Effects of Different Scan Duration on Brain Effective Connectivity among Default Mode Network Nodes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants in Study
2.2. Data Acquisition
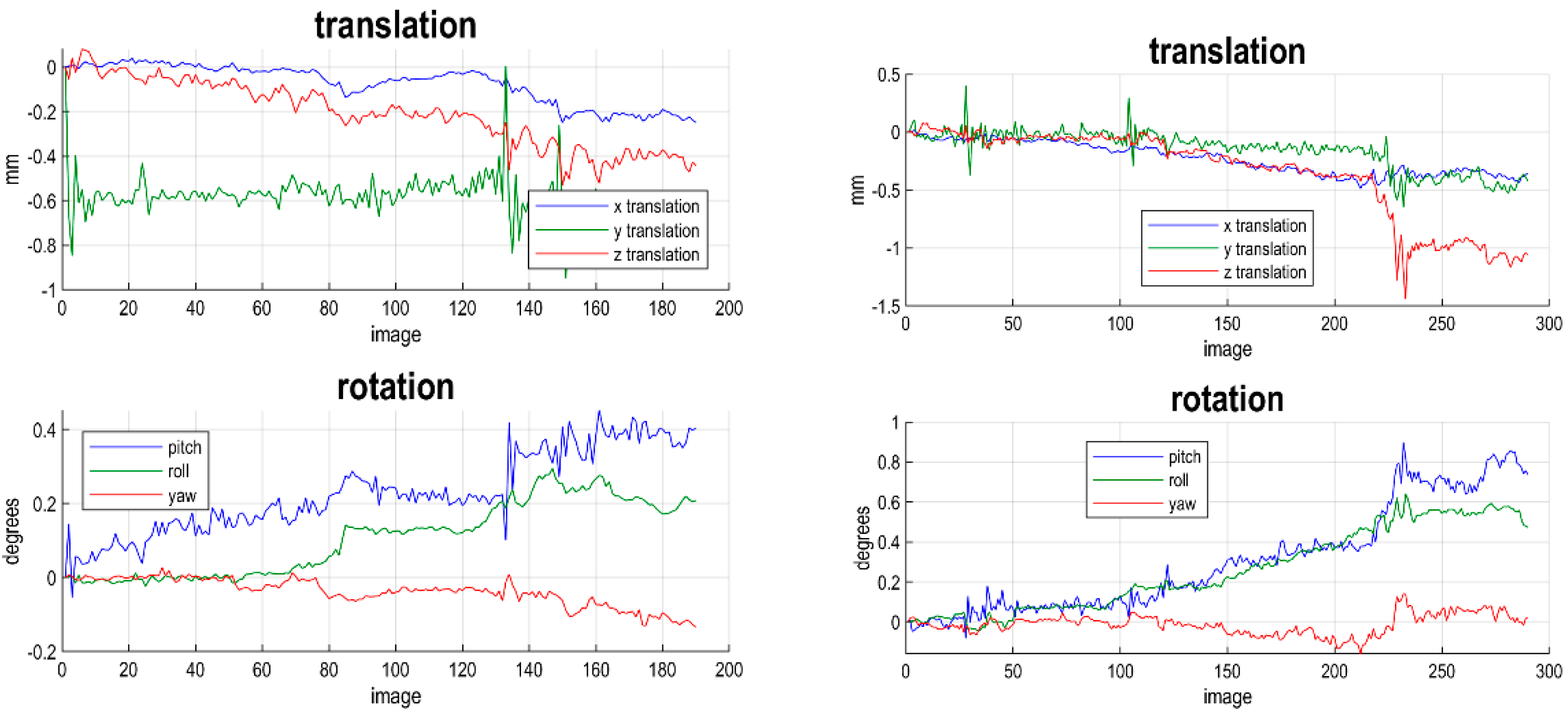
2.3. Pre-Processing
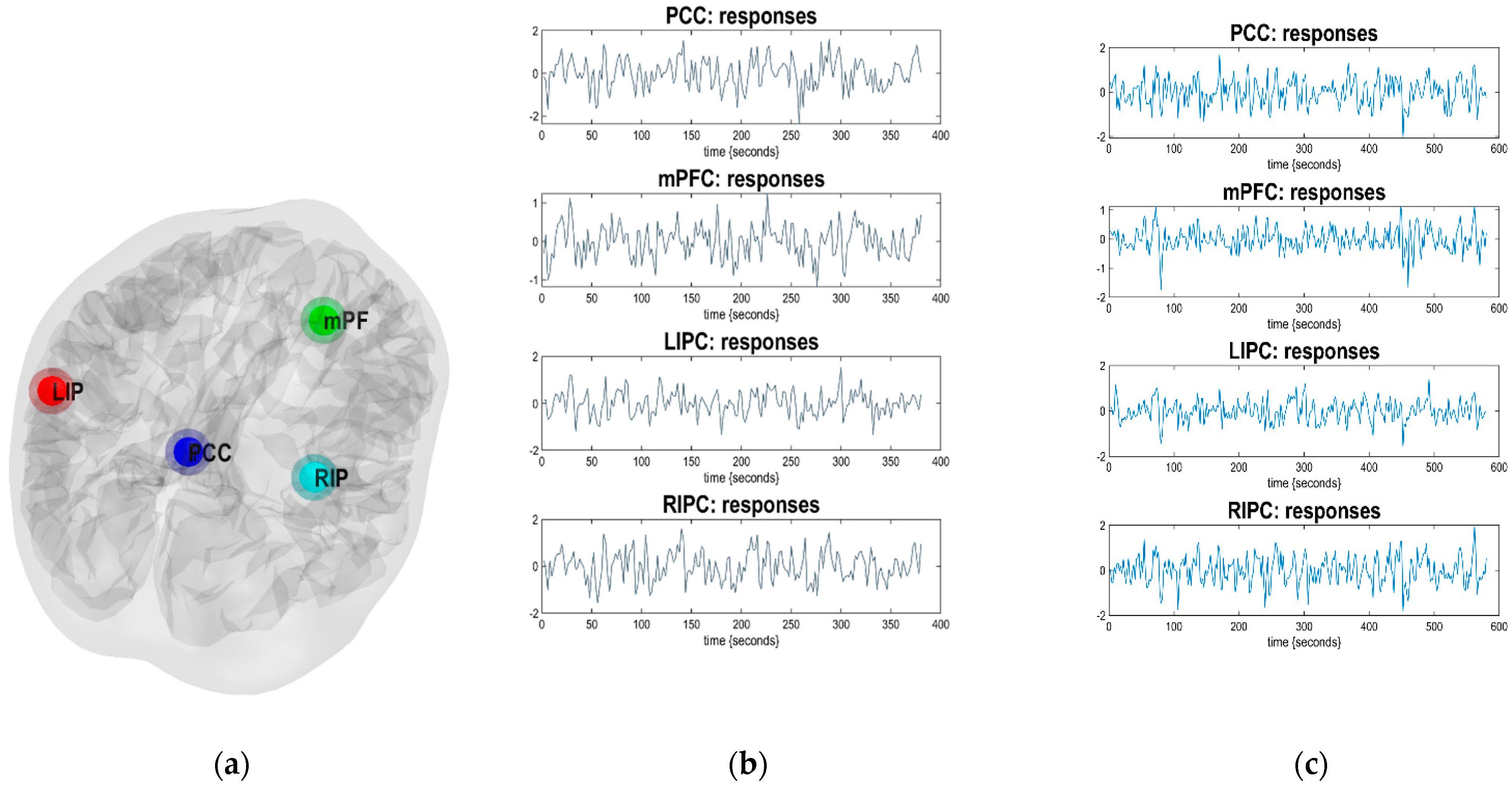
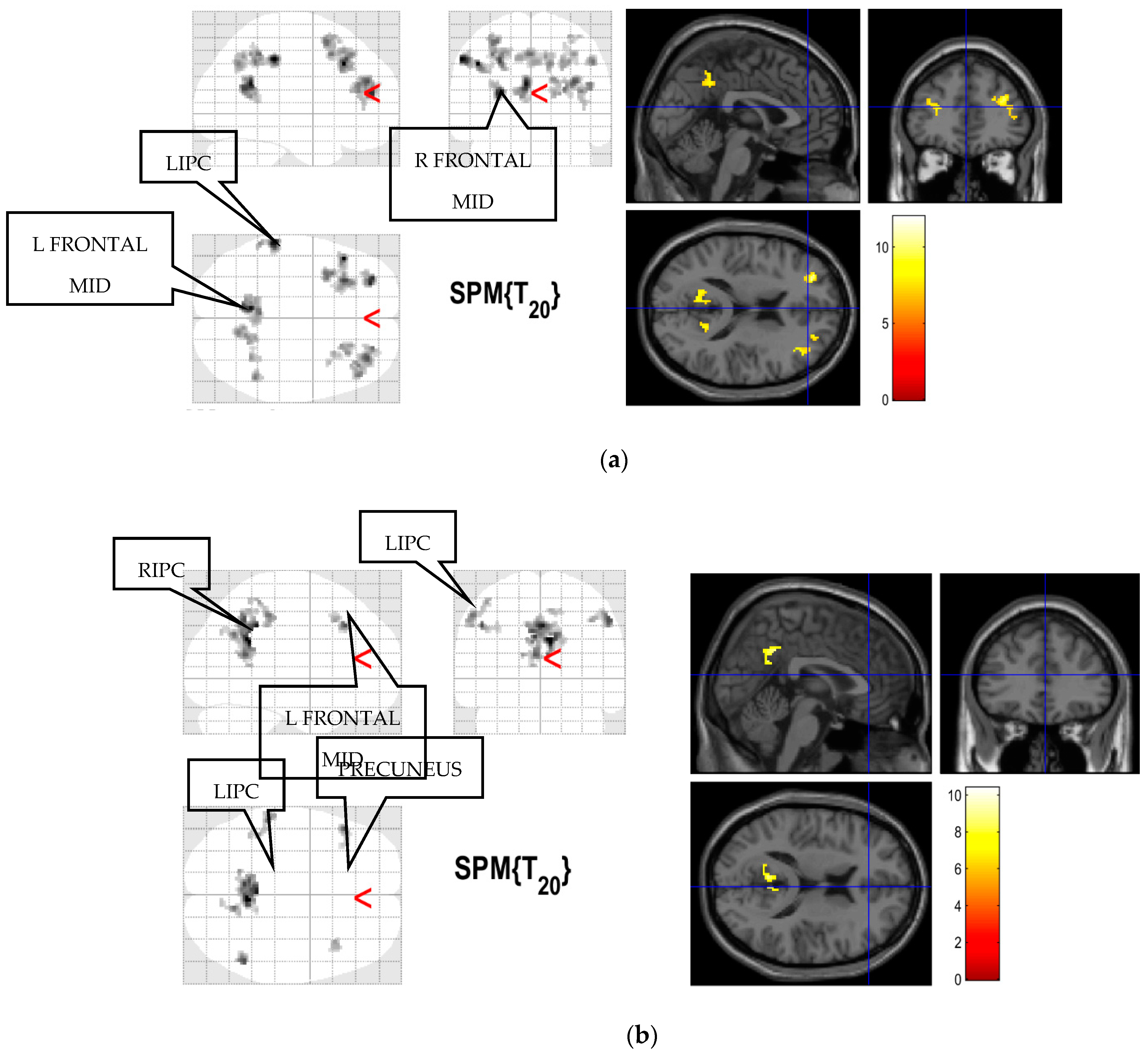
2.4. Selection of Regions of Interest
2.5. Modeling of Low-Frequency Fluctuations
2.6. Spectral Dynamic Causal Modeling
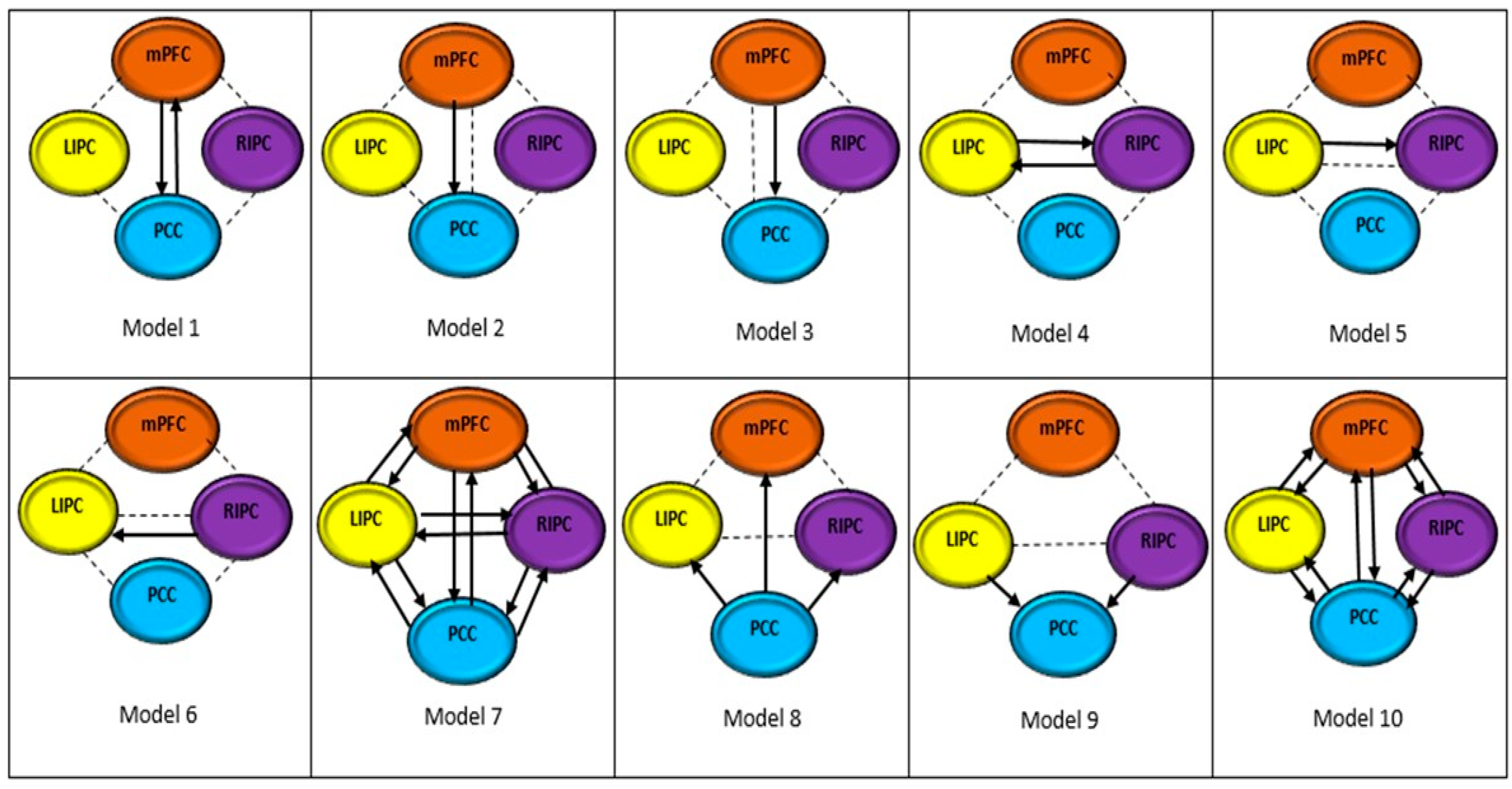
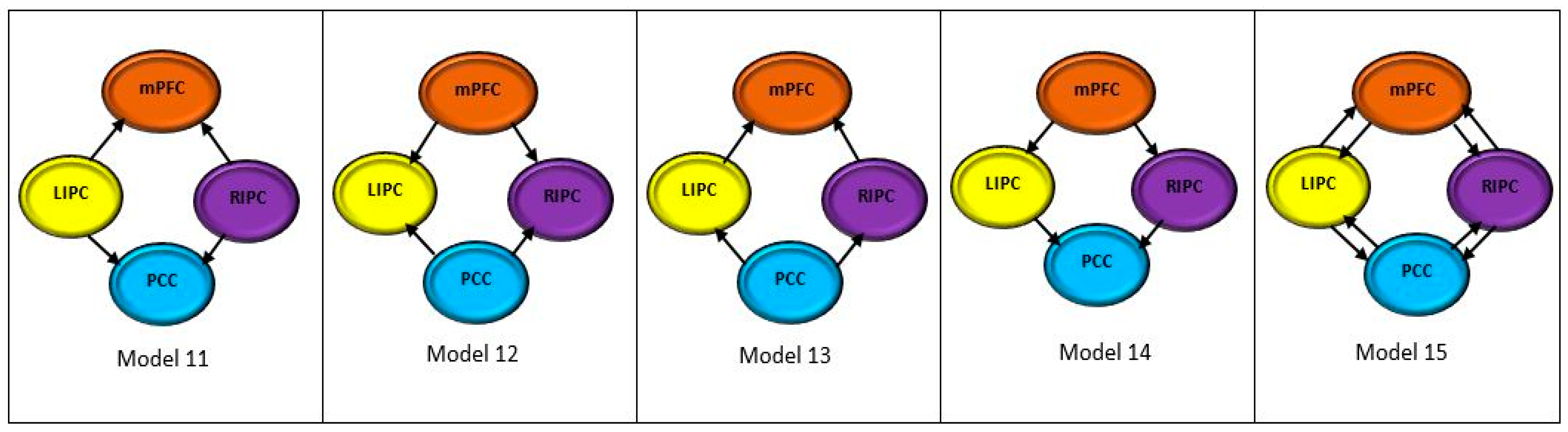
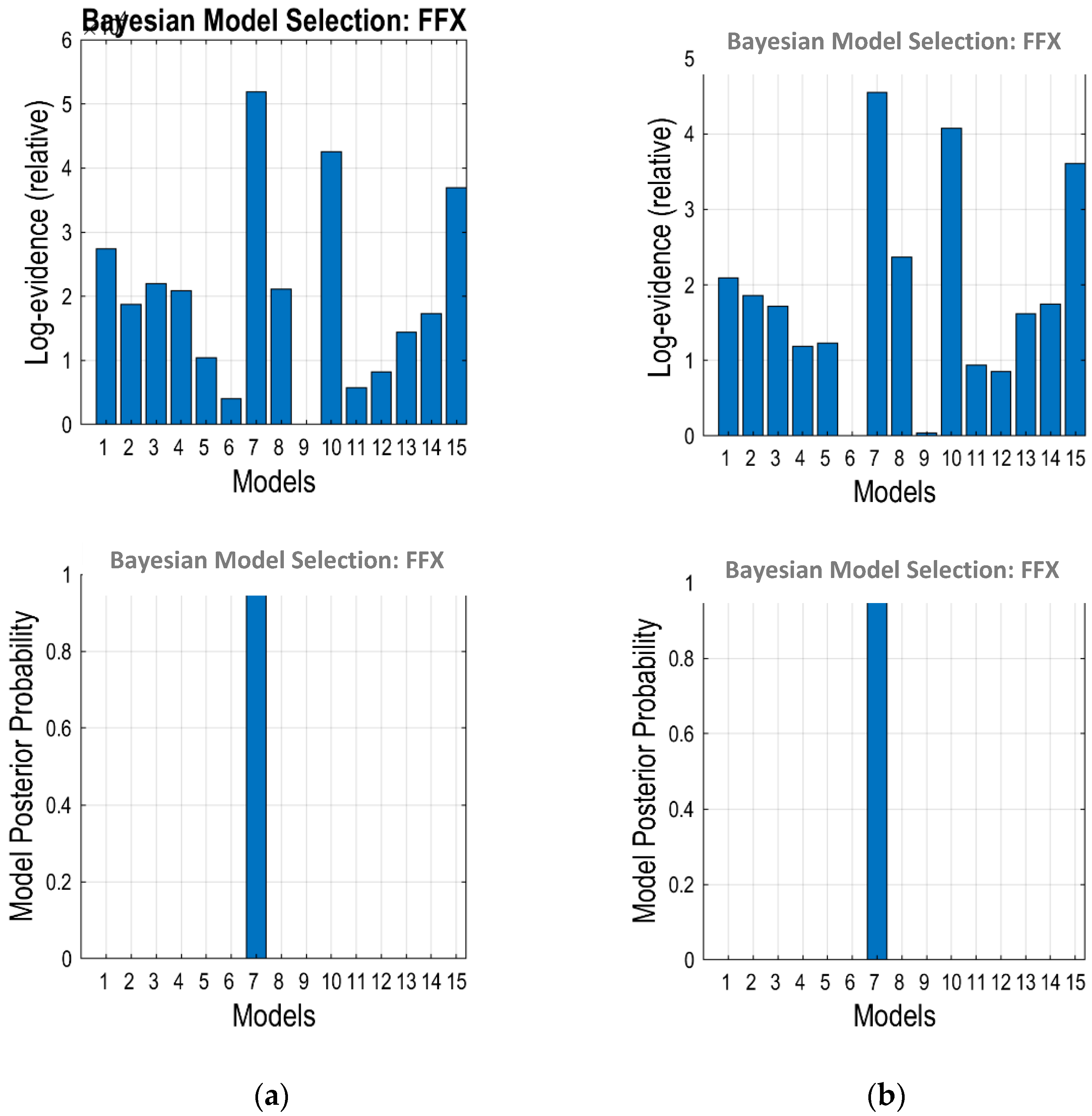
2.7. Bayesian Model Selection
2.8. Statistical Analysis on Effective Connectivity
2.9. Statistical Analysis on Brain Functional Connectivity
3. Results
3.1. Brain Functional Connectivity
3.2. Optimum Model
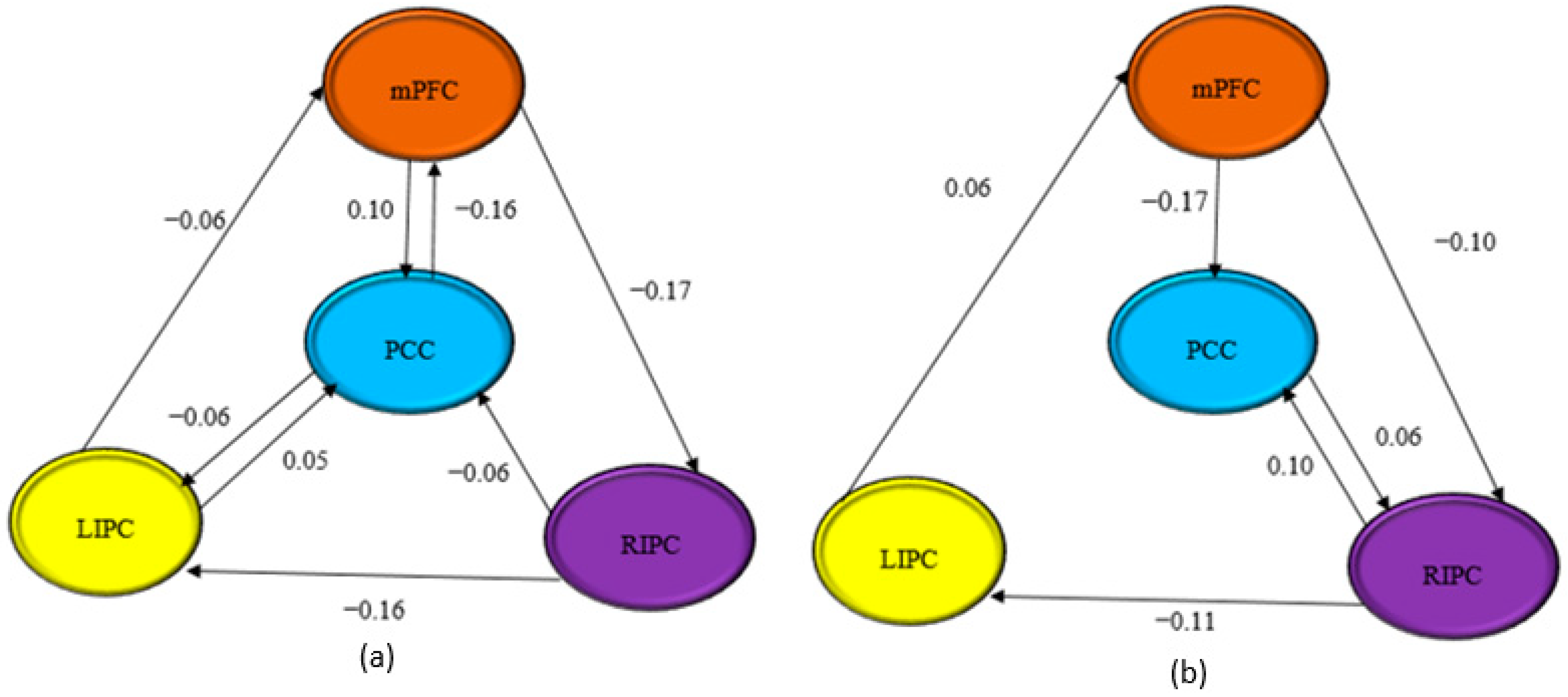
3.3. Effective Connectivity
3.4. Correlation Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghumman, S.; Fortin, D.; Noel-Lamy, M.; Cunnane, S.C.; Whittingstall, K. Exploratory study of the effect of brain tumors on the default mode network. J. Neurooncol. 2016, 128, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahyavi-Firouz-Abadi, N.; Pillai, J.J.; Lindquist, M.A.; Calhoun, V.D.; Agarwal, S.; Airan, R.D.; Caffo, B.; Gujar, S.K.; Sair, H.I. Presurgical Brain Mapping of the Ventral Somatomotor Network in Patients with Brain Tumors Using Resting-State fMRI. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, E.E.; Zeffiro, T.A. Why is Clinical fMRI in a Resting State? Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawi, N.M.; Rahmad, A.A.; Hamid, K.A.; Rahman, S.; Osman, S.S.; Surat, S.; Marzuki, M.A.; Chieng, Y.L.; Yusoff, A.N. Yusoff Effective Connectivity of a Default Mode Network In Human Brain: In Search of a Dominant Node Using Spectral Dynamic Causal Modeling. Phys. Technol. Med. Publ. Malays. Assoc. Med. Phys. 2020, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Scarapicchia, V.; Mazerolle, E.L.; Fisk, J.D.; Ritchie, L.J.; Gawryluk, J.R. Resting state BOLD variability in Alzheimer’s disease: A marker of cognitive decline or cerebrovascular status? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroll, H.; Zaharchuk, G.; Christen, T.; Heit, J.J.; Iv, M. Resting-State BOLD MRI for Perfusion and Ischemia. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 26, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.A.; See, A.P.; Essayed, W.I.; Golby, A.J.; Tie, Y. Challenges and techniques for presurgical brain mapping with functional MRI. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 17, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, M.G.; Price, S.J.; Suckling, J. Functional connectivity networks for preoperative brain mapping in neurosurgery. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 126, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierker, D.; Roland, J.L.; Kamran, M.; Rutlin, J.; Hacker, C.D.; Marcus, D.S.; Milchenko, M.; Miller-Thomas, M.M.; Benzinger, T.L.; Snyder, A.Z.; et al. Resting-state Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Presurgical Functional Mapping. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2017, 27, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maesawa, S.; Bagarinao, E.; Fujii, M.; Futamura, M.; Motomura, K.; Watanabe, H.; Mori, D.; Sobue, G.; Wakabayashi, T. Evaluation of Resting State Networks in Patients with Gliomas: Connectivity Changes in the Unaffected Side and Its Relation to Cognitive Function. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manan, H.A.; Franz, E.A.; Yahya, N. The utilisation of resting-state fMRI as a pre-operative mapping tool in patients with brain tumours in comparison to task-based fMRI and intraoperative mapping: A systematic review. Eur. J. Cancer Care (Engl.) 2021, 30, e13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manan, H.A.; Franz, E.A.; Yahya, N. Functional connectivity changes in patients with brain tumours—A systematic review on resting state-fMRI. Neurol. Psychiatry Brain Res. 2020, 36, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuovinen, N.; de Pasquale, F.; Caulo, M.; Caravasso, C.F.; Giudice, E.; Miceli, R.; Ingrosso, G.; Laprie, A.; Santoni, R.; Sabatini, U. Transient effects of tumor location on the functional architecture at rest in glioblastoma patients: Three longitudinal case studies. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohan, A.; Roberto, A.J.; Mohan, A.; Lorenzo, A.; Jones, K.; Carney, M.J.; Liogier-Weyback, L.; Hwang, S.; Lapidus, K.A.B. The Significance of the Default Mode Network (DMN) in Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Disorders: A Review. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2016, 89, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, B.; Suppiah, S.; Ibrahim, N.; Mohamad, M.; Hassan, H.A.; Nasser, N.S.; Saripan, M.I. Diagnostic power of resting-state fMRI for detection of network connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 2941–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Biswal, B.B. Identifying the default mode network structure using dynamic causal modeling on resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage 2014, 86, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yusoff, A.N.; Abdul Hamid, K.; Rahman, S.; Osman, S.S.; Surat, S.; Marzuki, M.A. Resting State Effective Connectivity between Inferior Parietal Lobe (IPL) and Inferior Temporal Gyrus (ITG) in the Left and Right Hemispheres. J. Sains Kesihat. Malays. 2018, 16, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, E.; Yusoff, A.N.; Mohamad, M.; Abdul Manan, H.; Giampietro, V.; Abd Hamid, A.I.; Dzulkifli, M.A.; Osman, S.S.; Wan Burhanuddin, W.I.D. Low intensity white noise improves performance in auditory working memory task: An fMRI study. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catalino, M.P.; Yao, S.; Green, D.L.; Laws, E.R.; Golby, A.J.; Tie, Y. Mapping cognitive and emotional networks in neurosurgical patients using resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurg. Focus 2020, 48, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Li, B.; Bai, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Leung, H.-C.; Tian, P.; Zhang, L.; Guo, F.; Cui, L.-B.; et al. Abnormal resting state effective connectivity within the default mode network in major depressive disorder: A spectral dynamic causal modeling study. Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Castañeda, C.; de Pasquale, F.; Caravasso, C.F.; Marano, M.; Maffi, S.; Migliore, S.; Sabatini, U.; Squitieri, F. Resting-state connectivity and modulated somatomotor and default-mode networks in Huntington disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2017, 23, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Liang, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, J. Cerebral functional activity and connectivity changes in anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis: A resting-state fMRI study. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 25, 102189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharaev, M.G.; Zavyalova, V.V.; Ushakov, V.L.; Kartashov, S.I.; Velichkovsky, B.M. Effective Connectivity within the Default Mode Network: Dynamic Causal Modeling of Resting-State fMRI Data. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Müller, N.C.J.; Dresler, M.; Janzen, G.; Beckmann, C.F.; Fernández, G.; Kohn, N. Medial prefrontal decoupling from the default mode network benefits memory. Neuroimage 2020, 210, 116543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euston, D.R.; Gruber, A.J.; McNaughton, B.L. The Role of Medial Prefrontal Cortex in Memory and Decision Making. Neuron 2012, 76, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schouwenaars, I.T.; De Dreu, M.J.; Rutten, G.J.M.; Ramsey, N.F.; Jansma, J.M. A functional MRI study of presurgical cognitive deficits in glioma patients. Neuro-Oncol. Pract. 2021, 8, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, E.A.; Yusoff, A.N.; Mohamad, M.; Abdul Manan, H.; Abd Hamid, A.I.; Dzulkifli, M.A.; Osman, S.S.; Wan Burhanuddin, W.I.D. Resting-state fMRI: Comparing default mode network connectivity between normal and low auditory working memory groups. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1248, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birn, R.M.; Molloy, E.K.; Patriat, R.; Parker, T.; Meier, T.B.; Kirk, G.R.; Nair, V.A.; Meyerand, M.E.; Prabhakaran, V. The effect of scan length on the reliability of resting-state fMRI connectivity estimates. Neuroimage 2013, 83, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dijk, K.R.A.; Hedden, T.; Venkataraman, A.; Evans, K.C.; Lazar, S.W.; Buckner, R.L. Intrinsic functional connectivity as a tool for human connectomics: Theory, properties, and optimization. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 103, 297–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.S.; Ferguson, M.A.; Lopez-Larson, M.; Yurgelun-Todd, D. Reproducibility of Single-Subject Functional Connectivity Measurements. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braun, U.; Plichta, M.M.; Esslinger, C.; Sauer, C.; Haddad, L.; Grimm, O.; Mier, D.; Mohnke, S.; Heinz, A.; Erk, S.; et al. Test–retest reliability of resting-state connectivity network characteristics using fMRI and graph theoretical measures. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friston, K.J.; Kahan, J.; Biswal, B.; Razi, A. A DCM for resting state fMRI. Neuroimage 2014, 94, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, P.; Zang, Y.; Hummel, C.; Faria, V.; Hummel, T. Short or long runs: An exploratory study of odor-induced fMRI design. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razi, A.; Kahan, J.; Rees, G.; Friston, K.J. Construct validation of a DCM for resting state fMRI. Neuroimage 2015, 106, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biswal, B.; Yetkin, F.Z.; Haughton, V.M.; Hyde, J.S. Functional Connectivity in the Motor Cortex of Resting. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 34, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, K.R.A.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Buckner, R.L. The influence of head motion on intrinsic functional connectivity MRI. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigoux, L.; Stephan, K.E.; Friston, K.J.; Daunizeau, J. Bayesian model selection for group studies — Revisited. Neuroimage 2014, 84, 971–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, K.E.; Penny, W.D.; Daunizeau, J.; Moran, R.J.; Friston, K.J. Bayesian model selection for group studies. Neuroimage 2009, 46, 1004–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davey, C.G.; Pujol, J.; Harrison, B.J. Mapping the self in the brain’s default mode network. Neuroimage 2016, 132, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Wang, X.; Yao, S.; Hu, D.; Friston, K. Task-dependent modulation of effective connectivity within the default mode network. Front. Psychol. 2012, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, Q.; Lu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, K.; Ding, M.; Liu, Y. Granger causal influence predicts BOLD activity levels in the default mode network. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2011, 32, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, M.D.; Snyder, A.Z.; Vincent, J.L.; Corbetta, M.; Van Essen, D.C.; Raichle, M.E. From The Cover:The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9673–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esposito, R.; Mattei, P.A.; Briganti, C.; Romani, G.L.; Tartaro, A.; Caulo, M. Modifications of Default-Mode Network Connectivity in Patients with Cerebral Glioma. PLoS One 2012, 7, e40231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Lu, Y.; He, Y.; Tian, L. Regional homogeneity approach to fMRI data analysis. Neuroimage 2004, 22, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.-N.; Xu, T.; Jiang, L.; Yang, Z.; Cao, X.-Y.; He, Y.; Zang, Y.-F.; Castellanos, F.X.; Milham, M.P. Toward reliable characterization of functional homogeneity in the human brain: Preprocessing, scan duration, imaging resolution and computational space. Neuroimage 2013, 65, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szameitat, A.J.; Shen, S.; Sterr, A. The functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) procedure as experienced by healthy participants and stroke patients - A pilot study. BMC Med. Imaging 2009, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadidi, D.N.N.; Cullen, D.K.R.; Hall, M.L.M.J.; Lindquist, D.R.; Buckwalter, D.K.C.; Mathews, M.E. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging as Experienced by Stroke Survivors. Res. Gerontol. Nurs. 2014, 176, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Parameters | Data |
|---|---|
| Gender (M/F) | 15/6 |
| Average age/years | 31.90 ± 1.77 |
| Age range/years | 21 to 60 years old |
| Handedness (R/L) | 17/4 |
| 10 min | 15 min | 10 min | 15 min | 10 min | 15 min | 10 min | 15 min | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMA | From PCC | From PCC | From mPFC | From mPFC | From LIPC | From LIPC | From RIPC | From RIPC |
| to PCC | −0.6887 | −0.8715 | 0.1023 | −0.1741 | 0.0530 | 0.0404 | −0.0575 | 0.0980 |
| to mPFC | −0.1626 | 0.0064 | −0.7410 | −0.5223 | −0.0561 | 0.0573 | 0.0301 | −0.0099 |
| to LIPC | −0.0554 | −0.0384 | −0.0427 | −0.0248 | −0.8941 | −1.0364 | −0.1556 | −0.1129 |
| to RIPC | 0.0397 | 0.0628 | −0.1739 | −0.0975 | −0.0258 | −0.0194 | −0.8883 | −0.4539 |
| Effective Connectivity 10 min vs. 15 min Scanning Time | Pearson Correlation (r) | R2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCC → mPFC | 0.418 | 0.175 | 0.059 |
| PCC → LIPC | 0.204 | 0.042 | 0.374 |
| PCC → RIPC | 0.350 | 0.122 | 0.120 |
| mPFC → PCC | −0.373 | 0.139 | 0.096 |
| mPFC →LIPC | 0.303 | 0.092 | 0.182 |
| mPFC → RIPC | −0.101 | 0.010 | 0.064 |
| LIPC → PCC | 0.420 | 0.177 | 0.058 |
| LIPC → mPFC | 0.348 | 0.121 | 0.123 |
| LIPC → RIPC | 0.495 | 0.245 | 0.022 |
| RIPC → PCC | 0.486 | 0.236 | 0.026 |
| RIPC → mPFC | 0.063 | 0.004 | 0.788 |
| RIPC → LIPC | 0.524 | 0.275 | 0.015 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdul Wahab, N.S.; Yahya, N.; Yusoff, A.N.; Zakaria, R.; Thanabalan, J.; Othman, E.; Bee Hong, S.; Athi Kumar, R.K.; Manan, H.A. Effects of Different Scan Duration on Brain Effective Connectivity among Default Mode Network Nodes. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051277
Abdul Wahab NS, Yahya N, Yusoff AN, Zakaria R, Thanabalan J, Othman E, Bee Hong S, Athi Kumar RK, Manan HA. Effects of Different Scan Duration on Brain Effective Connectivity among Default Mode Network Nodes. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(5):1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051277
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdul Wahab, Nor Shafiza, Noorazrul Yahya, Ahmad Nazlim Yusoff, Rozman Zakaria, Jegan Thanabalan, Elza Othman, Soon Bee Hong, Ramesh Kumar Athi Kumar, and Hanani Abdul Manan. 2022. "Effects of Different Scan Duration on Brain Effective Connectivity among Default Mode Network Nodes" Diagnostics 12, no. 5: 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051277
APA StyleAbdul Wahab, N. S., Yahya, N., Yusoff, A. N., Zakaria, R., Thanabalan, J., Othman, E., Bee Hong, S., Athi Kumar, R. K., & Manan, H. A. (2022). Effects of Different Scan Duration on Brain Effective Connectivity among Default Mode Network Nodes. Diagnostics, 12(5), 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051277







