Utility of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration and Biopsy for Histological Diagnosis of Type 2 Autoimmune Pancreatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
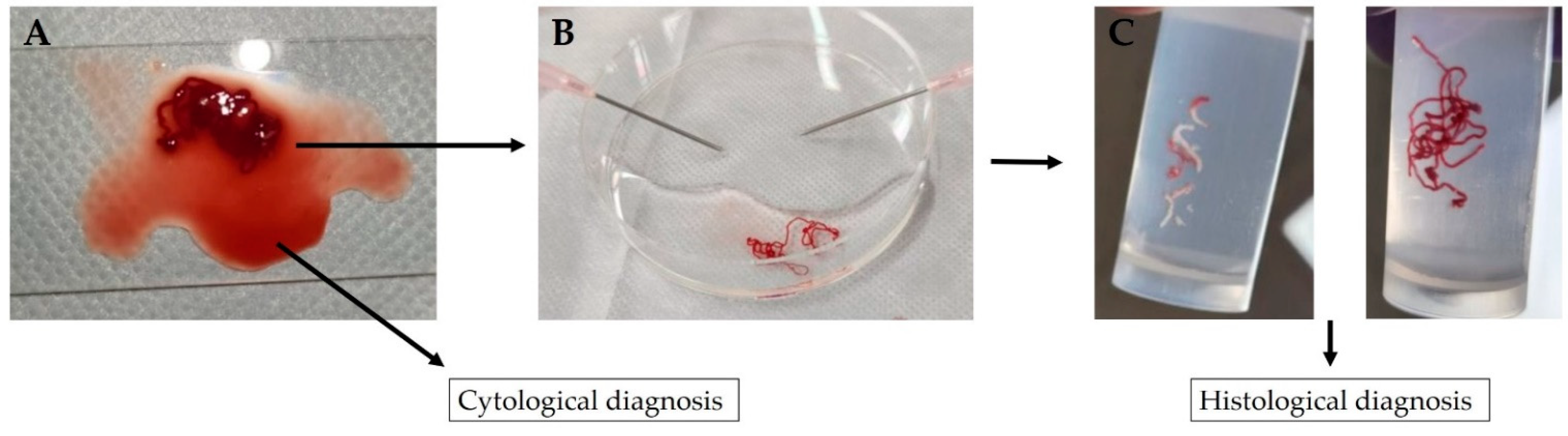
2. Materials and Methods
- A piece of tissue aspirated into the needle is pushed onto a glass slide with a stylet;
- The tubular tissue piece in blood is picked up and transferred to a formalin-soaked plate;
- The remaining bloody liquid portion is clamped between two glass slides, fixed with ethanol, stained with Papanicolaou stain and submitted as a cytology specimen; and
- The removed ductal tissue pieces, which consist of white-toned pancreatic tissue and red-toned pancreatic tissue, are separated using an 18-G disposable needle, transferred separately to a formalin-filled container and submitted to the pathologist as a histopathology specimen.
- The tissue specimens are quickly fixed in formalin and embedded in paraffin. The paraffin block is cut into thin serial sections and stained with hematoxylin-eosin stain, Masson’s trichrome stain and Elastica–Masson stain. Immune-histochemistry was then performed using IgG4 antibody and cluster of differentiation 38 (CD38) antibody.
3. Results
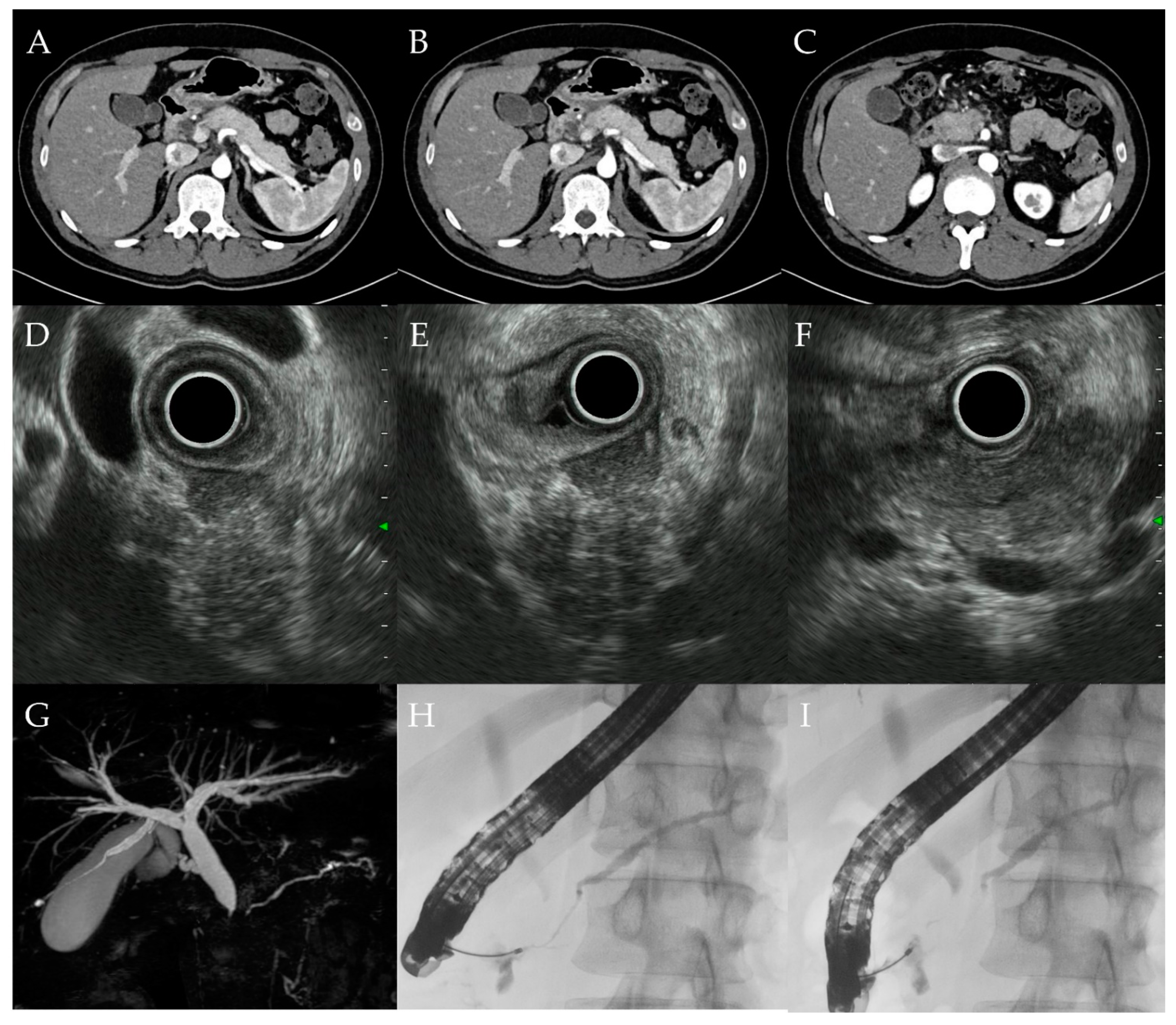
3.1. Clinical Findings
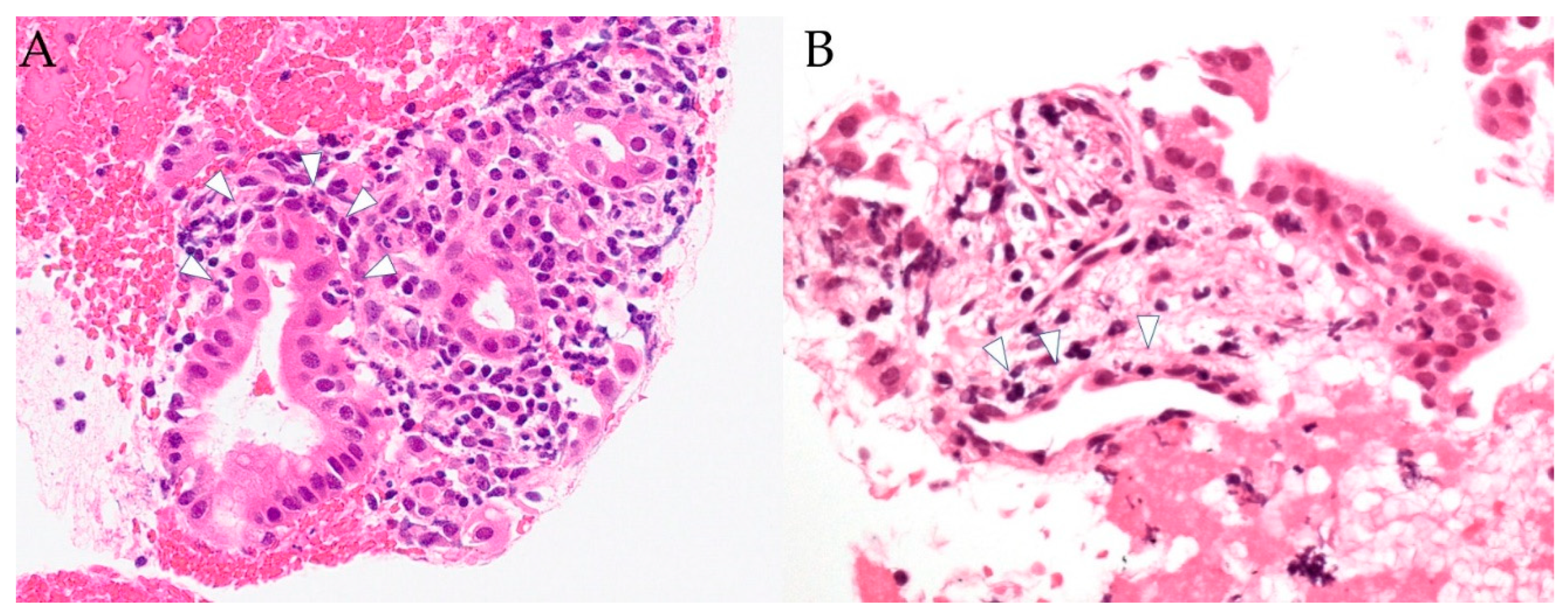
3.2. Histopathological Findings
3.3. Progress of Treatment
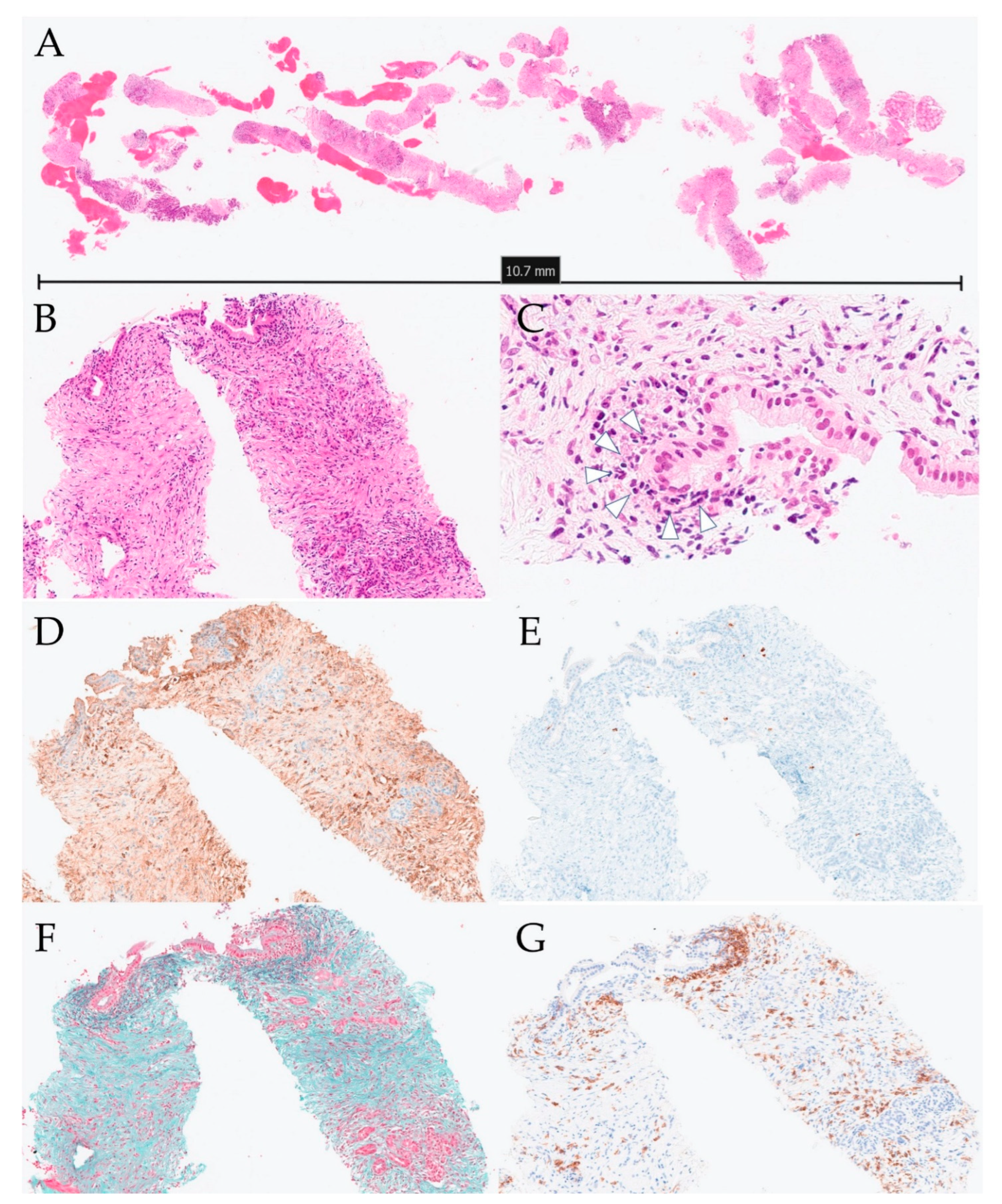
3.4. Case Report (Case 10)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shimosegawa, T.; Chari, S.T.; Frulloni, L.; Kamisawa, T.; Kawa, S.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Kim, M.H.; Klöppel, G.; Lerch, M.M.; Löhr, M.; et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: Guidelines of the International Association of Pancreatology. Pancreas 2011, 40, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhr, J.M.; Beuers, U.; Vujasinovic, M.; Alvaro, D.; Frøkjær, J.B.; Buttgereit, F.; Capurso, G.; Culver, E.L.; de-Madaria, E.; Della-Torre, E.; et al. European guideline on IgG4-related digestive disease—UEG and SGF evidence-based recommendations. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020, 8, 637–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.H.; Khosroshahi, A.; Deshpande, V.; Chan, J.K.; Heathcote, J.G.; Aalberse, R.; Azumi, A.; Bloch, D.B.; Brugge, W.R.; Carruthers, M.N.; et al. Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations. Arthritis Rheum 2012, 64, 3061–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamisawa, T.; Kim, M.H.; Liao, W.C.; Liu, Q.; Balakrishnan, V.; Okazaki, K.; Shimosegawa, T.; Chung, J.B.; Lee, K.T.; Wang, H.P.; et al. Clinical characteristics of 327 Asian patients with autoimmune pancreatitis based on Asian diagnostic criteria. Pancreas 2011, 40, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notohara, K.; Kamisawa, T.; Fukushima, N.; Furukawa, T.; Tajiri, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; Aishima, S.; Fukumura, Y.; Hirabayashi, K.; Iwasaki, E.; et al. Guidance for diagnosing autoimmune pancreatitis with biopsy tissues. Pathol. Int. 2020, 70, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, S.T.; Kloeppel, G.; Zhang, L.; Notohara, K.; Lerch, M.M.; Shimosegawa, T. Histopathologic and clinical subtypes of autoimmune pancreatitis: The Honolulu consensus document. Pancreas 2010, 39, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamboni, G.; Lüttges, J.; Capelli, P.; Frulloni, L.; Cavallini, G.; Pederzoli, P.; Leins, A.; Longnecker, D.; Klöppel, G. Histopathological features of diagnostic and clinical relevance in autoimmune pancreatitis: A study on 53 resection specimens and 9 biopsy specimens. Virchows. Arch. 2004, 445, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, M.J.; Reddy, R.P.; Wiersema, M.J.; Smyrk, T.C.; Clain, J.E.; Harewood, G.C.; Pearson, R.K.; Rajan, E.; Topazian, M.D.; Yusuf, T.E.; et al. EUS-guided trucut biopsy in establishing autoimmune pancreatitis as the cause of obstructive jaundice. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2005, 61, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, L. Second-generation fine-needle biopsy for autoimmune pancreatitis: Ready for prime time? Endoscopy 2020, 52, 986–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppong, K.W.; Bekkali, N.L.H.; Leeds, J.S.; Johnson, S.J.; Nayar, M.K.; Darné, A.; Egan, M.; Bassett, P.; Haugk, B. Fork-tip needle biopsy versus fine-needle aspiration in endoscopic ultrasound-guided sampling of solid pancreatic masses: A randomized crossover study. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashat, M.; Klair, J.S.; Rooney, S.L.; Vishal, S.J.; Jensen, C.; Sahar, N.; Murali, A.R.; El-Abiad, R.; Gerke, H. Randomized controlled trial comparing the Franseen needle with the Fork-tip needle for EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 140–150.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Kawashima, H.; Ohno, E.; Tanaka, H.; Sakai, D.; Iida, T.; Nishio, R.; Yamamura, T.; Furukawa, K.; Nakamura, M.; et al. Clinical Impact of EUS-Guided Fine Needle Biopsy Using a Novel Franseen Needle for Histological Assessment of Pancreatic Diseases. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 2019, 8581743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notohara, K.; Kamisawa, T.; Kanno, A.; Naitoh, I.; Iwasaki, E.; Shimizu, K.; Kuraishi, Y.; Motoya, M.; Kodama, Y.; Kasashima, S.; et al. Efficacy and limitations of the histological diagnosis of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis with endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle biopsy with large tissue amounts. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanno, A.; Ishida, K.; Hamada, S.; Fujishima, F.; Unno, J.; Kume, K.; Kikuta, K.; Hirota, M.; Masamune, A.; Satoh, K.; et al. Diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis by EUS-FNA by using a 22-gauge needle based on the International Consensus Diagnostic Criteria. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2012, 76, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, K.; Nakai, Y.; Mizuno, S.; Hirano, K.; Kanai, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Inokuma, A.; Sato, T.; Hakuta, R.; Ishigaki, K.; et al. Role of endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration/biopsy in the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Cruise, M.; Chahal, P. Endoscopic ultrasound guided 22-gauge core needle biopsy for the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, Q.; Chen, Q.; Wu, X.; Tang, S.J.; Cheng, B. The role of EUS-guided fine needle aspiration in autoimmune pancreatitis: A single center prospective study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 1604–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, T.; Itoh, A.; Kawashima, H.; Ohno, E.; Matsubara, H.; Itoh, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Hiramatsu, T.; Nakamura, M.; Miyahara, R.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration in the differentiation of type 1 and type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 3883–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Kawashima, H.; Ohno, E.; Suhara, H.; Hayashi, D.; Hiramatsu, T.; Matsubara, H.; Suzuki, T.; Kuwahara, T.; Ishikawa, E.; et al. Usefulness of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy for the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis using a 22-gauge Franseen needle: A prospective multicenter study. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detlefsen, S.; Joergensen, M.T.; Mortensen, M.B. Microscopic findings in EUS-guided fine needle (SharkCore) biopsies with type 1 and type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis. Pathol. Int. 2017, 67, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Ogawa, K.; Nakamura, M.; Hoki, S.; Kuroki, S.; Yano, Y.; Ikuta, K.; Senda, E.; Shio, S. Late-onset type-2 autoimmune pancreatitis with two mass lesions diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Matsubayashi, H.; Fukutomi, A.; Uesaka, K.; Sasaki, K.; Ono, H. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy using 22-gauge needle in diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2011, 43, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, S.J.S.; Sharma, A.; Chari, S.T. Autoimmune Pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishima, T.; Kawashima, H.; Ohno, E.; Yamamura, T.; Funasaka, K.; Nakamura, M.; Miyahara, R.; Watanabe, O.; Ishigami, M.; Shimoyama, Y.; et al. Prospective multicenter study on the usefulness of EUS-guided FNA biopsy for the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 84, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, P.; Tranesh, G.; Nassar, A.; Bingham, R.; Raimondo, M.; Woodward, T.A.; Gomez, V.; Wallace, M.B. EUS-guided fine needle biopsy sampling using a novel fork-tip needle: A case-control study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 84, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.B.; Moon, S.H.; Song, T.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.H. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration versus biopsy for diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis: Systematic review and comparative meta-analysis. Dig. Endosc. 2021, 33, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Del Prete, V.; Antonino, M.; Buccino, V.R.; Wani, S. Diagnostic yield of EUS-guided through-the-needle biopsy in pancreatic cysts: A meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 1–8.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkolfakis, P.; Crinò, S.F.; Tziatzios, G.; Ramai, D.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Papanikolaou, I.S.; Triantafyllou, K.; Arvanitakis, M.; Lisotti, A.; Fusaroli, P.; et al. Comparative diagnostic performance of end-cutting fine-needle biopsy needles for EUS tissue sampling of solid pancreatic masses: A network meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 1067–1077.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pretis, N.; Crinò, S.F.; Frulloni, L. The Role of EUS-Guided FNA and FNB in Autoimmune Pancreatitis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Takagi, T.; Suzuki, R.; Konno, N.; Asama, H.; Sato, Y.; Irie, H.; Watanabe, K.; Nakamura, J.; Kikuchi, H.; et al. Can the wet suction technique change the efficacy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for diagnosing autoimmune pancreatitis type 1? A prospective single-arm study. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, A.; Yasukawa, S.; Zen, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Ogura, T.; Ozawa, E.; Okabe, Y.; Asada, M.; Nebiki, H.; Shigekawa, M.; et al. Comparison of a 22-gauge Franseen-tip needle with a 20-gauge forward-bevel needle for the diagnosis of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis: A prospective, randomized, controlled, multicenter study (COMPAS study). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 91, 373–381.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notohara, K.; Kamisawa, T.; Furukawa, T.; Fukushima, N.; Uehara, T.; Kasashima, S.; Iwasaki, E.; Kanno, A.; Kawashima, A.; Kubota, K.; et al. Concordance of the histological diagnosis of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis and its distinction from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle biopsy specimens: An interobserver agreement study. Virchows. Arch. 2022, 480, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Barresi, L.; Cannizzaro, R.; Antonini, F.; Triantafyllou, K.; Tziatzios, G.; Muscatiello, N.; Hart, P.A.; Wani, S. Diagnostic yield of endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition in autoimmune pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc. Int. Open 2021, 9, E66–E75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | Value | Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, male-to-female ratio | 8:2 | Age (mean ± SD), years | 35.6 ± 15.5 |
| Symptom | Pancreatic imaging finding | ||
| Abdominal pain, n (%) | 4/10 (40.0%) | Enlargement, n (%) | 10/10 (100%) |
| Jaundice, n (%) | 2/10 (20.0%) | Diffuse enlargement, n (%) | 5/10 (50.0%) |
| Asymptomatic, n (%) | 4/10 (40.0%) | Segmental enlargement, n (%) | 2/10 (20.0%) |
| Serology variable | Focal enlargement, n (%) | 3/10 (30.0%) | |
| IgG4 level (mean ± SD), mg/dL | 34.9 ± 17.3 | MPD narrowing, n (%) | 8/10 (80.0%) |
| IgG4 level < 135 mg/dL | 10/10 (100%) | Diffuse narrowing, n (%) | 4/8 (50.0%) |
| OOI | Segmental narrowing, n (%) | 3/8 (37.5%) | |
| IBD (ulcerative colitis), n (%) | 10/10 (100%) | Focal narrowing, n (%) | 1/8 (12.5%) |
| Case | Sex/ Age, Years | Needle (Gauge) | HPF | IgG4/HPF | GEL | Granulocytic and Lymphoplasmacytic Acinar Infiltrate | Diagnosis
(ICDC) | Steroid
Administration (Response to Steroid) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M/37 | AC (22-G) | >10 | absent | − | − | n/d | − |
| 2 | F/49 | EX (22-G) | >10 | scant | + | + | Level 1 | − |
| 3 | M/30 | NA (22-G) | 6 | absent | − | + | Level 2 | − |
| 4 | M/68 | EX (19-G) | >10 | scant | − | + | Level 2 | − |
| 5 | M/21 | EX (22-G) | >10 | scant | + | + | Level 1 | − |
| 6 | M/53 | EZ (22-G) | >10 | scant | − | + | Level 2 | − |
| 7 | M/29 | NA (22-G) | >10 | scant | + | + | Level 1 | + (good) |
| 8 | M/18 | NA (22-G) | 4 | absent | − | + | Level 2 | − |
| 9 | F/20 | NA (22-G) | >10 | scant | − | + | Level 2 | − |
| 10 | M/31 | AC (22-G) | >10 | scant | + | + | Level 1 | + (good) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hayashi, H.; Miura, S.; Fujishima, F.; Kuniyoshi, S.; Kume, K.; Kikuta, K.; Hamada, S.; Takikawa, T.; Matsumoto, R.; Ikeda, M.; et al. Utility of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration and Biopsy for Histological Diagnosis of Type 2 Autoimmune Pancreatitis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102464
Hayashi H, Miura S, Fujishima F, Kuniyoshi S, Kume K, Kikuta K, Hamada S, Takikawa T, Matsumoto R, Ikeda M, et al. Utility of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration and Biopsy for Histological Diagnosis of Type 2 Autoimmune Pancreatitis. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(10):2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102464
Chicago/Turabian StyleHayashi, Hidehiro, Shin Miura, Fumiyoshi Fujishima, Shimpei Kuniyoshi, Kiyoshi Kume, Kazuhiro Kikuta, Shin Hamada, Tetsuya Takikawa, Ryotaro Matsumoto, Mio Ikeda, and et al. 2022. "Utility of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration and Biopsy for Histological Diagnosis of Type 2 Autoimmune Pancreatitis" Diagnostics 12, no. 10: 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102464
APA StyleHayashi, H., Miura, S., Fujishima, F., Kuniyoshi, S., Kume, K., Kikuta, K., Hamada, S., Takikawa, T., Matsumoto, R., Ikeda, M., Sano, T., Kataoka, F., Sasaki, A., Sakano, M., & Masamune, A. (2022). Utility of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration and Biopsy for Histological Diagnosis of Type 2 Autoimmune Pancreatitis. Diagnostics, 12(10), 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102464







