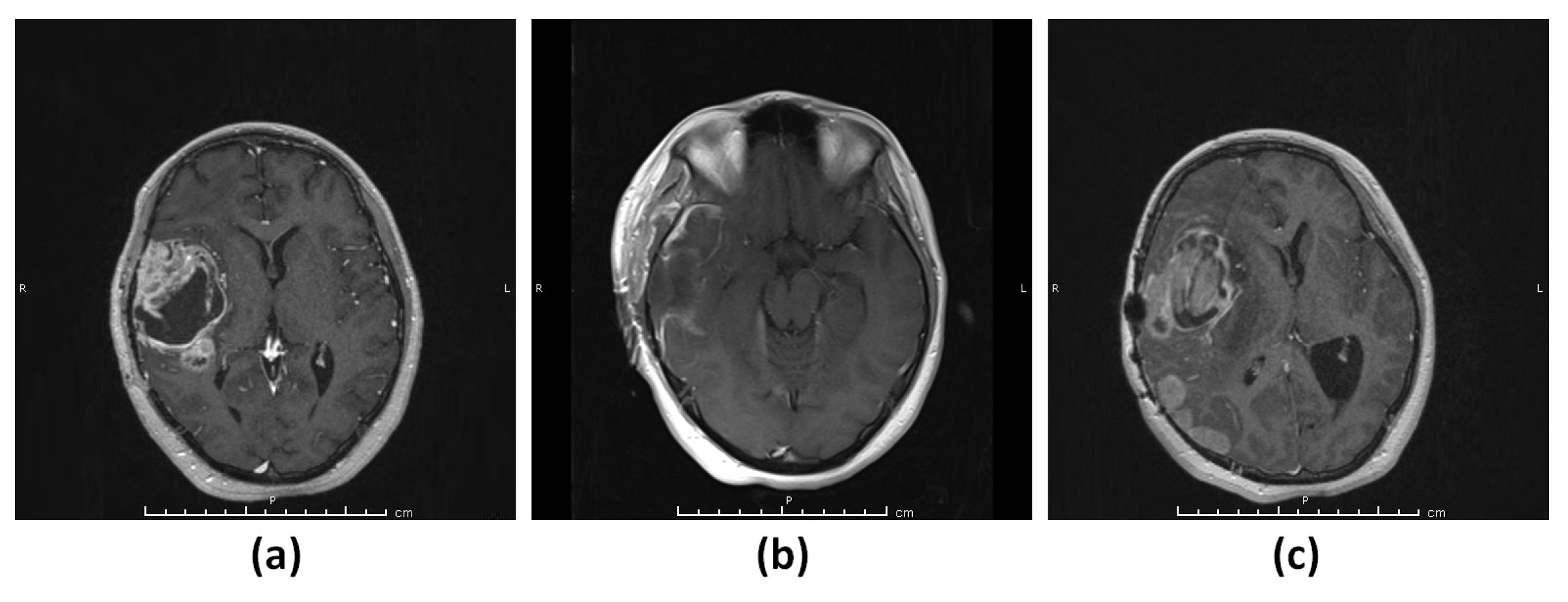
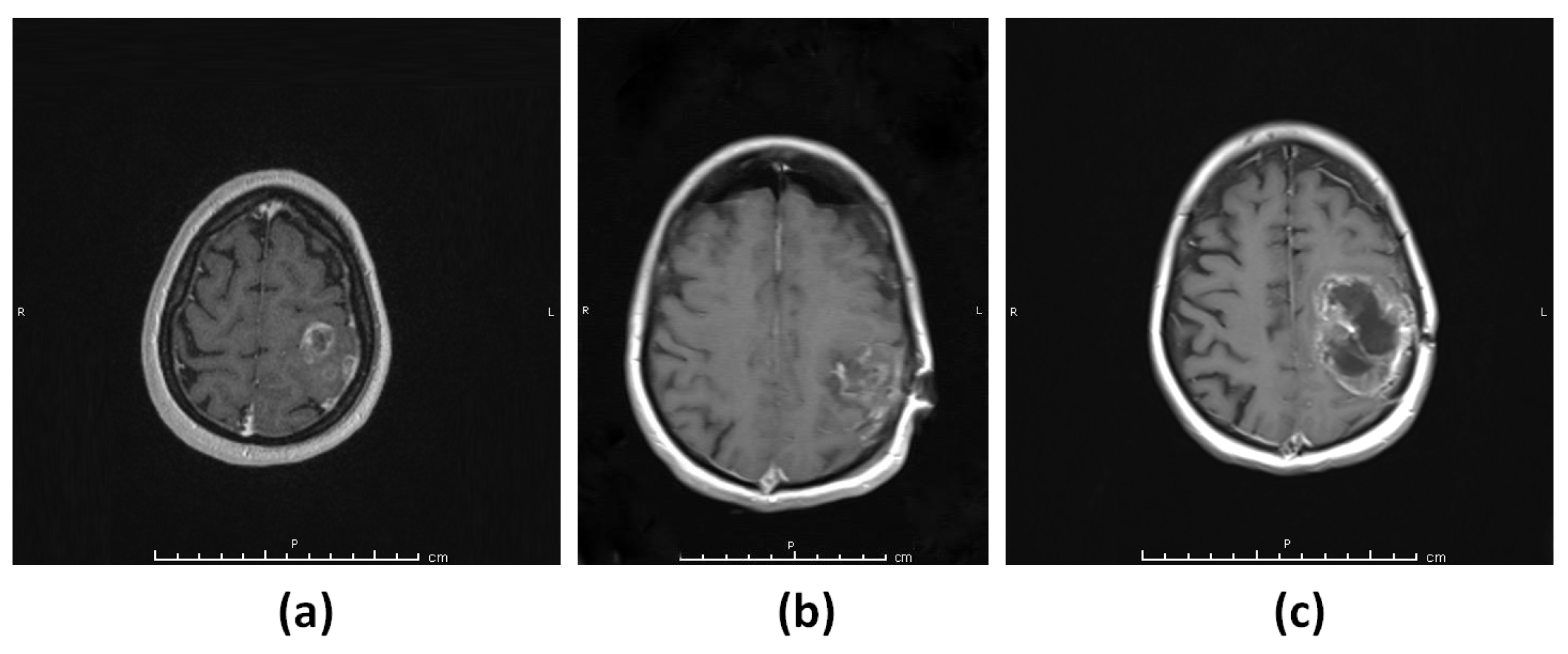
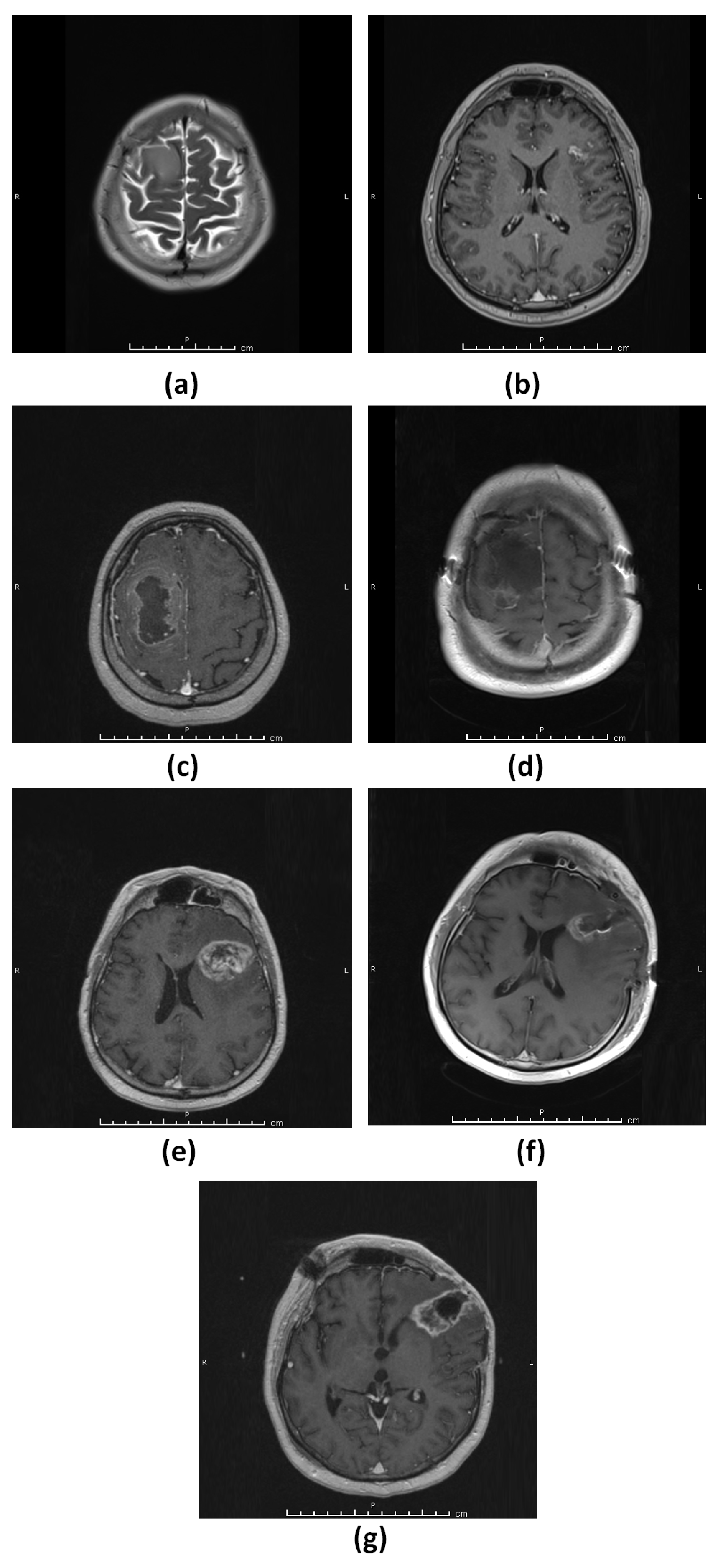
3.1.1. Patient 1 (G1)
3.1.2. Patient 2 (G2)
3.1.3. Patient 3 (G3–4)
3.1.4. Patient 4 (G5)
3.2. Whole Exome Sequencing and Variant Prioritization
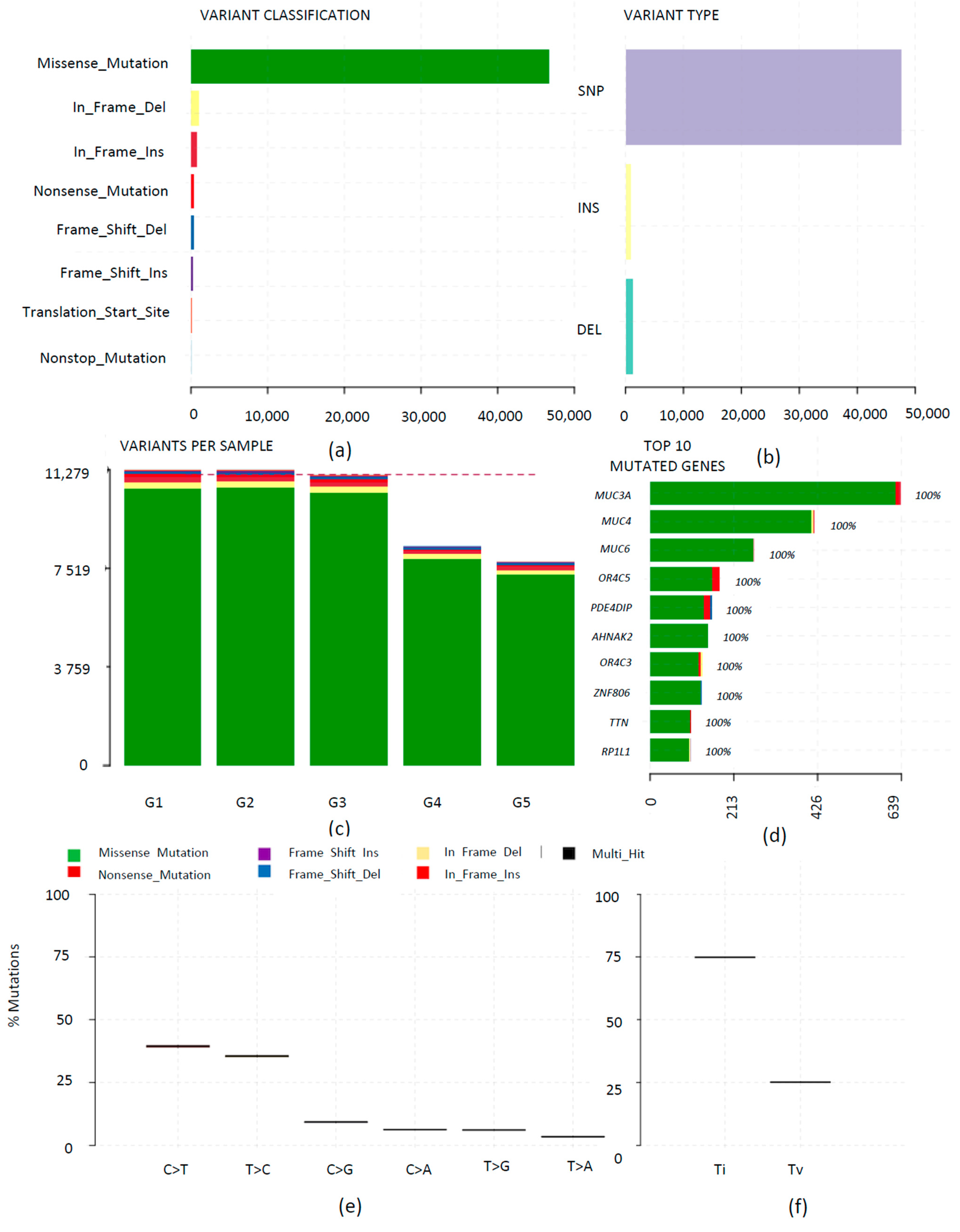
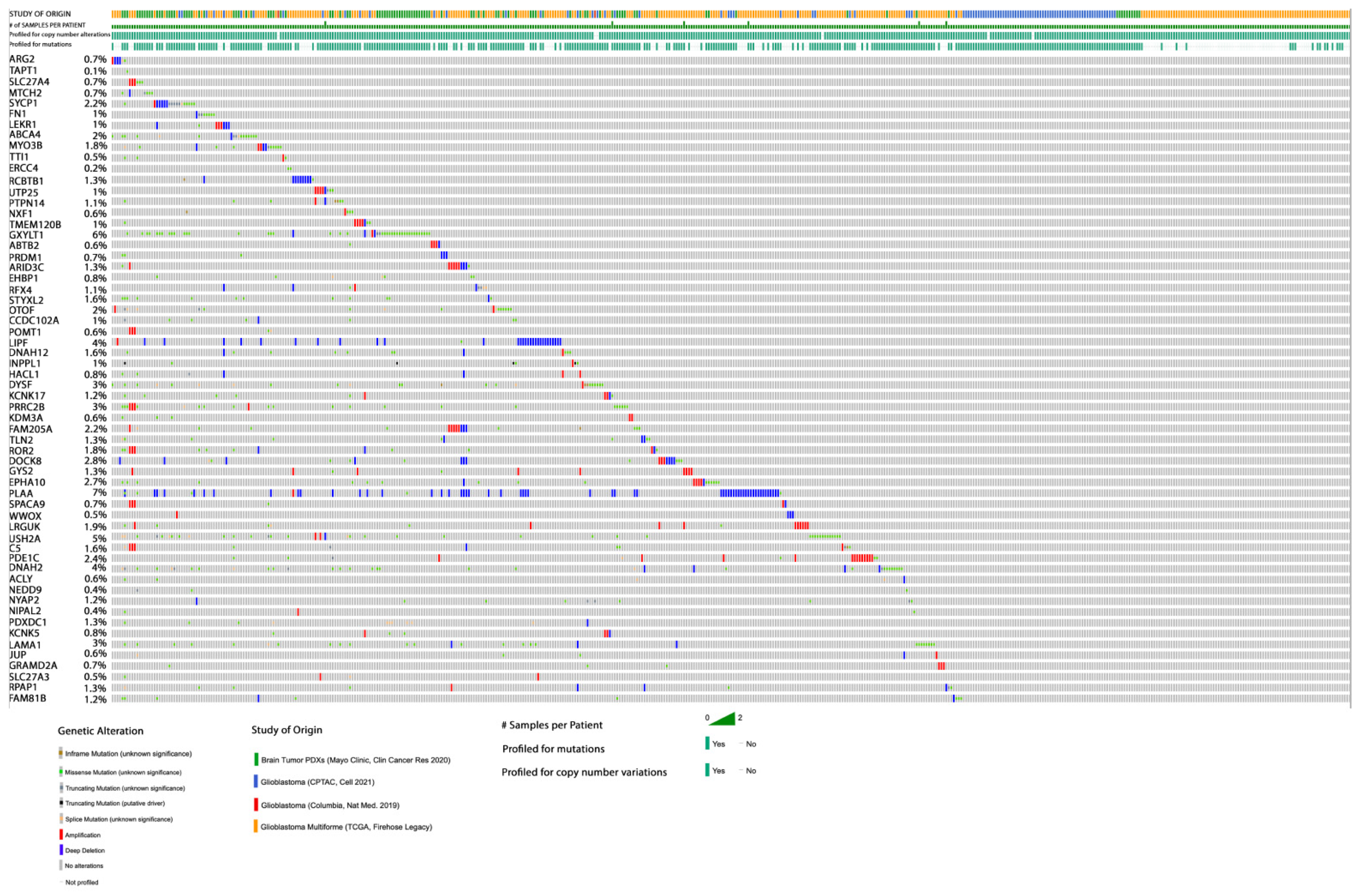
3.3. Mutational Landscape of Rapid Progressive Glioblastoma
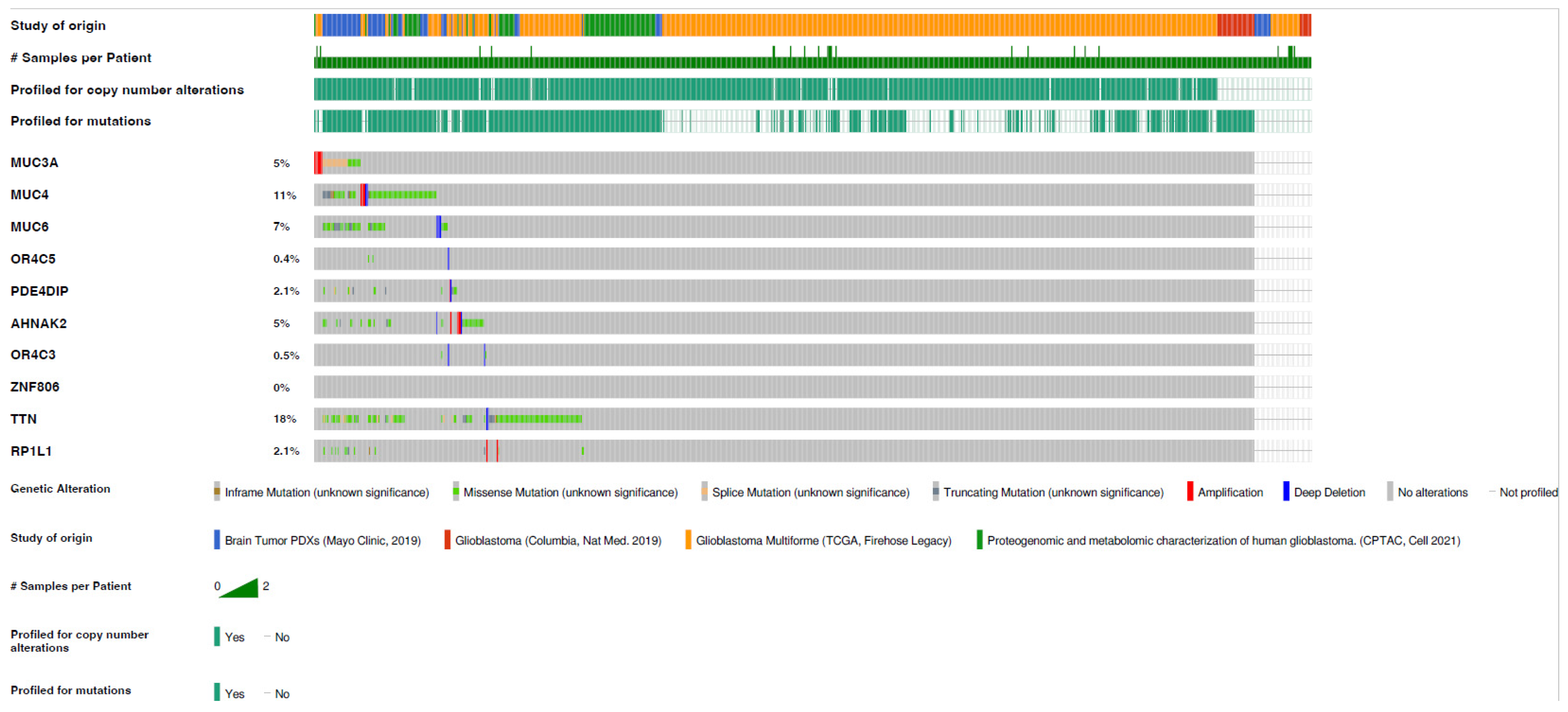
3.4. Gene Mutation in Glioblastoma of Rapid Progression, Cross-Compared to TCGA Datasets
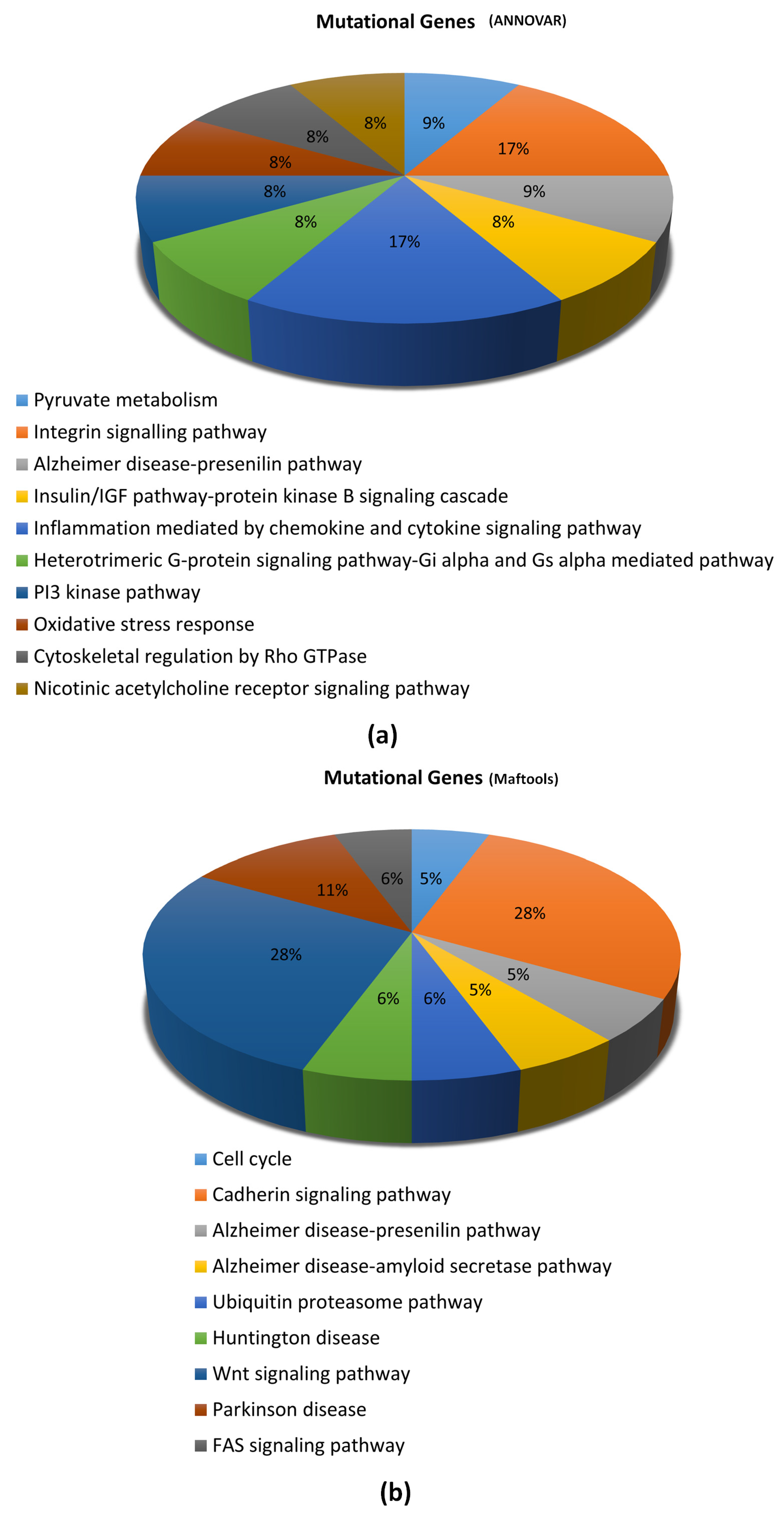
3.5. Signaling Pathways Associated with Gene Mutations in Glioblastoma of Rapid Progression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2014–2018. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23 Suppl. 3, iii1–iii105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiation Oncology Groups; National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Michaelsen, S.R.; Christensen, I.J.; Grunnet, K.; Stockhausen, M.-T.; Broholm, H.; Kosteljanetz, M.; Poulsen, H.S. Clinical variables serve as prognostic factors in a model for survival from glioblastoma multiforme: An observational study of a cohort of consecutive non-selected patients from a single institution. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szopa, W.; Burley, T.A.; Kramer-Marek, G.; Kaspera, W. Diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers in glioblastoma: Current status and future perspectives. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 8013575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Parada, L.F. The molecular and genetic basis of neurological tumors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huse, J.T.; Holland, E.C. Targeting brain cancer: Advances in the molecular pathology of malignant glioma and medulloblastoma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.P.; Tirosh, I.; Trombetta, J.J.; Shalek, A.K.; Gillespie, S.M.; Wakimoto, H.; Cahill, D.P.; Nahed, B.V.; Curry, W.T.; Martuza, R.L. Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intratumoral heterogeneity in primary glioblastoma. Science 2014, 344, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N. WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Degl’Innocenti, A.; di Leo, N.; Ciofani, G. Genetic Hallmarks and Heterogeneity of Glioblastoma in the Single-Cell Omics Era. Adv. Ther. 2020, 3, 1900152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noushmehr, H.; Weisenberger, D.J.; Diefes, K.; Phillips, H.S.; Pujara, K.; Berman, B.P.; Pan, F.; Pelloski, C.E.; Sulman, E.P.; Bhat, K.P. Identification of a CpG island methylator phenotype that defines a distinct subgroup of glioma. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaak, R.G.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Qi, Y.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, C.R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldape, K.; Zadeh, G.; Mansouri, S.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A. Glioblastoma: Pathology, molecular mechanisms and markers. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 829–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network Tissue. Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 2008, 455, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, D.W.; Jones, S.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.C.-H.; Leary, R.J.; Angenendt, P.; Mankoo, P.; Carter, H.; Siu, I.-M.; Gallia, G.L. An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma multiforme. Science 2008, 321, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, M.A.; Vora, P.; Venugopal, C.; Sidhu, S.S.; Moffat, J.; Swanton, C.; Singh, S.K. Intratumoral heterogeneity: Pathways to treatment resistance and relapse in human glioblastoma. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazor, T.; Pankov, A.; Johnson, B.E.; Hong, C.; Hamilton, E.G.; Bell, R.J.; Smirnov, I.V.; Reis, G.F.; Phillips, J.J.; Barnes, M.J. DNA methylation and somatic mutations converge on the cell cycle and define similar evolutionary histories in brain tumors. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, I.-H.; Cho, H.J.; Park, C.-K.; Jung, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.; Nam, S.H.; Kim, B.S.; Johnson, M.D.; Kong, D.-S. Spatiotemporal evolution of the primary glioblastoma genome. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.E.; Mazor, T.; Hong, C.; Barnes, M.; Aihara, K.; McLean, C.Y.; Fouse, S.D.; Yamamoto, S.; Ueda, H.; Tatsuno, K. Mutational analysis reveals the origin and therapy-driven evolution of recurrent glioma. Science 2014, 343, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Taylor, M.D. The amazing and deadly glioma race. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. Babraham Bioinformatics-FastQC a Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Kent, W.J.; Sugnet, C.W.; Furey, T.S.; Roskin, K.M.; Pringle, T.H.; Zahler, A.M.; Haussler, D. The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. GigaScience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudmant, P.H.; Rausch, T.; Gardner, E.J.; Handsaker, R.E.; Abyzov, A.; Huddleston, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, K.; Jun, G.; Fritz, M.H.-Y. An integrated map of structural variation in 2,504 human genomes. Nature 2015, 526, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alföldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.P. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Weisburd, B.; Thomas, B.; Solomonson, M.; Ruderfer, D.M.; Kavanagh, D.; Hamamsy, T.; Lek, M.; Samocha, K.E.; Cummings, B.B. The ExAC browser: Displaying reference data information from over 60,000 exomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D840–D845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shi, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhao, T.; Teng, H.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Ji, L.; et al. VarCards: An integrated genetic and clinical database for coding variants in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46, D1039–D1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaser, R.; Adusumalli, S.; Leng, S.N.; Sikic, M.; Ng, P.C. SIFT missense predictions for genomes. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reva, B.; Antipin, Y.; Sander, C. Predicting the functional impact of protein mutations: Application to cancer genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Cooper, D.N.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster2: Mutation prediction for the deep-sequencing age. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rentzsch, P.; Schubach, M.; Shendure, J.; Kircher, M. CADD-Splice—Improving genome-wide variant effect prediction using deep learning-derived splice scores. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihab, H.A.; Gough, J.; Cooper, D.N.; Stenson, P.D.; Barker, G.L.; Edwards, K.J.; Day, I.N.; Gaunt, T.R. Predicting the functional, molecular, and phenotypic consequences of amino acid substitutions using hidden Markov models. Hum. Mutat. 2013, 34, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.; Fay, J.C. Identification of deleterious mutations within three human genomes. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Ansari, I.A.; Singh, P.; Dass, J.F.P.; Khan, F. Identification and characterization of functional single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in Axin 1 gene: A molecular dynamics approach. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 76, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Ansari, I.A.; Singh, P.; Dass, J.F.P. Prediction of functionally significant single nucleotide polymorphisms in PTEN tumor suppressor gene: An in silico approach. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2017, 64, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayakonda, A.; Lin, D.-C.; Assenov, Y.; Plass, C.; Koeffler, H.P. Maftools: Efficient and comprehensive analysis of somatic variants in cancer. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, P.D.; Campbell, M.J.; Kejariwal, A.; Mi, H.; Karlak, B.; Daverman, R.; Diemer, K.; Muruganujan, A.; Narechania, A. PANTHER: A library of protein families and subfamilies indexed by function. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2129–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, F.; Muzaffar, K.; Perveen, K.; Malhi, S.M.; Simjee, S. Glioblastoma Multiforme: A Review of its Epidemiology and Pathogenesis through Clinical Presentation and Treatment. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 18, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Taillibert, S.; Kanner, A.; Read, W.; Steinberg, D.M.; Lhermitte, B.; Toms, S.; Idbaih, A.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Fink, K. Effect of tumor-treating fields plus maintenance temozolomide vs maintenance temozolomide alone on survival in patients with glioblastoma: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, C.; Zaltsman-Amir, Y.; Mostizky, Y.; Kollet, N.; Gross, A.; Friedler, A. Molecular basis of the interaction between proapoptotic truncated BID (tBID) protein and mitochondrial carrier homologue 2 (MTCH2) protein: Key players in mitochondrial death pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 15016–15023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arigoni, M.; Barutello, G.; Riccardo, F.; Ercole, E.; Cantarella, D.; Orso, F.; Conti, L.; Lanzardo, S.; Taverna, D.; Merighi, I.; et al. miR-135b coordinates progression of ErbB2-driven mammary carcinomas through suppression of MID1 and MTCH2. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 2058–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, D.H.; Mullokandov, M.; Wu, Y.; Voisin, V.; Gronda, M.; Hurren, R.; Wang, X.; MacLean, N.; Jeyaraju, D.V.; Jitkova, Y.; et al. Mitochondrial carrier homolog 2 is necessary for AML survival. Blood 2020, 136, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Yang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, T.; Zuo, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Xia, X.; Chen, M.; et al. Inhibition of mitochondrial carrier homolog 2 (MTCH2) suppresses tumor invasion and enhances sensitivity to temozolomide in malignant glioma. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.A.; Yarchoan, M.; Jaffee, E.; Swanton, C.; Quezada, S.A.; Stenzinger, A.; Peters, S. Development of tumor mutation burden as an immunotherapy biomarker: Utility for the oncology clinic. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ge, J.; Lan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Luo, Y.; Tan, Y.; Liang, M.; Deng, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; et al. Tumor mutational burden is associated with poor outcomes in diffuse glioma. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.C.; Duffy, C.R.; Allison, J.P. Fundamental Mechanisms of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1069–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromeier, M.; Brown, M.C.; Zhang, G.; Lin, X.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Z.; Beaubier, N.; Yan, H.; He, Y.; Desjardins, A.; et al. Very low mutation burden is a feature of inflamed recurrent glioblastomas responsive to cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schou Nørøxe, D.; Flynn, A.; Yde, C.W.; Østrup, O.; Nielsen, F.C.; Skjøth-Rasmussen, J.; Brennum, J.; Hamerlik, P.; Weischenfeldt, J.; Poulsen, H.S.; et al. Tumor mutational burden and purity adjustment before and after treatment with temozolomide in 27 paired samples of glioblastoma: A prospective study. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 16, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.; Benveniste, E.N. Fas ligand/Fas system in the brain: Regulator of immune and apoptotic responses. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2004, 44, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccarini, M.; Giuliani, P.; Ziberi, S.; Carluccio, M.; Iorio, P.D.; Caciagli, F.; Ciccarelli, R. The Role of Wnt Signal in Glioblastoma Development and Progression: A Possible New Pharmacological Target for the Therapy of This Tumor. Genes 2018, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, I.; Işık, E.B.; Mahfooz, S.; Khan, A.M.; Hatiboglu, M.A. Identification of Genetic Alterations in Rapid Progressive Glioblastoma by Use of Whole Exome Sequencing. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061017
Khan I, Işık EB, Mahfooz S, Khan AM, Hatiboglu MA. Identification of Genetic Alterations in Rapid Progressive Glioblastoma by Use of Whole Exome Sequencing. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(6):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061017
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Imran, Esra Büşra Işık, Sadaf Mahfooz, Asif M. Khan, and Mustafa Aziz Hatiboglu. 2023. "Identification of Genetic Alterations in Rapid Progressive Glioblastoma by Use of Whole Exome Sequencing" Diagnostics 13, no. 6: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061017
APA StyleKhan, I., Işık, E. B., Mahfooz, S., Khan, A. M., & Hatiboglu, M. A. (2023). Identification of Genetic Alterations in Rapid Progressive Glioblastoma by Use of Whole Exome Sequencing. Diagnostics, 13(6), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061017






