Abstract
This study aimed to determine whether apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and morphological features on diffusion-weighted MRI (DW-MRI) can discriminate metastatic axillary lymph nodes (ALNs) from benign in patients with breast cancer. Two radiologists measured ADC, long and short diameters, long-to-short diameter ratio, and cortical thickness and assessed eccentric cortical thickening, loss of fatty hilum, irregular margin, asymmetry in shape or number, and rim sign of ALNs on DW-MRI and categorized them into benign or suspicious ALNs. Pathologic reports were used as a reference standard. Statistical analysis was performed using the Mann–Whitney U test and chi-square test. Overall sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and diagnostic accuracy of DW-MRI were calculated. The ADC of metastatic ALNs was 0.905 × 10−3 mm2/s, and that of benign ALNs was 0.991 × 10−3 mm2/s (p = 0.243). All morphologic features showed significant difference between the two groups. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and diagnostic accuracy of the final categorization on DW-MRI were 77.1%, 93.3%, 79.4%, 92.5%, and 86.2%, respectively. Our results suggest that morphologic evaluation of ALNs on DWI can discriminate metastatic ALNs from benign. The ADC value of metastatic ALNs was lower than that of benign nodes, but the difference was not statistically significant.
1. Introduction
In breast cancer patients, the extent of axillary lymph node (ALN) metastasis and tumor size are two of the most important prognostic indicators for survival [1]. The regional lymph node (LN) status influences treatment options, extent of surgery, and need for chemotherapy or radiation therapy. The 5-year survival rate of breast cancer patients with regional LN metastasis is lower than that of breast cancer patients without LN metastasis [2].
For axillary nodal staging, sentinel lymph node biopsy is the standard method, followed by axillary dissection [3,4]. However, these two methods are associated with morbidity such as arm pain, seroma, hematoma, lymphedema, tingling sensations, and numbness [5]. As a result, non-invasive nodal staging techniques with appropriate diagnostic accuracy are in high demand. The non-invasive diagnostic alternatives, including physical examination, digital mammography, ultrasonography, computed tomographic scan (CT), positron emission tomographic imaging (PET), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are currently used and show variable success in predicting lymph node involvement [6]. However, physical examination of the axilla showed a high false-negative rate. While axillary US is routinely used in many centers, it shows a variable sensitivity of 45.2–86.2% and variable specificity of 40.5–86.6% [6,7,8,9,10].
MRI is regarded as the best diagnostic modality to reveal the anatomy and evaluate axillary node status. On contrast-enhanced MRI, suspicious nodal morphologic features were cortical thickening, loss of fatty hilum, heterogeneous enhancement, round shape, and low long-to-short diameter ratio (L/S ratio) [9]. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a valuable MRI sequence for distinguishing benign and malignant lesions without contrast agents. This sequence provides useful information by quantifying the restriction experienced by water in regions associated with malignancies and demands reliable mapping of ADC or other diffusivity-related parameters [11]. This sequence has no need for contrast agents and is advantageous in cases of contrast allergy or renal insufficiency and can shorten test times, lower patient cost, and increase accessibility. However, limited studies have examined DWI sequences with 3T MRI in regard to ADC value and morphological analysis of ALNs in breast cancer patients [12,13].
This study aimed to determine whether the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and morphological features on diffusion-weighted MRI (DW-MRI) can discriminate metastatic axillary lymph nodes (ALNs) from benign in patients with breast cancer.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients
This retrospective study was approved by our institutional ethical committee, which waived the requirement for written informed consent from patients.
The study group included 172 patients who were diagnosed with invasive breast cancer and had undergone MR imaging of breasts including DWI between May 2020 and February 2021 at our institution. Of these patients, 32 were excluded for the following reasons: subsequent neo-adjuvant chemotherapy (n = 24), no available DWI data due to exclusion from the field of view (FOV) on DWI (n = 5), MR imaging performed after LN biopsy (n = 2), and no available axillary LN pathology (n = 1).
Finally, a total of 140 cases from 139 patients (1 patient with bilateral breast cancer) was included for the analysis in this study. The patients’ ages ranged from 26 to 89 years with a mean of 56.3 years.
2.2. MRI Technique
MRI examinations were performed with patients in the prone position using a Magnetom Verio 3T system (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) in a dedicated eight-channel phase-array coil. We obtained MR images using the following sequences in Table 1. The images were acquired before and after the injection of gadolinium DTPA (0.1 mmol/kg Gadovist; Bayer Schering Pharma, Berlin, Germany).

Table 1.
MR protocol.
2.3. Imaging Analysis
Breast MRIs were retrospectively reviewed by two radiologists (19 years and 2 years of experience in breast MR imaging, respectively).
Suspicious morphologic features of ALNs on MRI were followed: eccentric cortical thickenings (3 mm or more), loss of fatty hilum, L/S ratio < 1.6, short diameter 10 mm or larger, irregular margin, and asymmetry either in shape or number compared with contralateral axilla [9,14,15,16]. We added “rim sign” as a suspicious feature on DW-MRI. Kang et al. defined a high peripheral signal in a breast tumor lesion in DW-MRI as a “rim sign” and suggested that the specificity of breast cancer detection is further increased when a rim sign is seen on DW-MRI [17]. Therefore, we applied this rim sign to ALNs of breast cancer patients and analyzed its presence on DWI.
Both radiologists reviewed the DWI together and chose one LN, either the most suspicious one or the most prominent one on DWI. They measured the long diameter, short diameter, L/S ratio, eccentric cortical thickening, and ADC value of ALNs on DWI. Regions of interests (ROIs) of ADC were drawn manually in the largest and most prominent ALN, avoiding the fatty hilum (Figure 1 and Figure 2). They also evaluated eccentric cortical thickening, loss of fatty hilum, irregular margin, asymmetry either in shape or number of ipsilateral ALN compared with contralateral ALN, and rim sign of LN on DWI. The final assessment of LN was decided by consensus between the two reviewers.
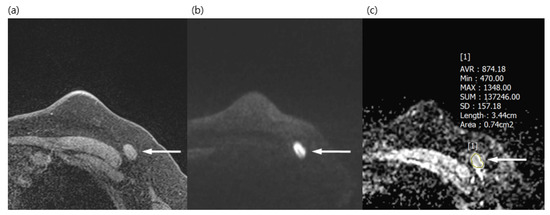
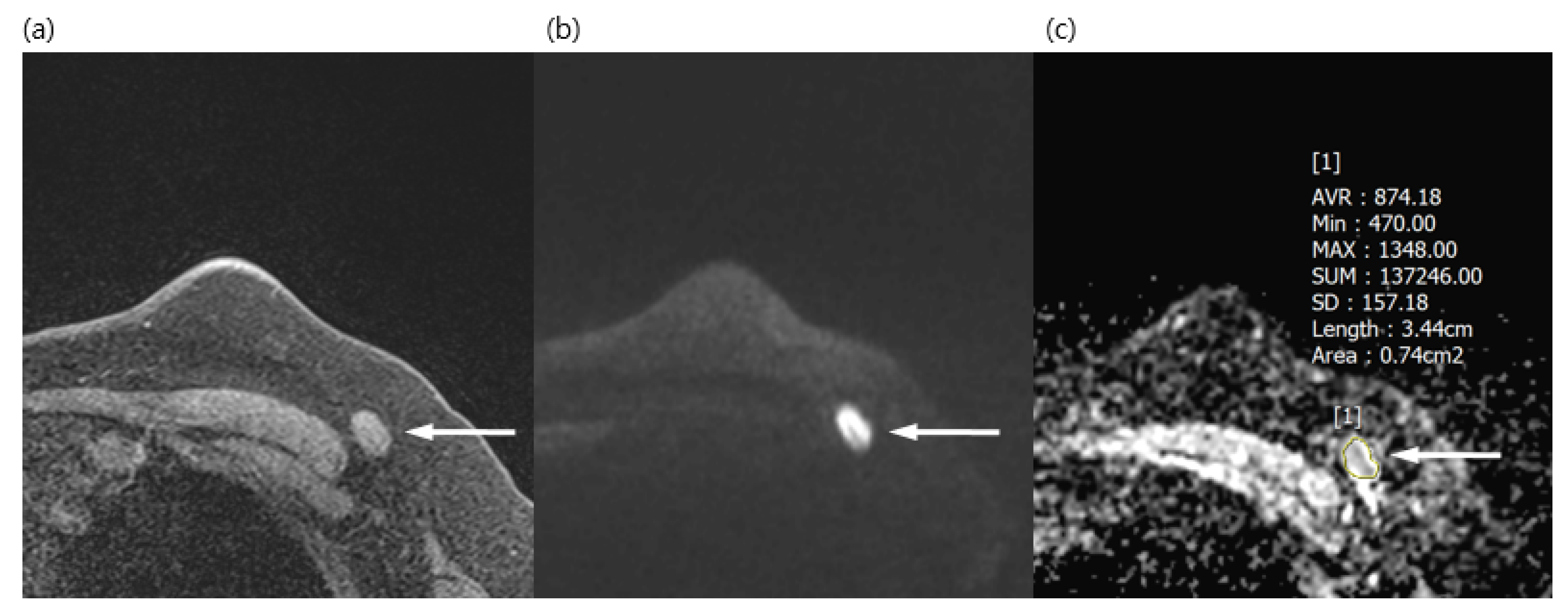
Figure 1.
A 50-year-old woman with a surgically verified metastatic lymph node in left axilla level I. (a) Axial pre-contrast T1WI of the left axilla shows a 1.5 cm lymph node with loss of fatty hilum (arrow). (b) Axial DWI (b values, 1000 mm2/s) shows a lymph node (arrow) as an area of high signal intensity. (c) Axial ADC map (b values, 1000mm2/s) shows the same lesion with restricted diffusion (arrow). The region of interest was manually drawn on the ADC map, guided by pre-contrast T1WI to avoid the fatty hilum. The mean ADC of the lesion was 0.874 × 10−3, which indicated a metastatic lymph node.
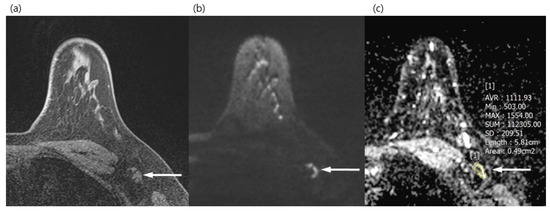
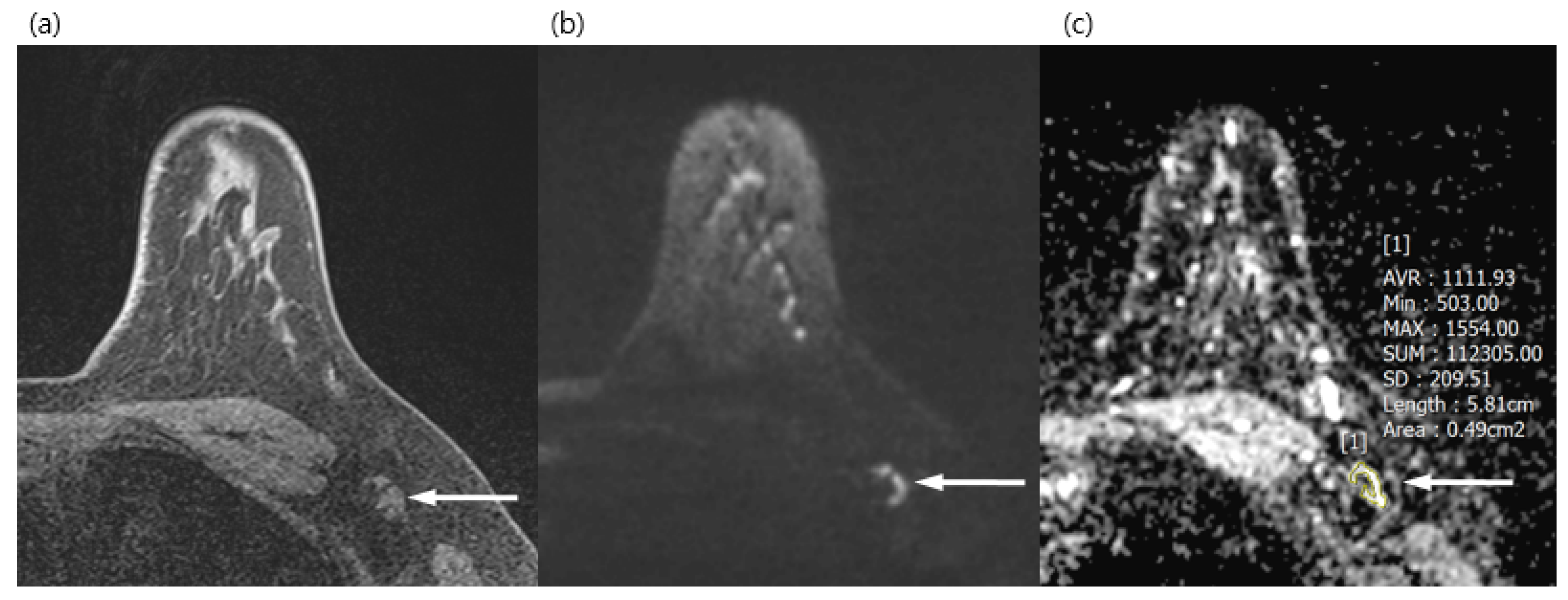
Figure 2.
A 34-year-old woman with a surgically verified benign lymph node in left axilla level I. (a) Axial pre-contrast T1WI of left axilla shows a 1.2 cm lymph node with eccentric cortical thickening (arrow). (b) Axial DWI (b values, 1000 mm2/s) shows a lymph node (arrow) as a mixed area of high and low signal intensity. (c) Axial ADC map (b values, 1000 mm2/s) shows the same lesion with unrestricted diffusion (arrow). The region of interest was manually drawn on the ADC map, avoiding the fatty hilum and guided by a pre-contrast T1WI. The mean ADC of the lesion was 1.111 × 10−3, which indicated a benign lymph node.
The radiologists analyzed each parameter only on DWI based on b1000 image or b1200. They referred to pre-contrast T1WI only to verify visualized ALNs and avoid fatty hilum or surrounding subcutaneous fat tissue when drawing the ROI for ADC. They were blinded to histopathologic findings during assessment.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical comparisons were performed using the Mann–Whitney U test for continuous variables and the chi-square test for categorical variables. Radiologists’ final assessment of benign or metastatic ALNs according to DWI findings was compared with pathologic results. Among the total of 140 cases, 10 did not visualize ALNs on DWI and were included in the benign group. Cases were classified into benign or metastatic groups according to surgical pathologic results. A micrometastatic LN (tumor within a lymph node ≤ 2.0 mm) or an LN with isolated tumor cells were classified into the benign group. All statistical tests were performed in both groups.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to determine the optimal ADC thresholds for discriminating benign and metastatic lymph nodes. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) of the final assessment according to DWI findings were calculated for diagnostic performance.
Statistical analyses were performed using statistical software (SPSS, version 17.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). A p-value < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
3. Results
The final histopathologic examination of 140 axillae revealed 35 cases with metastatic ALNs (25%) and 105 cases with benign ALNs (75%). The subtypes of primary breast cancer are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Subtypes of primary breast cancer.
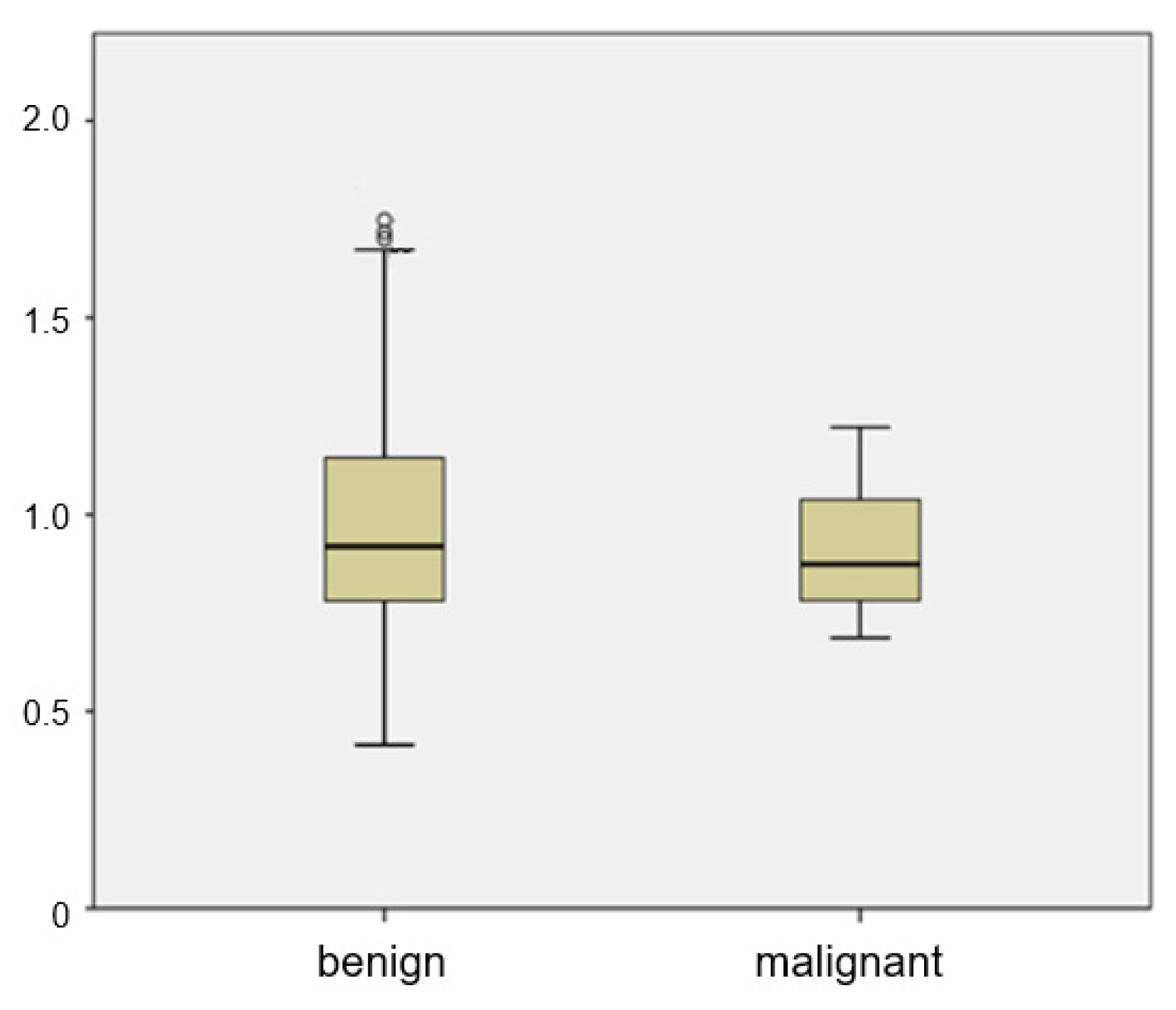
The mean ADC of metastatic ALNs was 0.905 × 10−3 mm2/s, and that of benign ALNs was 0.999 × 10−3 mm2/s. There was a wide range between the 25th and 75th percentiles of the ADC value of benign ALNs (Figure 3). There was no significant difference of ADC values between benign and metastatic groups (p = 0.185). The distribution of ADC values in benign ALNs showed an unbiased distribution and a wide range. Of the 35 malignant ALNs, only 4 had an ADC value greater than 1.1 × 10−3 mm2/s.
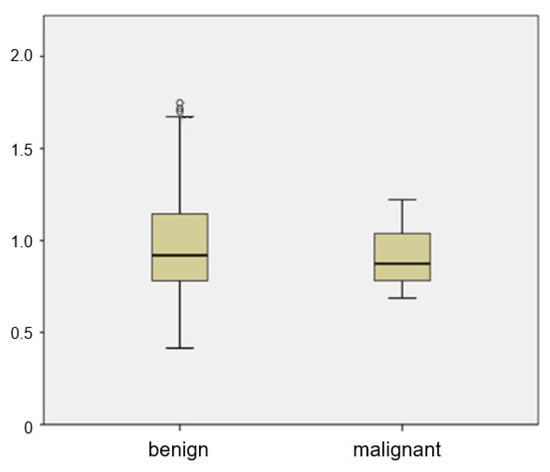
Figure 3.
Box plot of mean ADCs of benign and metastatic ALNs. The top and bottom of each box represent the 25th and 75th percentiles of the ADC, respectively. The horizontal line inside each box represents mean value.
3.1. Continuous Variables
In the morphologic analysis of ALNs on the DWI sequence, long diameter, short diameter, and cortical thickness showed significant statistical differences between benign and metastatic groups. The long diameter of metastatic ALNs was significantly longer than that of benign ALNs (14.8 ± 7.7 mm vs. 10.1 ± 4.1 mm, p < 0.001). The short diameter of metastatic ALNs was significantly longer than that of benign ALNs (9.2 ± 6.4 mm vs. 5.1 ± 1.6 mm, p < 0.001). The L/S ratio of metastatic ALNs was lower than that of benign ALNs (1.8 ± 0.6 vs. 2.1 ± 0.8, p = 0.059). The cortex of metastatic ALNs was significantly thicker than that of benign ALNs (7.6± 7.0 mm vs. 3.2 ± 1.0 mm, p < 0.001) (Table 3).

Table 3.
DW-MRI characteristics of axillary lymph nodes.
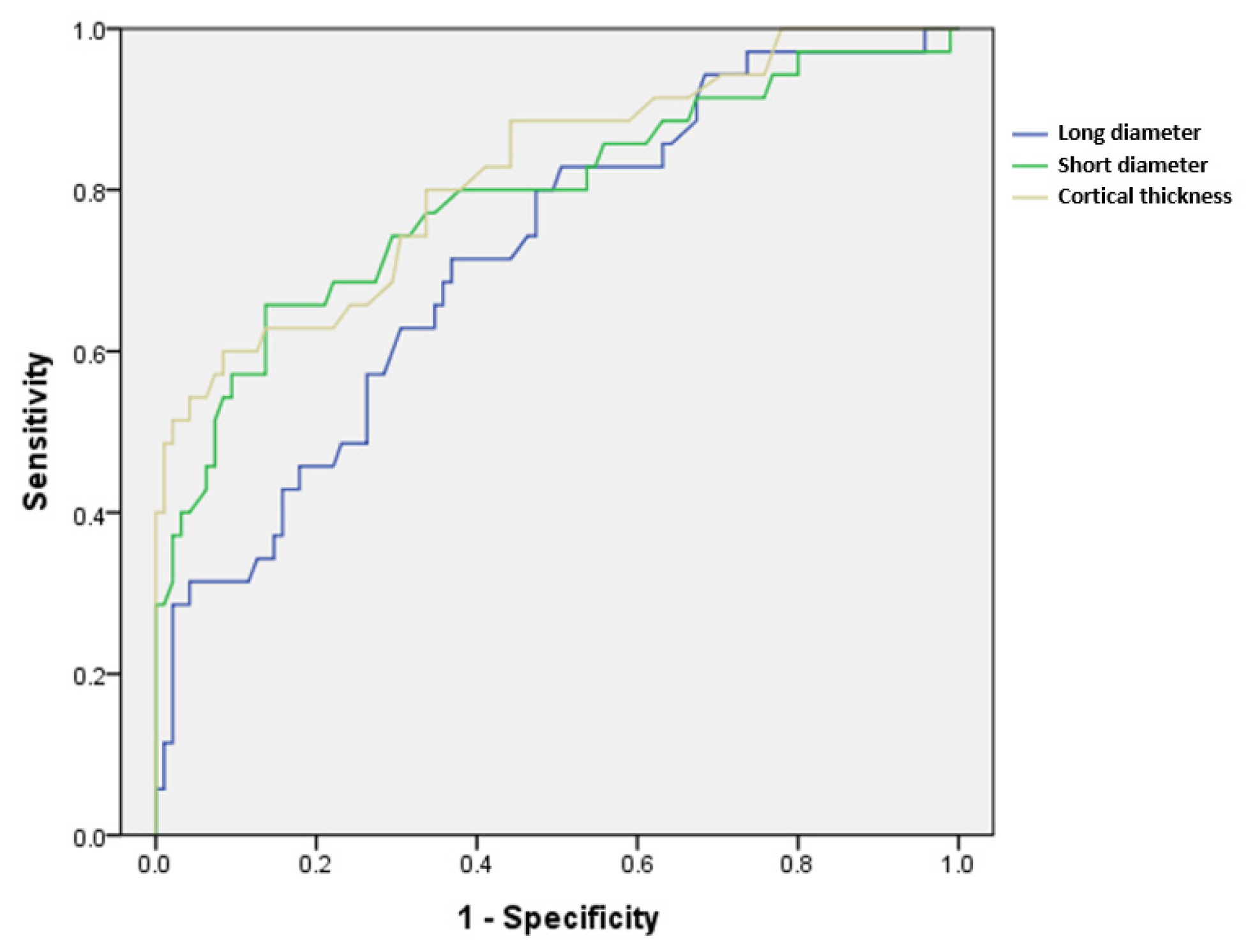
Regarding the accuracy of LN size and cortical thickness, the ROC curve is presented in Figure 4, and the area under the curve (AUC) is presented in Table 4. The cortical thickness showed the highest value of 0.816, and the cut-off level for metastatic ALNs was at 4.35 mm thickness of cortex, suggesting good accuracy (p < 0.001).
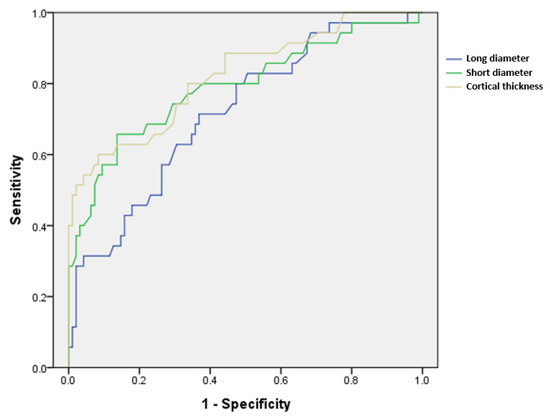
Figure 4.
ROC curves of the continuous variables long diameter, short diameter, and cortical thickness, which showed significant differences between metastatic and benign axillary lymph nodes.

Table 4.
Area under the curve of the ROC curve in Figure 4.
3.2. Categorical Variables
In the morphologic analysis of ALNs, eccentric thickening, loss of fatty hilum, irregular margin, asymmetry either in shape or number of ipsilateral ALNs compared with contralateral ALNs, and rim sign of ALNs were evaluated on the DWI sequence. Metastatic ALNs showed significant differences in all features except the L/S ratio (p ≤ 0.001) (Table 3).
3.3. Diagnostic Performance
We compared and evaluated the correlation between final assessments of benign and metastatic ALNs on DWI and pathology results. The diagnostic performance of DWI to assess benign or metastatic ALNs was as follows: 77.1% for sensitivity, 93.3% for specificity, 79.4% for PPV, 92.5% for NPV, and 86.2% for diagnostic accuracy (Table 5).

Table 5.
Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, diagnostic accuracy, and p-value of the following variables.
4. Discussion
Our results showed no significant difference in ADC values, and significant differences in morphologic features and high diagnostic accuracy between benign and metastatic ALNs.
The mean ADC value of metastatic ALNs was lower than that of benign ALNs, but the difference was not statistically significant (Figure 3).
While the ADC value plays an effective role in discriminating between breast cancer and benign breast lesions, the meaning and usefulness of DWI and ADC values of ALNs remain controversial. In previous studies, the mean ADC of breast cancer was lower than that of benign breast tissue, ranging from 0.75 × 103 mm2/s to 1.50 × 103 mm2/s [18,19,20,21]. The mean ADC of metastatic ALNs ranged from 0.787 × 10−3 mm2/s to 1.182 × 10−3 mm2/s in other reports [22,23,24,25]. These studies suggested cut-off values differentiating benign and metastatic ALNs ranging from 0.889 × 10−3 mm2/s to 1.351 × 10−3 mm2/s and showed variable sensitivities (75.8%~94.7%) and specificities (70.1%~93%) [22,23,24,25].
In our study, the mean ADC of metastatic ALNs was 0.905 × 10−3 mm2/s, which was similar to previous studies [22,23,24,25]. However, the mean ADC of benign ALNs (0.999 × 10−3 mm2/s) was lower than that from previous studies, which ranged from 1.043 × 10−3 mm2/s to 1.551 × 10−3 mm2/s [22,23,24,25]. In addition, there was a wide range between the 25th and 75th percentiles of the ADC values of benign ALNs. We speculate that the ADC measurement of a small benign ALN would be less accurate due to the small size, thin cortex of benign LN, or failure to avoid the fatty hilum or surrounding subcutaneous fat. We also speculate that this result may be from our grouping of micrometastatic LNs as benign. Even though these were small foci of metastatic cells less than 2 mm, they might have influenced the relatively low ADC values of benign ALNs. As a result, there is no significant difference in ADC values between benign and malignant ALNs in our study.
Morphologic characterization of breast mass is important for differentiating malignant mass from benign tissue. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI is useful, while DWI is limited for assessing morphologic features of breast masses because it shows low spatial resolution and artifacts. Instead, DWI yields functional measures of the tumor microenvironment such as cell density, membrane integrity, and microstructures and is represented by ADC values [26,27]. Studies about morphologic assessment of ALNs on DWI are rare. Although morphologic evaluation of DWI was usually not performed in breast mass or ALNs, we tried to measure the long and short diameters and cortical thickness of ALNs and to assess variable morphologic features, including eccentric thickening, loss of fatty hilum, irregular margin, asymmetry in either shape or number, and rim sign on DWI. Our study showed significant differences in morphologic features and high diagnostic accuracy. Based on these DWI findings without contrast-enhanced MRI, two radiologists classified ALNs into benign or metastatic groups, with high NPV (92.5%) and specificity (93.3%). We guess that analysis of morphology of ALNs on DWI—long and short diameters, cortical thickness of ALNs, eccentric thickening, loss of fatty hilum, irregular margin, asymmetry in either shape or number, and rim sign—would be less affected than that of breast mass, which needs high resolution for characterizing detailed margin and shape. Moreover, MRI at 3.0T may yield improved signal-to-noise ratios for DWI.
He et al. [23] reported higher diagnostic performance using conventional MRI with an enhanced dynamic sequence; the diagnostic performance of the MRI-based lymph node scoring system had a sensitivity of 93% and specificity of 91%. The researchers reported overall higher sensitivity in variables of long diameter, short diameter, L/S ratio, and irregular margin. Chayakulkheeree et al. [28] also reported good diagnostic performance with a sensitivity of 98.5%, specificity of 57.8%, NPV of 96.4%, and PPV of 71%, using conventional MRI with an enhanced dynamic sequence. Compared with these previous studies, our study reported a relatively lower sensitivity (77.1%) and similar or higher specificity (93.3%). Therefore, the sensitivity of DW-MRI is slightly lower and the specificity is similar to, or rather higher than, that of conventional enhanced MRI in distinguishing benign and metastatic ALNs. Although morphologic assessment of ALNs on DWI is limited due to low spatial resolution and artifacts, it is sufficient to assess ALNs when contrast-enhanced breast MRI cannot be performed.
Our study has several limitations. The first was the high b value of DWI at b = 1000 (n = 66) or b = 1200 (n = 74), which could result in signal loss or image distortion. In addition, ADC is intrinsically dependent on many individual factors such as patient age, body temperature, tissue pressure, and perfusion rate, and on magnetic features such as MR acquisition parameters, magnetic field, and location and area of the ROI [22,29,30,31,32,33]. This might compromise the consistency of the study. Thus, the radiologists in our study referred to pre-contrast T1WI only to determine whether a visualized lesion was a true LN or not. However, these processes might lead to biased results. Second, upper ALNs may not be included in the FOV. In our study, five cases were excluded because they were not shown on the DWI. Three of the five cases were shown on mammography and four were shown on ultrasonography. Thus, a correlation with other imaging modalities is required. Third, this study was performed retrospectively in a single center and involved a small number of subjects. A larger group from multiple centers should be examined in a future prospective study.
5. Conclusions
Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in breast cancer patients has been used widely for diagnosis and staging. Morphologic evaluation of features such as margin, shape, and enhancement pattern with analysis of the kinetic curve was important in discriminating malignant from benign lesions. For such analyses, DW-MRI offers not only functional information by qualifying restriction of water motion within a tumor, but also morphologic information. Our results suggest that morphologic evaluation of ALNs on DWI can discriminate metastatic ALNs from benign without contrast enhancement. The ADC value of metastatic ALNs was lower than that of benign nodes, but the difference was not significant. The DWI for ALN evaluation may be a good alternative MR sequence to contrast-enhanced MRI, especially in cases of contrast allergy or renal insufficiency.
In the future, study of breast cancer and ALN evaluation should be extended to combinations of basic imaging modalities with new technology such as radiomics, which is an emerging technique that converts medical images into high-dimensional, mineable, and quantitative features via automatic extraction of data-characterization algorithms [34,35]. Radiomics in breast imaging has been applied to most existing modalities, including MRI, mammography, ultrasound, and digital breast tomosynthesis [36]. Radiomic research in breast imaging has shown promising results from diagnosis to prognosis [37,38,39,40,41]. Texture analysis using radiomics extracted from variable MR sequences has been used not only to differentiate between benign and malignant lesions and to distinguish between breast cancer subtypes, but also to predict treatment responses after NAC and disease-free survival. Militello et al. [39] reported that their predictive model based on 3D radiomic features extracted from dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI sequences using only the strongest enhancement phase showed good accuracy and specificity in the differentiation of malignant from benign breast lesions. Dong Y et al. [40] reported that utilization of breast cancer-specific textural features extracted from T2-weighted fat-suppression and DW-MRI improved the performance of radiomics in predicting sentinel LN metastasis without biopsy, pre-operatively. In addition, Park et al. [41] reported that the radiomics signature would be an independent biomarker for the estimation of disease-free survival in patients with invasive breast cancer.
As a future direction, we are planning to apply radiomics to non-contrast-enhanced and functional MRI such as DWI. This integration could potentially be useful for precision medicine and clinical management in patients with contrast allergy or renal insufficiency, and avoid deposition of gadolinium in the brain.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H.K.; data curation, G.E.P.; investigation, C.S.P. and G.E.P.; methodology, S.H.K. and C.S.P.; resources, P.C. and C.S.P.; supervision, S.H.K., H.S.K. and S.-J.O.; validation, H.S.K. and S.-J.O.; writing—original draft, P.C.; writing—review and editing, C.S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the ethics committee of our institution.
Informed Consent Statement
The requirement for written informed consent from patients was waived due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Data Availability Statement
Due to privacy and institutional restrictions, the datasets analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the respective authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Carter, C.L.; Allen, C.; Henson, D.E. Relation of tumor size, lymph node status, and survival in 24,740 breast cancer cases. Cancer 1989, 63, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End RESULTS Program (SEER). Table 4.13: Cancer of the Female Breast (Invasive)—5 Year Relative and Period Survival by Race, Diagnosis Year, Ange and Stage at Diagnosis. In: SEER Cancer Statistics Review (CSR) 1975–2016. SEER Website. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2016/browse_csr.php?sectionSEL=4&pageSEL=sect_04_table.13 (accessed on 29 October 2019).
- Ahmed, M.; Douek, M. What is the future of axillary surgery for breast cancer? Ecancermedicalscience 2013, 7, 319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Cataldo, C.; Bruno, F.; Palumbo, P.; Di Sibio, A.; Arrigoni, F.; Clemente, A.; Di Cesare, E.; Barile, A.; Splendiani, A.; Masciocchi, C.; et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient magnetic resonance imaging (adc-mri) in the axillary breast cancer lymph node metastasis detection: A narrative review. Gland Surg. 2020, 9, 2225–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schijven, M.P.; Vingerhoets, A.J.; Rutten, H.J.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.; Roumen, R.M.; van Bussel, M.E.; Voogd, A.C. Comparison of morbidity between axillary lymph node dissection and sentinel node biopsy. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2003, 29, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, S.A.; Levine, G.M.; Silverstein, M.J.; Rayhanabad, J.A.; Weng-Grumley, J.G.; Ji, L.; Holmes, D.R.; Sposto, R.; Sener, S.F. Accuracy of predicting axillary lymph node positivity by physical examination, mammography, ultrasonography, and magnetic resonance imaging. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madej, B.; Maciejewski, R.; Wójtowicz, Z.; Burdan, F.; Torres, K.; Kadej, A.; Furtak, P. Axillary lymph node and early breast cancer diagnostics. A case report. Folia Morphol. 2003, 62, 523–525. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Masroor, I.; Khandwala, K.; Abbasi, S.U.; Tariq, M.U. Utility of ultrasound and mammography in detection of negative axillary nodal metastasis in breast cancer. Cureus 2020, 12, e6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecanow, J.S.; Abe, H.; Newstead, G.M.; Ecanow, D.B.; Jeske, J.M. Axillary staging of breast cancer: What the radiologist should know. Radiographics 2013, 33, 1589–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.M.; Leung, J.W.T.; Moy, L.; Ha, S.M.; Moon, W.K. Axillary nodal evaluation in breast cancer: State of the Art. Radiology 2020, 295, 500–515. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, E.; Liberman, G.; Nissan, N.; Furman-Haran, E.; Sklair-Levy, M.; Frydman, L. Diffusion-weighted breast MRI of malignancies with submillimeter resolution and immunity to artifacts by spatiotemporal encoding at 3T. Magn. Reason. Med. 2020, 84, 1391–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaranelo, A.M.; Eiada, R.; Jacks, L.M.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Crystal, P. Accuracy of unenhanced mr imaging in the detection of axillary lymph node metastasis: Study of reproducibility and reliability. Radiology 2012, 262, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Youk, J.H.; Kim, J.-A.; Gweon, H.M.; Kim, E.-K.; Ryu, Y.H.; Son, E.J. Role of diffusion-weighted MRI: Predicting axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer. Acta Radiol. 2014, 55, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, G.; Sakurai, T.; Oura, S.; Suzuma, T.; Tamaki, T.; Umemura, T.; Kokawa, Y.; Yang, Q. Evaluation of axillary lymph node status in breast cancer with MRI. Breast Cancer 1999, 6, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortellaro, V.E.; Marshall, J.; Singer, L.; Hochwald, S.N.; Chang, M.; Copeland, E.M.; Grobmyer, S.R. Magnetic resonance imaging for axillary staging in patients with breast cancer. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2009, 30, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltzer, P.A.; Dietzel, M.; Burmeister, H.P.; Zoubi, R.; Gajda, M.; Camara, O.; Kaiser, W.A. Application of MR mammography beyond local staging: Is there a potential to accurately assess axillary lymph nodes? Evaluation of an extended protocol in an initial prospective study. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, W641–W647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Lipson, J.A.; Planey, K.R.; Zackrisson, S.; Ikeda, D.M.; Kao, J.; Pal, S.; Moran, C.J.; Daniel, B.L. Rim sign in breast lesions on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: Diagnostic accuracy and clinical usefulness. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2015, 41, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahbar, H.; Partridge, S.C.; Eby, P.R.; Demartini, W.B.; Gutierrez, R.L.; Peacock, S.; Lehman, C.D. Characterization of ductal carcinoma in situ on diffusion weighted breast MRI. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 2011–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, T.; Isomoto, I.; Sueyoshi, E.; Yano, H.; Uga, T.; Abe, K.; Hayashi, T.; Honda, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Uetani, M. Diagnostic performance of ADC for Non-mass-like breast lesions on MR imaging. Magn. Reason. Med. Sci. 2010, 9, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeh, S.K.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, B.J.; Jeong, S.H.; Yim, H.W.; Song, B.J. Correlation of the apparent diffusion coefficient value and dynamic magnetic resonance imaging findings with prognostic factors in invasive ductal carcinoma. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2011, 33, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kul, S.; Cansu, A.; Alhan, E.; Dinc, H.; Gunes, G.; Reis, A. Contribution of diffusion-weighted imaging to dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in the characterization of breast tumor. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornasa, F.; Nesoti, M.V.; Bovo, C.; Bonavina, M.G. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the characterization of axillary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2012, 36, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, N.; Xie, C.; Wei, W.; Pan, C.; Wang, W.; Lv, N.; Wu, P. A new, preoperative, mri-based scoring system for diagnosing malignant axillary lymph nodes in women evaluated for breast cancer. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 2602–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, N.; Su, D.; Jin, G.; Liu, L.; Zhu, X.; Xie, D.; Liu, Y. Apparent diffusion coefficient ratio between axillary lymph node with primary tumor to detect nodal metastasis in breast cancer patients. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2013, 38, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, B.J.; Choi, B.G.; Song, B.J.; Choi, J.J. Diagnostic value of breast mri for predicting metastatic axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients: Diffusion-weighted mri and conventional mri. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2014, 32, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ei Khouli, R.H.; Jacobs, M.A.; Mezban, S.D.; Huang, P.; Kamel, I.R.; Macura, K.J.; Bluemke, D.A. Diffusion-weighted imaging improves the diagnostic accuracy of conventional 3.0 T breast MR imaging. Radiology 2010, 256, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patridge, S.C.; Nissan, N.; Rahbar, H.; Kitsch, A.E.; Sigmund, E.E. Diffusion-weighted breast MRI: Clinical application and emerging techniques. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2017, 45, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chayakulkheeree, J.; Pungrassami, D.; Prueksadee, J. Performance of breast magnetic resonance imaging in axillary nodal staging in newly diagnosed breast cancer patients. Pol. J. Radiol. 2019, 84, e413–e418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwee, T.C.; Takahara, T.; Luijten, P.R.; Nievelstein, R.A. ADC measurements of lymph nodes: Inter- and intra-obsever reproducibility study and an overview of the literature. Eur. J. Radiol. 2010, 75, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoehn-Berlage, M.; Eis, M.; Schmitx, B. Regional and directional anissotrpy of apparent diffusion coefficient in rat brain. NMR Biomed. 1999, 12, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, C.; Bai, R.; Sun, H. Differential diagnosis of axillary inflammatory and metastatic lymph nodes in rabbit models by using diffusion-weighted imaging: Compared with conventional magnetic resonance imaging. Korean J. Radiol. 2012, 13, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLano, M.C.; Cooper, T.G.; Siebert, J.E.; Potchen, M.J.; Kuppusamy, K. High-b-balue diffusion-weighted MR imaging of adult brain: Image contrast and appraent diffusion coefficient map features. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2000, 21, 1830–1836. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mulkern, R.V.; Barnes, A.S.; Haker, S.J.; Hung, Y.P.; Rybicki, F.J.; Maier, S.E.; Tempany, C.M. Biexponential characterization of prostate tissue water diffusion decay curves over an extended b-factor range. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2006, 24, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, H.J.; Velazquez, E.R.; Leijenaar, R.T.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Carvalho, S.; Bussink, J.; Monshouwer, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Rietveld, D.; et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, W.; Thulasi Seetha, S.; Refaee, T.A.G.; Lieverse, R.I.Y.; Granzier, R.W.Y.; Ibrahim, A.; Keek, S.; Sanduleanu, S.; Primakov, S.; Beuque, M.; et al. Radiomics: From qualitative to quantitative imaging. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.-M.; Wang, H.-T.; Yu, T. The application of radiomics in breast MRI: A Review. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820916191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickelhaupt, S.; Paech, D.; Kickingereder, P.; Steudle, F.; Lederer, W.; Daniel, H.; Götz, M.; Gählert, N.; Tichy, D.; Wiesenfarth, M.; et al. Prediction of malignancy by a radiomics signature from contrast agent-free diffusion MRI in suspicious breast lesions found on screening mammography. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2017, 46, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militello, C.; Rundo, L.; Dimarco, M.; Orlando, A.; Woitek, R.; D’Angelo, I.; Russo, G.; Bartolotta, T.V. 3D DCE-MRI radiomic analysis for malignant lesion prediction in breast cancer patients. Acad. Radiol. 2022, 29, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Feng, Q.; Yang, W.; Lu, Z.; Deng, C.; Zhang, L.; Lian, Z.; Liu, J.; Luo, X.; Pei, S.; et al. Preoperative prediction of sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer based on radiomics of T2-weighted fat-suppression and diffusion-weighted MRI. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Lim, Y.; Ko, E.S.; Cho, H.; Lee, J.E.; Han, B.; Choi, J.S.; Park, K.W. Radiomics signature on magnetic resonance imaging: Association with disease-free survival in patients with invasive breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4705–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).