The Clinical Value of Multimodal Ultrasound for the Differential Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma from Other Liver Tumors in Relation to Histopathology
Abstract
1. Introduction
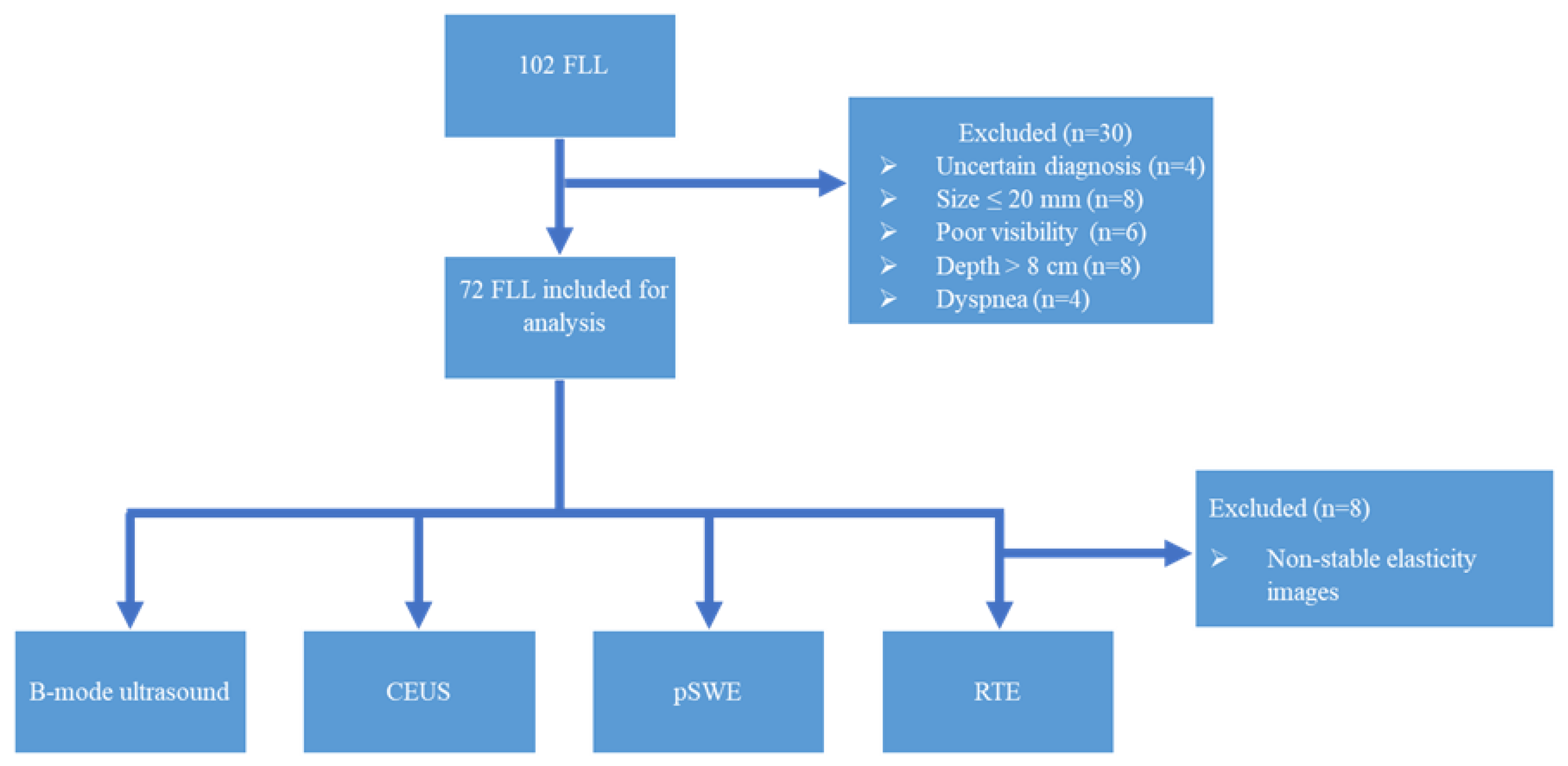
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Multimodal Ultrasound Examination
2.2. Reference Standard Method
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
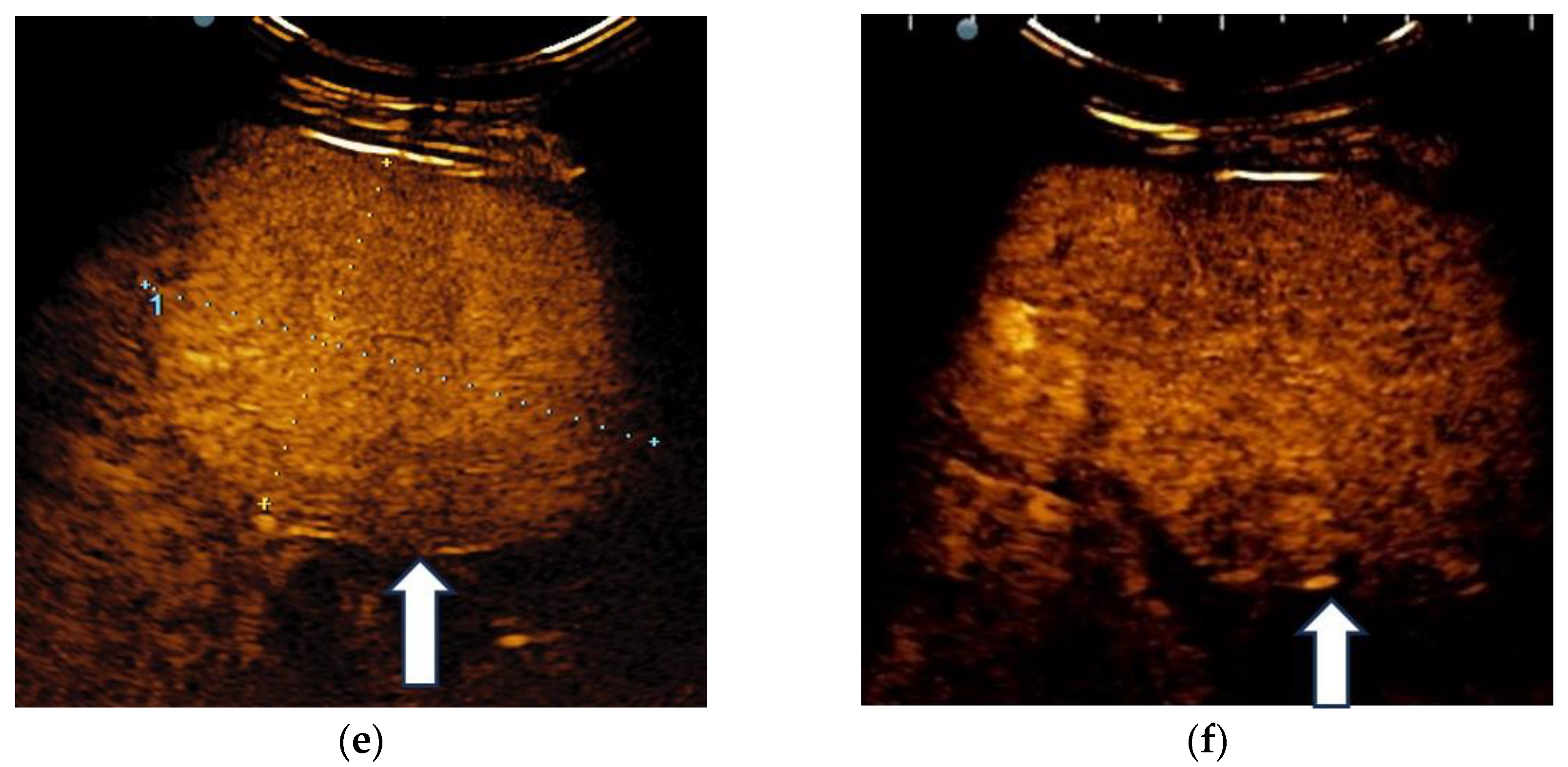
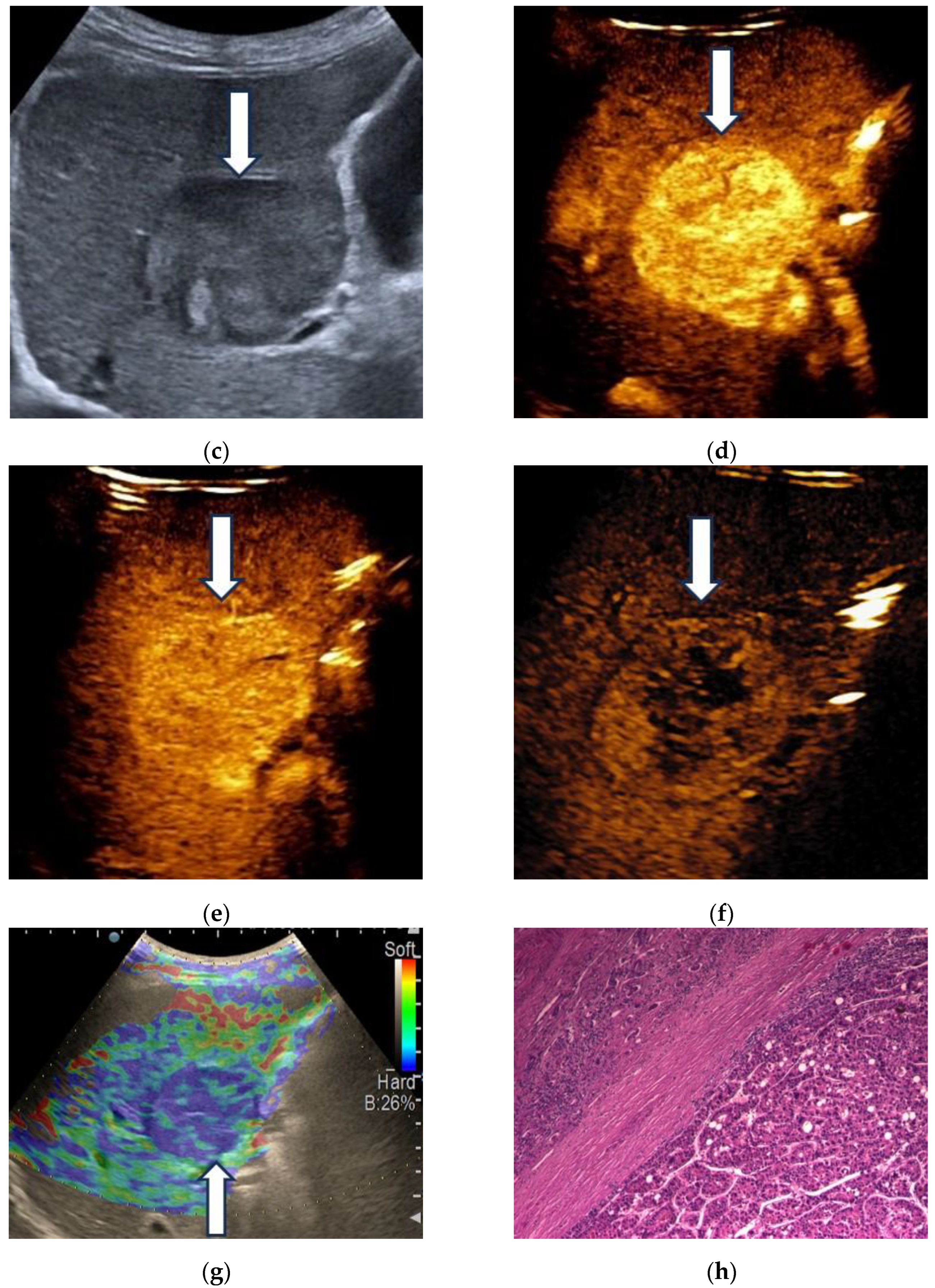
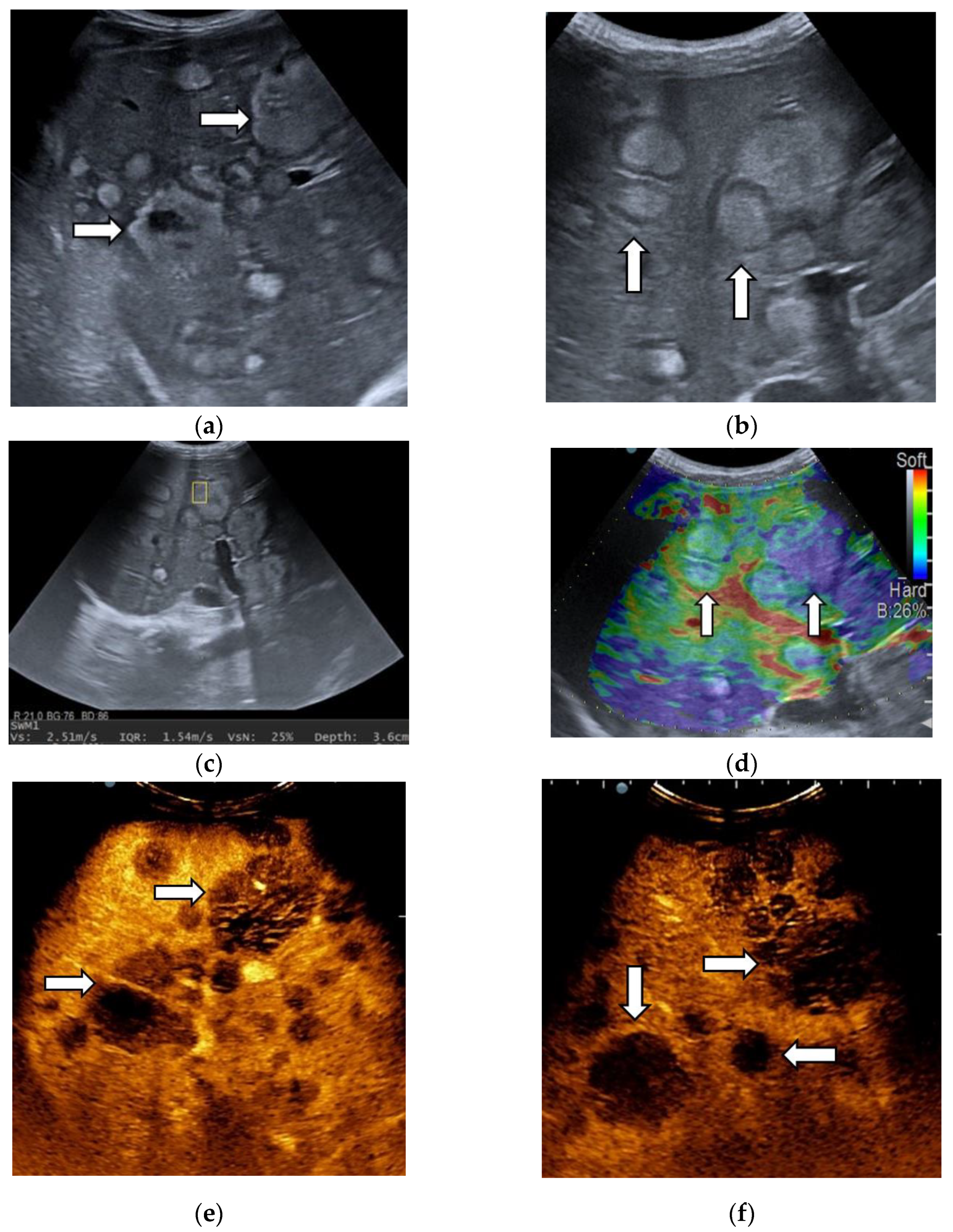
3.1. B-Mode Ultrasound
3.2. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound
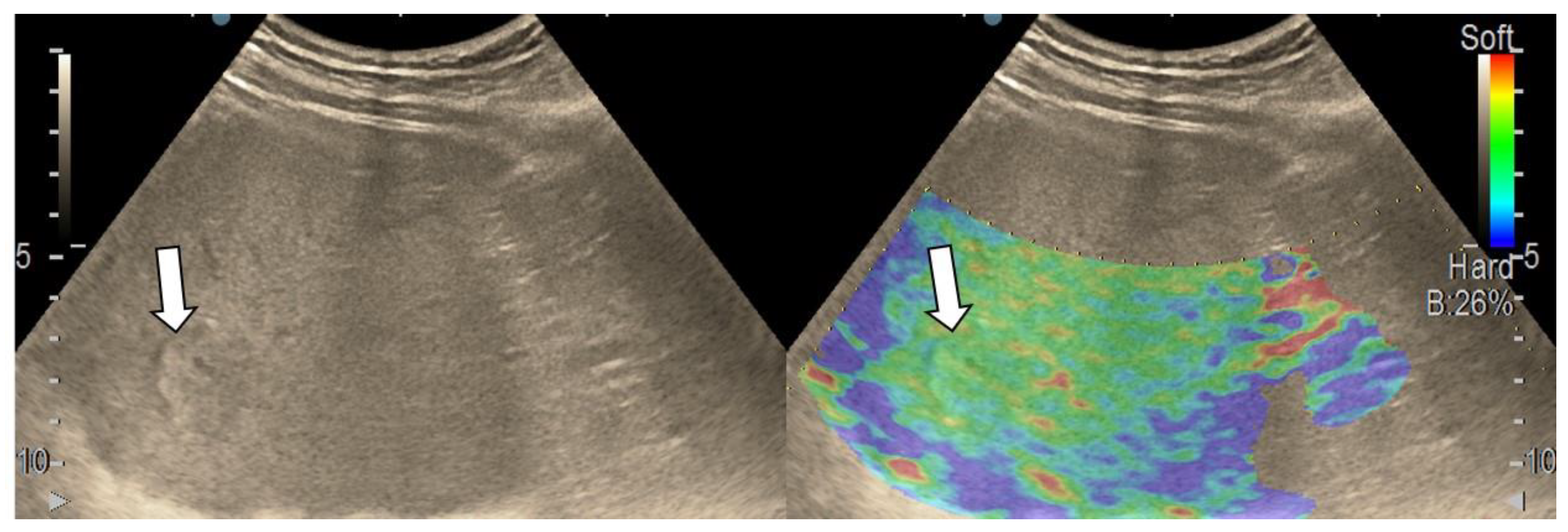
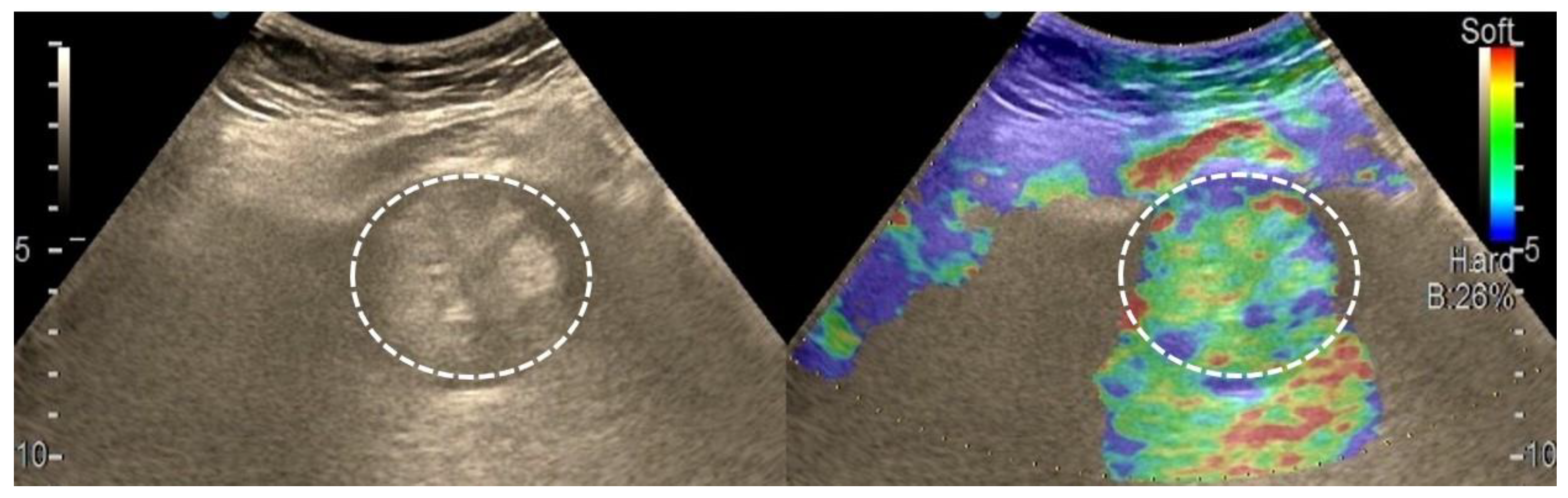
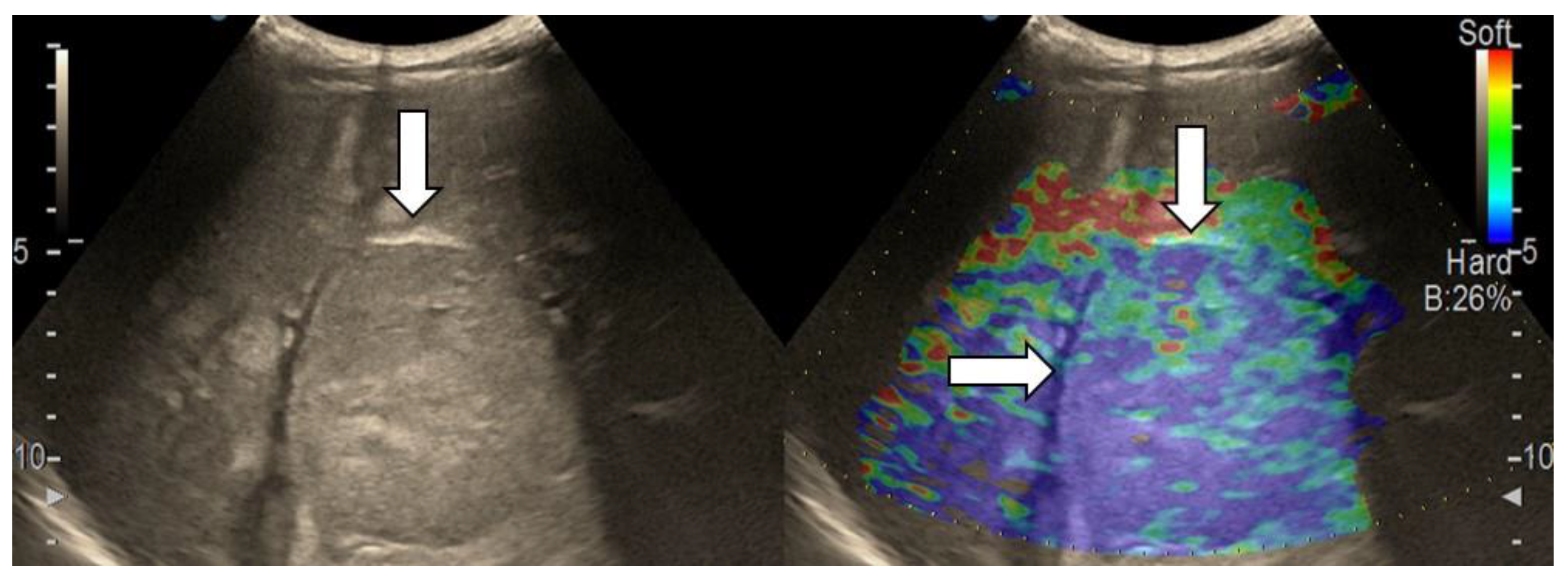
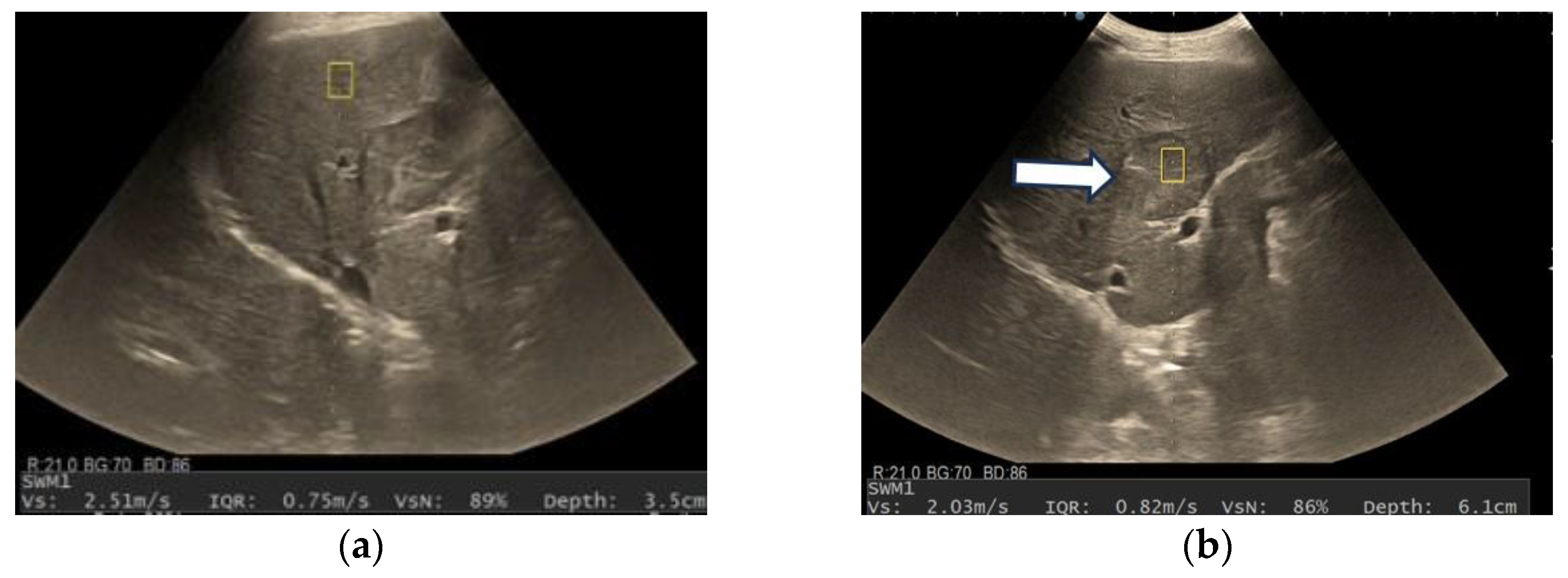
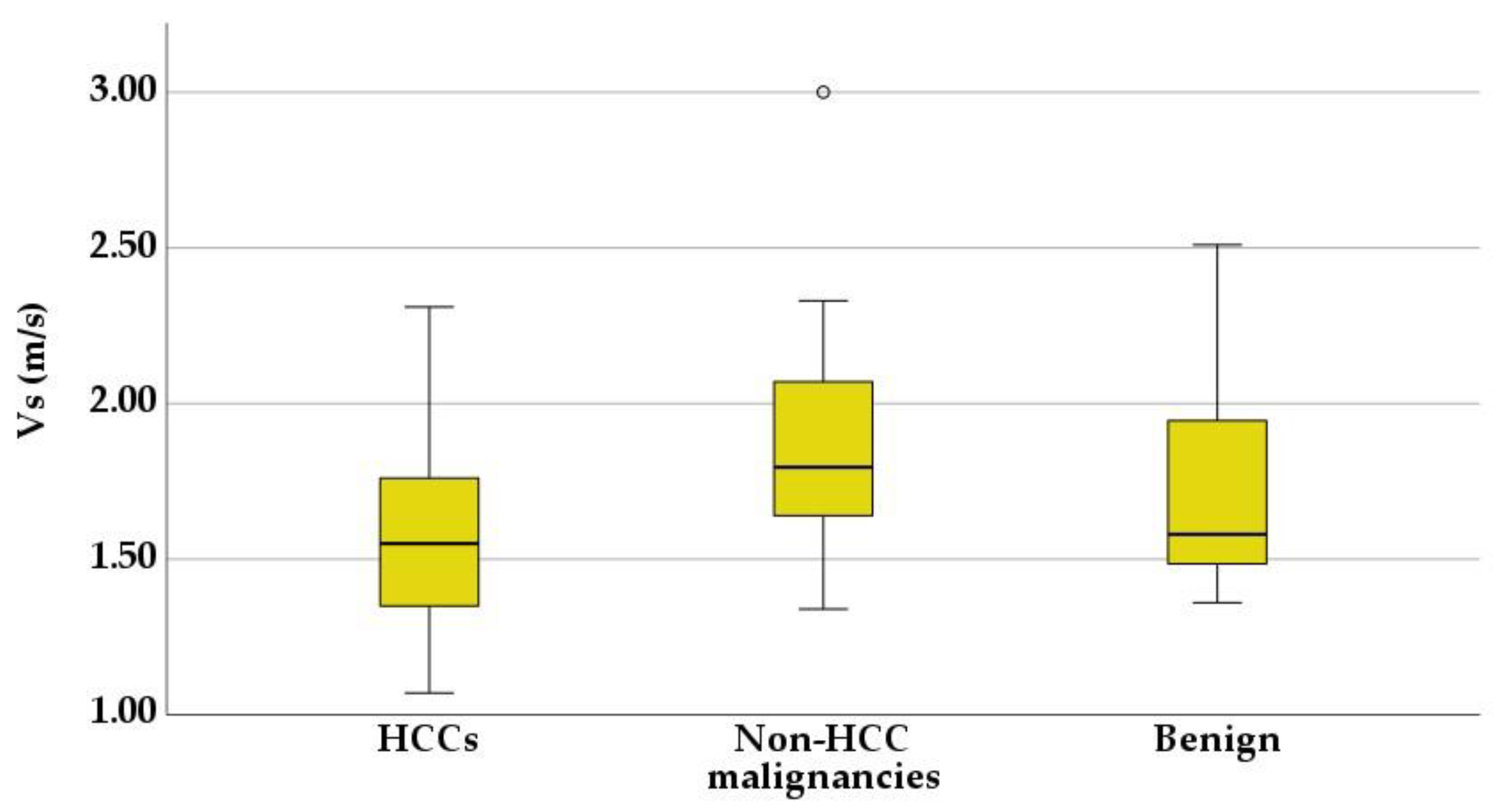
3.3. Shear Wave Measurements in Liver Tumors
3.4. Real-Time Tissue Elastography
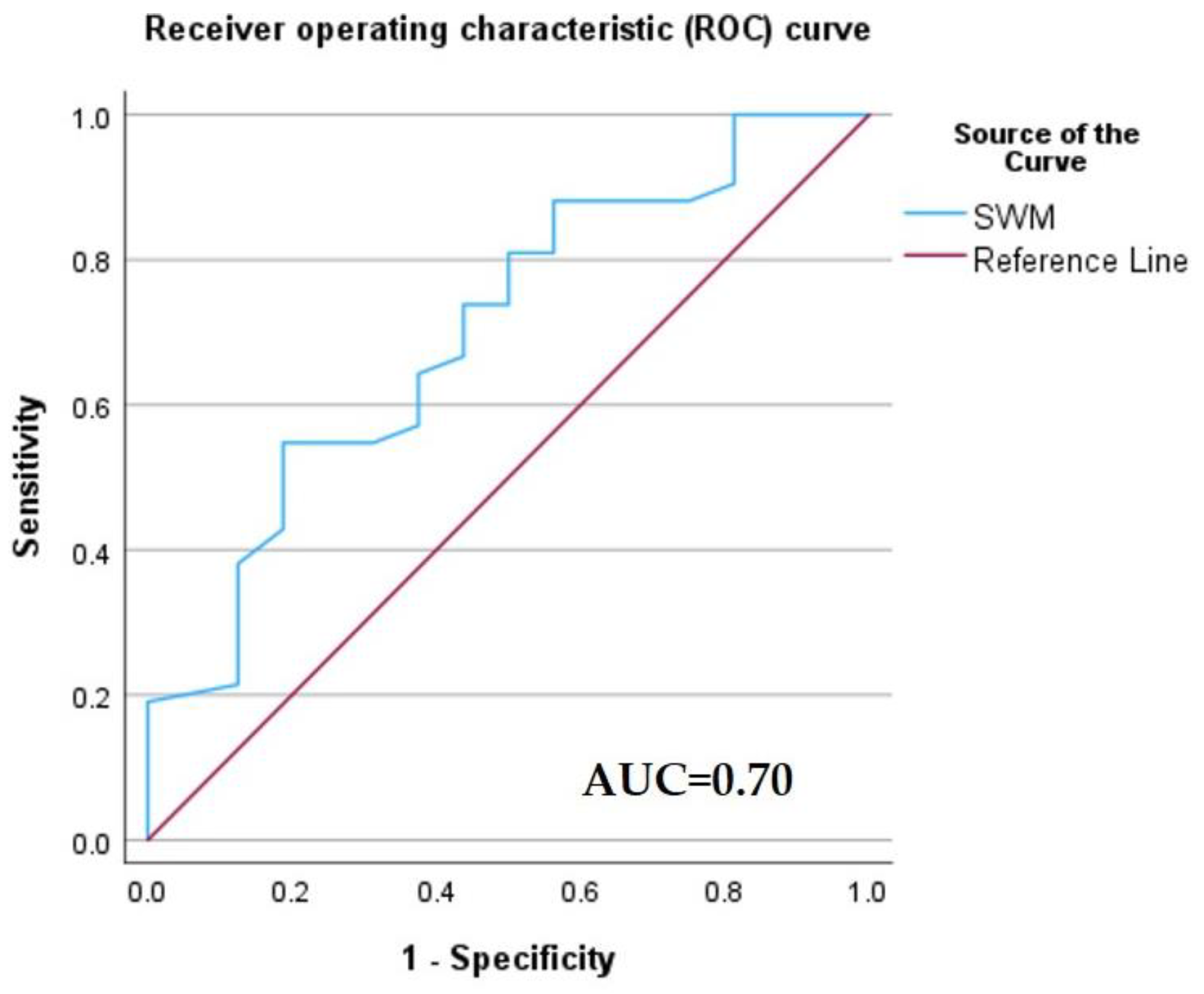
3.5. The Added Value of the SWM Method to Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Assessment of HCC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartolotta, T.V.; Taibbi, A.; Randazzo, A.; Gagliardo, C. New frontiers in liver ultrasound: From mono to multi parametricity. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 13, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marschner, C.A.; Rübenthaler, J.; Froelich, M.F.; Schwarze, V.; Clevert, D.A. Benefits of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for interventional procedures. Ultrasonography 2021, 40, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudon, M.; Dietrich, C.F.; Choi, B.I.; Cosgrove, D.O.; Kudo, M.; Nolsøe, C.P.; Piscaglia, F.; Wilson, S.R.; Barr, R.G.; Chammas, M.C.; et al. Guidelines and good clinical practice recommendations for Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) in the liver—Update 2012: A WFUMB-EFSUMB initiative in cooperation with representatives of AFSUMB, AIUM, ASUM, FLAUS and ICUS. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. Contrast-enhanced US for characterization of focal liver lesions: A comprehensive meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 2077–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Guang, Y.; Ding, H.; Cai, A.; Huang, Y. Diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging for focal liver lesions: A meta-analysis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2011, 37, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, C.; Luo, Y. Diagnostic value of liver contrast-enhanced ultrasound in early hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2023, 14, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Bamber, J.; Berzigotti, A.; Bota, S.; Cantisani, V.; Castera, L.; Cosgrove, D.; Ferraioli, G.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Gilja, O.H.; et al. EFSUMB Guidelines and Recommendations on the Clinical Use of Liver Ultrasound Elastography, Update 2017 (Long Version). Ultraschall Med. 2017, 38, e16–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Wong, V.W.; Castera, L.; Berzigotti, A.; Sporea, I.; Dietrich, C.F.; Choi, B.I.; Wilson, S.R.; Kudo, M.; Barr, R.G. Liver Ultrasound Elastography: An Update to the World Federation for Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology Guidelines and Recommendations. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 2419–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Dong, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Zheng, J.; Fan, H.; Gan, H.; Chen, L.; Li, M. Shear wave elastography imaging for detecting malignant lesions of the liver: A systematic review and pooled meta-analysis. Med. Ultrason. 2017, 19, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Lin, X.; Xie, Z.L.; Tang, F.Y.; Hu, Y.P.; Shi, K.Q. Clinical utility of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging for identification of malignant liver lesions: A meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 2798–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Huang, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, T.; Hou, J.; Song, A.; Ding, L.; Liu, W.; Wu, H.; Meng, F. Diagnostic effect of shear wave elastography imaging for differentiation of malignant liver lesions: A meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yada, N.; Sakurai, T.; Minami, T.; Arizumi, T.; Takita, M.; Hagiwara, S.; Ueshima, K.; Ida, H.; Nishida, N.; Kudo, M. A Newly Developed Shear Wave Elastography Modality: With a Unique Reliability Index. Oncology 2015, 89 (Suppl. S2), 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Maiocchi, L.; Lissandrin, R.; Tinelli, C.; De Silvestri, A.; Filice, C. Ruling-in and Ruling-out Significant Fibrosis and Cirrhosis in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Using a Shear Wave Measurement Method. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2017, 26, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jikuzono, T.; Ishibashi, O.; Kure, S.; Itoh, C.; Yamada, T.; Sugitani, I. VsN, a Reliability-index of Shear-wave Measurement in Sonoelastography, Is Useful for the Diagnosis of Thyroid Tumor Malignancy. In Vivo 2022, 36, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowell, B. Real-time Tissue Elastography. Ultrasound 2008, 16, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Q.; Hou, R.; Cai, X.; Lin, L.; Luo, Y.; Wei, F.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Real-Time Elastography in the diagnosis of prostate cancer: A systematic review. Med. Ultrason. 2019, 21, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Qian, L. Diagnostic potential of real-time elastography (RTE) and shear wave elastography (SWE) to differentiate benign and malignant thyroid nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Nakao, H.; Nishiyama, T.; Lin, Y.; Kikuchi, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Ishii, N.; Ohashi, T.; Satoh, K.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of real-time tissue elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis: A meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ai, H.; Guo, L.; Tan, L.; Gong, H.; Wei, W.; Ruan, L. Application of Real-Time Tissue Elastography with a Low Frequency Convex Array Probe: A Noninvasive Approach to Differential Diagnosis of Liver Tumors. ISRN Hepatol. 2014, 2014, 378243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandulescu, L.; Padureanu, V.; Dumitrescu, C.; Braia, N.; Streba, C.T.; Gheonea, D.I.; Cazacu, S.; Ciurea, T.; Rogoveanu, I.; Saftoiu, A. A pilot study of real time elastography in the differentiation of focal liver lesions. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2012, 38, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Omichi, K.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Arita, J.; Akamatsu, N.; Kaneko, J.; Sakamoto, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Kokudo, N. Intraoperative real-time tissue elastography during laparoscopic hepatectomy. HPB 2018, 20, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omichi, K.; Inoue, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Sakamoto, Y.; Okinaga, H.; Aoki, T.; Sugawara, Y.; Kurahashi, I.; Kokudo, N. Differential diagnosis of liver tumours using intraoperative real-time tissue elastography. Br. J. Surg. 2015, 102, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Sugimoto, H.; Kanazumi, N.; Nomoto, S.; Takeda, S.; Nakao, A. Intra-operative application of real-time tissue elastography for the diagnosis of liver tumours. Liver Int. 2008, 28, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Nolsøe, C.P.; Barr, R.G.; Berzigotti, A.; Burns, P.N.; Cantisani, V.; Chammas, M.C.; Chaubal, N.; Choi, B.I.; Clevert, D.A.; et al. Guidelines and Good Clinical Practice Recommendations for Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) in the Liver-Update 2020 WFUMB in Cooperation with EFSUMB, AFSUMB, AIUM, and FLAUS. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 2579–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236, Erratum in J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.G.; Llovet, J.M.; Yarchoan, M.; Mehta, N.; Heimbach, J.K.; Dawson, L.A.; Jou, J.H.; Kulik, L.M.; Agopian, V.G.; Marrero, J.A.; et al. AASLD practice guidance on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.; Volk, M.L.; Waljee, A.; Salgia, R.; Higgins, P.; Rogers, M.A.; Marrero, J.A. Meta-analysis: Surveillance with ultrasound for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 30, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzartzeva, K.; Obi, J.; Rich, N.E.; Parikh, N.D.; Marrero, J.A.; Yopp, A.; Waljee, A.K.; Singal, A.G. Surveillance Imaging and Alpha Fetoprotein for Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Cirrhosis: A Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2018, 154, 1706–1718.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartampilas, E.; Rafailidis, V.; Georgopoulou, V.; Kalarakis, G.; Hatzidakis, A.; Prassopoulos, P. Current Imaging Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, Y.; Kudo, M. Hepatic malignancies: Correlation between sonographic findings and pathological features. World J. Radiol. 2010, 2, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, T.; Hohmann, J.; Oldenburg, A.; Skrok, J.; Wolf, K.J. Detection and characterization of liver metastases. Eur. Radiol. 2004, 14 (Suppl. S8), 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuuchi, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Yamazaki, S.; Bandai, Y.; Watanabe, G.; Ito, T. Ultrasonic characteristics of the small hepatocellular carcinoma. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1983, (Suppl. S2), 489–491. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.G.; Xu, H.X.; Liu, L.N. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: The role of contrast-enhanced ultrasound. World J. Radiol. 2014, 6, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellhaas, B.; Jesper, D.; Strobel, D.; DEGUM CEUS HCC Study Group. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound pattern of hepatocellular carcinoma in noncirrhotic liver—Results from the prospective multicentre DEGUM CEUS HCC study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 35, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, W.P.; Lee, W.J.; Meloni, M.F.; Clevert, D.A.; Chammas, M.C.; Tannapfel, A.; Forgione, A.; Piscaglia, F.; Dietrich, C.F. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Features of Histopathologically Proven Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Non-cirrhotic Liver: A Multicenter Study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2022, 48, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, M.J.; Mo, L.R. The application of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for the characterization of hepatic tumors: An assessment focusing on hepatocellular carcinoma. Adv. Dig. Med. 2019, 6, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidili, G.; Arru, M.; Solinas, G.; Calvisi, D.F.; Meloni, P.; Sauchella, A.; Turilli, D.; Fabio, C.; Cossu, A.; Madeddu, G.; et al. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System: Lights and shadows in hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocellular carcinoma diagnosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 3488–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.R.; Lyshchik, A.; Piscaglia, F.; Cosgrove, D.; Jang, H.J.; Sirlin, C.; Dietrich, C.F.; Kim, T.K.; Willmann, J.K.; Kono, Y. CEUS LI-RADS: Algorithm, implementation, and key differences from CT/MRI. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordic, S.; Thung, S.N.; Roayaie, S.; Wagner, M.; Taouli, B. Hepatic adenomatosis in liver cirrhosis. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2017, 4, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.K.; Burns, P.N.; Jang, H.J.; Kono, Y.; Khalili, K.; Wilson, S.R.; Kim, T.K. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound approach to the diagnosis of focal liver lesions: The importance of washout. Ultrasonography 2019, 38, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.H.; Chen, M.H.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.B.; Yan, K.; Wu, W.; Yang, W.; Yin, S.S. Evaluation of primary malignancies of the liver using contrast-enhanced sonography: Correlation with pathology. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 186, 1512–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.J.; Kim, T.K.; Burns, P.N.; Wilson, S.R. Enhancement patterns of hepatocellular carcinoma at contrast-enhanced US: Comparison with histologic differentiation. Radiology 2007, 244, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdi, Z.; Ettel, M.G.; Gonzalez, R.S.; Hart, J.; Alpert, L.; Fang, J.; Liu, N.; Hammer, S.T.; Panarelli, N.; Cheng, J.; et al. Metastases can occur in cirrhotic livers with patent portal veins. Diagn. Pathol. 2021, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocan, L.P.; Rusu, I.; Melincovici, C.S.; Boșca, B.A.; Mocan, T.; Crăciun, R.; Spârchez, Z.; Iacobescu, M.; Mihu, C.M. The Role of Immunohistochemistry in the Differential Diagnosis between Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma, Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Liver Metastasis, as Well as Its Prognostic Value. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, R.K.; Strazielle, N.; Washington, K. Liver Neoplasms. In Gastrointestinal and Liver Pathology: A Volume in the Series: Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology, 2nd ed.; Iacobzio-Donahue, C.-A., Montgomery, E., Eds.; Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 626–677. ISBN 9781437709254. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiuchici, A.M.; Sporea, I.; Dănilă, M.; Șirli, R.; Moga, T.; Bende, F.; Popescu, A. Is There a Place for Elastography in the Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Bae, K.S.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for focal hepatic tumors: Usefulness for differentiating hemangiomas from malignant tumors. Korean J. Radiol. 2013, 14, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gerber, L.; Fitting, D.; Srikantharajah, K.; Weiler, N.; Kyriakidou, G.; Bojunga, J.; Schulze, F.; Bon, D.; Zeuzem, S.; Friedrich-Rust, M. Evaluation of 2D- Shear Wave Elastography for Characterisation of Focal Liver Lesions. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2017, 26, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.H.; Wang, S.J.; Xu, H.X.; Sun, L.P.; Zhang, Y.F.; Xu, J.M.; Wu, J.; Fu, H.J.; Xu, X.H. Differentiation of benign and malignant focal liver lesions: Value of virtual touch tissue quantification of acoustic radiation force impulse elastography. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Joo, I.; Lee, J.M. Atypical Appearance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Mimickers: How to Solve Challenging Cases Using Gadoxetic Acid-Enhanced Liver Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Korean J. Radiol. 2019, 20, 1019–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallotti, A.; D’Onofrio, M.; Romanini, L.; Cantisani, V.; Pozzi Mucelli, R. Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) ultrasound imaging of solid focal liver lesions. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, K.G.; Goodman, M.D.; Zachary, D.; Stocker, J.T. Tumors of the Liver and Intrahepatic Bile Ducts. Atlas of Tumor Pathology; 3rd Series; Fascicle 31; Armed Forces Institute of Pathology: Washinghton, DC, USA, 2001; p. 349. ISBN 1-881041-69-7. [Google Scholar]
- Raso, M.G.; Bota-Rabassedas, N.; Wistuba, I.I. Pathology and Classification of SCLC. Cancers 2021, 13, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Imai, Y.; Murakami, T.; Nishikawa, M.; Kurokawa, M.; Yonezawa, T.; Tokunaga, K.; Fukushima, Y.; Wakasa, K.; Kim, T.; et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with marked hypervascularity. Abdom. Imaging 1999, 24, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onofrio, M.; Crosara, S.; De Robertis, R.; Canestrini, S.; Mucelli, R.P. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound of Focal Liver Lesions. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 205, W56–W66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.-T. Benign Vascular Tumors. In Surgical Pathology of Liver Tumors; Mounajjed, T., Chandan, V.S., Torbenson, M.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 39–51. ISBN 978-3-319-16089-4. [Google Scholar]
- Frulio, N.; Laumonier, H.; Carteret, T.; Laurent, C.; Maire, F.; Balabaud, C.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Trillaud, H. Evaluation of liver tumors using acoustic radiation force impulse elastography and correlation with histologic data. J. Ultrasound Med. 2013, 32, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillette de Buy Wenniger, L.; Terpstra, V.; Beuers, U. Focal nodular hyperplasia and hepatic adenoma: Epidemiology and pathology. Dig. Surg. 2010, 27, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertin, C.; Egels, S.; Wagner, M.; Huynh-Charlier, I.; Vilgrain, V.; Lucidarme, O. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of focal nodular hyperplasia: A matter of size. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 2561–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollerieth, K.; Gaßmann, B.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Moog, P.; Vo-Cong, M.T.; Heemann, U.; Stock, K.F. Preclinical evaluation of acoustic radiation force impulse measurements in regions of heterogeneous elasticity. Ultrasonography 2016, 35, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
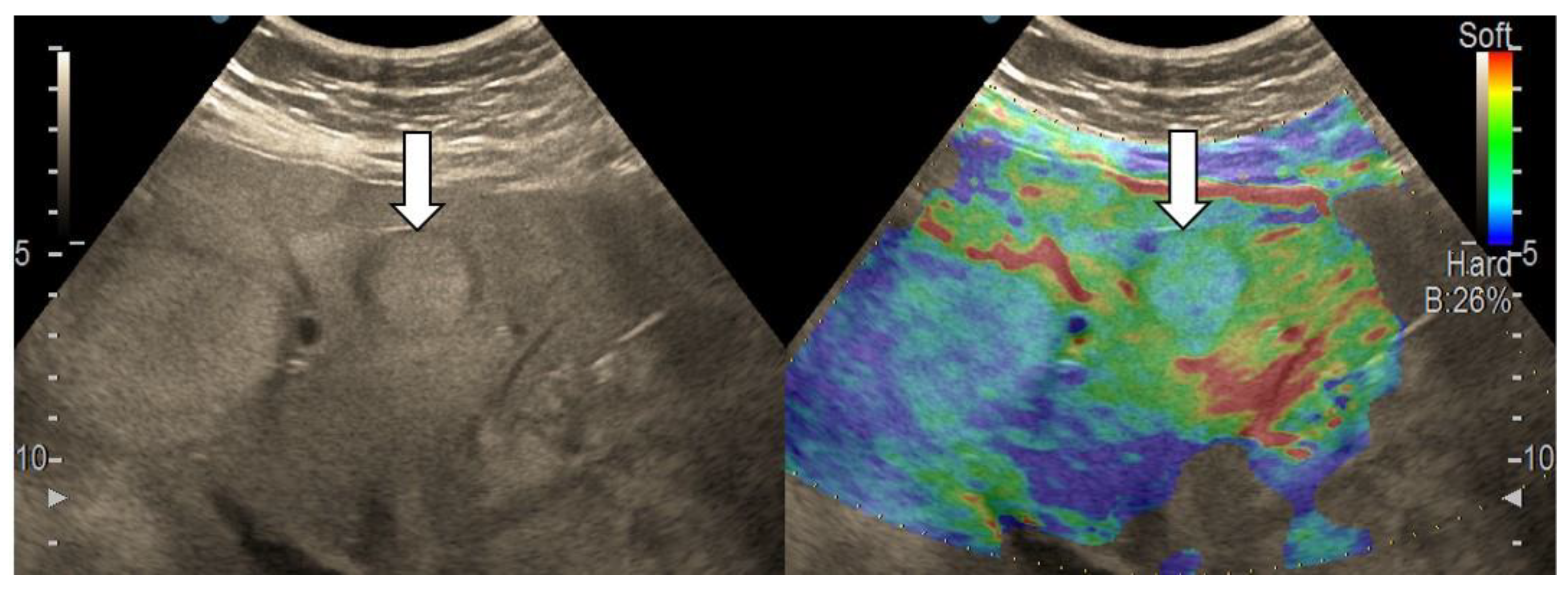
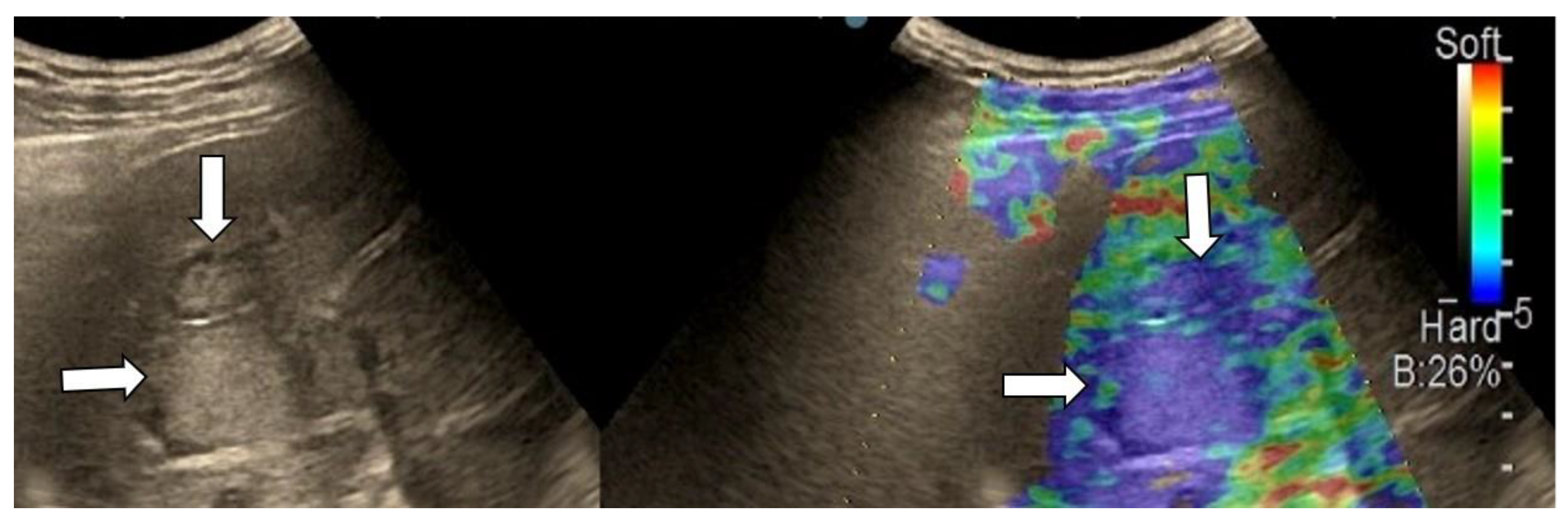
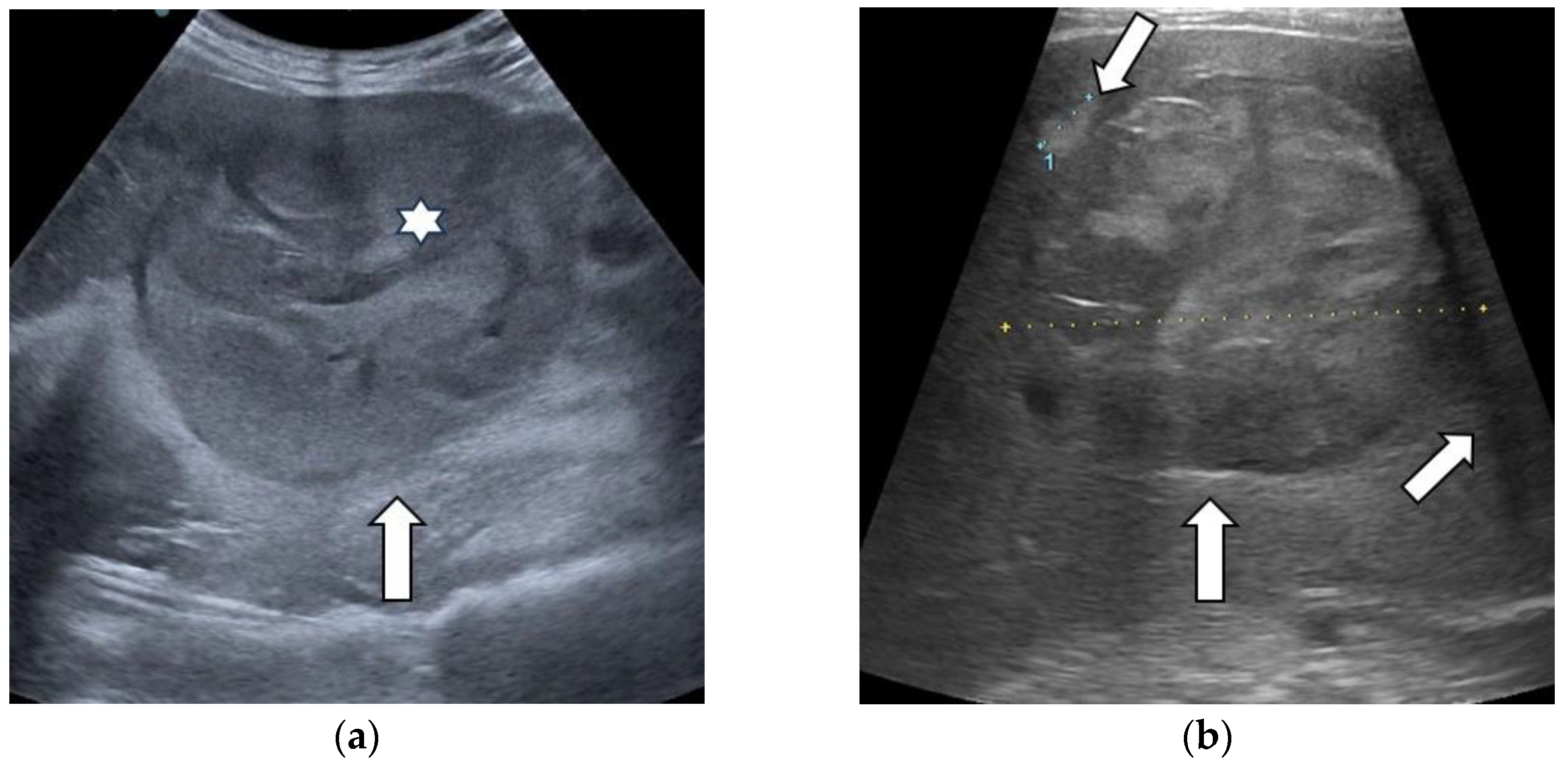
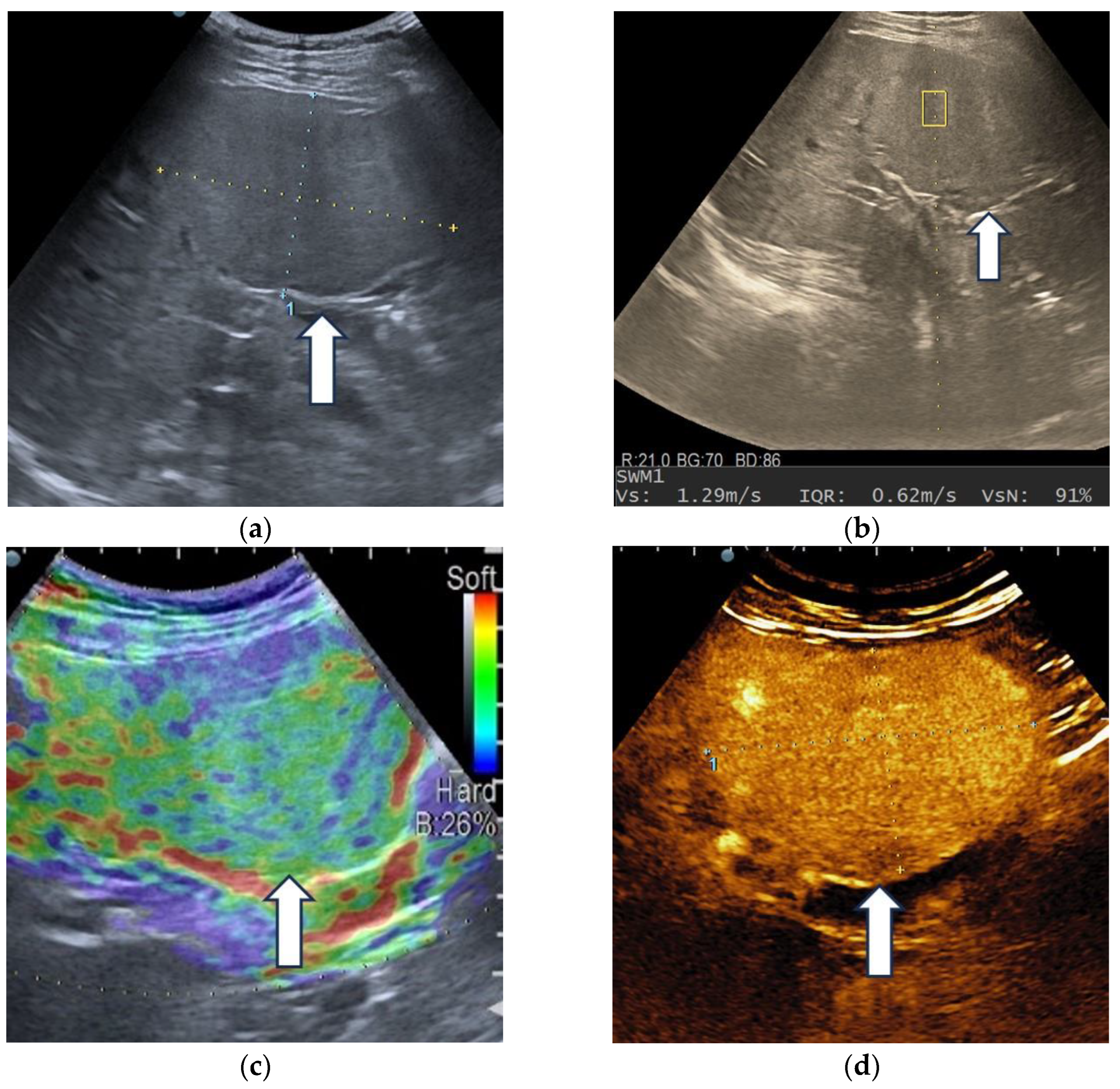
| Elasticity Type | Color Code |
|---|---|
| Type “a” | Homogenously green |
| Type “b” | Mosaic pattern with dominant green areas |
| Type “c” | Mosaic pattern with dominant blue areas |
| Type “d” | Homogenously light blue |
| Type “e” | Homogenously dark blue |
| Final Diagnosis | Number of Lesions | |
|---|---|---|
| Benign tumors (n = 11) | Hepatic adenoma | 3 |
| Hepatic hemangioma | 4 | |
| Complicated liver cyst | 1 | |
| Gharbi type IV hydatid cyst | 1 | |
| Focal nodular hyperplasia | 2 | |
| Malignant tumors (n = 61) | Hepatocellular carcinoma | 44 |
| Non-HCC malignancies | 17 | |
| 10 | |
| 6 | |
| 1 | |
| Clinical Features | Entire Study Group | HCCs | Non-HCC Malignancies | Benign Tumors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver cirrhosis | 29 (43.93%) | 24 (36.36%) | 3 (4.61%) | 2 (3.07%) |
| Chronic hepatitis B and C | 17 (26.15%) | 13 (19.69%) | 2 (3.07%) | 2 (3.07%) |
| Histopathologic evidence of chronic hepatitis (non-HBV, non-HCV) | 6 (9.09%) | 5 (7.57%) | 1 (1.51%) | 0 |
| No underlying liver disease | 14 (21.21%) | 0 | 9 (13.63%) | 5 (7.57%) |
| History of extrahepatic malignancy | 15 (22.72%) | 6 (9.09%) | 8 (12.12%) | 1 (1.51%) |
| Ascites | 14 (21.21%) | 12 (18.18%) | 2 (3.07%) | 0 |
| Portal vein thrombosis | 12 (18.18%) | 10 (15.15%) | 2 (3.07%) | 0 |
| Ultrasound Features | Entire Group | HCCs | Non-HCC Malignancies | Benign Tumors | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (mm) | 70.11 ± 38.97 | 76.73 ± 40.8 | 60.88 ± 30.86 | 57.93 ± 35.49 | |
| Echogenicity | Hypoechoic | 22 (30.6%) | 12 (16.67%) | 7 (9.72%) | 3 (4.17%) |
| Isoechoic | 14 (19.4%) | 9 (12.50%) | 2 (2.78%) | 3 (4.17%) | |
| Hyperechoic | 31 (43.1%) | 21 (29.17%) | 5 (6.94%) | 5 (6.94%) | |
| Mixed echogenicity | 5 (6.9%) | 2 (2.78%) | 3 (4.17%) | 0 | |
| Homogeneity | Homogenous | 5 (6.9%) | 2 (2.78%) | 1 (1.39%) | 2 (2.78%) |
| Non-homogenous | 67 (93.1%) | 42 (58.33%) | 16 (22.22%) | 9 (12.50%) | |
| Tumor boundaries | Well-delimited | 58 (80.6%) | 38 (52.78%) | 12 (16.67%) | 8 (11.11%) |
| Ill-delimited | 14 (19.4%) | 6 (8.33%) | 5 (6.94%) | 3 (4.17%) | |
| "Nodule-in-nodule” architecture | Yes | 18 (25%) | 17 (23.61%) | 1 (1.39%) | 0 |
| No | 54 (75%) | 27 (37.50%) | 16 (22.22%) | 11 (15.28%) | |
| Mosaic appearance | Yes | 16 (22.2%) | 16 (22.2%) | 0 | 0 |
| No | 56 (77.8%) | 28 (38.89%) | 17 (23.61%) | 11 (15.28%) | |
| Halo sign | Yes | 28 (38.9%) | 21 (29.17%) | 5 (6.94%) | 2 (2.78%) |
| No | 44 (61.1%) | 23 (31.94%) | 12 (16.67%) | 9 (12.50%) | |
| Satellite nodules | Yes | 8 (11.1%) | 7 (9.72%) | 1 (1.39%) | 0 |
| No | 64 (88.9%) | 37 (51.39%) | 16 (22.22%) | 11 (15.28%) | |
| Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | PPV (95% CI) | NPV (95% CI) | Accuracy (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 69.05% | 92.86% | 93.55% | 66.67% | 78.57% |
| (52.91–82.39%) | (76.50–99.12%) | (78.97–98.24%) | (55.72–76.07%) | (67.13–87.48%) |
| Tumor Type | Mean Vs (m/s) | Range |
|---|---|---|
| HCCs | 1.59 ± 0.29 | 1.07–2.31 m/s |
| Non-HCC malignancies | 1.9 ± 0.42 | 1.34–3 m/s |
| Benign tumors | 1.75 ± 0.4 | 1.36–2.51 m/s |
| Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | PPV (95% CI) | NPV (95% CI) | Accuracy (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 54.76% | 82.35% | 88.46% | 42.42% | 62.71% |
| (38.67–70.15%) | (56.57–96.20%) | (72.59–95.69%) | (33.09–52.34%) | (49.15–74.96%) |
| Variables | VsN ≥ 50% | VsN < 50% | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vs (m/s) | 1.66 ± 0.3 | 1.73 ± 0.44 | 0.74 |
| Depth of the lesion (cm) | 5.14 ± 1.16 | 5.73 ± 1.60 | 1.31 |
| Size (mm) | 75.59 ± 29.62 | 66.17 ± 45 | 0.06 |
| Presence of liver cirrhosis | 17 | 15 | 0.34 |
| RTE | Liver Adenoma | HMG | FNH | Complicated Liver Cyst | HCC | iCCA | Liver Metastases | Liver Lymphoma |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type “a” | 3 | 1 | ||||||
| Type “b” | 1 | 1 | 10 | 3 | 1 | |||
| Type “c” | 1 | 24 | 3 | 6 | ||||
| Type “d” | 1 | |||||||
| Type “e” | 5 | 3 | 1 |
| Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | PPV (95% CI) | NPV (95% CI) | Accuracy (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 79.55% | 89.29% | 92.11% | 73.53% | 83.33% |
| (64.70–90.20%) | (71.77–97.73%) | (79.85–97.17%) | (60.47–83.46%) | (72.70–91.08%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urhuț, M.-C.; Săndulescu, L.D.; Ciocâlteu, A.; Cazacu, S.M.; Dănoiu, S. The Clinical Value of Multimodal Ultrasound for the Differential Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma from Other Liver Tumors in Relation to Histopathology. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13203288
Urhuț M-C, Săndulescu LD, Ciocâlteu A, Cazacu SM, Dănoiu S. The Clinical Value of Multimodal Ultrasound for the Differential Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma from Other Liver Tumors in Relation to Histopathology. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(20):3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13203288
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrhuț, Marinela-Cristiana, Larisa Daniela Săndulescu, Adriana Ciocâlteu, Sergiu Marian Cazacu, and Suzana Dănoiu. 2023. "The Clinical Value of Multimodal Ultrasound for the Differential Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma from Other Liver Tumors in Relation to Histopathology" Diagnostics 13, no. 20: 3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13203288
APA StyleUrhuț, M.-C., Săndulescu, L. D., Ciocâlteu, A., Cazacu, S. M., & Dănoiu, S. (2023). The Clinical Value of Multimodal Ultrasound for the Differential Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma from Other Liver Tumors in Relation to Histopathology. Diagnostics, 13(20), 3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13203288







