Abdominal Compartment Syndrome in Acute Pancreatitis: A Narrative Review
Abstract
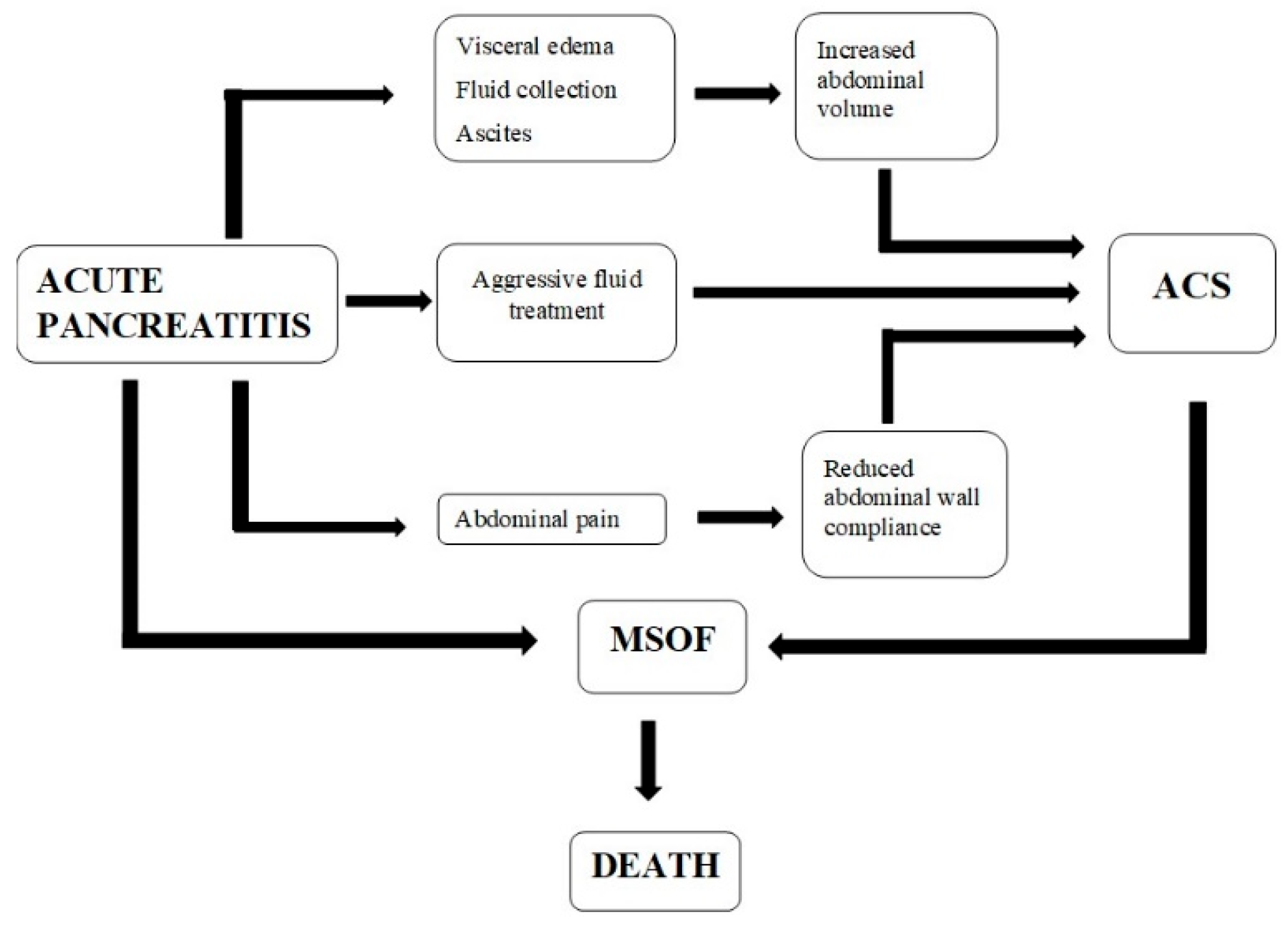
:1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology
2.1. Effects on the Reno-Urinary System
2.2. Effects on the Gastrointestinal System
2.3. Effects on the Respiratory System
2.4. Effects on the Cardiovascular System
2.5. Effects on the Central Nervous System
3. Classification of Intra-Abdominal Hypertension
- Grade I: intra-abdominal pressure: 12–15 mmHg.
- Grade II: intra-abdominal pressure: 16–20 mmHg.
- Grade III: intra-abdominal pressure: 21–25 mmHg.
- Grade IV: intra-abdominal pressure: >25 mmHg.
- Hyperacute: IAP increases in the order of seconds-minutes that occur in certain situations: laughter, coughing, sneezing, defecation.
- Acute: IAH lasting several hours in the trauma surgical patient or intra-abdominal bleeding; this entity can evolve fulminating in a few hours to the abdominal compartment syndrome.
- Subacute: IAH that appears progressively over days, frequently found in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. The typical example being patients with medical pathology hospitalized in the intensive care unit (massive resuscitation in the patient with severe burns, and leakage capillary syndrome associated with sepsis).
- Chronic: IAH that develops progressively in months or years in the context of pregnancy, morbid obesity, peritoneal dialysis, and liver cirrhosis with ascites); these patients are at risk of developing acute intra-abdominal hypertension in the event of a critical illness.
4. Classification of Abdominal Compartment Syndrome
- Primary ACS (surgical/postoperative/abdominal) is characterized by an acute/subacute increase in intra-abdominal pressure in certain circumstances: abdominal trauma, abdominal aneurysm dissection, hemoperitoneum, acute pancreatitis, secondary peritonitis, retroperitoneal hemorrhage, and liver transplantation; it frequently requires surgery early or radiological interventional therapy.
- Secondary ACS (medical/extra-abdominal) is characterized by a subacute/chronic increase in intra-abdominal pressure that occurs secondary to extra-abdominal causes: sepsis, capillary leakage, severe burns, or other conditions that require massive resuscitation.
- Recurrent ACS (tertiary) represents the reappearance of abdominal compartment syndrome after resolution of a previous episode of primary or secondary abdominal compartment syndrome; it is associated with acute intra-abdominal hypertension, being equivalent to a “second-hit”, having morbidity and significantly increased mortality.
5. Diagnosis
5.1. Clinical Diagnosis
5.2. Imaging Diagnosis
5.3. Laboratory Diagnosis
6. Treatment
6.1. Non-Surgical Management
6.1.1. Evacuate Intraluminal Contents
6.1.2. Improve Intra-Abdominal Compliance
6.1.3. Optimize Fluid Administration and Improve Systemic/Regional Perfusion
6.1.4. Antibiotics
6.1.5. Energy Nutrition
6.2. Percutaneous Drainage
6.3. Surgical Treatment
| First Author (Year) | Severe AP | IAH | IAH—Male (%) | ACS | Interventions | % Interventional Treatment of ACS | Time to Intervention | ACS Mortality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tao (2003) [123] | 345 | 2 | 14 (67%) | 21 | Midline laparotomy with Bogota bag (n = 18) | 85.7 | 9–22 h | 33.30% |
| De Waele (2005) [124] | 44 | 21 | 15 (71%) | 4 | Midline laparotomy, temporary abdominal closure system (n = 4) | 100% | - | 75% |
| Chen (2008) [8] | 74 | 44 | 23 (52%) | 20 | Percutaneous abdominal decompression and drainage (n = 8); Decompressive emergency laparotomy (n = 8) | 65% | 26–33 h | 75% |
| Mentula (2010) [28] | 26 | 0 | 23 (88%) | 26 | Open abdomen (n = 21) Subcutaneous linea alba fasciotomy (n = 5) | 100% | 1–5 days | 46% |
| Bezmarevic (2012) [12] | 51 | 27 | 23 (79%) | 6 | Midline laparotomy (n = 6) | 83% | 1–4 days | 83% |
| Davis (2013) [11] | 43 | 16 | 16 (100%) | 16 | Midline laparotomy with Bogota bag (n = 11) or wound VAC system (n = 5) | 100% | 3 h | 25% |
| Peng (2016) [117] | 273 | 273 | 168 (62%) | 273 | Midline laparotomy (n = 61) Percutaneous catheter drainage (n = 212) | 23.30% | 2–101 h | 52.50% |
| Smit (2016) [9] | 59 | 29 | 21 (72%) | 13 | Transverse subcostal laparotomy (n = 7), midline laparotomy (n = 3) | 10 (77%) | 1.9–15.5 days | 53% |
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Gooszen, H.G.; Johnson, C.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Vege, S.S.; Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working, G. Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2013, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, P.K.; Singh, V.P. Organ Failure Due to Systemic Injury in Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2008–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Samanta, J.; Shukla, J.; Birda, C.L.; Dhar, J.; Gupta, P.; Kumar, M.P.; Gupta, V.; Yadav, T.D.; Sinha, S.K.; et al. Impact of Different Patterns of Organ Failure on Mortality in Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2021, 50, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machicado, J.D.; Gougol, A.; Tan, X.; Gao, X.; Paragomi, P.; Pothoulakis, I.; Talukdar, R.; Kochhar, R.; Goenka, M.K.; Gulla, A.; et al. Mortality in acute pancreatitis with persistent organ failure is determined by the number, type, and sequence of organ systems affected. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2021, 9, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, N.; Liu, T.; de la Iglesia-Garcia, D.; Deng, L.; Jin, T.; Lan, L.; Zhu, P.; Hu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Singh, V.; et al. Duration of organ failure impacts mortality in acute pancreatitis. Gut 2020, 69, 604–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, A.E.; Trzeciak, S.; Kline, J.A. The Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score for predicting outcome in patients with severe sepsis and evidence of hypoperfusion at the time of emergency department presentation. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimball, E.J. Intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome: A current review. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2021, 27, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, F.; Sun, J.B.; Jia, J.G. Abdominal compartment syndrome in patients with severe acute pancreatitis in early stage. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 3541–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, M.; Buddingh, K.T.; Bosma, B.; Nieuwenhuijs, V.B.; Hofker, H.S.; Zijlstra, J.G. Abdominal Compartment Syndrome and Intra-abdominal Ischemia in Patients with Severe Acute Pancreatitis. World J. Surg. 2016, 40, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaipuria, J.; Bhandari, V.; Chawla, A.S.; Singh, M. Intra-abdominal pressure: Time ripe to revise management guidelines of acute pancreatitis? World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2016, 7, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.J.; Eltawil, K.M.; Abu-Wasel, B.; Walsh, M.J.; Topp, T.; Molinari, M. Effect of obesity and decompressive laparotomy on mortality in acute pancreatitis requiring intensive care unit admission. World J. Surg. 2013, 37, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bezmarevic, M.; Mirkovic, D.; Soldatovic, I.; Stamenkovic, D.; Mitrovic, N.; Perisic, N.; Marjanovic, I.; Mickovic, S.; Karanikolas, M. Correlation between procalcitonin and intra-abdominal pressure and their role in prediction of the severity of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2012, 12, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikudanathan, G.; Vege, S.S. Current concepts of the role of abdominal compartment syndrome in acute pancreatitis—An opportunity or merely an epiphenomenon. Pancreatology 2014, 14, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, V.; Jaipuria, J.; Singh, M.; Chawla, A.S. Intra-abdominal pressure in the early phase of severe acute pancreatitis: Canary in a coal mine? Results from a rigorous validation protocol. Gut Liver 2013, 7, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.Y.; Wang, X.B.; Liu, X.F.; Li, S.G. Prevalence and risk factors of organ failure in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 1, 201–204. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, A.; Myint, F.; Hamilton, G. Recognition and management of abdominal compartment syndrome in the United Kingdom. Intensive Care Med. 2006, 32, 906–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagosz, P.; Sokolski, M.; Biegus, J.; Tycinska, A.; Zymlinski, R. Elevated intra-abdominal pressure: A review of current knowledge. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 3005–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Roberts, D.J.; De Waele, J.; Jaeschke, R.; Malbrain, M.L.; De Keulenaer, B.; Duchesne, J.; Bjorck, M.; Leppaniemi, A.; Ejike, J.C.; et al. Intra-abdominal hypertension and the abdominal compartment syndrome: Updated consensus definitions and clinical practice guidelines from the World Society of the Abdominal Compartment Syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 1190–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Waele, J.J.; Leppaniemi, A.K. Intra-abdominal hypertension in acute pancreatitis. World J. Surg. 2009, 33, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbrain, M.L.; Peeters, Y.; Wise, R. The neglected role of abdominal compliance in organ-organ interactions. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smit, M.; van Meurs, M.; Zijlstra, J.G. Intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome in critically ill patients: A narrative review of past, present, and future steps. Scand. J. Surg. 2022, 111, 14574969211030128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malbrain, M.L.; De Laet, I.; De Waele, J.J.; Sugrue, M.; Schachtrupp, A.; Duchesne, J.; Van Ramshorst, G.; De Keulenaer, B.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Ahmadi-Noorbakhsh, S.; et al. The role of abdominal compliance, the neglected parameter in critically ill patients—A consensus review of 16. Part 2: Measurement techniques and management recommendations. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2014, 46, 406–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, A.R.; Bjorck, M.; De Keulenaer, B.; Regli, A. Abdominal compliance: A bench-to-bedside review. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015, 78, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbrain, M.L.; Roberts, D.J.; Sugrue, M.; De Keulenaer, B.L.; Ivatury, R.; Pelosi, P.; Verbrugge, F.; Wise, R.; Mullens, W. The polycompartment syndrome: A concise state-of-the-art review. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2014, 46, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malbrain, M.L.; Wilmer, A. The polycompartment syndrome: Towards an understanding of the interactions between different compartments! Intensive Care Med. 2007, 33, 1869–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, Z. Polycompartment syndrome—Intra-abdominal pressure measurement. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2019, 51, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbrain, M.L.; Cheatham, M.L.; Kirkpatrick, A.; Sugrue, M.; Parr, M.; De Waele, J.; Balogh, Z.; Leppaniemi, A.; Olvera, C.; Ivatury, R.; et al. Results from the International Conference of Experts on Intra-abdominal Hypertension and Abdominal Compartment Syndrome. I. Definitions. Intensive Care Med. 2006, 32, 1722–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentula, P.; Hienonen, P.; Kemppainen, E.; Puolakkainen, P.; Leppaniemi, A. Surgical decompression for abdominal compartment syndrome in severe acute pancreatitis. Arch. Surg. 2010, 145, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheatham, M.L.; White, M.W.; Sagraves, S.G.; Johnson, J.L.; Block, E.F. Abdominal perfusion pressure: A superior parameter in the assessment of intra-abdominal hypertension. J. Trauma 2000, 49, 621–627; discussion 626–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluso, P.; Olson, J.; Sarani, B. Abdominal Compartment Hypertension and Abdominal Compartment Syndrome. Crit. Care Clin. 2016, 32, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellinger, E.P.; Forsmark, C.E.; Layer, P.; Levy, P.; Maravi-Poma, E.; Petrov, M.S.; Shimosegawa, T.; Siriwardena, A.K.; Uomo, G.; Whitcomb, D.C.; et al. Determinant-based classification of acute pancreatitis severity: An international multidisciplinary consultation. Ann. Surg. 2012, 256, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbertson, C.M.; Christophi, C. Disturbances of the microcirculation in acute pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 2006, 93, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, M.; Standl, T.G.; Kleinhans, H.; Gottschalk, A.; Mann, O.; Rempf, C.; Bachmann, K.; Gocht, A.; Petri, S.; Izbicki, J.R.; et al. Improvement of impaired microcirculation and tissue oxygenation by hemodilution with hydroxyethyl starch plus cell-free hemoglobin in acute porcine pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2006, 6, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navadgi, S.; Pandanaboyana, S.; Windsor, J.A. Surgery for Acute Pancreatitis. Indian J. Surg. 2015, 77, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, P.J.; Papachristou, G.I. Management of Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2020, 18, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Chen, Z.; Niu, W.; Feng, L.; Fan, B.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, B.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Tong, B.; et al. Using a multidisciplinary team for the staged management and optimally minimally invasive treatment of severe acute pancreatitis. Biosci. Trends 2021, 15, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molitoris, B.A. Low-Flow Acute Kidney Injury: The Pathophysiology of Prerenal Azotemia, Abdominal Compartment Syndrome, and Obstructive Uropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 17, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copur, S.; Berkkan, M.; Hasbal, N.B.; Basile, C.; Kanbay, M. Abdominal compartment syndrome: An often overlooked cause of acute kidney injury. J. Nephrol. 2022, 35, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohmand, H.; Goldfarb, S. Renal dysfunction associated with intra-abdominal hypertension and the abdominal compartment syndrome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Waele, J.J. Abdominal Compartment Syndrome in Severe Acute Pancreatitis—When to Decompress? Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2008, 34, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullens, W.; Abrahams, Z.; Skouri, H.N.; Francis, G.S.; Taylor, D.O.; Starling, R.C.; Paganini, E.; Tang, W.H. Elevated intra-abdominal pressure in acute decompensated heart failure: A potential contributor to worsening renal function? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaussen, T.; Srinivasan, P.K.; Afify, M.; Herweg, C.; Tolba, R.; Conze, J.; Schachtrupp, A. Influence of two different levels of intra-abdominal hypertension on bacterial translocation in a porcine model. Ann. Intensive Care 2012, 2 (Suppl. 1), S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.X.; Huang, H.R.; Zhou, H. Indwelling catheter and conservative measures in the treatment of abdominal compartment syndrome in fulminant acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 5068–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, G.; Wang, P.; Ding, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J. The role of oxygen-free radical in the apoptosis of enterocytes and bacterial translocation in abdominal compartment syndrome. Free Radic. Res. 2009, 43, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Wei, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, J.; Chen, X.; Xiao, G.; Li, X. The role of intestinal mucosa injury induced by intra-abdominal hypertension in the development of abdominal compartment syndrome and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, J.; Criddle, L.M. Pathophysiology and management of abdominal compartment syndrome. Am. J. Crit. Care 2003, 12, 367–371; quiz 372–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegneswaran, B.; Kostis, J.B.; Pitchumoni, C.S. Cardiovascular manifestations of acute pancreatitis. J. Crit. Care 2011, 26, 225.e11–225.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadi, S.A.; Abdo, H.; Bihari, A.; Parry, N.; Lawendy, A.R. Hepatic microvascular changes in rat abdominal compartment syndrome. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 197, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Qi, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, C.; Ding, T.; Yang, C. Hepatorenal syndrome: Insights into the mechanisms of intra-abdominal hypertension. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 2523–2528. [Google Scholar]
- De Waele, J.J.; Ejike, J.C.; Leppaniemi, A.; De Keulenaer, B.L.; De Laet, I.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Roberts, D.J.; Kimball, E.; Ivatury, R.; Malbrain, M.L. Intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome in pancreatitis, paediatrics, and trauma. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2015, 47, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malbrain, M.L.; De Laet, I.E.; De Waele, J.J.; Kirkpatrick, A.W. Intra-abdominal hypertension: Definitions, monitoring, interpretation and management. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2013, 27, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.D.; Damani, Z. Intra-abdominal hypertension and the abdominal compartment syndrome. Anaesthesia 2004, 59, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, A.K.; Ball, C.G. Intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome in acute pancreatitis, hepato-pancreato-biliary operations and liver transplantation. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2017, 49, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, B.M. Abdominal compartment syndrome and intra-abdominal hypertension. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2019, 25, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo-Jave, E.E.; Espejel-Deloiza, M.; Chernitzky-Camano, J.; Pena-Perez, C.A.; Rivero-Sigarroa, E.; Ortega-Leon, L.H. Abdominal compartment syndrome: Current concepts and management. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. Engl. Ed. 2020, 85, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheatham, M.L.; Malbrain, M.L. Cardiovascular implications of abdominal compartment syndrome. Acta Clin. Belg. 2007, 62 (Suppl. 1), 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheatham, M.L. Abdominal compartment syndrome: Pathophysiology and definitions. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2009, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Laet, I.; Citerio, G.; Malbrain, M.L. The influence of intraabdominal hypertension on the central nervous system: Current insights and clinical recommendations, is it all in the head? Acta Clin. Belg. 2007, 62 (Suppl. 1), 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomfield, G.L.; Ridings, P.C.; Blocher, C.R.; Marmarou, A.; Sugerman, H.J. Effects of increased intra-abdominal pressure upon intracranial and cerebral perfusion pressure before and after volume expansion. J. Trauma 1996, 40, 936–941; discussion 941–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbrain, M.L.; Chiumello, D.; Cesana, B.M.; Reintam Blaser, A.; Starkopf, J.; Sugrue, M.; Pelosi, P.; Severgnini, P.; Hernandez, G.; Brienza, N.; et al. A systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis on intra-abdominal hypertension in critically ill patients: The wake-up project. World initiative on Abdominal Hypertension Epidemiology, a Unifying Project (WAKE-Up!). Minerva Anestesiol. 2014, 80, 293–306. [Google Scholar]
- De Waele, J.J.; De Laet, I.; Malbrain, M.L. Rational intraabdominal pressure monitoring: How to do it? Acta Clin. Belg. 2007, 62 (Suppl. 1), 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malbrain, M.L. Different techniques to measure intra-abdominal pressure (IAP): Time for a critical re-appraisal. Intensive Care Med. 2004, 30, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, D.; Webber, S.; Hamnegard, C.H.; Mills, G.H. Intra-abdominal pressure measurement: Validation of intragastric pressure as a measure of intra-abdominal pressure. Br. J. Anaesth 2007, 98, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, A.F.; Chica Yanten, J.; Sanchez, A.I.; Aldana, J.L.; Mejia, J.H.; Burbano, D.; Salazar, C. Bench Validation of a Handcrafted Prototype Catheter for Intra-gastric Pressure Monitoring. World J. Surg. 2020, 44, 1706–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasurya, V.; Surani, S. Abdominal compartment syndrome: Often overlooked conditions in medical intensive care units. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, B.M.; Pereira, R.G.; Wise, R.; Sugrue, G.; Zakrison, T.L.; Dorigatti, A.E.; Fiorelli, R.K.; Malbrain, M. The role of point-of-care ultrasound in intra-abdominal hypertension management. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2017, 49, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smereczynski, A.; Kolaczyk, K.; Bernatowicz, E. Ultrasonography in the diagnosis and monitoring of intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome: Ultrasonografia a nadcisnienie wewnatrzbrzuszne i zespol przedzialu brzusznego. J. Ultrason. 2020, 20, e201–e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.M.; Shaikh, N.A.; Aftab, Z.; Latif, E.; Sameer, M.; Khan, M.B.; Al-Tarakji, M. Peripartum Severe Acute Pancreatitis with Rare Complications: Case Report and Review of Literature. Case Rep. Surg. 2020, 2020, 5785413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barauskas, G.; Ignatavicius, P.; Vitkauskiene, A.; Pundzius, J.; Dambrauskas, Z. Impact of etiology on course and outcomes of severe acute pancreatitis. Medicina 2015, 51, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miko, A.; Vigh, E.; Matrai, P.; Soos, A.; Garami, A.; Balasko, M.; Czako, L.; Mosdosi, B.; Sarlos, P.; Eross, B.; et al. Computed Tomography Severity Index vs. Other Indices in the Prediction of Severity and Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis: A Predictive Accuracy Meta-analysis. Front. Physiol 2019, 10, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, P.; Pando, E.; Mata, R.; Vidal, L.; Roson, N.; Mast, R.; Armario, D.; Merino, X.; Dopazo, C.; Blanco, L.; et al. Evaluation of the modified computed tomography severity index (MCTSI) and computed tomography severity index (CTSI) in predicting severity and clinical outcomes in acute pancreatitis. J. Dig. Dis. 2021, 22, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Kamat, R.; Samanta, J.; Mandavdhare, H.; Sharma, V.; Sinha, S.K.; Dutta, U.; Kochhar, R. Computed Tomography Findings in Intraabdominal Hypertension in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Indian J. Radiol. Imaging 2021, 31, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Rana, S.S.; Kang, M.; Gorsi, U.; Gupta, R. Computed tomography features predictive of intra-abdominal hypertension in acute necrotizing pancreatitis: A prospective study. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 40, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickhardt, P.J.; Shimony, J.S.; Heiken, J.P.; Buchman, T.G.; Fisher, A.J. The abdominal compartment syndrome: CT findings. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1999, 173, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugrue, G.; Malbrain, M.; Pereira, B.; Wise, R.; Sugrue, M. Modern imaging techniques in intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome: A bench to bedside overview. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2018, 50, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouveresse, S.; Piton, G.; Badet, N.; Besch, G.; Pili-Floury, S.; Delabrousse, E. Abdominal compartment syndrome and intra-abdominal hypertension in critically ill patients: Diagnostic value of computed tomography. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 3839–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duzgun, A.P.; Gulgez, B.; Ozmutlu, A.; Ertorul, D.; Bugdayci, G.; Akyurek, N.; Coskun, F. The relationship between intestinal hypoperfusion and serum d-lactate levels during experimental intra-abdominal hypertension. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2006, 51, 2400–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, C.; Kirkegard, J.; Erlandsen, E.J.; Lindholt, J.S.; Mortensen, F.V. D-lactate is a valid biomarker of intestinal ischemia induced by abdominal compartment syndrome. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 194, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Fan, X.; Ding, W.; Liu, B.; Meng, J.; Wang, K.; Wu, X.; Li, J. D-dimer as an early marker of severity in patients with acute superior mesenteric venous thrombosis. Medicine 2014, 93, e270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strang, S.G.; Habes, Q.L.M.; Van der Hoven, B.; Tuinebreijer, W.E.; Verhofstad, M.H.J.; Pickkers, P.; Van Lieshout, E.M.M.; Van Waes, O.J.F. Intestinal fatty acid binding protein as a predictor for intra-abdominal pressure-related complications in patients admitted to the intensive care unit; a prospective cohort study (I-Fabulous study). J. Crit. Care 2021, 63, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strang, S.G.; Van Waes, O.J.; Van der Hoven, B.; Ali, S.; Verhofstad, M.H.; Pickkers, P.; Van Lieshout, E.M. Intestinal fatty acid binding protein as a marker for intra-abdominal pressure-related complications in patients admitted to the intensive care unit; study protocol for a prospective cohort study (I-Fabulous study). Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2015, 23, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ardasheva, R.G.; Argirova, M.D.; Turiiski, V.I.; Krustev, A.D. Biochemical Changes in Experimental Rat Model of Abdominal Compartment Syndrome. Folia Med. 2017, 59, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braganza, J.M.; Scott, P.; Bilton, D.; Schofield, D.; Chaloner, C.; Shiel, N.; Hunt, L.P.; Bottiglieri, T. Evidence for early oxidative stress in acute pancreatitis. Clues for correction. Int. J. Pancreatol. 1995, 17, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciskalska, M.; Oldakowska, M.; Marek, G.; Milnerowicz, H. Changes in the Activity and Concentration of Superoxide Dismutase Isoenzymes (Cu/Zn SOD, MnSOD) in the Blood of Healthy Subjects and Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakkampudi, A.; Jangala, R.; Reddy, R.; Reddy, B.; Venkat Rao, G.; Pradeep, R.; Nageshwar Reddy, D.; Talukdar, R. Fatty acid ethyl ester (FAEE) associated acute pancreatitis: An ex-vivo study using human pancreatic acini. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oiva, J.; Mustonen, H.; Kylanpaa, M.L.; Kyhala, L.; Kuuliala, K.; Siitonen, S.; Kemppainen, E.; Puolakkainen, P.; Repo, H. Acute pancreatitis with organ dysfunction associates with abnormal blood lymphocyte signaling: Controlled laboratory study. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Bahrani, A.Z.; Abid, G.H.; Holt, A.; McCloy, R.F.; Benson, J.; Eddleston, J.; Ammori, B.J. Clinical relevance of intra-abdominal hypertension in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 2008, 36, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, P.; Peng, C.; Zhao, L.; Wan, C. The Decrease of Peripheral Blood CD4+ T Cells Indicates Abdominal Compartment Syndrome in Severe Acute Pancreatitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cui, Y.; Tian, X. Early Continuous Veno-Venous Hemofiltration Is Effective in Decreasing Intra-Abdominal Pressure and Serum Interleukin-8 Level in Severe Acute Pancreatitis Patients with Abdominal Compartment Syndrome. Blood Purif. 2017, 44, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bodnar, Z.; Keresztes, T.; Kovacs, I.; Hajdu, Z.; Boissonneault, G.A.; Sipka, S. Increased serum adenosine and interleukin 10 levels as new laboratory markers of increased intra-abdominal pressure. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2010, 395, 969–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, M.; Chavez, L.; Surani, S. Abdominal compartment syndrome among surgical patients. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2021, 13, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheatham, M.L.; De Waele, J.J.; De Laet, I.; De Keulenaer, B.; Widder, S.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Cresswell, A.B.; Malbrain, M.; Bodnar, Z.; Mejia-Mantilla, J.H.; et al. The impact of body position on intra-abdominal pressure measurement: A multicenter analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 2187–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheatham, M.L. Nonoperative management of intraabdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome. World J. Surg. 2009, 33, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Chen, P.; Lei, Y.; Xia, L.; Liu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Wu, Y.; Ke, H.; Huang, X.; et al. Randomized controlled trial: Neostigmine for intra-abdominal hypertension in acute pancreatitis. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.J.; Ball, C.G.; Kirkpatrick, A.W. Increased pressure within the abdominal compartment: Intra-abdominal hypertension and the abdominal compartment syndrome. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2016, 22, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laet, I.; Hoste, E.; Verholen, E.; De Waele, J.J. The effect of neuromuscular blockers in patients with intra-abdominal hypertension. Intensive Care Med. 2007, 33, 1811–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Aghahoseini, A.; Crawford, J.; Alexander, D.J. To close or not to close? Treatment of abdominal compartment syndrome by neuromuscular blockade without laparostomy. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2010, 92, e8–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokoe, M.; Takada, T.; Mayumi, T.; Yoshida, M.; Isaji, S.; Wada, K.; Itoi, T.; Sata, N.; Gabata, T.; Igarashi, H.; et al. Japanese guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis: Japanese Guidelines 2015. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2015, 22, 405–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines. IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2013, 13, e1–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppaniemi, A.; Tolonen, M.; Tarasconi, A.; Segovia-Lohse, H.; Gamberini, E.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Ball, C.G.; Parry, N.; Sartelli, M.; Wolbrink, D.; et al. 2019 WSES guidelines for the management of severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2019, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Italian Association for the Study of the Pancreas (AISP); Pezzilli, R.; Zerbi, A.; Campra, D.; Capurso, G.; Golfieri, R.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; Billi, P.; Butturini, G.; Calculli, L.; et al. Consensus guidelines on severe acute pancreatitis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malbrain, M.; Van Regenmortel, N.; Saugel, B.; De Tavernier, B.; Van Gaal, P.J.; Joannes-Boyau, O.; Teboul, J.L.; Rice, T.W.; Mythen, M.; Monnet, X. Principles of fluid management and stewardship in septic shock: It is time to consider the four D’s and the four phases of fluid therapy. Ann. Intensive Care 2018, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, R.; Wise, R.D.; Myatchin, I.; Vanhonacker, D.; Minini, A.; Mekeirele, M.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Pereira, B.M.; Sugrue, M.; De Keulenaer, B.; et al. Fluid Management, Intra-Abdominal Hypertension and the Abdominal Compartment Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Life 2022, 12, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warndorf, M.G.; Kurtzman, J.T.; Bartel, M.J.; Cox, M.; Mackenzie, T.; Robinson, S.; Burchard, P.R.; Gordon, S.R.; Gardner, T.B. Early fluid resuscitation reduces morbidity among patients with acute pancreatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, B.U.; Hwang, J.Q.; Gardner, T.H.; Repas, K.; Delee, R.; Yu, S.; Smith, B.; Banks, P.A.; Conwell, D.L. Lactated Ringer’s solution reduces systemic inflammation compared with saline in patients with acute pancreatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 710–717.e711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, G.; Woitalla, J.; Wellhoner, P.; Schmidt, K.; Buning, J.; Fellermann, K. Detrimental effect of high volume fluid administration in acute pancreatitis—A retrospective analysis of 391 patients. Pancreatology 2014, 14, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Madaria, E.; Buxbaum, J.L.; Maisonneuve, P.; Garcia Garcia de Paredes, A.; Zapater, P.; Guilabert, L.; Vaillo-Rocamora, A.; Rodriguez-Gandia, M.A.; Donate-Ortega, J.; Lozada-Hernandez, E.E.; et al. Aggressive or Moderate Fluid Resuscitation in Acute Pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosignani, A.; Spina, S.; Marrazzo, F.; Cimbanassi, S.; Malbrain, M.; Van Regenemortel, N.; Fumagalli, R.; Langer, T. Intravenous fluid therapy in patients with severe acute pancreatitis admitted to the intensive care unit: A narrative review. Ann. Intensive Care 2022, 12, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentula, P.; Leppaniemi, A. Position paper: Timely interventions in severe acute pancreatitis are crucial for survival. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2014, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leppaniemi, A.; Tolonen, M.; Tarasconi, A.; Segovia-Lohse, H.; Gamberini, E.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Ball, C.G.; Parry, N.; Sartelli, M.; Wolbrink, D.; et al. Executive summary: WSES Guidelines for the management of severe acute pancreatitis. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020, 88, 888–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaharai, K.; Morita, K.; Jo, T.; Matsui, H.; Fushimi, K.; Yasunaga, H. Early prophylactic antibiotics for severe acute pancreatitis: A population-based cohort study using a nationwide database in Japan. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrie, J.; Jamdar, S.; Smith, N.; McPherson, S.J.; Siriwardena, A.K.; O’Reilly, D.A. Mis-use of antibiotics in acute pancreatitis: Insights from the United Kingdom’s National Confidential Enquiry into patient outcome and death (NCEPOD) survey of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, M.M.; Evans, R.; Kalidindi, V.; Navaratnam, R.; Dvorkin, L.; Bramhall, S.R. Prophylactic antibiotics in acute pancreatitis: Endless debate. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2017, 99, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulountsi, V.; Schizodimos, T. Use of antibiotics in acute pancreatitis: Ten major concerns. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.K.; Li, W.Q.; Ke, L.; Tong, Z.H.; Ni, H.B.; Li, G.; Zhang, L.Y.; Nie, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Ye, X.H.; et al. Early enteral nutrition prevents intra-abdominal hypertension and reduces the severity of severe acute pancreatitis compared with delayed enteral nutrition: A prospective pilot study. World J. Surg. 2013, 37, 2053–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, M.S.; Pylypchuk, R.D.; Uchugina, A.F. A systematic review on the timing of artificial nutrition in acute pancreatitis. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 101, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, T.; Dong, L.M.; Zhao, X.; Xiong, J.X.; Zhou, F.; Tao, J.; Cui, J.; Yang, Z.Y. Minimally invasive percutaneous catheter drainage versus open laparotomy with temporary closure for treatment of abdominal compartment syndrome in patients with early-stage severe acute pancreatitis. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technolog. Med. Sci. 2016, 36, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, B.; Zureikat, A.; Hughes, S.J.; Moser, A.J.; Yadav, D.; Zeh, H.J.; Lee, K.K. Abdominal compartment syndrome is an early, lethal complication of acute pancreatitis. Am. Surg. 2013, 79, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.A., Jr.; Eddy, V.A.; Blinman, T.A.; Rutherford, E.J.; Sharp, K.W. The staged celiotomy for trauma. Issues in unpacking and reconstruction. Ann. Surg. 1993, 217, 576–584; discussion 584–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L.; Ni, H.B.; Tong, Z.H.; Li, W.Q.; Li, N.; Li, J.S. The importance of timing of decompression in severe acute pancreatitis combined with abdominal compartment syndrome. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013, 74, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henn, J.; Lingohr, P.; Branchi, V.; Semaan, A.; von Websky, M.W.; Glowka, T.R.; Kalff, J.C.; Manekeller, S.; Matthaei, H. Open Abdomen Treatment in Acute Pancreatitis. Front. Surg. 2020, 7, 588228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebert, M.; Le Fouler, A.; Sitbon, N.; Cohen, J.; Abba, J.; Poupardin, E. Management of abdominal compartment syndrome in acute pancreatitis. J. Visc. Surg. 2021, 158, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Yang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, J.; Zhou, F. Diagnosis and management of severe acute pancreatitis complicated with abdominal compartment syndrome. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technolog. Med. Sci. 2003, 23, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Waele, J.J.; Hoste, E.; Blot, S.I.; Decruyenaere, J.; Colardyn, F. Intra-abdominal hypertension in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. Crit. Care 2005, 9, R452–R457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Radenkovic, D.V.; Johnson, C.D.; Milic, N.; Gregoric, P.; Ivancevic, N.; Bezmarevic, M.; Bilanovic, D.; Cijan, V.; Antic, A.; Bajec, D. Interventional Treatment of Abdominal Compartment Syndrome during Severe Acute Pancreatitis: Current Status and Historical Perspective. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 5251806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, S.; Kagami, T.; Tani, S.; Uotani, T.; Yamade, M.; Hamaya, Y.; Morita, Y.; Sakaguchi, T.; Osawa, S.; Sugimoto, K. Decompressive laparotomy for abdominal compartment syndrome resulting from severe acute pancreatitis: A case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheatham, M.L.; Fowler, J.; Pappas, P. Subcutaneous linea alba fasciotomy: A less morbid treatment for abdominal compartment syndrome. Am. Surg. 2008, 74, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchesne, J.C.; Howell, M.P.; Eriksen, C.; Wahl, G.M.; Rennie, K.V.; Hastings, P.E.; McSwain, N.E., Jr.; Malbrain, M.L. Linea alba fasciotomy: A novel alternative in trauma patients with secondary abdominal compartment syndrome. Am. Surg. 2010, 76, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Kamidani, R.; Okada, H.; Nakashima, Y.; Yamaji, F.; Fukuta, T.; Yoshida, T.; Yoshida, S.; Ogura, S. Midline fasciotomy for severe acute pancreatitis with abdominal compartment syndrome: Case report. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 79, 104081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppaniemi, A.; Hienonen, P.; Mentula, P.; Kemppainen, E. Subcutaneous linea alba fasciotomy, does it really work? Am. Surg. 2011, 77, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.K.; Du, X.J.; Li, A.; Ke, N.W.; Hu, W.M. A minimally invasive management for abdominal compartment syndrome in severe acute pancreatitis. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 29, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waele, J.J.; Kimball, E.; Malbrain, M.; Nesbitt, I.; Cohen, J.; Kaloiani, V.; Ivatury, R.; Mone, M.; Debergh, D.; Bjorck, M. Decompressive laparotomy for abdominal compartment syndrome. Br. J. Surg. 2016, 103, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, M.; Benjamin, E.R.; Demetriades, D. Intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome. Curr. Probl. Surg. 2021, 58, 100971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartelli, M.; Abu-Zidan, F.M.; Ansaloni, L.; Bala, M.; Beltran, M.A.; Biffl, W.L.; Catena, F.; Chiara, O.; Coccolini, F.; Coimbra, R.; et al. The role of the open abdomen procedure in managing severe abdominal sepsis: WSES position paper. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2015, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leppaniemi, A. Surgical management of abdominal compartment syndrome; indications and techniques. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2009, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Vries Reilingh, T.S.; van Goor, H.; Charbon, J.A.; Rosman, C.; Hesselink, E.J.; van der Wilt, G.J.; Bleichrodt, R.P. Repair of giant midline abdominal wall hernias: “components separation technique” versus prosthetic repair : Interim analysis of a randomized controlled trial. World J. Surg. 2007, 31, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharrock, A.E.; Barker, T.; Yuen, H.M.; Rickard, R.; Tai, N. Management and closure of the open abdomen after damage control laparotomy for trauma. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Injury 2016, 47, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zarnescu, N.O.; Dumitrascu, I.; Zarnescu, E.C.; Costea, R. Abdominal Compartment Syndrome in Acute Pancreatitis: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13010001
Zarnescu NO, Dumitrascu I, Zarnescu EC, Costea R. Abdominal Compartment Syndrome in Acute Pancreatitis: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleZarnescu, Narcis Octavian, Ioana Dumitrascu, Eugenia Claudia Zarnescu, and Radu Costea. 2023. "Abdominal Compartment Syndrome in Acute Pancreatitis: A Narrative Review" Diagnostics 13, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13010001
APA StyleZarnescu, N. O., Dumitrascu, I., Zarnescu, E. C., & Costea, R. (2023). Abdominal Compartment Syndrome in Acute Pancreatitis: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics, 13(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13010001






