Abstract
Mediastinal lymphadenopathy is a condition in which one or more mediastinal lymph nodes are enlarged for malignant or benign causes, generally more than 10 mm. For a long time, the only way to approach the mediastinum was surgery, while in last decades endoscopic techniques gained their role in neoplastic diseases. At the present time, EBUS is the technique of choice for studying the mediastinum in the suspicion of cancer, while there are not strong indications in guidelines for the study of benign mediastinal lymphadenopathy. We reviewed the literature, looking for evidence of the role of EBUS in the diagnostics of non-neoplastic mediastinal lymphadenopathy, with special regard for granulomatous disease, both infectious and non-infectious. EBUS is a reliable alternative to surgery in non-neoplastic mediastinal lymphadenopathy, even if more evidence is needed for granulomatous diseases other than tuberculosis and sarcoidosis.
1. Introduction
The term “lymphadenopathy” refers to a condition in which one or more lymph nodes are enlarged for a known or unknown cause, generally for the hyperplasia of one or more cell types [1]. Studying mediastinal lymph nodes has always been challenging because of their position and the relative difficulty in reaching the mediastinal structure. Formerly surgery was the only way to access them: the main surgical procedures used were parasternal mediastinotomy and some mini-invasive surgical procedures such as extended cervical mediastinoscopy (ECM), video-assisted mediastinoscopy (VAM), and video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) [2,3]. However, mediastinal surgery is burdened by some potential life-threatening complications, such as bleeding, mediastinitis, pneumothorax, and/or subcutaneous emphysema, and rarely damage to adjacent organs [2].
Between the 1980s and 1990s, the endoscopic study of the mediastinum was studied and developed, which gained progressive importance for its minimal invasiveness and a minor rate of complications compared with surgery, in addition to a good accuracy. Endoscopic mediastinal procedures using ultrasound are represented by endoscopic (transoesophageal) ultrasound (EUS) and endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) [2].
The main aims in studying mediastinal lymph nodes are the diagnosis and staging of malignancies, especially lymphomas and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLCs), as well as metastases from other organs’ tumours (oesophago-gastric cancer [4,5], thyroid cancer [6], seminoma [7], breast cancer [8]).
Mediastinal lymph nodes’ alterations may also be due to benign diseases, including infectious or inflammatory diseases such as tuberculosis or sarcoidosis, which are the principal causes. The purpose of the present review is to examine the role and the diagnostic yield of endobronchial ultrasound in studying benign mediastinal lymphadenopathy.
2. Mediastinal Lymph Nodes Stations
The mediastinum is an anatomic compartment placed at the middle of the thoracic cavity, extending from diaphragm to superior thoracic inlet in continuity with neck structures, inside which are included all the thoracic organs except for lungs and pleurae. There is not a universally accepted partition; however, more often it is divided in three parts named anterior, middle, and posterior mediastinum. Some authors identify also a “superior” mediastinum. The anterior or prevascular mediastinum extends from the superior thoracic inlet to the site of connection of the heart with the thoracic wall; the middle mediastinum is the space containing the heart and great vessels; the posterior or postvascular mediastinum is delimited anteriorly by the posterior face of the pericardium and great vessels and posteriorly by the anterior face of the vertebral bodies. The superior mediastinum may be defined as the region above an imaginary line extending from the sternal angle or above the aortic arch [9,10]. All of these compartments contain lymph nodes. A nodal map is provided by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) [11], which divides mediastinal lymph nodes into fourteen stations, classified by their anatomical position. A “R” or a “L” is added to specify whether they are on the right or on the left side, respectively, as well as “A” and “P” are for “anterior” or “posterior” (Figure 1).
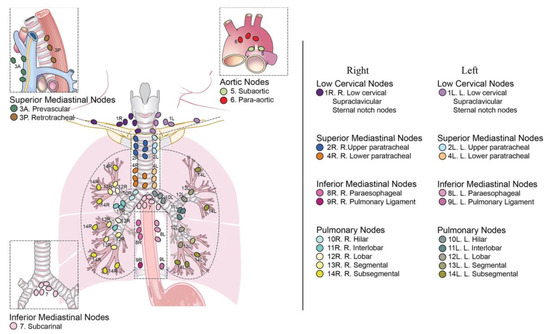
Figure 1.
IASLC mediastinal lymph node map, courtesy of El-Sherief et al. [11].
- Supraclavicular region contains the supraclavicular, low cervical, and sternal notch lymph nodes, named stations 1R and 1L;
- Upper zone (superior mediastinum region) contains the right and left upper paratracheal lymph nodes (stations 2R and 2L), prevascular lymph nodes (station 3A), retrotracheal lymph nodes (station 3P), and right and left paratracheal lymph nodes (stations 4R and 4L);
- Aortopulmonary zone contains the subaortic (station 5) and paraaortic (station 6) lymph nodes;
- Subcarinal zone contains the subcarinal lymph node (station 7);
- Lower zone contains the paraesophageal (station 8) and pulmonary ligament (station 9) lymph nodes;
- Hilar and interlobar zone contains the hilar (station 10) and interlobar (station 11) lymph nodes;
- Peripheral zone refers to pulmonary nodes, and includes the lobar (station 12), segmental (station 13), and subsegmental (station 14) lymph nodes.
All of the lymph node stations described may be studied with both non-invasive and invasive or minimally invasive techniques.
3. Studying Mediastinal Lymph Nodes
3.1. Non-Invasive Techniques
Non-invasive techniques are represented by imaging studies.
3.1.1. Chest Radiography
Chest radiography is a less sensitive exam. It can identify lymph node enlargement when it causes an alteration in the mediastinal contour, but it must be completed with further exams. A normal chest radiograph in a patient with signs of mediastinal mass or suspected of a disease involving the mediastinum does not exclude diagnosis, and so it should be avoided as a first-line exam [12].
3.1.2. CT
Computed tomography (CT) has dramatically changed the non-invasive study of mediastinal lymph nodes. Compared with chest radiography, it allows precise evaluation of the size, shape, extension, localization, and relation with adjacent organs [13]. The diameter of most of thoracic lymph nodes is less than 10 mm, and when this diameter is increased, a neoplastic or inflammatory/infective disease must be excluded, even if lymphadenopathy may be subsequent also to pulmonary hypertension and cardiac failure [14]. Additionally, the shape may suggest the malignant nature of the lymphadenopathy. Differences in attenuation and density may enhance suspicion of the nature of the lymphadenopathy, but in most cases, it must be confirmed by histological sampling [10].
3.1.3. MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the mediastinum allows the avoidance of ionizing radiations and the acquisition of multiplanar images, together with the possibility of administering liquid of contrast even in nephropathic patients; nevertheless, the prolonged time for the acquisition of the images, which may be disturbed by artifacts due to cardiac and respiratory movements, and the inferior yield in studying pulmonary parenchyma affects the advantages. Indications of MRI in mediastinal study are limited, and it should probably be reserved only in those patients who cannot undergo CT or in whom post-contrast CT is inconclusive [15].
3.1.4. PET and PET/CT
18-Fluorodesoxyglucose positron emission tomography (18FDG-PET) provides information about activity and behaviour of lymph nodes, integrating information about the size and shape provided by CT (PET/CT). However, it is not quite sensitive, for both neoplastic and inflammatory lymph nodes may pick up FDG. As for the CT, the diagnostic yield is impaired by lymph node dimension, with higher rate of false negative exams when lymph node diameter is <10 mm [16].
3.2. Endoscopic Minimally Invasive Techniques
Ultrasound allows the study of the architecture [17], perfusion [18], resistance index, and elasticity of lymph nodes [19]. Nakajima et al. described also a ultrasonographic vascular pattern classification ranging between grade 0, which means no blood flow, to grade 3, which means more than four vessels and/or twist helical flow signal [20]. Endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) is currently indicated as the first-line exam in staging mediastinal lymph nodes in NSCLC [21,22,23], but several studies demonstrated a sensitivity and specificity equivalent to mediastinoscopy in the evaluation of thoracic lymph nodes enlargement [24,25,26,27]; the positive rate seems to decrease in the elderly, but with maintained specimen quality and safety [28]. Its diagnostic yield is enhanced by ancillary techniques such as rapid onsite evaluation (ROSE), which should evaluate the sample for the presence of lymphocytes and material from lesion [27,29]; Plit et al. demonstrated a positive predictive value of 97.7% for EBUS-TBNA plus ROSE in diagnosing sarcoidosis [30]. Many other randomized trials compared in a meta-analysis demonstrated no increase in diagnostic accuracy with ROSE [26], so at the present time, guidelines do not suggest its use after every procedure; however, it can reduce complications by reducing the number of passages needed for diagnosis [31,32,33,34]. Furthermore, there is evidence that a trained pulmonologist can correctly assess the material obtained [35]. Cell block, another ancillary technique, may improve the diagnostic yield of EBUS-TBNA in sarcoidosis [36]. In Figure 2 is shown a granuloma sampled with EBUS-TBNA and stained with Diff Quick for rapid on-site evaluation.
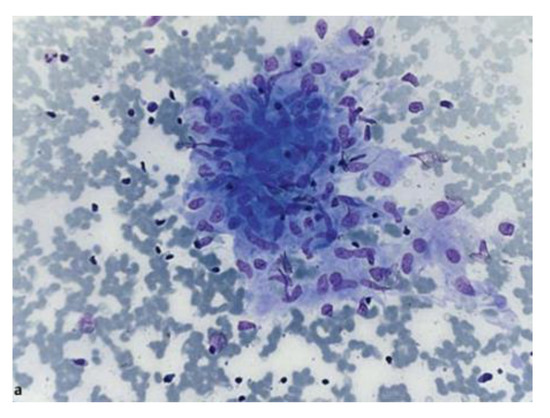
Figure 2.
Cytological sample showing loosely aggregated epithelioid cells without necrosis, stained in Diff Quick for rapid on-site evaluation. Courtesy of von Bartheld et al. [37] who own the copyright.
EBUS allows cytological or histological samples (for example via mini-forceps [38]) to be reached, evaluated, and obtained from central masses or lymph nodes localized near the trachea and principal bronchi. It can be realized with radial or longitudinal (convex) probes. Radial probes provide a 360-degree view, with higher definition of the layers of the bronchial wall, thus also allowing evaluation of an eventual infiltration of the structures. Radial probes (which may be classified also in central and peripheral probes on the base of the MHz) are placed within the operative channel of a flexible or rigid bronchoscope inside a guide-sheath. However, a radial probe does not allow real-time sampling. Longitudinal probes allow real-time transbronchial needle aspiration (TBNA): they are placed on the tip of the bronchoscope and provide a 90-degree angled view of what is parallel to the bronchoscope shaft. Usually, they use a frequency of 7–7.5 MHz; Doppler and elastography may be implemented. Some authors suggest sampling each lymph node at least twice [39,40], while others at least thrice [27,36,41].
Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is performed via transoesophageal access and allows central masses and lymph node sampling with a fine needle aspiration technique. Its role is complementary to EBUS because it can sample lymph node stations localized far from the carina (stations 8 and 9); also, via EUS it is possible to reach adrenal gland metastasis (Figure 3).
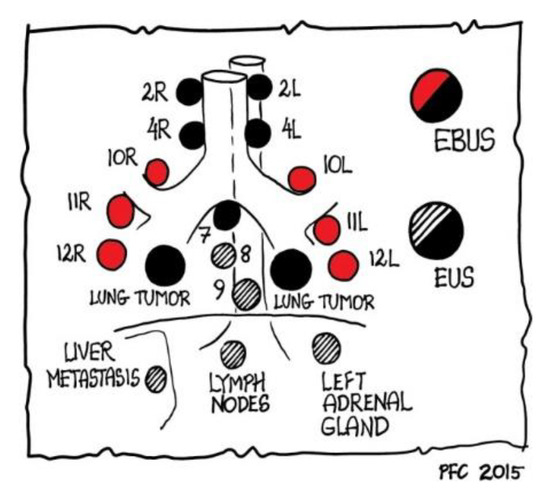
Figure 3.
Role of EBUS and EUS in reaching mediastinal lymph nodes, as outlined by Paul Clementsen [2] who is the owner of the copyright.
The two of them are efficient and safe: the diagnostic yield in investigating a generic mediastinal lymphadenopathy has been calculated to be 88% for EUS-FNA and 92% for EBUS-TBNA [42], with a mortality rate inferior to 1% (0% for EUS-FNA and 0–0.8% for EBUS-TBNA, individually); Santos et al. reported a general diagnostic yield for EBUS-TBNA in isolated mediastinal lymphadenopathy of 77.6% [43]. In addition, the morbidity rate is 0–2.3% for EUS-FNA and 0–1.2% for EBUS-TBNA [2,42,44]. Kuo et al. demonstrated on a sample of 83 patients who underwent EBUS-TBNA a very similar diagnostic yield for malignant and non-malignant diseases [39,45]. Independent predictors of better predictive value are short diameter of lymph node >16.5 millimetres and sampling mediastinal lymph nodes rather than hilar ones [39]. Among granulomatous diseases, the diagnostic accuracy of EBUS-TBNA is reported to range between 74.5% and 96% [39,46,47,48,49,50]. The sensitivity, diagnostic accuracy, and negative predictive value of EBUS-TBNA in patients with a previous negative conventional TBNA are 87.8%, 90.1%, and 65.7%, respectively [51]. Shen et al. showed that EBUS-TBNA compared with conventional TBNA has a greater diagnostic yield both for granulomatous and non-granulomatous benign lymphadenopathy, especially when the diameter of the lymph node sampled was lower than 20 mm [52]. In a single centre study conducted on 100 patients, the use of EBUS-transbronchial fine needle biopsy (TBNB) with Fransen needle had a diagnostic yield of 97% [53].
3.3. Surgical Techniques
As previously stated, the mediastinum can be surgically explored principally with parasternal mediastinotomy (Chamberlain procedure), mediastinoscopy (both cervical extended or video-assisted), and video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery. Surgery is currently reserved for those cases in which an endoscopic procedure is not indicated or does not provide a diagnosis, and furthermore, surgery may also provide a therapeutic intent by removing lymph nodes [2].
4. Causes of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy
Mediastinal lymph nodes enlargement with short axis diameter >10 mm is conventionally defined a mediastinal lymphadenopathy. Some authors suggest that the normal short axis diameter may vary between nodal stations: in particular, 10 mm is the limit for station 4 lymph nodes, while for station 7 lymph nodes it is 12 mm, and for the other stations it is 8 mm [54]. The causes of mediastinal lymphadenopathy may be summarized as:
- Malignant causes, principally represented by neoplastic causes.
- Benign causes, represented by infectious, inflammatory, and reactive causes.
A resumptive scheme of the principal causes of mediastinal lymph node enlargement is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Scheme of principal causes of mediastinal lymph node enlargement.
A neoplastic involvement of mediastinal lymph nodes is generally due to NSCLCs’ metastasis or haematological malignancies, such as lymphomas, myeloma, or leukaemia. Nodal metastasis may come from a gastrointestinal or oesophageal tumour, as well as from a tumour of the breast, testicle, or thyroid, as previously reported.
Numerous infective pathogens may cause mediastinal lymph node enlargement: the major responsible pathogen worldwide is Mycobacterium (both M. tuberculosis and atypical M.), but also fungi (Coccidioides, Histoplasma), other bacteria (F. tularensis, B. anthracis), and viruses (HIV, Epstein–Barr virus). Based on the type of material obtained by fine needle aspiration (FNA), infective lymphadenopathy can be further classified as suppurative and granulomatous; different stains are indicated for each type [55].
Inflammatory causes include sarcoidosis, rheumatological and autoimmune diseases (e.g., SLE, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic sclerosis), cystic fibrosis, pneumoconiosis, hypersensitivity pneumonia, amyloidosis, Whipple disease, Rosai–Dorfman disease, and Castleman’s disease.
In the end, a (usually temporary) lymphadenopathy may appear during pneumonia or in case of pulmonary oedema, as well as in pulmonary hypertension, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), COPD, and chronic heart failure [56]. Many drugs are associated with lymph node enlargement secondary to a hypersensitivity reaction [57]. Anecdotally, a granulomatous mediastinal nodal involvement secondary to silicone breast implant has been described [58].
Since it was principally developed for this purpose, the role of EBUS in neoplastic disease, most of all NSCLC, is extensively treated in the literature. Conversely, its role in investigating benign causes of lymphadenopathy is less known. The aim of the present review is to focus on the principal benign causes of mediastinal lymphadenopathy.
4.1. Non-Infectious Causes
4.1.1. Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is one of the most frequent causes of mediastinal granulomatous lymphadenopathy in non-developing countries, although a study from Kuo et al. demonstrated its prevalence in intrathoracic lymphadenopathy without pulmonary lesion also in a TB-endemic country [45]. The cause is unknown, even though many studies suggest a role for Mycobacteria and Propionibacterium [59]. Immunopathogenesis is not fully understood but seems to imply a role for T-cell receptors and HLA dysfunction in response to exposition to an unknown antigen [59]. Diagnosis requires clinical and radiological criteria, evidence of non-caseating granuloma on histopathology, and exclusion of other granulomatous diseases such as tuberculosis and lymphoma [60]. A radiological classification (Scadding) identifies five stages: lymphadenopathy is seen in stage 1 (lymphadenopathy alone) and stage 2 (lymphadenopathy with parenchymal infiltration) [60]. In these stages, the typical imaging finding is a bilateral, symmetrical perivascular cluster of lymph nodes with a tropism for pleura (pleural avidity). The enlargement of right paratracheal and bilateral hilar lymph nodes is known as Garland’s sign. Although in the ATS/ERS guidelines transbronchial lung biopsy is the diagnostic procedure of choice, its importance has decreased in recent decades thanks to the development of endobronchial ultrasound techniques [61]. Nodal ultrasound findings are represented by a mixed echogenicity, but no change in architectural structure should be seen when using CEUS and Doppler, and the hilum is conserved [41,62,63]. Elastography may help to identify the lymph nodes involved, which usually appear with a blue pattern, meaning an increased stiffness [64]. If conventional “blind” TBNA fails to diagnose sarcoidosis in one third or half of the cases, EBUS-TBNA and EUS-FNA show a sensitivity of 80–90% [46,65,66,67] with a diagnostic yield on 2097 patients of 79% [68]; Ortakoylu et al. report a diagnostic accuracy of 86% [39]. Pooled sensitivity for EBUS-TBNA is reported to be 84% and pooled specificity around 100% [68]. The diagnostic accuracy is around 90% even for Scadding stage 1 [37,45]. A summary of diagnostic yield of EBUS-TBNA in sarcoidosis is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Resumptive table of diagnostic yield of EBUS-TBNA in sarcoidosis.
Diagnostic yield seems to be increased by ancillary methods such as liquid-based cytology and cell block [37,69]. In EBUS-guided procedures, neither lymph node location, lymph node size, needle size, nor number of aspirates for node seem to alter sensitivity and specificity [69]. However, endoscopist experience may alter the diagnostic yield: for Pedro et al., 37–44 procedures are required to achieve an accuracy of 80% [61]. A common blood test such as red-cell distribution width (RDW) has been shown to be significantly higher in stage II sarcoidosis compared with stage I sarcoidosis and tubercular lymphadenitis [70]. Furthermore, the analysis of the transcriptional profile on the sample can help to discriminate sarcoidosis from other granulomatous diseases [71].
The main complication described is mediastinitis with abscess formation after EUS [37], while 13% of the complications following EBUS with 8–10 passages were reported in one RCT [30].
4.1.2. Sarcoid like Reaction (SLR)
In some patients affected with malignancy, a mediastinal lymphadenopathy secondary to a noncaseating granulomatous lymph node involvement may occur: it is named a sarcoid-like reaction (SLR), and it is considered a paraneoplastic manifestation, but it may appear even after chemotherapy or radiotherapy [72]. The cause is yet unknown: Urbanski et al. suggested an “antigen shedding” from cancer as being responsible [73]. The tumour more often associated with SLR is testicular germ cells cancer [73,74], but it is also described to have an association with NSCLC [75]. EBUS-TBNA is useful in settling a differential diagnosis between SLR and metastasis [76].
4.1.3. Silicosis
Silicosis is caused by inhalation of free silica particles, which cause the formation of noncaseating granulomas. Hilar nodal enlargement may precede parenchymal involvement [77], and it is present in 74% of patients [78]. Lymph nodes usually show calcification with eggshell or punctate distribution [78]; under polarized light, histological and cytological samples show nodules of fibroblasts and histiocytes in addition to birefringent particles [79]. In a small multicentre study, Shitrit et al. demonstrated specificity of 100% and sensitivity of 88% for EBUS-TBNA in diagnosing silicosis in patients with consistent exposure history [80].
4.1.4. Berylliosis
Berylliosis is caused by exposure to beryllium compounds. Up to 25% of cases may show a nodal enlargement and noncaseating granulomas similar to sarcoidosis, usually in association with parenchymal fibrosing alterations [81]. Currently there are no studies on diagnostic yield of EBUS in this disease.
4.1.5. Amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is characterized by deposition of abnormally folded fibrillar proteins in lymph nodes and organs and may be classified as being primary or secondary. Bilateral mediastinal lymph nodes enlargement, sometimes with calcification, is most typical of the primary form and may resemble sarcoidosis [82]. Many case reports show a role for EBUS-TBNA in diagnosis [83,84,85].
4.1.6. Castleman’s Disease
It is an uncommon idiopathic lymphoproliferative disease, which may be unifocal (a mediastinal or hilar mass rather than the enlargement of a single nodal compartment) or, more frequently in HIV patients, multifocal. Lymph nodes’ architecture is maintained and during CEUS they gain contrast homogeneously; vascularization is usually increased [86]. Nodal sampling is necessary for establishing the diagnosis.
4.1.7. Other Non-Infectious Causes
Mediastinal lymph node enlargement with maintained architecture may be observed in patients affected with COPD, IPF, and chronic heart failure, probably secondary to pulmonary hypertension and/or diffuse intrathoracic oedema [87]. In chronic left heart failure, the lymph nodes more often enlarged are the hilar, subcarinal, and paratracheal ones [57].
Up to 68% [88] of IPF patients show mediastinal lymphadenopathy, which has a correlation with disease severity and progression risk [89]. Furthermore, they have a higher risk of developing lung cancer, so in IPF patients, EBUS has a major role in early lymph node evaluation during follow-up [90].
Half of COPD patients have enlarged lymph nodes, especially those showing a bronchitic phenotype [91]. The lymph nodes involved, usually oval-shaped and showing signs of reactive enlargement, are those in the aorto-pulmonary windows, the paratracheal ones, and the subcarinal ones [57].
4.2. Infectious Causes
4.2.1. Mycobacterial Diseases
Mycobacterium tuberculosis or Koch bacillus and other Mycobacteria usually cause the formation of granulomas in lung and lymph nodes. Tubercular lymphadenopathy is the most frequent extrapulmonary manifestation of tuberculosis, especially in the primary subtype [92]. In countries where it is still endemic, in patients showing mediastinal lymphadenopathy, a mycobacterial disease should be excluded [93,94], in particular in those patients without clear home exposure to tubercular patients [45]. Clinical presentation may be similar to sarcoidosis, and so the imaging features. Microbiological exams (Ziehl–Neelsen stain, polymerase chain reaction, microbiological culture) on sputum are diagnostic, but also show also low sensitivity; additionally, sarcoidotic granuloma sometimes may also show necrosis [95]. In recent decades, EBUS-TBNA has been gaining importance in the differential diagnosis between those two granulomatous diseases [96,97]. The diagnosis is based on the presence of epithelioid granulomas with or without caseous necrosis associated with presence of Mycobacterium in the same sample or sputum treated with appropriate stain (acid-fast bacilli or Ziehl–Neelsen stain) [55]. Culture is the gold standard for the diagnosis, and together with microscopic exam reaches a specificity of 95% [55]. A positive tuberculin skin reaction supports the diagnosis. The overall sensitivity, predictive negative value, and diagnostic accuracy range between 64% and 81%, 33% and 43%, and 70% and 83%, respectively [98,99] (Table 3). The sensitivity of EBUS-TBNA in diagnosing tuberculosis is reported to be 74–85% [39,100]. TB-PCR on the sample increases the diagnostic rate [101], with a sensitivity of 56%, specificity and positive predictive value of 100%, negative predictive value of 81%, and diagnostic rate of 85–96% [102,103].

Table 3.
A resumptive table of diagnostic yield of EBUS for mycobacterial disease.
EBUS can be useful in suspected tubercular lymphadenitis, also with a simple sonographic evaluation of lymph nodes: in tuberculosis, the echogenicity of lymph node is more often heterogeneous, and necrosis signs are more frequent [40,57].
EBUS may have a therapeutic role in the drainage of tubercular abscesses, a rare complication of colliquation of multiple lymph nodes [104].
4.2.2. Fungal Diseases
Fungal nodal involvement seems to be associated more frequently with caseous granulomas, and thus in endemic areas or whether there is high suspicion of fungal disease, an appropriate stain should be applied in samples obtained [105]. The most frequent fungal infections associated with mediastinal lymphadenopathy are cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, and coccidioidomycosis [57]. Cryptococcus neoformans not only may cause pneumonia but also may cause disseminated infections with lymph node involvement, especially in immunocompromised hosts. Typical findings are neutrophils associated with some lymphocytes, granulomas, and histiocytes and yeasts surrounded by a “halo” capsule [55].
Histoplasmosis is a systemic infection caused by the inhalation of spores of Histoplasma capsulatum; in the acute form, it may be associated with enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes with central necrosis or colliquation, surrounded by a fibrous capsule. Granulomas may be seen as well [57]. Loosely formed granulomas may be observed in subacute pulmonary histoplasmosis [106]. However, rarely is the culture positive on the sample obtained by EBUS-TBNA, and the diagnosis is aided by infectious serologies and antigen testing [106].
Coccidioidomycosis is caused by the inhalation of spores of Coccidioides sp. Mediastinal lymphadenopathy is most typical of the acute form of the disease and usually correlates with a systemic dissemination [107]. Lymph node enlargement may persist even after resolution of the parenchymal lesions [108].
4.2.3. Viral Diseases
Mediastinal lymphadenopathy may appear during viral illnesses, but it is not common and, when present, it is associated with pneumonia or, as it happens in Epstein–Barr virus infection, together with systemic lymph nodes enlargement [109]. It is not specific and more often resolves after healing.
In HIV patients showing mediastinal lymphadenopathy, EBUS-TBNA is useful both to exclude an infection and a lymphoma degeneration or Kaposi’s sarcoma, which sometimes may occur with only visceral involvement. Typical cytopathological findings include casually arranged spindle cells which may resemble granulomas [110].
5. Conclusions
Despite its main role in the diagnosis and staging of cancer, the literature demonstrates that EBUS-TBNA is a safe and reliable procedure for diagnosing non-neoplastic diseases involving mediastinal lymph nodes, especially sarcoidosis, instead of surgery. More randomized controlled trials are needed to establish its effective diagnostic yield in benign diseases other than sarcoidosis and tuberculosis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.S., A.G.F. and P.P. (Pietro Pirina); writing—original draft preparation, V.S., A.M., F.B. and C.C.; writing—review and editing, V.S., A.Z. and P.P. (Panos Paliogiannis); supervision, A.G.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zeppa, P.; Cozzolino, I. Lymphadenitis and Lymphadenopathy. Monogr. Clin. Cytol. 2018, 23, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Annema, J.T.; Clementsen, P.; Cui, X.W.; Borst, M.M.; Jenssen, C. Ultrasound techniques in the evaluation of the mediastinum, part I: Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS), endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) and transcutaneous mediastinal ultrasound (TMUS), introduction into ultrasound techniques. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 9, E311–E325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Call, S.; Obiols, C.; Rami-Porta, R. Present indications of surgical exploration of the mediastinum. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S2601–S2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokawa, Y.; Hiki, N.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kishi, K.; Ito, Y.; Ohi, M.; Wada, N.; Takiguchi, S.; Mine, S.; Haegawa, S.; et al. Mediastinal lymph node metastasis and recurrence in adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction. Surgery 2015, 157, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, N.; Yoshizawa, J.; Hanaoka, T. Solitary metastasis to a superior mediastinal lymph node after distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer: A case report. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moritani, S. Impact of superior mediastinal metastasis on the prognosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Endocr. J. 2016, 63, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kageyama, S.; Ueda, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Tsuzuki, M.; Yonese, J.; Kawai, T.; Ida, T. Mediastinal lymph node metastasis 38 months after surveillance for stage I seminoma: A case report. Hinyokika Kiyo 1994, 40, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, T.; Watahiki, M.; Asai, K. Mediastinal Metastasis of Breast Cancer Mimicking a Primary Mediastinal Tumor. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e925275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansell, D.M.; Bankier, A.A.; MacMahon, H.; McLoud, T.C.; Müller, N.L.; Remy, J. Fleischner Society: Glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiology 2008, 246, 697–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugalde, P.A.; Pereira, S.T.; Araujo, C.; Irion, K.L. Correlative anatomy for the mediastinum. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2011, 21, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherief, A.H.; Lau, C.T.; Wu, C.C.; Drake, R.L.; Abbott, G.F.; Rice, T.W. International association for the study of lung cancer (IASLC) lymph node map: Radiologic review with CT illustration. Radiographics 2014, 34, 1680–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priola, S.M.; Priola, A.M.; Cardinale, L.; Perotto, F.; Fava, C. The anterior mediastinum: Anatomy and imaging procedures. Radiol. Med. 2006, 111, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, D.M.; Kressel, H.; Gefter, W.; Axel, L.; Thickman, D.; Aronehick, J.; Miller, W. MR imaging of the mediastinum: A retrospective comparison with computed tomography. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1984, 8, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, C.E.; Belli, A.M.; Lewars, M.D.; Reznek, R.H.; Husband, J.E. Normal lymph node size in the mediastinum: A retrospective study in two patient groups. Clin. Radiol. 1989, 40, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, R.G.; Glazer, H.S.; Roper, C.L.; Lee, J.K.; Murphy, W.A. Magnetic resonance imaging of mediastinal and hilar masses: Comparison with CT. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1985, 145, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sarraf, N.; Gately, K.; Lucey, J.; Wilson, L.; McGovern, E.; Young, V. Lymph node staging by means of positron emission tomography is less accurate in non-small cell lung cancer patients with enlarged lymph nodes: Analysis of 1,145 lymph nodes. Lung Cancer 2008, 60, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, T.; Yasufuku, K.; Nakajima, T.; Chiyo, M.; Yoshida, S.; Suzuki, M.; Shibuya, K.; Hiroshima, K.; Nakatani, Y.; Yoshino, I. The utility of sonographic features during endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for lymph node staging in patients with lung cancer: A standard endobronchial ultrasound image classification system. Chest 2010, 138, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscaglia, F.; Nolsøe, C.; Dietrich, C.F.; Cosgrove, D.O.; Gilja, O.H.; Bachmann Nielsen, M.; Albrecht, T.; Barozzi, L.; Bertolotto, M.; Catalano, O.; et al. The EFSUMB Guidelines and Recommendations on the Clinical Practice of Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS): Update 2011 on non-hepatic applications. Ultraschall Med. 2012, 33, 33–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, J.; Dietrich, C.F.; Will, U.; Greiner, L. Endosonographic elastography in the diagnosis of mediastinal lymph nodes. Endoscopy 2007, 39, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Anayama, T.; Shingyoji, M.; Kimura, H.; Yoshino, I.; Yasufuku, K. Vascular image patterns of lymph nodes for the prediction of metastatic disease during EBUS-TBNA for mediastinal staging of lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detterbeck, F.C.; Postmus, P.E.; Tanoue, L.T. The stage classification of lung cancer: Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2013, 143, e191S–e210S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansteenkiste, J.; De Ruysscher, D.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Lim, E.; Senan, S.; Felip, E.; Peters, S.; on behalf of the ESMO Guidelines Working Group. Early and locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, vi89–vi98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leyn, P.; Dooms, C.; Kuzdzal, J.; Lardinois, D.; Passlick, B.; Rami-Porta, R.; Turna, A.; van Schil, P.; Venuta, F.; Waller, D.; et al. Revised ESTS guidelines for preoperative mediastinal lymph node staging for non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2014, 45, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detterbeck, F.C.; Jantz, M.A.; Wallace, M.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Silvestri, G.A. American College of Chest Physicians. Invasive mediastinal staging of lung cancer: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition). Chest 2007, 132, 202S–220S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, K.; Shah, P.L.; Edmonds, L.; Lim, E. Test performance of endobronchial ultrasound and transbronchial needle aspiration biopsy for mediastinal staging in patients with lung cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorax 2009, 64, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Nehra, M.; Agarwal, D.; Mohan, A. Diagnostic accuracy of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle biopsy in mediastinal lymphadenopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir. Care 2012, 57, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.M.; da Cunha Santos, G.; Darling, G.; Pierre, A.; Yasufuku, K.; Boerner, S.L.; Geddie, W.R. Diagnosis and subclassification of lymphomas and non-neoplastic lesions involving mediastinal lymph nodes using endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2013, 41, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhooria, S.; Sehgal, I.S.; Gupta, N.; Prasad, K.T.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Agarwal, R. Diagnostic Utility and Safety of Endobronchial Ultrasound-guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration in the Elderly. J. Bronchol. Interv. Pulmonol. 2020, 27, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokadia, H.K.; Mehta, A.; Culver, D.A.; Patel, J.; Machuzak, M.; Almeida, F.; Gildea, T.; Sethi, S.; Zell, K.; Cicenia, J. Rapid On-Site Evaluation in Detection of Granulomas in the Mediastinal Lymph Nodes. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plit, M.L.; Havryk, A.P.; Hodgson, A.; James, D.; Field, A.; Carbone, S.; Glanville, A.R.; Bashirzadeh, F.; Chay, A.M.; Hundloe, J.; et al. Rapid cytological analysis of endobronchial ultrasound-guided aspirates in sarcoidosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisolini, R.; Cancellieri, A.; Tinelli, C.; Paioli, D.; Scudeller, L.; Casadei, G.P.; Forti Parri, S.; Livi, V.; Arrigo, B.; Boaron, M.; et al. Rapid on-site evaluation of transbronchial aspirates in the diagnosis of hilar and mediastinal adenopathy: A randomized trial. Chest 2011, 139, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, M.; Saka, H.; Kitagawa, C.; Hogure, Y.; Murata, N.; Adachi, T.; Ando, M. Rapid on-site cytologic evaluation during endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for diagnosing lung cancer: A randomized study. Respiration 2013, 85, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahidi, M.M.; Herth, F.; Yasufuku, K.; Shepher, R.W.; Yarmus, L.; Chawla, M.; Lamb, C.; Casey, K.R.; Patel, S.; Silvestri, G.A.; et al. Technical Aspects of Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest 2016, 149, 816–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappelle, W.F.W.; Van Leerdam, M.E.; Schwartz, M.P.; Bülbül, M.; Buikhuisen, W.A.; Brink, M.A.; Sie-Go, D.M.D.S.; Pullens, H.J.M.; Nikolakopoulos, S.; Van Diest, P.J.; et al. Rapid on-site evaluation during endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of lymph nodes does not increase diagnostic yield: A randomized, multicenter trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natali, F.; Cancellieri, A.; Tinelli, C.; De Silvestri, A.; Livi, V.; Ferrari, M.; Romagnoli, M.; Paioli, D.; Trisolini, R. A Trained Pulmonologist Can Reliably Assess Endosonography-Derived Lymph Node Samples during Rapid On-Site Evaluation. Respiration 2019, 97, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erer, O.F.; Erol, S.; Anar, C.; Aydoğdu, Z.; Özkan, S.A. Contribution of cell block obtained by endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in the diagnosis of malignant diseases and sarcoidosis. Endosc. Ultrasound 2017, 6, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bartheld, M.B.; Veseliç-Charvat, M.; Rabe, K.F.; Annema, J.T. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for the diagnosis of sarcoidosis. Endoscopy 2010, 42, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrissian, A.; Misselhorn, D.; Chen, A. Endobronchial-ultrasound guided miniforceps biopsy of mediastinal and hilar lesions. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 92, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortakoylu, M.G.; Iliaz, S.; Bahadir, A.; Aslan, A.; Iliaz, R.; Ozgul, M.A.; Urer, H.N. Diagnostic value of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in various lung diseases. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2015, 41, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, S.; Anar, C.; Erer, O.F.; Biçmen, C.; Aydoğdu, Z. The Contribution of Ultrasonographic Characteristics of Mediastinal Lymph Nodes on Differential Diagnosis of Tuberculous Lymphadenitis from Sarcoidosis. Tanaffos 2018, 17, 250–256. [Google Scholar]
- Jenssen, C.; Annema, J.T.; Clementsen, P.; Cui, X.W.; Borst, M.M.; Dietrich, C.F. Ultrasound techniques in the evaluation of the mediastinum, part 2: Mediastinal lymph node anatomy and diagnostic reach of ultrasound techniques, clinical work up of neoplastic and inflammatory mediastinal lymphadenopathy using ultrasound techniques and how to learn mediastinal endosonography. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, E439–E458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, F.; Aoe, M.; Ohsaki, Y.; Okada, Y.; Sasada, S.; Sato, S.; Suzuki, E.; Semba, H.; Fukuoka, K.; Fujino, S.; et al. Complications associated with endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration: A nationwide survey by the Japan Society for Respiratory Endoscopy. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.M.; Figueiredo, V.R.; Demarzo, S.E.; Palomino, A.L.M.; Jacomelli, M. The role of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in isolated intrathoracic lymphadenopathy in non-neoplastic patients: A common dilemma in clinical practice. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2020, 46, e20180183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annema, J.T.; van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Rintoul, R.C.; Dooms, C.; Deschepper, E.; Dekkers, O.M.; De Leyn, P.; Braun, J.; Carroll, N.R.; Praet, M.; et al. Mediastinoscopy vs endosonography for mediastinal nodal staging of lung cancer: A randomized trial. JAMA 2010, 304, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.H.; Lin, S.M.; Lee, K.Y.; Chung, F.T.; Feng, P.H.; Hsiung, T.C.; Lo, Y.L.; Liu, C.Y.; Kuo, H.P. Algorithmic approach by endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for isolated intrathoracic lymphadenopathy: A study in a tuberculosis-endemic country. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2014, 113, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navani, N.; Booth, H.L.; Kocjan, G.; Falzon, M.; Capitanio, A.; Brown, J.M.; Porter, J.C.; Janes, S.M. Combination of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration with standard bronchoscopic techniques for the diagnosis of stage I and stage II pulmonary sarcoidosis. Respirology 2011, 16, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasufuku, K.; Nakajima, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Yoshino, I.; Keshavjee, S. Utility of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in the diagnosis of mediastinal masses of unknown etiology. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 91, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navani, N.; Lawrence, D.R.; Kolvekar, S.; Hayward, M.; McAsey, D.; Kocjan, G.; Falzon, M.; Capitanio, A.; Shaw, P.; Morris, S.; et al. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration prevents mediastinoscopies in the diagnosis of isolated mediastinal lymphadenopathy: A prospective trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Dadhwal, D.S.; Agarwal, R.; Gupta, N.; Bal, A.; Aggarwal, A.N. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration vs conventional transbronchial needle aspiration in the diagnosis of sarcoidosis. Chest 2014, 146, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyan, C.C.; Machuca, T.; Czarnecka, K.; Ko, H.M.; da Cunha Santos, G.; Boerner, S.L.; Piere, A.; Cypel, M.; Waddell, T.; Darling, G.; et al. Performance of Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration for the Diagnosis of Isolated Mediastinal and Hilar Lymphadenopathy. Respiration 2017, 94, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetinkaya, E.; Ozgül, M.A.; Tutar, N.; Ozgül, G.; Cam, E.; Bilaçeroglu, S. The diagnostic utility of real-time EBUS-TBNA for hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes in conventional TBNA negative patients. Ann. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 20, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Lou, L.; Chen, T.; Zoum, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhihao, X.; Ye, q.; Shen, H.; Li, W.; Xia, W. Comparison of transbronchial needle aspiration with and without ultrasound guidance for diagnosing benign lymph node adenopathy. Diagn. Pathol. 2020, 15, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balwan, A.; Bixby, B.; Grotepas, C.; Witt, B.L.; Iravani, A.; Ansari, S.; Reddy, C.B. Core needle biopsy with endobronchial ultrasonography: Single center experience with 100 cases. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2020, 9, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyono, K.; Sone, S.; Sakai, F.; Imai, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Izuno, I.; Oguchi, M.; Kawai, T.; Shigematsu, H.; Watanabe, M. The number and size of normal mediastinal lymph nodes: A postmortem study. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol 1988, 150, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, A.S.; Geddie, W.R. Role of fine needle aspiration biopsy cytology in the diagnosis of infections. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2016, 44, 1024–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evison, M.; Crosbie, P.A.; Morris, J.; Martin, J.; Barber, P.V.; Booton, R. A study of patients with isolated mediastinal and hilar lymphadenopathy undergoing EBUS-TBNA. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2014, 1, e000040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nin, C.S.; de Souza, V.V.; do Amaral, R.H.; Neto, R.S.; Tronco Alves, G.R.; Marchiori, E.; Irion, K.L.; Balbinot, F.; de Souza Portes Meirelles, G.; Santana, P.; et al. Thoracic lymphadenopathy in benign diseases: A state of the art review. Respir. Med. 2016, 112, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naur, T.M.H.; Bodtger, U.; Nessar, R.; Salih, G.N.; Clementsen, P.F. Asymptomatic silicone induced granulomatous disease diagnosed by endobronchial ultrasound with real-time guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA). Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 30, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.P.; Culver, D.A.; Judson, M.A. A concise review of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS); The European Respiratory Society (ERS); The World Association of Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders (WASOG). Statement on sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 736–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, C.; Melo, N.; Novais, E.; Bastos, H.; Magalhaes, A.; Fernandes, G.; Martins, N.; Morais, A.; Mota, P.C. Role of Bronchoscopic Techniques in the Diagnosis of Thoracic Sarcoidosis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirche, T.O.; Hirche, H.; Cui, X.W.; Wagner, T.O.; Dietrich, C.F. Ultrasound evaluation of mediastinal lymphadenopathy in patients with sarcoidosis. Med. Ultrason. 2014, 16, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Trisolini, R.; Baughman, R.P.; Spagnolo, P.; Culver, D.A. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in sarcoidosis: Beyond the diagnostic yield. Respirology 2019, 24, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livi, V.; Cancellieri, A.; Pirina, P.; Fois, A.; van der Heijden, E.H.F.M.; Trisolini, R. Endobronchial Ultrasound Elastography Helps Identify Fibrotic Lymph Nodes in Sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, e24–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, A.; Stather, D.R.; MacEachern, P.; Khalil, M.; Field, S.K. A randomized controlled trial of standard vs endobronchial ultrasonography-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in patients with suspected sarcoidosis. Chest 2009, 136, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, T.; Yasufuku, K.; Kurosu, K.; Takiguchi, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Chiyo, M.; Shibuya, K.; Hiroshima, K.; Natakani, Y.; Yoshino, I. The role of EBUS-TBNA for the diagnosis of sarcoidosis—Comparisons with other bronchoscopic diagnostic modalities. Respir. Med. 2009, 103, 1796–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bartheld, M.B.; Dekkers, O.M.; Szlubowski, A.; Eberhardt, R.; Herth, F.; Johannes, C.C.M.; de Long, Y.P.; van der Heijden, H.F.M.; Tournoy, K.G.; Claussen, M.; et al. Endosonography vs conventional bronchoscopy for the diagnosis of sarcoidosis: The GRANULOMA randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013, 309, 2457–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisolini, R.; Lazzari Agli, L.; Tinelli, C.; De Silvestri, A.; Scotti, V.; Patelli, M. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for diagnosis of sarcoidosis in clinically unselected study populations. Respirology 2015, 20, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, A.; Khalil, M.; Stather, D.R.; MacEachern, P.; Field, S.K.; Tremblay, A. Cytologic assessment of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspirates in sarcoidosis. J. Bronchol. Interv. Pulmonol. 2012, 19, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karataş, M.; Öztürk, A. The utility of RDW in discrimination of sarcoidosis and tuberculous lymphadenitis diagnosed by ebus. Ebus ile tanı konulan tüberküloz ve sarkoidoza bağlı granülomatöz lenfadenitte RDW’nin tanı değeri. Tuberk Toraks 2018, 66, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, G.S.; Thomas, N.; Chain, B.M.; Best, K.; Simpson, N.; Hardavella, G.; Brown, J.; Bhowmik, A.; Navani, N.; Janes, S.M.; et al. Transcriptional Profiling of Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Lymph Node Samples Aids Diagnosis of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy. Chest 2016, 149, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePew, Z.S.; Gonsalves, W.I.; Roden, A.C.; Bungum, A.O.; Mullon, J.J.; Maldonado, F. Granulomatous inflammation detected by endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in patients with a concurrent diagnosis of cancer: A clinical conundrum. J. Bronchol. Interv. Pulmonol. 2012, 19, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanski, S.J.; Alison, R.E.; Jewett, M.A.; Gospodarowicz, M.K.; Sturgeon, J.F. Association of germ cell tumours of the testis and intrathoracic sarcoid-like lesions. CMAJ 1987, 137, 416–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, L.H.; Huss, S.; Schuelke, C.; Schulze, A.; Evers, G.; Schliemann, C.; Hansmeier, A.; Schilling, B.; Lauterbach, B.; Barth, P.; et al. Noncaseating granulomatous diseases in germ cell cancer patients-A single-center experience. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37, e17–e531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinfort, D.P.; Irving, L.B. Sarcoidal reactions in regional lymph nodes of patients with non-small cell lung cancer: Incidence and implications for minimally invasive staging with endobronchial ultrasound. Lung Cancer 2009, 66, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, M.P.; Jimenez, C.A.; Mhatre, A.D.; Morice, R.C.; Eapen, G.A. Clinical implications of granulomatous inflammation detected by endobronchial ultrasound transbronchial needle aspiration in patients with suspected cancer recurrence in the mediastinum. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2008, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.R.; Lambert, L.; Pantin, C.F.; Prowse, K.; Cole, R.B. Silicosis presenting as bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy. Thorax 1996, 51, 1165–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antao, V.C.; Pinheiro, G.A.; Terra-Filho, M.; Kavakama, J.; Müller, N.L. High-resolution CT in silicosis: Correlation with radiographic findings and functional impairment. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2005, 29, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.R.; Kelley, T.R. A brief review of silicosis in the United States. Environ. Health Insights 2010, 4, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitrit, D.; Adir, Y.; Avriel, A.; King, D.; Shochet, G.E.; Guber, A.; Schnaer, S.; Kassirer, M.; Blanc, P.D.; Abramovich, A. EBUS-TBNA is Sufficient for Successful Diagnosis of Silicosis with Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy. Lung 2018, 196, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitani, E.M.; Altemani, A.M.A.; Kawakama, J.I. Pulmonary berylliosis: Literature review and case report. J. Pneumol. 1995, 21, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.R.; Skarin, A.T. Clinical mimics of lymphoma. Oncologist 2004, 9, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Sivasailam, B.; Marciniak, E.; Deepak, J. EBUS-TBNA diagnosis of localised amyloidosis presenting as mediastinal lymphadenopathy. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 11, e226619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ogasa, T.; Ohsaki, Y. Primary Mediastinal Amyloidosis Diagnosed by Transbronchial Needle Aspiration. Intern. Med. 2016, 55, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiro, V.; Fernández-Villar, A.; Bandrés, R.; Gonzalez, A.; Represas, C.; Barros, J.C.; Pineiro, L. Primary amyloidosis involving mediastinal lymph nodes: Diagnosis by transbronchial needle aspiration. Respiration 2008, 76, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAdams, H.P.; Rosado-de-Christenson, M.; Fishback, N.F.; Templeton, P.A. Castleman disease of the thorax: Radiologic features with clinical and histopathologic correlation. Radiology 1998, 209, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngom, A.; Dumont, P.; Diot, P.; Lemarié, E. Benign mediastinal lymphadenopathy in congestive heart failure. Chest 2001, 119, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.A.; Müller, N.L.; Lee, K.S.; Johkoh, T.; Mitsuhiro, H.; Chong, S. Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: Prevalence of mediastinal lymph node enlargement in 206 patients. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 186, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.I.; Kim, H.H.; Jung, Y.J.; Park, S.H.; Lee, J.M.; Hahn, S.T. Mediastinal lymphadenopathy in pulmonary fibrosis: Correlation with disease severity. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2000, 24, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, R.; Massaro, D. Idiopathic diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis (fibrosing alveolitis), atypical epithelial proliferation and lung cancer. Am. J. Med. 1968, 45, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, J.; Kirchner, E.M.; Goltz, J.P.; Obermann, A.; Kickuth, R. Enlarged hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol 2010, 54, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.J.; Lee, K.S. Pulmonary tuberculosis: Up-to-date imaging and management. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 191, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geake, J.; Hammerschlag, G.; Nguyen, P.; Wallbridge, P.; Jenkin, G.A.; Korman, T.M.; Jennings, B.; Johnson, D.F.; Irving, L.B.; Farmer, M.; et al. Utility of EBUS-TBNA for diagnosis of mediastinal tuberculous lymphadenitis: A multicentre Australian experience. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangakunam, B.; Isaac, B.T.J.; Christopher, D.J. Endobronchial ultrasound experience in a high tuberculosis prevalence setting. Indian J. Tuberc. 2017, 64, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elatre, W.; Ma, Y.; Koss, M.N. Pathology of the Lung in Sarcoidosis. AJSP Rev. Rep. 2017, 22, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garwood, S.; Judson, M.A.; Silvestri, G.; Hoda, R.; Fraig, M.; Doelken, P. Endobronchial ultrasound for the diagnosis of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Chest 2007, 132, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Zhang, R.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Ying, K. Diagnostic Efficacy and Safety of Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration in Intrathoracic Tuberculosis: A Meta-analysis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2015, 34, 1645–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çağlayan, B.; Salepçi, B.; Fidan, A.; Kıral, N.; Cömert, S.S.; Yavuzer, D.; Recep, D.; Saraç, G. Sensitivity of convex probe endobronchial sonographically guided transbronchial needle aspiration in the diagnosis of granulomatous mediastinal lymphadenitis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2011, 30, 1683–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, S.Y.; Koh, M.S.; Ong, T.H.; Phua, G.C.; Anantham, D. Use of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) in the diagnosis of granulomatous mediastinal lymphadenopathy. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2014, 43, 250–254. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Teng, J.; Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, H.; Garfield, D.H.; Han, B. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in diagnosing intrathoracic tuberculosis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 96, 2021–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navani, N.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Breen, R.A.; Connell, D.W.; Jepson, A.; Nankivell, M.; Brown, J.M.; Morris-Jones, S.; Ng, B.; Wickremasinghe, M.; et al. Utility of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in patients with tuberculous intrathoracic lymphadenopathy: A multicentre study. Thorax 2011, 66, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senturk, A.; Arguder, E.; Hezer, H.; Babaoglu, E.; Kilic, H.; Karalezli, A.; Hasanoglu, H.C. Rapid diagnosis of mediastinal tuberculosis with polymerase chain reaction evaluation of aspirated material taken by endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration. J. Investig. Med. 2014, 62, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, J.S.; Mok, J.H.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, K.; Kim, M.J.; Jang, S.M.; Na, H.J.; Song, S.E.; Lee, G.; Jo, E.J.; et al. Efficacy of TB-PCR using EBUS-TBNA samples in patients with intrathoracic granulomatous lymphadenopathy. BMC Pulm. Med. 2015, 15, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Guo, J.; Wu, C.; Gu, Y.; You, X.; Sha, W. Application of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in the diagnosis and treatment of mediastinal lymph node tuberculous abscess: A case report and literature review. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 15, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.; Zamora, F.; Podgaetz, E.; Andrade, R.; Dincer, H.E. Usefulness of lymphoid granulomatous inflammation culture obtained by endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in a fungal endemic area. Endosc. Ultrasound 2016, 5, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egressy, K.V.; Mohammed, M.; Ferguson, J.S. The Use of Endobronchial Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Subacute Pulmonary Histoplasmosis. Diagn. Ther. Endosc. 2015, 2015, 510863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.P.; Morris, M.F.; Panse, P.M.; Ko, M.G.; Files, J.A.; Ruddy, B.E.; Blair, J.E. Does the presence of mediastinal adenopathy confer a risk for disseminated infection in immunocompetent persons with pulmonary coccidioidomycosis? Mycoses 2013, 56, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jude, C.M.; Nayak, N.B.; Patel, M.K.; Deshmukh, M.; Batra, P. Pulmonary coccidioidomycosis: Pictorial review of chest radiographic and CT findings. Radiographics 2014, 34, 912–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.A.; Lee, K.S.; Primack, S.L.; Yoon, H.K.; Byun, H.S.; Kim, T.S.; Suh, G.Y.; Kwon, O.J.; Han, J. Viral pneumonias in adults: Radiologic and pathologic findings. Radiographics 2002, 22, S137–S149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A.S. Infectious Disease. In FNA Cytology, 5th ed.; Orell, S.R., Sterrett, G.F., Eds.; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 2012; Chapter 17. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).