Breath Tests Used in the Context of Bariatric Surgery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Breath Tests
2.1. History of Breath Tests
2.2. Description of Breath Tests
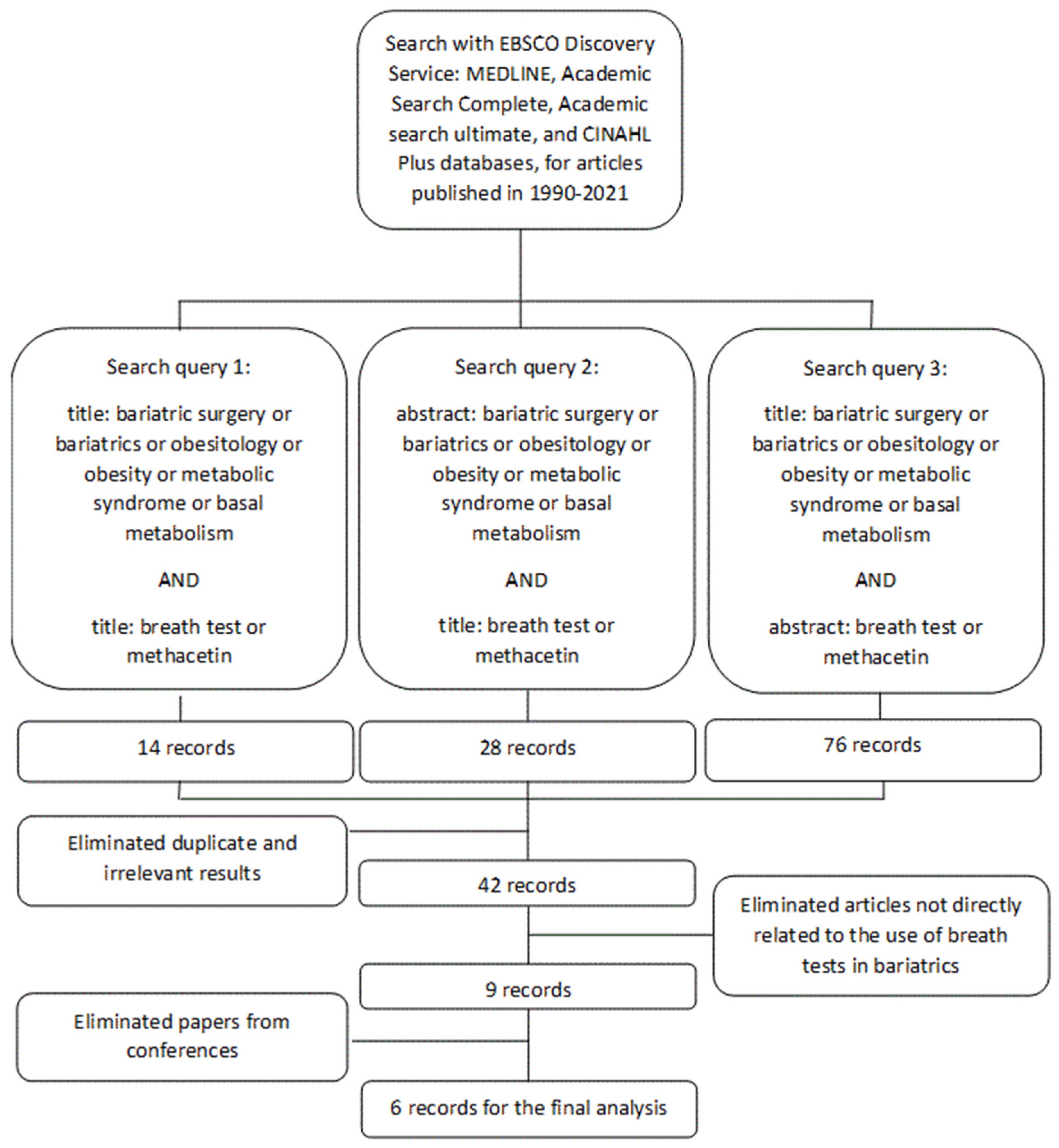
3. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
Application of Breath Tests in Bariatrics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prokopcová, I.; Dujsíková, H.; Mišejková, M.; Prokešová, J. Přínos dechových testů v gastroenterologii. Med. Praxi 2008, 5, 308–309. [Google Scholar]
- Kocna, P. Dechové testy-moderní, neinvazivní diagnostika. Interní Med. 2006, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, H.F.; Fox, M.R.; Keller, J.; Salvatore, S.; Basilisco, G.; Hammer, J.; Lopetuso, L.; Benninga, M.; Borrelli, O.; Dumitrascu, D.; et al. European guideline on indications, performance, and clinical impact of hydrogen and methane breath tests in adult and pediatric patients: European Association for Gastroenterology, Endoscopy and Nutrition, European Society of Neurogastroenterology and Motility, and European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition consensus. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2022, 10, 15–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kocna, P. Funkční dechové testy–neinvazivní diagnostika v gastroenterologii. Klin. Biochem. Metab. 2021, 29, 124–131. [Google Scholar]
- Campro Scientific GmbH. Available online: https://campro-webshop.eu/epages/8d71b479-42b8-40eb-bc7c-8545d1a52e04.sf/en_GB/?ObjectPath=/Shops/8d71b479-42b8-40eb-bc7c-8545d1a52e04/Categories/Documents/Breath_Test (accessed on 13 December 2022).
- Berger, D. A brief history of medical diagnosis and the birth of the clinical laboratory. Part 1—Ancient times through the 19th century. MLO Med. Lab. Obs. 1999, 31, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, J.P. Trace constituents in breath as related to flatulence. In Proceedings of the Fifth Annual Dry Bean Research Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 5–7 December 1961; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe, A.D.; Cozzetto, F.J.; Bennett, L.R.; Mellinkoff, S.M. Estimation of fat absorption by monitoring of expired radioactive carbon dioxide after feeding a radioactive fat. Gastroenterology 1962, 42, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A. Breath-analysis tests in gastroenterology. Gut 1974, 15, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lacroix, M.; Mosora, F.; Pontus, M.; Lefebvre, P.; Luyckz, A.; Lopez-Habib, G. Glucose naturally labeled with carbon-13: Use for metabolic studies in man. Science 1973, 181, 445–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.Y.; Klein, P.D.; Evans, D.J., Jr.; Evans, D.G.; Alpert, L.C.; Opekun, A.R.; Boutton, T.W. Campylobacter pylori detected noninvasively by the 13C-urea breath test. Lancet 1987, 1, 1174–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, B.J.; Surveyor, I. Carbon-14 urea breath test for the diagnosis of Campylobacter pylori associated gastritis. J. Nucl. Med. 1988, 29, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Alving, K.; Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.M. Increased amount of nitric oxide in exhaled air of asthmatics. Eur. Respir. J. 1993, 6, 1368–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrik, C.S.; Lange, P.; Hilberg, O. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide as a determinant for the clinical course of asthma: A systematic review. Eur. Clin. Respir. J. 2021, 8, 1891725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Som, S.; Dutta Banik, G.; Maity, A.; Chaudhuri, S.; Pradhan, M. Exhaled nitric oxide as a potential marker for detecting non-ulcer dyspepsia and peptic ulcer disease. J. Breath Res. 2018, 12, 026005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christl, S.U.; Murgatroyd, P.R.; Gibson, G.R.; Cummings, J.H. Production, metabolism, and excretion of hydrogen in the large intestine. Gastroenterology 1992, 102, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoshal, U.C. How to interpret hydrogen breath tests. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 17, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, K.; Hasanagic, H.; Memaran, N.; Huber, W.D.; Hammer, J. Relevance of Methane and Carbon Dioxide Evaluation in Breath Tests for Carbohydrate Malabsorption in a Paediatric Cohort. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 72, e71–e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer-Englar, T.; Rezaie, A.; Gupta, K.; Pichetshote, N.; Sedighi, R.; Lin, E.A.; Chua, K.; Pimentel, M. Validation of a 4-Gas Device for Breath Testing in the Determination of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Duan, Y. Current status of methods and techniques for breath analysis. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2007, 37, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peron, G.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Sorrenti, V.; Carrara, M.; Fortinguerra, S.; Zorzi, G.; Buriani, A. Retrospective analysis of a lactose breath test in a gastrointestinal symptomatic population of Northeast Italy: Use of (H2+2CH4) versus H2 threshold. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, C.; Maity, A.; Banik, G.D.; Som, S.; Chakraborty, A.; Selvan, C.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, B.; Chowdhury, S.; Pradhan, M. Non-invasive 13C-glucose breath test using residual gas analyzer-mass spectrometry: A novel tool for screening individuals with pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, e036001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peuhkuri, K.; Poussa, T.; Korpela, R. Comparison of a portable breath hydrogen analyser (Micro H2) with a Quintron MicroLyzer in measuring lactose maldigestion, and the evaluation of a Micro H2 for diagnosing hypolactasia. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1998, 58, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, A.; Prodhan, U.K.; Mitchell, S.M.; Sharma, P.; Barnett, M.P.G.; Milan, A.M.; Cameron-Smith, D. Validity of a Portable Breath Analyser (AIRE) for the Assessment of Lactose Malabsorption. Nutrients 2019, 11, e1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucero, D.P. An analytical model of the pneumatic nondispersive infrared detector. J. Phys. E Sci. Instrum. 1973, 6, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chleboun, J.; Kocna, P. Isotope Selective Nondispersive Infrared Spectrometry Can Compete with Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry in Cumulative 13CO2 Breath Tests: Assessment of Accuracy. Klin. Biochem. Metab. 2005, 13, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Savarino, V.; Landi, F.; Dulbecco, P.; Ricci, C.; Tessieri, L.; Biagini, R.; Gatta, L.; Miglioli, M.; Celle, G.; Vaira, D. Isotope ratio mass spectrometry (IRMS) versus laser-assisted ratio analyzer (LARA): A comparative study using two doses of. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2000, 45, 2168–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, I.; Butcher, H.L.; Macleod, N.A.; Weidmann, D. Hollow waveguide integrated laser spectrometer for 13CO2/12CO2 analysis. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 35670–35688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O‘Brien, D.M.; Niles, K.R.; Black, J.; Schoeller, D.A. The Breath Carbon Isotope Ratio Reflects Short-term Added-Sugar Intake in a Dose-Response, Crossover Feeding Study of 12 Healthy Adults. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Pal, N. Review—Non-Invasive Monitoring of Human Health by Exhaled Breath Analysis: A Comprehensive Review. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, e037562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhleh, M.K.; Amal, H.; Jeries, R.; Broza, Y.Y.; Aboud, M.; Gharra, A.; Ivgi, H.; Khatib, S.; Badarneh, S.; Har-Shai, L.; et al. Diagnosis and Classification of 17 Diseases from 1404 Subjects via Pattern Analysis of Exhaled Molecules. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Malderen, K.; De Winter, B.Y.; De Man, J.G.; De Schepper, H.U.; Lamote, K. Volatomics in inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome. eBioMedicine 2020, 54, e102725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryahina, K.; Smith, D.; Bortlík, M.; Machková, N.; Lukáš, M.; Španěl, P. Pentane and other volatile organic compounds, including carboxylic acids, in the exhaled breath of patients with Crohn‘s disease and ulcerative colitis. J. Breath Res. 2018, 12, e016002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, L.K.; Carvalho, N.S.; Navarro-Rodriguez, T.; Marson, F.A.L.; Carvalho, P.J.P.C. Lactulose Breath Testing Can Be a Positive Predictor Before Weight Gain in Participants with Obesity Submitted to Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 3457–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, R.K.; Faintuch, J.; Paula, A.M.; Risttori, C.A.; Silva, S.N.; Gomes, E.S.; Mattar, R.; Kuga, R.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Sakai, P.; et al. Microbial flora of the stomach after gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Obes. Surg. 2007, 17, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhani, S.V.; Shah, H.N.; Alexander, K.; Finelli, F.C.; Kirkpatrick, J.R.; Koch, T.R. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and thiamine deficiency after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery in obese patients. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andalib, I.; Shah, H.; Bal, B.S.; Shope, T.R.; Finelli, F.C.; Koch, T.R. Breath Hydrogen as a Biomarker for Glucose Malabsorption after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 102760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabaté, J.M.; Coupaye, M.; Ledoux, S.; Castel, B.; Msika, S.; Coffin, B.; Jouet, P. Consequences of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in obese patients before and after bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouillot, T.; Rhyman, N.; Gauthier, C.; Paris, J.; Lang, A.-S.; Lepers-Tassy, S.; Manfredi, S.; Lepage, C.; Leloup, C.; Jacquin-Piques, A. Study of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in a cohort of patients with abdominal symptoms who underwent bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 2331–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, R.; Mundi, M.S.; Chua, K.S.; Lorentz, P.A.; Barlow, G.M.; Lin, E.; Burch, M.; Youdim, A.; Pimentel, M. Intestinal methane production is associated with decreased weight loss following bariatric surgery. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 10, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerink, F.; Beijderwellen, H.; Huibregtse, I.; De Hoog, M.; De Brauw, L.; Brandjes, D.; Gerdes, V.A. Lactose after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity, is it a problem? Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Uribarri-Gonzalez, L.; Nieto-Garcia, L.; Martis-Sueiro, A.; Dominguez-Munoz, J.E. Exocrine pancreatic function and dynamic of digestion after restrictive and malabsorptive bariatric surgery: A prospective, cross-sectional, and comparative study. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2021, 17, 1766–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, M.; Zuccato, E.; Restelli, A.; Mazzoleni, L.; Mussini, E.; Doldi, S.B. Utility of Hydrogen and Methane Breath Tests in Combination with X-Ray Examination after a Barium Meal in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Bacterial Overgrowth after Jejuno-Ileal Bypass for Morbid Obesity. Obes. Surg. 1994, 4, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newberry, C.; Tierney, A.; Pickett-Blakely, O. Lactulose Hydrogen Breath Test Result Is Associated with Age and Gender. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1064029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mattsson, J.; Minaya, M.T.; Monegro, M.; Lebwohl, B.; Lewis, S.K.; Green, P.H.; Stenberg, R. Outcome of breath tests in adult patients with suspected small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2017, 10, 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Sendino, T.; Sandúa, A.; Calleja, S.; González, Á.; Alegre, E. Lactose tolerance test as an alternative to hydrogen breath test in the study of lactose malabsorption. Adv. Lab. Med. 2020, 1, 20200102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantrappen, G.R.; Rutgeerts, P.J.; Ghoos, Y.F.; Hiele, M.I. Mixed triglyceride breath test: A noninvasive test of pancreatic lipase activity in the duodenum. Gastroenterology 1989, 96, 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löser, C.; Brauer, C.; Aygen, S.; Hennemann, O.; Fölsch, U.R. Comparative clinical evaluation of the 13C-mixed triglyceride breath test as an indirect pancreatic function test. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 33, 327–334. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, J.; Bruckel, S.; Jahr, C.; Layer, P. A modified 13C-mixed triglyceride breath test detects moderate pancreatic exocrine insufficiency. Pancreas 2011, 40, 1201–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocna, P. Laboratorní diagnostika exokrinní funkce pankreatu. Klin. Biochem. Metab. 2020, 28, 150–160. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, J.; Meier, V.; Wolfram, K.U.; Rosien, U.; Layer, P. Sensitivity and specificity of an abbreviated (13)C-mixed triglyceride breath test for measurement of pancreatic exocrine function. United Eur. Gastroenterol. 2014, 2, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gottlieb, K.; Le, C.; Wacher, V.; Sliman, J.; Cruz, C.; Porter, T.; Carter, S. Selection of a cut-off for high- and low-methane producers using a spot-methane breath test: Results from a large north American dataset of hydrogen, methane and carbon dioxide measurements in breath. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2017, 5, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Observed Organ | Observed Substances | Observed Process or Phenomenon | Administered Substrate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small intestine | Hydrogen and methane 1 | Lactose intolerance and malabsorption | 25 or 50 g lactose |
| Fructose intolerance and malabsorption | 25–50 g fructose | ||
| SIBO 2 | 50–80 g glucose or 10 g lactulose | ||
| OCTT 3 | 10 g lactulose or inulin | ||
| Stomach | 13CO2 | Helicobacter pylori in the stomach (13C-urea breath test) | 10–100 mg 13C-labeled urea |
| Gastric evacuation rate (13C-gastric emptying breath tests) | 13C-octanoate for solid diet; 13C-acetate for liquid diet; 13C-Spirulina platensis | ||
| Pancreas | Diagnosis of exocrine pancreas and determination of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency | 13C-triolein, 13C-tripalmitin, 13C-trioctanoin, or 13C-hiolen, for lipase activity; 13C-cholesteryl octanoate, for esterase activity; 13C-starch, for amylase activity; or egg-white containing 13C-leucine or 13C-dipeptide (benzoyl-l-tyrosyl-[1-13C]-alanine), for pancreatic peptidase activity. The most widely used substrate is 13C-mixed triglyceride, composed of 1,3-distearyl-2[carboxyl-13C]octanoylglycerol | |
| Liver | Liver functions (microsomal, mitochondrial, and cytosolic functions) | 13C-aminopyrine, 13C-methacetin, 13C-erythromycin, or 13C-caffeine, for monitoring microsomal functions; 13C-alpha-ketoisocaproic acid or 13C-methionine, for monitoring mitochondrial functions; 13C-phenylalanine, 13C-galactose, or 13C-octanoate, for monitoring cytosolic functions | |
| 13C glucose (the latest clinical studies) | Prediabetes screening | 100 mg 13C-labeled glucose | |
| Type 2 diabetes screening | |||
| Insulin resistance | |||
| Metabolic syndrome screening |
| Author(s) | Breath Test Used | Process or Phenomenon | Bariatric Method | Patients (N) | Positive Tests (N) | Positivity Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coelho et al., 2019 [34] | Hydrogen breath test with lactulose | SIBO | RYGB | 18 | 7 | 38.8% |
| Ishida et al., 2007 [35] * | Hydrogen breath test with lactulose | SIBO | RYGB | 37 | 15 | 40.5% |
| Lakhani et al., 2008 [36] * | Hydrogen breath test with glucose | SIBO | RYGB | 21 | 21 | 100% |
| Andalib et al., 2015 [37] * | Hydrogen breath test with glucose | SIBO | RYGB | 63 | 46 | 73% |
| Sabate et al., 2016 [38] * | Hydrogen breath test with glucose | SIBO | RYGB, AGB | 357 (before surgery) | 55 (before surgery) | 15.4% (before surgery) |
| 20 (after AGB) | 2 (after AGB) | 10% (after AGB) | ||||
| 65 (after RYGB) | 26 (after RYGB) | 40% (after RYGB) | ||||
| Mouillot et al., 2020 [39] | Hydrogen breath test with glucose | SIBO | RYGB, OAGB, SG | 101 | 84 | 83% |
| Mathur et al., 2016 [40] | Gas chromatography to monitor methane and hydrogen in exhaled air | Methane and hydrogen produced by intestinal bacteria | RYGB and SG | 156 | 13 | 8.3% |
| Westerink et al., 2020 [41] | Hydrogen breath test with lactose | Lactose malabsorption | RYGB | 84 before treatment, 84 after treatment | 15 before treatment, 25 after treatment | 17.9% before treatment. 29.8% after treatment |
| Uribarri-Gonzalez et al., 2001 [42] | Breath test with 13C-mixed triglycerides | Pancreatic function, digestion, and nutrient absorption after bariatric treatment | SG, RYGB, and BPD/DS | 95 (36 BDP/DS, 36 RYGB, 23 SG) | EPI: N = 27 BDP/DS, N = 3 RYGB, N = 1 SG | EPI: 75% in BDP/DS; 8.3% in RYGB; 4.3% in SG patients |
| Venturi et al., 1994 [43] | Hydrogen breath test with lactulose | SIBO | JIB | 30 | 9 | 30% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karas, D.; Bužga, M.; Stejskal, D.; Kocna, P.; Holéczy, P.; Novotná, A.; Švagera, Z. Breath Tests Used in the Context of Bariatric Surgery. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3170. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123170
Karas D, Bužga M, Stejskal D, Kocna P, Holéczy P, Novotná A, Švagera Z. Breath Tests Used in the Context of Bariatric Surgery. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):3170. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123170
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaras, Daniel, Marek Bužga, David Stejskal, Petr Kocna, Pavol Holéczy, Adéla Novotná, and Zdeněk Švagera. 2022. "Breath Tests Used in the Context of Bariatric Surgery" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 3170. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123170
APA StyleKaras, D., Bužga, M., Stejskal, D., Kocna, P., Holéczy, P., Novotná, A., & Švagera, Z. (2022). Breath Tests Used in the Context of Bariatric Surgery. Diagnostics, 12(12), 3170. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123170






