Application of Machine Learning Techniques for Characterization of Ischemic Stroke with MRI Images: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Classification of Stroke
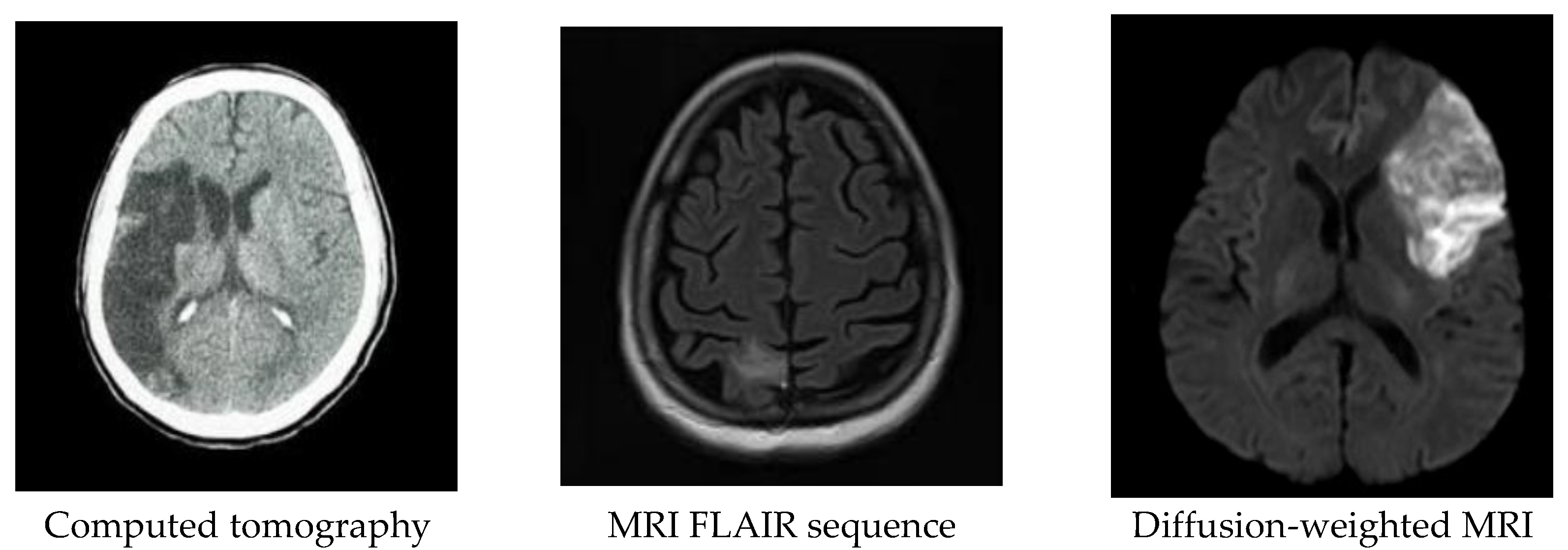
1.2. Acute Stroke Imaging
1.3. Image Segmentation
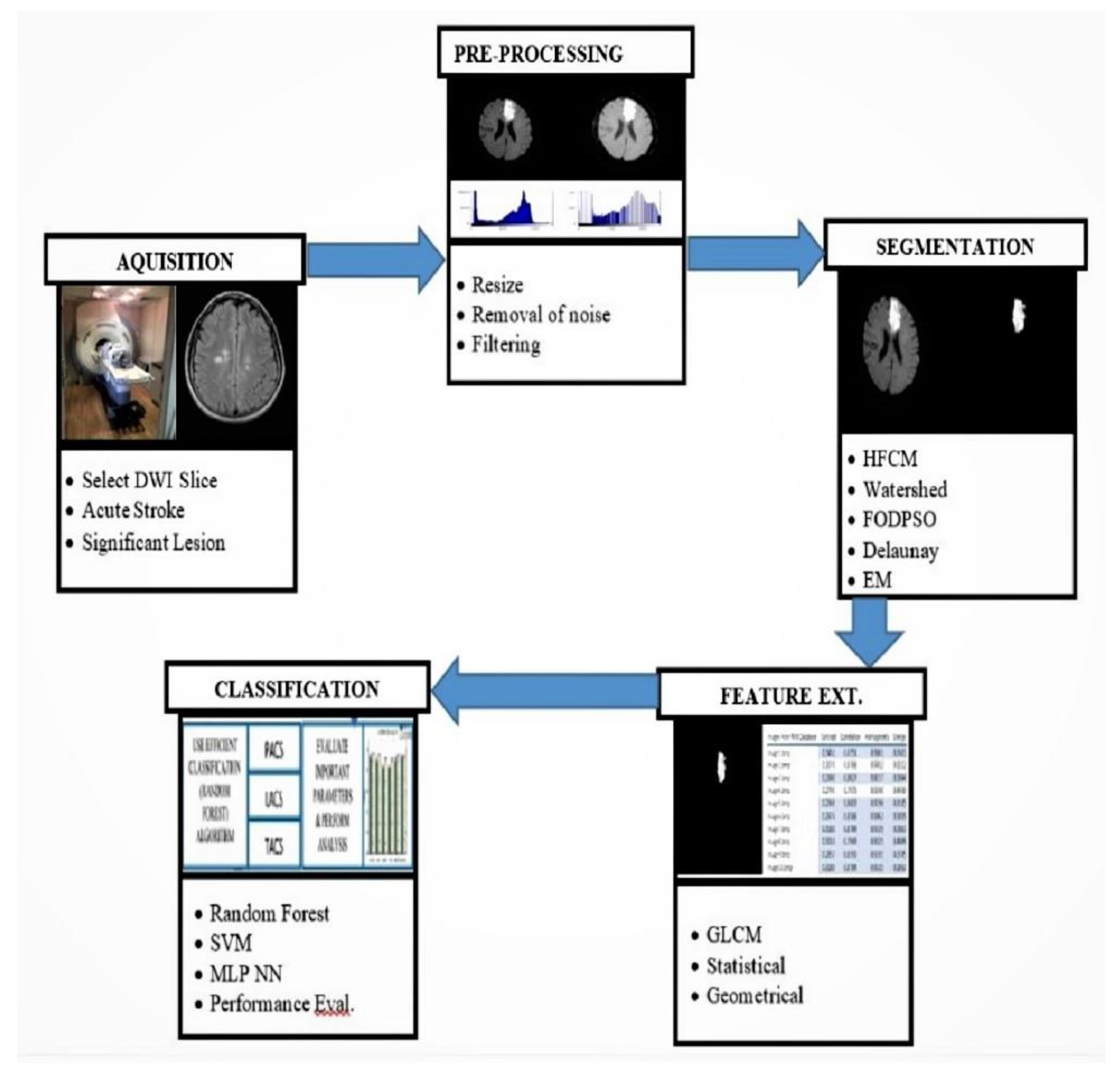
1.4. Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) for Detection of Stroke
- Image acquisition and pre-processing stage: For acute ischemic stroke detection, DWI sequence of MRI is the modality of choice. In the pre-processing stage, the images were first normalized using linear scaling, followed by background removal using simple thresholding. The quality of the image is enhanced further with contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE).
- Image segmentation: Lesions are segmented using various methods, including clustering, watershed, and optimization and classified with different classifiers.
- Features extraction: Extracted statistical or morphological features are used as input to the classifiers for classification of stroke and its sub-types.
- Classification: Rule-based classifiers, such as neural network, support vector machine (SVM), decision tree, and random forest classifier, are implemented to classify ischemic brain lesions according to established standards, e.g., the Oxfordshire Community Stroke Project classification scheme.
2. Materials and Methods
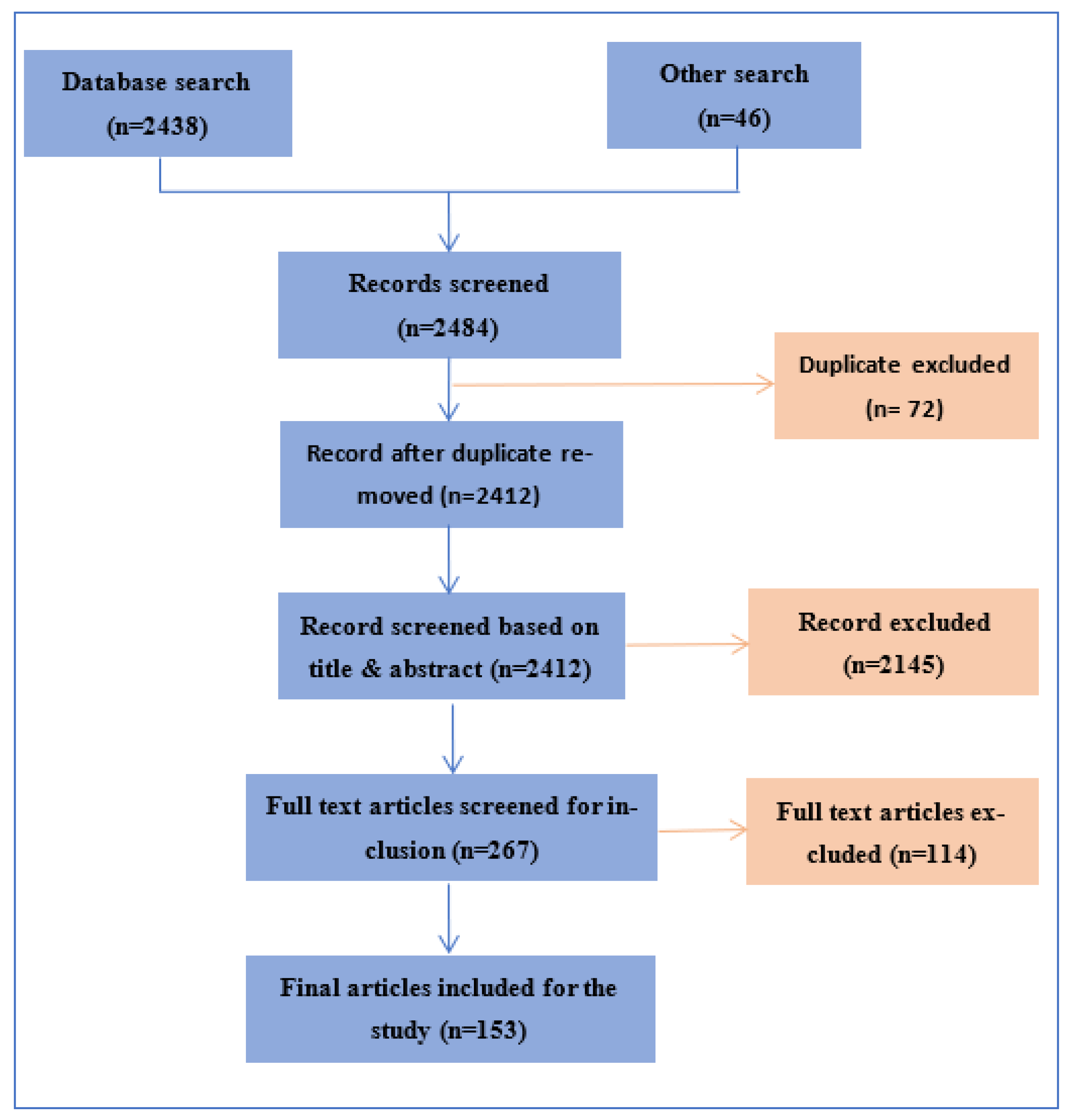
2.1. Article Search Strategy
2.2. Article Selection
3. Results
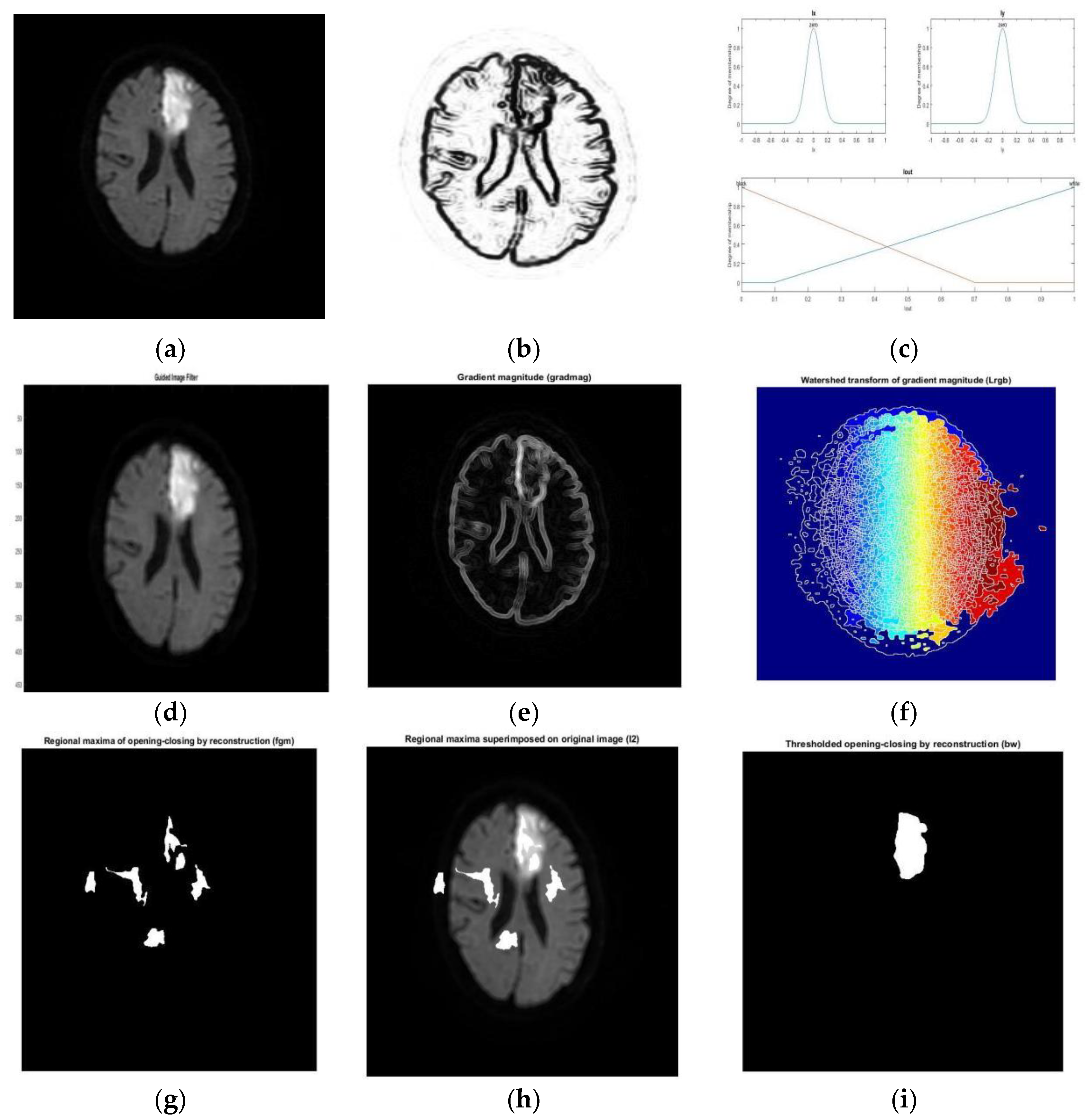
3.1. Segmentation Techniques
3.1.1. Overview
3.1.2. Clustering
3.1.3. Watershed Transformation (WT)
3.1.4. Intelligent Optimization
3.2. Machine Learning
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, C.D.A. The impact of stroke. Br. Med. Bull. 2000, 56, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigin, V.L.; Lawes, C.M.; Bennett, D.A.; Barker-Collo, S.L.; Parag, V. Worldwide stroke incidence and early case fatality reported in 56 population-based studies: A systemic review. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalakannan, S.; Gudlavalleti, A.S.V.; Gudlavalleti, V.S.M.; Goenka, S.; Kuper, H. Incidence & prevalence of stroke in India: A systematic review. Indian J. Med. Res. 2017, 146, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khurana, S.; Gourie-Devi, M.; Sharma, S.; Kushwaha, S. Burden of stroke in India during 1960 to 2018: A systematic review and meta-analysis of community based surveys. Neurol. India 2021, 69, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursunov, D.; Akbarkhodjaeva, Z. Risk factors of developing transient ischemic attack. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 381, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, K.K.; Olsen, T.S.; Dehlendorff, C.; Kammersgaard, L.P. Hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes compared: Stroke severity, mortality, and risk factors. Stroke 2009, 40, 2068–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriakose, D.; Xiao, Z. Pathophysiology and treatment of stroke: Present status and future perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamford, J.; Sandercock, P.; Dennis, M.; Burn, J.; Warlow, C. Classification and natural history of clinically identifiable subtypes of cerebral infarction. Lancet 1991, 337, 1521–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M. Antithrombotic and thrombolytic therapy for ischemic stroke. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 1999, 7, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, P.A.; Darby, D.G.; Desmond, P.M.; Gerraty, R.P.; Yang, Q.; Li, T.; Jolley, D.; Donnan, G.; Tress, B.M.; Davis, S.M. Identification of major ischemic change. Diffusion-weighted imaging versus computed tomography. Stroke 1999, 30, 2059–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vymazal, J.; Rulseh, A.M.; Keller, J.; Janouskova, L. Comparison of CT and MR imaging in ischemic stroke. Insights Imaging 2012, 3, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Bhatta, S.; Gerzanich, V.; Simard, J.M. Cytotoxic edema: Mechanisms of pathological cell swelling. Neurosurg. Focus 2007, 22, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagmann, P.; Jonasson, L.; Maeder, P.; Thiran, J.; Wedeen, V.; Meuli, R. Understanding diffusion MR imaging techniques: From scalar diffusion-weighted imaging to diffusion tensor imaging and beyond. Radiographics 2006, 26 (Suppl. S1), S205–S223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moseley, M.; Kucharczyk, J.; Mintorovitch, J.; Cohen, Y.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Derugin, N.; Asgari, H.; Norman, D. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of acute stroke: Correlation with T2-weighted and magnetic susceptibility-enhanced MR imaging in cats. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1990, 11, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wardlaw, J.M. Neuroimaging in acute ischemic stroke: Insights into unanswered questions of pathophysiology (review). J. Intern. Med. 2010, 267, 172–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, E.; Tian, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Dai, J. The application of diffusion-and perfusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis and therapy of acute cerebral infarction. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2006, 2006, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, D.; Thijs, V.; Albers, G.; Moseley, M.; Marks, M. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in acute ischemia: Value of apparent diffusion coefficient and signal intensity thresholds in predicting tissue at risk and final infarct size. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004, 25, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Fiebach, J.B.; Schellinger, P.D.; Jansen, O.; Meyer, M.; Wilde, P.; Bender, J.; Schramm, P.; Juttler, E.; Oehler, J.; Hartmann, M.; et al. CT and diffusion-weighted MR imaging in randomized order: Diffusion-weighted imaging results in higher accuracy and lower interrater variability in the diagnosis of hyperacute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2002, 33, 2206–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.S.; Harris, A.D.; Sevick, R.J.; Frayne, R. Effect of b value on contrast during diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging assessment of acute ischemic stroke. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2002, 15, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Choi, C.G.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Suh, D.C. High-b-value diffusion-weighted MR imaging of hyperacute ischemic stroke at 1.5 t. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Delano, M.; Cao, Y. High b-value diffusion imaging. Neuroimaging Clin. 2002, 12, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.; Gutierrez, A.; Mock, B.; Hebron, D.; Prager, J.; Gorey, M.; Homer, D. High-b-value diffusion weighted MR imaging of suspected brain infarction. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2000, 21, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Norouzi, A.; Shafry, M.; Rahim, M.; Altameem, A.; Saba, T.; Rad, A.E.; Rehman, A.; Uddin, M. Medical image segmentation methods, algorithms, and applications. IETE Tech. Rev. 2014, 31, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrick, N.; Sahiner, B.; Armato, S.G.; Bert, A.; Correale, L.; Delsanto, S.; Freedman, M.T.; Fryd, D.; Gur, D.; Hadjiiski, L.; et al. Evaluation of computer-aided detection and diagnosis systems. Med. Phys. 2013, 40, 087001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Sandham, W.; Granat, M.; Sterr, A. MRI fuzzy segmentation of brain tissue using neighborhood attraction with neural network optimization. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2005, 9, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, Y.; Dojat, M.; Scherrer, B.; Forbes, F.; Garbay, C. Multimodal MRI segmentation of ischemic stroke lesions. In Proceedings of the 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22 October 2007; pp. 1595–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Fiez, J.A.; Damasio, H.; Grabowski, T.J. Lesion segmentation and manual warping to a reference brain: Intra-and interobserver reliability. Hum. Brain Ma. 2000, 9, 192–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaga, T.; Katsuragawa, S.; Uchiyama, Y.; Hirai, T.; Shiraishi, J. Computerized detection of metastatic brain tumors in brain MR images. Int. J. CARS 2012, 7 (Suppl. S1), 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despotovic, I.; Goossens, B.; Philips, W. MRI segmentation of the human brain: Challenges, methods, and applications. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2015, 2015, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Timmeren, J.; Cester, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B. Radiomics in medical imaging—“How-to” guide and critical reflection. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ripplinger, C.M.; Sato, D. Automated object detection in experimental data using Ccmbination of unsupervised and supervised methods. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 805161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Aggarwal, L.M. Automated medical image segmentation techniques. J. Med. Phys. 2010, 35, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xiang, S.; Pan, C.; Wang, L.; Meng, G. Level set evolution with locally linear classification for image segmentation. Pattern Recogn. 2013, 46, 1734–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, S.; Galun, M.; Brandt, A.; Basri, R. Image segmentation by probabilistic bottom-up aggregation and cue integration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, N.M.; Bakar, S.A.; Muda, S.; Mokji, M.M. Brain lesion segmentation of diffusion-weighted MRI using thresholding technique. In Proceedings of the 5th Kuala Lumpur International Conference on Biomedical Engineering 2011, London, UK, 13–15 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Caldairou, B.; Passat, N.; Habas, P.A.; Studholme, C.; Rousseau, F. A non-local fuzzy segmentation method: Application to brain MRI. Pattern Recogn. 2011, 44, 1916–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boykov, Y.; Veksler, O.; Zabih, R. Fast approximate energy minimization via graph cuts. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 1222–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, H.; Li, P.; Dorent, R.; Bradford, R.; Saeed, S.; Bisdas, S.; Ourselin, S.; Shapey, J.; Vercauteren, T. Manual segmentation versus semi-automated segmentation for quantifying vestibular schwannoma volume on MRI. Int. J. CARS 2020, 15, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastidar, P.; Heinonen, T.; Ahonen, J.P.; Jehkonen, M.; Molnar, G. Volumetric measurements of right cerebral hemisphere infarction: Use of a semiautomatic MRI segmentation technique. Comput. Biol. Med. 2000, 30, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matesin, M.; Loncaric, S.; Petravic, D. A rule-based approach to stroke lesion analysis from CT brain images. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis. In conjunction with 23rd International Conference on Information Technology Interfaces, Pula, Croatia, 19–21 June 2001; pp. 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Usinskas, E.; Pranckeviciene, A.; Wittenberg, T.; Hastreiter, P.; Tomand, B. Automatic ischemic stroke segmentation using various techniques. Neural Netw. Soft Comput. 2002, 19, 498–503. [Google Scholar]
- Meilunas, M.; Usinskas, A.; Kirvaitis, R.; Dobrovolskis, R. Automatic contouring of segmented human brain ischemic stroke region on CT images. Math. Model. Anal. 2003, 8, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, K.W.; Baird-Gunning, J.; Walker, L.; Baird, T.; McCormick, M.; Coutts, S.B. Can the ischemic penumbra be identified on noncontrast CT of acute stroke? Stroke 2007, 38, 2485–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, J.R.; Yoder, K.K.; Osuntokun, O.; Kalnin, A.; Bruno, A.; Morris, E.D. A supervised method for calculating perfusion/diffusion mismatch volume in acute ischemic stroke. Comput. Biol. Med. 2006, 36, 1268–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangla, A.R.; Kolar, B.; Almast, J.; Ekholm, S.E. Border zone infarcts: Pathophysiologic and imaging characteristics. Radiographics 2011, 31, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezgin, M.; Sankur, B. Survey over image thresholding techniques and quantitative performance evaluation. J. Electron. Imaging 2004, 13, 146–168. [Google Scholar]
- Martel, A.; Allder, S.; Delay, G.; Morgan, P.; Moody, A. Measurement of infarct volume in stroke patients using adaptive segmentation of diffusion weighted MR images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–12 October 2023; pp. 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Usinskas, A.; Dobrovolskis, R.A.; Tomandl, B. Ischemic stroke segmentation on CT images using joint features. Informatica 2004, 15, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paing, M.P.; Tungjitkusolmun, S.; Bui, T.H.; Visitsattapongse, S.; Pintavirooj, C. Automated Segmentation of Infarct Lesions in T1-Weighted MRI Scans Using Variational Mode Decomposition and Deep Learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, A.C.; Yan, H. An adaptive spatial fuzzy clustering algorithm for 3-D MR image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2003, 22, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leemput, K.; Maes, F.; Vandermeulen, D.; Suetens, P. Automated model-based tissue classification of MR images of the brain. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1999, 18, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.L.; Prince, J.L. Adaptive fuzzy segmentation of magnetic resonance images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1999, 18, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldjian, J.A.; Chalela, J.; Kasner, S.E.; Liebeskind, D.; Detre, J.A. Automated CT segmentation and analysis for acute middle cerebral artery stroke. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol 2001, 22, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Tian, J.; Li, E.; Dai, J. Robust unsupervised segmentation of infarct lesion from diffusion tensor MR images using multiscale statistical classification and partial volume voxel reclassification. NeuroImage 2004, 23, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, K.N.; Gupta, V.; Jianbo, H.; Nowinski, W.L. Identification, segmentation, and image property study of acute infarcts in diffusion-weighted images by using a probabilistic neural network and adaptive gaussian mixture model. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2006, 13, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Hevia-Montiel, N.; Jimenez-Alaniz, J.R.; Medina-Banuelos, V.; Yanez-Suarez, O.; Rosso, C.; Samson, Y.; Baillet, S. Robust nonparametric segmentation of infarct lesion from diffusion-weighted MR images. In Proceedings of the 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Glasgow, UK, 5 March 2007; pp. 2102–2105. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.; Prakash, B.; Nowinski, W.L. Automatic and rapid identification of infarct slices and hemisphere in DWI scans. Acad. Radiol. 2008, 15, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Szameitat, A.J.; Sterr, A. Detection of infarct lesions from single MRI modality using inconsistency between voxel intensity and spatial location-a 3-D automatic approach. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2008, 12, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Kong, J.; Lu, Y.; Qi, M.; Zhang, B. A modified FCM algorithm for MRI brain image segmentation using both local and non-local spatial constraints. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2008, 32, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramathilagama, S.; Pandiyarajanc, R.; Sathyac, A.; Devic, R.; Kannan, S.R. Modified fuzzy-means algorithm for segmentation of T1-T2-weighted brain MRI. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2011, 235, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.N.; Isa, N.A.M. Adaptive fuzzy-K-means clustering algorithm for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2010, 56, 2661–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Image segmentation by fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm with a novel penalty term. Comput. Inform. 2007, 26, 17–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, C.; Zhou, Y.X.; Narayana, P. A fast algorithm for calculation of inhomogeneity gradient in MRI data. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 32, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogita, K.; Dubey, K.; Mushrif, M. FCM Clustering Algorithms for Segmentation of Brain MR Images. Adv. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 2016, 3406406. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Chung, F.-L.; Shitong, W. Robust fuzzy clustering-based image segmentation. Appl. Soft Comput. 2009, 9, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.H.; Pizurica, A.; Philips, W.; Kerre, E.; van de Walle, R.; Lemahieu, I. An integrated method of adaptive enhancement for unsupervised segmentation of MRI brain images. Pattern Recog. Lett. 2003, 24, 2549–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayachitra, S.; Prasanth, A. Multi-Feature Analysis for Automated Brain Stroke Classification Using Weighted Gaussian Naïve Bayes Classifier. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2021, 30, 2150178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghier, M.L.; Ramlackhansingh, A.; Crinion, J.; Leff, A.P.; Price, C.J. Lesion identification using unified segmentation-normalization models and fuzzy clustering. Neuroimage 2008, 41, 1253–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Jeon, B.; Xu, D.; Wu, Q.M.; Zhang, H. Image segmentation by generalized hierarchical fuzzy c-means algorithm. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 28, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.; Shah, S.; Kosta, Y.P. Novel improved fuzzy c-mean algorithm for MR-Image segmentation. Int. J. Soft Comput. Eng. 2012, 2, 355–357. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Wen, Y.; Wan, M.; Liu, S. Multi-channel features based automated segmentation of diffusion tensor imaging using an improved FCM with spatial constraints. Neurocomputing 2014, 137, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Yamany, S.; Mohamed, N.; Farag, A.; Moriarty, T. A modified fuzzy c-means algorithm for bias field estimation and segmentation of MRI data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2002, 21, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, A.W.C.; Yan, H.; Law, N.F. Image segmentation based on adaptive cluster prototype estimation. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2005, 13, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krinidis, S.; Chatzis, V. A robust fuzzy local information c-means clustering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assia, C.; Yazid, C.; Said, M. Segmentation of brain MRIs by support vector machine: Detection and characterization of strokes. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2015, 15, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subudhi, A.; Jena, S.S.; Sabut, S. Automated detection of brain stroke in MRI with hybrid fuzzy c-means clustering and random forest classifier and applications. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Appl. 2019, 18, 1950018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beucher, S.; Meyer, F. The morphological approach to segmentation: The watershed transform. In Mathematical Morphology in Image Processing; Dougherty, E., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; Volume 12, pp. 433–481. [Google Scholar]
- Moga, A.N.; Gabbouj, M. Parallel image component labelling with watershed transformation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1997, 19, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagyard, D.; Razaz, M.; Atkin, P. Analysis of watershed algorithms for grayscale images. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Lausanne, Switzerland, 16–19 September 1996; pp. 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Karantzalos, K.; Argialas, D. Improving edge detection and watershed segmentation with anisotropic. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 5427–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, C.C.; Lajish, V.L.; Kumar, R. Brain tumor extraction from MRI brain images using marker based watershed algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), Kerala, India, 10–13 August 2015; pp. 318–323. [Google Scholar]
- Warscotte, V.; Macq, B.; Thiran, J.; Michel, C. Accurate segmentation of 3-d magnetic resonance images of the head using a directional watershed transform. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Montrkal, QC, Canada, 20–23 September 1995; pp. 491–492. [Google Scholar]
- Grau, V.; Mewes, A.J.; Alcaniz, M.; Kikinis, R.; Warfield, S.K. Improved watershed transform for medical image segmentation using prior information. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2004, 23, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Fu, J. Watershed algorithm for medical image segmentation based on morphology and total variation model. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2019, 33, 1954019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macenko, M.; Celenk, M.; Ma, L. Lesion detection using morphological watershed segmentation and model based inverse filtering. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06), Hong Kong, China, 20–24 August 2006; pp. 669–682. [Google Scholar]
- Letteboer, M.J.; Olsen, O.F.; Dam, E.B.; Willems, P.A.; Viergever, M.A.; Niessen, W.J. Segmentation of tumors in magnetic resonance brain images using an interactive multiscale watershed algorithm. Acad. Radiol. 2004, 1, 1125–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subudhi, A.; Jena, S.; Sabut, S. Delineation of the ischemic stroke lesion based on watershed and relative fuzzy connectedness in brain MRI. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018, 56, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotjonen, J.M.; WolzKoikkalainen, R.; Thurfjell, L.; Waldemar, G.; Soininen, H.; Rueckert, D. Fast and robust multi-atlas segmentation of brain magnetic resonance images, Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative. Neuroimage 2010, 49, 2352–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, T.; De, A.; Bhattacharjee, A.K. Grammatical swarm based segmentation methodology for lesion segmentation in brain MRI. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2015, 121, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Das, R.L.; Bhattacharjee, A.K.; Sharma, D. Masking based segmentation of diseased MRI images. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Information Science and Applications, Seoul, Korean, 21–23 April 2010; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Nabizadeh, N.; John, N.; Wright, C. Histogram-based gravitational optimization algorithm on single MR modality for automatic brain lesion detection and segmentation. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 7820–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, R.; Menaka, R. A multi-scale approach for detection of ischemic stroke from brain MR images using discrete curvelet transformation. Measurement 2017, 100, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.X.; Siarry, P.; Oulhadj, H. Integrating fuzzy entropy clustering with an improved PSO for MRI brain image segmentation. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 65, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.; Recker, R.; Shah, A.; Bhanu, B.; Obenaus, S.A. Automated ischemic lesion detection in a neonatal model of hypoxic ischemic injury. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 33, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, R.V.; Venayagamoorthy, G.K. Bio-inspired algorithms for autonomous deployment and localization of sensor. IEEE Trans. Syst. 2010, 40, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Subudhi, A.; Sahoo, S.; Biswal, P.; Sabut, S.K. Segmentation and classification of ischemic stroke using optimized features in brain MRI. Biomed. Eng. Appl. Basis Commun. 2018, 30, 1850011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couceiro, M.S.; Ferreira, N.F.; Machado, J.T. Fractional Order Darwinian Particle Swarm Optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo-Valdes, M.; Sanchez-Ortiz, G.I.; Elkington, A.G.; Mohiaddin, R.H.; Rueckert, D. Segmentation of 4D cardiac MR images using a probabilistic atlas and the EM algorithm. Med. Image Anal. 2004, 8, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.L.; Rubin, D.B.; Donal. Maximum likelihood estimation via the ECM algorithm: A general framework. Biometrika 1993, 80, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, U.C.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, I.Y.; Kim, S.I. Adaptable fuzzy C-Means for improved classification as a preprocessing procedure of brain parcellation. J. Digit. Imaging 2001, 14 (Suppl. S1), 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Niu, M.; Zhao, Q.; Li, H. Comparison of EM-based algorithms and image segmentation evaluation. In International Conference on Intelligent Computing; Huang, D.S., Jo, K.H., Wang, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.K.; Liu, D.H. Segmentation of color image using EM algorithm in HSV color space. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Information Acquisition, Seogwipo, Korea, 8–11 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mahjoub, M.A.; Kalti, K. Image segmentation by adaptive distance based on EM algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2011, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marroquin, J.L.; Vemuri, B.C.; Botello, S.; Calderon, E.; Fernandez-Bouzas, A. An accurate and efficient Bayesian method for automatic segmentation of brain MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2002, 21, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, G.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, D. Hybrid genetic and variational expectation-maximization algorithm for Gaussian-mixture-model-based brain MR image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2011, 15, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, M.; Kumari, R.S. Spatial Fuzzy C means and expectation maximization algorithms with bias correction for segmentation of MR brain images. J. Med Syst. 2017, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G.R.; Basukala, D.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, K.H.; Kang, M. Brain image segmentation using a combination of expectation-maximization algorithm and watershed transform. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2016, 26, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouainia, M.; Medjram, M.S.; Doghmane, N. Brain MRI Segmentation and lesions detection by EM algorithm. Int. J. Med. Health Sci. 2008, 2, 379–382. [Google Scholar]
- Pennisi, A.; Bloisi, D.D.; Nardi, D.; Giampetruzzi, A.R.; Mondino, C.; Facchiano, A. Skin lesion image segmentation using Delaunay Triangulation for melanoma detection. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2016, 52, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häfner, M.; Liedlgruber, M.; Uhl, A.; Vécsei, A.; Wrba, F. Delaunay triangulation-based pit density estimation for the classification of polyps in high-magnification chromo-colonoscopy. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 2012, 107, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Subudhi, A.; Acharya, U.R.; Dash, M.; Jena, S.; Sabut, S. Automated approach for detection of ischemic stroke using Delaunay Triangulation in brain MRI images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 103, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, M.; de Haan, B.; Juenger, H.; Karnath, H.O. Manual, semi-automated, and automated delineation of chronic brain lesions: A comparison of methods. Neuroimage 2011, 56, 2038–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, J.; Bourgeat, P.; Fripp, J.; Ghose, S.; Rose, S.; Salvado, O.; Connelly, A.; Campbell, B.; Palmer, S.; Sharma, G.; et al. Lesion segmentation from multimodal MRI using random forest following ischemic stroke. Neuroimage 2014, 98, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, O.; Wilms, M.; von der Gablentz, J.; Kramer, U.M.; Munte, T.F.; Handels, H. Extra Tree forests for sub-acute ischemic stroke lesion segmentation in MR sequences. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 240, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, O.; Wilms, M.; Gablentz, J.; Kramer, U.; Handels, H. Ischemic stroke lesion segmentation in multi-spectral MR images with support vector machine classifiers. In Medical Imaging, Computer-Aided Diagnosis; SPIE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; Volume 9035. [Google Scholar]
- Griffis, J.C.; Allendorfer, J.B.; Szaflarski, J.P. Voxel-based Gaussian naive Bayes classification of ischemic stroke lesions in individual T1-weighted MRI scans. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 257, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Elazab, A.; Qingmao, H. Segmentation of hyper-acute cerebral infarct based on random forest and sparse coding from diffusion weighted imaging. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju Island, Korea, 11–15 July 2017; 3425–3428. [Google Scholar]
- Mah, Y.H.; Jager, R.; Kennard, R.; Husain, M.; Nachev, P. A new method for automated high-dimensional lesion segmentation evaluated in vascular injury and applied to the human occipital lobe. Cortex 2014, 56, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muda, A.F.; Saad, N.M.; Abu-Bakar, S.R.; Muda, A.S.; Abdullah, A.R. Brain lesion segmentation using fuzzy C-means on diffusion-weighted imaging. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2015, 10, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Fridriksson, J.; Fillmore, P.; Rorden, C.; Yu, H.; Zheng, K.; Wang, S. Automated lesion detection on MRI scans using combined unsupervised and supervised methods. BMC Med. Imaging 2015, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Katsaggelos, A.K.; Wang, X.; Parrish, T.B. A deep symmetry convnet for stroke lesion segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Bentley, P.; Rueckert, D. Fully automatic acute ischemic lesion segmentation in DWI using convolutional neural networks. Neuroimage Clin. 2017, 15, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Thamm, T.; Gong, E.; Ouyang, J.; Huang, C.; Christensen, S.; Marks, M.P.; Lansberg, M.G.; Albers, G.W.; et al. Use of Deep Learning to Predict Final Ischemic Stroke Lesions From Initial Magnetic Resonance Imaging. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e200772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.F.; Hsu, J.; Xu, X.; Ramachandran, S.; Wang, V.; Miller, M.I.; Hillis, A.E.; Faria, A.V.; The STIR and VISTA Imaging investigators. Deep learning-based detection and segmentation of diffusion abnormalities in acute ischemic stroke. Commun. Med. 2021, 1, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, V.; Goyal, N.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Hosseinichimeh, N.; Hontecillas, R.; Bassaganya-Riera, J.; Elijovich, L.; Metter, J.E.; Alexandrov, A.W.; Liebeskind, D.S.; et al. Novel screening tool for stroke using artificial neural network. Stroke 2017, 48, 1678–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Shen, Q.; Duong, T.Q. Artificial neural network prediction of ischemic tissue fate in acute stroke imaging. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledezma, C.J.; Wintermark, M. Multimodal CT in stroke imaging: New concepts. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 47, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasasbeh, A.S.; Christensen, S.; Parsons, M.W.; Campbell, B.; Albers, G.W.; Lansberg, M.G. Artificial neural network computer tomography perfusion prediction of ischemic core. Stroke 2019, 50, 1578–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chyzhyk, D.; Dacosta-Aguayo, R.; Mataro, M.; Grana, M. An active learning approach for stroke lesion segmentation on multimodal MRI data. Neurocomputing 2015, 150, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.C.; Speier, W.; Zhang, H.; Scalzo, F.; El-Saden, F.; Arnold, C.W. A Machine Learning Approach for Classifying Ischemic Stroke Onset Time From Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 1666–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, L.; Azarpazhouh, R.; Farzadfar, M.; Mousavi, S.A.; Jazaieri, F.; Khorvash, F.; Norouzi, R.; Toghianfar, N. Prediction and control of stroke by data mining. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4 (Suppl. S2), S245–S249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tomita, N.; Jiang, S.; Maeder, M.E.; Hassanpour, S. Automatic post-stroke lesion segmentation on MR images using 3D residual convolu-tional neural network. Neuroimage Clin. 2020, 27, 102276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Maddikunta, P.K.R.; Hakak, S.; Khan, W.Z.; Bashir, A.K.; Jolfaei, A.; Tariq, U. Antlion re-sampling based deep neural network model for classification of imbalanced multimodal stroke dataset. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, O.; Schroder, C.; Forkert, N.D.; Martinetz, T.; Handels, H. Correction: Classifiers for ischemic stroke lesion segmentation: A comparison study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibas, L.J.; Stolfi, J. Primitives for the manipulation of general subdivisions and the computation of Voronoi diagrams. ACM Trans. Graphics 1985, 4, 74–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanel, M.; Krsek, P.; Svub, M.; Stancl, V.; Siler, O. Delaunay-Based Vector Segmentation of Volumetric Medical Images. In Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns; Kropatsch, W.G., Kampel, M., Hanbury, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 4673. [Google Scholar]
- Akkus, Z.; Galimzianova, A.; Hoogi, A.; Rubin, D.L.; Erickson, B.J. Deep Learning for Brain MRI Segmentation: State of the Art and Future Directions. J. Digit. Imaging 2017, 30, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, D.R.; Das, D.; Dash, R.; Majhi, S.; Majhi, B. Deep extreme learning machine with leaky rectified linear unit for multiclass classification of pathological brain images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 15381–15396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leea, E.J.; Kima, Y.H.; Kimb, N.; Kanga, D.W. Deep into the brain: Artificial intelligence in stroke imaging. J. Stroke 2017, 19, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soun, J.E.; Chow, D.S.; Nagamine, M.; Takhtawala, R.S.; Filippi, C.G.; Yu, W.; Chang, P.D. Artificial Intelligence and acute stroke imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.; Badgeley, M.; Mocco, J.; Oermann, E.K. Deep learning guided stroke management: A review of clinical applications. J. Neurointerv Surg. 2018, 10, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskins, G.; Kruger, U.; Yan, P. Deep learning in medical image registration: A survey. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2020, 31, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, T.; Gandhi, T.K. Deep convolutional neural networks with transfer learning for automated brain image classification. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2020, 31, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winzeck, S.; Mocking, S.J.T.; Bezerra, R.; Bouts, M.J.R.J.; McIntosh, E.C.; Diwan, I.; Garg, P.; Chutinet, A.; Kimberly, W.T.; Copen, W.A.; et al. Ensemble of convolutional neural networks improves automated segmentation of acute ischemic lesions using multiparametric diffusion-weighted MRI. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Farhat, F.G.; Boukrina, O.; Barrett, A.M.; Binder, J.R.; Roshan, U.W.; Graves, W.W. A multi-path 2.5 dimensional convolutional neural network system for segmenting stroke lesions in brain MRI images. Neuroimage Clin. 2020, 25, 102118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, C.P.; Bizzo, B.C.; Hillis, J.M.; Chin, J.K.; Comeau, D.S.; Gauriau, R.; Macruz, F.; Pawar, J.; Noro, F.T.C.; Sharaf, E.; et al. Development and clinical application of a deep learning model to identify acute infarct on magnetic resonance imaging. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.D.; Kuoy, E.; Grinband, J.; Weinberg, B.D.; Thompson, M.; Homo, R.; Chen, J.; Abcede, H.; Shafie, M.; Sugrue, L.; et al. Hybrid 3D/2D convolutional neural network for hemorrhage evaluation on head CT. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, N.M.; Unberath, M.; Hager, G.D.; Hui, F.K. Artificial intelligence to diagnose ischemic stroke and identify large vessel occlusions: A systematic review. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2020, 12, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Zhang, R.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, L.; He, M.; You, C.; Tian, R. Machine learning-based approaches for prediction of patients’ functional outcome and mortality after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Kwon, Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, B.J.; Paik, M.C.; Won, J.H. Ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks for prognosis of ischemic stroke. In International Workshop on Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 10154. [Google Scholar]
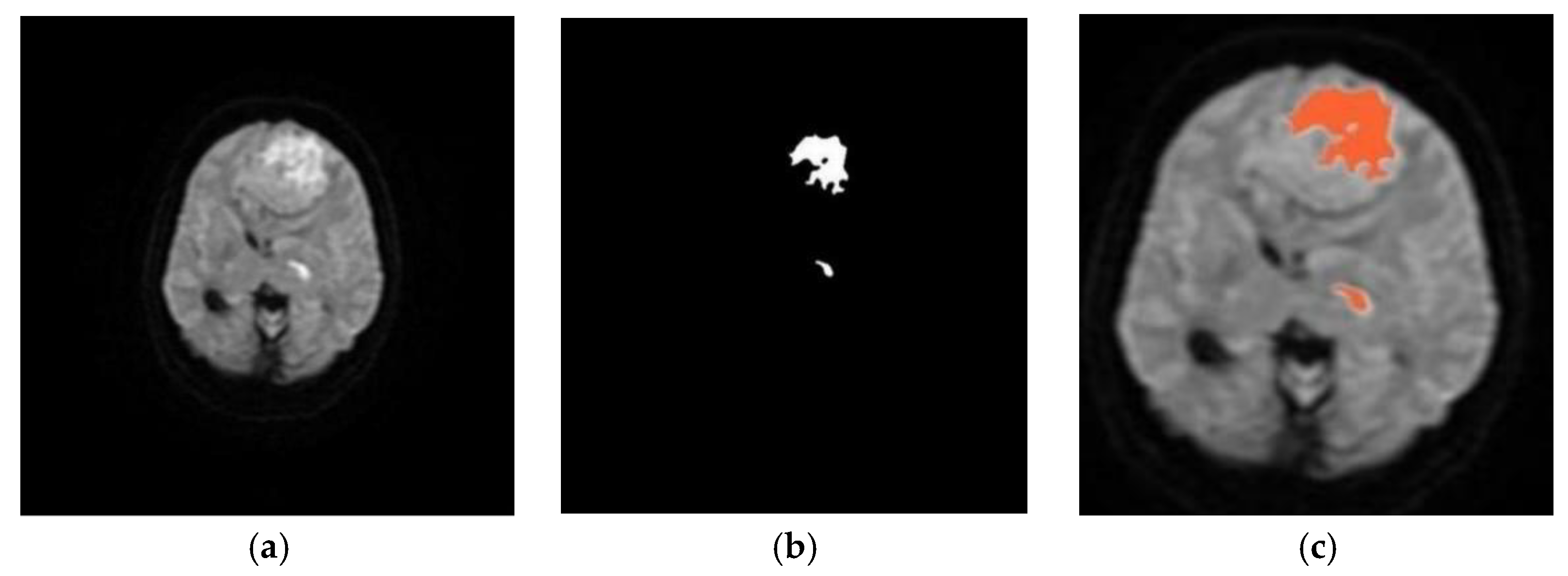

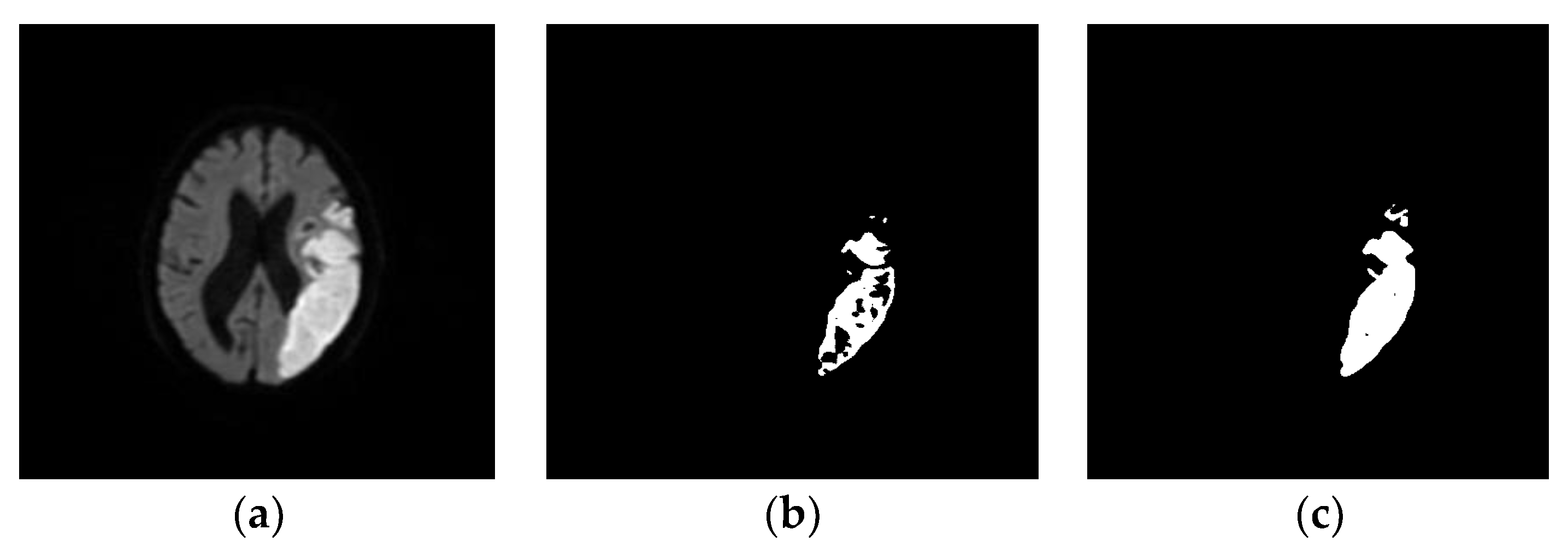

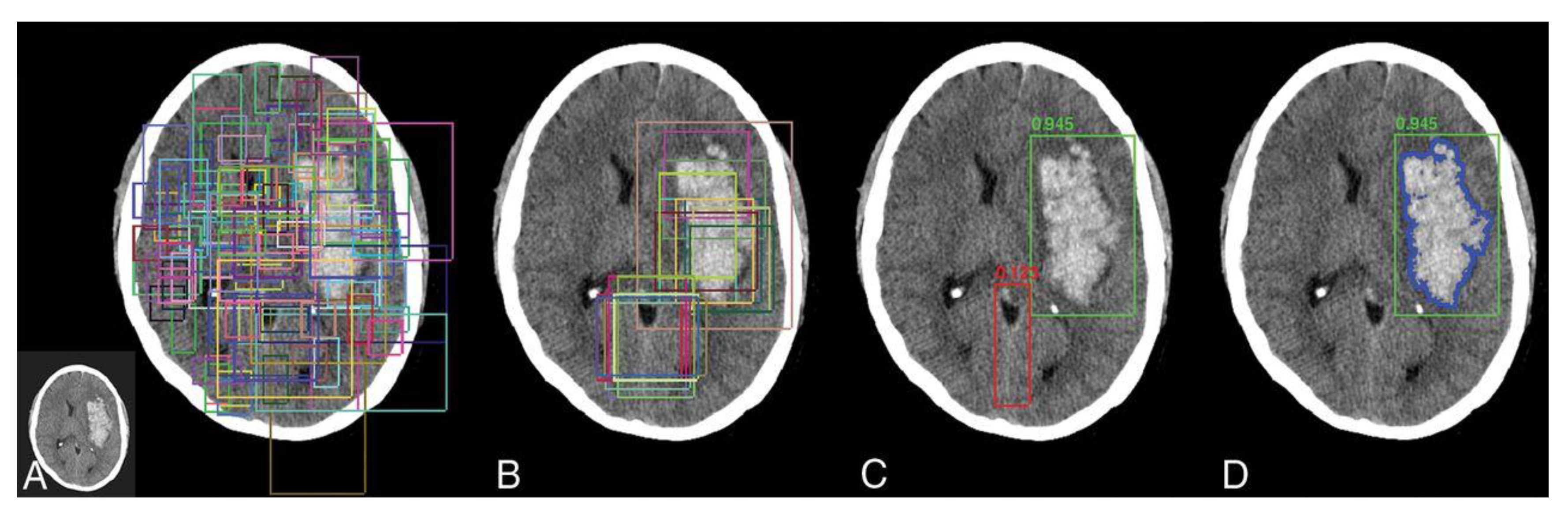
| Literature | Modality | No. of Images | Segmentation Approach | Classifier | Dice Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prakash et al. (2008) [57] | DWI scans | 13 patients; 361 images | Divergence based algorithms | ProbabilisticNN | 0.6 |
| Seghier et al. (2008) [70] | T1-weighted | 10 images | Generative model | Fuzzy clustering | 0.64 |
| Subudhi et al. (2015) [78] | DWI scans | 05 subjects | Hybrid FCM with thresholding | Random forest | 0.79 |
| Subudhi et al. (2018) [89] | DWI scans | 142 images | Watershed and fuzzy connectedness | Random forest | 0.96 |
| Wilke et al. (2011) [115] | T1 weighted | 11 subjects | Automatic lesion identification | Expert | 0.49 |
| Asit et al. (2018) [114] | DWI scan | 192 images | Delaunay triangulation | Random forest | 0.93 |
| Mitra et al. (2014) [116] | Multimodal MRI | 36 subjects | Bayesian-Markov random field | Random forest | 0.60 |
| Maier et al. (2015) [117] | FLAIR sequences | 37 subjects | Intensity derived image features | Extra trees | 0.65 |
| Maier et al. (2015) [118] | FLAIR sequences | 37 subjects | Fuzzy clustering | SVM | 0.72 |
| Griffs et al. (2016) [119] | T1 weighted | 30 subjects | Probabilistic tissue segmentation | Naive Bayes classifier | 0.66 |
| Zhang et al. (2014) [120] | DWI | 98 subjects | General segmentation | Random forest | 0.77 |
| Mah et al. (2014) [121] | DWI scan | 435 images | Unsupervised algorithm | Neural network | 0.73 |
| Muda et al. (2015) [122] | DWI scan | 30 subjects | Fuzzy C-means algorithm | Expert | 0.73 |
| Guo et al. (2015) [123] | T1 weighted | 60 subjects | Unsupervised and supervised methods | SVM | 0.73 |
| Wang et al. (2016) [124] | T1 weighted | 18 subjects | Deep lesion symmetry ConvNet | Neural network | 0.78 |
| Chen et al. (2017) [125] | DWI scan | 741 subjects | Novel framework | CNN | 0.67 |
| Yu et al. (2020) [126] | DWI scan | 182 subjects | U-net framework | Deep learning | 0.53 |
| Liu et al. (2021) [127] | DWI scan | 2348 images | DAGMNet | Deep learning | 0.74 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Subudhi, A.; Dash, P.; Mohapatra, M.; Tan, R.-S.; Acharya, U.R.; Sabut, S. Application of Machine Learning Techniques for Characterization of Ischemic Stroke with MRI Images: A Review. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102535
Subudhi A, Dash P, Mohapatra M, Tan R-S, Acharya UR, Sabut S. Application of Machine Learning Techniques for Characterization of Ischemic Stroke with MRI Images: A Review. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(10):2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102535
Chicago/Turabian StyleSubudhi, Asit, Pratyusa Dash, Manoranjan Mohapatra, Ru-San Tan, U. Rajendra Acharya, and Sukanta Sabut. 2022. "Application of Machine Learning Techniques for Characterization of Ischemic Stroke with MRI Images: A Review" Diagnostics 12, no. 10: 2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102535
APA StyleSubudhi, A., Dash, P., Mohapatra, M., Tan, R.-S., Acharya, U. R., & Sabut, S. (2022). Application of Machine Learning Techniques for Characterization of Ischemic Stroke with MRI Images: A Review. Diagnostics, 12(10), 2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102535







