Budd-Chiari Syndrome Imaging Diagnosis: State of the Art and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Diagnosis of Budd-Chari Syndrome
3. Imaging of Budd-Chiari Syndrome
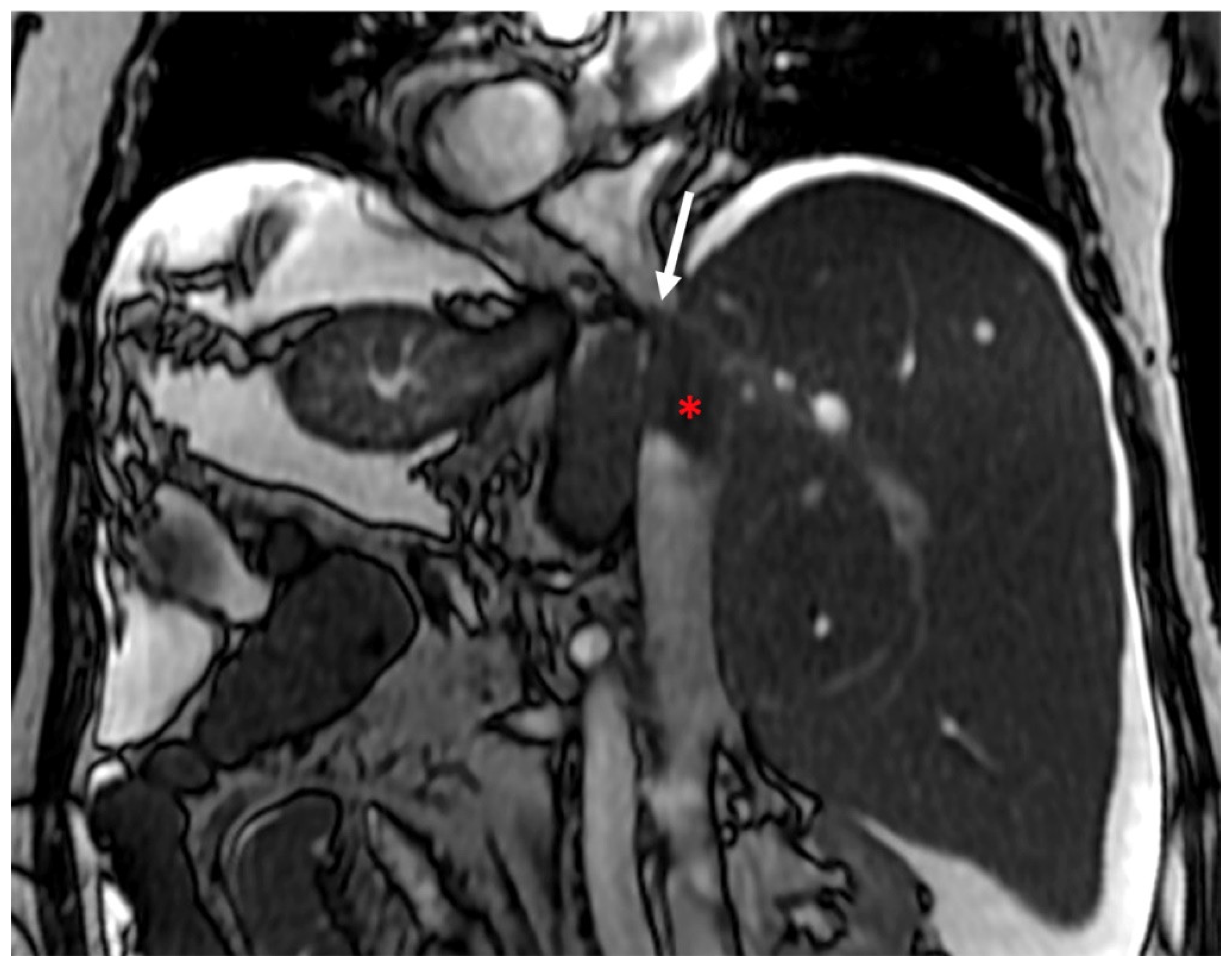
- Direct signs: venous anomalies and the visualization of occluded, stagnant, or inverted venous flow in the HV or in the ICV.
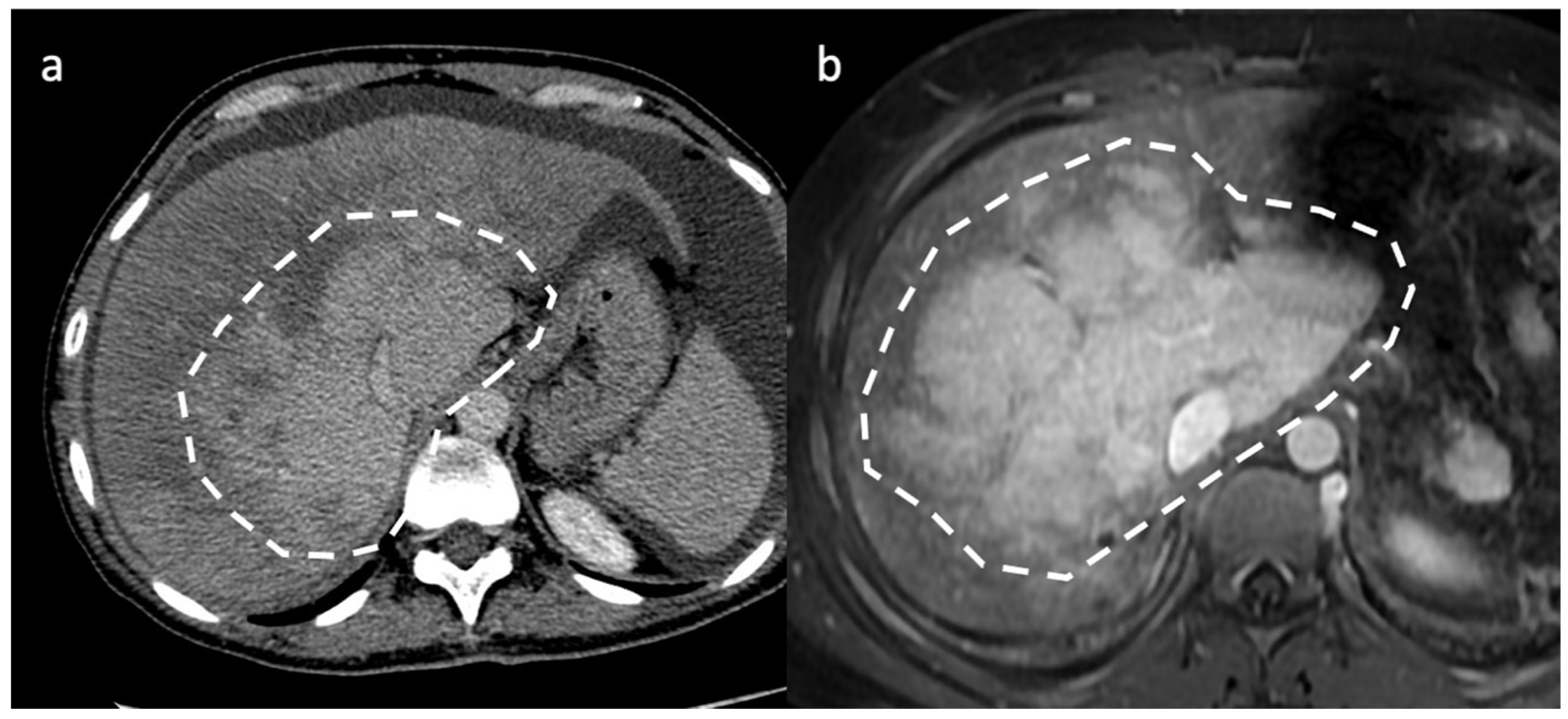
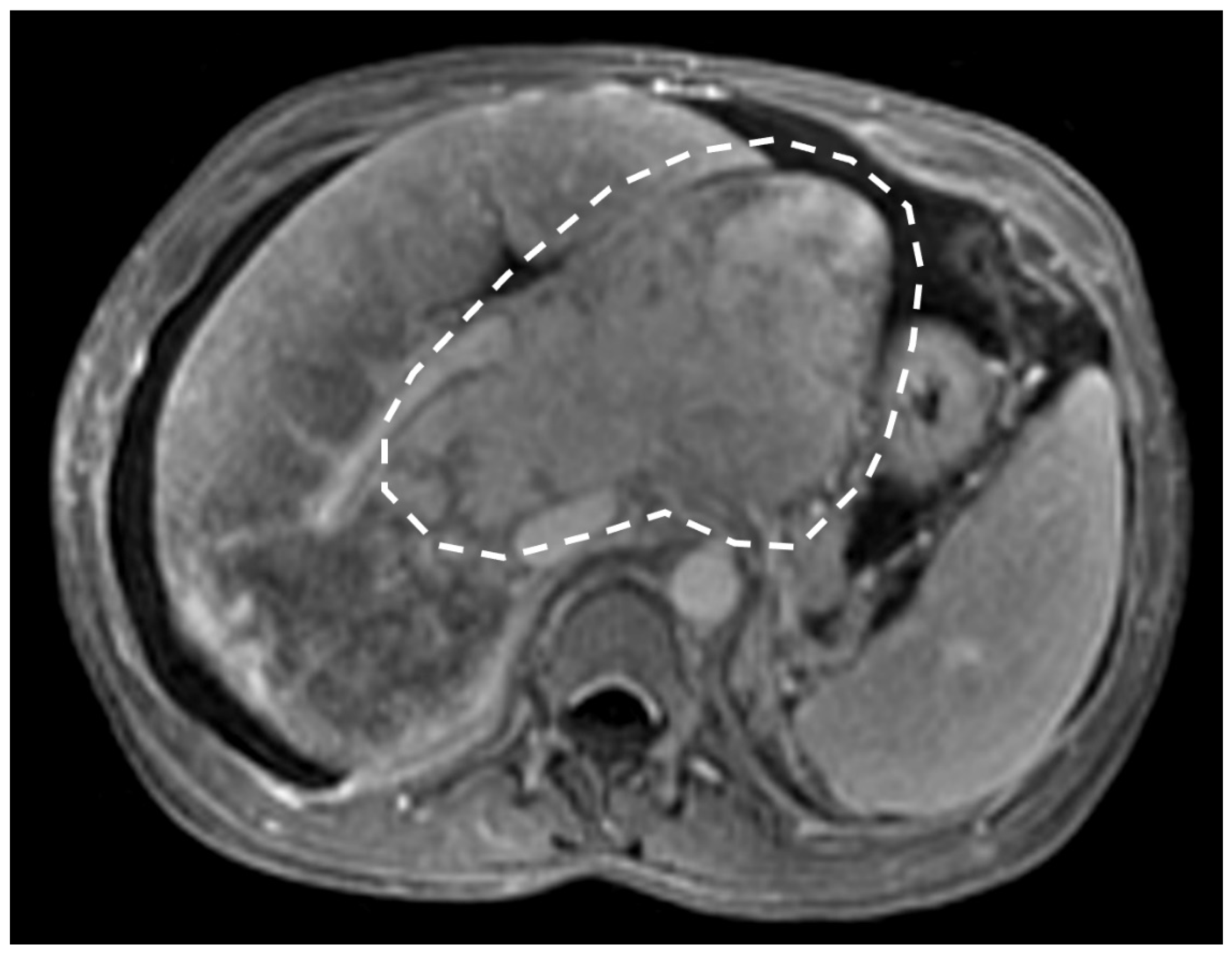
- Indirect signs: non-specific. They represent the consequences of long-standing hepatic venous impairment, including liver parenchymal changes with fibrosis and atrophy of involved segments and hypertrophy of unaffected territories (e.g., caudate lobe hypertrophy). On CT and MRI, centrilobular or sinusoidal congestion, represented as heterogeneous ”mosaic” enhancement after contrast media is also characteristic. Other signs include ascites, portal hypertension, and the presence of benign regenerative nodules, as well as hepatocellular carcinoma [6].
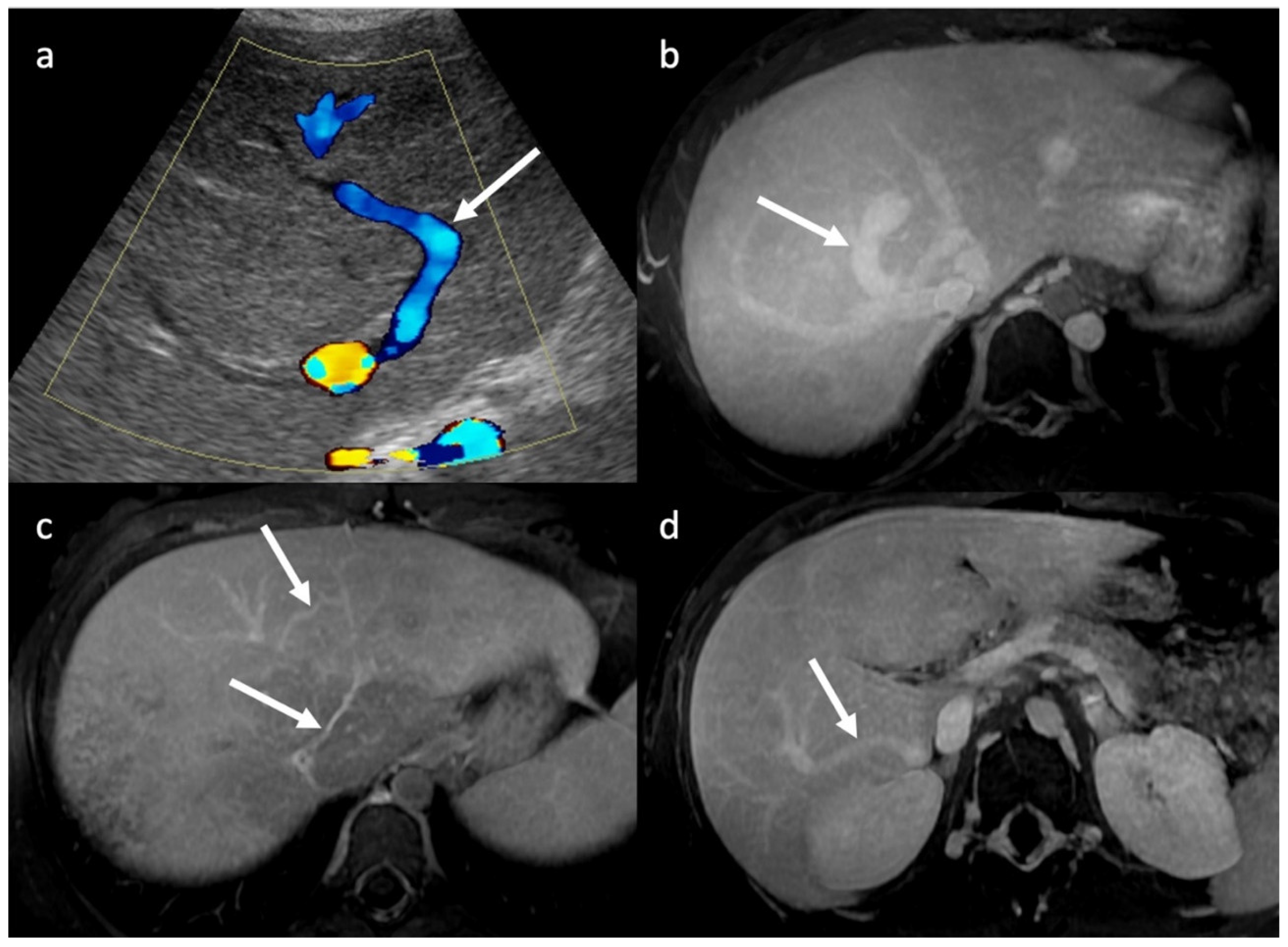
3.1. Ultrasounds: What to Look For
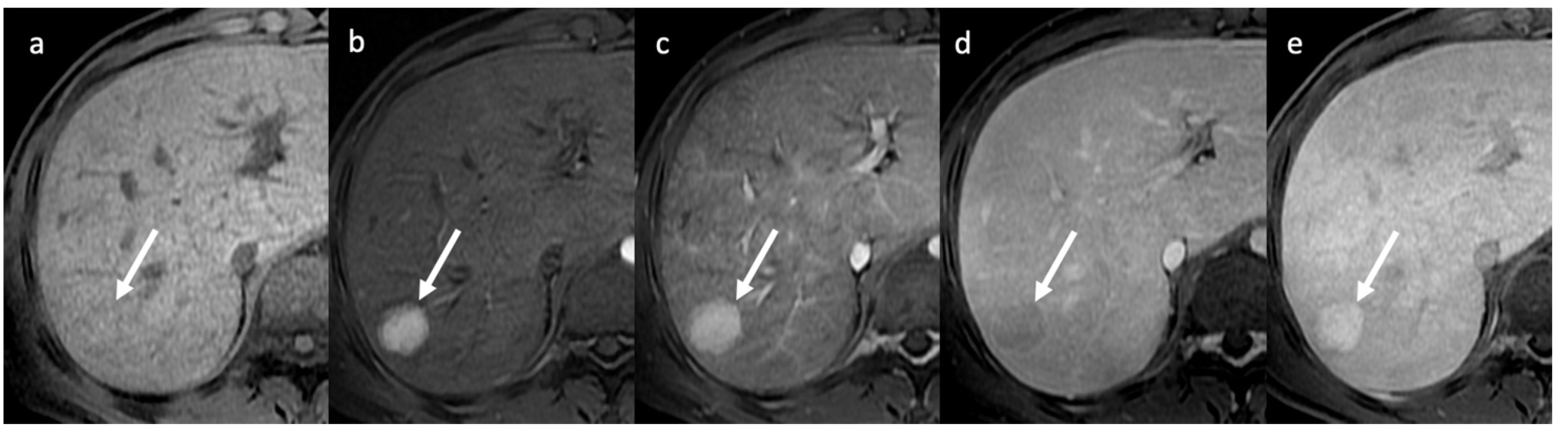
3.2. Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance: What to Look For
4. Hepatic Nodules
New Techniques, Future Perspectives and Open Questions
- Number of occluded hepatic veins (when all occluded, angioplasty, and stenting are not indicated)
- Extension of hepatic vein occlusions (short occlusions are better manageable in interventional procedures).
- Visibility and size of the caudate lobe vein
- Presence and size of intrahepatic venous collaterals
- Patency of IVC, intra- and extrahepatic portal vein
- Presence of accessory right hepatic veins [6]
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valla, D.C. Budd-Chiari syndrome/hepatic venous outflow tract obstruction. Hepatol. Int. 2018, 12 (Suppl. 1), 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; De Stefano, V.; Li, H.; Zheng, K.; Bai, Z.; Guo, X.; Qi, X. Epidemiology of Budd-Chiari syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2019, 43, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, N.; Ageno, W. Epidemiology of Budd-Chiari Syndrome. In Budd-Chiari Syndrome; Qi, X., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, V.; Gupta, P.; Sinha, S.; Dhaka, N.; Kalra, N.; Vijayvergiya, R.; Dutta, U.; Kochhar, R. Budd-Chiari syndrome: Imaging review. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20180441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wettere, M.; Bruno, O.; Rautou, P.E.; Vilgrain, V.; Ronot, M. Diagnosis of Budd-Chiari syndrome. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 1896–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamone, G.; Carollo, V.; Di Piazza, A.; Cortis, K.; Degiorgio, S.; Miraglia, R. Budd-Chiari Syndrome and hepatic regenerative nodules: Magnetic resonance findings with emphasis of hepatobiliary phase. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 117, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudhan, K.S.; Sharma, S. Ultrasonography in pediatric Budd-Chiari syndrome. Pediatr. Radiol. 2020, 50, 1768–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Keshava, S.N.; Eapen, A.; Elias, E.; Eapen, C.E. An Update on the Management of Budd-Chiari Syndrome. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 1780–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qi, X.; Zhang, X.; Su, H.; Zhong, H.; Shi, J.; Xu, K. Budd-Chiari Syndrome in China: A Systematic Analysis of Epidemiological Features Based on the Chinese Literature Survey. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, 738548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langlet, P.; Escolano, S.; Valla, D.; Coste-Zeitoun, D.; Denie, C.; Mallet, A.; Levy, V.G.; Franco, D.; Vinel, J.P.; Belghiti, J.; et al. Clinicopathological forms and prognostic index in Budd-Chiari syndrome. J. Hepatol. 2003, 39, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valla, D.-C. Hepatic venous outflow tract obstruction etiopathogenesis: Asia versus the West. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2004, 19, S204–S211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, H.; Ozer, A.; Yilmaz, T.U.; Keceoglu, S.; Can, M.G.; Emiroglu, R. Liver transplantation for Budd-Chiari syndrome: A challenging but handable procedure. Asian J. Surg. 2022, 45, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.; Kale, A.; Shukla, A. Efficacy and Safety of Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Creation for Budd-Chiari Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 33, 1301–1312.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Zhao, H.; Dai, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Yue, Z.; Fan, Z.; Dong, X.; Liu, F. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for Budd-Chiari syndrome with diffuse occlusion of hepatic veins. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shukla, A.; Shreshtha, A.; Mukund, A.; Bihari, C.; Eapen, C.E.; Han, G.; Deshmukh, H.; Cua, I.H.Y.; Lesmana, C.R.A.; Al Meshtab, M.; et al. Budd-Chiari syndrome: Consensus guidance of the Asian Pacific Association for the study of the liver (APASL). Hepatol. Int. 2021, 15, 531–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuluvath, P.J.; Alukal, J.J.; Zhang, T. Acute liver failure in Budd-Chiari syndrome and a model to predict mortality. Hepatol. Int. 2021, 15, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Vascular diseases of the liver. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 179–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, M.; Choi, H.Y.; Kim, K.A.; Kim, B.H.; Jang, E.S.; Jeong, S.H. Incidence, prevalence and complications of Budd-Chiari syndrome in South Korea: A nationwide, population-based study. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish Murad, S.; Plessier, A.; Hernandez-Guerra, M.; Fabris, F.; Eapen, C.E.; Bahr, M.J.; Trebicka, J.; Morard, I.; Lasser, L.; Heller, J.; et al. EN-Vie (European Network for Vascular Disorders of the Liver). Etiology, management, and outcome of the Budd-Chiari syndrome. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ageno, W.; Dentali, F.; Pomero, F.; Fenoglio, L.; Squizzato, A.; Pagani, G.; Re, R.; Bonzini, M. Incidence rates and case fatality rates of portal vein thrombosis and Budd-Chiari Syndrome. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish Murad, S.; Valla, D.C.; de Groen, P.C.; Zeitoun, G.; Haagsma, E.B.; Kuipers, E.J.; Janssen, H.L. Pathogenesis and treatment of Budd-Chiari syndrome combined with portal vein thrombosis. Am. J Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilgrain, V.; Condat, B.; Bureau, C.; Hakimé, A.; Plessier, A.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Valla, D.C. Atrophy-hypertrophy complex in patients with cavernous transformation of the portal vein: CT evaluation. Radiology 2006, 241, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, F.G.; Magnano San Lio, P.; De Molo, C.; Bakken, S.; Ferronato, M.; Dietrich, C.F.; Serra, C. Budd-Chiari syndrome (BCS): A challenging diagnosis not to be overlooked-single center report and pictorial essay. J. Ultrasound. 2023, 26, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilgrain, V.; Lagadec, M.; Ronot, M. Pitfalls in Liver Imaging. Radiology 2016, 278, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancatelli, G.; Federle, M.P.; Grazioli, L.; Golfieri, R.; Lencioni, R. Benign regenerative nodules in Budd-Chiari syndrome and other vascular disorders of the liver: Radiologic-pathologic and clinical correlation. Radiographics 2002, 22, 847–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, P.; Bansal, V.; Kumar-M, P.; Sinha, S.K.; Samanta, J.; Mandavdhare, H.; Sharma, V.; Dutta, U.; Kochhar, R. Diagnostic accuracy of Doppler ultrasound, CT and MRI in Budd Chiari syndrome: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boozari, B.; Bahr, M.J.; Kubicka, S.; Klempnauer, J.; Manns, M.P.; Gebel, M. Ultrasonography in patients with Budd-Chiari syndrome: Diagnostic signs and prognostic implications. J. Hepatol. 2008, 49, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancatelli, G.; Vilgrain, V.; Federle, M.P.; Hakime, A.; Lagalla, R.; Iannaccone, R.; Valla, D. Budd-Chiari syndrome: Spectrum of imaging findings. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, W168–W176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargalló, X.; Gilabert, R.; Nicolau, C.; García-Pagán, J.C.; Ayuso, J.R.; Brú, C. Sonography of Budd-Chiari syndrome. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 187, W33–W41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, D.; Vasile, N.; Menu, Y.; Van Beers, B.; Lorphelin, J.M.; Pringot, J. Budd-Chiari syndrome: Dynamic CT. Radiology 1987, 165, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilawari, J.B.; Bambery, P.; Chawla, Y.; Kaur, U.; Bhusnurmath, S.R.; Malhotra, H.S.; Sood, G.K.; Mitra, S.K.; Khanna, S.K.; Walia, B.S. Hepatic outflow obstruction (Budd-Chiari syndrome). Experience with 177 patients and a review of the literature. Medicine 1994, 73, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noone, T.C.; Semelka, R.C.; Siegelman, E.S.; Balci, N.C.; Hussain, S.M.; Kim, P.N.; Mitchell, D.G. Budd-Chiari syndrome: Spectrum of appearances of acute, subacute, and chronic disease with magnetic resonance imaging. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2000, 11, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamone, G.; Miraglia, R. The “mosaic pattern” in hepatic sinusoidal dilatation. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 2949–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, O.K.; Koo, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Rhim, H.C.; Koh, B.H.; Seo, H.S. Collateral pathways in Budd-Chiari syndrome: CT and venographic correlation. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1996, 167, 1163–1167, Erratum in AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1997, 168, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, P.; Lyu, L.; Sami, M.U.; Lu, X.; Ge, H.; Rong, Y.; Hu, C.; Xu, K. Diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance angiography for Budd-Chiari syndrome: A meta-analysis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 4873–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Chen, X.H.; Zhou, K.R.; Chen, Z.W.; Wang, J.H.; Yan, Z.P.; Wang, P. Budd-Chiari syndrome: Diagnosis with three-dimensional contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography. World J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 9, 2317–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Lyu, L.; Ge, H.; Sami, M.U.; Liu, P.; Hu, C.; Xu, K. Segmental Liver Stiffness Evaluated with Magnetic Resonance Elastography Is Responsive to Endovascular Intervention in Patients with Budd-Chiari Syndrome. Korean J. Radiol. 2019, 20, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panvini, N.; Dioguardi Burgio, M.; Sartoris, R.; Maino, C.; Van Wettere, M.; Plessier, A.; Payancé, A.; Rautou, P.E.; Ladouceur, M.; Vilgrain, V.; et al. MR imaging features and long-term evolution of benign focal liver lesions in Budd-Chiari syndrome and Fontan-associated liver disease. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2022, 103, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.Y.; Wang, M.Q.; Duan, F.; Fan, Q.S.; Song, P.; Wang, Y. Hepatocellular carcinoma associated with Budd-Chiari syndrome: Imaging features and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.S.; Guo, S.; Chen, Y.X.; Zhang, Z.L. Budd-Chiari syndrome and its associated hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical risk factors and potential immunotherapeutic benefit analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1075685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilgrain, V.; Lewin, M.; Vons, C.; Denys, A.; Valla, D.; Flejou, J.F.; Belghiti, J.; Menu, Y. Hepatic nodules in Budd-Chiari syndrome: Imaging features. Radiology 1999, 210, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moucari, R.; Rautou, P.E.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Geara, A.; Bureau, C.; Consigny, Y.; Francoz, C.; Denninger, M.H.; Vilgrain, V.; Belghiti, J.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma in Budd-Chiari syndrome: Characteristics and risk factors. Gut 2008, 57, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakr, M.; Abdelhakam, S.M.; Dabbous, H.; Hamed, A.; Hefny, Z.; Abdelmoaty, W.; Shaker, M.; El-Gharib, M.; Eldorry, A. Characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients with primary Budd-Chiari syndrome. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flor, N.; Zuin, M.; Brovelli, F.; Maggioni, M.; Tentori, A.; Sardanelli, F.; Cornalba, G.P. Regenerative nodules in patients with chronic Budd-Chiari syndrome: A longitudinal study using multiphase contrast-enhanced multidetector CT. Eur. J. Radiol. 2010, 73, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanless, I.R. Micronodular transformation (nodular regenerative hyperplasia) of the liver: A report of 64 cases among 2,500 autopsies and a new classification of benign hepatocellular nodules. Hepatology 1990, 11, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Ahn, H.S.; Park, H.; Seo, Y.R.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, C.W.; Kim, H.Y. Hepatocellular carcinoma hidden by multiple infarcted regenerative nodules. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2016, 31, 1178–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Baron, R.L.; Nalesnik, M.A. Infarcted regenerative nodules in cirrhosis: CT and MR imaging findings with pathologic correlation. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 175, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, G.; Merrick, L.; Miller, F.H. MR imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma. Magn. Reason. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2010, 18, 421–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Radiology—Liver Reporting & Data System (LI-RADS®) Edition. 2018. Available online: https://www.acr.org/Clinical-Resources/Reporting-and-Data-Systems/LI-RADS/CT-MRI-LI-RADS-v2018 (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- Takayasu, K.; Muramatsu, Y.; Moriyama, N.; Wakao, F.; Makuuchi, M.; Takayama, T.; Kosuge, T.; Okazaki, N.; Yamada, R. Radiological study of idiopathic Budd-Chiari syndrome complicated by hepatocellular carcinoma. A report of four cases. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1994, 89, 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, W.; Qi, X.; Yang, Z.; Han, G.; Fan, D. Prevalence and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma in Budd-Chiari syndrome: A systematic review. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 25, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wettere, M.; Purcell, Y.; Bruno, O.; Payancé, A.; Plessier, A.; Rautou, P.E.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Valla, D.; Vilgrain, V.; Ronot, M. Low specificity of washout to diagnose hepatocellular carcinoma in nodules showing arterial hyperenhancement in patients with Budd-Chiari syndrome. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.C.; Duarte, A.G.; Boin, I.F.; Almeida, J.R.; Escanhoela, C.A. Large benign hepatocellular nodules in cirrhosis due to chronic venous outflow obstruction: Diagnostic confusion with hepatocellular carcinoma. Transplant Proc. 2010, 42, 4116–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, T.; Ohtani, T.; Kioka, H.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Onishi, T.; Nakamoto, K.; Katsimichas, T.; Sengoku, K.; Chimura, M.; Hashimoto, H.; et al. Liver Stiffness Reflecting Right-Sided Filling Pressure Can Predict Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dajti, E.; Ravaioli, F.; Colecchia, A.; Marasco, G.; Vestito, A.; Festi, D. Liver and Spleen Stiffness Measurements for Assessment of Portal Hypertension Severity in Patients with Budd Chiari Syndrome. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 2019, 1673197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

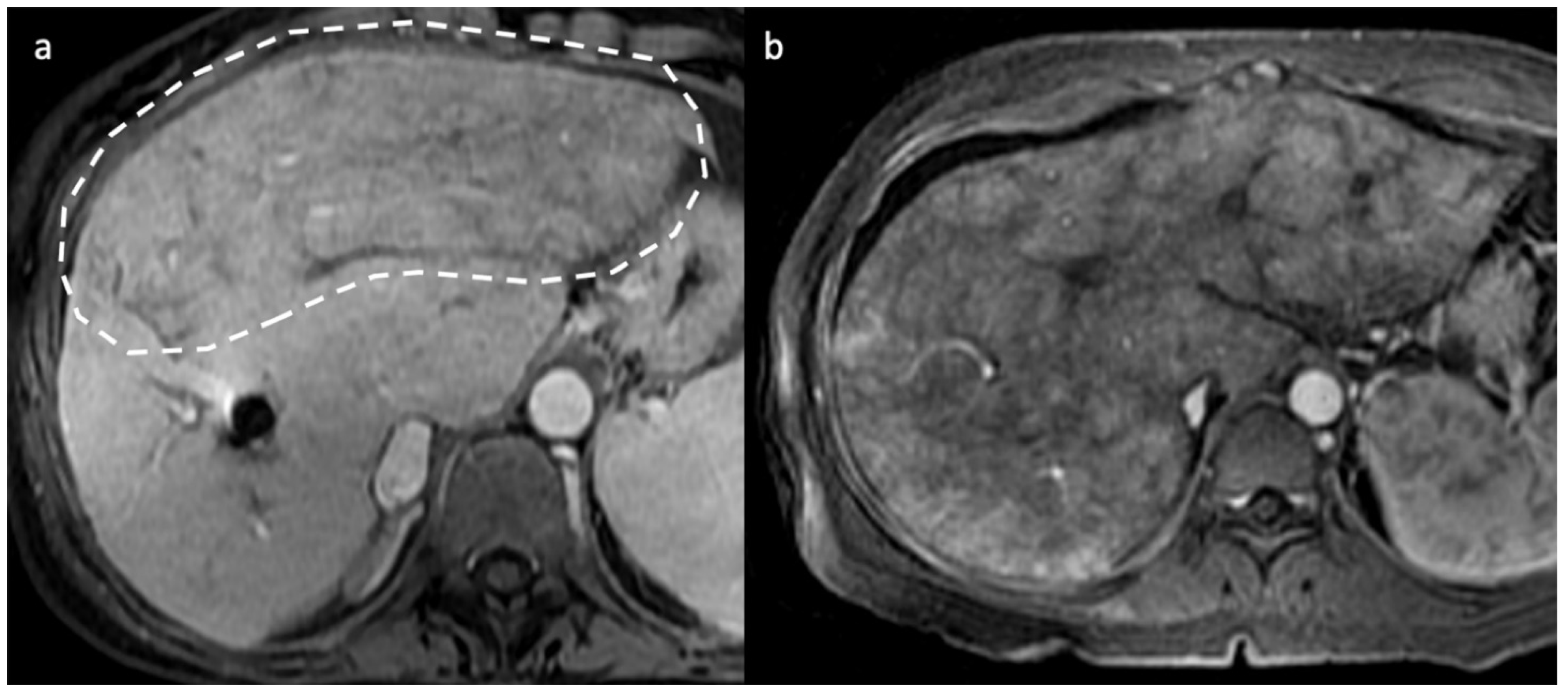
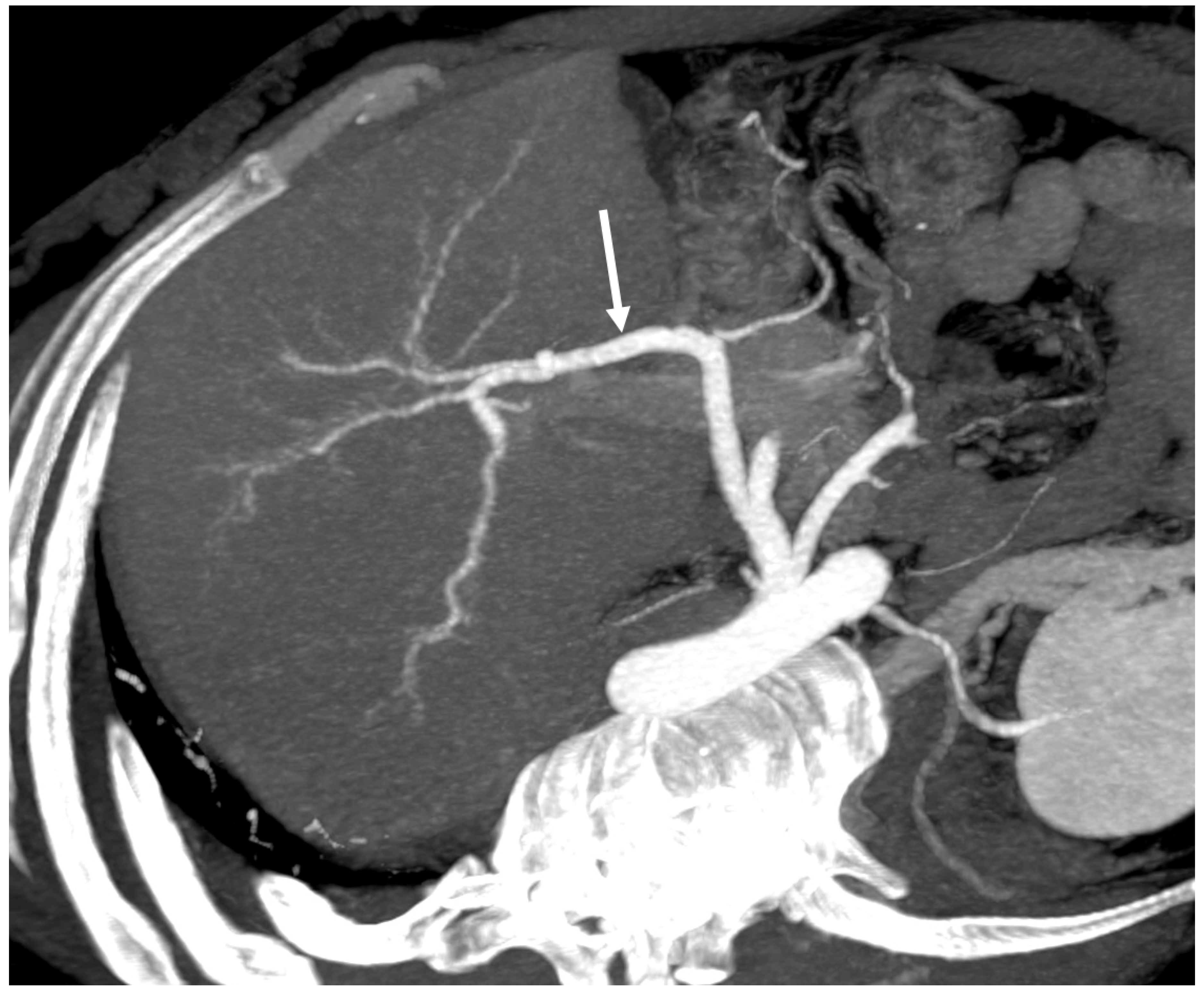
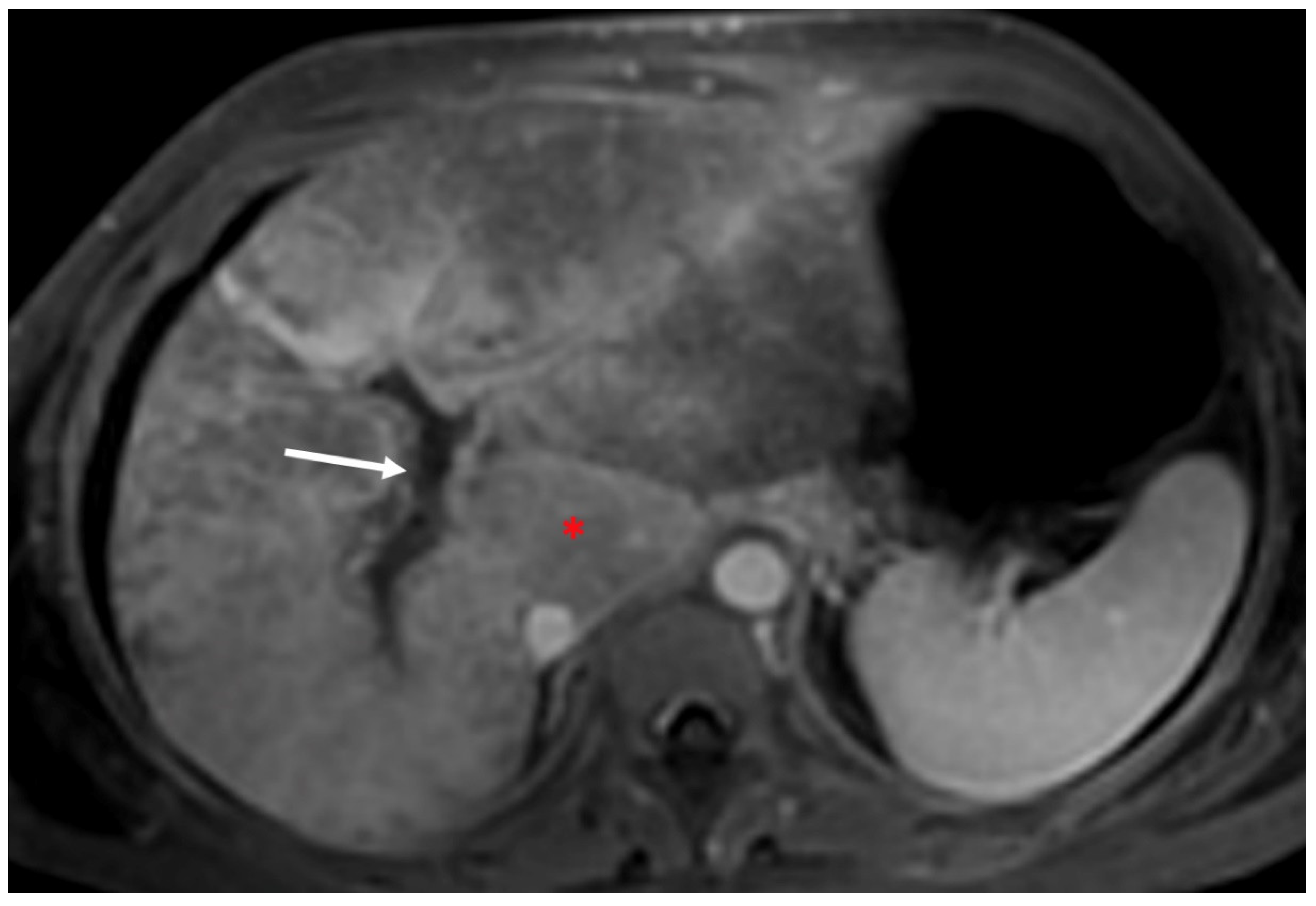
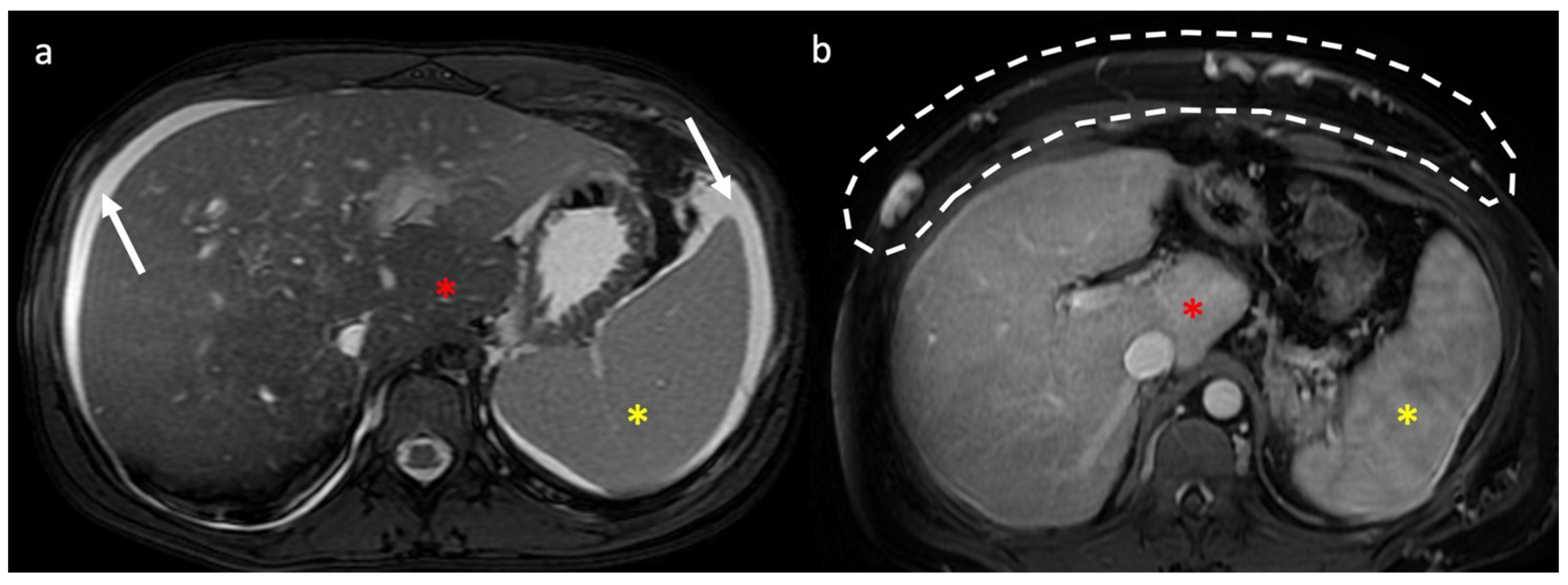
| Budd-Chiari Forms | Clinical Presentation |
|---|---|
| Acute | Acute hepatic impairment Ascites Pain Kidney impairment and failure |
| Subacute/Chronic | Impaired liver function Liver morphology alteration (+hypertrophy of caudate) and fibrosis Portal hypertension Ascites Venous collaterals (if IVC obstruction: parietal collaterals) Variceal bleeding Thrombosis |
| Asymptomatic | Incidentally seen. Multiple chronic venous occlusions Venous collaterals Liver Morphology alteration with fibrosis |
| Fulminant | Acute liver failure |
| Imaging Technique | Findings |
|---|---|
| CDUS | HV thrombosis ICV thrombosis and compression (better studied on CT/MRI) PV thrombosis HV demodulation Intra-hepatic collateral vessels Stagnant, reduced and/or hepatofugal PV flow Focal acceleration of velocity corresponding to stenosis Ascites Caudal lobe enlargement |
| CT | Liver morphology alteration Acute phase: “zonal” or “flip-flop” perfusion Chronic phase: “mosaic” perfusion Extra- and intra-hepatic collaterals Site and extension of thrombosis Pre-endovascular treatment assessment Hepatic artery and caudate vein enlargement Hepatic Nodules Ascites and caudal lobe enlargement |
| MRI | Characterization of nodules (FNH-like nodules vs. HCC) T1-w decreased signal in hypoperfused regions, corresponding to high T2-w SI T2*-w flow void corresponding to thrombus. Hypointensity along the occluded vessels |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Porrello, G.; Mamone, G.; Miraglia, R. Budd-Chiari Syndrome Imaging Diagnosis: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132256
Porrello G, Mamone G, Miraglia R. Budd-Chiari Syndrome Imaging Diagnosis: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(13):2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132256
Chicago/Turabian StylePorrello, Giorgia, Giuseppe Mamone, and Roberto Miraglia. 2023. "Budd-Chiari Syndrome Imaging Diagnosis: State of the Art and Future Perspectives" Diagnostics 13, no. 13: 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132256
APA StylePorrello, G., Mamone, G., & Miraglia, R. (2023). Budd-Chiari Syndrome Imaging Diagnosis: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Diagnostics, 13(13), 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132256







