Fracture-Related Infection in Bicolumnar Acetabular Fracture: A Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
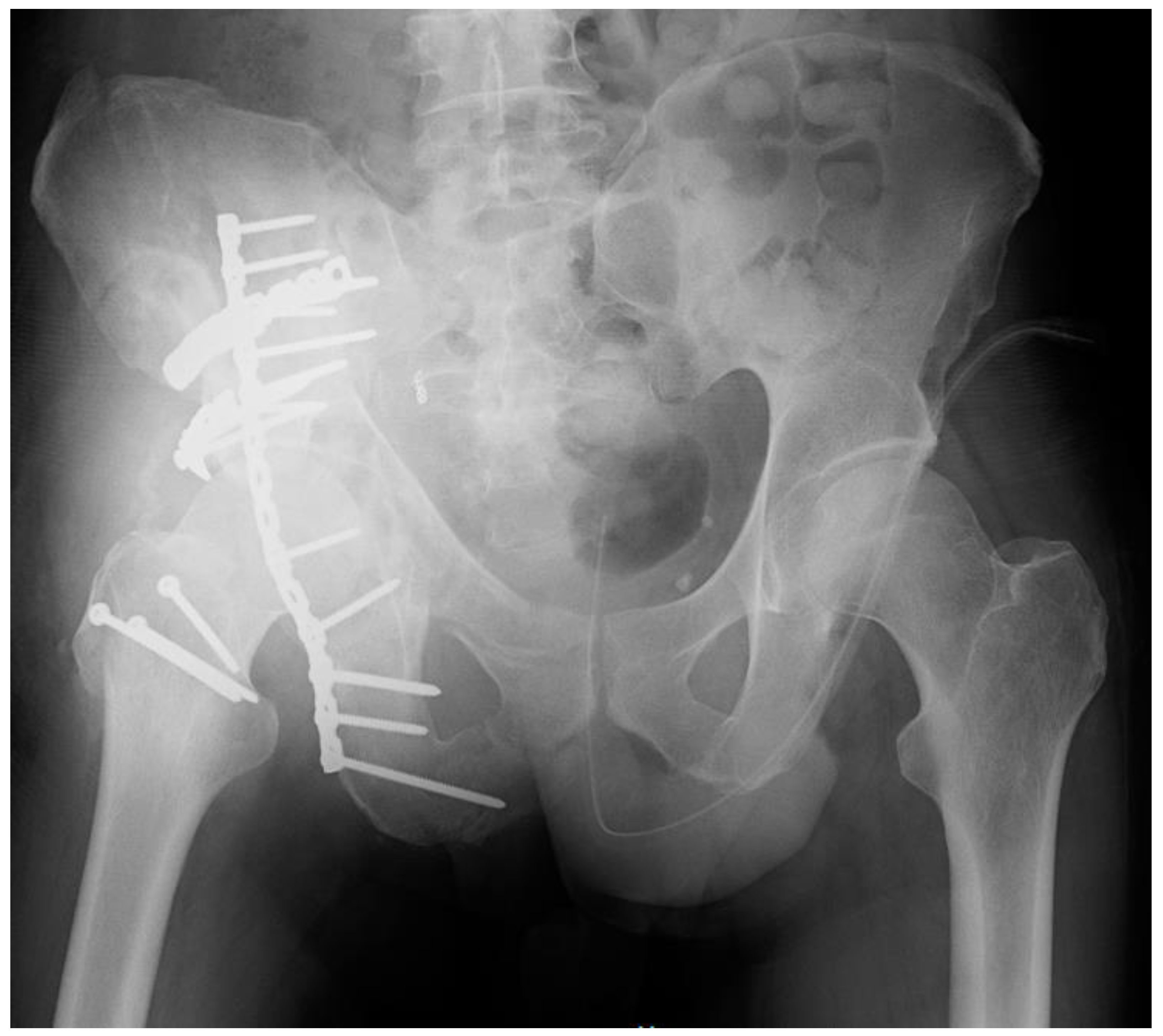
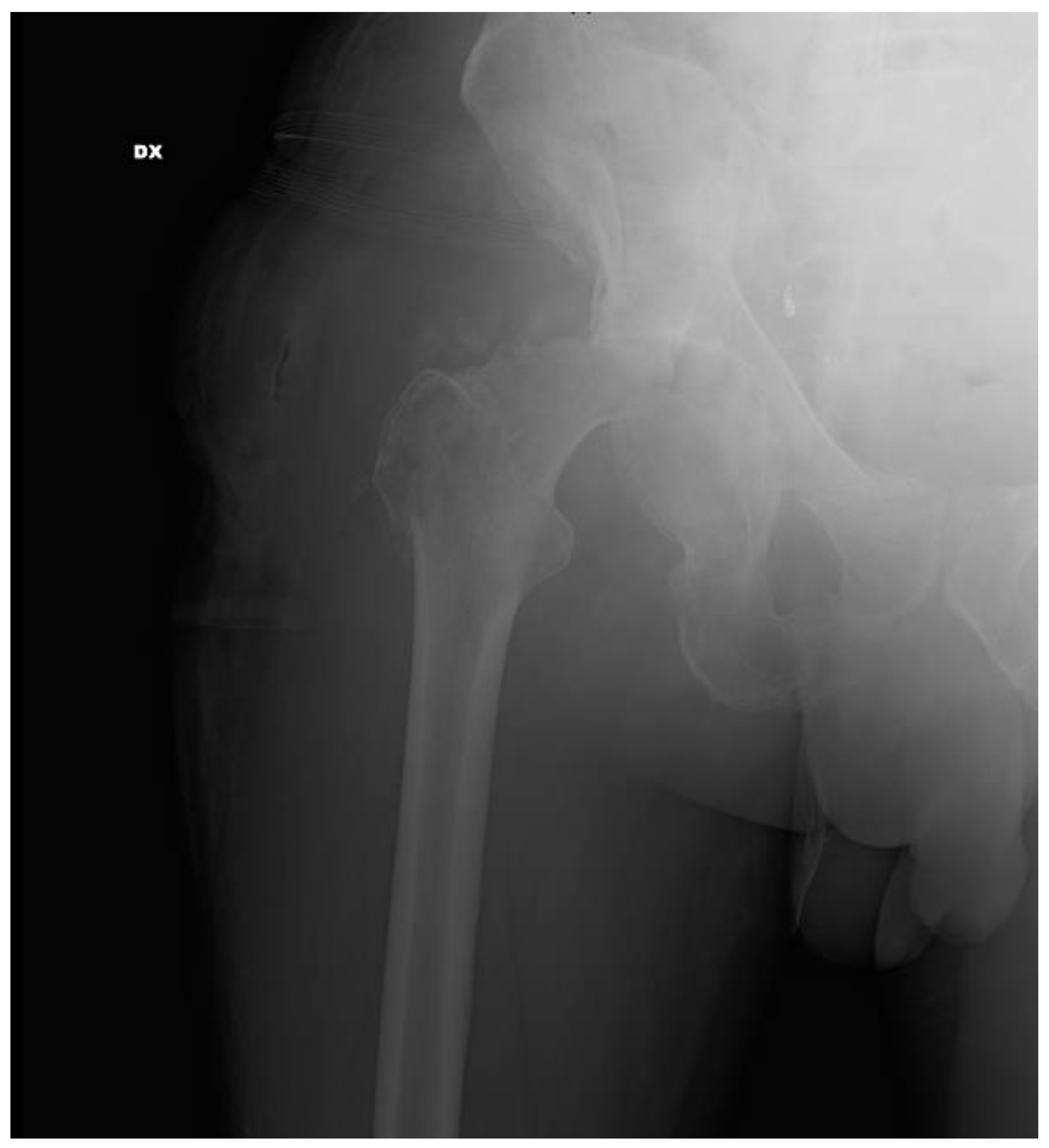
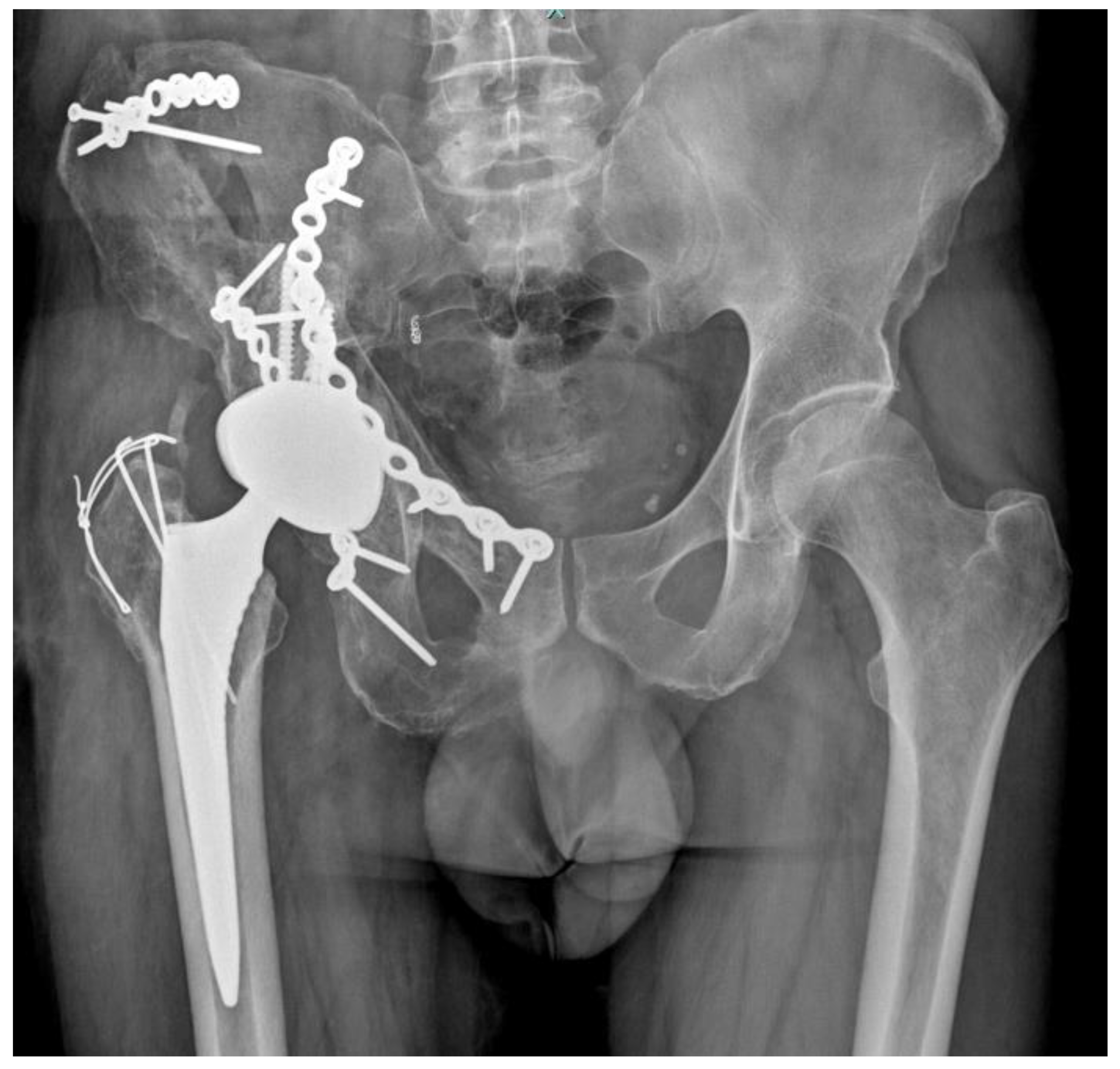
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Depypere, M.; Morgenstern, M.; Kuehl, R.; Senneville, E.; Moriarty, T.F.; Obremskey, W.T.; Zimmerli, W.; Trampuz, A.; Lagrou, K.; Metsemakers, W.-J. Pathogenesis and management of fracture-related infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metsemakers, W.J.; Morgenstern, M.; McNally, M.A.; Moriarty, T.F.; McFadyen, I.; Scarborough, M.; Athanasou, N.A.; Ochsner, P.E.; Kuehl, R.; Raschke, M.; et al. Fracture-related infection: A consensus on definition from an international expert group. Injury 2018, 49, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsemakers, W.-J.; Morgenstern, M.; Senneville, E.; Borens, O.; Govaert, G.A.M.; Onsea, J.; Depypere, M.; Richards, R.G.; Trampuz, A.; Verhofstad, M.H.J.; et al. General treatment principles for fracture-related infection: Recommendations from an international expert group. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2020, 140, 1013–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, D.; Nagoya, S.; Takashima, H.; Tateda, K.; Yamashita, T. Three-dimensional orientation of the acetabulum. Clin. Anat. 2017, 30, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, V.; Incavo, S.J.; Shields, W.H. The anatomy of the acetabulum: What is normal? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 467, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Iacono, V.; De Franco, C.; Auletta, N.; Zarra, A.; D’addona, A.; Rosa, D.; Zorzi, C. New plates with polyaxial locking system and PSI technique in medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy: Preliminary results. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 111–113. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.C. 3D-printed patient-specific applications in orthopedics. Orthop. Res. Rev. 2016, 8, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, H.; Patralekh, M.K. 3D printing and its applications in orthopaedic trauma: A technological marvel. J. Clin. Orthop. trauma 2018, 9, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küper, M.A.; Konrads, C.; Trulson, A.; Bahrs, C.; Stöckle, U.; Stuby, F.M. Complications of surgical approaches for osteosynthesis treatment of acetabular fractures: Analysis of pitfalls and how to avoid them. Injury 2020, 51, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, G.; Sagi, H.C. Septic arthritis of the hip after nonoperative treatment of a pelvic fracture associated with bladder rupture. J. Orthop. Trauma 2012, 26, e40–e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NISSEN, K.I. Osteomyelitis of the acetabulum with intra-pelvic protrusion of the head of the femur. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1950, 43, 306–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooraie, H.; Ensafdaran, A.; Arasteh, M.M.; Droodchi, H. Surgically treated acetabular fractures in adult patients. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 1996, 115, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.J. Septic Arthritis of Native Joints. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 31, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balato, G.; de Matteo, V.; Ascione, T.; de Giovanni, R.; Marano, E.; Rizzo, M.; Mariconda, M. Management of septic arthritis of the hip joint in adults. A systematic review of the literature. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, A.L.; Moriarty, T.F.; Trampuz, A.; Jaiprakash, A.; Burch, M.A.; Crawford, R.; Paterson, D.L.; Metsemakers, W.-J.; Schuetz, M.; Richards, R.G. Fracture-related infection: Current methods for prevention and treatment. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsemakers, W.J.; Kuehl, R.; Moriarty, T.F.; Richards, R.G.; Verhofstad, M.H.J.; Borens, O.; Kates, S.; Morgenstern, M. Infection after fracture fixation: Current surgical and microbiological concepts. Injury 2018, 49, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govaert, G.A.M.; Kuehl, R.; Atkins, B.L.; Trampuz, A.; Morgenstern, M.; Obremskey, W.T.; Verhofstad, M.H.J.; McNally, M.A.; Metsemakers, W.-J. Diagnosing Fracture-Related Infection: Current Concepts and Recommendations. J. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 34, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letournel, E. Acetabulum Fractures: Classification and Management. J. Orthop. Trauma 2019, 33 (Suppl. S2), S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhu, H.; Gao, C. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 3D Printing Technology for the Treatment of Acetabular Fractures. Biomed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5018791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurts, J.; Chris Arts, J.J.; Walenkamp, G.H.I.M. Bone graft substitutes in active or suspected infection. Contra-indicated or not? Injury 2011, 42 (Suppl. S2), S82–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wu, Y.-P.; Qian, S.-J.; Teng, C.; Chen, S.; Li, H. Research progress in the mechanism of effect of PRP in bone deficiency healing. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 134582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oryan, A.; Alidadi, S.; Moshiri, A. Platelet-rich plasma for bone healing and regeneration. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogikyan, N.D.; Kana, L.A.; Shuman, A.G.; Firn, J.I. Patient perceptions of trust formation in the surgeon-patient relationship: A thematic analysis. Patient Educ. Couns. 2021, 104, 2338–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wong, T.-M.; To, K.K.; Wong, S.S.; Lau, T.-W.; Leung, F. Infection after fracture osteosynthesis—Part II. J. Orthop. Surg. 2017, 25, 2309499017692714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wong, T.-M.; Lau, T.-W.; To, K.K.; Wong, S.S.; Leung, F. Infection after fracture osteosynthesis—Part I. J. Orthop. Surg. 2017, 25, 2309499017692712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balato, G.; De Matteo, V.; De Franco, C.; Lenzi, M.; Verrazzo, R.; de Giovanni, R.; Smeraglia, F.; Rizzo, M.; Ascione, T. Prevention and treatment of peri-prosthetic joint infection using surgical wound irrigation. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Nasser, A.A.H.; Fenton, P.; Bose, D. Single stage versus two-stage orthoplastic management of bone infection. Injury 2022, 53, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilowitz, N.R.; Berger, J.S. Perioperative Cardiovascular Risk Assessment and Management for Noncardiac Surgery: A Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikebe, S.; Sonohata, M.; Kitajima, M.; Kawano, S.; Mawatari, M. Total hip arthroplasty following Girdlestone arthroplasty. J. Orthop. Sci. Off. J. Japanese Orthop. Assoc. 2018, 23, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipp, J.O.; Lamm, M.; Søballe, K.; Jakobsen, S.S. Periprosthetic hip infection treated with two-stage stage-one Select Spacer- complication rate and restoration of anatomy. J. Orthop. 2020, 18, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Xiang, Y.; Ni, M.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Yu, B.; Liu, K.; Zhou, Y.; Hao, L. The use of augmented antibiotic-loaded cement spacer in periprosthetic joint infection patients with acetabular bone defect. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Franco, C.; Artiaco, S.; de Matteo, V.; Bistolfi, A.; Balato, G.; Vallefuoco, S.; Massè, A.; Rosa, D. The eradication rate of infection in septic knee arthritis according to the Gächter Classification: A systematic review. Orthop. Rev. 2022, 14, 33754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecki, K.; Hoang, V.; LeCavalier, D.; Bradford, M. An Alternative One-Stage Exchange Arthroplasty Technique: For the Chronic Infected Total Hip. Cureus 2020, 12, e11138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel, M.P.; Akgün, D.; Akin, G.; Akinola, B.; Alencar, P.; Amanatullah, D.F.; Babazadeh, S.; Borens, O.; Vicente Cabral, R.M.; Cichos, K.H.; et al. Hip and Knee Section, Diagnosis, Pathogen Isolation, Culture: Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections. J. Arthroplasty 2019, 34, S361–S367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Franco, C.; Colò, G.; Melato, M.; Battini, A.; Cambursano, S.; Logrieco, G.P.; Balato, G.; Zoccola, K. Fracture-Related Infection in Bicolumnar Acetabular Fracture: A Case Report. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102476
De Franco C, Colò G, Melato M, Battini A, Cambursano S, Logrieco GP, Balato G, Zoccola K. Fracture-Related Infection in Bicolumnar Acetabular Fracture: A Case Report. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(10):2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102476
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Franco, Cristiano, Gabriele Colò, Marco Melato, Alberto Battini, Simone Cambursano, Giuseppe Pietro Logrieco, Giovanni Balato, and Kristijan Zoccola. 2022. "Fracture-Related Infection in Bicolumnar Acetabular Fracture: A Case Report" Diagnostics 12, no. 10: 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102476
APA StyleDe Franco, C., Colò, G., Melato, M., Battini, A., Cambursano, S., Logrieco, G. P., Balato, G., & Zoccola, K. (2022). Fracture-Related Infection in Bicolumnar Acetabular Fracture: A Case Report. Diagnostics, 12(10), 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102476





