Early Assessment of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response Using Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Luminal B-like Subtype of Breast Cancer Patients: A Single-Center Prospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
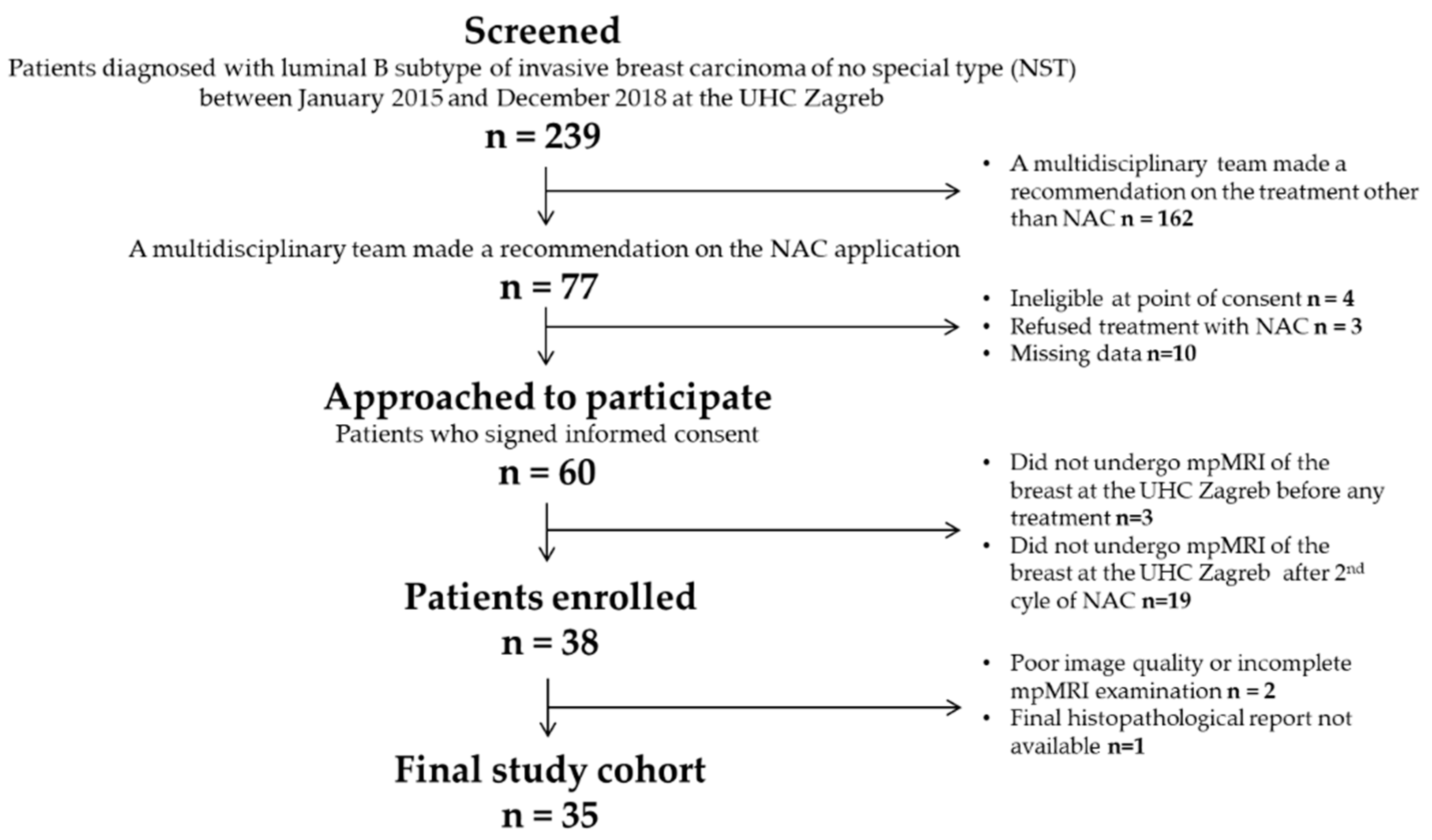
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Aquisition Protocol
2.3. Image Analysis
2.4. Histopathological Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørlie, T.; Perou, C.M.; Tibshirani, R.; Aas, T.; Geisler, S.; Johnsen, H.; Hastie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10869–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perou, C.M.; Sørlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; Van De Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldhirsch, A.; Winer, E.P.; Coates, A.S.; Gelber, R.D.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.; Thürlimann, B.; Senn, H.-J. Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: Highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2013. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2206–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, F.; Kyriakides, S.; Ohno, S.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Poortmans, P.; Rubio, I.T.; Zackrisson, S.; Senkus, E.; on behalf of the ESMO Guidelines Committee. Early breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1194–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanac, G.; Dzoic Dominikovic, M.; Bojanic, K.; Kelava, T.; Dumic-Cule, I.; Canecki-Varzic, S.; Smolic, M.; Vcev, A.; Smolic, R.; Brkljacic, B. Imaging Features of Triple N Negative Breast Cancers—Mammography, Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Coll. Antropol. 2021, 45, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.M.; Moulder-Thompson, S.L. Neoadjuvant treatment of breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2012, 23 (Suppl. 10), x231–x236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, M.; von Minckwitz, G.; Bear, H.D.; Buzdar, A.; McGale, P.; Bonnefoi, H.; Colleoni, M.; Denkert, C.; Eiermann, W.; Jackesz, R.; et al. Recommendations from an international expert panel on the use of neoadjuvant (primary) systemic treatment of operable breast cancer: New perspectives 2006. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 1927–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselain, B.; Barlow, W.; Bartlett, J.; Bergh, J.; Bergsten-Nordström, E.; Bliss, J.; Boccardo, F.; Boddington, C.; Bogaerts, J.; Bonadonna, G.; et al. Long-term outcomes for neoadjuvant versus adjuvant chemotherapy in early breast cancer: Meta-analysis of individual patient data from ten randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooperating Investigators of the EORTC; van Nes, J.G.H.; Putter, H.; Julien, J.P.; Tubiana-Hulin, M.; van de Vijver, M.; Bogaerts, J.; De Vos, M.; Van de Velde, C.J. Preoperative chemotherapy is safe in early breast cancer, even after 10 years of follow-up; clinical and translational results from the EORTC trial 10902. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2009, 115, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, D.; Pavlidis, N.; Ioannidis, J.P.A. Neoadjuvant Versus Adjuvant Systemic Treatment in Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deo, S.V.S.; Bhutani, M.; Shukla, N.K.; Raina, V.; Rath, G.K.; Purkayasth, J. Randomized trial comparing neo-adjuvant versus adjuvant chemotherapy in operable locally advanced breast cancer (T4b N0-2 M0). J. Surg. Oncol. 2003, 84, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Mao, X. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 2423–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symmans, W.F.; Peintinger, F.; Hatzis, C.; Rajan, R.; Kuerer, H.; Valero, V.; Assad, L.; Poniecka, A.; Hennessy, B.; Green, M.; et al. Measurement of Residual Breast Cancer Burden to Predict Survival after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4414–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamy, A.S.; Darrigues, L.; Laas, E.; De Croze, D.; Topciu, L.; Lam, G.-T.; Evrevin, C.; Rozette, S.; Laot, L.; Lerebours, F.; et al. Prognostic value of the Residual Cancer Burden index according to breast cancer subtype: Validation on a cohort of BC patients treated by neoadjuvant chemotherapy. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laas, E.; Labrosse, J.; Hamy, A.S.; Benchimol, G.; de Croze, D.; Feron, J.G.; Coussy, F.; Balezeau, T.; Guerin, J.; Lae, M.; et al. Determination of breast cancer prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: Comparison of Residual Cancer Burden (RCB) and Neo-Bioscore. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, C.; Osdoit, M.; van der Noordaa, M.; Shad, S.; Wei, J.; de Croze, D.; Hamy, A.S.; Laé, M.; Reyal, F.; Sonke, G.S.; et al. Residual cancer burden after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and long-term survival outcomes in breast cancer: A multicentre pooled analysis of 5161 patients. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, E.; Gentile, D.; Bottini, A.; Sagona, A.; Gatzemeier, W.; Losurdo, A.; Fernandes, B.; Tinterri, C. Neo-Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Luminal, Node Positive Breast Cancer: Characteristics, Treatment and Oncological Outcomes: A Single Center’s Experience. Eur. J. Breast Health 2021, 17, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieog, J.S.D.; van der Hage, J.A.; van de Velde, C.J.H. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for operable breast cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2007, 94, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, R.M.; Balleyguier, C.; Baltzer, P.A.; Bick, U.; Colin, C.; Cornford, E.; Evans, A.N.; Fallenberg, E.M.; Forrai, G.; Fuchsjäger, M.H.; et al. Breast MRI: EUSOBI recommendations for women’s information. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 3669–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinovich, M.; Sardanelli, F.; Ciatto, S.; Mamounas, E.; Brennan, M.; Macaskill, P.; Irwig, L.; von Minckwitz, G.; Houssami, N. Early prediction of pathologic response to neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer: Systematic review of the accuracy of MRI. Breast Edinb. Scotl. 2012, 21, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinovich, M.L.; Houssami, N.; Macaskill, P.; Sardanelli, F.; Irwig, L.; Mamounas, E.P.; Von Minckwitz, G.; Brennan, M.; Ciatto, S. Meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging in detecting residual breast cancer after neoadjuvant therapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croshaw, R.; Shapiro-Wright, H.; Svensson, E.; Erb, K.; Julian, T. Accuracy of clinical examination, digital mammogram, ultrasound, and MRI in determining postneoadjuvant pathologic tumor response in operable breast cancer patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 3160–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Chae, E.Y.; Cha, J.H.; Shin, H.J.; Choi, W.J.; Choi, Y.-W.; Kim, H.H. Comparison of mammography, digital breast tomosynthesis, automated breast ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging in evaluation of residual tumor after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 108, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheel, J.; Kim, E.; Partridge, S.C.; Lehman, C.D.; Rosen, M.A.; Bernreuter, W.K.; Pisano, E.D.; Marques, H.S.; Morris, E.A.; Weatherall, P.T.; et al. MRI, Clinical Examination, and Mammography for Preoperative Assessment of Residual Disease and Pathologic Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer: ACRIN 6657 Trial. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 210, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Song, B.J.; Kang, B.J.; Yim, K.-I.; Lee, A.; Nam, Y. Early Prediction of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI and Ultrasound in Breast Cancer. Korean J. Radiol. 2018, 19, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reig, B.; Lewin, A.A.; Du, L.; Heacock, L.; Toth, H.K.; Heller, S.L.; Gao, Y.; Moy, L. Breast MRI for Evaluation of Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy. Radiographics 2021, 41, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, F.; Fischer, U.; Vosshenrich, R.; Grabbe, E. Classification of hypervascularized lesions in CE MR imaging of the breast. Eur. Radiol. 2002, 12, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiou, K.; Kanavou, T.; Vlychou, M.; Poultsidi, A.; Athanasiou, E.; Arvanitis, D.L.; Fezoulidis, I.V. Characterization of breast lesions with CE-MR multimodal morphological and kinetic analysis: Comparison with conventional mammography and high-resolution ultrasound. Eur. J. Radiol. 2009, 70, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozaki, M.; Igarashi, T.; Matsushima, S.; Fukuda, K. High-spatial-resolution MR imaging of focal breast masses: Interpretation model based on kinetic and morphological parameters. Radiat. Med. 2005, 23, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Loo, C.E.; Teertstra, H.J.; Rodenhuis, S.; van de Vijver, M.J.; Hannemann, J.; Muller, S.H.; Peeters, M.-J.V.; Gilhuijs, K.G.A. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for prediction of breast cancer response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy: Initial results. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 191, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martincich, L.; Montemurro, F.; De Rosa, G.; Marra, V.; Ponzone, R.; Cirillo, S.; Gatti, M.; Biglia, N.; Sarotto, I.; Sismondi, P.; et al. Monitoring response to primary chemotherapy in breast cancer using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2004, 83, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhani, A.R.; Hayes, C.; Assersohn, L.; Powles, T.; Makris, A.; Suckling, J.; Leach, M.; Husband, J.E. Prediction of clinicopathologic response of breast cancer to primary chemotherapy at contrast-enhanced MR imaging: Initial clinical results. Radiology 2006, 239, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hylton, N.M.; Blume, J.D.; Bernreuter, W.K.; Pisano, E.D.; Rosen, M.A.; Morris, E.A.; Weatherall, P.T.; Lehman, C.D.; Newstead, G.M.; Polin, S.; et al. Locally advanced breast cancer: MR imaging for prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy--results from ACRIN 6657/I-SPY TRIAL. Radiology 2012, 263, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Forgia, D.; Vestito, A.; Lasciarrea, M.; Comes, M.; Diotaiuti, S.; Giotta, F.; Latorre, A.; Lorusso, V.; Massafra, R.; Palmiotti, G.; et al. Response Predictivity to Neoadjuvant Therapies in Breast Cancer: A Qualitative Analysis of Background Parenchymal Enhancement in DCE-MRI. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, M.; Fukuyama, N.; Kikuchi, S.; Shiraishi, Y.; Takimoto, Y.; Kamei, Y.; Kurata, M.; Kitazawa, R.; Kido, T. Utility of synthetic MRI in predicting pathological complete response of various breast cancer subtypes prior to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Clin. Radiol. 2022, 77, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesapane, F.; Rotili, A.; Botta, F.; Raimondi, S.; Bianchini, L.; Corso, F.; Ferrari, F.; Penco, S.; Nicosia, L.; Bozzini, A.; et al. Radiomics of MRI for the Prediction of the Pathological Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients: A Single Referral Centre Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granzier, R.W.Y.; van Nijnatten, T.J.A.; Woodruff, H.C.; Smidt, M.L.; Lobbes, M.B.I. Exploring breast cancer response prediction to neoadjuvant systemic therapy using MRI-based radiomics: A systematic review. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 121, 108736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.-M.; Wang, H.-T.; Yu, T. The Application of Radiomics in Breast MRI: A Review. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820916191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braman, N.M.; Etesami, M.; Prasanna, P.; Dubchuk, C.; Gilmore, H.; Tiwari, P.; Plecha, D.; Madabhushi, A. Intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics for the pretreatment prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy based on breast DCE-MRI. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 57, Erratum in Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliafico, A.S.; Piana, M.; Schenone, D.; Lai, R.; Massone, A.M.; Houssami, N. Overview of radiomics in breast cancer diagnosis and prognostication. Breast 2019, 49, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alduk, A.M.; Brcic, I.; Podolski, P.; Prutki, M. Correlation of MRI features and pathohistological prognostic factors in invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Acta Clin. Belg. 2016, 72, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Criteria | Points | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | |
| Shape | Round, oval | Irregular | - |
| Margins | Circumscribed | Not-circumscribed | - |
| Enhancement pattern | Homogeneous | Heterogeneous | Rim enhancement |
| Sinitial | <50% | 50–100% | >100% |
| Spostinitial | Continous increase | Plateau | Wash-out |
| Patient Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| Value (mean, range) | 55 (30–73) |
| Clinical Staging | |
| I (N, %) | 13 (37%) |
| IIA (N, %) | 12 (34%) |
| IIB (N, %) | 8 (23%) |
| IIIA (N, %) | 2 (6%) |
| Histological type | |
| Non-special type invasive carcinoma | 35 (100%) |
| Lobular infiltrating carcinoma | - |
| Other | - |
| Nuclear grade | |
| 1 | - |
| 2 | 18 (52%) |
| 3 | 17 (48%) |
| Estrogen receptor status | |
| Positive (N, %) | 35 (100%) |
| Negative (N, %) | - |
| Progesterone receptor status | |
| Positive (N, %) | 29 (83%) |
| Negative (N, %) | 6 (17%) |
| HER2 receptor status | |
| Positive (N, %) | 13 (37%) |
| Negative (N, %) | 22 (63%) |
| Ki-67 | |
| Value (mean, range) | 41% (12–87%) |
| Lymph node status | |
| Positive (N, %) | 21 (60%) |
| Negative (N, %) | 14 (40%) |
| Tumor response after the completion of NAC based on the Residual Cancer Burden (RCB) grading system | |
| Responders (N, %) | 29 (83%) |
| non-Responders (N, %) | 6 (17%) |
| Imaging Features | Before Application of NAC | After 2nd Cycle of NAC |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor size | ||
| Value (mean, range) | 35 mm (15–95 mm) | 25 mm (11–93 mm) |
| Tumor shape | ||
| Round, oval (N, %) | 2 (6%) | 1 (3%) |
| Irregular (N, %) | 33 (94%) | 34 (97%) |
| Tumor margins | ||
| Circumscribed (N, %) | 2 (6%) | 5 (14%) |
| Not-circumscribed (N, %) | 33 (94%) | 30 (86%) |
| Tumor enhancement pattern | ||
| Homogeneous (N, %) | - | - |
| Heterogeneous (N, %) | 18 (51%) | 24 (69%) |
| Rim enhancement (N, %) | 17 (49%) | 11 (31%) |
| Sinitial | ||
| <50% (N, %) | 3 (9%) | 12 (34%) |
| 50–100% (N, %) | 20 (57%) | 19 (54%) |
| >100% (N, %) | 12 (34%) | 4 (12%) |
| Spostinitial | ||
| Continous increase (N, %) | - | 9 (26%) |
| Plateau (N, %) | 13 (37%) | 18 (51%) |
| Wash-out (N, %) | 22 (63%) | 8 (23%) |
| Göttingen score | ||
| Value (mean, range) | 6 (4–8) | 5 (3–8) |
| Tumor Characteristics | Difference in Tumor Characteristics before and after Two Cycles of NAC (Mean Value, Range) | Proportion of the Difference from the Initial Value (Mean VALUE, Range) | Wilcoxon Test p (Z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor size | 5 mm (−3–47 mm) | 14% (−12–70%) | p < 0.001 (Z = 4.78) |
| Göttingen score difference | 1 (0–4) | 20% (0–50%) | p < 0.001 (Z = 4.62) |
| Analysis | OR | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate regression | |||
| Tumor size difference | 0.84 | 0.65–1.01 | 0.131 |
| The proportion of tumor size difference | 0.004 | <0.001–3.12 | 0.087 |
| Göttingen score difference | 0.09 | 0.02–0.65 | 0.016 |
| The proportion of Göttingen score difference | 0.001 | <0.001–0.04 | 0.012 |
| Multivariate regression | |||
| The proportion of tumor size difference | 0.001 | <0.001–7285.65 | 0.151 |
| Göttingen score difference | 0.003 | <0.001–3.01 | 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovacevic, L.; Petrovecki, M.; Korsa, L.; Marusic, Z.; Dumic-Cule, I.; Prutki, M. Early Assessment of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response Using Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Luminal B-like Subtype of Breast Cancer Patients: A Single-Center Prospective Study. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13040694
Kovacevic L, Petrovecki M, Korsa L, Marusic Z, Dumic-Cule I, Prutki M. Early Assessment of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response Using Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Luminal B-like Subtype of Breast Cancer Patients: A Single-Center Prospective Study. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(4):694. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13040694
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovacevic, Lucija, Marko Petrovecki, Lea Korsa, Zlatko Marusic, Ivo Dumic-Cule, and Maja Prutki. 2023. "Early Assessment of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response Using Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Luminal B-like Subtype of Breast Cancer Patients: A Single-Center Prospective Study" Diagnostics 13, no. 4: 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13040694
APA StyleKovacevic, L., Petrovecki, M., Korsa, L., Marusic, Z., Dumic-Cule, I., & Prutki, M. (2023). Early Assessment of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response Using Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Luminal B-like Subtype of Breast Cancer Patients: A Single-Center Prospective Study. Diagnostics, 13(4), 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13040694





