Evaluation of the Abbott Alinity i Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor Antibody (TRAb) Chemiluminescent Microparticle Immunoassay (CMIA)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
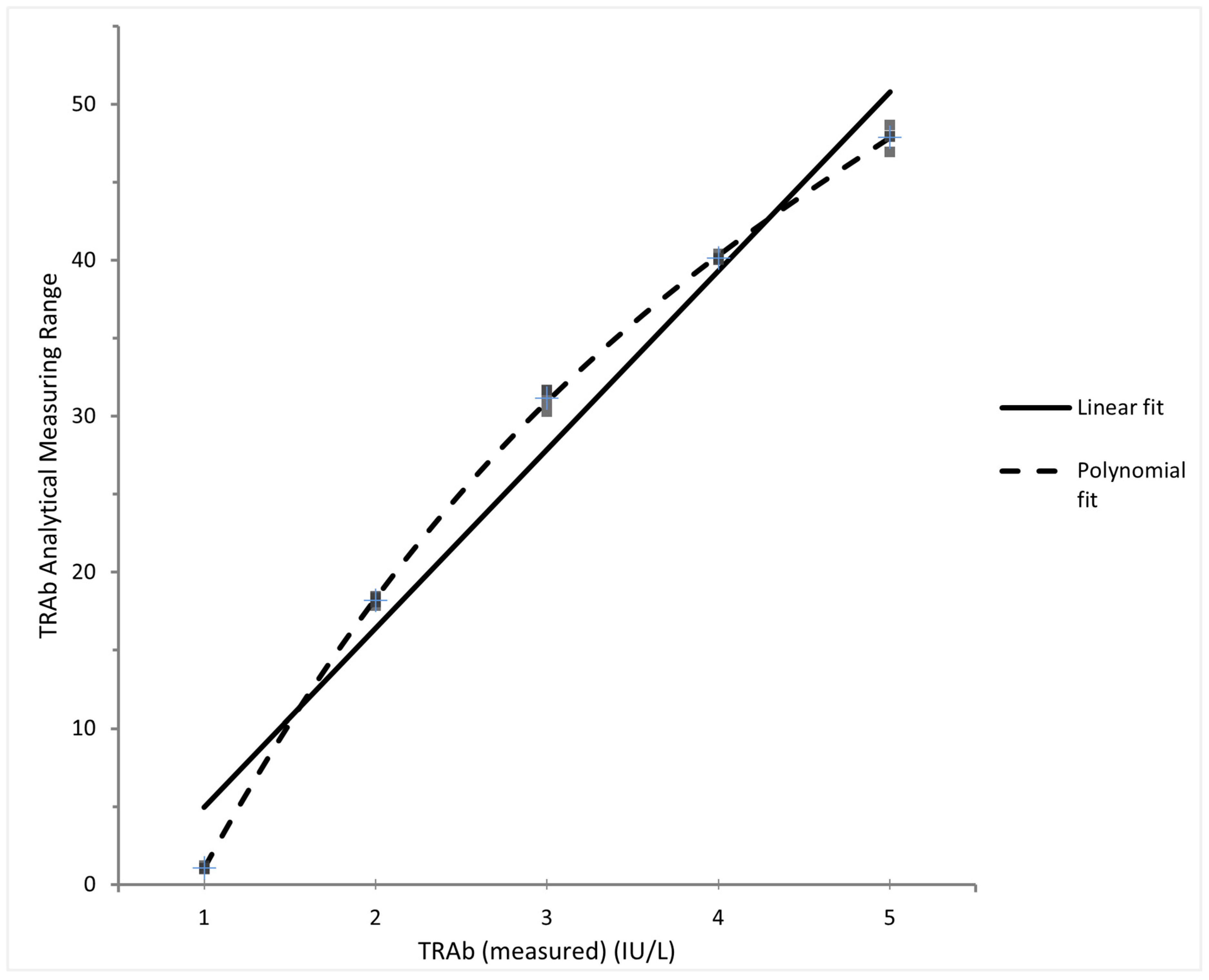
3.1. Performance
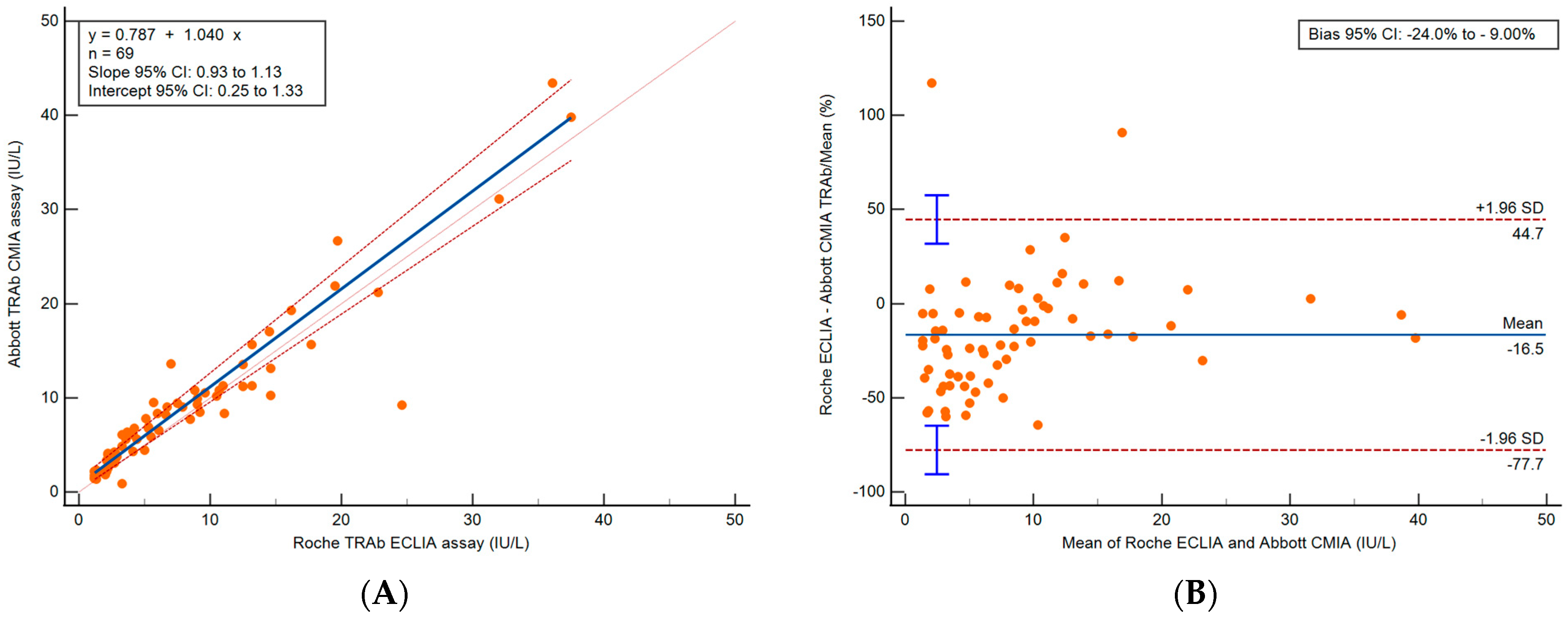
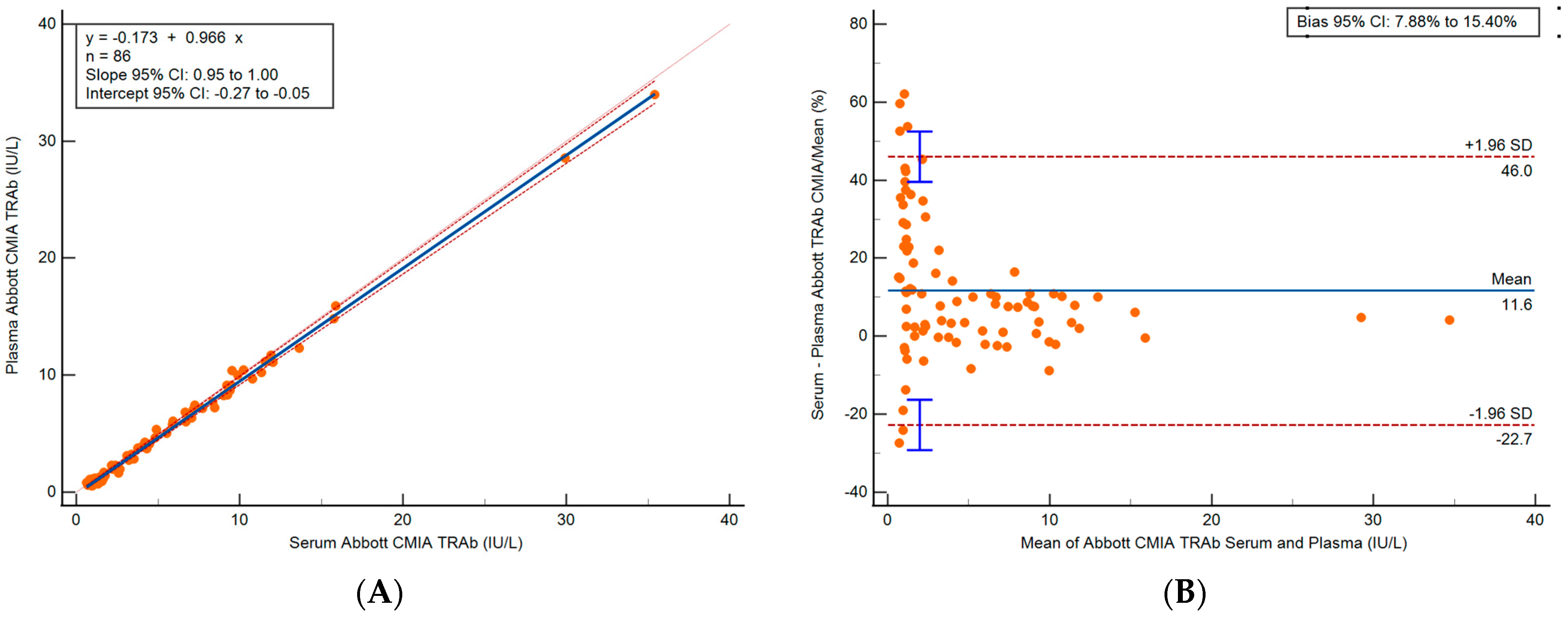
3.2. Method Comparison
3.2.1. Abbott CMIA and Roche CLIA Method Comparison
3.2.2. Abbott Serum and Plasma Method Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Anti-TPO | Anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| CMIA | Chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay |
| CV | Imprecision |
| ECLIA | Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| LOB | Limit of the blank |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| TRAb | Thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor antibody |
| TRAK | Thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor kit |
| TSH | Thyroid-stimulating hormone |
| TSHR | Thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor |
References
- Hesarghatta Shyamasunder, A.; Abraham, P. Measuring TSH Receptor Antibody to Influence Treatment Choices in Graves’ Disease. Clin. Endocrinol. 2017, 86, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, D.S.; Burch, H.B.; Cooper, D.S.; Greenlee, M.C.; Laurberg, P.; Maia, A.L.; Rivkees, S.A.; Samuels, M.; Sosa, J.A.; Stan, M.N.; et al. 2016 American Thyroid Association Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management of Hyperthyroidism and Other Causes of Thyrotoxicosis. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1343–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brent, G.A. Clinical Practice. Graves’ Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2594–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J. Long-Term Management of Graves Disease: A Narrative Review. J. Yeungnam Med. Sci. 2023, 40, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morshed, S.A.; Ando, T.; Latif, R.; Davies, T.F. Neutral Antibodies to the TSH Receptor Are Present in Graves’ Disease and Regulate Selective Signaling Cascades. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 5537–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soh, S.-B.; Aw, T.-C. Laboratory Testing in Thyroid Conditions—Pitfalls and Clinical Utility. Ann. Lab. Med. 2019, 39, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. User Verification of Precision and Estimation of Bias, 3rd ed.; CLSI Document EP15-A3; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Measurement Procedure Comparison and Bias Estimation Using Patient Samples, 3rd ed.; CLSI Guideline EP09c; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Evaluation of the Linearity of Quantitative Measurement Procedures, 2nd ed.; CLSI Document EP06; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- TRAb Alinity I [Product Insert]; Abbott: Dublin, Ireland, 2020.
- Elecsys Anti-TSHr [Product Insert]; V 4.0; Roche Diagnostics: Mannheim, Germany, 2021.
- Chin-Shern, L.A.U.; Tar-Choon, A.W. TRAb Measurements: Ready for Prime Time. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. Disord. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lu, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Xun, C. Predicting Relapse of Graves’ Disease Following Treatment with Antithyroid Drugs. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 1453–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahida, B.; Tsoumani, K.; Planck, T.; Modhukur, V.; Asp, P.; Sundlöv, A.; Tennvall, J.; Åsman, P.; Lindgren, O.; Lantz, M. Increased Risk of Graves’Ophthalmopathy in Patients with Increasing TRAb after Radioiodine Treatment and the Impact of Ctla4 on Trab Titres. Endocrine 2022, 75, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, A.; Ferrari, S.M.; Ragusa, F.; Elia, G.; Paparo, S.R.; Ruffilli, I.; Patrizio, A.; Giusti, C.; Gonnella, D.; Cristaudo, A.; et al. Graves’ Disease: Epidemiology, Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors and Viruses. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 34, 101387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, T.D.; Stocker, D.J.; Chou, E.L.; Burch, H.B. 2022 update on Clinical Management of Graves Disease and Thyroid Eye Disease. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 51, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, T.; Evered, D.; Smith, B.; Yeo, P.; Clark, F.; Hall, R. Value of Thyroid-Stimulating-Antibody Determinations in Predicting Short-Term Thyrotoxic Relapse in Graves’ Disease. Lancet 1977, 309, 1181–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.; McKILLOP, J.H.; Henderson, N.; Pearson, D.W.; Thomson, J.A. The Ability of the Serum Thyrotrophin Receptor Antibody (TRAb) Index and HLA Status to Predict Long-Term Remission of Thyrotoxicosis Following Medical Therapy for Graves’ Disease. Clin. Endocrinol. 1986, 25, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choksi, H.; Li, S.H.; Bhandari, M.; Cheng, P.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Kulasingam, V. Analytical Performance of Abbott’s Architect and Alinity TSH-Receptor Antibody (TRAb) Assays. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2023, 61, e152–e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Ferguson, A.; A Cervinski, M.; Lynch, K.L.; Kyle, P.B. AACC Guidance Document on Biotin Interference in Laboratory Tests. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2020, 5, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Measurand | Level (IU/L) | Design | Measured Repeatability, CV% | Manufacturer Claimed Repeatability, CV% | Measured Within-Laboratory Imprecision, CV% | Manufacturer Claimed Within-Laboratory Imprecision, CV% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRAb | 3.0 | 5 × 5 CLSI EP15-A3 | 4.07 | 4.8 | 4.07 | 5.2 |
| 10.0 | 1.56 | 1.8 | 1.90 | 2.0 | ||
| 30.0 | 0.71 | 1.1 | 0.71 | 1.2 |
| Characteristics | Abbott Alinity i TRAb CMIA | Roche Cobas Elecsys Anti-TSHR ECLIA |
|---|---|---|
| Sample volume | 100 µL | 30 µL |
| Assay time | 29 min | 27 min |
| Reference standard | NIBSC 2nd IS 08/204 | NIBSC 1st IS 90/672 |
| Reagent, calibrator, and control preparation | Nil (ready-to-use) | Pretreatment required |
| Reagent onboard stability | 7 days | 16 weeks (with daily calibration) |
| Calibration | Six-point calibration | Two-point calibration |
| Controls | 3.0, 10.0, 30.0 IU/L | 4.0, 10.0 IU/L |
| Dilution of high samples | Auto-dilution (1:10 for samples > 50 IU/L) | Manual dilution (1:10 for samples > 40 IU/L) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.J.W.; Phua, S.K.; Liang, Y.; Chen, C.; Aw, T.-C. Evaluation of the Abbott Alinity i Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor Antibody (TRAb) Chemiluminescent Microparticle Immunoassay (CMIA). Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162707
Lee DJW, Phua SK, Liang Y, Chen C, Aw T-C. Evaluation of the Abbott Alinity i Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor Antibody (TRAb) Chemiluminescent Microparticle Immunoassay (CMIA). Diagnostics. 2023; 13(16):2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162707
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Deborah J. W., Soon Kieng Phua, Yali Liang, Claire Chen, and Tar-Choon Aw. 2023. "Evaluation of the Abbott Alinity i Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor Antibody (TRAb) Chemiluminescent Microparticle Immunoassay (CMIA)" Diagnostics 13, no. 16: 2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162707
APA StyleLee, D. J. W., Phua, S. K., Liang, Y., Chen, C., & Aw, T.-C. (2023). Evaluation of the Abbott Alinity i Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor Antibody (TRAb) Chemiluminescent Microparticle Immunoassay (CMIA). Diagnostics, 13(16), 2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162707







