Esophageal Mucosal Resistance in Reflux Esophagitis: What We Have Learned So Far and What Remains to Be Learned
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Components of the Mucosal Barrier That Provide Resistance to the Esophageal Mucosa in Conditions of GERD
3. Methods for Diagnosing Reflux Esophagitis and Assessing the Resistance of the Esophageal Mucosa
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yadlapati, R.; Gyawali, C.P.; Pandolfino, J.E.; CGIT GERD Consensus Conference Participants. AGA Clinical Practice Update on the Personalized Approach to the Evaluation and Management of GERD: Expert Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 984–994.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delshad, S.D.; Almario, C.V.; Chey, W.D.; Spiegel, B.M.R. Prevalence of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Proton Pump Inhibitor-Refractory Symptoms. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1250–1261.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakil, N.; van Zanten, S.V.; Kahrilas, P.; Dent, J.; Jones, R.; Global Consensus Group. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: A global evidence-based consensus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 1900–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, K.H.; DeMeester, T.R.; Otte, F.; Broderick, R.C.; Breithaupt, W.; Varga, G.; Musial, F. Severity of GERD and disease progression. Dis. Esophagus 2021, 34, doab006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prichard, D.O.; Byrne, A.M.; Murphy, J.O.; Reynolds, J.V.; O’Sullivan, J.; Feighery, R.; Doyle, B.; Eldin, O.S.; Finn, S.P.; Maguire, A.; et al. Deoxycholic acid promotes development of gastroesophageal reflux disease and Barrett’s oesophagus by modulating integrin-αv trafficking. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3612–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilski, J.; Pinkas, M.; Wojcik-Grzybek, D.; Magierowski, M.; Korbut, E.; Mazur-Bialy, A.; Krzysiek-Maczka, G.; Kwiecien, S.; Magierowska, K.; Brzozowski, T. Role of Obesity, Physical Exercise, Adipose Tissue-Skeletal Muscle Crosstalk and Molecular Advances in Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Wang, X.; Gai, Z.; Song, X.; Jia, X.; Tian, H. Bile acids but not acidic acids induce Barrett’s esophagus. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Shang, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Xin, C.; Yan, X.; Zhai, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z. Current Advancement on the Dynamic Mechanism of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 4154–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Shrestha, P.; Qiu, Z.; Harman, D.G.; Teoh, W.-C.; Al-Sohaily, S.; Liem, H.; Turner, I.; Ho, V. Distinct Microbiota Dysbiosis in Patients with Non-Erosive Reflux Disease and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, F.; Biancani, P.; Harnett, K.; Yerian, L.; Falk, G.W. Inflammatory mediators in gastroesophageal reflux disease: Impact on esophageal motility, fibrosis, and carcinogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G571–G581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejat Pish-Kenari, F.; Qujeq, D.; Maghsoudi, H. Some of the effective factors in the pathogenesis of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 6401–6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevins, C.H.; Dierkhising, R.A.; Geno, D.M.; Johnson, M.L.; Vela, M.F.; Ravi, K.; Iyer, P.G.; Katzka, D.A. Obesity and GERD impair esophageal epithelial permeability through 2 distinct mechanisms. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badgery, H.; Chong, L.; Iich, E.; Huang, Q.; Georgy, S.R.; Wang, D.H.; Read, M. Recent insights into the biology of Barrett’s esophagus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1481, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GadEl-Hak, N.A.; El-Hemaly, M.; Hamdy, E.; AbdEl-Raouf, A.; Mostafa, M.; Haleem, M. Bile reflux measurement and its contribution to the severity of reflux esophagitis. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, C.; Neumann, H.; Vieth, M. Esophageal epithelial resistance. Dig. Dis. 2014, 32, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storonova, O.A.; Trukhmanov, A.S.; Ivashkin, V.T. Esophageal mucosa protective factors at the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Clin. Persp. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 5, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Niv, Y.; Ho, S.B.; Fass, R.; Rokkas, T. Mucin Expression in the Esophageal Malignant and Pre-malignant States: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 52, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pilato, V.; Freschi, G.; Ringressi, M.N.; Pallecchi, L.; Rossolini, G.M.; Bechi, P. The esophageal microbiota in health and disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1381, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewhirst, F.E.; Chen, T.; Izard, J.; Paster, B.J.; Tanner, A.C.; Yu, W.H.; Lakshmanan, A.; Wade, W.G. The human oral microbiome. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5002–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, W.G. The oral microbiome in health and disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corning, B.; Copland, A.P.; Frye, J.W. The Esophageal Microbiome in Health and Disease. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2018, 20, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, R.C. Review article: Oesophageal mucosal resistance. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 12, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blevins, C.H.; Iyer, P.G.; Vela, M.F.; Katzka, D.A. The Esophageal Epithelial Barrier in Health and Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, R.C. The integrity of the esophageal mucosa. Balance between offensive and defensive mechanisms. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 24, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, A.D.; Georgiou, M. The multifarious regulation of the apical junctional complex. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 190278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simanenkov, V.I.; Maev, I.V.; Tkacheva, O.N.; Alekseenko, S.A.; Andreev, D.N.; Bordin, D.S.; Vlasov, T.D.; Vorobyeva, N.M.; Grinevich, V.; Gubonina, I.V.; et al. Syndrome of increased epithelial permeability in clinical practice. Multidisciplinary national Consensus. Cardiovasc. Ther. Prev. 2021, 20, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zeng, H.; Lei, L.; Tong, X.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, L.; Huang, J.; et al. Tight junctions and their regulation by non-coding RNAs. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 712–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, S.M.; Fromm, M. Special Issue on “The Tight Junction and Its Proteins: More than Just a Barrier”. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, T.; Miwa, H. Gastrointestinal mucosal barrier function and diseases. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.A.; Nelson, W.J.; Chavez, N. Cell-Cell Junctions Organize Structural and Signaling Networks. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a029181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becskeházi, E.; Korsós, M.M.; Erőss, B.; Hegyi, P.; Venglovecz, V. OEsophageal Ion Transport Mechanisms and Significance Under Pathological Conditions. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, C.P.; Kahrilas, P.J.; Savarino, E.; Zerbib, F.; Mion, F.; Smout, A.J.P.M.; Vaezi, M.; Sifrim, D.; Fox, M.R.; Vela, M.F.; et al. Modern diagnosis of GERD: The Lyon Consensus. Gut 2018, 67, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farre, R.; Blondeau, K.; Clement, D.; Vicario, M.; Cardozo, L.; Vieth, M.; Mertens, V.; Pauwels, A.; Silny, J.; Jimenez, M.; et al. Evaluation of oesophageal mucosa integrity by the intraluminal impedance technique. Gut 2011, 60, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Duan, L.; Wang, K.; Xu, Z.; Ge, Y.; Yang, C.; Han, Y. Esophageal intraluminal baseline impedance is associated with severity of acid reflux and epithelial structural abnormalities in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, E.; de Bortoli, N.; Zentilin, P.; Furnari, M.; Marchi, S.; Mastracci, L.; Fiocca, R.; Savarino, V. Esophageal baseline impedance values correlate with presence and severity of microscopic esophagitis in patients with gastro-esophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, S-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, A.; Basting, N.; Goetz, M.; Tresch, A.; Mudter, J.; Biesterfeld, S.; Galle, P.; Neurath, M.; Kiesslich, R. High-definition endoscopy with i-Scan and Lugol’s solution for more precise detection of mucosal breaks in patients with reflux symptoms. Endoscopy 2009, 41, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Wani, S.; Bansal, A.; Hall, S.; Puli, S.; Mathur, S.; Rastogi, A. A feasibility trial of narrow band imaging endoscopy in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 454–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swager, A.; Curvers, W.L.; Bergman, J.J. Diagnosis by endoscopy and advanced imaging. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 29, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymak, T.; Hruz, P.; Niess, J.H. Immune system and microbiome in the esophagus: Implications for understanding inflammatory diseases. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 4758–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morozov, S.; Sentsova, T. Local inflammatory response to gastroesophageal reflux: Association of gene expression of inflammatory cytokines with esophageal multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH data. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 9254–9263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobey, N.A.; Hosseini, S.S.; Argote, C.M.; Dobrucali, A.M.; Awayda, M.S.; Orlando, R.C. Dilated intercellular spaces and shunt permeability in nonerosive acid-damaged esophageal epithelium. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantos, C.; Koukias, N.; Karamanolis, G.; Thomopoulos, K. Changes in the esophageal mucosa of patients with non erosive reflux disease: How far have we gone? World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 5762–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yerian, L.; Fiocca, R.; Mastracci, L.; Riddell, R.; Vieth, M.; Sharma, P.; Franzen, S.; Fernstrom, P.; Ruth, M. Refinement and reproducibility of histologic criteria for the assessment of microscopic lesions in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: The Esohisto Project. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 2656–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savarino, E.; Zentilin, P.; Mastracci, L.; Dulbecco, P.; Marabotto, E.; Gemignani, L.; Bruzzone, L.; de Bortoli, N.; Frigo, A.C.; Fiocca, R.; et al. Microscopic esophagitis distinguishes patients with non-erosive reflux disease from those with functional heartburn. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Zhang, C. The Oxidative Damage and Inflammation Mechanisms in GERD-Induced Barrett’s Esophagus. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 885537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.W.; Pouw, R.E. Risk-stratification models for Barrett’s esophagus: Will we get to the perfect classifier? Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 1123–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, B.J.; Li, X.; Galipeau, P.C.; Vaughan, T.L. Barrett’s oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma: Time for a new synthesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binato, M.; Fagundes, R.; Gurski, R.; Meurer, L.; Edelweiss, M.I. Immunohistochemical overexpression of the p53 protein and Ki-67 (MIB-1) antigen in patients with GERD and chronic esophagitis. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2010, 18, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binato, M.; Gurski, R.R.; Fagundes, R.B.; Meurer, L.; Edelweiss, M.I. P53 and Ki-67 overexpression in gastroesophageal reflux disease—Barrett’s esophagus and adenocarcinoma sequence. Dis. Esophagus. 2009, 22, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Hanzawa, M.; Sueyoshi, S.; Fujita, H.; Shirouzu, K.; Yamana, H. Immunohistological study of cell cycle-related factors, oncogene expression, and cell proliferation in adenocarcinoma developed in Barrett’s esophagus. Oncol. Rep. 2003, 10, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polkowski, W.; van Lanschot, J.J.; Ten Kate, F.J.; Baak, J.P.; Tytgat, G.N.; Obertop, H.; Voorn, W.; Offerhaus, G. The value of p53 and Ki67 as markers for tumour progression in the Barrett’s dysplasia-carcinoma sequence. Surg. Oncol. 1995, 4, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemons, N.J.; Phillips, W.A.; Lord, R.V. Signaling pathways in the molecular pathogenesis of adenocarcinomas of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kaz, A.M.; Grady, W.M.; Stachler, M.D.; Bass, A.J. Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations in Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 44, 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feber, A.; Xi, L.; Luketich, J.D.; Pennathur, A.; Landreneau, R.J.; Wu, M.; Swanson, S.J.; Godfrey, T.E.; Litle, V.R. MicroRNA expression profiles of esophageal cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2008, 2, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, W.M.; Yu, M. Molecular Evolution of Metaplasia to Adenocarcinoma in the Esophagus. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2059–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duits, L.C.; Lao-Sirieix, P.; Wolf, W.A.; O’Donovan, M.; Galeano-Dalmau, N.; Meijer, S.L.; Offerhaus, G.J.A.; Redman, J.; Crawte, J.; Zeki, S.; et al. A biomarker panel predicts progression of Barrett’s esophagus to esophageal adenocarcinoma. Dis. Esophagus 2019, 32, doy102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, A.; Baba, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Shigaki, H.; Miyake, K.; Karashima, R.; Imamura, Y.; Ida, S.; Ishimoto, T.; Iwagami, S.; et al. p53 immunohistochemical expression and patient prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, K.; Zhao, R.; Lim, H.J.; Casson, A.G. Prognostic value of p53 mutations in oesophageal adenocarcinoma: Final results of a 15-year prospective study. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2010, 37, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, J.; Li, F. Prognostic significance of p53 expression in patients with esophageal cancer: A meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
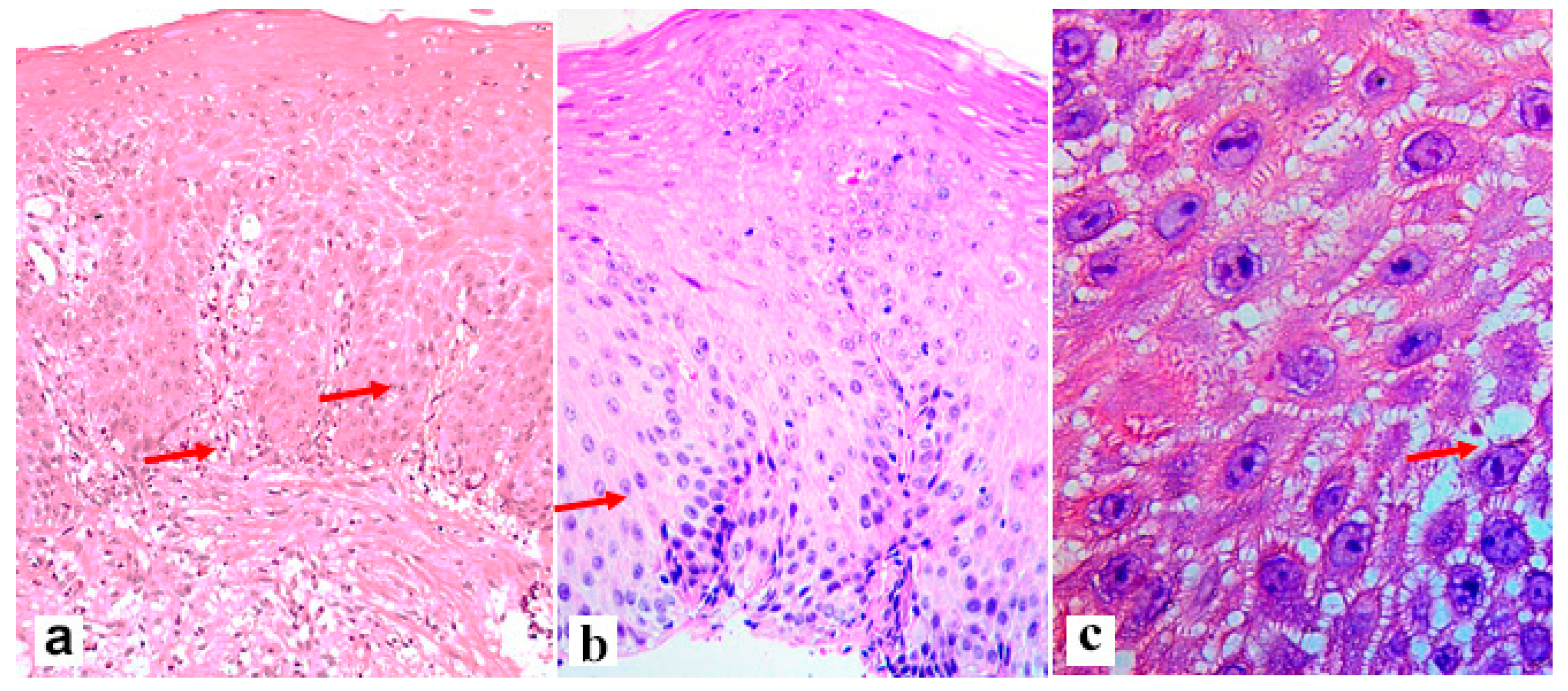
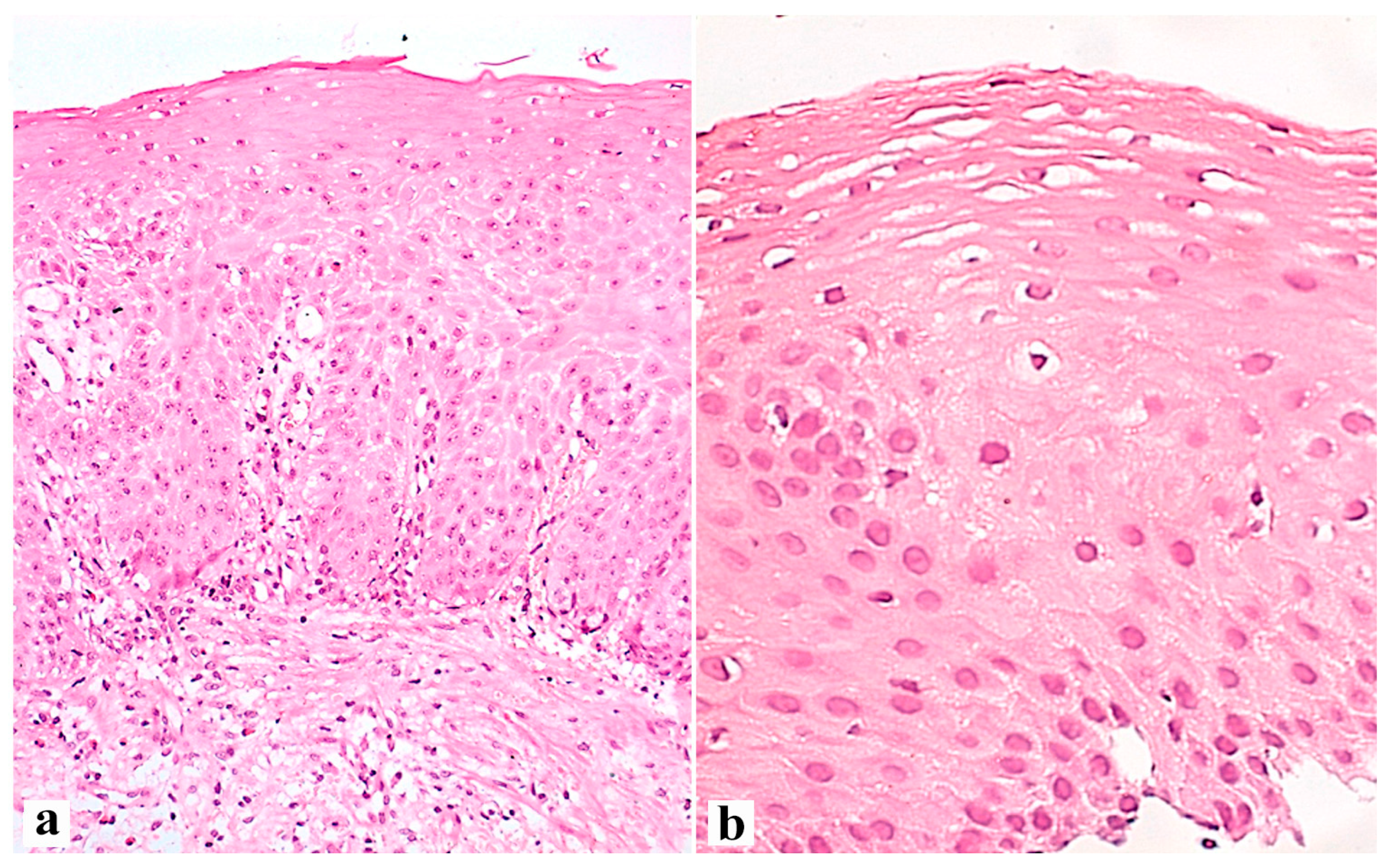
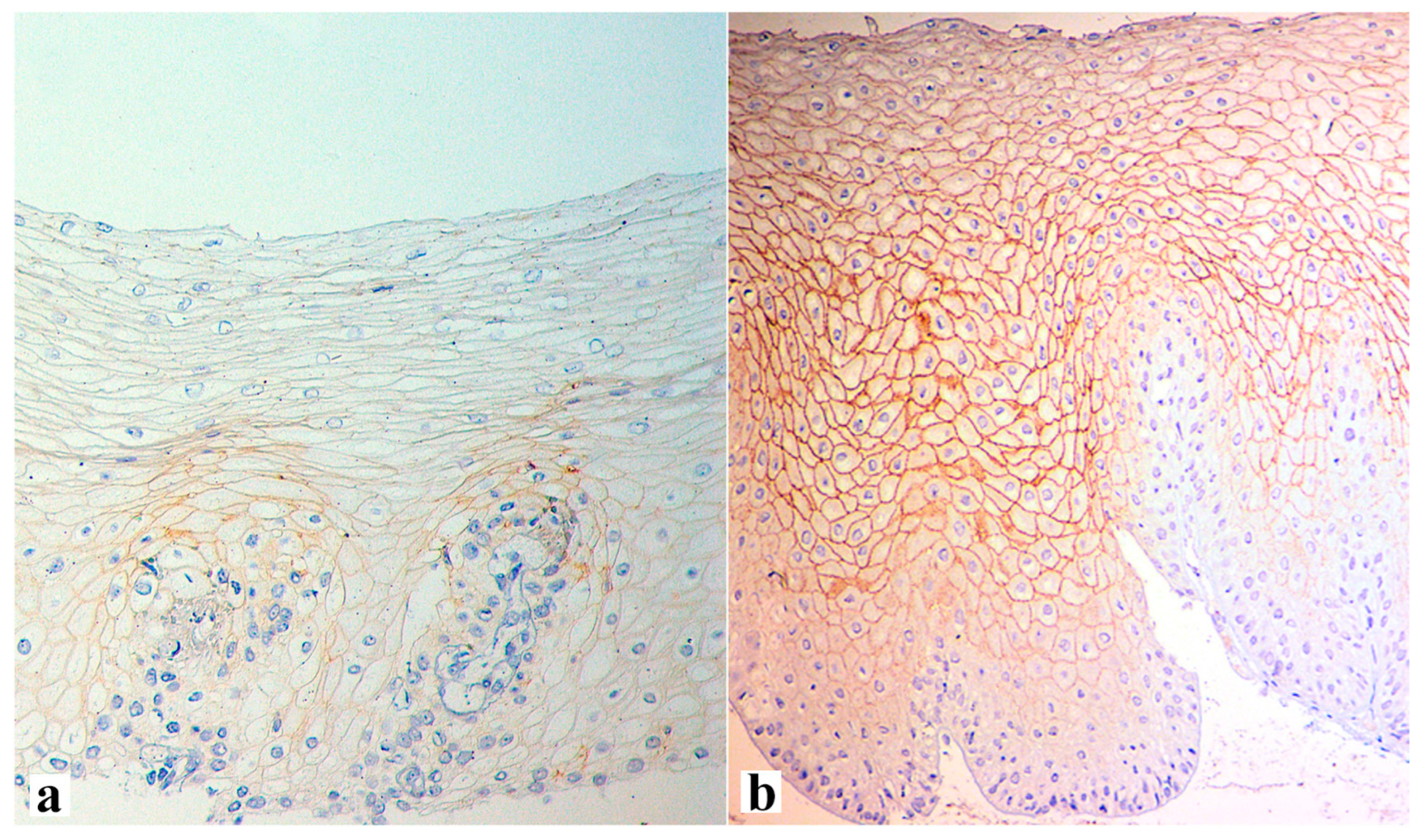

| Criterion | Definition of the Lesions and Their Assessment | Severity Score |
|---|---|---|
| Measure basal cell layer 1 in μm and express as a proportion of total epithelial thickness 2 | 0 (absent < 15%), 1 (15–30%), and 2 (>30%). For Z-line 1 (>20%) |
| Measure papillary length in μm and express as a proportion (%) of total epithelial thickness | 0 (absent < 50%), 1 (50–75%), and 2 (>75%). For Z-line 1 (>66%) |
| Include irregular round dilations or diffuse widening of the intercellular space 3 Small intercellular space = diameter < 1 lymphocyte Large intercellular spaces = diameter ≥ 1 lymphocyte | 0 (≤5 small), 1 (≥6 small and ≤5 large), and 2 (≥6 large) |
| Count cells in the most affected power field 3 | 0 (0 cells in one high-power field), 1 (1–2 cells), 2 (>2 cells) |
| Combined severity score | Sum of lesion severity scores divided by four (the number of lesions assessed) | |
| Diagnostic criteria: 0–0.25 normal mucosa, 0.5–0.75 mild esophagitis, ≥1 severe esophagitis | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maev, I.V.; Livzan, M.A.; Mozgovoi, S.I.; Gaus, O.V.; Bordin, D.S. Esophageal Mucosal Resistance in Reflux Esophagitis: What We Have Learned So Far and What Remains to Be Learned. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162664
Maev IV, Livzan MA, Mozgovoi SI, Gaus OV, Bordin DS. Esophageal Mucosal Resistance in Reflux Esophagitis: What We Have Learned So Far and What Remains to Be Learned. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(16):2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162664
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaev, Igor V., Maria A. Livzan, Sergei I. Mozgovoi, Olga V. Gaus, and Dmitry S. Bordin. 2023. "Esophageal Mucosal Resistance in Reflux Esophagitis: What We Have Learned So Far and What Remains to Be Learned" Diagnostics 13, no. 16: 2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162664
APA StyleMaev, I. V., Livzan, M. A., Mozgovoi, S. I., Gaus, O. V., & Bordin, D. S. (2023). Esophageal Mucosal Resistance in Reflux Esophagitis: What We Have Learned So Far and What Remains to Be Learned. Diagnostics, 13(16), 2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162664








