Human Transcriptome Array Analysis Identifies CDR2 as a Novel Suppressed Gene for Kawasaki Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subject Recruitment
2.2. Human Transcriptome Array
2.3. mRNA Expression with Quantitative Real Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
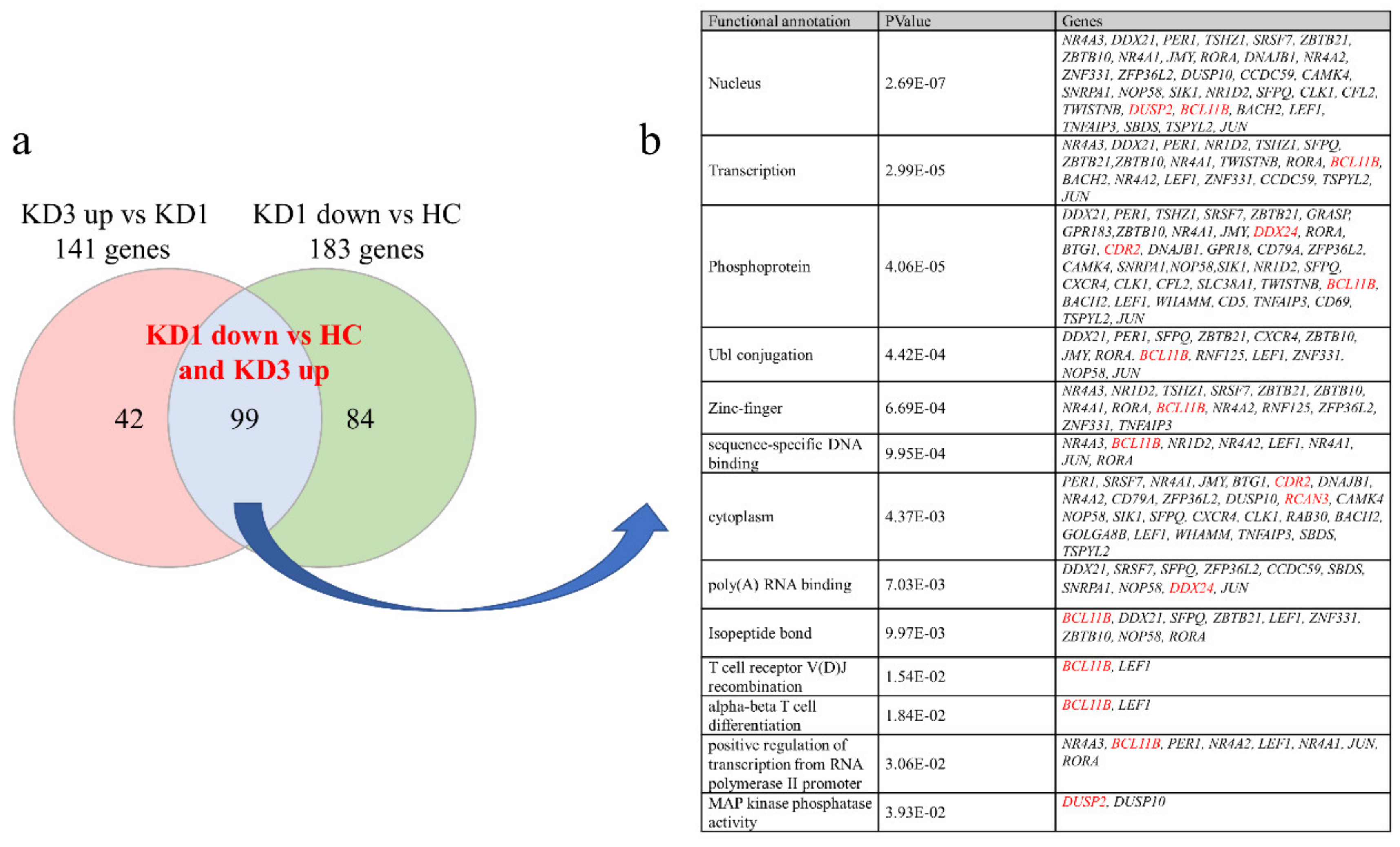
3.2. Patients with Acute KD Have Less Suppressed Than Increased Genes Expression Compared to Controls Using HTA 2.0
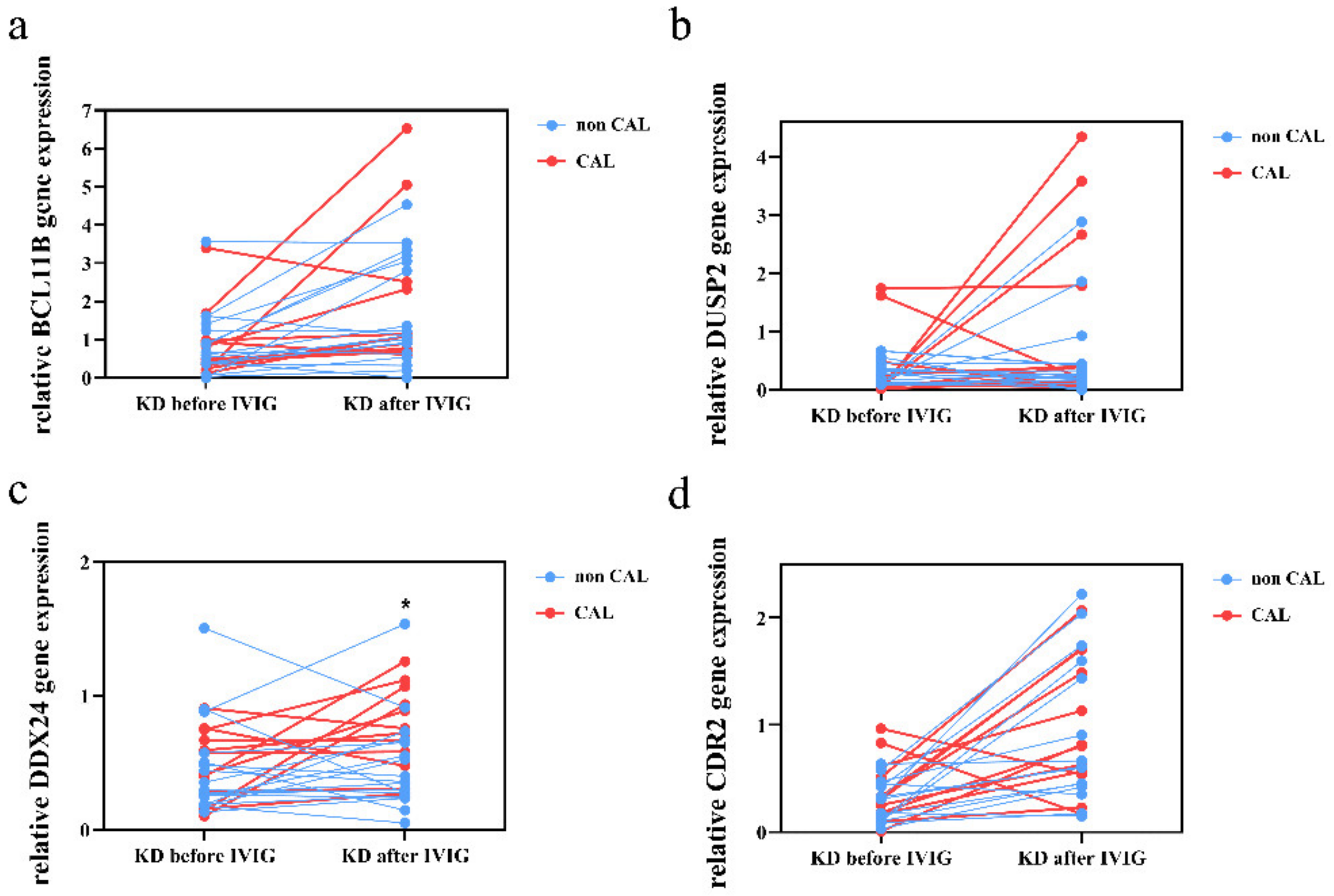
3.3. Validation of These Suppressed Genes Expression in KD Patients by qRT-PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, M.H.; Lin, M.T.; Chen, H.C.; Kao, F.Y.; Huang, S.K. Postnatal Risk of Acquiring Kawasaki Disease: A Nationwide Birth Cohort Database Study. J. Pediatr. 2017, 80, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Yashiro, M.; Uehara, R.; Sadakane, A.; Chihara, I.; Aoyama, Y.; Kotani, K.; Yanagawa, H. Epidemiologic features of Kawasaki disease in Japan: Results of the 2007–2008 nationwide survey. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 20, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.H.; Lin, K.M.; Ho, S.C.; Yan, J.H.; Lo, M.H.; Kuo, H.C. Increased Incidence of Kawasaki Disease in Taiwan in Recent Years: A 15 Years Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Front Pediatr. 2019, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrindle, B.W.; Rowley, A.H.; Newburger, J.W.; Burns, J.C.; Bolger, A.F.; Gewitz, M.; Baker, A.L.; Jackson, M.A.; Takajashi, M.; Shah, P.B.; et al. Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term Management of Kawasaki Disease: A Scientific Statement for Health Professionals From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017, 135, e927–e999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.C.; Glode, M.P. Kawasaki syndrome. Lancet 2004, 364, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newburger, J.W.; Takahashi, M.; Beiser, A.; Burns, J.C.; Bastian, J.; Chung, K.J.; Colan, S.D.; Duffy, C.E.; Fulton, D.R.; Glode, M.P.; et al. A Single Intravenous Infusion of Gamma Globulin as Compared with Four Infusions in the Treatment of Acute Kawasaki Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 1633–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newburger, J.W.; Takahashi, M.; Burns, J.C.; Beiser, A.; Chung, K.J.; Duffy, C.E.; Glode, M.P.; Mason, W.H.; Reddy, V.; Sanders, S.; et al. The Treatment of Kawasaki Syndrome with Intravenous Gamma Globulin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, Y.; Matsubara, D.; Ae, R.; Kosami, K.; Aoyama, Y.; Yashiro, M.; Makino, N.; Matsubara, S.; Nakamura, Y. Cumulative incidence of Kawasaki disease with cardiac sequelae in Japan. Pediatr. Int. 2020, 62, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Li, S.-C.; Huang, L.-H.; Chen, P.-C.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Lin, C.-C.; Kuo, H.-C. Identifying genetic hypomethylation and upregulation of toll-like receptors in Kawasaki disease. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 11249–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Lo, M.-H.; Cai, X.-Y.; Liu, S.-F.; Kuo, H.-C. Increase expression of CD177 in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2019, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuo, K.-C.; Yang, Y.-L.; Lo, M.-H.; Cai, X.-Y.; Kuo, H.-C.; Huang, Y.-H. The Expression of Glycoprotein Genes in the Inflammatory Process of Kawasaki Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 592122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Kuo, H.-C.; Li, S.-C.; Cai, X.-Y.; Liu, S.-F.; Kuo, H.-C. HAMP promoter hypomethylation and increased hepcidin levels as biomarkers for Kawasaki disease. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2018, 117, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goulopoulou, S.; McCarthy, C.G.; Webb, R.C. Toll-like Receptors in the Vascular System: Sensing the Dangers Within. Pharmacol. Rev. 2016, 68, 142–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.-Y.; Huang, Y.-H.; Guo, M.M.-H.; Chang, L.-S.; Kuo, H.-C. Kawasaki Disease and Allergic Diseases. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 8, 614386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.M.; Tseng, W.; Ko, C.; Pan, H.; Hsieh, K.-S.; Kuo, H.-C. Th17- and Treg-related cytokine and mRNA expression are associated with acute and resolving Kawasaki disease. Allergy 2015, 70, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menikou, S.; Langford, P.R.; Levin, M. Kawasaki Disease: The Role of Immune Complexes Revisited. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McAlpine, S.M.; Roberts, S.E.; Heath, J.J.; Käsermann, F.; Issekutz, A.C.; Issekutz, T.B.; Derfalvi, B. High Dose Intravenous IgG Therapy Modulates Multiple NK Cell and T Cell Functions in Patients With Immune Dysregulation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 660506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onouchi, Y.; Gunji, T.; Burns, J.C.; Shimizu, C.; Newburger, J.W.; Yashiro, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Yanagawa, H.; Wakui, K.; Fukushima, Y.; et al. ITPKC functional polymorphism associated with Kawasaki disease susceptibility and formation of coronary artery aneurysms. Nat. Genet. 2007, 40, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.-C.; Yang, K.D.; Juo, S.-H.H.; Liang, C.-D.; Chen, W.-C.; Wang, Y.-S.; Lee, C.-H.; Hsi, E.; Yu, H.-R.; Woon, P.-Y.; et al. ITPKC Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Associated with the Kawasaki Disease in a Taiwanese Population. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoggart, C.; Shimizu, C.; Galassini, R.; Wright, V.J.; Shailes, H.; Bellos, E.; Herberg, J.A.; Pollard, A.J.; O’Connor, D.; Choi, S.W.; et al. Identification of novel locus associated with coronary artery aneurysms and validation of loci for susceptibility to Kawasaki disease. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 29, 1734–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JCS Joint Working Group. Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management of Cardiovascular Sequelae in Kawasaki Disease (JCS 2008)-Digest Version-. Circ. J. Off. J. Jpn. Circ. Soc. 2010, 74, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara, H.; Izumida, N.; Hosaki, J. Criterion for early prediction of coronary artery involvement by clinical manifestations in patients with Kawasaki disease. Bull. Tokyo Med. Dent. Univ. 1985, 32, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.-D.; Huang, Y.-H.; Guo, M.M.-H.; Lin, T.-Y.; Weng, W.-T.; Yang, H.-J.; Yang, K.D.; Kuo, H.-C. The human blood DNA methylome identifies crucial role of β-catenin in the pathogenesis of Kawasaki disease. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 28337–28350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuda, H.; Sato, A.; Shizuno, T.; Yokoyama, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Tokunaga, M.; Asahara, T. Batroxobin accelerated tissue repair via neutrophil extracellular trap regulation and defibrinogenation in a murine ischemic hindlimb model. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serebrovska, Z.O.; Serebrovska, T.V.; Kholin, V.A.; Tumanovska, L.; Shysh, A.M.; Pashevin, D.A.; Goncharov, S.V.; Stroy, D.; Grib, O.N.; Shatylo, V.B.; et al. Intermittent Hypoxia-Hyperoxia Training Improves Cognitive Function and Decreases Circulating Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, Y.; Ding, M.; Fu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Neutrophil extracellular trap from Kawasaki disease alter the biologic responses of PBMC. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20200928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Nakaoka, H.; Takasaki, I.; Hirono, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Kinoshita, K.; Miyao, N.; Ibuki, K.; Ozawa, S.; Watanabe, K.; et al. MicroRNA-93 may control vascular endothelial growth factor A in circulating peripheral blood mononuclear cells in acute Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 80, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, N.A.; Pereverzeva, L.; Leopold, V.; Ramirez-Moral, I.; Roelofs, J.J.T.H.; van Heijst, J.W.J.; de Vos, A.F.; van der Poll, T. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α in Macrophages, but Not in Neutrophils, Is Important for Host Defense during Klebsiella pneumoniae-Induced Pneumosepsis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 9958281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Miyashita, M.; Murakami, S.; Igarashi, A.; Motomura, K.; Abe, J.; Matsumoto, K.; Matsuda, A. IL-1β and IL-17A are involved in IVIG resistance through activation of C/EBPβ and δ in a coronary artery model of Kawasaki disease. Allergy 2020, 75, 2102–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodge, K.; Cowburn, A.S.; Li, W.; Condliffe, A.M. The Impact of Hypoxia on Neutrophil Degranulation and Consequences for the Host. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwang, J.-Y.; Lee, J.; Oh, C.-K.; Kang, H.W.; Hwang, I.-Y.; Um, J.W.; Park, H.C.; Kim, S.; Shin, J.-H.; Park, W.-Y.; et al. Proteolytic degradation and potential role of onconeural protein cdr2 in neurodegeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venkatraman, A.; Opal, P. Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration with anti-Yo antibodies—A review. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2016, 3, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buenafe, A.C.; Andrew, S.; Offner, H.; Vandenbark, A.A. Regulatory T cells play a role in T-cell receptor CDR2 peptide regulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Immunology 2012, 135, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiara, V.; Daxinger, L.; Staal, F. The Route of Early T Cell Development: Crosstalk between Epigenetic and Transcription Factors. Cells 2021, 10, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balamurugan, K.; Luu, V.-D.; Kaufmann, M.R.; Hofmann, V.; Boysen, G.; Barth, S.; Bordoli, M.R.; Stiehl, D.; Moch, H.; Schraml, P.; et al. Onconeuronal cerebellar degeneration-related antigen, Cdr2, is strongly expressed in papillary renal cell carcinoma and leads to attenuated hypoxic response. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3274–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Chen, C.; Zhong, M.; Geng, S.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Deng, C.; Zeng, L.; Wu, P.; Lu, Z.; et al. Lower BCL11B expression is associated with adverse clinical outcome for patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Biomark. Res. 2021, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Liu, L.; Ji, X.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. The phosphatase DUSP2 controls the activity of the transcription activator STAT3 and regulates TH17 differentiation. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Liu, L.; Sun, Y.; Song, J.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, G.; Qi, F.; Hu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; et al. The phosphatase PAC1 acts as a T cell suppressor and attenuates host antitumor immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Dai, C.; Qin, J.; Gu, W. Negative regulation of the p300-p53 interplay by DDX24. Oncogene 2016, 35, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | Healthy Controls (n = 19) | Febrile Controls (n = 20) | Kawasaki Disease (n = 31) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male gender, n (%) | 11 (58%) | 15 (75%) | 20 (65%) | 0.522 |
| Age (y) | 3.2 ± 0.4 a | 3.5 ± 0.5 a | 1.7 ± 0.2 b | <0.001 |
| Age range (y) | 1–6 | 0–8 | 0–5 | |
| White blood cell (1000/µL) | 9.3 ± 0.5 a | 7.5 ± 0.9 a | 11.4 ± 0.6 b | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 12.5 ± 0.2 a | 12.2 ± 0.2 a | 11.3 ± 0.2 b | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 18.2 ± 6.0 | 58.2 ± 11.1 | 0.003 | |
| CAL formation (%) | 14 (45.2%) | |||
| IVIG resistance (%) | 1 (3.2%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.-H.; Chen, K.-D.; Kuo, K.-C.; Guo, M.M.-H.; Chang, L.-S.; Yang, Y.-L.; Kuo, H.-C. Human Transcriptome Array Analysis Identifies CDR2 as a Novel Suppressed Gene for Kawasaki Disease. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020240
Huang Y-H, Chen K-D, Kuo K-C, Guo MM-H, Chang L-S, Yang Y-L, Kuo H-C. Human Transcriptome Array Analysis Identifies CDR2 as a Novel Suppressed Gene for Kawasaki Disease. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(2):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020240
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Ying-Hsien, Kuang-Den Chen, Kuang-Che Kuo, Mindy Ming-Huey Guo, Ling-Sai Chang, Ya-Ling Yang, and Ho-Chang Kuo. 2022. "Human Transcriptome Array Analysis Identifies CDR2 as a Novel Suppressed Gene for Kawasaki Disease" Diagnostics 12, no. 2: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020240
APA StyleHuang, Y.-H., Chen, K.-D., Kuo, K.-C., Guo, M. M.-H., Chang, L.-S., Yang, Y.-L., & Kuo, H.-C. (2022). Human Transcriptome Array Analysis Identifies CDR2 as a Novel Suppressed Gene for Kawasaki Disease. Diagnostics, 12(2), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020240








