Evaluation of Hepatic/Renal and Splenic/Renal Echointensity Ratio Using Ultrasonography in Diabetic Nephropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analyses
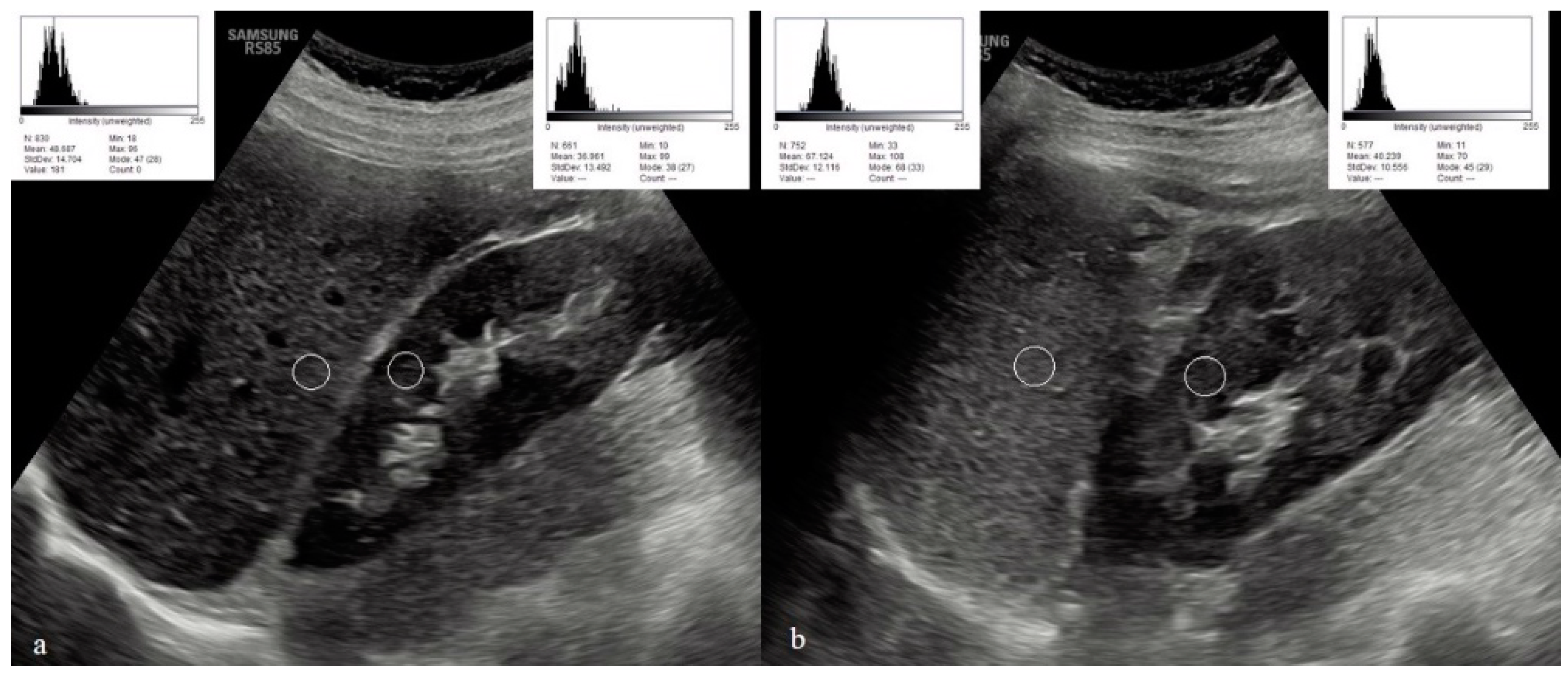
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2014, 37 (Suppl. S1), S81–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W. Epidemiology in diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Endocrinol. 2017, 6, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safiri, S.; Kolahi, A.A.; Naghavi, M. Global, regional and national burden of bladder cancer and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study 2019. BMJ Glob. Health 2021, 6, e004128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report, 2017-Estimates of Diabetes and Its Burden in the United States Background; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lindström, J.; Ilanne-Parikka, P.; Peltonen, M.; Aunola, S.; Eriksson, J.G.; Hemiö, K.; Hämäläinen, H.; Härkönen, P.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Laakso, M.; et al. Sustained reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes by lifestyle intervention: Follow-up of the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study. Lancet 2006, 368, 1673–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, W.M.; Florez, H. How to prevent the microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes beyond glucose control. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2017, 356, i6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, N.R.; Hora, I.; Geiss, L.S.; Gregg, E.W.; Albright, A. Incidence of End-Stage Renal Disease Attributed to Diabetes Among Persons with Diagnosed Diabetes—United States and Puerto Rico, 2000–2014. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2017, 66, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Long, J.; Jiang, W.; Shi, Y.; He, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Yeung, R.O.; Wang, J.; Matsushita, K.; et al. Trends in Chronic Kidney Disease in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 905–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Gui, D.; Zheng, L.; Zhai, R.; Wang, F.; Wang, N. Mechanistic Insight and Management of Diabetic Nephropathy: Recent Progress and Future Perspective. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 1839809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheith, O.; Farouk, N.; Nampoory, N.; Halim, M.A.; Al-Otaibi, T. Diabetic kidney disease: World wide difference of prevalence and risk factors. J. Nephropharmacol. 2016, 5, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, A.N.; Dagogo-Jack, S. Comorbidities of diabetes and hypertension: Mechanisms and approach to target organ protection. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2011, 13, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Rooney, M.T.; Tuttle, K.R. Diabetic Kidney Disease: Challenges, Progress, and Possibilities. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2017, 12, 2032–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umanath, K.; Lewis, J.B. Update on Diabetic Nephropathy: Core Curriculum 2018. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2018, 71, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Li, G.; Cui, X.F.; Zhang, D.L.; Yang, Q.H.; Mu, X.Y.; Pan, W.J. Methodological evaluation and comparison of five urinary albumin measurements. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2011, 25, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, B.M.; Hostetter, T.H.; Humes, H.D. Molecular basis of proteinuria of glomerular origin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1978, 298, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jim, B.; Santos, J.; Spath, F.; Cijiang He, J. Biomarkers of diabetic nephropathy, the present and the future. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2012, 8, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insana, M.F.; Hall, T.J.; Fishback, J.L. Identifying acoustic scattering sources in normal renal parenchyma from the anisotropy in acoustic properties. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1991, 17, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosansky, S.J. Renal function trajectory is more important than chronic kidney disease stage for managing patients with chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2012, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meola, M.; Samoni, S.; Petrucci, I. Imaging in Chronic Kidney Disease. Contrib. Nephrol. 2016, 188, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degrassi, F.; Quaia, E.; Martingano, P.; Cavallaro, M.; Cova, M.A. Imaging of haemodialysis: Renal and extrarenal findings. Insights Imaging 2015, 6, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfield, A.T.; Siegel, N.J. Renal parenchymal disease: Histopathologic-sonographic correlation. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1981, 137, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Becker, C.; Inker, L.A. Glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria for detection and staging of acute and chronic kidney disease in adults: A systematic review. JAMA 2015, 313, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaia, E.; Martingano, P.; Cavallaro, M.; Premm, M.; Angileri, R. Normal radiological anatomy and anatomical variants of the kidney. In Radiological Imaging of the Kidney, 2nd ed.; Quaia, E., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Brenbridge, A.N.; Chevalier, R.L.; Kaiser, D.L. Increased renal cortical echogenicity in pediatric renal disease: Histopathologic correlations. J. Clin. Ultrasound 1986, 14, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, F.; Barozzi, L. The role of ultrasonography in the study of medical nephropathy. J. Ultrasound 2007, 10, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Bughio, S.; Hassan, M.; Lal, S.; Ali, M. Role of Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease and its Correlation with Serum Creatinine Level. Cureus 2019, 11, e4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hricak, H.; Cruz, C.; Romanski, R.; Uniewski, M.H.; Levin, N.W.; Madrazo, B.L.; Sandler, M.A.; Eyler, W.R. Renal parenchymal disease: Sonographic-histologic correlation. Radiology 1982, 144, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, A.C.; Graebe, A.C.; Pelmore, J.M.; Thompson, J.R. Ultrasound assessment of renal cortical brightness in infants: Is naked eye evaluation reliable? Investig. Radiol. 1990, 25, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manley, J.A.; O’Neill, W.C. How echogenic is echogenic? Quantitative acoustics of the renal cortex. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2001, 37, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, M.A.A.; Eljack, A.H.; Gar-alnabi, M.E.; Mahmoud, M.Z.; Elseid, M.; Edam, G.A. Ultrasonographic Characteristics of Diabetes Impacts in Kidneys’ Morphology. Open J. Radiol. 2014, 4, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldo, D.; Brkljacic, B.; Bozikov, V.; Drinkovic, I.; Hauser, M. Diabetic nephropathy. Comparison of conventional and duplex Doppler ultrasonographic findings. Acta Radiol. 1997, 38, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ding, F.; Chen, T.; Xia, L.H.; Qian, J.; Lv, G.Y. Ultrasound hepatic/renal ratio and hepatic attenuation rate for quantifying liver fat content. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 17985–17992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaia, E.; Correas, J.M.; Mehta, M.; Murchison, J.T.; Gennari, A.G.; van Beek, E.J.R. Gray Scale Ultrasound, Color Doppler Ultrasound, and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound in Renal Parenchymal Diseases. Ultrasound Q. 2018, 34, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.F.; Yan, H.M.; He, W.Y.; Li, X.M.; Li, C.L.; Yao, X.Z.; Li, R.K.; Zeng, M.S.; Gao, X. Standardized ultrasound hepatic/renal ratio and hepatic attenuation rate to quantify liver fat content: An improvement method. Obesity 2012, 20, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaka, M.; Sugimoto, K.; Yasunobe, Y.; Akasaka, H.; Fujimoto, T.; Kurinami, H.; Takeya, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Rakugi, H. The Usefulness of an Alternative Diagnostic Method for Sarcopenia Using Thickness and Echo Intensity of Lower Leg Muscles in Older Males. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2019, 20, 1185.e1–1185.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, S.; Kan, S.; An, Y.; Zheng, C.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Xie, G. Body Mass Index and Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy: A Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hukportie, D.N.; Li, F.R.; Zhou, R.; Zheng, J.Z.; Wu, X.X.; Wu, X.B. Anthropometric Measures and Incident Diabetic Nephropathy in Participants With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hukportie, D.N.; Li, F.R.; Zhou, R.; Zou, M.C.; Wu, X.X.; Wu, X.B. Association of Predicted Lean Body Mass and Fat Mass With Incident Diabetic Nephropathy in Participants With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Post Hoc Analysis of ACCORD Trial. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 719666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartziokas, K.; Kyriakopoulos, C.; Dounousi, E.; Kostikas, K. Microalbuminuria on admission for acute exacerbation of COPD as a predictor of all-cause mortality and future exacerbations. Postgrad. Med. J. 2023, 99, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govardi, E.; Yulianda, D.; Habib, F.; Pakpahan, C. Microalbuminuria and mortality in individuals with coronary heart disease: A meta-analysis of a prospective study. Indian Heart J. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härtig, F.; Ross, M.; Dammeier, N.M.; Fedtke, N.; Heiling, B.; Axer, H.; Décard, B.F.; Auffenberg, E.; Koch, M.; Rattay, T.W.; et al. Nerve Ultrasound Predicts Treatment Response in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy—A Prospective Follow-Up. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. NeuroTher. 2018, 15, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, L.; Aktas, G.; Enginyurt, O.; Cakir, S.A. Mean platelet volume increases in type 2 diabetes mellitus independent of HbA1c level. Acta Med. Mediterr. 2014, 30, 425–428. [Google Scholar]
- Kocak, M.Z.; Aktas, G.; Erkus, E.; Duman, T.T.; Atak, B.M.; Savli, H. Mean Platelet Volume to Lymphocyte Ratio as a Novel Marker for Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2018, 28, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilgin, S.; Kurtkulagi, O.; Atak Tel, B.M.; Duman, T.T.; Kahveci, G.; Khalid, A.; Aktas, G. Does C-reactive protein to serum Albumin Ratio correlate with diabEtic nephropathy in patients with Type 2 dIabetes MEllitus? The CARE TIME study. Prim. Care Diabetes 2021, 15, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kin Tekce, B.; Tekce, H.; Aktas, G.; Sit, M. Evaluation of the urinary kidney injury molecule-1 levels in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Clinical and investigative medicine. Med. Clin. Et Exp. 2014, 37, E377–E383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atak, B.M.; Duman, T.T.; Aktas, G.; Kocak, M.Z.; Savli, H. Platelet distribution width is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy and neuropathy. Natl. J. Health Sci. 2018, 3, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, M.Z.; Aktas, G.; Duman, T.T.; Atak, B.M.; Savli, H. Is Uric Acid elevation a random finding or a causative agent of diabetic nephropathy? Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2019, 65, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, M.Z.; Aktas, G.; Duman, T.T.; Atak, B.M.; Kurtkulagi, O.; Tekce, H.; Bilgin, S.; Alaca, B. Monocyte lymphocyte ratio As a predictor of Diabetic Kidney Injury in type 2 Diabetes mellitus; The MADKID Study. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2020, 19, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, M.Z.; Aktas, G.; Atak, B.M.; Duman, T.T.; Yis, O.M.; Erkus, E.; Savli, H. Is Neuregulin-4 a predictive marker of microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus? Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, G.; Yilmaz, S.; Kantarci, D.B.; Duman, T.T.; Bilgin, S.; Balci, S.B.; Atak Tel, B.M. Is serum uric acid-to-HDL cholesterol ratio elevation associated with diabetic kidney injury? Postgrad. Med. 2023, 135, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhir, R.; Mohan, V. Postprandial hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Treat. Endocrinol. 2002, 1, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, I.M.; Adler, A.I.; Neil, H.A.; Matthews, D.R.; Manley, S.E.; Cull, C.A.; Hadden, D.; Turner, R.C.; Holman, R.R. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): Prospective observational study. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2000, 321, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Diabetic Nephropathic Subjects (n = 24) | Diabetic Non-Nephropathic Subjects (n = 35) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Women | 10 (42%) | 20 (57%) | 0.24 |
| Men | 14 (58%) | 15 (43%) | 0.24 | |
| Age (years) | 61.7 ± 10 | 58.5 ± 12 | 0.29 | |
| Diabetic Nephropathic Subjects (n = 24) | Diabetic Non-Nephropathic Subjects (n = 35) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (±Std) | Mean (±Std) | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 32.4 ± 1 | 29.1 ± 0.7 | 0.02 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 4.7 ± 0.4 | 0.58 |
| Right renal width (mm) | 45 ± 5.5 | 44 ± 5.4 | 0.58 |
| Left renal length (mm) | 112 ± 10.7 | 110 ± 9.9 | 0.42 |
| Left renal width (mm) | 51 ± 6.7 | 49 ± 6.2 | 0.17 |
| Left renal cortical thickness (mm) | 14.5 ± 0.4 | 16.2 ± 0.4 | 0.006 |
| Spleen length (mm) | 103 ± 15.6 | 99 ± 13.3 | 0.27 |
| Splenic/renal echointensity ratio % | 0.60 ± 0.2 | 1.02 ± 0.2 | <0.001 |
| Median (min–max) | |||
| Microalbumin in Urine (mcg/mL) | 122.5 (33–2000) | 5 (4–18) | <0.001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 158 (89–432) | 137 (73–313) | 0.046 |
| HbA1C (%) | 8.5 (7.1–12.6) | 7.2 (5.2–12.2) | <0.001 |
| AST (U/L) | 18 (10–46) | 18 (10–41) | 0.91 |
| ALT (U/L) | 21 (11–58) | 19 (10–49) | 0.62 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 35 (12–92) | 35(23–58) | 0.88 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.92 (0.58–9) | 0.80 (0.51–1.31) | 0.01 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 81 (119–187) | 90 (55–111) | 0.13 |
| Liver length (mm) | 135 (24–56) | 141(113–175) | 0.85 |
| Liver echogenicity (grade) | 2 (0–3) | 1 (0–2) | 0.29 |
| Right renal length (mm) | 102 (88–130) | 108.5 (96–133) | 0.04 |
| Right renal cortical thickness (mm) | 15 (11–18) | 14 (8–18) | 0.06 |
| Right renal echogenicity (grade) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–2) | 0.17 |
| Left renal echogenicity (grade) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–1) | 0.06 |
| Liver echointensity | 92 (32–111) | 67 (34–103) | 0.40 |
| Right renal echointensity % | 59.6 (44.6–80.8) | 32.7 (28.7–52) | <0.001 |
| Left renal echointensity % | 58 (41.4–83.5) | 33.9 (29.1–58.7) | <0.001 |
| Spleen echointensity | 35 (31–39) | 35 (31–57) | 0.62 |
| Hepatic/renal echointensity ratio % | 1.43 (0.44–2.2) | 1.9 (1.05–3.3) | 0.025 |
| Sensitivity % | Specificity % | AUC | p | 95% CI (U-L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right renal echointensity > 44.15 | 100 | 97 | 0.99 | <0.001 | 0.98–1 |
| Left renal echointensity > 39.18 | 100 | 91 | 0.98 | <0.001 | 0.95–1 |
| Hepatic/renal echointensity ratio < 1.9 | 87 | 51 | 0.67 | 0.03 | 0.53–0.81 |
| Splenic/renal echointensity ratio < 1.2 | 100 | 97 | 0.98 | <0.001 | 0.94–1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalfaoglu, M.E. Evaluation of Hepatic/Renal and Splenic/Renal Echointensity Ratio Using Ultrasonography in Diabetic Nephropathy. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2401. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13142401
Kalfaoglu ME. Evaluation of Hepatic/Renal and Splenic/Renal Echointensity Ratio Using Ultrasonography in Diabetic Nephropathy. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(14):2401. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13142401
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalfaoglu, Melike Elif. 2023. "Evaluation of Hepatic/Renal and Splenic/Renal Echointensity Ratio Using Ultrasonography in Diabetic Nephropathy" Diagnostics 13, no. 14: 2401. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13142401
APA StyleKalfaoglu, M. E. (2023). Evaluation of Hepatic/Renal and Splenic/Renal Echointensity Ratio Using Ultrasonography in Diabetic Nephropathy. Diagnostics, 13(14), 2401. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13142401






