Performance of Point-of-Care Ultrasonography in Confirming Feeding Tube Placement in Mechanically Ventilated Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
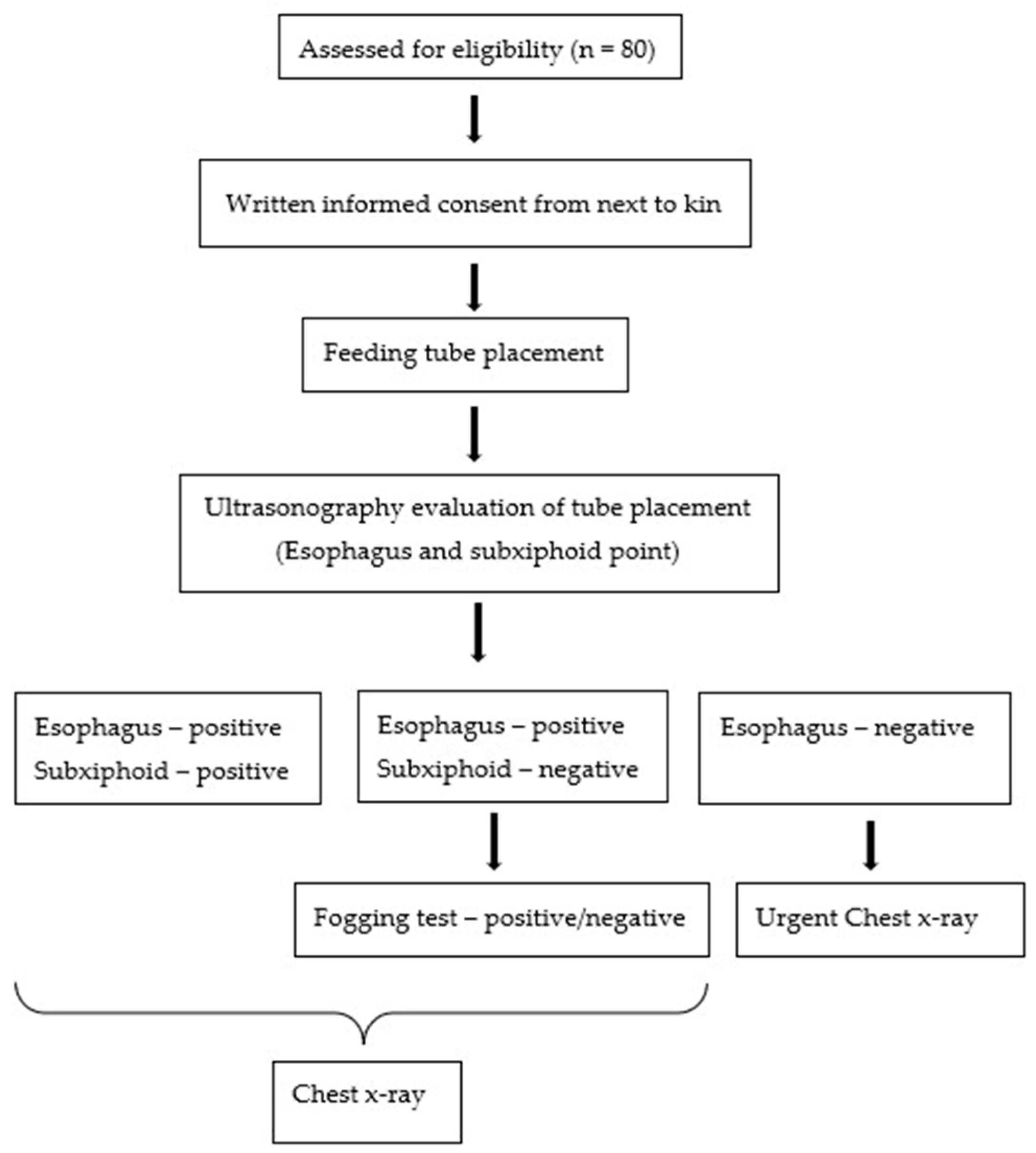
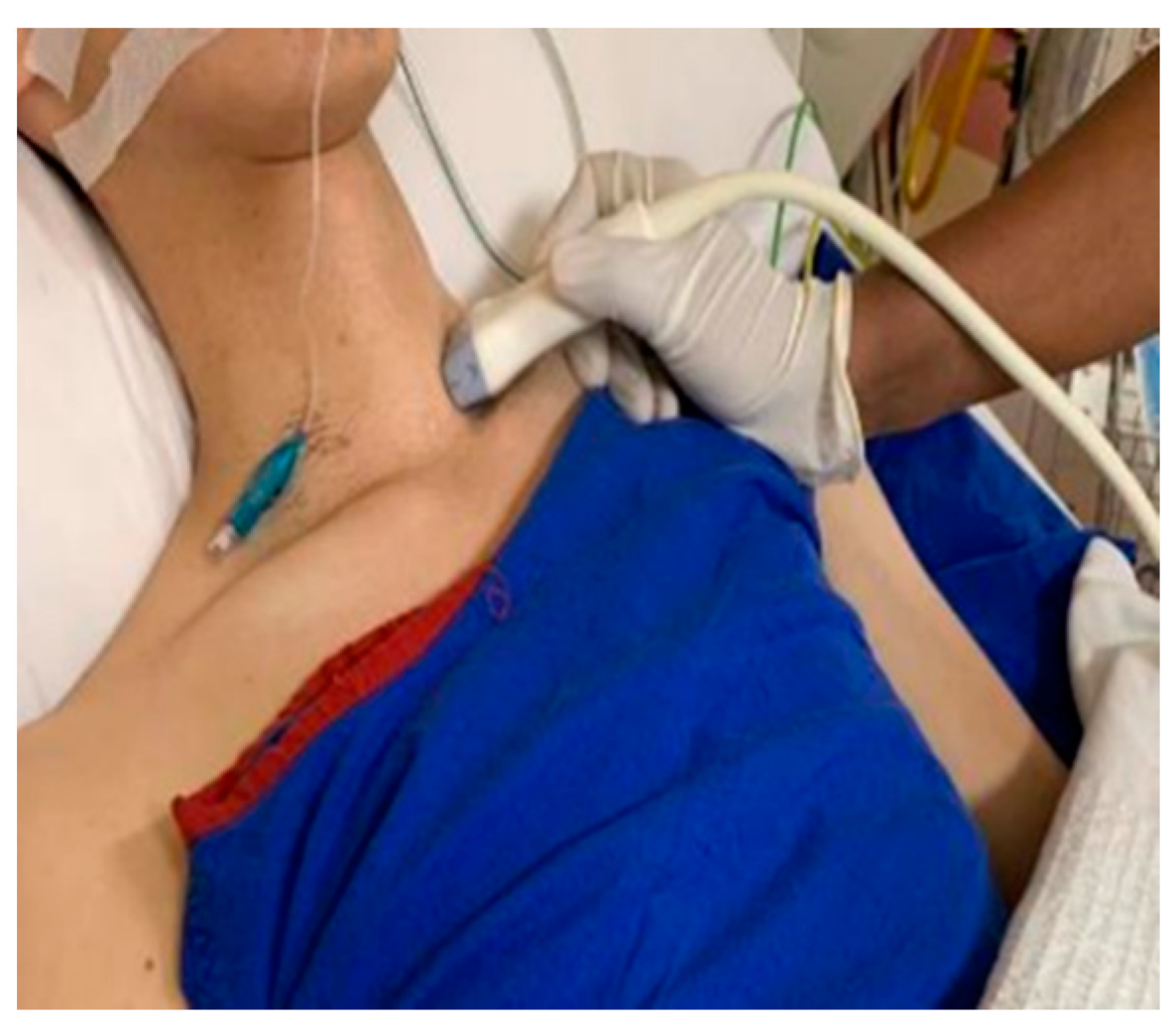
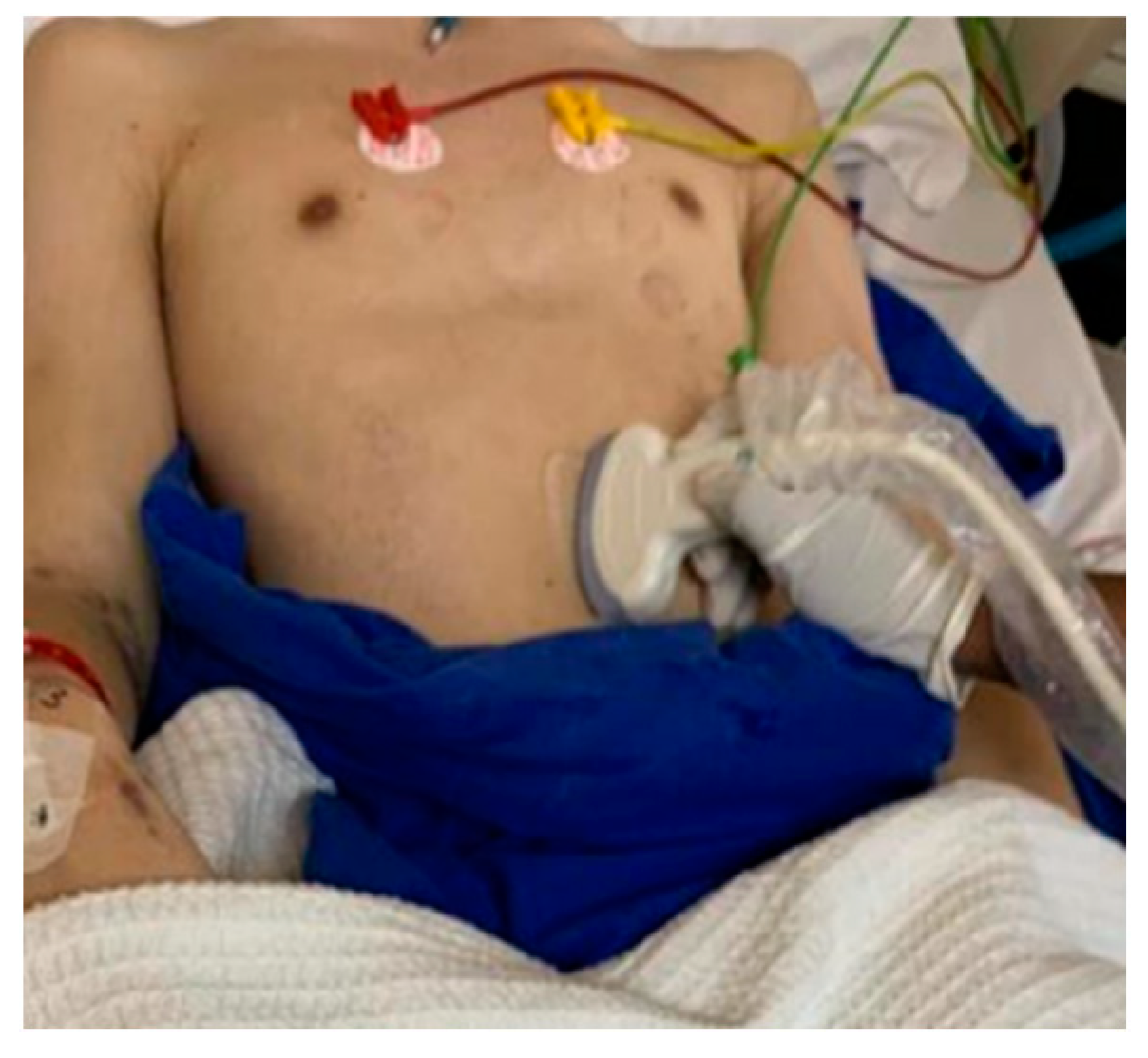
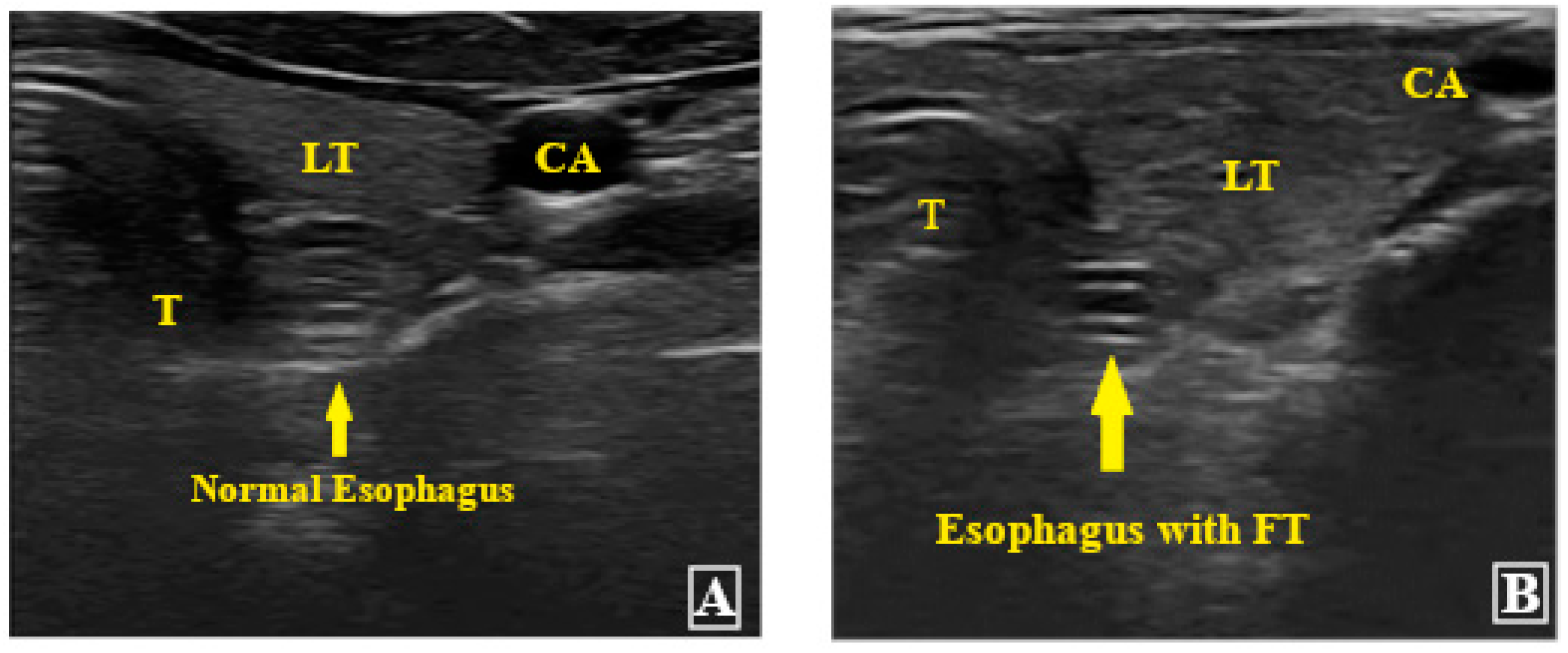
2. Materials and Methods
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bankier, A.A.; Wiesmayr, M.N.; Henk, C.; Turetschek, K.; Winkelbauer, F.; Mallek, R.; Fleischmann, D.; Janata, K.; Herold, C.J. Radiographic detection of intrabronchial malpositions of nasogastric tubes and subsequent complications in intensive care unit patients. Intensiv. Care Med. 1997, 23, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.R.R.M.; Huseby, J.S. Pulmonary complications from nasoenteral feeding tube insertion in an intensive care unit: Incidence and prevention. Crit. Care Med. 1989, 17, 917–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeykens, K.; Steeman, E.; Duysburgh, I. Reliability of pH measurement and the auscultatory method to confirm the position of a nasogastric tube. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2014, 51, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; So, B.H.; Jeong, W.J.; Choi, S.M.; Park, K.N. The effectiveness of ultrasonography in verifying the placement of a nasogastric tube in patients with low consciousness at an emergency center. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2012, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, J.P.; Lo, S.H.; Thompson, D.R.; Fernandez, R.; Griffiths, R. Use of end-tidal carbon dioxide detection to determine correct placement of nasogastric tube: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2011, 48, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.-A.; Choi, K.; Yang, J.H.; Lee, D.-S.; Suh, G.Y.; Jeon, K.; Cho, J.; Chung, C.R.; Sohn, I.; Kim, K.; et al. Clinical usefulness of capnographic monitoring when inserting a feeding tube in critically ill patients: Retrospective cohort study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2016, 16, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metheny, N.A.; Stewart, B.J.; Smith, L.; Yan, H.; Diebold, M.; Clouse, R.E. pH and Concentration of Bilirubin in Feeding Tube Aspirates As Predictors of Tube Placement. Nurs. Res. 1999, 48, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.J. Confirming nasogastric feeding tube position versus the need to feed. Intensiv. Crit. Care Nurs. 2013, 29, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snaith, B.; Flintham, K. Radiology responsibilities post NPSA guidelines for nasogastric tube insertion: A single centre review. Radiography 2015, 21, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgault, A.M.; Upvall, M.J.; Nicastro, S.; Powers, J. Challenges of de-implementing feeding tube auscultation: A qualitative study. Int. J. Nurs. Pract. 2022, 28, e13026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgault, A.M.P.; Powers, J.P.; Aguirre, L.D.; Hines, R.B.; Sebastian, A.T.M.; Upvall, M.J.P. National Survey of Feeding Tube Verification Practices: An Urgent Call for Auscultation Deimplementation. Dimens. Crit. Care Nurs. 2020, 39, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, E.M.P.; Tan, S.B.; Ang, S.Y. Nasogastric tube placement confirmation: Where we are and where we should be heading. Proc. Singap. Healthc. 2017, 26, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.-W.; Chen, H.-S.; Chen, Y.-T.; Hung, K.-C. To characterize the incidence of airway misplacement of nasogastric tubes in anesthetized intubated patients by using a manometer technique. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2017, 31, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, M.J.; Meyer, C.T.; Dutton, J.L.; Smith, R. Hold that x-ray: Aspirate pH and auscultation prove enteral tube place-ment. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1995, 20, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgay, A.S.; Khorshid, L. Effectiveness of the auscultatory and pH methods in predicting feeding tube placement. J. Clin. Nurs. 2010, 19, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.; Lewiss, R.E.; Drew, J.; Saul, T. A novel approach to confirming nasogastric tube placement in the ED. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 30, 1662.e5–1662.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gok, F.; Kilicaslan, A.; Yosunkaya, A. Ultrasound-Guided Nasogastric Feeding Tube Placement in Critical Care Patients. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2015, 30, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitpas, F.; Kerforne, T.; Lacroix, C.; Mimoz, O. Comment on “A novel approach to confirming nasogastric tube placement in the ED”. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 30, 631–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, M.Y.; Tam, G. Ultrasonography for nasogastric tube placement verification: An additional reference. Br. J. Community Nurs. 2020, 25, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Sirois, M.; Laupland, K.B.; Liu, D.; Rowan, K.; Ball, C.G.; Hameed, S.M.; Brown, R.; Simons, R.; Dulchavsky, S.A.; et al. Hand-Held Thoracic Sonography for Detecting Post-Traumatic Pneumothoraces: The Extended Focused Assessment With Sonography For Trauma (EFAST). J. Trauma Acute Care Surg 2004, 57, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, D.A. BLUE-protocol and FALLS-protocol: Two applications of lung ultrasound in the critically ill. Chest 2015, 147, 1659–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yıldırım, Ç.; Coşkun, S.; Gökhan, Ş.; Pamukçu Günaydın, G.; Özhasenekler, A.; Özkula, U. Verifying the Placement of Nasogastric Tubes at an Emergency Center: Comparison of Ultrasound with Chest Radiograph. Emerg. Med. Int. 2018, 2018, 2370426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajian-Tilaki, K. Sample size estimation in diagnostic test studies of biomedical informatics. J. Biomed. Inform. 2014, 48, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, R.; Cheng, X.; Chai, H.; Peng, C.; Liu, J.; Jing, J. A systemic ultrasound positioning protocol for nasointestinal tube in critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneau, C.; Baudel, J.-L.; Guidet, B.; Offenstadt, G.; Maury, E. Sonography as an alternative to radiography for nasogastric feeding tube location. Intensiv. Care Med. 2005, 31, 1570–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagli, R.; Bayir, H.; Dadali, Y.; Tokmak, T.T.; Erbesler, Z.A. Role of Ultrasonography in Detecting the Localisation of the Nasoenteric Tube. Turk. J. Anesthesia Reanim. 2017, 45, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenaitia, H.; Brun, P.-M.; Querellou, E.; Leyral, J.; Bessereau, J.; Aimé, C.; Bouaziz, R.; Georges, A.; Louis, F. Ultrasound to confirm gastric tube placement in prehospital management. Resuscitation 2012, 83, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, Y.; Polat, A.; Ozkan, E.; Tomak, L.; Aygun, C.; Tobias, J.D. Bedside ultrasonography for the confirmation of gastric tube placement in the neonate. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2019, 13, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.; Manara, A.R. X-ray checks of NG tube position: A case for guided tube placement. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedemonte, N.A.; Bagilet, D.; Rocchetti, N.; Torresan, G.; Rodríguez, N.; Settecase, C. Color doppler ultrasound is a precise method to evaluate the position of the nasogastric tube in critical ill patients. Med. Intensiv. 2021, 45, e11–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedel, W.L.; Jost, M.N.F.; Filho, J.W.F. A simple and fast ultrasonographic method of detecting enteral feeding tube placement in mechanically ventilated, critically ill patients. J. Intensiv. Care 2017, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komagata, K.; Yabunaka, K.; Nakagami, G.; Ikeda, M.; Takehara, K.; Takemura, Y.; Sanada, H. Confirming the placement of nasogastric tubes by hand-carried ultrasonography device. J. Nurs. Sci. Eng. 2018, 5, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Mean ± SD | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 52.95 ± 18.28 | |
| Weight (kg) | 69.41 ± 14.50 | |
| Height (cm) | 163.45 ± 6.62 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.99 ± 4.81 | |
| Variables | n (%) | |
| Gender | Male Female | 50 (62.5) 30 (37.5) |
| Race | Malay Chinese Indian Others | 39 (48.8) 24 (30.0) 4 (17.5) 3 (3.8) |
| Diabetes mellitus Hypertension | 35 (43.8) 21 (26.3) | |
| Renal disease | 11 (13.8) | |
| IHD | 13 (16.3) | |
| Others (bronchial asthma, cancer, etc.) | 20 (25.0) |
| Variables | n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Discipline | Medical Surgery | 53 (66.3) 27 (33.7) |
| Size (Fr) | 12 14 | 9 (11.3) 71 (88.8) |
| Ultrasonography Outcomes | ||
| Placement in esophagus | Yes No | 78 (97.5) 2 (2.5) |
| Placement in subxiphoid | Yes No | 60 (75.0) 18 (25.0) |
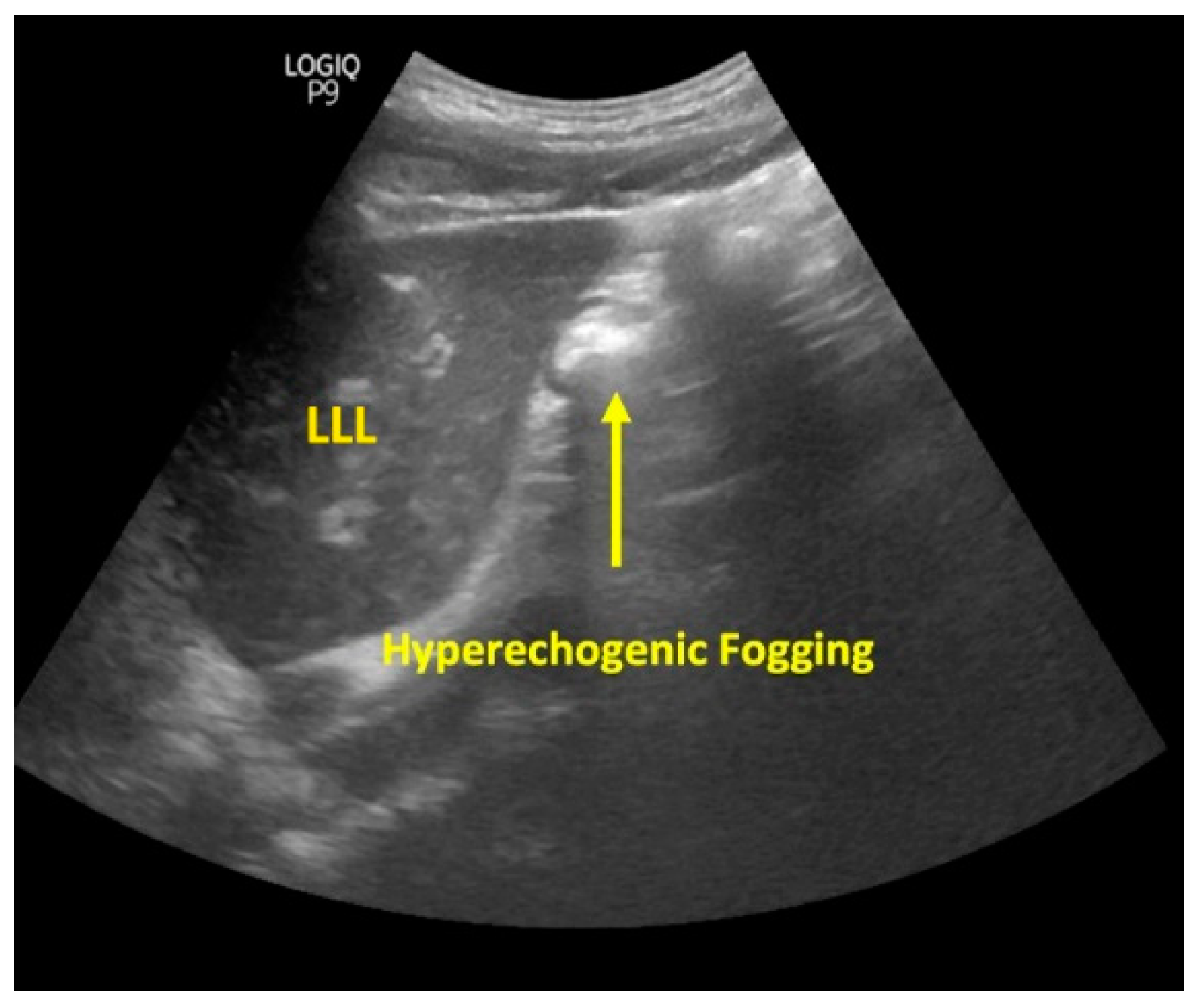
| Presence of fogging | Yes No | 11 (61.1) 7 (38.9) |
| Overall ultrasonography findings | Positive Negative | 71 (88.7) 9 (11.3) |
| Duration of ultrasound assessment in minutes, mean ± SD | 15.50 ± 2.43 | |
| Chest X-ray findings | Yes No | 76 (95.0) 4 (5.0) |
| USG | Chest X-ray * (n) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | |||||
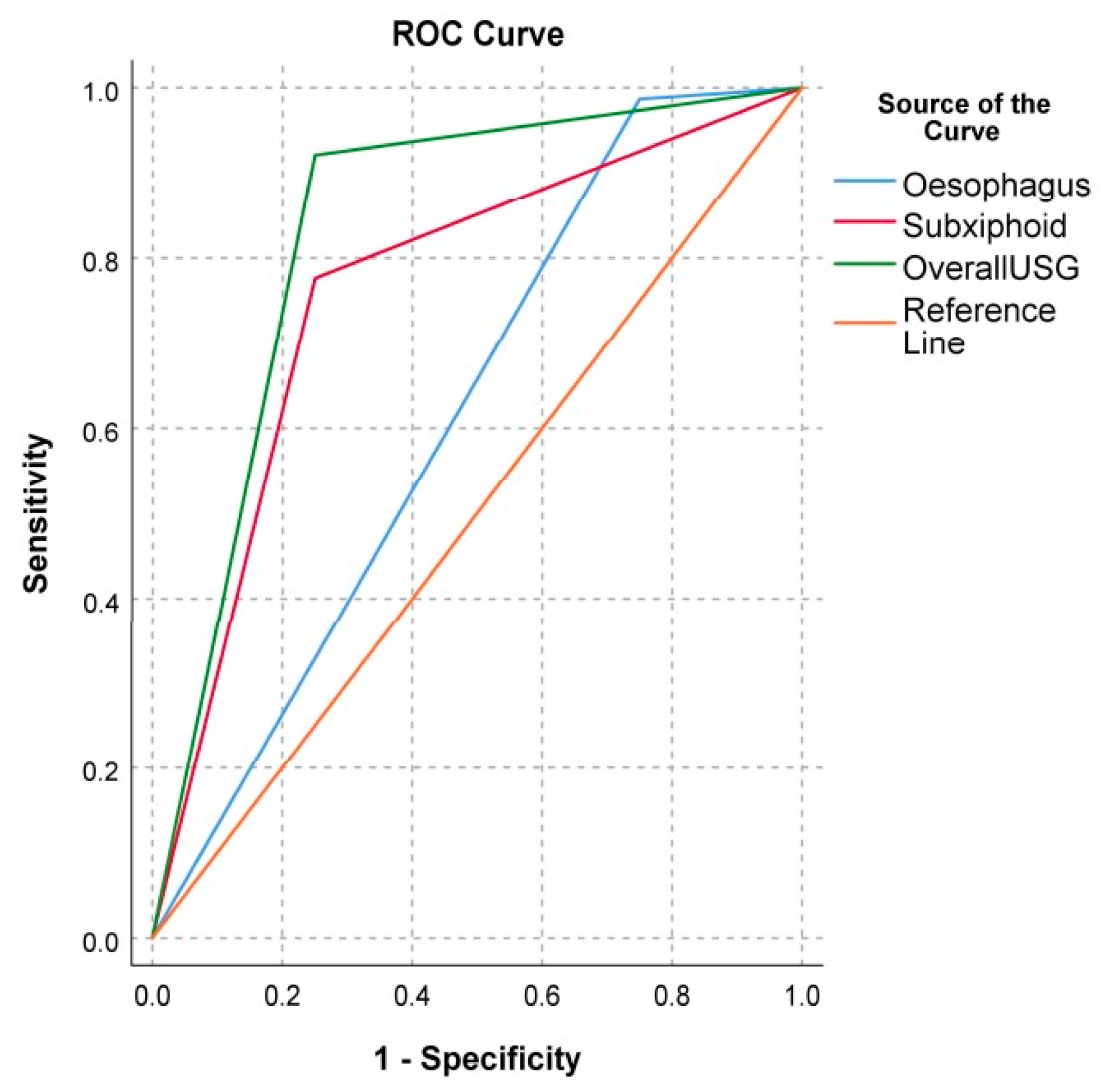
| Esophagus | 98.68 (96.19, 100.00) | 25.00 (15.51, 34.49) | 96.15 (91.94, 100.00) | 50.00% (39.04, 60.96) | ||
| - Negative | 1 | 1 | ||||
| - Positive | 3 | 75 | ||||
| Subxiphoid | 77.63 (68.50, 86.76) | 75.00 (65.51, 84.49) | 98.33 (95.53, 100.00) | 15.00 (7.18, 22.82) | ||
| - Negative | 3 | 17 | ||||
| - Positive | 1 | 59 | ||||
| Overall # | 92.11 (86.20, 98.01) | 75.00 (65.51, 84.49) | 98.59 (96.01, 100.00) | 33.33 (23.00, 43.66) | ||
| - Negative | 3 | 6 | ||||
| - Positive | 1 | 70 | ||||
| Overall USG | Mean Difference | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive, n (%) | Negative, n (%) | |||
| Gastric tube size (Fr) | ||||
| 12 | 5 (7.0) | 4 (44.4) | - | 0.008 a,* |
| 14 | 66 (93.0) | 5 (55.6) | ||
| Mean BMI (Kg/m2) | 24.96 ± 3.67 | 34.10 ± 5.27 | −7.24 (95% CI: −12.15, −2.33) | <0.001 b,* |
| Study | Sensitivity Rate (%) | Specificity Rate (%) | Number of Patients (n) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present study | 92.1 | 75.0 | 80 | |
| Ye, Cheng, Chai, Peng, Liu, and Jing [24] | 96.4 | 90.0 | 157 | Studied nasointestinal tube placement with USG |
| Vigneau, Baudel, Guidet, Offenstadt, and Maury [25] | 97 | - | 35 procedures in 33 patients | Usage of metal nose FT |
| Gok, Kilicaslan, and Yosunkaya [17] | 93 | 56 | - | |
| Dağlı, Bayır, Dadalı, Tokmak, and Erbesler [26] | 97 | - | 34 | - |
| Yıldırım, Coşkun, Gökhan, Pamukçu Günaydın, Özhasenekler, and Özkula [22] | 95.7 | 100 | 49 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ragunathan, T.; Teo, R.; Mohamad Yusof, A.; Mohamad Mahdi, S.N.; Izaham, A.; Liu, C.Y.; Budiman, M.; Sayed Masri, S.N.N.; Abdul Rahman, R. Performance of Point-of-Care Ultrasonography in Confirming Feeding Tube Placement in Mechanically Ventilated Patients. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162679
Ragunathan T, Teo R, Mohamad Yusof A, Mohamad Mahdi SN, Izaham A, Liu CY, Budiman M, Sayed Masri SNN, Abdul Rahman R. Performance of Point-of-Care Ultrasonography in Confirming Feeding Tube Placement in Mechanically Ventilated Patients. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(16):2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162679
Chicago/Turabian StyleRagunathan, Thanalachumy, Rufinah Teo, Aliza Mohamad Yusof, Siti Nidzwani Mohamad Mahdi, Azarinah Izaham, Chian Yong Liu, Maryam Budiman, Syarifah Noor Nazihah Sayed Masri, and Raha Abdul Rahman. 2023. "Performance of Point-of-Care Ultrasonography in Confirming Feeding Tube Placement in Mechanically Ventilated Patients" Diagnostics 13, no. 16: 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162679
APA StyleRagunathan, T., Teo, R., Mohamad Yusof, A., Mohamad Mahdi, S. N., Izaham, A., Liu, C. Y., Budiman, M., Sayed Masri, S. N. N., & Abdul Rahman, R. (2023). Performance of Point-of-Care Ultrasonography in Confirming Feeding Tube Placement in Mechanically Ventilated Patients. Diagnostics, 13(16), 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162679







