Lung Microbiota in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, and Unclassified Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Preliminary Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
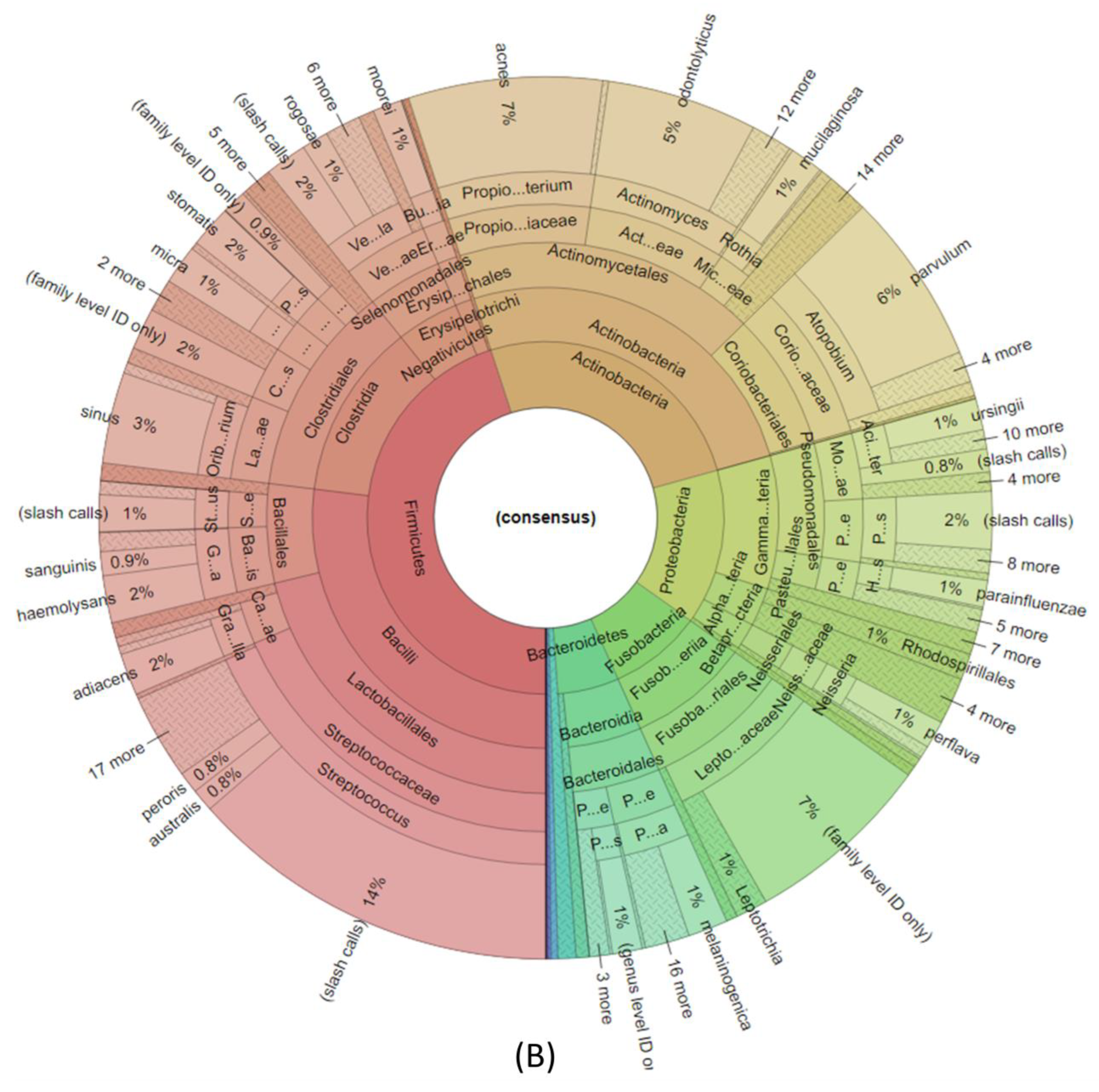
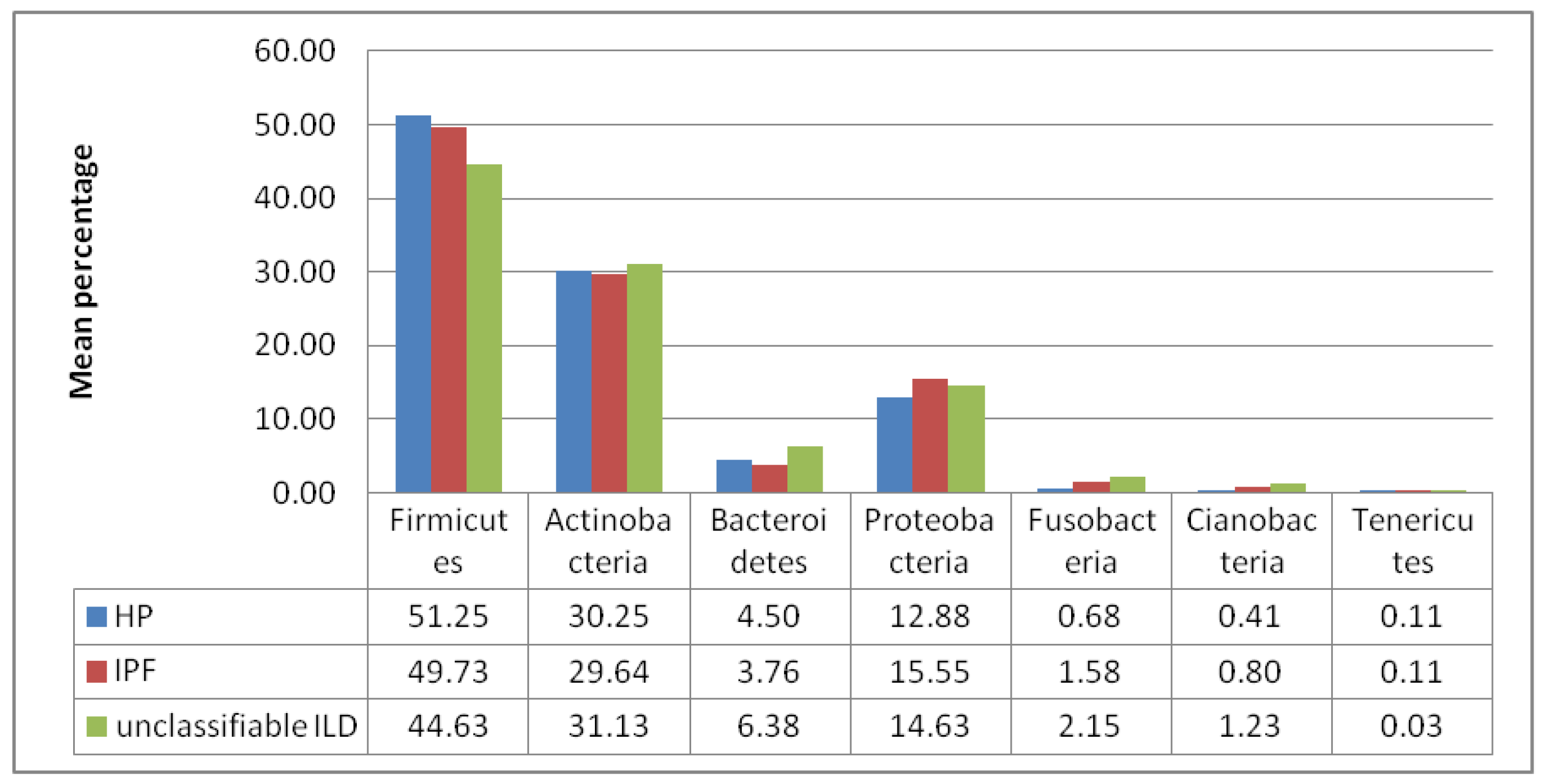
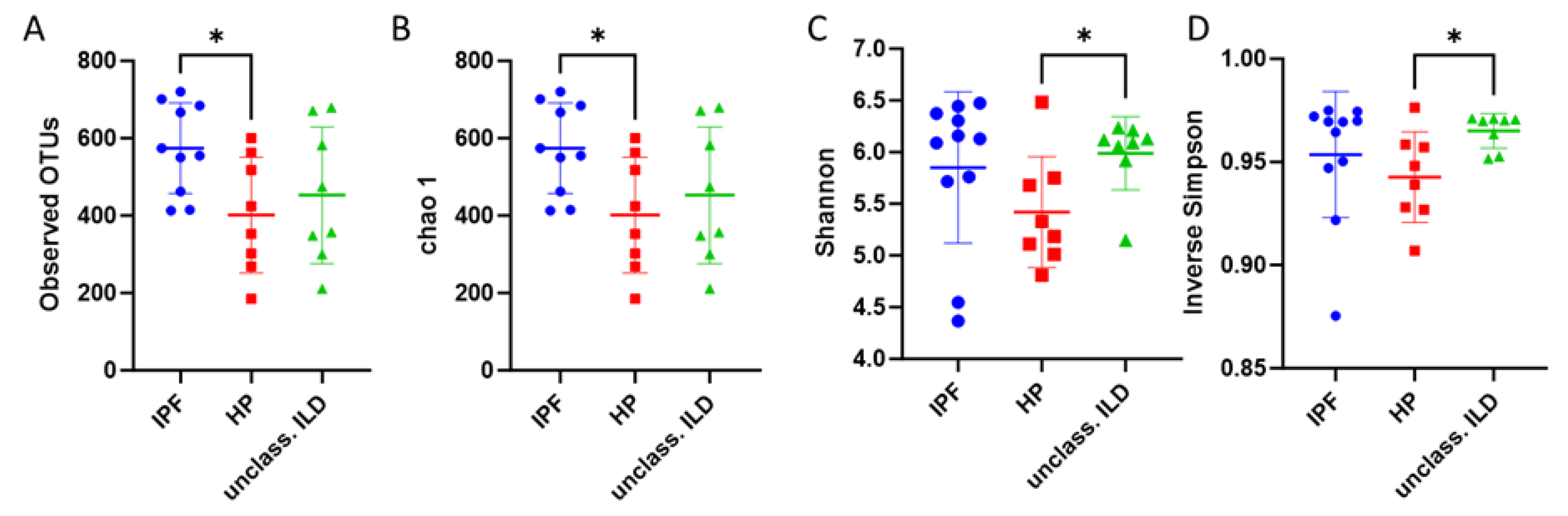
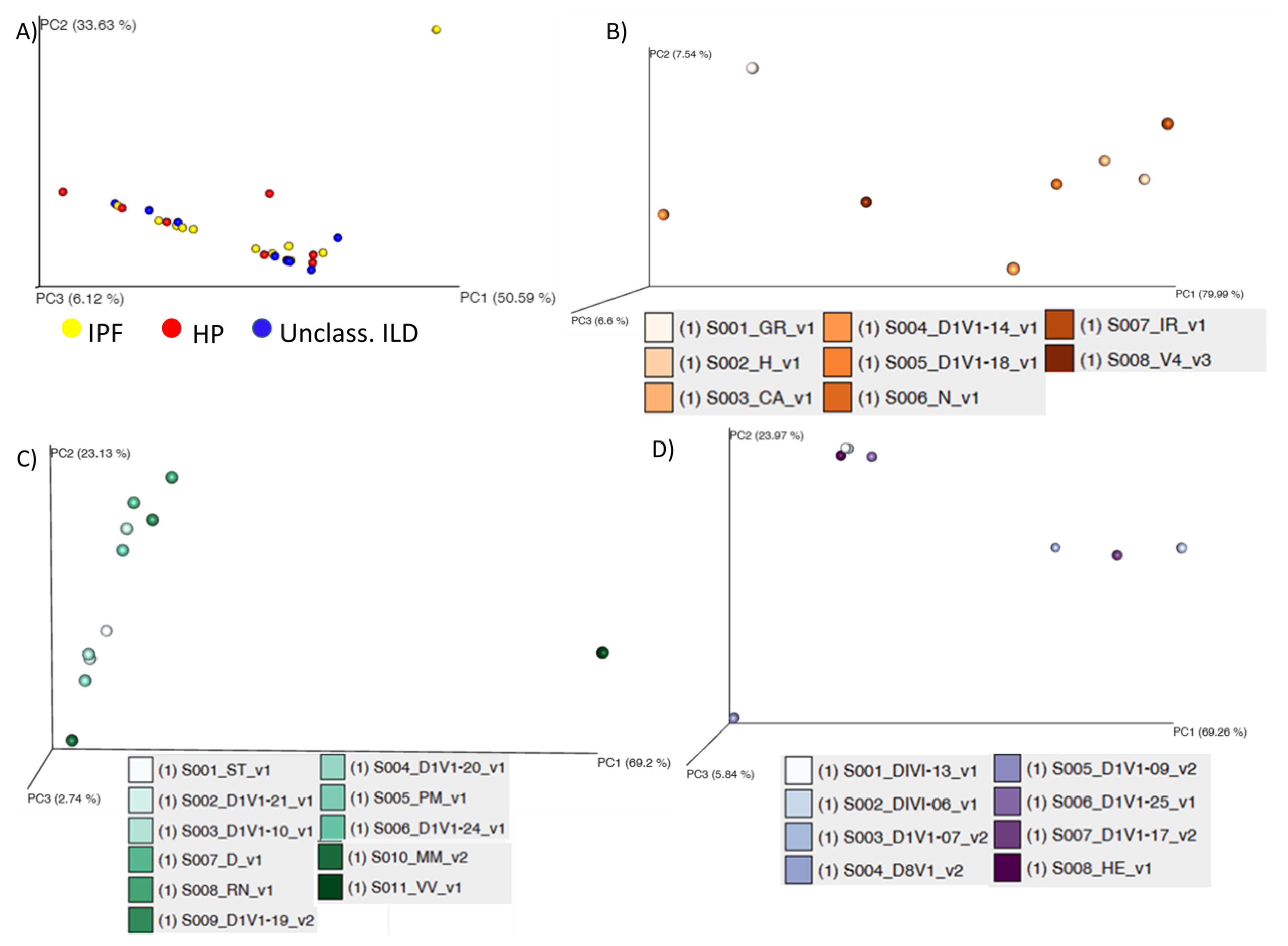
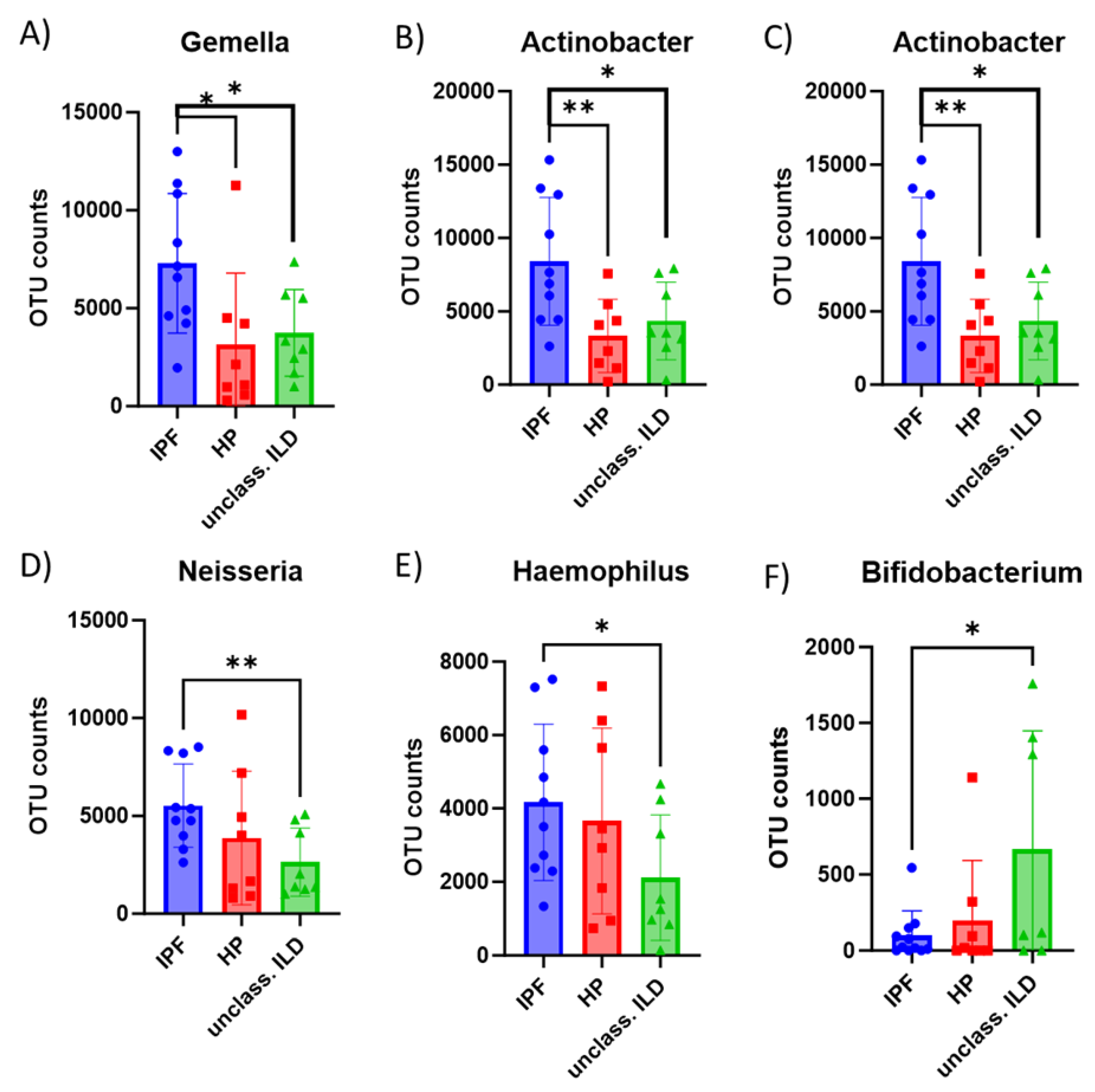
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amati, F.; Stainer, A.; Mantero, M.; Gramegna, A.; Simonetta, E.; Suigo, G.; Voza, A.; Nambiar, A.M.; Cariboni, U.; Oldham, J.; et al. Lung Microbiome in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Other Interstitial Lung Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpellini, E.; Ianiro, G.; Attili, F.; Bassanelli, C.; De Santis, A.; Gasbarrini, A. The human gut microbiota and virome: Potential therapeutic implications. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes, A.M.; Walter, J.; Segal, E.; Spector, T.D. Role of theGutMicrobiota in NutritionandHealth. BMJ 2018, 361, k2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettigrew, M.M.; Tanner, W.; Harris, A.D. The Lung Microbiome and Pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 223, S241–S245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommariva, M.; Le Noci, V.; Bianchi, F.; Camelliti, S.; Balsari, A.; Tagliabue, E.; Sfondrini, L. The lung microbiota: Role in maintaining pulmonary immune homeostasis and its implications in cancer development and therapy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 2739–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huffnagle, G.B.; Dickson, R.P.; Lukacs, N.W. The respiratory tract microbiome and lung inflammation: A two-way street. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 10, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yao, M.; Lv, L.; Ling, Z.; Li, L. The Human Microbiota in Health and Disease. Engineering 2017, 3, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiley, J.P.; Caler, E.V. The Lung Microbiome. A New Frontier in Pulmonary Medicine. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11 (Suppl. S1), S66–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassis, C.M.; Erb-Downward, J.R.; Dickson, R.P.; Freeman, C.M.; Schmidt, T.M.; Young, V.B.; Beck, J.M.; Curtis, J.L.; Huffnagle, G.B. Analysis of the Upper Respiratory Tract Microbiotas as the Source of the Lung and Gastric Microbiotas in Healthy Individuals. mBio 2015, 6, e00037-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilty, M.; Burke, C.; Pedro, H.; Cardenas, P.; Bush, A.; Bossley, C.; Davies, J.; Ervine, A.; Poulter, L.; Pachter, L.; et al. Disordered Microbial Communities in Asthmatic Airways. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.N.; Costa, F.M.D.; Campos, S.V.; Salles, R.K.; Athanazio, R.A. The pulmonary microbiome: Challenges of a new paradigm. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2018, 44, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, T.; Ye, C.; Zhong, J.; Huang, J.D.; Ke, Y.; Sun, H. The Lung Microbiome: A New Frontier for Lung and Brain Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotelli, N.J. Colwell RKJBdfim, assessment. Estim. Species Richness 2011, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lande, R. Statistics and partitioning of species diversity, and similarity among multiple communities. Oikos 1996, 76, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalini, J.G.; Singh, S.; Segal, L.N. The dynamic lung microbiome in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 21, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, R.P.; Erb-Downward, J.R.; Martinez, F.J.; Huffnagle, G.B. The microbiome and the respiratory tract. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016, 78, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invernizzi, R.; Hewitt, R.; Ghai, P.; Swann, J.; Wu, B.; Segal, L.; Byrne, A.; Maher, T.; Lloyd, C.; Molyneaux, P. The respiratory microbiome and metabolome in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, J.A. Our unique microbial identity. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invernizzi, R.; Wu, B.G.; Barnett, J.; Ghai, P.; Kingston, S.; Hewitt, R.J.; Feary, J.; Li, Y.; Chua, F.; Wu, Z.; et al. The Respiratory Microbiome in Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Is Distinct from That of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, R.P.; Huffnagle, G.B. The Lung Microbiome: New Principles for Respiratory Bacteriology in Health and Disease. Goldman WE, editor. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.; Gibson, K.; Collman, R.G. The Lung Microbiome in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. What Does It Mean and What Should We Do about It? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 850–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.K.; Zhou, Y.; Murray, S.; Tayob, N.; Noth, I.; Lama, V.N.; Moore, B.B.; White, E.S.; Flaherty, K.R.; Huffnagle, G.B.; et al. Lung microbiome and disease progression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An analysis of the COMET study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Simone, S.K.; Rudloff, I.; Nold-Petry, C.A.; Forster, S.C.; Nold, M.F. Understanding respiratory microbiome–immune system interactions in health and disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabq5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosens, R.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Adcock, I.M.; Bracke, K.R.; Dickson, R.P.; Hansbro, P.M.; Krauss-Etschmann, S.; Smits, H.H.; Stassen, F.R.M.; Bartel, S. Host-microbe cross-talk in the lung microenvironment: Implications for understanding and treating chronic lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 1902320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.E.; De la Rosa, M.A. Entering the second decade: FEBS Open Bio in 2022. FEBS Open Bio 2022, 12, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, W.H.; de Steenhuijsen Piters, W.A.A.; Bogaert, D. The microbiota of the respiratory tract: Gatekeeper to respiratory health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Shawcross, D.L. Chapter 9—The Gut Microbiota in Hepatic Encephalopathy [Internet]. In The Complex Interplay between Gut-Brain, Gut-Liver, and Liver-Brain Axes; Stasi, C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 187–204. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, C.W.; Kurs-Lasky, M.; McElheny, C.L.; Bridwell, S.; Liu, H.; Shaikh, N. Performance of Conventional Urine Culture Compared to 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing in Children with Suspected Urinary Tract Infection. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e01861-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Loeches, I.; Dickson, R.; Torres, A.; Hanberger, H.; Lipman, J.; Antonelli, M.; de Pascale, G.; Bozza, F.; Vincent, J.L.; Murthy, S.; et al. The importance of airway and lung microbiome in the critically ill. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsheh, M.Y.; Haldar, K.; Esteve-Codina, A.; Purser, L.F.; Richardson, M.; Müller-Quernheim, J.; Greulich, T.; Nowinski, A.; Barta, I.; Stendardo, M.; et al. Lung microbiome composition and bronchial epithelial gene expression in patients with COPD versus healthy individuals: A bacterial 16S rRNA gene sequencing and host transcriptomic analysis. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e300–e310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veillette, M.; Racine, C.; Joubert, P.; Duchaine, C. Development of a robust protocol for the characterization of the pulmonary microbiota. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.J.; Hermes, B.M.; Gupta, Y.; Ibrahim, S.; Belheouane, M.; Baines, J.F. Genome-wide mapping of gene-microbe interactions in the murine lung microbiota based on quantitative microbial profiling. Anim. Microbiome 2023, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameter | IPF (n = 10) | HP (n = 10) | Unclassified ILDs (n = 8) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 53.3 ± 12.96 | 62.3 ± 5.79 | 58.75 ± 16.36 | NS |
| Gender, F, n (%) | 6 (60%) | 5 (50%) | 5 (62.5%) | NS |
| Active smoker | 1 (10%) | 3 (30%) | 4 (50%) | NS |
| Never smoker | 8 (80%) | 7 (70%) | 4 (50%) | NS |
| Former smokers | 1 (10%) | 0 | 0 | NS |
| Blood neutrophils | 5.58 ± 2.41 | 4.67 ± 2.42 | 3.97 ± 0.99 | NS |
| Blood lymphocites | 1.89 ± 0.58 | 1.76 ± 0.64 | 1.68 ± 0.9 | NS |
| NLR | 2.99 ± 1.15 | 3.04 ± 2.28 | 2.96 ± 1.39 | NS |
| Honey combing HRCT | 5 (50%) | 4 (40%) | 0 (0%) | <0.05 |
| Macrophage (BAL) | 1.26 (0.55–5.16) | 0.56 (0.24–2.18) | 1.06 (0.56–1.89) | NS |
| lymphocites (BAL) | 3.78 (1.72–8.08) | 5.7 (1.80–14.69) | 8.35 (5.25–13.74) | NS |
| Neutrophils (BAL) | 0.53 (0.11–1.23) | 0.6 (0.19–0.93) | 0.33 (0.03–1.68) | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Man, M.A.; Ungur, R.A.; Motoc, N.S.; Pop, L.A.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Ruta, V.M. Lung Microbiota in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, and Unclassified Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Preliminary Pilot Study. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13193157
Man MA, Ungur RA, Motoc NS, Pop LA, Berindan-Neagoe I, Ruta VM. Lung Microbiota in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, and Unclassified Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Preliminary Pilot Study. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(19):3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13193157
Chicago/Turabian StyleMan, Milena Adina, Rodica Ana Ungur, Nicoleta Stefania Motoc, Laura Ancuta Pop, Ioana Berindan-Neagoe, and Victoria Maria Ruta. 2023. "Lung Microbiota in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, and Unclassified Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Preliminary Pilot Study" Diagnostics 13, no. 19: 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13193157
APA StyleMan, M. A., Ungur, R. A., Motoc, N. S., Pop, L. A., Berindan-Neagoe, I., & Ruta, V. M. (2023). Lung Microbiota in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, and Unclassified Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Preliminary Pilot Study. Diagnostics, 13(19), 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13193157










