Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Comparison of SICMF–SIPMO and AAOMS Guidelines
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. MRONJ History
1.2. Definition
- Current or previous treatment with antiresorptive therapy alone or in combination with immune modulators or antiangiogenic medications.
- Exposed bone or bone that can be probed through an intraoral or extraoral fistula(e) in the maxillofacial region that has persisted for more than eight weeks.
- No history of radiation therapy to the jaws or metastatic disease in the jaws.
1.3. Etiology and Pathogenesis
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Diagnosis and Staging—Case History
2.2. Diagnosis and Staging—Examination
- Assess the oral hygiene status.
- Outline the dental formula, paying close attention to radicular remnants, caries, dental fractures, erosion, abrasion, and abfractions.
- Assess and classify the periodontal condition and eventual gingival recesses.
- Identify intraoral fistulas, oral–nasal or oral–antral communications, spots of purulent fluid leakage, areas of exposed necrotic bone
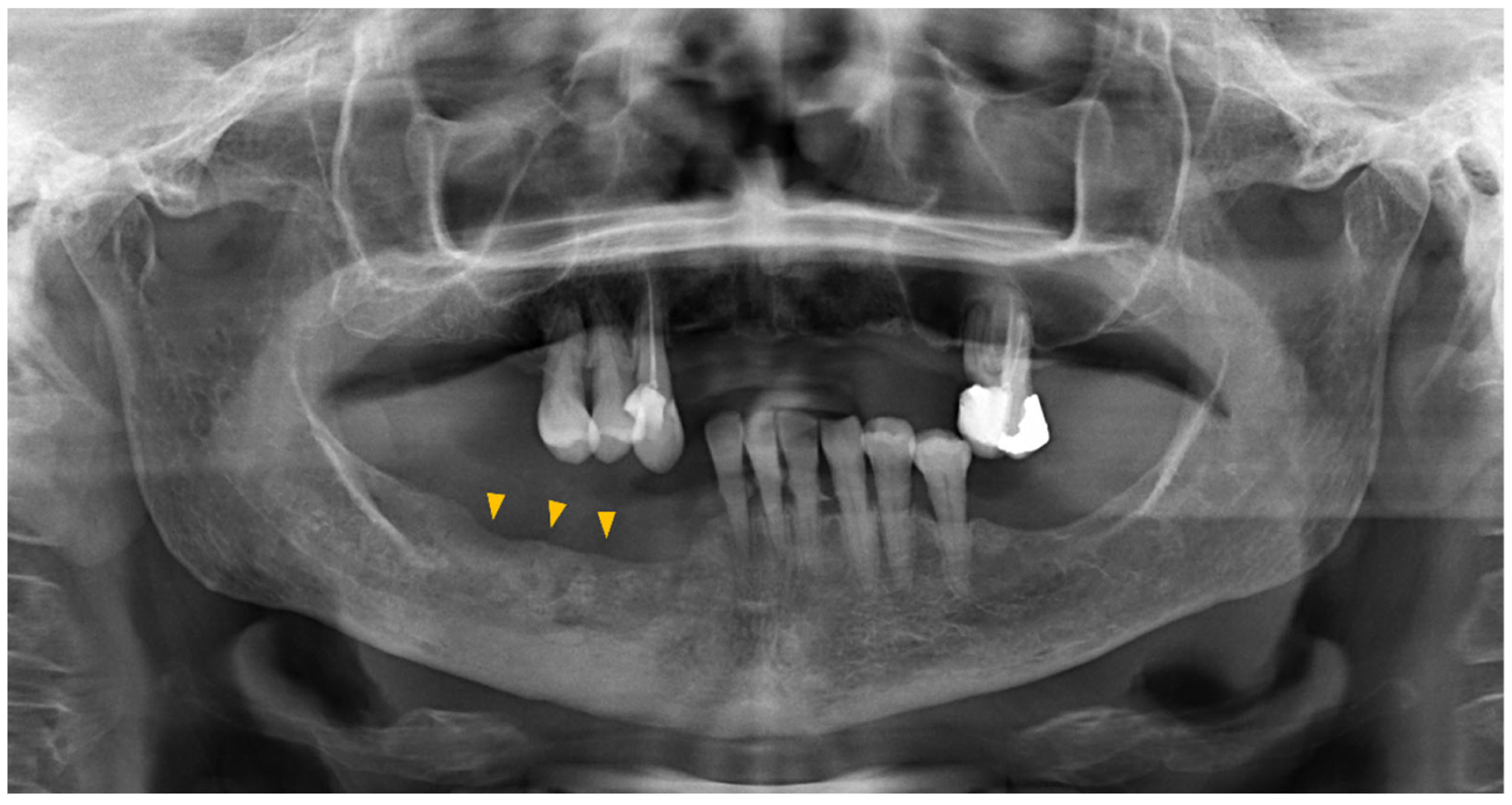
2.3. Diagnosis and Staging—Imaging
2.4. Staging
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. MRONJ Management—Prevention
- Drug-related risk factors
- Systemic risk factors
- Local risk factors
- Drug class
- Bioavailability
- Administration route
- Cumulative drug dose, which is influenced by the drug half-life
- Duration of treatment
3.2. MRONJ Treatment
3.2.1. Conservative Treatment
3.2.2. Surgical Treatment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Goodger, N.M.; Pogrel, M.A. Osteonecrosis of the jaws associated with cancer chemotherapy. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2003, 61, 1104–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Advisory Task Force on Bisphosphonate-Related Ostenonecrosis of the Jaws, American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 65, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Dodson, T.B.; Assael, L.A.; Landesberg, R.; Marx, R.E.; Mehrotra, B. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws—2009 update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 67 (Suppl. 5), 2–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Dodson, T.B.; Fantasia, J.; Goodday, R.; Aghaloo, T.; Mehrotra, B.; O’Ryan, F. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw—2014 update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 1938–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Dodson, T.B.; Aghaloo, T.; Carlson, E.R.; Ward, B.B.; Kademani, D. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons’ Position Paper on Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws—2022 Update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 80, 920–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarom, N.; Shapiro, C.L.; Peterson, D.E.; Van Poznak, C.H.; Bohlke, K.; Ruggiero, S.L.; Migliorati, C.A.; Khan, A.; Morrison, A.; Anderson, H.; et al. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: MASCC/ISOO/ASCO Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2270–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, G.; Bedogni, A.; Fusco, V. Raccomandazioni Clinico-Terapeutiche sull’Osteonecrosi delle ossa Mascellari (ONJ) Farmaco-Relata e sua Prevenzione. Version 2.0-July 2020. Available online: https://www.sipmo.it/versione-2-0-delle-raccomandazioni-clinico-terapeutiche-sullosteonecrosi-delle-ossa-mascellari-onj-farmaco-relata-e-sua-prevenzione/ (accessed on 31 January 2020).
- Aguirre, J.I.; Castillo, E.J.; Kimmel, D.B. Biologic and pathologic aspects of osteocytes in the setting of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ). Bone 2021, 153, 116168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, S.L. Reply: AAOMS Position Paper on Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws-2022 Update. Diagnostic Milestones, Doubts, and Perspectives on MRONJ. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 80, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, G.; Mauceri, R.; Bedogni, A.; Fusco, V. Re: AAOMS Position Paper on Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw-2022 Update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 80, 1723–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorati, C.A.; Epstein, J.B.; Abt, E.; Berenson, J.R. Osteonecrosis of the jaw and bisphosphonates in cancer: A narrative review. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremers, S.; Papapoulos, S. Pharmacology of bisphosphonates. Bone 2011, 49, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limones, A.; Sáez-Alcaide, L.M.; Díaz-Parreño, S.A.; Helm, A.; Bornstein, M.M.; Molinero-Mourelle, P. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (MRONJ) in cancer patients treated with denosumab vs. zoledronic acid: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2020, 25, e326–e336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.E.; Coleman, C.M. Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Bone Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi-Nedjat, R.K.; Sagheb, K.; Pabst, A.; Olk, L.; Walter, C. Diabetes Mellitus and Its Association to the Occurrence of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Dent. J. 2016, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, F.R.; Nascimento, G.G.; Scheutz, F.; Lopez, R. Effect of Smoking on Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-regression. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 54, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halperin-Sternfeld, M.; Levin, L. Do we really know how to evaluate tooth prognosis? A systematic review and suggested approach. Quintessence Int. 2013, 44, 447–456. [Google Scholar]
- Freiberger, J.J.; Padilla-Burgos, R.; McGraw, T.; Suliman, H.B.; Kraft, K.H.; Stolp, B.W.; Moon, R.E.; Piantadosi, C.A. What Is the Role of Hyperbaric Oxygen in the Management of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Hyperbaric Oxygen as an Adjunct to Surgery and Antibiotics. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 70, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashutski, J.D.; Eber, R.M.; Kinney, J.S.; Benavides, E.; Maitra, S.; Braun, T.M.; Giannobile, W.V.; McCauley, L.K. Teriparatide and osseous regeneration in the oral cavity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2396–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohbayashi, Y.; Iwasaki, A.; Nakai, F.; Mashiba, T.; Miyake, M. A comparative effectiveness pilot study of teriparatide for medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: Daily versus weekly administration. Osteoporos. Int. 2020, 31, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narongroeknawin, P.; Danila, M.I.; Humphreys, L.G., Jr.; Barasch, A.; Curtis, J.R. Bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw, with healing after teriparatide: A review of the literature and a case report. Spec. Care Dent. 2010, 30, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralow, J.R.; Biermann, J.S.; Farooki, A.; Fornier, M.N.; Gagel, R.F.; Kumar, R.; Litsas, G.; Mckay, R.; Podoloff, D.A.; Srinivas, S.; et al. NCCN Task Force Report: Bone Health in Cancer Care. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2009, 7 (Suppl. 3), S1–S32, quiz S33-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedogni, A.; Saia, G.; Bettini, G.; Tronchet, A.; Totola, A.; Bedogni, G.; Ferronato, G.; Nocini, P.F.; Blandamura, S. Long-term outcomes of surgical resection of the jaws in cancer patients with bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis. Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corraini, P.; Heide-Jørgensen, U.; Schiødt, M.; Nørholt, S.E.; Acquavella, J.; Sørensen, H.T.; Ehrenstein, V. Osteonecrosis of the jaw and survival of patients with cancer: A nationwide cohort study in Denmark. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 2271–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amato, S.; Troiano, A.; Lo Giudice, G.; De Cicco, D.; Rusciano, M.; Tartaro, G.; Colella, G. Resective surgery versus debridement in stage 2 medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, S.; Ristow, O.; Pache, C.; Troeltzsch, M.; Fliefel, R.; Ehrenfeld, M.; Pautke, C. Fluorescence-guided surgery for the treatment of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: A prospective cohort study. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2016, 44, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristow, O.; Otto, S.; Geiß, C.; Kehl, V.; Berger, M.; Troeltzsch, M.; Koerdt, S.; Hohlweg-Majert, B.; Freudlsperger, C.; Pautke, C. Comparison of auto-fluorescence and tetracycline fluorescence for guided bone surgery of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: A randomized controlled feasibility study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedogni, A.; Blandamura, S.; Lokmic, Z.; Palumbo, C.; Ragazzo, M.; Ferrari, F.; Tregnaghi, A.; Pietrogrande, F.; Procopio, O.; Saia, G.; et al. Bisphosphonate-associated jawbone osteonecrosis: A correlation between imaging techniques and histopathology. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2008, 105, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisdas, S.; Pinho, N.C.; Smolarz, A.; Sader, R.; Vogl, T.J.; Mack, M.G. Biphosphonate-induced osteonecrosis of the jaws: CT and MRI spectrum of findings in 32 patients. Clin. Radiol. 2008, 63, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, R.; Sacco, N.; Hamid, U.; Ali, S.H.; Singh, M.; Blythe, J.S.J. Microsurgical Reconstruction of the Jaws Using Vascularised Free Flap Technique in Patients with Medication-Related Osteonecrosis: A Systematic Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9858921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, R.E. Reconstruction of defects caused by bisphosphonate-induced osteonecrosis of the jaws. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 67 (Suppl. 5), 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, E.; Mazul, A.; Zenga, J.; Graboyes, E.M.; Jackson, R.; Puram, S.V.; Doering, M.; Pipkorn, P. Complications After Soft Tissue With Plate vs Bony Mandibular Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 164, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cicco, D.; Tartaro, G.; Ciardiello, F.; Fasano, M.; Rauso, R.; Fiore, F.; Spuntarelli, C.; Troiano, A.; Lo Giudice, G.; Colella, G. Health-related quality of life in oral cancer patients: Scoping review and critical appraisal of investigated determinants. Cancers 2021, 13, 4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cicco, D.; Tartaro, G.; Colella, G.; Dell’Aversana Orabona, G.; Santagata, M.; Ferrieri, I.; Troiano, A.; Staglianò, S.; Volgare, A.S.; D’Amato, S. Fat graft in surgical treatment of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (Mronj). Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Zhao, J.; Nie, F.; Qin, Z.; Xue, H.; Wang, G.; Li, D. Exosomes from Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) Overexpressing miR-21 Promote Vascularization of Endothelial Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (BRONJ) | Intravenous or oral bisphosphonates |
| Non-Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the jaws (non-BRONJ) | Denosumab (anti-RANKL) |
| Bevacizumab, Aflibercept (anti-VEGFR) | |
| Sunitinib, Sorafenib, Cabozatinib (tyrosine kinase inhibitors) | |
| Everolimus (anti-mTOR) |
| Grade | Mobility |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0.2 mm (healthy) |
| 1 | 0.2–1 mm |
| 2 | 1–2 mm |
| 3 | More than 3–4 mm, with both vertical, vestibolo-lingual, and mesio-distal mobility |
| Early | Bone cortical erosion |
| Thickening of alveolar crest and lamina dura | |
| Thickening of the trabecular bone | |
| Focal medullary osteonecrosis | |
| Persistance of the post-extraction socket | |
| Widening of the periodontal space | |
| Tardive | Oro-antral, oro-nasal, or oro-cutaneous fistula |
| Phatological fracture | |
| Thickening of the inferior alveolar canal | |
| Extended osteolysis of the maxillary sinus | |
| Diffused osteosclerosis of the jaws | |
| Osteosclerosis of the zygoma and/or hard palate | |
| Periosteal reaction | |
| Sinusitis |
| Stage | SICMF–SIPMO 2020 | AAOMS 2022 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | - | Patients with no clinical evidence of necrotic bone but who present with nonspecific symptoms or clinical and radiographic findings (i.e., odontalgia, bone pain, sinus pain, altered neurosensory function, teeth loosening, swelling, alveolar bone loss not related to periodontal disease, osteosclerosis, thickening of the periodontal space) |
| 1 | Focal MRONJ: at least one minor clinical sign *; bone addensation observed at the CT scan limited to the alveolar process | Exposed and necrotic bone or fistula that probes to the bone in patients who are asymptomatic and have no evidence of infection/inflammation |
| 2 | Diffused MRONJ: at least one minor clinical sign *; bone addensation extended to the basal bone | Exposed and necrotic bone, or fistula that probes to the bone, with evidence of infection/inflammation |
| 3 | Severe MRONJ: one or more major ** clinical signs or CT scan demonstrating a mandibular fracture, or an extended osteolysis of the maxillary walls, the zygoma, or the hard palate | Exposed and necrotic bone or fistulae that probes to the bone, with evidence of infection, and one or more of the following:
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Cicco, D.; Boschetti, C.E.; Santagata, M.; Colella, G.; Staglianò, S.; Gaggl, A.; Bottini, G.B.; Vitagliano, R.; D’amato, S. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Comparison of SICMF–SIPMO and AAOMS Guidelines. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132137
De Cicco D, Boschetti CE, Santagata M, Colella G, Staglianò S, Gaggl A, Bottini GB, Vitagliano R, D’amato S. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Comparison of SICMF–SIPMO and AAOMS Guidelines. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(13):2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132137
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Cicco, Davide, Ciro Emiliano Boschetti, Mario Santagata, Giuseppe Colella, Samuel Staglianò, Alexander Gaggl, Gian Battista Bottini, Rita Vitagliano, and Salvatore D’amato. 2023. "Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Comparison of SICMF–SIPMO and AAOMS Guidelines" Diagnostics 13, no. 13: 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132137
APA StyleDe Cicco, D., Boschetti, C. E., Santagata, M., Colella, G., Staglianò, S., Gaggl, A., Bottini, G. B., Vitagliano, R., & D’amato, S. (2023). Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Comparison of SICMF–SIPMO and AAOMS Guidelines. Diagnostics, 13(13), 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132137








