Abstract
Drugs are widely used to treat different diseases in modern medicine, but they are often associated with adverse events. Those located in the gastrointestinal tract are common and often mild, but they can be serious or life-threatening and determine the continuation of treatment. The stomach is often affected not only by drugs taken orally but also by those administered parenterally. Here, we review the mechanisms of damage, risk factors and specific endoscopic, histopathological and clinical features of those drugs more often involved in gastric damage, namely NSAIDs, aspirin, anticoagulants, glucocorticosteroids, anticancer drugs, oral iron preparations and proton pump inhibitors. NSAID- and aspirin-associated forms of gastric damage are widely studied and have specific features, although they are often hidden by the coexistence of Helicobacter pylori infection. However, the damaging effect of anticoagulants and corticosteroids or oral iron therapy on the gastric mucosa is controversial. At the same time, the increased use of new antineoplastic drugs, such as checkpoint inhibitors, has opened up a new area of gastrointestinal damage that will be seen more frequently in the near future. We conclude that there is a need to expand and understand drug-induced gastrointestinal damage to prevent and recognize drug-associated gastropathy in a timely manner.
1. Introduction
Drug therapy is one of the key elements of the armamentarium employed to treat many different diseases. Clinical trials and real changes in the mucous membrane are associated with the actions of various etiological factors, while drug-induced gastritis is characterized by various structural changes in the gastric mucosa with minimal signs of inflammation, which has led to the more frequent use of the collective term “gastropathy” as a synonym for drug-induced gastritis. In this case, damage to the gastric mucosa can be acute or chronic.
This publication was prepared in order to systematize the available data on modern diagnostic criteria for drug-induced gastropathy (DIG)—lesions of the gastric mucosa associated with a negative manifestation of either a drug or its metabolites.
The diagnosis of DIG should be based on the identification of gastric damage chronologically caused by the use of the drugs followed by recovery or a pronounced decrease in the signs of gastropathy after discontinuation of the medication. In this regard, thorough history taking, including medical history, with a clarification of previous signs is one of the first reasons for a diagnostic search in the case of DIG [1].
Clinical symptoms of DIG are variable. Often, patients with DIG may be asymptomatic or have mild symptoms which can be overshadowed by the presence of symptoms of the underlying disease, which means that it is difficult to assess or detect the presence of DIG in a timely manner. Some patients, however, may have dyspepsia, as well as clinical symptoms showing that other parts of the digestive tract are concerned. Finally, patients with DIG may have more severe symptoms, including severe pain or a complicated course with anemia, or overt bleeding and perforation associated with ulceration.
The clinical signs of DIG upon physical examination are not specific and often reveal only signs of the underlying disease treated with the drug inducing the gastroduodenal damage. In some cases, epigastric tenderness can be present, and in cases of a complicated course, pallor of the skin and the presence of visible mucous membranes, hypotension and compensatory tachycardia are common.
Non-invasive tests have low informative value but may have diagnostic value, either for detecting a complicated course of the disease (signs of posthemorrhagic iron deficiency anemia according to the results of a blood test, a positive fecal occult blood test, transferrin or fecal hemoglobin) or when conducting a differential diagnosis with other types of gastritis (for example, a gastropanel with the determination of parietal cell antibodies in autoimmune gastritis).
The next step in the diagnostic process of DIG is an endoscopic examination with the collection of gastric biopsy specimens. It should be taken into account that the majority of endoscopic and histopathological changes in the gastric mucosa caused by taking drugs are nonspecific and reflect inflammation, erosions or uncomplicated or complicated ulcers. Biopsies of the gastric mucosa, however, may show morphological changes in the so-called reactive gastropathy pattern, most clearly represented as damage induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (see below). However, the coexistence of H. pylori-associated gastritis often hides these features linked to DIG. Nevertheless, there are individual characteristic features of the morphological picture associated with the action of a particular drug agent, which may be specific. These features are reviewed in this article.
2. Non-Steroid Anti-Inflammatory Drugs/Acetylsalicylic Acid (NSAIDs/Aspirin)
The first description of the endoscopic picture of the damage to the gastric mucosa associated with the use of aspirin was published by A. Douthwait and J. Lintoff in 1938 [2].
2.1. Epidemiology
NSAIDs are one of the most commonly prescribed classes of medication with a wide range of indications and availability in over-the-counter forms. According to some studies, the prevalence of NSAID and aspirin use among older people is 24.7% [3]. Gastric erosions occur in approximately half of patients receiving NSAIDs, and peptic ulcer disease occurs in 15–30% of cases. Symptomatic peptic ulcers can be observed in 3–4.5% of patients taking NSAIDs, and serious complications (perforation, obstruction or bleeding) occur in approximately 1.5% of patients after 1 year of treatment [4].
According to two large cohort studies, ESTHER (N = 7737) and British Biobank (N = 213,598), taking low doses of aspirin is an independent risk factor for the development of gastric and duodenal ulcers in the early period after the start of treatment [5]. The stomach and duodenal ulcer risk ratios were found to be 1.82 [1.58–2.11] and 1.66 [1.36–2.04] in the case of British Biobank and 2.83 [1.40–5.71] and 3.89 [1.46–10.42] in the ESTHER study, respectively.
According to data from Spain, the mortality rate associated with the use of NSAIDs or aspirin is 5.6%, which is equivalent to 15.3 cases of death per 100,000 users [6].
2.2. Risk Factors
Risk factors for the development of NSAID/aspirin-associated gastropathy include >60-year-olds (and, in particular, >70-year-olds), high-dose NSAID treatment, a previous history of peptic ulcers with or without complications, co-therapy with low-dose aspirin, anticoagulants, serotonin re-uptake inhibitors or steroids and H. pylori infection [7,8,9].
2.3. Mechanism of Gastric Damage
Gastrointestinal-associated NSAID/aspirin damage is based on the blockade of the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which regulates the synthesis of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid. COX exists in two isoforms: structural COX-1 and induced COX-2. The COX-2 isoform is not detected in normal tissues. Its expression is induced by inflammatory mediators (lipopolysaccharides, interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor alpha, macrophages, monocytes) and causes all the clinical manifestations of inflammatory processes: soreness, fever, swelling and dysfunction. Therefore, it is the blockade of COX-2 that causes the main targeted pharmacological effects of NSAIDs/aspirin, including the anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic. At the same time, COX-1 blockade induces a systemic decrease in the synthesis of prostaglandins (PGs), which have cytoprotective effects.
It has been established that PGE2 inhibits the formation of H+ ions and pepsinogen in the stomach, reducing the volume of gastric secretion and its acid and peptic activity; however, the main effect is the increase in the production of mucus and bicarbonates, stimulation of the processes of cell proliferation and physiological regeneration of the epitheliocytes of the gastric mucosa [10]. Thus, a decrease in PG synthesis is associated with a decrease in the resistance of the gastric mucosa [11], as well as a reduction in the gastric mucosal blood flow due to the ability of NSAIDs/aspirin to inhibit the synthesis of nitric oxide (NO) through the suppression of the activity of the NO synthetase enzyme [12]. At the same time, a decrease in the formation of PG leads to the activation of the lipoxygenase pathway, with an increase in the synthesis of leukotrienes (LTs), primarily LT-B4, and pro-inflammatory cytokines (C5-compliment, tumor necrosis factor-α), which aggravate the inflammation and ischemia of the gastric mucosa [13,14].
The direct (topical) interaction between NSAIDs and phospholipids and the uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria cause cell membrane damage, with a disruption of the phospholipid layer and tight junctions. This action increases transcellular permeability. The inhibition of COX, as a systemic effect, reduces microvascular blood flow, and luminal aggressive factors modify and amplify this reaction, leading to inflammation, erosions and ulcers [9].
Depending on their blockade of one COX isoform or another, NSAIDs are divided into those that are selective (inhibiting only COX-2) and non-selective (inhibiting both COX-1 and COX-2). Selective drugs, called “coxibs”, have a less damaging effect on the gastric and duodenal mucosa and were initially used to prevent NSAID-associated damage to the digestive tract. However, it was later discovered that as gastrointestinal risks decrease when taking selective NSAIDs, the risk of fatal cardiovascular events increases [15,16,17]. Considering DIG, we should also note that the damaging effects of these drugs can be realized throughout the digestive tract and proceed with an awareness of the involvement of other organs and systems (liver, kidneys, etc.).
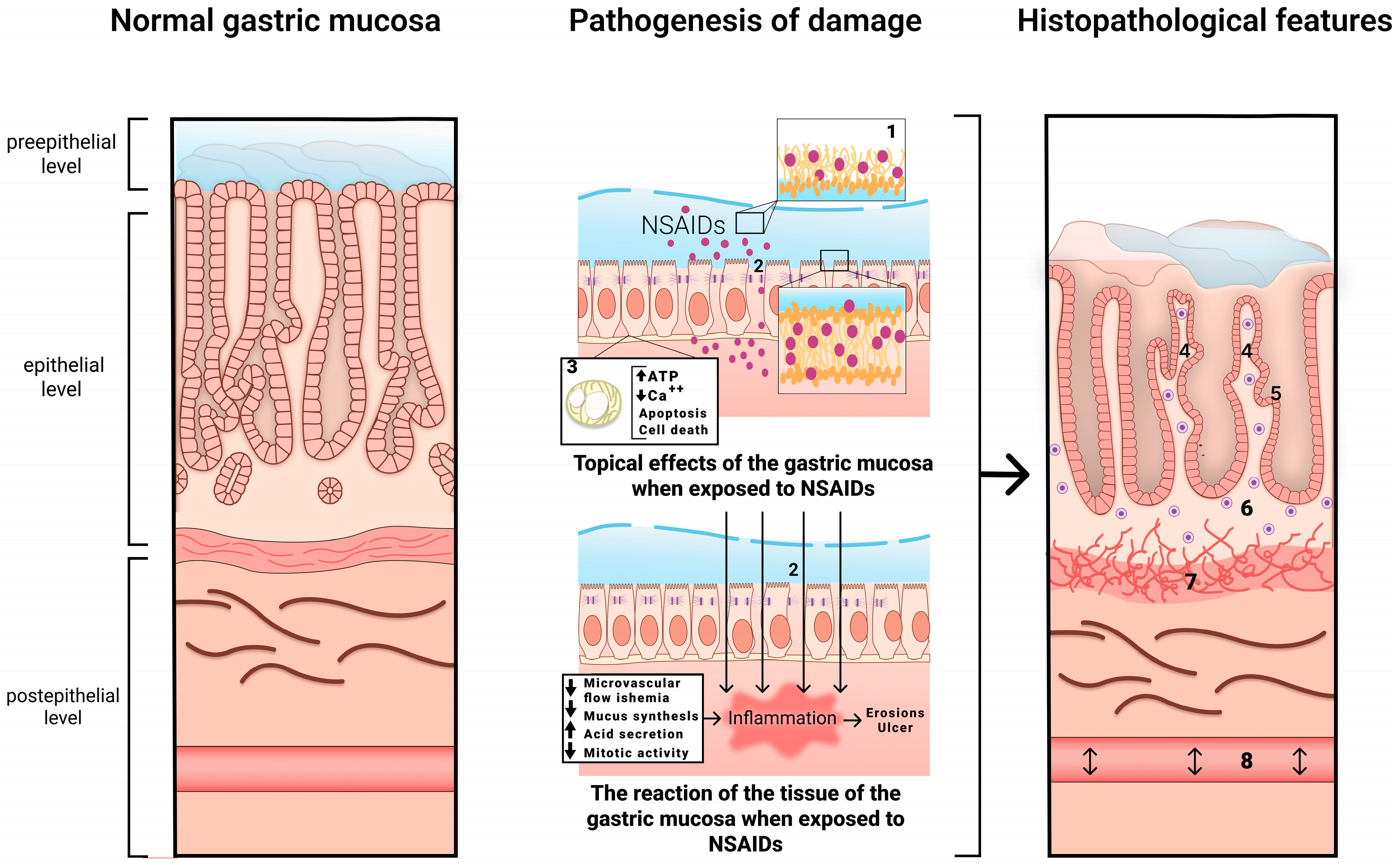
The mechanism of development of NSAID-associated gastropathy is shown in Figure 1.
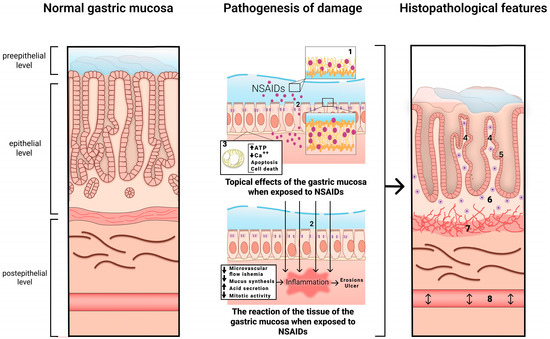
Figure 1.
The mechanism of development of NSAID-associated gastropathy. 1—disrupted phospholipid monolayer, 2—damage to tight junction proteins, 3—uncoupled mitochondria, 4—pronounced regenerative changes in the epithelium (foveolar hyperplasia with hyperchromic cell nuclei, decreased mucus formation), 5—subnuclear vacuolated mucous cells, 6—mild diffuse mononuclear infiltration, 7—bundles of smooth muscle cells in the lamina propria, 8—edema with ectatic blood vessels.
2.4. Clinical Manifestations
As a rule, most patients taking NSAIDs have no gastrointestinal symptoms. However, dyspeptic symptoms may occur in a significant number of patients, including epigastric pain (17–20%) and nausea (22%). In some cases, there might be symptoms such as heartburn, sour belching, constipation (19.3%) or diarrhea (9.2%) showing that other parts of the digestive tract are concerned [18].
A rare but clinically important feature of NSAID/aspirin-associated gastropathy is the development of complications, mainly gastrointestinal bleeding [19,20], with the risk of bleeding being greatest during the first 3 months of taking NSAIDs (OR 11.7; 6.5–21.0) and decreasing with the continued use, becoming minimal 1 week after the deprescribing (OR 3.2; 2.1–5.1) [21,22]. The absolute rate of peptic ulcer bleeding in patients taking these compounds has been reported to be 1% per year, but this rate may be increased substantially in patients with risk factors such as advanced age, a history of peptic ulcers and concomitant use of other drugs, such as anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, corticosteroids and serotonin re-uptake inhibitors [4,21,22]. Bleeding ulcers can be indicated by the presence of hematemesis and/or melena, but some patients may report only general symptoms of blood loss such as a decrease in blood pressure, tachycardia, pallor of the skin, dizziness or anemia. Some patients with NSAID/aspirin-induced gastropathy may be asymptomatic.
It is important to note that damage to the digestive tract while taking NSAIDs/aspirin is not limited to the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum but can also affect the small and large intestines, as has been shown in a number of large, randomized clinical trials [23,24]. Most often, NSAID/aspirin-associated damage to the lower GI tract is accompanied by hidden blood loss and the development of chronic iron deficiency anemia, which aggravates the course of cardiovascular diseases and bronchopulmonary pathology and increases the risk of thromboembolic complications. NSAID/aspirin-associated enteropathy is accompanied, in addition to iron deficiency, by protein loss and hypoalbuminemia. A pathognomonic sign of damage to the small (rarely large) intestine, associated with the long-term use of NSAIDs, is the formation of circular, diaphragm-like strictures as a result of a chronic inflammatory process, which can cause intestinal obstruction [23,25,26].
2.5. Endoscopic Picture
A typical localization of erosive and ulcerative lesions is the antrum of the stomach, but all areas of the gastroduodenal tract can be affected. This condition is characterized by damage of a multifarious nature, which can be both acute and chronic. Signs of bleeding and subepithelial hemorrhages are often noted [3]. During the healing of an ulcer defect, as a rule, rough scars and deformities do not form [27].
2.6. Histological Examination
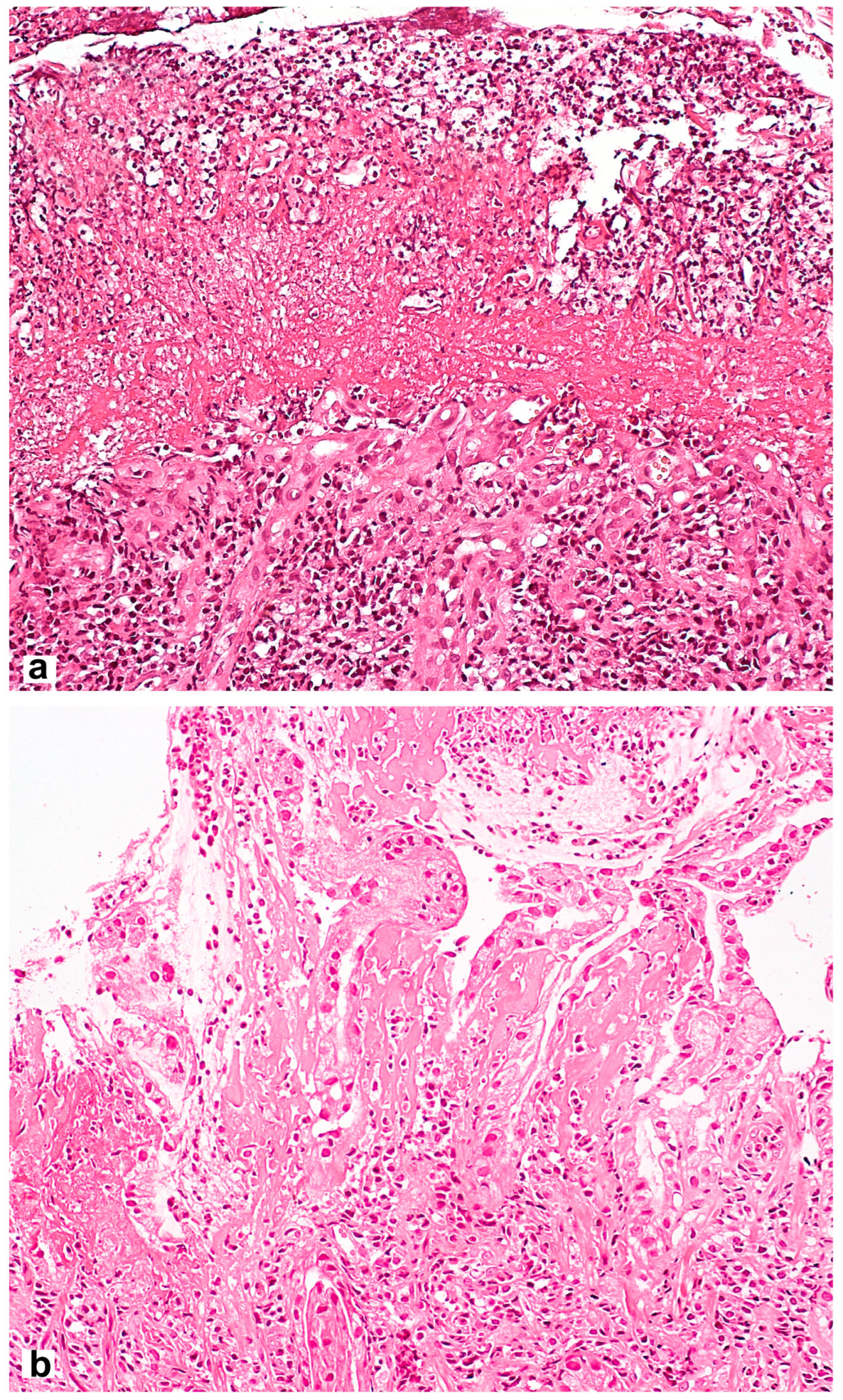
Microscopic signs comprise the picture of the so-called reactive gastropathy, which is not strictly specific to NSAIDs. There is a weak–diffuse, predominantly mononuclear inflammatory infiltration of the lamina propria, often revealing erosive and/or ulcerative defects, pronounced regenerative changes in the epithelium (foveolar hyperplasia with hyperchromic cell nuclei, decreased mucus formation), mucosal edema with vascular ectasia in the lamina propria and lamina propria expansion with fibromuscular proliferation. Subnuclear vacuolated mucous cells may be an additional criterion, which is associated with operated stomach syndrome. Interestingly, the nature of the necrotic masses at the bottom of the defect may be the starting point for the differential diagnosis between NSAID-associated lesions with a homogeneous eosinophilic zone of necrotic masses and a defect caused by Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) [28] with the presence of necrotic masses that are loosely associated with the lamina propria, with immured fragments, necrotic cells and neutrophilic leukocytes (Figure 2). NSAID exposure, in very rare cases, is accompanied by the formation of diaphragms (diaphragm disease) in the stomach. This phenomenon is more typical of damage to the small and large intestines.
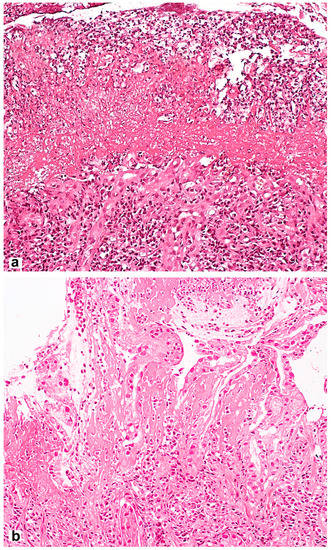
Figure 2.
Differential diagnosis between NSAID-associated lesions and a defect caused by Helicobacter pylori. (a) Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric erosion. Inhomogeneous masses of fibrinoid necrosis with cell debris and granulocytes. (b) NSAID-associated gastric erosion. Homogeneous eosinophilic ischemic necrosis blending into the adjacent lamina propria. Hematoxylin and eosin stain ×200.
3. Anticoagulants
Anticoagulants are among the most commonly prescribed drugs worldwide. Over the past few decades, new second-generation oral anticoagulants (NOACs) that directly inhibit factor Xa (rivaroxaban, apixaban) or thrombin (dabigatran) have been introduced into a wide range of areas of clinical practice. They can be prescribed in fixed doses, without the need for laboratory monitoring, for the treatment and prevention of venous thrombosis and thromboembolism, including stroke, in non-valvular atrial fibrillation, while gastrointestinal bleeding is the “Achilles’ heel” affecting the application of this class of drugs [29].
3.1. Epidemiology
The possible negative risks of gastric mucosal damage in the establishment of anticoagulant therapy have been studied in numerous clinical trials, followed by evaluations in meta-analyses. At the same time, only the risk of upper digestive tract bleeding was studied as a phenomenon of interest without any assessment of its possible links with gastritis or gastropathy. In the latest review published in January 2023, which examined pharmacovigilance data registered with EudraVigilance [30], adverse reactions during treatment with anticoagulants were associated with bleeding in about half of the cases studied (n = 28,992/53,471). Of these bleeding events, >25% were associated with the gastrointestinal tract. The majority of patients with gastrointestinal bleeding were between the ages of 65 and 85 years old, with no clear differences between males and females. Gastric, ulcerative duodenal and rectal bleeding were the most common types of gastrointestinal bleeding, with fatal outcomes in 5.8%, 7.5% and 9.8% of cases with the use of rivaroxaban, apixaban and dabigatran, respectively.
An analysis of 16 RCTs showed that the greatest number of refusals to pursue further therapy occurred while taking dabigatran, while warfarin and factor Xa inhibitors slightly increased the incidence of adverse events involving the digestive tract [31]. A systematic review and meta-analysis published in 2019, including 43 RCTs with 183,752 patients, as well as data from real clinical practice (1,879,428 patients), showed no difference in the risk of major gastrointestinal bleeding between NOAC treatment and traditional treatment (warfarin or antiplatelet agents). However, in an indirect comparison of NOACs, rivaroxaban was associated with a 39% increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding [32]. This meta-analysis found a non-significant association between dabigatran and an increased risk of major gastrointestinal bleeding (p = 0.95). In any case, there are multiple meta-analyses of either clinical trials or observational studies concerning the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding associated with NOACs and vitamin K inhibitors published in the last decade. All highlight an increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding with the use of these agents with some differences between them, but these differences are of uncertain clinical significance.
3.2. Risk Factors
The major risk factors for gastrointestinal bleeding with NOACs are designated as follows [33]:
- -
- A history of gastrointestinal bleeding;
- -
- A history of gastric and/or duodenal ulcers;
- -
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease, reflux esophagitis;
- -
- Chronic H. pylori-associated gastritis;
- -
- Other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract: inflammatory bowel disease, diverticula, hemorrhoids and angiodysplasia;
- -
- Neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract in history;
- -
- Age > 65 years;
- -
- Concomitant use of NSAIDs (including LDA) or other drugs that affect blood coagulation or have a contact damaging effect on the gastrointestinal tract;
- -
- Impaired renal function: glomerular filtration rate (GFR) < 50 mL/min;
- -
- Use of high doses of NOACs (dabigatran 300 mg/day, edoxaban 60 mg/day).
However, some of the presented factors require further assessment and study. Thus, the consensus on H. pylori Maastricht VI, published in August 2022, states that there is no evidence to suggest that anticoagulants (coumarins, new oral anticoagulants and vitamin K antagonists) increase the risk of bleeding in patients with H. pylori infection (consensus level 91%, evidence level 1A) [34]. The potential impact of H. pylori infection on the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding is not well understood in patients taking anticoagulants. Further research is needed to understand the interaction between these two factors.
3.3. Mechanism of Gastric Damage
It is assumed that anticoagulants may increase the risk of bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract through several mechanisms or their combinations: (1) a systemic anticoagulant effect; (2) local anticoagulant effect; (3) local irritant effect; and (4) a local action of the drug not that is not associated with coagulation (for example, the inhibition of mucosal healing) [35,36,37].
The local and systemic anticoagulant effect is associated with the drug’s bioavailability. Thus, NOACs are characterized by low bioavailability (dabigatran 6%, apixaban 50%, rivaroxaban 60–80%); that is, a significant amount of the drug turns into an active anticoagulant during its passage through the gastrointestinal tract under the action of the intestinal esterases and, theoretically, can potentiate bleeding from vulnerable foci of pre-existing lesions (in combination with systemic action). In contrast, warfarin is absorbed at a level of more than 95%; thus, the increase in major gastrointestinal bleeding in patients taking warfarin probably reflects the systemic anticoagulant effect of the drug. The hypothesis that the tartaric acid in dabigatran may contribute to gastrointestinal bleeding due to a direct damaging effect seems unlikely.
3.4. Clinical Manifestations
The clinical manifestations of DIG resulting from the use of anticoagulants are highly controversial. On the one hand, anticoagulants, including aspirin, as well as NSAIDs are often taken simultaneously with anticoagulants. This situation highlights the need to study the risk of gastropathy development against the background of joint administration of anticoagulants with other potentially ulcerogenic drugs [38,39,40]. On the other hand, reviews and meta-analyses emphasize the importance of assessing hemorrhage as the major clinical complication [41,42,43]; thus, the clinical equivalent of gastropathy associated with anticoagulants is not clearly defined.
3.5. Endoscopic Picture
An upper endoscopy reveals changes ranging from erythema and petechiae to hemorrhagic gastropathy, Cameron’s lesions, erosion and stomach ulcers. The risks of peptic ulcers and bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract against the background of the use of NSAIDs and anticoagulants are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Risks of peptic ulcers and bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract against the background of the use of NSAIDs and anticoagulants [44].
4. Cytostatics
Cytostatics comprise a group of antitumor drugs that are relatively heterogeneous in terms of their chemical structure and pharmacokinetic properties; therefore, data on the incidence of DIG and its development mechanisms, clinical course and endoscopic and morphological patterns are different for individual drugs in this group. In the literature, the greatest amount of data concerns DIG associated with the use of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF).
4.1. Epidemiology
Gastropathy and erosive and ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum occur in 40–50% of patients taking MMF, while perforation and bleeding occur in 3–8% of cases, usually during the first 6 months after the start of MMF therapy [45,46].
4.2. Risk Factors
MMF intake is an independent risk factor for erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastric mucosa, with an odds ratio of 1.83 (95% CI 1.02–3.29, p = 0.043), while the risk increases with combination therapy based on MMF with other cytostatics and/or glucocorticosteroids [47].
4.3. Mechanism of Gastric Damage
The mechanism of DIG associated with cytostatics is not clear. It is assumed that the damaging effect is due to the inhibition of cell renewal in the mucous membrane and the induction of cell death by drug metabolites [48]. The direct toxicity of acyl glucuronide, a by-product of MMF metabolism, to the gastric mucosa has been described [49]. It has also been established that cells exposed to MMF demonstrate an association with the dysfunction of the cellular cytoskeleton as a result of a decrease in the content of proteins contained within it: vinculin, actin and tubulin [50].
4.4. Clinical Manifestations
When taking MMF, 45–80% of patients experience decreased appetite, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting [51,52]. In 40–50% of patients, gastrointestinal side effects are the main reason for dose adjustment, changes in the drug regimen or the discontinuation of immunosuppressive therapy [53].
4.5. Endoscopic Picture
Most often, in cases of erythema and edema of the gastric mucosa, multiple erosive lesions are detected. In some cases, the development of giant gastric and duodenal ulcers (more than 5 cm in size) is described [50,51].
4.6. Histological Examination
Characteristic morphological changes in the gastric mucosa against the background of cytostatic consumption include hyaline degeneration of cells in the submucosal and muscle layers and, in the case of large doses, cell vacuolization, necrotic changes and desquamation of the epithelium [54,55].
MMF-associated gastropathy is characterized by impaired mucosal architectonics with inflammatory infiltration and edema of the lamina propria of the gastric mucosa, the enlargement of the glands and increased apoptotic activity of the epithelium, less often resulting in changes resembling those observed in Crohn’s disease [52].
5. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
5.1. Epidemiology
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are a relatively new class of anticancer drugs; hence, data on the incidence of side effects resulting from their use are still limited. The first representative of this class, ipilimumab, was approved for the treatment of melanoma in 2011 [56]. It has been reported that 5% of patients taking immune checkpoint inhibitors experience mucosal damage limited to the stomach and duodenum [57].
5.2. Risk Factors
The risk of developing unwanted side effects affecting the digestive tract is determined primarily by the types of immune response checkpoint inhibitors used, among which are the inhibitors of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) and programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1). Separate observational studies have shown that the incidence of gastric injury is higher for CTLA-4 than PD-1/PD-L1 and increases significantly with combination therapy [58,59,60]. The relative risk is also increased by the concomitant presence of H. pylori infection [61].
It is assumed that the risk of developing severe lesions of the stomach is increased in genetically predisposed individuals. Thus, a severe gastric lesion was described in a patient homozygous for the rs2241880 gene variant of the autophagy-related 16-like protein (ATG16L1), which is associated with Crohn’s disease [62].
5.3. Mechanism of Gastric Damage
The mechanism underlying the negative effects of inhibitors of immune response checkpoints on the gastric mucosa is not fully understood. It is assumed that during the use of this group of drugs, together with an increase in the antitumor activity of lymphocytes, an autoreactive immune response is activated against healthy tissues. A larger number of T- and B-lymphocytes are formed with the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines tropic to the gastric mucosa [63,64,65].
5.4. Clinical Manifestations
The complaints of patients taking immune response checkpoint inhibitors are nonspecific and correspond to dyspepsia syndrome. The main complaints include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and loss of appetite [62].
5.5. Endoscopic Picture
Endoscopic examination reveals erythematous and edematous gastric mucosa without obvious manifestations. The mucous membrane of the stomach is covered with a whitish fibrin-like film. When examining the body of the stomach with the applied magnification in narrow-spectrum imaging, the destruction of the glandular structure is visible. With air infusion, oozing hemorrhages are often noted, which indicates the friability of the mucous membrane [62].
5.6. Histological Examination
DIG associated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy exhibits two distinct patterns of damage [62]. The pattern observed in most cases has an outward resemblance to H. pylori-associated gastritis; however, unlike H. pylori-associated gastritis, it is diffuse in nature, captures not only the antrum but also the body, and is characterized by an increase in the number of interepithelial lymphocytes and a pronounced increase in the number of apoptotic bodies in the epithelium, often accompanied by ulceration. Another pattern is characterized by lymphoid infiltration, lymphocytes being the foci of cellular aggregates, often mixed with neutrophils and eosinophils resembling epithelioid granulomas, which may mimic granulomatous gastritis in infections, sarcoidosis or Crohn’s disease [62,66].
6. Glucocorticosteroids (GCSs)
6.1. Epidemiology
Data on the prevalence of gastropathy during GCS consumption are contradictory. Despite the generally accepted view that the use of corticosteroids increases the risk of developing peptic ulcers, large meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials have not shown a significant association between the use of corticosteroids and gastric ulcers [67]. Hence, according to the results of a meta-analysis published in 1994, combining the results of 93 placebo-controlled studies with the inclusion of 6602 patients, the incidence of peptic ulcers of the stomach while taking GCSs was 0.4%, which was comparable to that of the placebo group (0.3%) [68]. In general, the incidence of adverse events while taking GCSs, including gastropathy, dyspepsia and erosive and ulcerative lesions of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, does not exceed 5%.
6.2. Risk Factors
The main risk factor for peptic ulcer bleeding in patients taking glucocorticosteroids is the concomitant use of NSAIDs/ASA. Recently, another study also reported an increased risk with the concomitant use of glucocorticosteroids and serotonin re-uptake inhibitors. Other risk factors for damage to the gastric mucosa while taking GCSs include older age (65 years and older), long-term use (a month or more) with a total intake of high doses (more than 1000 mg in regard to prednisone) and erosive and ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum intestines, including those complicated by a history of gastrointestinal bleeding and H. pylori infection [67,69].
In the meta-analysis conducted by Narum S. et al., which combined data from 159 studies involving 33,253 patients, it was shown that an increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding and ulcer perforation while taking corticosteroids is typical of only hospitalized patients, compared with outpatients receiving corticosteroids (40% versus 0.13% of cases) [70]. At the same time, additional risk factors are the severity of the course of the underlying disease, the presence of a severe comorbid pathology (diabetes mellitus, cancer) and the concomitant use of other drugs that damage the gastric mucosa [71]. In particular, epidemiological studies have shown that the relative risk of developing gastrointestinal complications is increased by 4–6 times in patients receiving corticosteroids together with NSAIDs [72,73].
6.3. Mechanism of Gastric Damage
GCSs inhibit the production of prostaglandin by regulating the activity of prostaglandin synthesis and the expression of type 2 cyclooxygenase [74]. It has been experimentally shown that under the action of GCSs, the production of mucins and the secretion of bicarbonates by the gastric mucosa decrease, which leads to a decrease in its resistance to aggressive factors [75] and the deterioration of the mechanisms of angiogenesis and epithelial repair [76]. In addition, corticosteroids increase gastric acid secretion and reduce peroxidase activity, with an increase in endogenous H2O2 levels being responsible for mucosal damage [77].
6.4. Clinical Manifestations
There are no specific clinical manifestations of this condition. The most common manifestations of dyspepsia syndrome are epigastric pain, nausea and a feeling of heaviness in the epigastrium. It is possible that the affected parents will be asymptomatic. The most severe manifestations include hemorrhagic gastropathy and erosive and ulcerative lesions of the stomach and/or duodenum, with the development of bleeding and posthemorrhagic iron deficiency anemia.
6.5. Endoscopic Picture
Single and multiple erosions with foci of hemorrhage and gastric or duodenal ulcers can be detected [78]. Ulcers are more often localized in the pyloric and prepyloric regions and are described as soft and pliable, with a weak fibrotic reaction [79]. Most of these lesions have been described in cases involving the concomitant use of other gastrotoxic drugs.
6.6. Histological Examination
The main possible manifestation of the action of GCSs on the gastric mucosa is the formation of erosive and ulcerative defects. This effect is most pronounced in combination therapy with NSAIDs [68,80].
A similar situation involving an increase in the effect of GCSs in combination with NSAIDs is reflected in the publications on gastric bleeding (upper gastrointestinal bleeding). This relationship has been demonstrated with particular clarity in patients with a history of previous bleeding [80]. In animal studies, the effect of GCSs on the hyperplasia of parietal and gastrin-producing G cells was shown, leading to a prolongation of the healing process of gastric ulcers (a delay in the healing of ulcers) [81].
7. Iron Drugs
The accumulation of iron in the gastric mucosa is known as gastric siderosis and was first described in the literature in the 1980s [82].
7.1. Epidemiology
The prevalence of iron-associated DIG is 0.7% in the adult population [83]. However, in 16% of patients taking oral iron preparations, iron granules are found in gastric biopsy specimens [84]. It is also worth noting that damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract during the consumption of iron preparations is not limited to the stomach and can occur in the duodenum [85].
7.2. Risk Factors
Studies have not been conducted on the search for risk factors for the development of gastritis induced by iron preparations. Based on the pathogenetic mechanisms underlying the effect of iron on the gastric mucosa, it can be assumed that concomitant diseases of the gastroduodenal zone may be predictors of more severe damage to the gastric mucosa while taking iron tablets.
7.3. Mechanism of Gastric Damage
Our knowledge of the pathogenesis of iron-associated DIG is limited. There are two hypotheses for the mechanism of damage. Firstly, iron can cause local effects in the gastric mucosa, mimicking a chemical burn. This is due to the fact that ferrous and ferric iron ions are catalysts for the formation of reactive oxygen species and highly toxic radicals, which can damage the components of the epithelial cells of the gastric mucosa [86,87,88]. In addition, the long-term intake of iron preparations may increase the concentration of free iron, which, in itself, is highly toxic in large doses and can lead to damage to various tissues [89].
7.4. Clinical Manifestations
The symptoms are nonspecific and may present as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain or, in complicated cases, upper gastrointestinal bleeding [90].
7.5. Endoscopic Picture
Typical manifestations of iron-induced DIG are erythema, mucosal discoloration (brown, yellow or even cyanotic) and erosions [91].
7.6. Histological Examination
For the differential diagnosis of the side effects of iron tablets and other sideropenic conditions, a classification was proposed by Marginean et al., consisting of three models of iron deposition in the stomach. In the scheme of these authors, the most common pattern of gastric siderosis is the deposition of iron in the stroma and macrophages, mainly due to inflammation of the stomach, ulceration and previous bleeding and rarely due to iron supplementation. The second type is represented by extracellular iron deposition and is most often associated with the consumption of iron supplements. The third type is associated with iron overload and/or portal hypertension/cirrhosis, in which gastric cells are exposed to high concentrations of iron, possibly as a result of porto-caval shunting [86].
When staining biopsy specimens of the gastric mucosa with hematoxylin and eosin, characteristic features are chronic inflammation, the presence of superficial edema and a layer of brown granular pigment that covers the surface of the epithelium, spreads into the gastric pits, and may be present in macrophages localized in the lamina propria. By carrying out a histochemical reaction for iron (using Perls’ Prussian blue), it is possible to identify the substrate based on the appearance of a diffuse bluish color of the macrophage cytoplasm and the mucosal lamina propria [90].
The key features of DIG associated with different groups of drugs are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Characteristic features of DIG associated with various medications.
8. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
Regarding DIG, it is necessary to make a few remarks about possible changes in the structure of the gastric mucosa in people who have undergone long-term PPI treatment. On the one hand, as part of the safety assessment of long-term PPI use, the risk of possible structural changes in the gastric mucosa is being actively studied and critically analyzed. On the other hand, these changes are difficult to interpret as either gastritis or gastropathy.
Undoubtedly, the most important changes have been described in relation to long-term acid suppression under the conditions of H. pylori colonization, namely a change in the topography of gastritis with an increase in the likelihood of atrophy of the gastric mucosa. In this regard, eradication is necessary for all patients with H. pylori infection undergoing long-term PPI therapy. However, these changes are probably related to the pro-carcinogenic potential of H. pylori rather than the independent effects of PPIs.
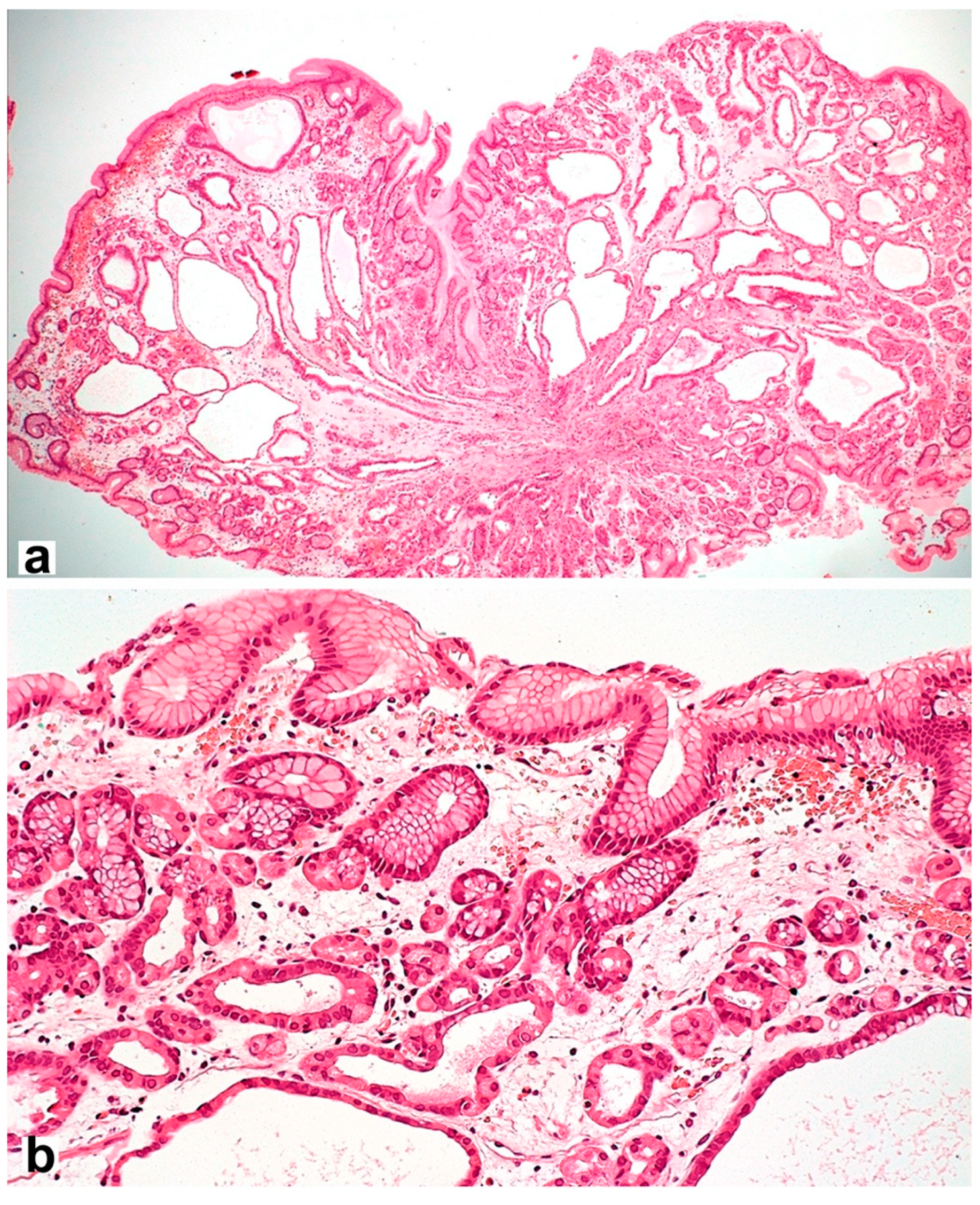
However, the long-term use of PPIs is associated with hyperplasia of enterochromaffin-like cells (ECL cells) and can provoke the formation of gastric fundus polyps [92] with specific morphological features (Figure 3). ECL cells play a key role in regulating gastric acid production through the release of histamine, which stimulates parietal cell acid secretion by binding to histamine-2 receptors. The risk of developing hyperplasia is likely to be influenced by both the duration and daily dose of PPIs, as well as the genetic factors of patients.
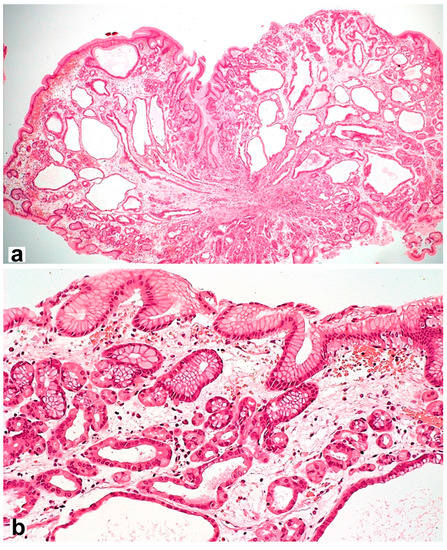
Figure 3.
Fundic gland polyp with cystically dilated glands and hyperplastic parietal cells spreading up to the pits. Hematoxylin and eosin stain. (a) ×40, (b) ×200.
9. Conclusions
The expansion of opportunities for the management of both infectious and, above all, chronic non-communicable diseases is accompanied by an increase in the duration and number of drugs used by patients. The undoubted success of such treatment is accompanied by risks of drug damage to the digestive tract, including the stomach. For some of the drugs (e.g., NSAIDs/aspirin), sufficient experience has already been gained with regard to the possible manifestations, while for other, new groups of drugs (e.g., checkpoint inhibitors), we are only at the beginning of the journey towards the acquisition of scientific evidence. It is important to expand and understand not only the mechanism of damage and the risk factors but also the specific features of drug-induced gastrointestinal damage in order to prevent and recognize DIG in a timely manner.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.L., D.S.B. and A.L.; investigation, O.V.G. and S.I.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.L., O.V.G. and S.I.M.; writing—review and editing, D.S.B., M.A.L., A.L. and O.V.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sugano, K.; Tack, J.; Kuipers, E.J.; Graham, D.Y.; El-Omar, E.M.; Miura, S.; Haruma, K.; Asaka, M.; Uemura, N.; Malfertheiner, P.; et al. Kyoto global consensus report on Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Gut 2015, 64, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douthwaite, A.H.; Lintott, G.A. Gastroscopic observation of the effect of aspirin and certain other substances on the stomach. Lancet 1938, 232, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilotto, A.; Franceschi, M.; Leandro, G.; Di Mario, F.; Geriatric Gastroenterology Study Group (Societe Italiana Gerontologie Geriatria). NSAID and aspirin use by the elderly in general practice: Effect on gastrointestinal symptoms and therapies. Drugs Aging. 2003, 20, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, L. Approaches to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use in the high-risk patient. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.N.M.; Sha, S.; Cnen, L.J.; Holleczek, B.; Brenner, H.; Schottker, B. Strongly increased risk of gastric and duodenal ulcers among new users of low-dose aspirin: Results from two large cohorts with new-user design. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 56, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanas, A.; Perez-Aisa, M.A.; Feu, F.; Ponce, J.; Saperas, E.; Santolaria, S.; Rodrigo, L.; Balanzo, J.; Bajador, E.; Almero, P.; et al. A nationwide study of mortality associated with hospital admission due to severe gastrointestinal events and those associated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, M.K.; Park, C.H.; Kim, J.S.; Park, J.M.; Ahn, J.Y.; Lee, B.E.; Lee, J.H.; Yang, H.J.; Cho, Y.K.; Bang, C.S.; et al. Clinical Guidelines for Drug-Related Peptic Ulcer, 2020 Revised Edition. Gut Liver 2020, 14, 707–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanas, A. A review of the gastrointestinal safety data-a gastroenterologist’s perspective. Rheumatology 2010, 49, ii3–ii10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnason, I.; Scarpignato, C.; Holmgren, E.; Olszewski, M.; Rainsford, K.D.; Lanas, A. Mechanisms of Damage to the Gastrointestinal Tract FromNonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 500–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Huang, H.; Guo, Z.; Chang, Y.; Li, Z. Role of prostaglandin E2 in tissue repair and regeneration. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8836–8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laporte, J.R.; Ibáñez, L.; Vidal, X.; Vendrell, L.; Leone, R. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding associated with the use of NSAIDs: Newer versus older agents. Drug Saf. 2004, 27, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Rodríguez, L.A.; Hernández-Díaz, S. Risk of uncomplicated peptic ulcer among users of aspirin and nonaspirin nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 159, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorucci, S.; Antonelli, E.; Morelli, A. Mechanism of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-gastropathy. Dig. Liver Dis. 2001, 33, S35–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santucci, L.; Fiorucci, S.; Giansanti, M.; Brunori, P.M.; Di Matteo, F.M.; Morelli, A. Pentoxifylline prevents indomethacin induced acute gastric mucosal damage in rats: Role of tumour necrosis factor alpha. Gut 1994, 35, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bresalier, R.S.; Sandler, R.S.; Quan, H.; Bolognese, J.A.; Oxenius, B.; Horgan, K.; Lines, C.; Riddell, R.; Morton, D.; Lanas, A.; et al. Cardiovascular events associated with rofecoxib in a colorectal adenoma chemoprevention trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Wittes, J.; Fowler, R.; Finn, P.; Anderson, W.F.; Zauber, A.; Hawk, E.; Bertagnolli, M.; et al. Cardiovascular risk associated with celecoxib in a clinical trial for colorectal adenoma prevention. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coxib and Traditional NSAID Trialists’ (CNT) Collaboration; Bhala, N.; Emberson, J.; Merhi, A.; Abramson, S.; Arber, N.; Baron, J.A.; Bombardier, C.; Cannon, C.; Farkouh, M.E.; et al. Vascular and upper gastrointestinal effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Meta-analyses of individual participant data from randomised trials. Lancet 2013, 382, 769–779. [Google Scholar]
- Maev, I.V.; Andreev, D.N.; Dicheva, D.T.; Partsvania-Vinogradova, E.V. NSAID-induced gastropathies: Pathogenetically substantiated approaches to prevention and therapy. Farmateka 2016, 2, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Laine, L. Proton pump inhibitor co-therapy with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs--nice or necessary? Rev. Gastroenterol. Disord. 2004, 4, S33–S41. [Google Scholar]
- Fries, J.F.; Murtagh, K.N.; Bennett, M.; Zatarain, E.; Lingala, B.; Bruce, B. The rise and decline of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug-associated gastropathy in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 2433–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanas, Á.; Carrera-Lasfuentes, P.; Arguedas, Y.; García, S.; Bujanda, L.; Calvet, X.; Ponce, J.; Perez-Aísa, Á.; Castro, M.; Muñoz, M.; et al. Risk of upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding in patients taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antiplatelet agents, or anticoagulants. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 906–912.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanza, F.L.; Chan, F.K.; Quigley, E.M.; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Guidelines for prevention of NSAID-related ulcer complications. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Otani, K.; Tanigawa, T.; Watanabe, T.; Shimada, S.; Nadatani, Y.; Nagami, Y.; Tanaka, F.; Kamata, N.; Yamagami, H.; Shiba, M.; et al. Microbiota Plays a Key Role in Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug-Induced Small Intestinal Damage. Digestion 2017, 95, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiden, L.; Thjodleifsson, B.; Theodors, A.; Gonzalez, J.; Bjarnason, I. A quantitative analysis of NSAID-induced small bowel pathology by capsule enteroscopy. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Sanati, S.; Eltorky, M. Diaphragm disease: Complete small bowel obstruction after long-term nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs use. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2005, 9, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattagliano, I.; Ubaldi, E.; Portincasa, P. Drug-induced enterocolitis: Prevention and management in primary care. J. Dig. Dis. 2018, 19, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillen, D.; McColl, K.E. Problems associated with the clinical use of proton pump inhibitors. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 89, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolte, M.; Panayiotou, S.; Schmitz, J. Can NSAID/ASA-induced erosions of the gastric mucosa be identified at histology? Pathol. Res. Pract. 1999, 195, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalkanin, L.; Stancak, B. The Impact of Novel Anticoagulants on the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Mucosa. Medicina 2020, 56, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudallel, S.; Eynde, C.v.D.; Malý, J.; Rydant, S.; Steurbaut, S. Retrospective analysis of gastrointestinal bleedings with direct oral anticoagulants reported to EudraVigilance. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2023, 396, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieraj, D.M.; White, C.M.; Alikhanov, S.; Winkler, S.; Mediouni, M.; Kluger, J.; Coleman, C.I. The impact of antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapies on gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with atrial fibrillation: A systematic review. Ann. Pharmacother. 2012, 46, 1220–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.C.; Wei, A.H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.H.; Zhang, L.; Shen, L.; Li, Z.; Pan, M.M.; Liu, X.Y.; Pu, J.; et al. Risk of Major Gastrointestinal Bleeding With New vs Conventional Oral Anticoagulants: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 792–799.e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.S.; Leung, W.K. Gastrointestinal bleeding in patients on novel oral anticoagulants: Risk, prevention and management. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 1954–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; Rokkas, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; Liou, J.M.; Schulz, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Hunt, R.H.; Leja, M.; O’Morain, C.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection: The Maastricht VI/Florence consensus report. Gut 2022, 71, 1724–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, J.; Kolb, J.M.; Weitz, J.I.; Aisenberg, J. Gastrointestinal bleeding with the new oral anticoagulants-defining the issues and the management strategies. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 110, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanassche, T.; Hirsh, J.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Ginsberg, J.S. Organ-specific bleeding patterns of anticoagulant therapy: Lessons from clinical trials. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 112, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, A.; Sardar, P.; Sen, P.; Chatterjee, S.; Huston, J.; Nairooz, R.; Ryan, J.J.; Aronow, W.S. Patient Taking A Novel Oral Anticoagulant Presents with Major GI Bleeding. J. Atr. Fibrillation. 2015, 8, 1218. [Google Scholar]
- Roffi, M.; Patrono, C.; Collet, J.P.; Mueller, C.; Valgimigli, M.; Andreotti, F.; Bax, J.J.; Borger, M.A.; Brotons, C.; Chew, D.P.; et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: Task Force for the Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes in Patients Presenting without Persistent ST-Segment Elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 267–315. [Google Scholar]
- Lauffenburger, J.C.; Rhoney, D.H.; Farley, J.F.; Gehi, A.K.; Fang, G. Predictors of gastrointestinal bleeding among patients with atrial fibrillation after initiating dabigatran therapy. Pharmacotherapy 2015, 35, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlowski, A.; Gale, C.P.; Ashton, R.; Petrungaro, B.; Slater, R.; Nadarajah, R.; Cowan, J.C.; Buck, J.; Smith, W.; Wu, J. Clinical and budget impacts of changes in oral anticoagulation prescribing for atrial fibrillation. Heart Br. Card. Soc. 2021, 107, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarajlic, P.; Simonsson, M.; Jernberg, T.; Bäck, M.; Hofmann, R. Incidence, associated outcomes, and predictors of upper gastrointestinal bleeding following acute myocardial infarction: A SWEDEHEART-based nationwide cohort study. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2022, 8, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holster, I.L.; Valkhoff, V.E.; Kuipers, E.J.; Tjwa, E.T.T.L. New oral anticoagulants increase risk for gastrointestinal bleeding: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 105–112.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.-Q.; Chen, X.-H.; Tian, X.-Y.; Li, L. Differences In Gastrointestinal Safety Profiles Among Novel Oral Anticoagulants: Evidence From A Network Meta-Analysis. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugisaki, N.; Iwakiri, R.; Tsuruoka, N.; Sakata, Y.; Shimoda, R.; Fujimoto, S.; Eguchi, Y.; Fujimoto, K. A case-control study of the risk of upper gastrointestinal mucosal injuries in patients prescribed concurrent NSAIDs and antithrombotic drugs based on data from the Japanese national claims database of 13 million accumulated patients. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponticelli, C.; Passerini, P. Gastrointestinal complications in renal transplant recipients. Transpl. Int. 2005, 18, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjarnason, I. Enteric coating of mycophenolate sodium: A rational approach to limit topical gastrointestinal lesions and extend the therapeutic index of mycophenolate. Transplant. Proc. 2001, 33, 3238–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telkes, G.; Peter, A.; Tulassay, Z.; Asderakis, A. High frequency of ulcers, not associated with Helicobacter pylori, in the stomach in the first year after kidney transplantation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennelli, G.; Grillo, F.; Galuppini, F.; Ingravallo, G.; Pilozzi, E.; Rugge, M.; Fiocca, R.; Fassan, M.; Mastracci, L. Gastritis: Update on etiological features and histological practical approach. Pathologica 2020, 112, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staatz, C.E.; Tett, S.E. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of mycophenolate in solid organ transplant recipients. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2007, 46, 13–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbass, A.; Khalid, S.; Boppana, V.; Hanson, J.; Lin, H.; McCarthy, D. Giant Gastric Ulcers: An Unusual Culprit. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 2811–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, V.C.; Mai, D.; Park, M.; Lee, D.; Samarasena, J. Mycophenolate mofetil-induced non-healing gastric and duodenal ulcers. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, S1089–S1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfitt, J.R.; Jayakumar, S.; Driman, D.K. Mycophenolate mofetil-related gastrointestinal mucosal injury: Variable injury patterns, including graft-versus-host disease-like changes. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2008, 32, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnapradist, S.; Ambühl, P.M. Impact of gastrointestinal-related side effects on mycophenolate mofetil dosing and potential therapeutic strategies. Clin. Transplant. 2008, 22, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfitt, J.R.; Driman, D.K. Pathological effects of drugs on the gastrointestinal tract: A review. Hum. Pathol. 2007, 38, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chehade, M.; Benkov, K. Gastrointestinal issues in children with rheumatologic disease. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2002, 4, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schadendorf, D.; Hodi, F.S.; Robert, C.; Weber, J.S.; Margolin, K.; Hamid, O.; Patt, D.; Chen, T.T.; Berman, D.M.; Wolchok, J.D. Pooled Analysis of Long-Term Survival Data From Phase II and Phase III Trials of Ipilimumab in Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, K.E.; Blansfield, J.A.; Tran, K.Q.; Feldman, A.L.; Hughes, M.S.; Royal, R.E.; Kammula, U.S.; Topalian, S.L.; Sherry, R.M.; Kleiner, D.; et al. Enterocolitis in patients with cancer after antibody blockade of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2283–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, J.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Grob, J.J.; Cowey, C.L.; Lao, C.D.; Schadendorf, D.; Dummer, R.; Smylie, M.; Rutkowski, P.; et al. Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab or Monotherapy in Untreated Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Kluger, H.; Callahan, M.K.; Postow, M.A.; Rizvi, N.A.; Lesokhin, A.M.; Segal, N.H.; Ariyan, C.E.; Gordon, R.A.; Reed, K.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postow, M.A.; Chesney, J.; Pavlick, A.C.; Robert, C.; Grossmann, K.; McDermott, D.; Linette, G.P.; Meyer, N.; Giguere, J.K.; Agarwala, S.S.; et al. Nivolumab and ipilimumab versus ipilimumab in untreated melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2006–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Yasuda, M.; Ocho, K.; Iwamuro, M.; Yamasaki, O.; Tanaka, T.; Otsuka, F. Severe Gastritis after Administration of Nivolumab and Ipilimumab. Case Rep. Oncol. 2018, 11, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johncilla, M.; Grover, S.; Zhang, X.; Jain, D.; Srivastava, A. Morphological spectrum of immune check-point inhibitor therapy-associated gastritis. Histopathology 2020, 76, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.; Sofiya, L.; Sykiotis, G.P.; Lamine, F.; Maillard, M.; Fraga, M.; Shabafrouz, K.; Ribi, C.; Cairoli, A.; Guex-Crosier, Y.; et al. Adverse effects of immune-checkpoint inhibitors: Epidemiology, management and surveillance. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, D.; Parker, S.M.; Siegel, J.; Chasalow, S.D.; Weber, J.; Galbraith, S.; Targan, S.R.; Wang, H.L. Blockade of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 by ipilimumab results in dysregulation of gastrointestinal immunity in patients with advanced melanoma. Cancer Immun. 2010, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fessas, P.; Possamai, L.A.; Clark, J.; Daniels, E.; Gudd, C.; Mullish, B.H.; Alexander, J.L.; Pinato, D.J. Immunotoxicity from checkpoint inhibitor therapy: Clinical features and underlying mechanisms. Immunology 2020, 159, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Ozono, D.; Nagumo, H.; Yoshimura, M.; Masuzawa, Y. Temporal observation of endoscopic and histological findings of gastritis after administration of an immune checkpoint inhibitor: A case report. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, H.O.; Blitzer, B.L. Nonassociation of adrenocorticosteroid therapy and peptic ulcer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1976, 294, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, H.O.; Poynard, T. Corticosteroids and peptic ulcer: Meta-analysis of adverse events during steroid therapy. J. Intern. Med. 1994, 236, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ahmet, A.; Ward, L.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Mandelcorn, E.D.; Leigh, R.; Brown, J.P.; Cohen, A.; Kim, H. A practical guide to the monitoring and management of the complications of systemic corticosteroid therapy. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narum, S.; Westergren, T.; Klemp, M. Corticosteroids and risk of gastrointestinal bleeding: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e004587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). Clinical Knowledge Summaries: Corticosteroids-Oral. 2012. Available online: http://www.cks.nhs.uk/corticosteroids_oral (accessed on 6 November 2022).
- Piper, J.M.; Ray, W.A.; Daugherty, J.R.; Griffin, M.R. Corticosteroid use and peptic ulcer disease: Role of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Ann. Intern. Med. 1991, 114, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalykke, C.; Lauritsen, K. Epidemiology of NSAID-related gastroduodenal mucosal injury. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2001, 15, 705–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam-Kia, S.; Werth, V.P. Prevention and treatment of systemic glucocorticoid side effects. Int. J. Dermatol. 2010, 49, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpani de Kaski, M.; Rentsch, R.; Levi, S.; Hodgson, H.J. Corticosteroids reduce regenerative repair of epithelium in experimental gastric ulcers. Gut 1995, 37, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.C.; Shin, V.Y.; Liu, E.S.; Ye, Y.N.; Wu, W.K.; So, W.H.; Chang, F.Y.; Cho, C.H. Dexamethasone delays ulcer healing by inhibition of angiogenesis in rat stomachs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 485, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandyopadhyay, U.; Biswas, K.; Bandyopadhyay, D.; Ganguly, C.K.; Banerjee, R.K. Dexamethasone makes the gastric mucosa susceptible to ulceration by inhibiting prostaglandin synthetase and peroxidase–two important gastroprotective enzymes. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1999, 202, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, S.; Mokuda, S.; Matoba, K.; Yamada, A.; Jouyama, K.; Murata, Y.; Ozaki, Y.; Ito, T.; Nomura, S.; Okuda, Y. The prevalence of endoscopic gastric mucosal damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, P., Jr. Glucocorticoids and the gastrointestinal tract: Current status. Gut 1970, 11, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alan, I.S.; Alan, B. Side Effects of Glucocorticoids. In Pharmacokinetics and Adverse Effects of Drugs–Mechanisms and Risks Factors; InTech: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Díaz, S.; Rodríguez, L.A. Steroids and risk of upper gastrointestinal complications. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 153, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, D.; Velio, P.; Brunelli, L.; Mandelli, C.; Cesana, M.; Ferrario, L.; Quatrini, M.; Bianchi, P.A. Stainable iron in gastric and duodenal mucosa of primary hemochromatosis patients and alcoholics. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1987, 82, 237–240. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, S.C.; Yardley, J.H.; Wu, T.T. Erosive injury to the upper gastrointestinal tract in patients receiving iron medication: An underrecognized entity. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1999, 23, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, P.; Abdulla, K.; Wood, J.; James, P.; Foley, S.; Ragunath, K.; Atherton, J. Iron-induced mucosal pathology of the upper gastrointestinal tract: A common finding in patients on oral iron therapy. Histopathology 2008, 53, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, R.; Ribeiro, A.; Paiva, D.; Rios, E.; Rodrigues, S.; Macedo, G. Iron pill-induced gastroduodenopathy. Porto Biomed. J. 2017, 2, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marginean, E.C.; Bennick, M.; Cyczk, J.; Robert, M.E.; Jain, D. Gastric siderosis: Patterns and significance. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2006, 30, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Yardley, J.H. Iron medication-associated gastric mucosal injury. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2004, 128, 821–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Pantopoulos, K. Regulation of cellular iron metabolism. Biochem. J. 2011, 434, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angoro, B.; Motshakeri, M.; Hemmaway, C.; Svirskis, D.; Sharma, M. Non-transferrin bound iron. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2022, 531, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onorati, M.; Nicola, M.; Renda, A.; Lancia, M.; Di Nuovo, F. Iron Overload in Gastric Mucosa: Underdiagnosed Condition Rarely Documented in Clinical and Pathology Reports. Cureus 2020, 12, e8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino-Mathews, A.; Broman, J.H.; Westra, W.H.; Illei, P.B. Iron pill-induced tumefactive mucosal injury of the hypopharynx. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 1720–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran-Duy, A.; Spaetgens, B.; Hoes, A.W.; de Wit, N.J.; Stehouwer, C.D. Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors and Risks of Fundic Gland Polyps and Gastric Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 1706–1719.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).