Diagnostic Accuracy of Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for the Diagnosis of Skin Carcinomas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Setting
2.3. Participants
2.4. Imaging Examination
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Diagnostic Performances of Dermoscopy and LC-OCT Considering Only Cases with Histological Diagnoses
3.1.1. Dermoscopy and LC-OCT Diagnostic Performances for BCC
3.1.2. Dermoscopy and LC-OCT Diagnostic Performances for the Diagnosis of SCC/Bowen Disease
3.1.3. Dermoscopy and LC-OCT Diagnostic Performances for the Diagnosis of AK/SCC/Bowen Disease
3.1.4. Dermoscopy and LC-OCT Diagnostic Performances for Malignant Tumour
3.1.5. Diagnostic Performances of Dermoscopy and LC-OCT Considering Both Histological and Follow-Up Diagnoses
3.1.6. Dermoscopy and LC-OCT Diagnostic Performances for BCC (Including 13 Cases without a Histological Diagnosis)
3.1.7. Dermoscopy and LC-OCT Diagnostic Performances for Malignant Tumours (Including 17 Cases without a Histological Diagnosis)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Our real-life study confirmed that dermoscopy can select lesions at risk of being malignant skin tumours (very sensitive tool).
- LC-OCT could be positioned in a second line to rule out malignancy to spare useless biopsy without decreasing sensitivity (very specific tool).
- LC-OCT can help in the identification of BCC with only 10 diagnostic errors in our entire database covering more than one year.
- LC-OCT seems to also be promising for keratinocyte tumours (AK, SCC, and Bowen’s disease) by increasing the specificity and reducing FP cases compared to dermoscopy.
- Further studies should be performed to confirm our data and investigate the possible role of LC-OCT for the different malignant skin tumours.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubois, A.; Levecq, O.; Azimani, H.; Siret, D.; Barut, A.; Suppa, M.; Del Marmol, V.; Malvehy, J.; Cinotti, E.; Rubegni, P.; et al. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for High-Resolution Noninvasive Imaging of Skin Tumors. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.; Levecq, O.; Azimani, H.; Siret, D.; Dubois, A. Simultaneous Dual-Band Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography: Application to Skin Imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tognetti, L.; Cinotti, E.; Falcinelli, F.; Miracco, C.; Suppa, M.; Perrot, J.-L.; Rubegni, P. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography: A New Tool for Non-Invasive Differential Diagnosis of Pustular Skin Disorders. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1873–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallay, C.; Ventéjou, S.; Gaide, O.; Christen-Zaech, S. Cutaneous visualization by different non-invasive skin imaging methods. Rev. Med. Suisse 2021, 17, 624–629. [Google Scholar]
- Chauvel-Picard, J.; Bérot, V.; Tognetti, L.; Orte Cano, C.; Fontaine, M.; Lenoir, C.; Pérez-Anker, J.; Puig, S.; Dubois, A.; Forestier, S.; et al. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography as a Tool for Three-Dimensional in Vivo Quantification of Healthy Epidermis: A Pilot Study. J. Biophotonics 2021, 15, e202100236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruini, C.; Schuh, S.; Sattler, E.; Welzel, J. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography-Practical Applications in Dermatology and Comparison with Established Imaging Methods. Skin Res. Technol. 2021, 27, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, J.; Tognetti, L.; Miyamoto, M.; Suppa, M.; Cinotti, E.; Fontaine, M.; Perez, J.; Orte Cano, C.; Yélamos, O.; Puig, S.; et al. In Vivo Characterization of Healthy Human Skin with a Novel, Non-Invasive Imaging Technique: Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 2914–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogien, J.; Levecq, O.; Azimani, H.; Dubois, A. Dual-Mode Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for Ultrahigh-Resolution Vertical and Horizontal Section Imaging of Human Skin in Vivo. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuh, S.; Ruini, C.; Sattler, E.; Welzel, J. Confocal line-field OCT. Hautarzt Z. Dermatol. Venerol. Verwandte Geb. 2021, 72, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischman, S.; Pérez-Anker, J.; Tognetti, L.; Di Naro, A.; Suppa, M.; Cinotti, E.; Viel, T.; Monnier, J.; Rubegni, P.; Del Marmol, V.; et al. Non-Invasive Scoring of Cellular Atypia in Keratinocyte Cancers in 3D LC-OCT Images Using Deep Learning. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Ogien, J.; Bulkin, P.; Coutrot, A.-L.; Dubois, A. Mirau-Based Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for Three-Dimensional High-Resolution Skin Imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2022, 27, 086002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Anker, J.; Puig, S.; Alos, L.; García, A.; Alejo, B.; Cinotti, E.; Orte Cano, C.; Tognetti, L.; Lenoir, C.; Monnier, J.; et al. Morphologic Evaluation of Melanocytic Lesions with Three-Dimensional Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography: Correlation with Histopathology and Reflectance Confocal Microscopy. A Pilot Study. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 47, 2222–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waszczuk, L.; Ogien, J.; Perrot, J.-L.; Dubois, A. Co-Localized Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography and Confocal Raman Microspectroscopy for Three-Dimensional High-Resolution Morphological and Molecular Characterization of Skin Tissues Ex Vivo. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 2467–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, A.; Xue, W.; Levecq, O.; Bulkin, P.; Coutrot, A.-L.; Ogien, J. Mirau-Based Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 7918–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuh, S.; Ruini, C.; Perwein, M.K.E.; Daxenberger, F.; Gust, C.; Sattler, E.C.; Welzel, J. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography: A New Tool for the Differentiation between Nevi and Melanomas? Cancers 2022, 14, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappilli, S.; Cinotti, E.; Lenoir, C.; Tognetti, L.; Perez-Anker, J.; Rubegni, P.; Puig, S.; Malvehy, J.; Perrot, J.L.; Del Marmol, V.; et al. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography of Basosquamous Carcinoma: A Case Series with Histopathological Correlation. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1214–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyachi, K.; Murakami, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Yoshioka, H.; Hirose, O.; Yamada, T.; Hasegawa, S.; Arima, M.; Iwata, Y.; Sugiura, K.; et al. UVA Causes Dysfunction of ETBR and BMPR2 in Vascular Endothelial Cells, Resulting in Structural Abnormalities of the Skin Capillaries. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2022, 105, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tognetti, L.; Carraro, A.; Lamberti, A.; Cinotti, E.; Suppa, M.; Luc Perrot, J.; Rubegni, P. Kaposi Sarcoma of the Glans: New Findings by Line Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography Examination. Skin Res. Technol. 2021, 27, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognetti, L.; Cinotti, E.; Suppa, M.; Guazzo, R.; Habougit, C.; Santi, F.; Diet, G.; Fontaine, M.; Berot, V.; Monnier, J.; et al. Line Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Bullous Diseases. J. Biophotonics 2021, 14, e202000449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacarrubba, F.; Verzì, A.E.; Puglisi, D.F.; Broggi, G.; Caltabiano, R.; Micali, G. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography of Xanthogranuloma: Correlation with Vertical and Horizontal Histopathology. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2021, 48, 1208–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognetti, L.; Carraro, A.; Cinotti, E.; Suppa, M.; Del Marmol, V.; Perrot, J.L.; Rubegni, P. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Lichenoid Dermatoses of the Childhood: A Case Series. Skin Res. Technol. 2021, 27, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognetti, L.; Rizzo, A.; Fiorani, D.; Cinotti, E.; Perrot, J.L.; Rubegni, P. New Findings in Non-Invasive Imaging of Aquagenic Keratoderma: Line-Field Optical Coherence Tomography, Dermoscopy and Reflectance Confocal Microscopy. Skin Res. Technol. 2020, 26, 956–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verzì, A.E.; Broggi, G.; Micali, G.; Sorci, F.; Caltabiano, R.; Lacarrubba, F. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography of Psoriasis, Eczema and Lichen Planus: A Case Series with Histopathological Correlation. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1884–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruini, C.; Schuh, S.; Hartmann, D.; French, L.; Welzel, J.; Sattler, E. Noninvasive Real-Time Imaging of Mite Skin Infestations with Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruini, C.; Schuh, S.; Pellacani, G.; French, L.; Welzel, J.; Sattler, E. In Vivo Imaging of Sarcoptes Scabiei Infestation Using Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, e808–e809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruini, C.; Schuh, S.; Gust, C.; Kendziora, B.; Frommherz, L.; French, L.E.; Hartmann, D.; Welzel, J.; Sattler, E. Line-Field Optical Coherence Tomography: In Vivo Diagnosis of Basal Cell Carcinoma Subtypes Compared with Histopathology. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 46, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppa, M.; Fontaine, M.; Dejonckheere, G.; Cinotti, E.; Yélamos, O.; Diet, G.; Tognetti, L.; Miyamoto, M.; Orte Cano, C.; Perez-Anker, J.; et al. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography of Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Descriptive Study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verzì, A.E.; Micali, G.; Lacarrubba, F. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography May Enhance Monitoring of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma Treated with Imiquimod 5% Cream: A Pilot Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruini, C.; Schuh, S.; Gust, C.; Hartmann, D.; French, L.E.; Sattler, E.C.; Welzel, J. In-Vivo LC-OCT Evaluation of the Downward Proliferation Pattern of Keratinocytes in Actinic Keratosis in Comparison with Histology: First Impressions from a Pilot Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejonckheere, G.; Suppa, M.; Del Marmol, V.; Meyer, T.; Stockfleth, E. The Actinic Dysplasia Syndrome-Diagnostic Approaches Defining a New Concept in Field Carcinogenesis with Multiple CSCC. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33 (Suppl. S8), 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinotti, E.; Tognetti, L.; Cartocci, A.; Lamberti, A.; Gherbassi, S.; Orte Cano, C.; Lenoir, C.; Dejonckheere, G.; Diet, G.; Fontaine, M.; et al. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for Actinic Keratosis and Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Descriptive Study. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 46, 1530–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruini, C.; Schuh, S.; Gust, C.; Kendziora, B.; Frommherz, L.; French, L.E.; Hartmann, D.; Welzel, J.; Sattler, E.C. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for the in Vivo Real-Time Diagnosis of Different Stages of Keratinocyte Skin Cancer: A Preliminary Study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenoir, C.; Perez-Anker, J.; Diet, G.; Tognetti, L.; Cinotti, E.; Trépant, A.; Rubegni, P.; Puig, S.; Perrot, J.; Malvehy, J.; et al. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography of Benign Dermal Melanocytic Proliferations: A Case Series. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, e399–e401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, C.; Cinotti, E.; Tognetti, L.; Orte Cano, C.; Diet, G.; Miyamoto, M.; Rocq, L.; Trépant, A.-L.; Perez-Anker, J.; Puig, S.; et al. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography of Actinic Keratosis: A Case Series. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, e900–e902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, C.; Diet, G.; Cinotti, E.; Tognetti, L.; Orte Cano, C.; Rocq, L.; Trépant, A.-L.; Monnier, J.; Perez-Anker, J.; Rubegni, P.; et al. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography of Sebaceous Hyperplasia: A Case Series. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, e509–e511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weedon, D. Weedon’s Skin Pathology, 3rd ed.; Churchill Livingstone Elsevier: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gust, C.; Schuh, S.; Welzel, J.; Daxenberger, F.; Hartmann, D.; French, L.E.; Ruini, C.; Sattler, E.C. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography Increases the Diagnostic Accuracy and Confidence for Basal Cell Carcinoma in Equivocal Lesions: A Prospective Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
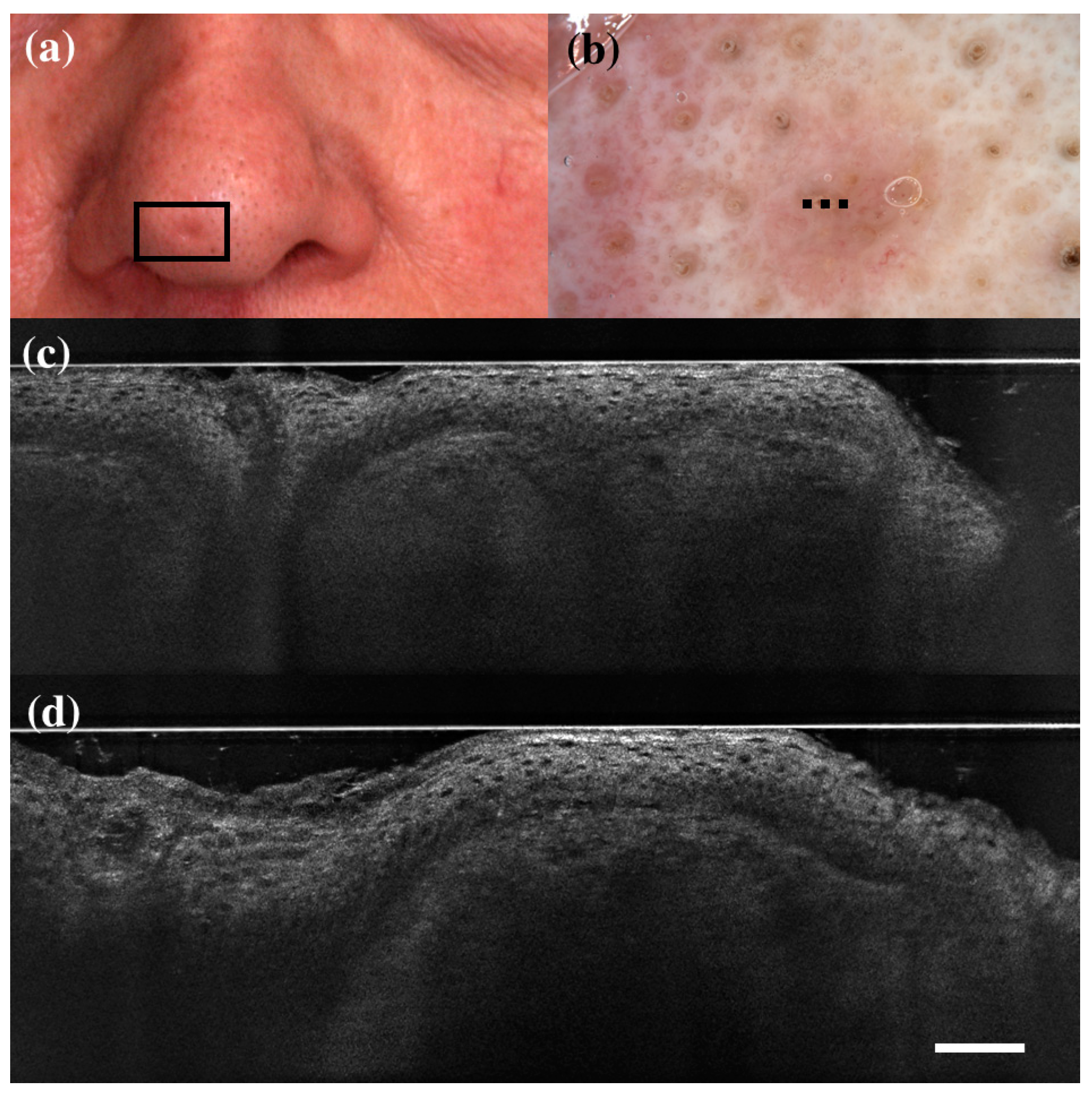
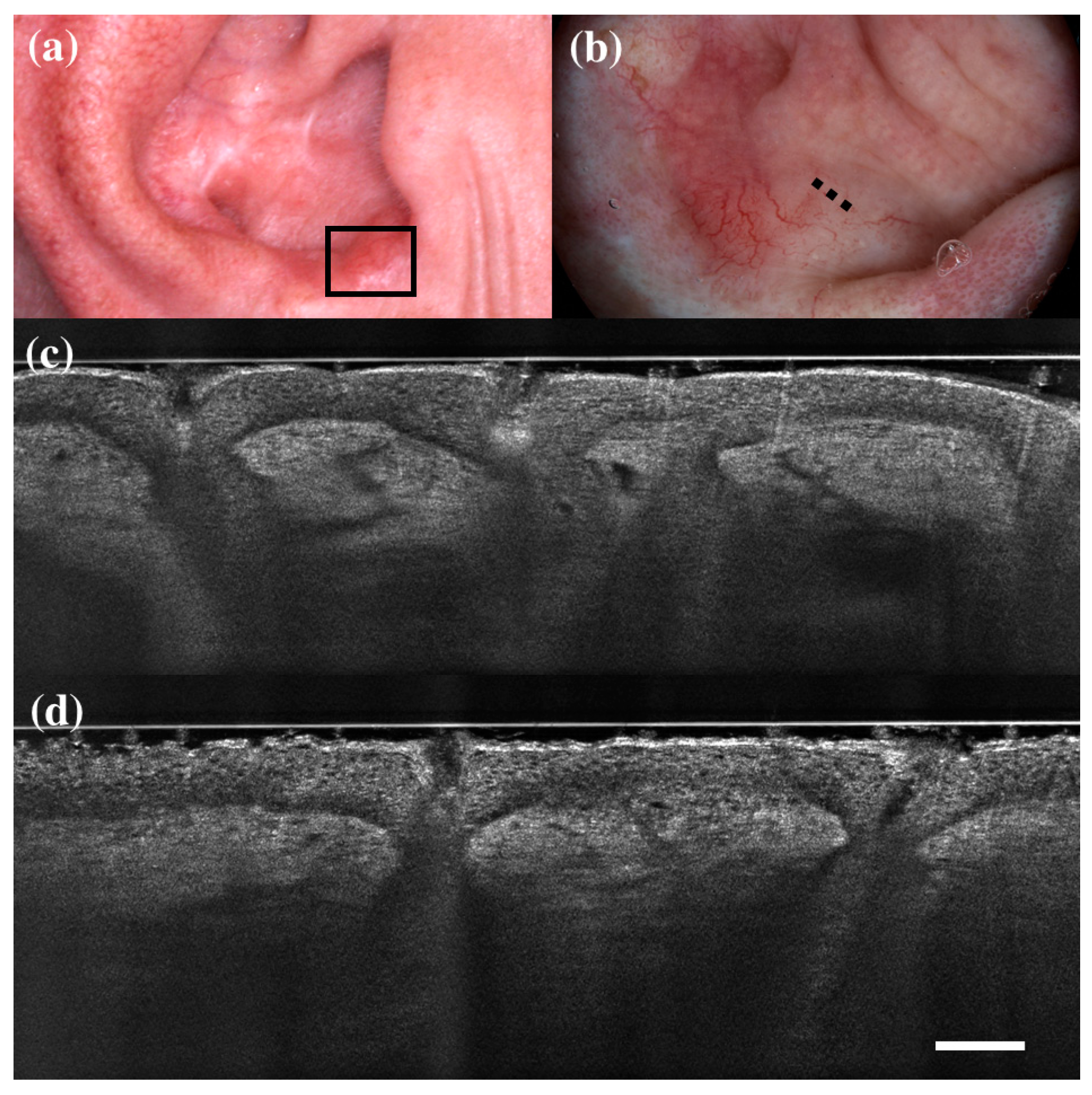
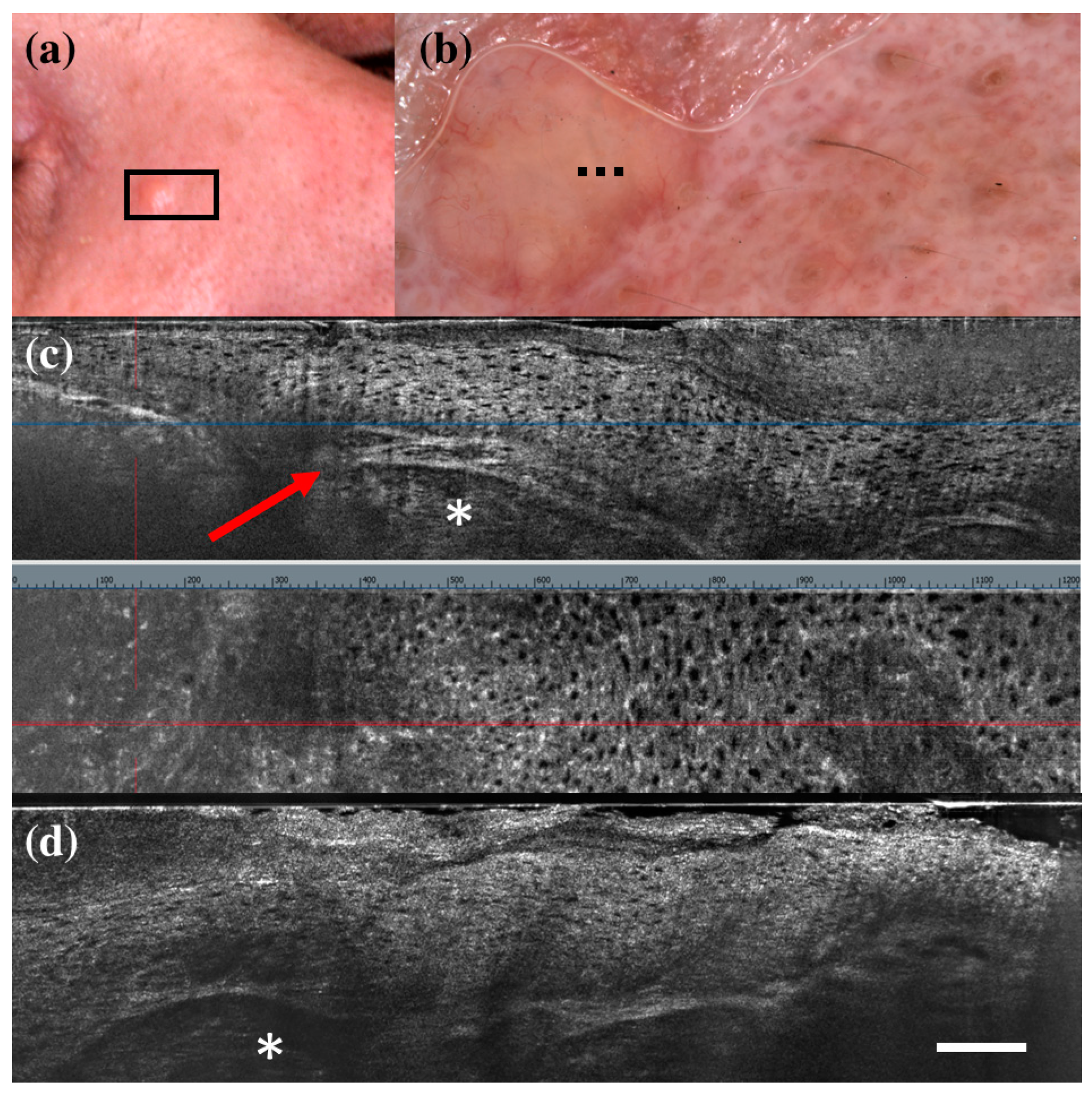

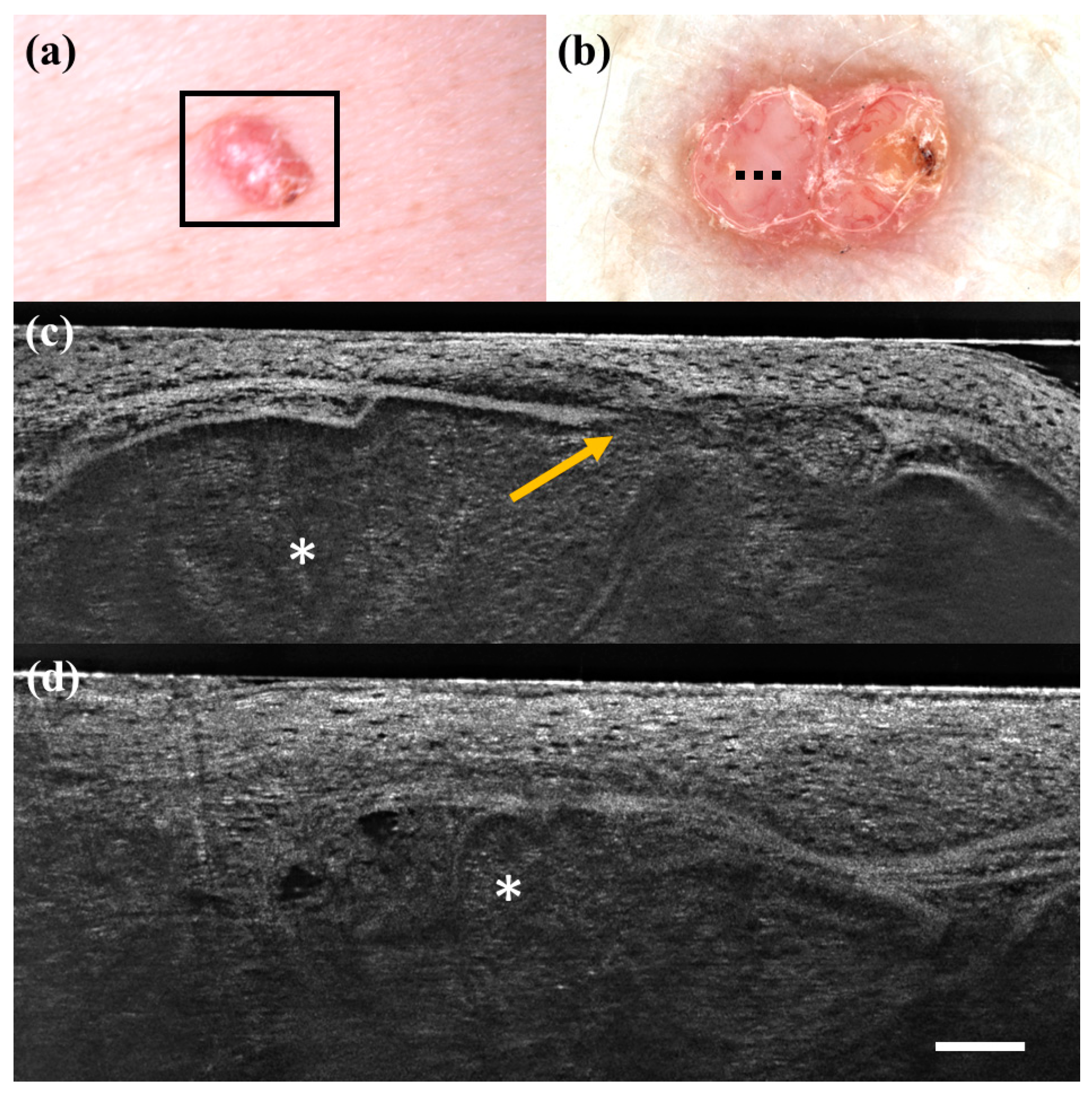
| HISTOLOGY | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCC (n = 79) | Benign ML (n = 22) | Melanoma (n = 10) | AK (n = 16) | SCC (n = 22) | Inflammatory Lesion(n = 14) | Rare Disease (n = 5) | Other (n = 58) | ||
| DERMOSCOPY (in case of multiple diagnoses on dermoscopy, the worst diagnosis was retained) | BCC (n = 96) | 76 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 12 |
| Benign ML (n = 17) | 0 | 15 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Melanoma (n = 14) | 0 | 5 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| AK (n = 15) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| SCC (n = 26) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 17 | 2 | 0 | 3 | |
| Inflammatory lesion (n = 6) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 | |
| Rare disease (n = 5) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | |
| Other (n = 47) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 40 | |
| LC-OCT (in case of multiple diagnoses on LC-OCT, the worst diagnosis was retained) | BCC (n = 84) | 77 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 |
| benign ML (n = 20) | 0 | 17 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| Melanoma (n = 13) | 0 | 3 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| AK (n = 18) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| SCC (n = 24) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 19 | 1 | 0 | 2 | |
| Inflam (n = 9) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 1 | |
| rare disease (n = 5) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | |
| Other (n = 53) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 46 | |
| DERMOSCOPY | LC-OCT | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCC (n = 79) | TP/P | 76/79 | 77/79 | |
| TN/N | 127/147 | 140/147 | ||
| Sensitivity (CI) | 0.96 (0.89–0.99) | 0.97 (0.91–1.00) | 1 | |
| Specificity (CI) | 0.86 (0.80–0.91) | 0.95 (0.90–0.98) | 0.015 | |
| SCC/Bowen (n = 19) | TP/P | 17/22 | 19/22 | |
| TN/N | 195/204 | 199/204 | ||
| Sensitivity (CI) | 0.77 (0.55–0.92) | 0.86 (0.65–0.97) | 0.696 | |
| Specificity (CI) | 0.96 (0.92–0.98) | 0.98 (0.94–0.99) | 0.415 | |
| AK/Bowen/SCC (n = 36) | TP/P | 33/38 | 36/38 | |
| TN/N | 180/188 | 182/188 | ||
| Sensitivity (CI) | 0.87 (0.72–0.96) | 0.95 (0.82–0.99) | 0.428 | |
| Specificity (CI) | 0.96 (0.92–0.98) | 0.97 (0.93–0.99) | 0.785 | |
| Malignant vs. non Malignant (n = 111) | TP/P | 105/111 | 106/111 | |
| TN/N | 84/115 | 100/115 | ||
| Sensitivity (CI) | 0.95 (0.89–0.98) | 0.95 (0.90–0.99) | 1 | |
| Specificity (CI) | 0.73 (0.64–0.81) | 0.87 (0.79–0.93) | 0.013 |
| DERMOSCOPY | LC-OCT | p Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCC (n = 79) | TP/P | 76/79 | 77/79 | |
| TN/N | 127/160 | 153/160 | ||
| Sensitivity (CI) | 0.96 (0.89–0.99) | 0.97 (0.91–1.00) | 1 | |
| Specificity (CI) | 0.79 (0.72–0.85) | 0.96 (0.91–0.98) | p < 0.001 | |
| Malignant vs. non Malignant (n = 111) | TP/P | 105/111 | 106/111 | |
| TN/N | 84/132 | 117/132 | ||
| Sensitivity (CI) | 0.95 (0.89–0.98) | 0.95 (0.90–0.99) | 1 | |
| Specificity (CI) | 0.64 (0.55–0.72) | 0.89 (0.82–0.93) | p < 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cinotti, E.; Brunetti, T.; Cartocci, A.; Tognetti, L.; Suppa, M.; Malvehy, J.; Perez-Anker, J.; Puig, S.; Perrot, J.L.; Rubegni, P. Diagnostic Accuracy of Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for the Diagnosis of Skin Carcinomas. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030361
Cinotti E, Brunetti T, Cartocci A, Tognetti L, Suppa M, Malvehy J, Perez-Anker J, Puig S, Perrot JL, Rubegni P. Diagnostic Accuracy of Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for the Diagnosis of Skin Carcinomas. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(3):361. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030361
Chicago/Turabian StyleCinotti, Elisa, Tullio Brunetti, Alessandra Cartocci, Linda Tognetti, Mariano Suppa, Josep Malvehy, Javiera Perez-Anker, Susanna Puig, Jean Luc Perrot, and Pietro Rubegni. 2023. "Diagnostic Accuracy of Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for the Diagnosis of Skin Carcinomas" Diagnostics 13, no. 3: 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030361
APA StyleCinotti, E., Brunetti, T., Cartocci, A., Tognetti, L., Suppa, M., Malvehy, J., Perez-Anker, J., Puig, S., Perrot, J. L., & Rubegni, P. (2023). Diagnostic Accuracy of Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography for the Diagnosis of Skin Carcinomas. Diagnostics, 13(3), 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030361







