Contextual Features and Information Bottleneck-Based Multi-Input Network for Breast Cancer Classification from Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Methods and Materials
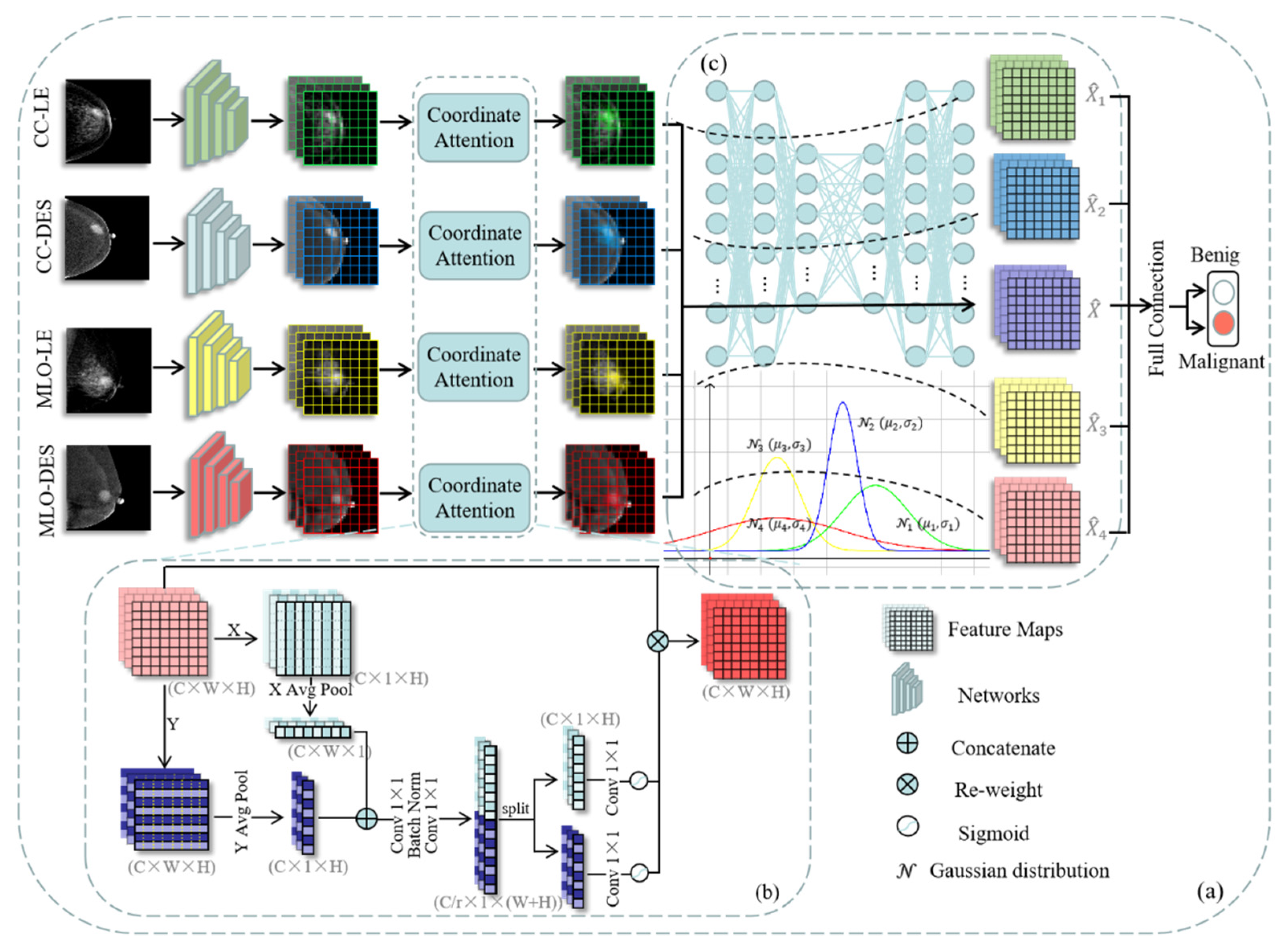
3.1. The Proposed CESM Classification Method
3.1.1. Feature Extraction Module
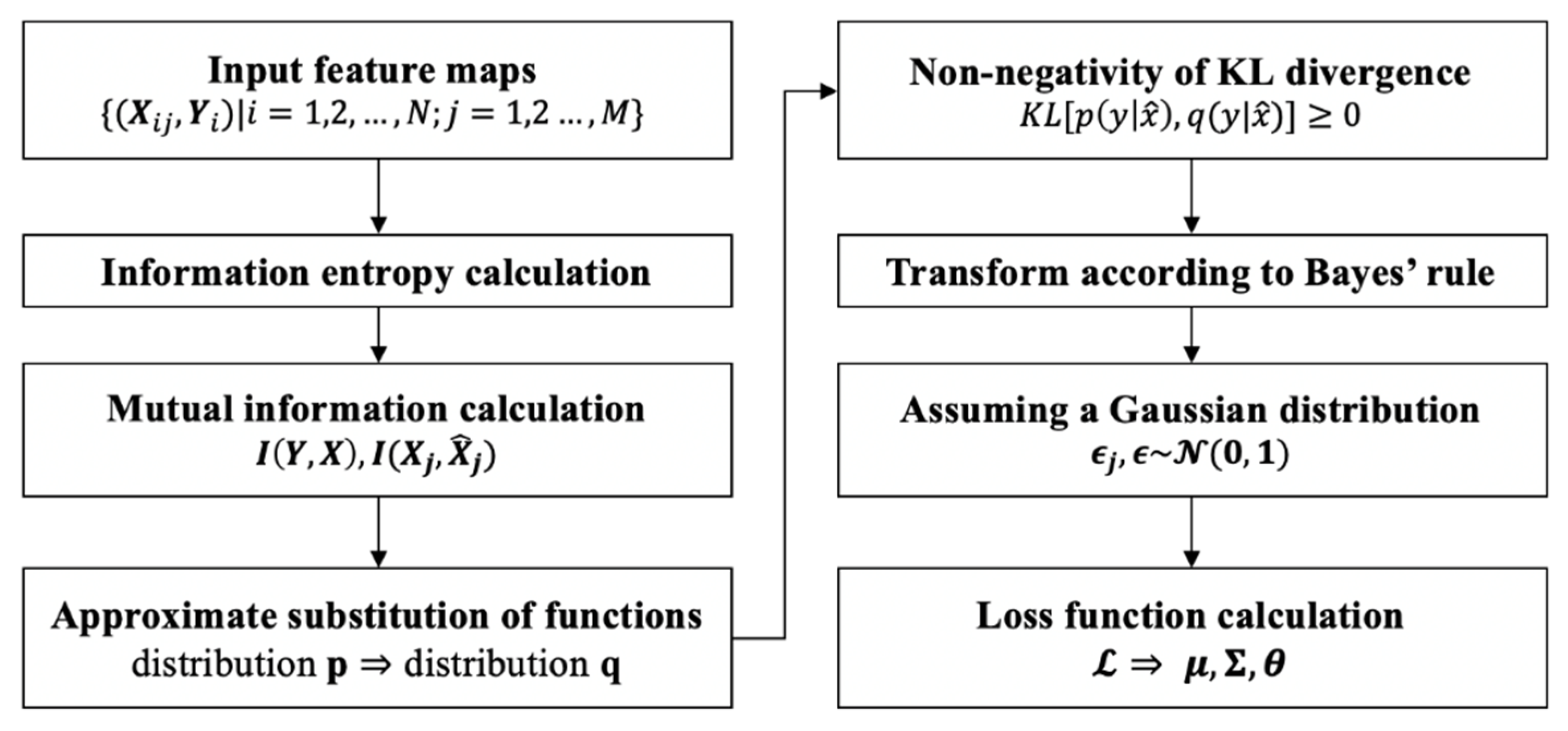
3.1.2. Feature Selection Module
3.2. Materials
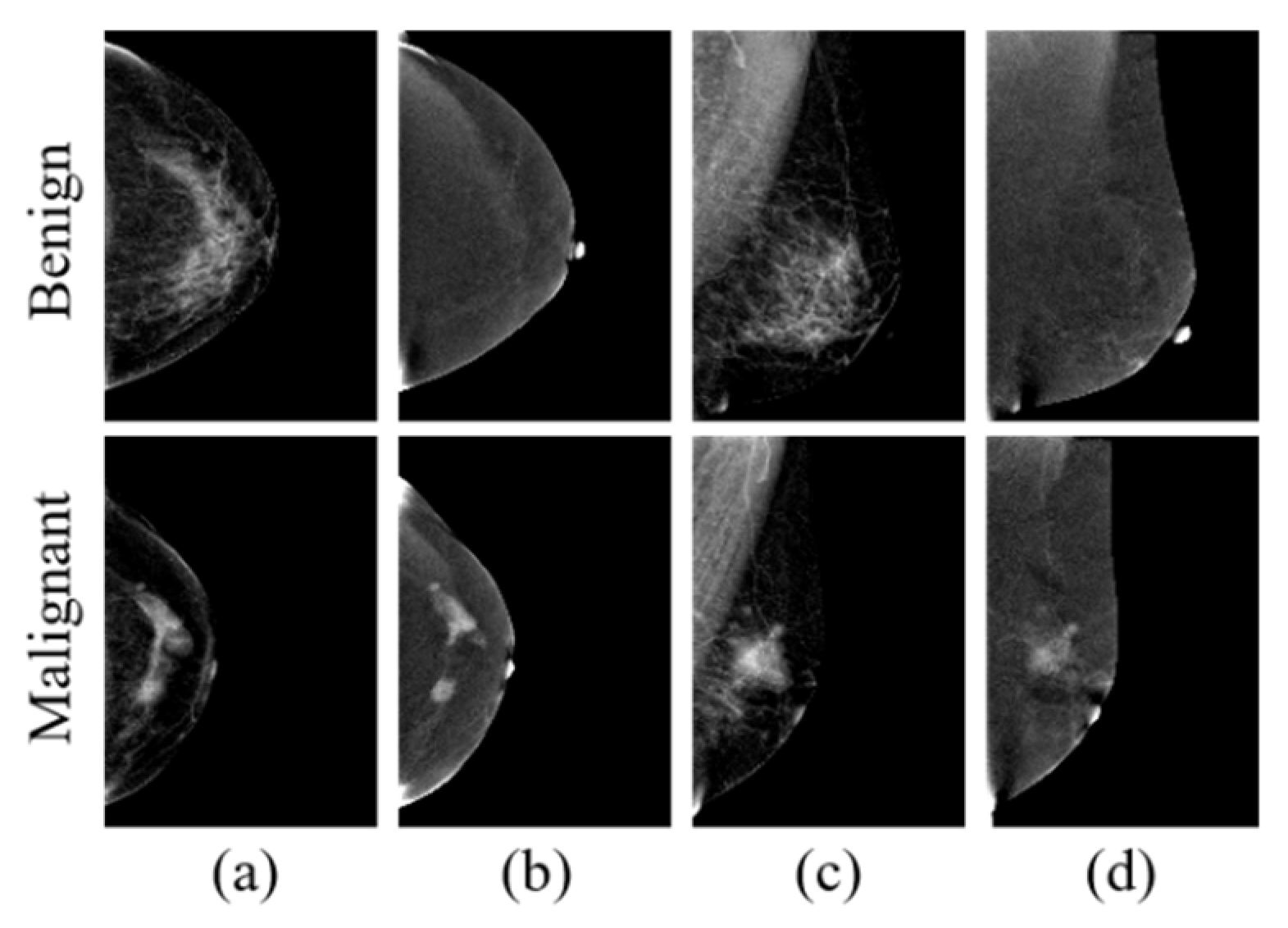
3.2.1. Data and Preprocessing
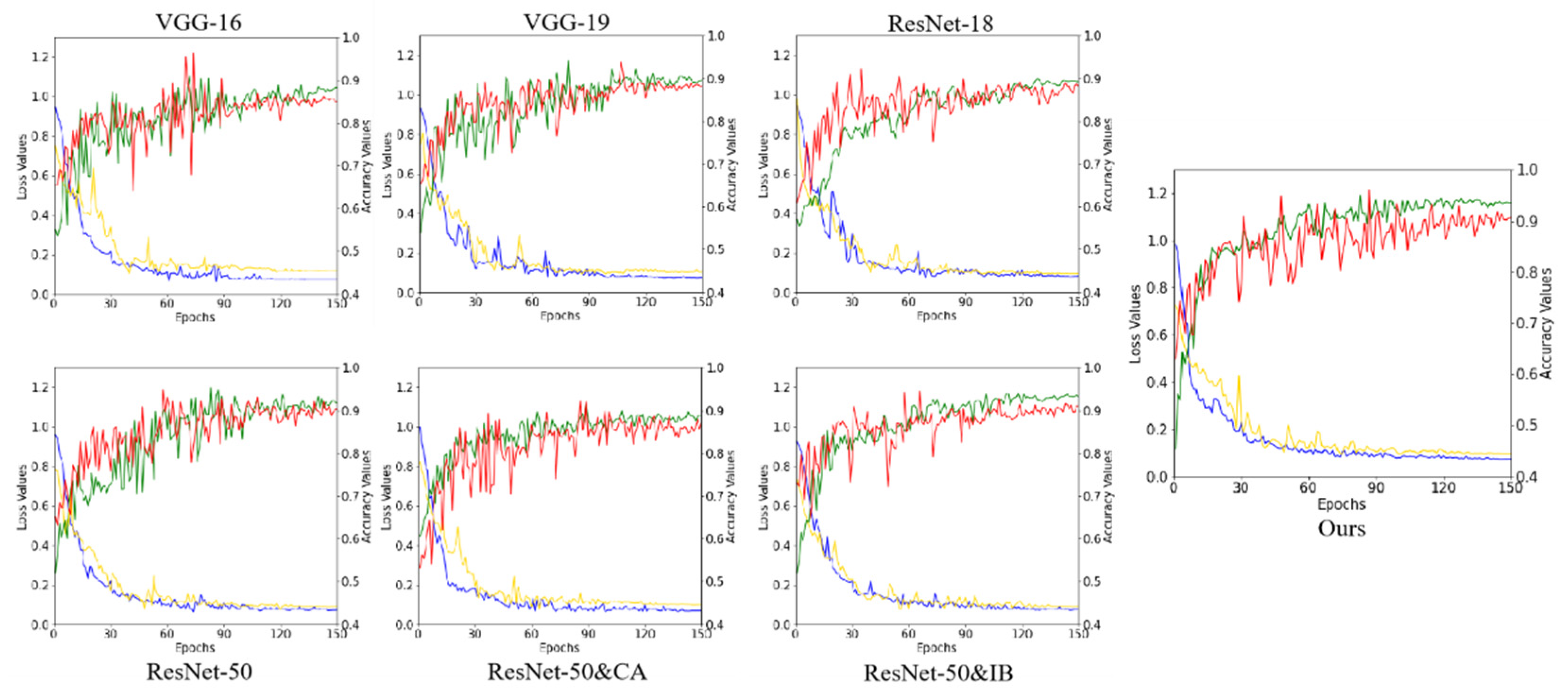
3.2.2. Details of Training
4. Results
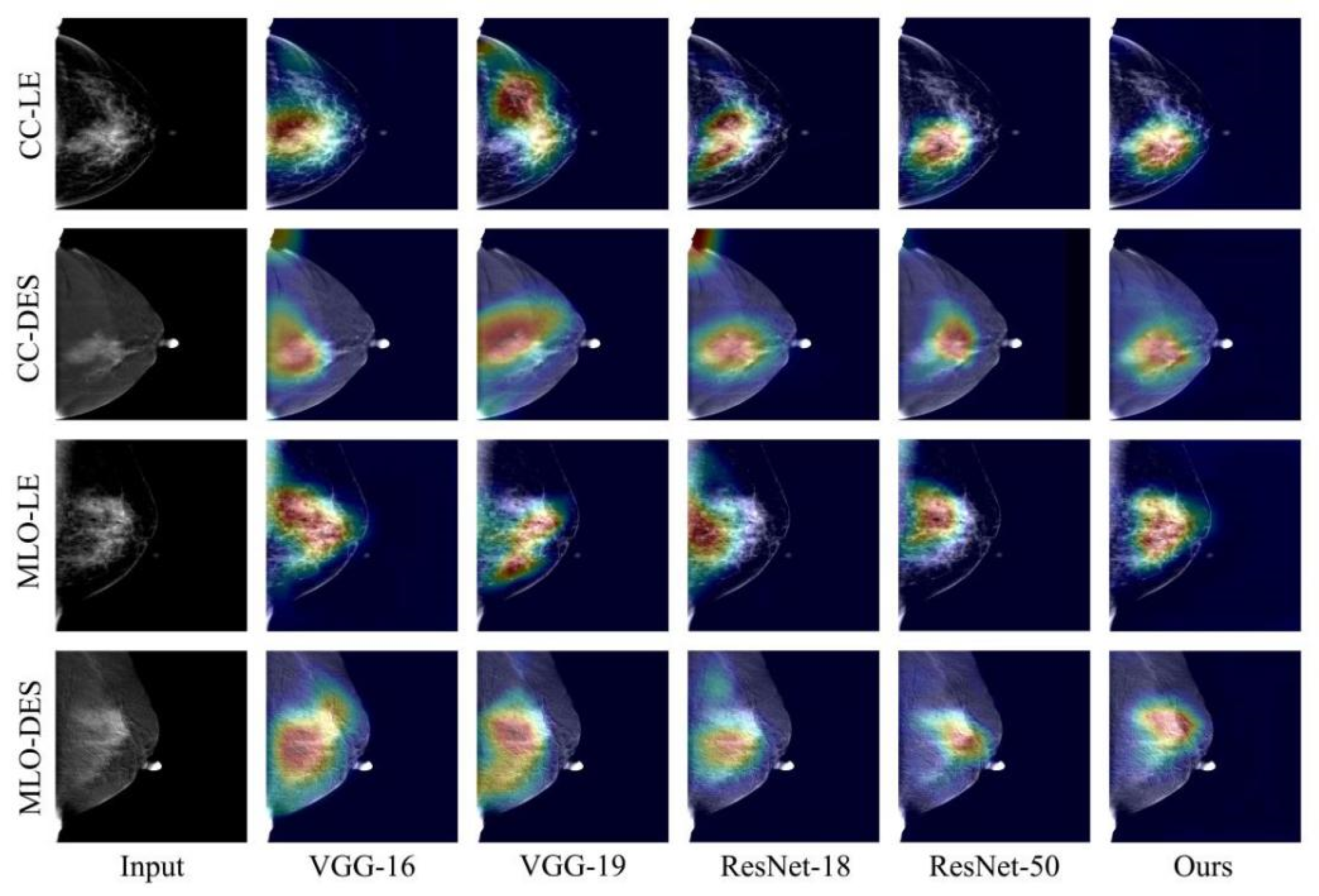
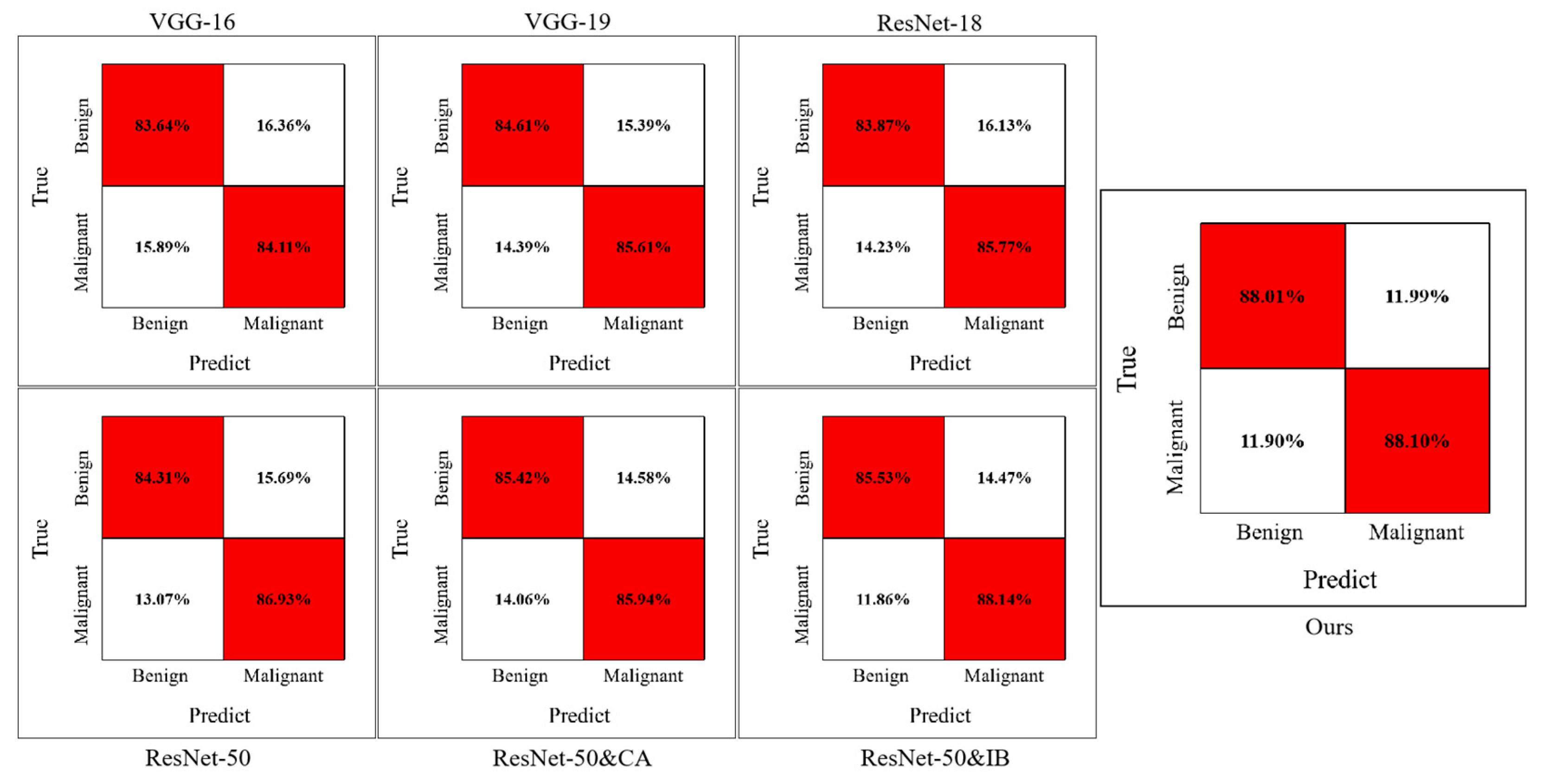
4.1. Qualitative Comparison
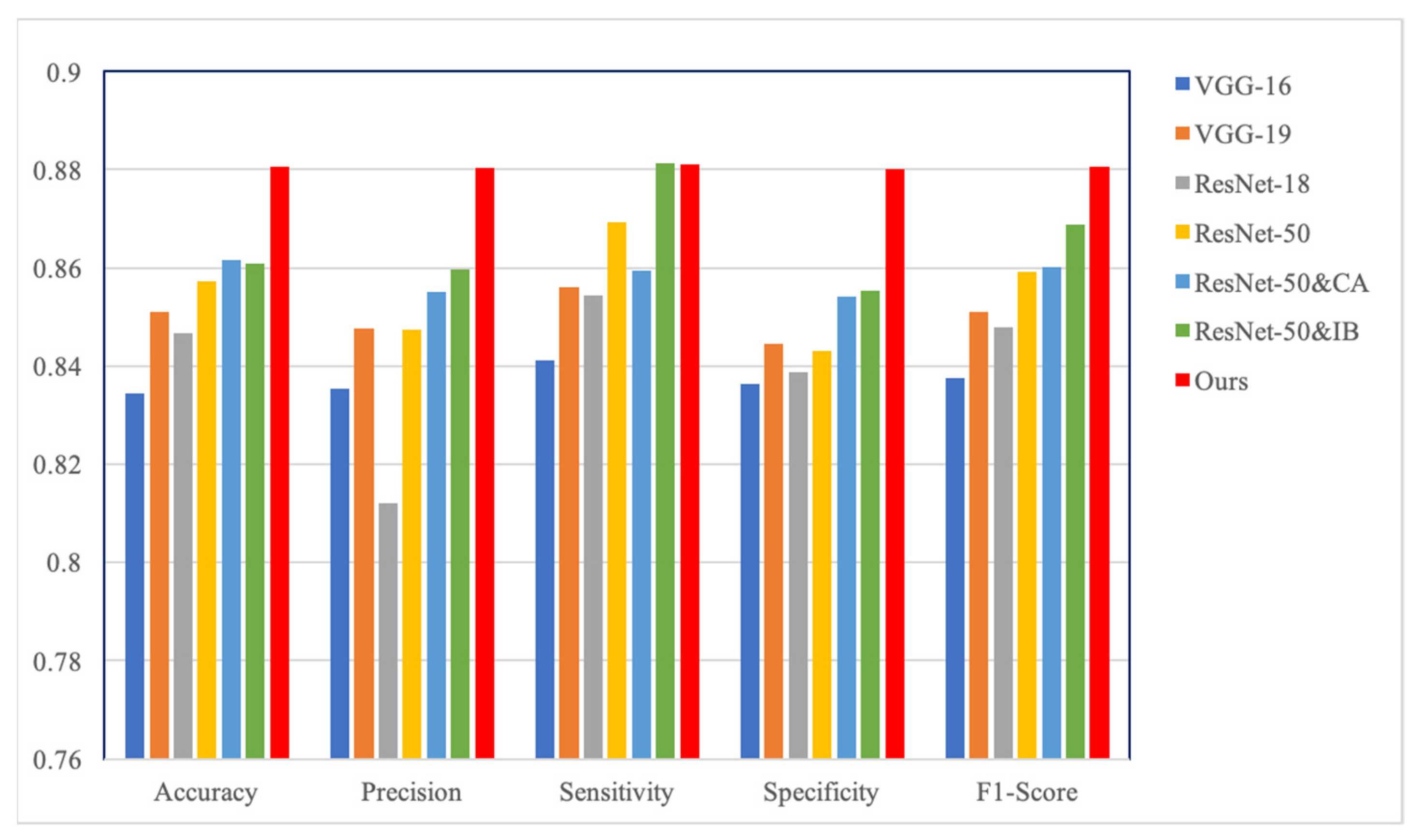
4.2. Quantitative Comparison
4.3. Ablation Studies
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobbes, M.B.; Lalji, U.; Houwers, J.; Nijssen, E.C.; Nelemans, P.J.; van Roozendaal, L.; Smidt, M.L.; Heuts, E.; Wildberger, J.E. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography in patients referred from the breast cancer screening programme. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 1668–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, S.M.; Sieniek, M.; Godbole, V.; Godwin, J.; Antropova, N.; Ashrafian, H.; Back, T.; Chesus, M.; Corrado, G.S.; Darzi, A. International evaluation of an ai system for breast cancer screening. Nature 2020, 577, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmers, J.; van Doorne-Nagtegaal, H.; Verbeek, A.; Den Heeten, G.; Broeders, M. A dedicated bi-rads training programme: Effect on the inter-observer variation among screening radiologists. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 2184–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhimani, C.; Matta, D.; Roth, R.G.; Liao, L.; Tinney, E.; Brill, K.; Germaine, P. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography: Technique, indications, and clinical applications. Acad. Radiol. 2017, 24, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallenberg, E.M.; Schmitzberger, F.F.; Amer, H.; Ingold-Heppner, B.; Balleyguier, C.; Diekmann, F.; Engelken, F.; Mann, R.M.; Renz, D.M.; Bick, U. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography vs. Mammography and mri–clinical performance in a multi-reader evaluation. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 2752–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.; Tennant, S. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (cesm). Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochelson, M.S.; Dershaw, D.D.; Sung, J.S.; Heerdt, A.S.; Thornton, C.; Moskowitz, C.S.; Ferrara, J.; Morris, E.A. Bilateral contrast-enhanced dual-energy digital mammography: Feasibility and comparison with conventional digital mammography and mr imaging in women with known breast carcinoma. Radiology 2013, 266, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Akashi-Tanaka, S.; Suzuki, S.; Daniels, M.I.; Watanabe, C.; Hirose, M.; Nakamura, S. Diagnostic accuracy of contrast-enhanced spectral mammography in comparison to conventional full-field digital mammography in a population of women with dense breasts. Breast Cancer 2017, 24, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Roth, R.; Germaine, P.; Ren, S.; Lee, M.; Hunter, K.; Tinney, E.; Liao, L. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (cesm) versus breast magnetic resonance imaging (mri): A retrospective comparison in 66 breast lesions. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2017, 98, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Phillips, J.; Cole, E.; Brook, A.; Mehta, T.; Slanetz, P.; Fishman, M.D.; Karimova, E.; Mehta, R.; Lotfi, P. Comparison of contrast-enhanced mammography with conventional digital mammography in breast cancer screening: A pilot study. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2019, 16, 1456–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, M.; Montella, R.A.; Fadda, M.P.; Tondolo, V.; Franceschini, G.; Bove, S.; Garganese, G.; Rinaldi, P.M. Diagnostic challenge of invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: What is the news? Breast magnetic resonance imaging and emerging role of contrast-enhanced spectral mammography. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia, L.; Bozzini, A.C.; Palma, S.; Montesano, M.; Signorelli, G.; Pesapane, F.; Latronico, A.; Bagnardi, V.; Frassoni, S.; Sangalli, C. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography and tumor size assessment: A valuable tool for appropriate surgical management of breast lesions. La Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Bentley, P.; Mori, K.; Misawa, K.; Fujiwara, M.; Rueckert, D. Self-supervised learning for medical image analysis using image context restoration. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 58, 101539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yuan, Y. Semi-supervised wce image classification with adaptive aggregated attention. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 64, 101733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Eric, I.; Chang, C.; Lai, M.; Tu, Z. Weakly supervised histopathology cancer image segmentation and classification. Med. Image Anal. 2014, 18, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Shen, J.; Wei, F.; Li, X.; Sangaiah, A.K. Medical image classification based on multi-scale non-negative sparse coding. Artif. Intell. Med. 2017, 83, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, M.R.H.; Haghighi, F.; Gotway, M.B.; Liang, J. Caid: Context-aware instance discrimination for self-supervised learning in medical imaging. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.07344. [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen, E.L.; Carlsen, J.F.; Vejborg, I.M.; Nielsen, M.B.; Lauridsen, C.A. The efficacy of using computer-aided detection (cad) for detection of breast cancer in mammography screening: A systematic review. Acta Radiol. 2019, 60, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, D.A.; Sharkas, M.; Attallah, O. Breast cancer diagnosis using an efficient cad system based on multiple classifiers. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witowski, J.; Heacock, L.; Reig, B.; Kang, S.K.; Lewin, A.; Pysarenko, K.; Patel, S.; Samreen, N.; Rudnicki, W.; Łuczyńska, E. Improving breast cancer diagnostics with deep learning for mri. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabo4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Q. Multi-region radiomics for artificially intelligent diagnosis of breast cancer using multimodal ultrasound. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 149, 105920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, X.Y.; Hameed, N.; Clos, J. An investigation of xgboost-based algorithm for breast cancer classification. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2021, 6, 100154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, E.; Ma, H.; Li, H.; Qi, S. An optimized framework for breast cancer classification using machine learning. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 8482022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, M.A.; Pinker, K.; Leithner, D.; Sung, J.; Avendano, D.; Morris, E.A.; Jochelson, M. Contrast-enhanced mammography and radiomics analysis for noninvasive breast cancer characterization: Initial results. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2020, 22, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losurdo, L.; Fanizzi, A.; Basile, T.M.A.; Bellotti, R.; Bottigli, U.; Dentamaro, R.; Didonna, V.; Lorusso, V.; Massafra, R.; Tamborra, P. Radiomics analysis on contrast-enhanced spectral mammography images for breast cancer diagnosis: A pilot study. Entropy 2019, 21, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danala, G.; Patel, B.; Aghaei, F.; Heidari, M.; Li, J.; Wu, T.; Zheng, B. Classification of breast masses using a computer-aided diagnosis scheme of contrast enhanced digital mammograms. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 46, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberman, L.; Menell, J.H. Breast imaging reporting and data system (bi-rads). Radiol. Clin. 2002, 40, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.; Broeders, M.; de Wolf, C.; Törnberg, S.; Holland, R.; von Karsa, L. European guidelines for quality assurance in breast cancer screening and diagnosis. -summary document. Oncol. Clin. Pract. 2008, 4, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wu, T.; Li, J.; Zheng, B.; Ruan, L.; Shang, D.; Patel, B. Sd-cnn: A shallow-deep cnn for improved breast cancer diagnosis. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2018, 70, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanizzi, A.; Losurdo, L.; Basile, T.M.A.; Bellotti, R.; Bottigli, U.; Delogu, P.; Diacono, D.; Didonna, V.; Fausto, A.; Lombardi, A. Fully automated support system for diagnosis of breast cancer in contrast-enhanced spectral mammography images. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perek, S.; Kiryati, N.; Zimmerman-Moreno, G.; Sklair-Levy, M.; Konen, E.; Mayer, A. Classification of contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (cesm) images. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominique, C.; Callonnec, F.; Berghian, A.; Defta, D.; Vera, P.; Modzelewski, R.; Decazes, P. Deep learning analysis of contrast-enhanced spectral mammography to determine histoprognostic factors of malignant breast tumours. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 4834–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, F.; Wang, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Xu, C.; Zhao, F. Artificial Intelligence-Based Classification of Breast Lesion from Contrast Enhanced Spectral Mammography: A Multicenter Study. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4028538 (accessed on 30 October 2022).
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual Conference, 19–25 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, M.-M.; Feng, J. Strip Pooling: Rethinking Spatial Pooling for Scene Parsing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 4003–4012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Tishby, N.; Pereira, F.C.; Bialek, W. The information bottleneck method. arXiv 2000, arXiv:physics/0004057. [Google Scholar]
- Tishby, N.; Zaslavsky, N. Deep Learning and the Information Bottleneck Principle. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), Jerusalem, Israel, 26 April–1 May 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Saxe, A.M.; Bansal, Y.; Dapello, J.; Advani, M.; Kolchinsky, A.; Tracey, B.D.; Cox, D.D. On the information bottleneck theory of deep learning. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2019, 2019, 124020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemi, A.A.; Fischer, I.; Dillon, J.V.; Murphy, K. Deep variational information bottleneck. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.00410. [Google Scholar]
- Veyrat-Charvillon, N.; Standaert, F.-X. Mutual Information Analysis: How, When and Why? In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Lausanne, Switzerland, 6–9 September 2009; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 429–443. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-Cam: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks Via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Wen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wu, J.; Xu, Y. Two-view attention-guided convolutional neural network for mammographic image classification. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Dataset | Accuracy | AUC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Source | Number | |||
| Multilayer Perceptron Classifier (Danala et al., 2018) [28] | LE & DES | Clinical Database of Mayo Clinic Arizona | 111 | - | 0.848 |
| SD-CNN (Gao et al., 2018) [31] | LE & DES | Mayo Clinic Arizona & INbreast | 49 & 89 | 0.900 | 0.920 |
| Support Vector Machine (Losurdo et al., 2019) [27] | CC-DES & MLO-DES | Istituto Tumori “Giovanni Paolo II” | 55 | 0.800 | - |
| Random Forest Classifier (Fanizzi et al., 2019) [32] | CC-DES & MLO-DES | Istituto Tumori “Giovanni Paolo II” | 58 | 0.825 | 0.850 |
| Fine-tuning Pretrained AlexNet (Perek et al., 2019) [33] | CC-DES & MLO-DES & text | - | 129 | 0.880 | 0.897 |
| Radiomics Analysis (Marino et al., 2020) [26] | DES | Tertiary Referral Academic Center | 100 | - | - |
| Fine-tuning CheXNet (Dominique et al., 2022) [34] | LE & DES | Henri Becquerel Cancer Center | 447 | 0.874 | 0.910 |
| RefineNet with XGBoost Classifier (Zhang et al., 2022) [35] | CC-LE & CC-DES | Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital and Fudan University Cancer Center | 1355 | 0.802 | 0.867 |
| Method | Accuracy | Precision | Sensitivity | Specificity | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGG-16 | 0.8348 | 0.8354 | 0.8411 | 0.8364 | 0.8376 |
| VGG-19 | 0.8511 | 0.8476 | 0.8561 | 0.8461 | 0.8510 |
| ResNet-18 | 0.8467 | 0.8412 | 0.8547 | 0.8387 | 0.8479 |
| ResNet-50 | 0.8572 | 0.8474 | 0.8693 | 0.8431 | 0.8592 |
| Ours | 0.8806 | 0.8803 | 0.8810 | 0.8801 | 0.8806 |
| Method | Accuracy | Precision | Sensitivity | Specificity | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet-50 | 0.8572 | 0.8474 | 0.8693 | 0.8431 | 0.8592 |
| ResNet-50&CA | 0.8617 | 0.8550 | 0.8594 | 0.8542 | 0.8602 |
| ResNet-50&IB | 0.8609 | 0.8597 | 0.8814 | 0.8553 | 0.8689 |
| Ours (full) | 0.8806 | 0.8803 | 0.8810 | 0.8801 | 0.8806 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Cui, J.; Song, J.; Jia, M.; Zou, Z.; Ding, G.; Zheng, Y. Contextual Features and Information Bottleneck-Based Multi-Input Network for Breast Cancer Classification from Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123133
Li X, Cui J, Song J, Jia M, Zou Z, Ding G, Zheng Y. Contextual Features and Information Bottleneck-Based Multi-Input Network for Breast Cancer Classification from Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123133
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinmeng, Jia Cui, Jingqi Song, Mingyu Jia, Zhenxing Zou, Guocheng Ding, and Yuanjie Zheng. 2022. "Contextual Features and Information Bottleneck-Based Multi-Input Network for Breast Cancer Classification from Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123133
APA StyleLi, X., Cui, J., Song, J., Jia, M., Zou, Z., Ding, G., & Zheng, Y. (2022). Contextual Features and Information Bottleneck-Based Multi-Input Network for Breast Cancer Classification from Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography. Diagnostics, 12(12), 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123133






