Tumor Segmentation in Colorectal Ultrasound Images Using an Ensemble Transfer Learning Model: Towards Intra-Operative Margin Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We acquired the first annotated extraluminal US dataset for colorectal cancer, with ground truth tumor annotation-based histopathology results.
- To combat data scarcity, we used transfer learning techniques to optimize models pre-trained on breast US data for colorectal US data.
- We applied ensemble learning methods to enhance overall tumor segmentation accuracy.
- We developed a new custom loss function (GWDice), focusing on the clinically relevant top margin of the tumor.
- We present the first study on automatic colorectal US segmentation for real-time intra-operative margin assessment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. Data Labeling
2.3. Data Pre-Processing
2.4. Transfer Learning Using Pre-Trained Networks
2.5. Loss Functions
2.5.1. Generalized Dice Loss
2.5.2. Gradient-Weighted Dice Loss
| Algorithm 1 Gradient weighted ground truth mask. |
|
2.6. Ensemble Learning
2.7. Post-Processing
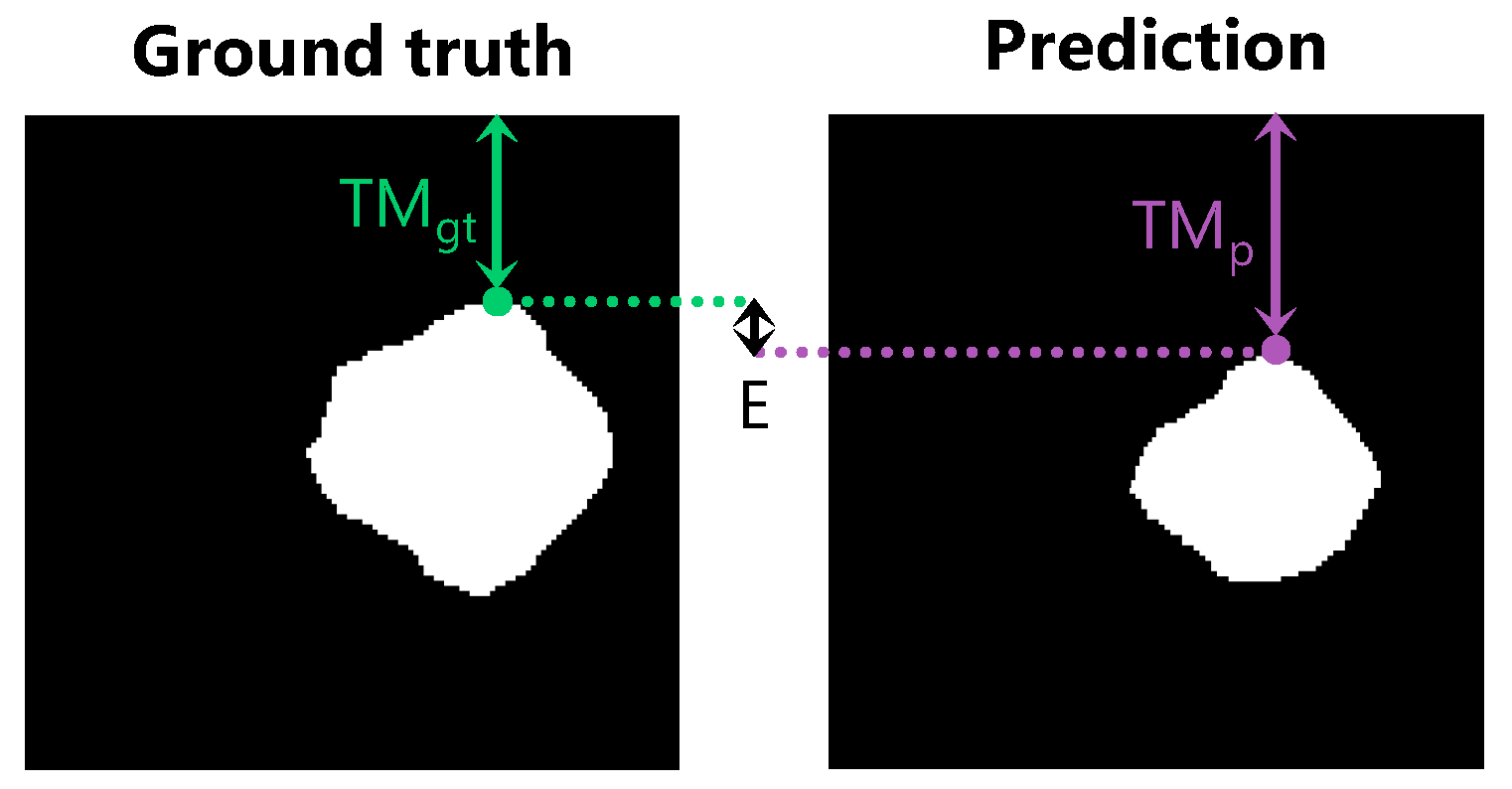
2.8. Performance Measures
3. Results
3.1. Patient and Tumor Characteristics
3.2. Comparison between Scratch Training, Pre-Trained Models, and Transfer Learning
3.3. Comparison between GenDice and GWDice Loss Functions
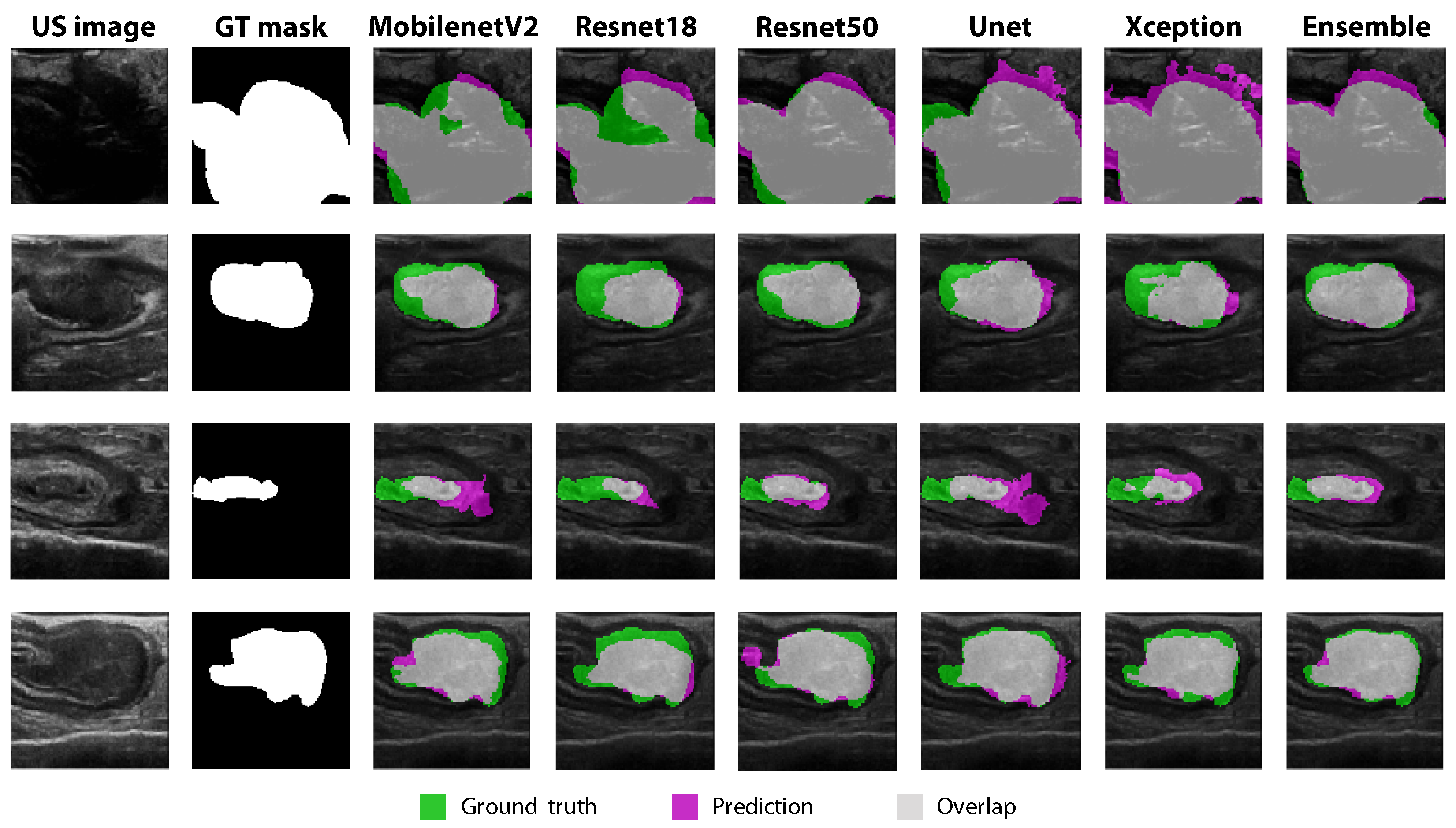
3.4. Comparison between Individual Models and Ensemble Learning
3.5. Resection Margin Prediction
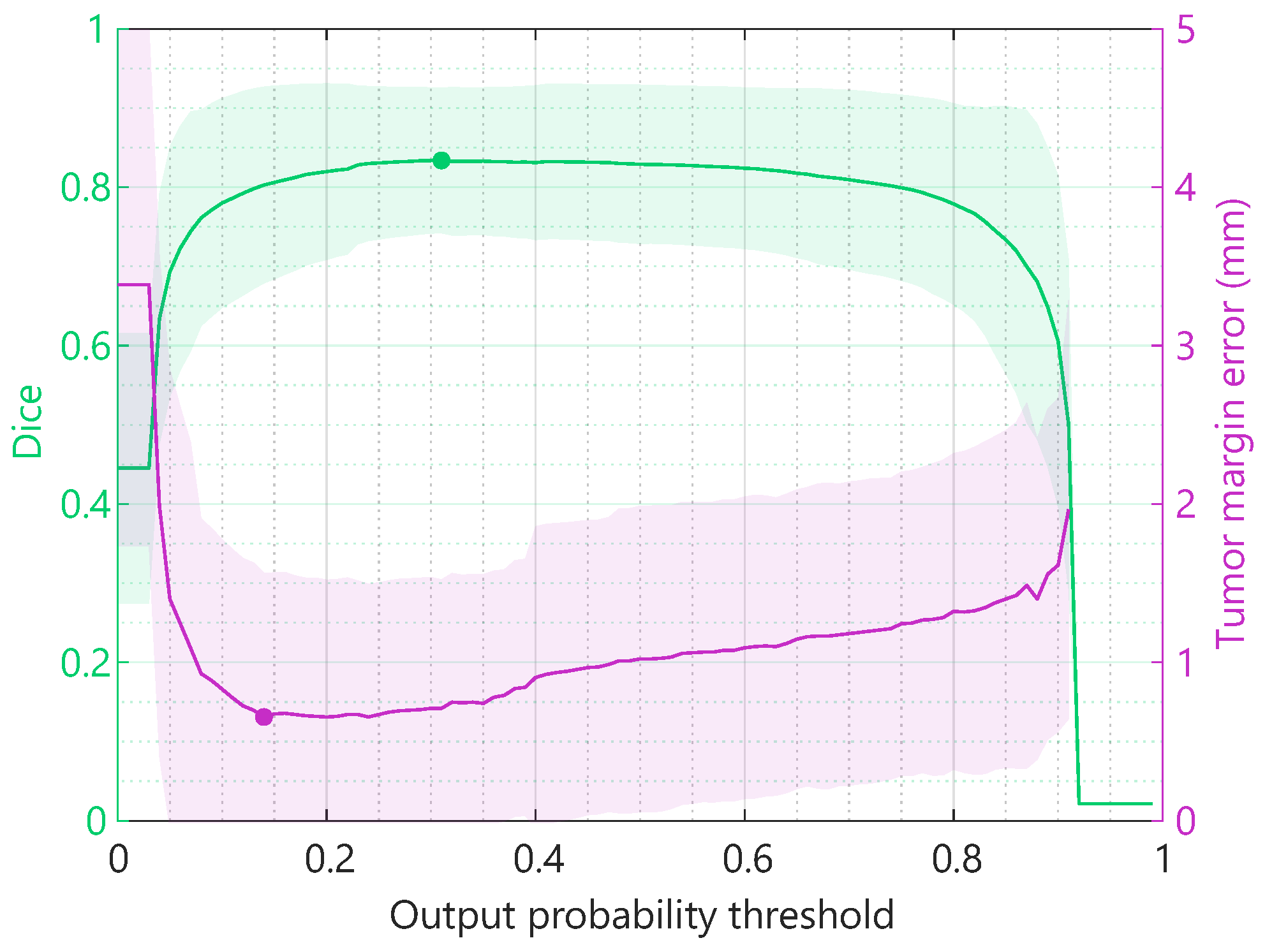
3.6. Optimization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Xu, P. Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 1936–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detering, R.; Saraste, D.; de Neree tot Babberich, M.P.; Dekker, J.W.; Wouters, M.W.; van Geloven, A.A.; Bemelman, W.A.; Tanis, P.J.; Martling, A.; Westerterp, M.; et al. International evaluation of circumferential resection margins after rectal cancer resection: Insights from the Swedish and Dutch audits. Color. Dis. 2020, 22, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.B.; Lee, W.Y.; Yun, H.R.; Lee, W.S.; Yun, S.H.; Chun, H.K. Tumor localization for laparoscopic colorectal surgery. World J. Surg. 2007, 31, 1491–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frager, D.H.; Frager, J.D.; Wolf, E.L.; Beneventano, T.C. Problems in the colonoscopic localization of tumors: Continued value of the barium enema. Gastrointest. Radiol. 1987, 12, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, W.; Abboud, W.; Hershkovitz, D.; Duek, S.D. Frozen section examination may facilitate reconstructive surgery for mid and low rectal cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 110, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.M.; Bhandare, M.; Desouza, A.; Bal, M.; Saklani, A.P. Role of intraoperative frozen section for assessing distal resection margin after anterior resection. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2015, 30, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, D.L.; Addona, T.; Forde, K.A.; Arnell, T.D.; Carter, J.J.; Huang, E.H.; Whelan, R.L. Safety and reliability of tattooing colorectal neoplasms prior to laparoscopic resection. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2004, 8, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, W.; Wu, X.; Yang, A. Clip or Tattooing: A Comparative Study for Preoperative Colon Cancer Endoscopic Localization. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 846900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, K.; Choxi, S.C.; Orkin, B.A. Accuracy of colonoscopic localization. Surg. Endosc. 2010, 24, 2502–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Sohn, D.K.; Hong, C.W.; Han, K.S.; Choi, D.H.; Chang, H.J.; Lim, S.B.; Choi, H.S.; Jeong, S.Y. The usefulness of preoperative colonoscopic tattooing using a saline test injection method with prepackaged sterile India ink for localization in laparoscopic colorectal surgery. Surg. Endosc. Other Interv. Tech. 2008, 22, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.L.; Chen, C.P.; Chiang, F.F.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, M.C.; Chen, C.T.; Lin, C.Y.; Cheng, H.H.; Shao, Y.C. Tattooing or Metallic Clip Placement? A Review of the Outcome Surrounding Preoperative Localization Methods in Minimally Invasive Anterior Resection Performed at a Single Center. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. Percutaneous Tech. 2022, 32, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, K.K.; Fennerty, M.B. Marking and identifying colon lesions: Tattoos, clips, and radiology in imaging the colon. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 1997, 7, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conaghan, P.J.; Maxwell-Armstrong, C.A.; Garrioch, M.V.; Hong, L.; Acheson, A.G. Leaving a mark: The frequency and accuracy of tattooing prior to laparoscopic colorectal surgery. Color. Dis. 2011, 13, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmora, O.; Dinnewitzer, A.J.; Pikarsky, A.J.; Efron, J.E.; Weiss, E.G.; Nogueras, J.J.; Wexner, S.D. Intraoperative endoscopy in laparoscopic colectomy. Surg. Endosc. Other Interv. Tech. 2002, 16, 808–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaafsma, B.E.; Mieog, J.S.D.; Hutteman, M.; van der Vorst, J.R.; Kuppen, P.J.K.; Löwik, C.W.G.M.; Frangioni, J.V.; van de Velde, C.J.H.; Vahrmeijer, A.L. The clinical use of indocyanine green as a near-infrared fluorescent contrast agent for image-guided oncologic surgery. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 104, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Han, K.S.; Kim, B.C.; Hong, C.W.; Park, S.C.; Kim, M.J.; Park, B.K.; Oh, J.H.; Kyung Sohn, D. Preoperative tattooing using indocyanine green in laparoscopic colorectal surgery. Ann. Coloproctol. 2018, 34, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galema, H.A.; Meijer, R.P.; Lauwerends, L.J.; Verhoef, C.; Burggraaf, J.; Vahrmeijer, A.L.; Hutteman, M.; Keereweer, S.; Hilling, D.E. Fluorescence-guided surgery in colorectal cancer; A review on clinical results and future perspectives. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 48, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, E.N.; Eppenga, R.; Kuhlmann, K.F.; Groen, H.C.; van Veen, R.; van Dieren, J.M.; de Wijkerslooth, T.R.; van Leerdam, M.; Lambregts, D.M.; Heerink, W.J.; et al. Accurate surgical navigation with real-time tumor tracking in cancer surgery. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, H.C.; Den Hartog, A.G.; Heerink, W.J.; Kuhlmann, K.F.; Kok, N.F.; van Veen, R.; Hiep, M.A.; Snaebjornsson, P.; Grotenhuis, B.A.; Beets, G.L.; et al. Use of Image-Guided Surgical Navigation during Resection of Locally Recurrent Rectal Cancer. Life 2022, 12, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beynon, J.; Roe, A.M.; Foy, D.M.; Channer, J.L.; Virjee, J.; Mortensen, N.J. Preoperative staging of local invasion in rectal cancer using endoluminal ultrasound. J. R. Soc. Med. 1987, 80, 23–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limberg, B. Diagnosis and Staging of Colonic Tumors by Conventional Abdominal Sonography as Compared with Hydrocolonic Sonography. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 327, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, M.B.; Qvitzau, S.; Pedersen, J.F.; Christiansen, J. Endosonography for preoperative staging of rectal tumours. Acta Radiol. 1996, 37, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massari, M.; De Simone, M.; Cioffi, U.; Rosso, L.; Chiarelli, M.; Gabrielli, F. Value and limits of endorectal ultrasonography for preoperative staging of rectal carcinoma. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. 1998, 8, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Aguilar, J.; Pollack, J.; Lee, S.H.; Hernandez De Anda, E.; Mellgren, A.; Wong, W.D.; Finne, C.O.; Rothenberger, D.A.; Madoff, R.D. Accuracy of endorectal ultrasonography in preoperative staging of rectal tumors. Dis. Colon Rectum 2002, 45, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, N.; Tjandra, J.; Solomon, M. Endoanal and endorectal ultrasound: Applications in colorectal surgery. ANZ J. Surg. 2004, 74, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ares, D.; Martín-Granizo Barrenechea, I.; Souto-Ruzo, J.; Yáñez López, J.; Pallarés Peral, A.; Vázquez-Iglesias, J.L. The value of abdominal ultrasound in the diagnosis of colon cancer. Rev. EspañOla Enfermedades Dig. 2005, 97, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phang, P.T.; Gollub, M.J.; Loh, B.D.; Nash, G.M.; Temple, L.K.; Paty, P.B.; Guillem, J.G.; Weiser, M.R. Accuracy of endorectal ultrasound for measurement of the closest predicted radial mesorectal margin for rectal cancer. Dis. Colon Rectum 2012, 55, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bor, R.; Fábián, A.; Szepes, Z. Role of ultrasound in colorectal diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 9477–9487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartana, E.T.; Gheonea, D.I.; Saftoiu, A. Advances in endoscopic ultrasound imaging of colorectal diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 1756–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, W. Judgment of benign and early malignant colorectal tumors from ultrasound images with deep multi-View fusion. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 215, 106634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luck, A.J.; Thomas, M.L.; Roediger, W.E.; Hewett, P.J. Localization of the nonpalpable colonic lesion with intraoperative ultrasound. Surg. Endosc. 1999, 13, 526–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montorsi, M.; Opocher, E.; Santambrogio, R.; Bianchi, P.; Faranda, C.; Arcidiacono, P.; Passoni, G.R.; Cosentino, F. Original technique for small colorectal tumor localization during laparoscopic surgery. Dis. Colon Rectum 1999, 42, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luck, A.; Copley, J.; Hewett, P. Ultrasound of colonic neoplasia: An intraoperative tool? Surg. Endosc. 2000, 14, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panaro, F.; Casaccia, M.; Cavaliere, D.; Torelli, P. Laparoscopic colon resection with intraoperative polyp localisation with high resolution ultrasonography coupled with colour power Doppler. Postgrad. Med. J. 2003, 79, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greif, F.; Belenky, A.; Aranovich, D.; Yampolski, I.; Hannanel, N. Intraoperative ultrasonography: A tool for localizing small colonic polyps. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2005, 20, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, K.; Endo, S.; Tatsukawa, K.; Kudo, S.E. Intraoperative fluoroscopy vs. intraoperative laparoscopic ultrasonography for early colorectal cancer localization in laparoscopic surgery. Surg. Endosc. 2008, 22, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greif, F.; Aranovich, D.; Hananel, N.; Knizhnik, M.; Belenky, A. Intraoperative ultrasound in colorectal surgery. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2009, 37, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greif, F.; Aranovich, D.; Zilbermints, V.; Hannanel, N.; Belenky, A. Intraoperative hydrocolonic ultrasonography for localization of small colorectal tumors in laparoscopic surgery. Surg. Endosc. 2010, 24, 3144–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Flores, W.; Coelho de Albuquerque Pereira, W. A comparative study of pre-trained convolutional neural networks for semantic segmentation of breast tumors in ultrasound. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 126, 104036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, S.; Chang, C. Automatic tumor segmentation in breast ultrasound images using a dilated fully convolutional network combined with an active contour model. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakanski, A.; Xian, M.; Freer, P.E. Attention-Enriched Deep Learning Model for Breast Tumor Segmentation in Ultrasound Images. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 2819–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Yap, P.T.; Shen, D. Multi-task learning for segmentation and classification of tumors in 3D automated breast ultrasound images. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 70, 101918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Almekkawy, M. ASU-Net++: A nested U-Net with adaptive feature extractions for liver tumor segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvancarova, M.; Albregtsen, F.; Brabrand, K.; Samset, E. Segmentation of ultrasound images of liver tumors applying snake algorithms and GVF. Int. Congr. Ser. 2005, 1281, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.J.; Yang, Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2010, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Yu, Z.; Cao, W.; Shi, Y.; Ma, Q. A survey on ensemble learning. Front. Comput. Sci. 2020, 14, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2015), Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the Proceedings—30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crum, W.R.; Camara, O.; Hill, D.L. Generalized overlap measures for evaluation and validation in medical image analysis. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2006, 25, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudre, C.H.; Li, W.; Vercauteren, T.; Ourselin, S.; Jorge Cardoso, M. Generalised dice overlap as a deep learning loss function for highly unbalanced segmentations. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics). Europe PMC Funders; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Method | Number of Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Female | 39 (53%) |
| Male | 35 (47%) |
| Tumor location | |
| Colon | 26 (35%) |
| Sigmoid | 18 (24%) |
| Rectum | 30 (41%) |
| Neoadjuvant therapy | |
| Yes | 30 (41%) |
| No | 44 (59%) |
| T-stage * | |
| pT1 | 2 (3%) |
| pT2 | 11 (15%) |
| pT3 | 44 (59%) |
| pT4 | 17 (23%) |
| Tumor diameter | 4.1 ± 1.9 cm |
| Tumor margin | 6.4 ± 3.7 mm |
| Method | Dice | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Scratch | Pre-Trained on Breast US | After Transfer Learning | |
| MobilenetV2 | 0.70 | 0.65 | 0.76 |
| Resnet18 | 0.72 | 0.65 | 0.77 |
| Resnet50 | 0.70 | 0.63 | 0.78 |
| U-net | 0.59 | 0.55 | 0.79 |
| Xception | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.80 |
| Mean | 0.68 | 0.63 | 0.78 |
| Method | Dice | Tumor Margin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MobilenetV2 | 0.76 | 0.80 | 1.03 mm | 0.96 mm |
| Resnet18 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 1.25 mm | 0.99 mm |
| Resnet50 | 0.78 | 0.81 | 1.26 mm | 0.96 mm |
| U-net | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.83 mm | 0.88 mm |
| Xception | 0.80 | 0.81 | 1.02 mm | 0.83 mm |
| Mean | 0.78 | 0.80 | 1.08 mm | 0.92 mm |
| Method | Dice | Tumor Margin | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Individual models (mean) | 0.80 | 0.92 mm | 0.95 |
| Unweighted averaging | 0.84 | 0.68 mm | 0.97 |
| Weighted averaging | 0.84 | 0.68 mm | 0.96 |
| Voting | 0.84 | 0.67 mm | 0.95 |
| Classification model | 0.83 | 0.67 mm | 0.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geldof, F.; Pruijssers, C.W.A.; Jong, L.-J.S.; Veluponnar, D.; Ruers, T.J.M.; Dashtbozorg, B. Tumor Segmentation in Colorectal Ultrasound Images Using an Ensemble Transfer Learning Model: Towards Intra-Operative Margin Assessment. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3595. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233595
Geldof F, Pruijssers CWA, Jong L-JS, Veluponnar D, Ruers TJM, Dashtbozorg B. Tumor Segmentation in Colorectal Ultrasound Images Using an Ensemble Transfer Learning Model: Towards Intra-Operative Margin Assessment. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(23):3595. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233595
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeldof, Freija, Constantijn W. A. Pruijssers, Lynn-Jade S. Jong, Dinusha Veluponnar, Theo J. M. Ruers, and Behdad Dashtbozorg. 2023. "Tumor Segmentation in Colorectal Ultrasound Images Using an Ensemble Transfer Learning Model: Towards Intra-Operative Margin Assessment" Diagnostics 13, no. 23: 3595. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233595
APA StyleGeldof, F., Pruijssers, C. W. A., Jong, L.-J. S., Veluponnar, D., Ruers, T. J. M., & Dashtbozorg, B. (2023). Tumor Segmentation in Colorectal Ultrasound Images Using an Ensemble Transfer Learning Model: Towards Intra-Operative Margin Assessment. Diagnostics, 13(23), 3595. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233595






