Development of Advanced Imaging and Molecular Imaging for Barrett’s Neoplasia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Non-Endoscopic and Endoscopic Technologies
2.1. Development in Non-Endoscopic Technologies
2.1.1. Biomarker Candidates for Biopsy Specimens
2.1.2. Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization for Cytology
2.2. Development in Endoscopic Technologies
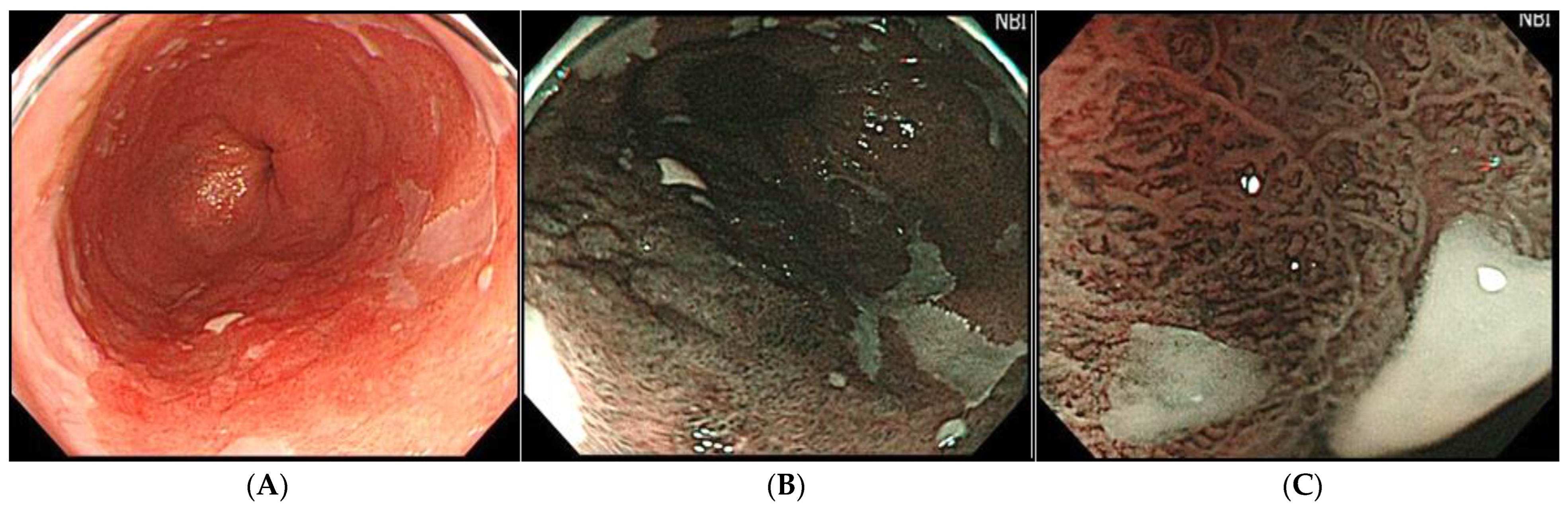
2.2.1. Wide-Field Imaging Systems
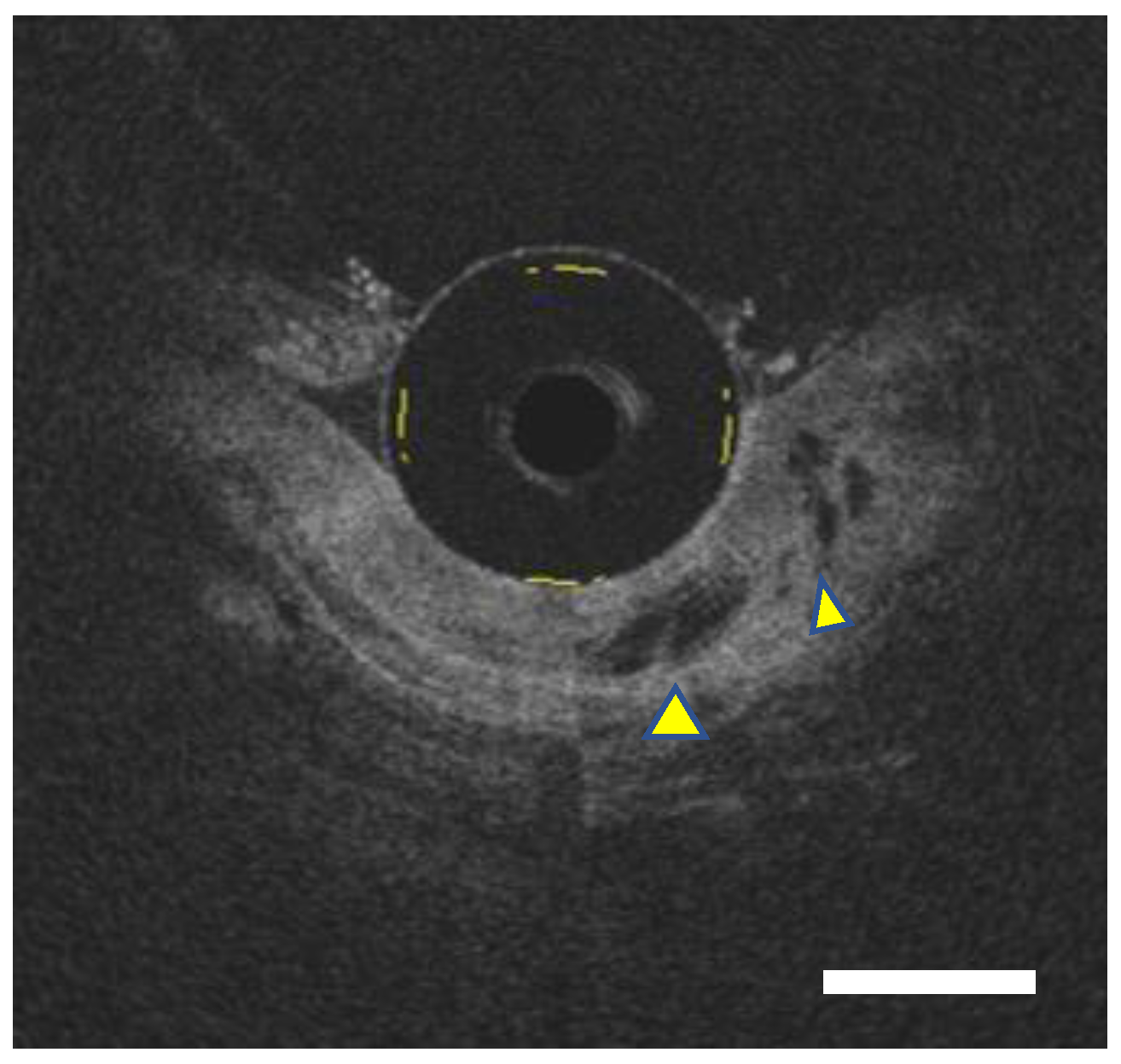
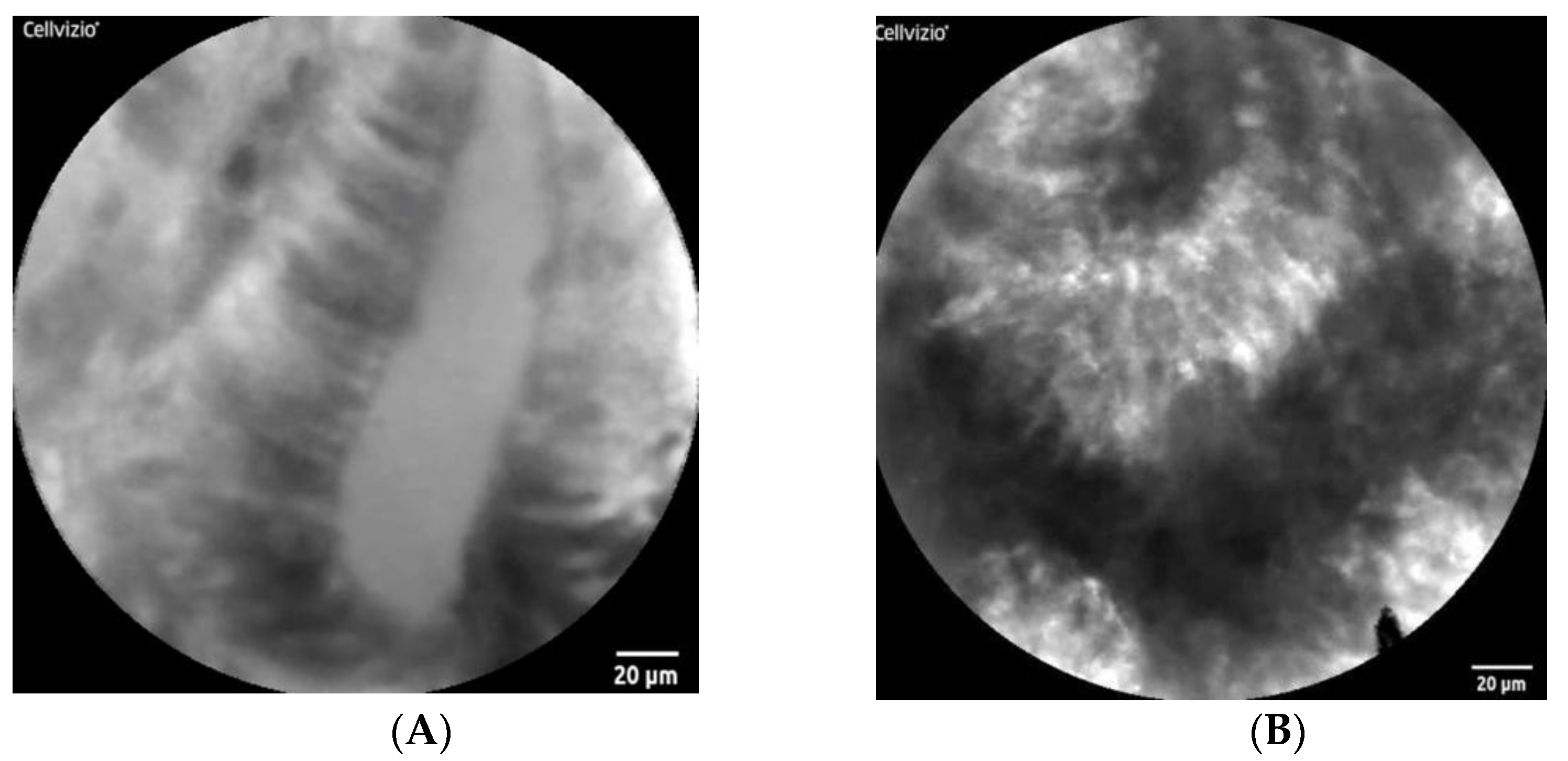
2.2.2. Small-Field Imaging System
2.3. Fluorescence Imaging for Molecular Biomarkers (Molecular Imaging)
2.3.1. Fluorescence Molecular Endoscopy
2.3.2. Tracers
2.3.3. Fluorescence-Labelled Biomarkers Specific for Oncoproteins
2.4. Development of Computer-Aided Detection and Computer-Aided Diagnosis
2.4.1. CAD for OCT/VLE
2.4.2. CAD for FME
3. Another Issue in Diagnosing Barrett’s Neoplasia
4. Perspective
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BE | Barrett esophagus |
| EAC | esophageal adenocarcinoma |
| HRWLE | high-resolution white-light endoscopy |
| SP | the Seattle protocol |
| CLE | confocal laser endomicroscopy |
| AFI | autofluorescence imaging |
| OCT | optical coherence tomography |
| AUC | an area under the receiving operator characteristics curve |
| FISH | fluorescence in situ hybridization |
| CAD | computer-assisted diagnosis |
| VLE | volumetric laser endomicroscopy |
| VLEL | a VLE laser marking system |
| ROI | regions of interest |
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| IEE | image-enhanced endoscopy |
| NBI | narrow band imaging |
| MNBI | high-definition magnification NBI |
| ETMI | endoscopic trimodal imaging |
| CLE | confocal laser endomicroscopy |
| pCLE | the probe-based CLE |
| eCLE | the endoscopy-integrated CLE |
| NIR | near-infrared range |
| FME | fluorescence molecular endoscopy |
| NPs | nanoparticles |
| WGA | wheat germ agglutinin |
| T/B ratio | tumor-to-background ratio |
| ASYNYDA | sequences ASY*-fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| Hsp-TPP | membrane-bound Hsp70-specific contrast agent Tumor-Penetrating peptide |
| IHC | the immunohistochemical study |
| NDBE | non-dysplastic Barrett esophagus |
| LGD | low-grade dysplasia |
| HGD | high-grade dysplasia |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| HER2 | human epidermal growth factor receptor |
| NIR-FME | wide-field near-infrared FME |
| VEGFA | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| CXCR4 | chemokine receptor 4 |
| PpIX | protoporphyrin IX |
| 2NBDG | 2-[N-(7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diaxol-4- yl)amino]-2-deoxyglucose |
| GLUT | glucose transporters |
References
- Wang, K.K.; Sampliner, R.E. Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Updated guidelines 2008 for the diagnosis, surveillance and therapy of Barrett’s esophagus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, T.K.; Krishnan, K.; Samala, N.; Singh, J.; Cluley, J.; Perla, S.; Howden, C.W. The incidence of oesophageal adenocarcinoma in non-dysplastic Barrett’s oesophagus: A meta-analysis. Gut 2012, 61, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duits, L.C.; Phoa, K.N.; Curvers, W.L.; Kate, F.J.W.T.; Meijer, G.A.; A. Seldenrijk, C.; Offerhaus, G.J.; Visser, M.; Meijer, S.L.; Krishnadath, K.K.; et al. Barrett’s oesophagus patients with low-grade dysplasia can be accurately risk-stratified after histological review by an expert pathology panel. Gut 2015, 64, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, N.J.; Sharma, P.; Overholt, B.F.; Wolfsen, H.C.; Sampliner, R.E.; Wang, K.K.; Galanko, J.A.; Bronner, M.P.; Goldblum, J.R.; Bennett, A.E.; et al. Radiofrequency Ablation in Barrett’s Esophagus with Dysplasia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Grobmyer, S.R.; Smith, R.; Ben-David, K.; Ang, D.; Vogel, S.B.; Hochwald, S.N. Esophageal cancer—The five year survivors. J. Surg Oncol. 2011, 103, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Munster, S.; Nieuwenhuis, E.; Weusten, B.L.; Herrero, L.A.; Bogte, A.; Alkhalaf, A.; Schenk, B.E.; Schoon, E.J.; Curvers, W.; Koch, A.D.; et al. Long-term outcomes after endoscopic treatment for Barrett’s neoplasia with radiofrequency ablation ± endoscopic resection: Results from the national Dutch database in a 10-year period. Gut 2022, 71, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoa, K.N.; Van Vilsteren, F.G.; Weusten, B.L.; Bisschops, R.; Schoon, E.J.; Ragunath, K.; Fullarton, G.; Di Pietro, M.; Ravi, N.; Visser, M.; et al. Radiofrequency Ablation vs Endoscopic Surveillance for Patients with Barrett Esophagus and Low-Grade Dysplasia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2014, 311, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, N.J.; Falk, G.W.; Iyer, P.G.; Gerson, L.B. ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Barrett’s Esophagus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, R.C.; Di Pietro, M.; Ragunath, K.; Ang, Y.; Kang, J.Y.; Watson, P.; Trudgill, N.; Patel, P.; Kaye, P.V.; Sanders, S.; et al. British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines on the diagnosis and management of Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut 2014, 63, 7–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, S.; Puli, S.R.; Shaheen, N.J.; Westhoff, B.; Slehria, S.; Bansal, A.; Rastogi, A.; Sayana, H.; Sharma, P. Esophageal adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus after endoscopic ablative therapy: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Risk factors for progression of low-grade dysplasia in patients with Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, J.A.; Kapel, R.C.; Lindberg, G.M.; Saboorian, M.H.; Genta, R.M.; Neugut, A.I.; Lightdale, C.J. Adherence to Biopsy Guidelines for Barrett’s Esophagus Surveillance in the Community Setting in the United States. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithayathil, M.; Modolell, I.; Ortiz-Fernandez-Sordo, J.; Oukrif, D.; Pappas, A.; Januszewicz, W.; O’Donovan, M.; Hadjinicolaou, A.; Bianchi, M.; Blasko, A.; et al. Image-Enhanced Endoscopy and Molecular Biomarkers Vs Seattle Protocol to Diagnose Dysplasia in Barrett’s Esophagus. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 17, S1542–S3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerson, L.B.; Triadafilopoulos, G. Screening for esophageal adenocarcinoma: An evidence-based approach. Am. J. Med. 2002, 113, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, D.S.; Blount, P.L.; Rudolph, R.E.; Reid, B.J. Safety of a systematic endoscopic biopsy protocol in patients with Barrett’s esophagus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, D.M.; Ek, W.E.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Onstad, L.; Sather, C.; Lao-Sirieix, P.; Gammon, M.D.; Corley, D.A.; Shaheen, N.J.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for esophageal adenocarcinoma and Barrett’s esophagus. Nat. Genet 2013, 45, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galipeau, P.; Li, X.; Blount, P.L.; Maley, C.C.; Sanchez, C.A.; Odze, R.D.; Ayub, K.; Rabinovitch, P.S.; Vaughan, T.L.; Reid, B.J. NSAIDs Modulate CDKN2A, TP53, and DNA Content Risk for Progression to Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, P.V.; Haider, S.A.; Ilyas, M.; James, P.D.; Soomro, I.; Faisal, W.; Catton, J.; Parsons, S.L.; Ragunath, K. Barrett’s dysplasia and the Vienna classification: Reproducibility, prediction of progression and impact of consensus reporting and p53 immunohistochemistry. Histopathology 2009, 54, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastelein, F.; Biermann, K.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Verheij, J.; Kalisvaart, M.; Looijenga, L.H.J.; Stoop, H.A.; Walter, L.; Kuipers, E.J.; Spaander, M.C.W.; et al. Aberrant p53 protein expression is associated with an increased risk of neoplastic progression in patients with Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut 2012, 62, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirieix, P.S.; O’Donovan, M.; Brown, J.; Save, V.; Coleman, N.; Fitzgerald, R.C. Surface expression of minichromosome maintenance proteins provides a novel method for detecting patients at risk for developing adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 2560–2566. [Google Scholar]
- Timmer, M.R.; Sun, G.; Gorospe, E.C.; Leggett, C.L.; Lutzke, L.; Krishnadath, K.K.; Wang, K.K. Predictive biomarkers for Barrett’s esophagus: So near and yet so far. Dis. Esophagus 2013, 26, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Galipeau, P.; Prevo, L.J.; Sanchez, C.A.; Longton, G.M.; Reid, B.J. Clonal Expansion and Loss of Heterozygosity at Chromosomes 9p and 17p in Premalignant Esophageal (Barrett’s) Tissue. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1999, 91, 2087–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skacel, M.; Petras, R.E.; Gramlich, T.L.; Sigel, J.E.; Richter, J.E.; Goldblum, J.R. The diagnosis of low-grade dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus and its implications for disease progression. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 3383–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao-Sirieix, P.; Lovat, L.; Fitzgerald, R.C. Cyclin A Immunocytology as a Risk Stratification Tool for Barrett’s Esophagus Surveillance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulmann, K.; Sterian, A.; Berki, A.; Yin, J.; Sato, F.; Xu, Y.; Olaru, A.; Wang, S.; Mori, Y.; Deacu, E.; et al. Inactivation of p16, RUNX3, and HPP1 occurs early in Barrett’s-associated neoplastic progression and predicts progression risk. Oncogene 2005, 24, 4138–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Gu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Sato, F.; Mori, Y.; Olaru, A.V.; Paun, B.C.; Yang, J.; Kan, T.; et al. A Multicenter, Double-Blinded Validation Study of Methylation Biomarkers for Progression Prediction in Barrett’s Esophagus. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4112–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilonis, N.D.; Killcoyne, S.; Tan, W.K.; O’Donovan, M.; Malhotra, S.; Tripathi, M.; Miremadi, A.; Debiram-Beecham, I.; Evans, T.; Phillips, R.; et al. Use of a Cytosponge biomarker panel to prioritise endoscopic Barrett’s oesophagus surveillance: A cross-sectional study followed by a real-world prospective pilot. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, G.; Chittajallu, R.; Goldblum, J.; Biscotti, C.; Geisinger, K.; Petras, R.; Birgisson, S.; Rice, T.; Richter, J. Surveillance of patients with Barrett’s esophagus for dysplasia and cancer with balloon cytology. Gastroenterology 1997, 112, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk, G.W.; Skacel, M.; Gramlich, T.L.; Casey, G.; Goldblum, J.R.; Tubbs, R.R. Fluorescence in situ hybridization of cytologic specimens from Barrett’s esophagus: A pilot feasibility study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2004, 60, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poneros, J. Optical coherence tomography and the detection of dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2005, 62, 832–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatta, W.; Uno, K.; Koike, T.; Ara, N.; Asano, N.; Iijima, K.; Imatani, A.; Fujishima, F.; Shimosegawa, T. Feasibility of optical coherence tomography for the evaluation of Barrett’s mucosa buried underneath esophageal squamous epithelium. Dig. Endosc. 2015, 28, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.H.; Tearney, G.J.; Vakoc, B.J.; Shishkov, M.; Oh, W.Y.; Desjardins, A.E.; Suter, M.J.; Chan, R.C.; Evans, J.A.; Jang, I.-K.; et al. Comprehensive volumetric optical microscopy in vivo. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1429–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swager, A.; Boerwinkel, D.F.; de Bruin, D.M.; Weusten, B.L.; Faber, D.J.; Meijer, S.L.; van Leeuwen, T.G.; Curvers, W.L.; Bergman, J.J. Volumetric laser endomicroscopy in Barrett’s esophagus: A feasibility study on histological correlation. Dis. Esophagus 2016, 29, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swager, A.-F.; Tearney, G.J.; Leggett, C.L.; van Oijen, M.G.; Meijer, S.L.; Weusten, B.L.; Curvers, W.L.; Bergman, J.J. Identification of volumetric laser endomicroscopy features predictive for early neoplasia in Barrett’s esophagus using high-quality histological correlation. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 85, 918–926.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshelleh, M.; Inamdar, S.; McKinley, M.; Stewart, M.; Novak, J.S.; Greenberg, R.E.; Sultan, K.; Devito, B.; Cheung, M.; Cerulli, M.A.; et al. Incremental yield of dysplasia detection in Barrett’s esophagus using volumetric laser endomicroscopy with and without laser marking compared with a standardized random biopsy protocol. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 88, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struyvenberg, M.R.; De Groof, A.J.; Kahn, A.; Weusten, B.L.A.M.; Fleischer, D.E.; Ganguly, E.K.; A. Konda, V.J.; Lightdale, C.J.; Pleskow, D.K.; Sethi, A.; et al. Multicenter study on the diagnostic performance of multiframe volumetric laser endomicroscopy targets for Barrett’s esophagus neoplasia with histopathology correlation. Dis. Esophagus 2020, 33, doaa062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamoto, Y.; Endo, T.; Nosho, K.; Arimura, Y.; Sato, M.; Imai, K. Usefulness of narrow-band imaging endoscopy for diagnosis of Barrett?s esophagus. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 39, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konda, V.J.A.; Hart, J.; Lin, S.; Tretiakova, M.; Gordon, I.O.; Campbell, L.; Kulkarni, A.; Bissonnette, M.; Seewald, S.; Waxman, I. Evaluation of microvascular density in Barrett’s associated neoplasia. Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goda, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Ishihara, R.; Fujisaki, J.; Takahashi, A.; Takaki, Y.; Hirasawa, D.; Momma, K.; Amano, Y.; Yagi, K.; et al. Diagnostic utility of a novel magnifying endoscopic classification system for superficial Barrett’s esophagus-related neoplasms: A nationwide multicenter study. Esophagus 2021, 18, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struyvenberg, M.R.; De Groof, A.J.; van der Putten, J.; van der Sommen, F.; Baldaque-Silva, F.; Omae, M.; Pouw, R.; Bisschops, R.; Vieth, M.; Schoon, E.J.; et al. A computer-assisted algorithm for narrow-band imaging-based tissue characterization in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Rubenstein, J.H.; Wang, T.D.; Seibel, E.J. Toward real-time quantification of fluorescence molecular probes using target/background ratio for guiding biopsy and endoscopic therapy of esophageal neoplasia. J. Med. Imaging 2017, 4, 024502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Giacchino, M.; Bansal, A.; Kim, R.E.; Singh, V.; Hall, S.B.; Singh, M.; Rastogi, A.; Moloney, B.; Wani, S.B.; Gaddam, S.; et al. Clinical utility and interobserver agreement of autofluorescence imaging and magnification narrow-band imaging for the evaluation of Barrett’s esophagus: A prospective tandem study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2013, 77, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerwinkel, D.F.; Holz, J.A.; Aalders, M.C.G.; Visser, M.; Meijer, S.L.; Henegouwen, M.I.V.B.; Weusten, B.L.A.M.; Bergman, J.J.G.H.M. Third-generation autofluorescence endoscopy for the detection of early neoplasia in Barrett’s esophagus: A pilot study. Dis. Esophagus 2014, 27, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curvers, W.L.; Herrero, L.A.; Wallace, M.B.; Song, L.W.K.; Ragunath, K.; Wolfsen, H.C.; Prasad, G.A.; Wang, K.K.; Subramanian, V.; Weusten, B.L.; et al. Endoscopic Tri-Modal Imaging Is More Effective Than Standard Endoscopy in Identifying Early-Stage Neoplasia in Barrett’s Esophagus. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1106–1114.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curvers, W.L.; van Vilsteren, F.G.; Baak, L.C.; Böhmer, C.; Mallant-Hent, R.C.; Naber, A.H.; van Oijen, A.; Ponsioen, C.Y.; Scholten, P.; Schenk, E.; et al. Endoscopic trimodal imaging versus standard video endoscopy for detection of early Barrett’s neoplasia: A multicenter, randomized, crossover study in general practice. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 73, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pietro, M.; Bird-Lieberman, E.L.; Liu, X.; Nuckcheddy-Grant, T.; Bertani, H.; O’Donovan, M.; Fitzgerald, R.C. Autofluorescence-Directed Confocal Endomicroscopy in Combination With a Three-Biomarker Panel Can Inform Management Decisions in Barrett’s Esophagus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muldoon, T.J.; Thekkek, N.; Roblyer, D.; Maru, D.; Harpaz, N.; Potack, J.; Anandasabapathy, S.; Richards-Kortum, R. Evaluation of quantitative image analysis criteria for the high-resolution microendoscopic detection of neoplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 026027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, M.A.; Peters, F.P.; Fockens, P.; Kate, F.J.T.; Bergman, J.J. Endoscopic video-autofluorescence imaging followed by narrow band imaging for detecting early neoplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2006, 64, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, M.A.; Peters, F.; Kate, F.J.T.; van Deventer, S.J.; Fockens, P.; Bergman, J.J. Endoscopic video autofluorescence imaging may improve the detection of early neoplasia in patients with Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2005, 61, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, M.; Boerwinkel, D.F.; Shariff, M.K.; Liu, X.; Telakis, E.; Lao-Sirieix, P.; Walker, E.; Couch, G.; Mills, L.; Nuckcheddy-Grant, T.; et al. The combination of autofluorescence endoscopy and molecular biomarkers is a novel diagnostic tool for dysplasia in Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut 2015, 64, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerwinkel, D.F.; Di Pietro, M.; Liu, X.; Shariff, M.K.; Lao-Sirieix, P.; Walker, C.E.; Visser, M.; Donovan, M.O.; Kaye, P.; Bergman, J.J.G.H.M.; et al. Endoscopic TriModal imaging and biomarkers for neoplasia conjoined: A feasibility study in Barrett’s esophagus. Dis. Esophagus 2014, 27, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukasawa, K.; Choi, T.; Kuriyama, R.; Rulong, S.; Woude, G.F.V. Abnormal Centrosome Amplification in the Absence of p53. Science 1996, 271, 1744–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poehlmann, A.; Kuester, D.; Malfertheiner, P.; Guenther, T.; Roessner, A. Inflammation and Barrett’s carcinogenesis. Pathol.—Res. Pract. 2012, 208, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaddam, S.; Mathur, S.C.; Singh, M.; Arora, J.; Wani, S.B.; Gupta, N.; Overhiser, A.; Rastogi, A.; Singh, V.; Desai, N.; et al. Novel Probe-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy Criteria and Interobserver Agreement for the Detection of Dysplasia in Barrett’s Esophagus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pietro, M.; Bertani, H.; O’Donovan, M.; Santos, P.; Alastal, H.; Phillips, R.; Ortiz-Fernández-Sordo, J.; Iacucci, M.; Modolell, I.; Bonetti, L.R.; et al. Development and validation of confocal endomicroscopy diagnostic criteria for low-grade dysplasia in barrett’s esophagus. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesslich, R.; Gossner, L.; Goetz, M.; Dahlmann, A.; Vieth, M.; Stolte, M.; Hoffman, A.; Jung, M.; Nafe, B.; Galle, P.R. In Vivo Histology of Barrett’s Esophagus and Associated Neoplasia by Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Chen, Y.; Dekker, E.; Fockens, P.; Sharma, P.; Meining, A. Miami classification for probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy. Laryngo-Rhino-Otologie 2011, 43, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohl, H.J.; Rosch, T.; Vieth, M.; Koch, M.; Becker, V.; Anders, M.; Khalifa, A.C.; Meining, A. Miniprobe confocal laser microscopy for the detection of invisible neoplasia in patients with Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut 2008, 57, 1648–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.B.; Sharma, P.; Lightdale, C.; Wolfsen, H.; Coron, E.; Buchner, A.; Bajbouj, M.; Bansal, A.; Rastogi, A.; Abrams, J.; et al. Preliminary accuracy and interobserver agreement for the detection of intraepithelial neoplasia in Barrett’s esophagus with probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 72, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leggett, C.L.; Gorospe, E.C.; Chan, D.K.; Muppa, P.; Owens, V.; Smyrk, T.C.; Anderson, M.; Lutzke, L.S.; Tearney, G.; Wang, K.K. Comparative diagnostic performance of volumetric laser endomicroscopy and confocal laser endomicroscopy in the detection of dysplasia associated with Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 83, 880–888.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorospe, E.C.; Leggett, C.L.; Sun, G.; Anderson, M.A.; Gupta, M.; Penfield, J.D.; Lutzke, L.; Lewis, J.T.; Song, L.M.W.K.; Wang, K.K. Diagnostic performance of two confocal endomicroscopy systems in detecting Barrett’s dysplasia: A pilot study using a novel bioprobe in ex vivo tissue. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2012, 76, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thekkek, N.; Maru, D.M.; Polydorides, A.D.; Bhutani, M.S.; Anandasabapathy, S.; Richards-Kortum, R. Pre-Clinical Evaluation of Fluorescent Deoxyglucose as a Topical Contrast Agent for the Detection of Barrett’s-Associated Neoplasia during Confocal Imaging. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 10, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunbar, K.B. Endomicroscopy in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 23, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canto, M.I.; Anandasabapathy, S.; Brugge, W.; Falk, G.; Dunbar, K.B.; Zhang, Z.; Woods, K.; Almario, J.A.; Schell, U.; Goldblum, J.; et al. In vivo endomicroscopy improves detection of Barrett’s esophagus–related neoplasia: A multicenter international randomized controlled trial (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2014, 79, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middelburg, T.; Hoy, C.; Neumann, H.; Amelink, A.; Robinson, D. Correction for tissue optical properties enables quantitative skin fluorescence measurements using multi-diameter single fiber reflectance spectroscopy. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 79, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.; Chang, T.-S.; Joshi, B.; Zhou, J.; Rubenstein, J.H.; Wamsteker, E.J.; Kwon, R.S.; Appelman, H.; Beer, D.G.; et al. Multiplexed endoscopic imaging of Barrett’s neoplasia using targeted fluorescent heptapeptides in a phase 1 proof-of-concept study. Gut 2021, 70, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atreya, R.; Goetz, M. Molecular imaging in gastroenterology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoetker, M.S.; Goetz, M. Molecular imaging in endoscopy. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2013, 1, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bézière, N.; Ntziachristos, V. Optoacoustic Imaging: An Emerging Modality for the Gastrointestinal Tract. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1979–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthi, R.; Iyer, P.G. Molecular biomarkers added to image-enhanced endoscopic imaging: Will they further improve diagnostic accuracy? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 29, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zuo, X.; Li, C.; Yu, T.; Gu, X.; Zhou, C.; Li, Z.; Goetz, M.; Kiesslich, R.; Li, Y. In vivo molecular imaging of epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with colorectal neoplasia using confocal laser endomicroscopy. Cancer Lett. 2013, 330, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird-Lieberman, E.L.; Neves, A.A.; Lao-Sirieix, P.; O’Donovan, M.; Novelli, M.; Lovat, L.B.; Eng, W.S.; Mahal, L.K.; Brindle, K.M.; Fitzgerald, R.C. Molecular imaging using fluorescent lectins permits rapid endoscopic identification of dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medarova, Z.; Rashkovetsky, L.; Pantazopoulos, P.; Moore, A. Multiparametric Monitoring of Tumor Response to Chemotherapy by Noninvasive Imaging. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Realdon, S.; Dassie, E.; Fassan, M.; Dall’Olmo, L.; Hatem, G.; Buda, A.; Arcidiacono, D.; Diamantis, G.; Zhang, H.; Greene, M.I.; et al. In vivo molecular imaging of HER2 expression in a rat model of Barrett’s esophagus adenocarcinoma. Dis. Esophagus 2015, 28, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Chang, Y.; Cui, C.; Sun, L.; Wang, D.H.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, M. Near infrared fluorescent peptide nanoparticles for enhancing esophageal cancer therapeutic efficacy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Kreft, A.; Chowdhury, E.H.; Hossain, S.M.; Galle, P.R.; Neumann, H. Molecular endoscopic imaging for the detection of Barrett’s metaplasia using biodegradable inorganic nanoparticles: An ex-vivo pilot study on human tissue. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, M.B.; Joshi, B.P.; Lu, S.; Piraka, C.; Khondee, S.; Elmunzer, B.J.; Kwon, R.S.; Beer, D.G.; Appelman, H.D.; Turgeon, D.K.; et al. Targeted Imaging of Esophageal Neoplasia with a Fluorescently Labeled Peptide: First-in-Human Results. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 184ra61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.-Y.; Stangl, S.; Marcazzan, S.; Carvalho, M.J.B.; Baumeister, T.; Anand, A.; Strangmann, J.; Huspenina, J.S.; Wang, T.C.; Schmid, R.M.; et al. Targeted Hsp70 fluorescence molecular endoscopy detects dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 49, 2049–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, J.V.; Waller, C.A.; Timpl, R.; Schirrmacher, V. Surface sialic acid reduces attachment of metastatic tumour cells to collagen type IV and fibronectin. Nature 1982, 300, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, B.P.; Duan, X.; Kwon, R.S.; Piraka, C.; Elmunzer, B.J.; Lu, S.; Rabinsky, E.F.; Beer, D.G.; Appelman, H.D.; Owens, S.R.; et al. Multimodal endoscope can quantify wide-field fluorescence detection of Barrett’s neoplasia. Laryngo-Rhino-Otologie 2016, 48, A1–A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Anastassiades, C.P.; Joshi, B.; Komarck, C.M.; Piraka, C.; Elmunzer, B.J.; Turgeon, D.K.; Johnson, T.D.; Appelman, H.; Beer, D.G.; et al. Affinity Peptide for Targeted Detection of Dysplasia in Barrett’s Esophagus. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multhoff, G.; Botzler, C.; Wiesnet, M.; Müller, E.; Meier, T.; Wilmanns, W.; Issels, R.D. A stress-inducible 72-kDa heat-shock protein (HSP72) is expressed on the surface of human tumor cells, but not on normal cells. Int. J. Cancer 1995, 61, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrmann, M.; Liebisch, G.; Schmitz, G.; Anderson, R.; Steinem, C.; De Maio, A.; Pockley, G.; Multhoff, G. Tumor-Specific Hsp70 Plasma Membrane Localization Is Enabled by the Glycosphingolipid Gb3. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moasser, M.M. The oncogene HER2: Its signaling and transforming functions and its role in human cancer pathogenesis. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6469–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, D.G.; Whitney-Miller, C. HER2 Testing in Gastric and Gastroesophageal Junction Cancers: A New Therapeutic Target and Diagnostic Challenge. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2011, 19, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, T.; Nentwich, M.F.; Lüth, M.; Yekebas, E.; Schumacher, U. Trastuzumab has anti-metastatic and anti-angiogenic activity in a spontaneous metastasis xenograft model of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2011, 308, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beales, I.L.P.; Ogunwobi, O.; Cameron, E.; El-Amin, K.; Mutungi, G.; Wilkinson, M. Activation of Akt is increased in the dysplasia-carcinoma sequence in Barrett’s oesophagus and contributes to increased proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis: A histopathological and functional study. BMC Cancer 2007, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagengast, W.B.; Hartmans, E.; Garcia-Allende, P.B.; Peters, F.T.M.; Linssen, M.D.; Koch, M.; Koller, M.; Tjalma, J.; Karrenbeld, A.; Jorritsma-Smit, A.; et al. Near-infrared fluorescence molecular endoscopy detects dysplastic oesophageal lesions using topical and systemic tracer of vascular endothelial growth factor A. Gut 2017, 68, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Gabriëls, R.Y.; Hooghiemstra, W.T.R.; Koller, M.; Meersma, G.J.; Buist-Homan, M.; Visser, L.; Robinson, D.J.; Tenditnaya, A.; Gorpas, D.; et al. Validation of Novel Molecular Imaging Targets Identified by Functional Genomic mRNA Profiling to Detect Dysplasia in Barrett’s Esophagus. Cancers 2022, 14, 2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcazzan, S.; Carvalho, M.J.B.; Konrad, M.; Strangmann, J.; Tenditnaya, A.; Baumeister, T.; Schmid, R.M.; Wester, H.-J.; Ntziachristos, V.; Gorpas, D.; et al. CXCR4 peptide-based fluorescence endoscopy in a mouse model of Barrett’s esophagus. EJNMMI Res. 2022, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.-C.A.; Sahli, S.; Andrews, D.W.; Patterson, M.S.; Armstrong, D.; Provias, J.; Fang, Q. 5-aminolevulinic acid induced protoporphyrin IX as a fluorescence marker for quantitative image analysis of high-grade dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus cellular models. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 036010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocca, R.; Mastracci, L.; Milione, M.; Parente, P.; Savarino, V. Microscopic esophagitis and Barrett’s esophagus: The histology report. Dig. Liver Dis. 2011, 43, S319–S330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblum, J.R. Barrett’s Esophagus and Barrett’s-Related Dysplasia. Mod2 Pathol. 2003, 16, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nitin, N.; Carlson, A.L.; Muldoon, T.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Gillenwater, A.; Richards-Kortum, R. Molecular imaging of glucose uptake in oral neoplasia following topical application of fluorescently labeled deoxy-glucose. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 124, 2634–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neil, R.G.; Wu, L.; Mullani, N. Uptake of a Fluorescent Deoxyglucose Analog (2-NBDG) in Tumor Cells. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2005, 7, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, K.; Saito, M.; Oh, K.-B.; Nemoto, Y.; Matsuoka, H.; Natsume, M.; Abe, H. Intracellular Fate of 2-NBDG, a Fluorescent Probe for Glucose Uptake Activity, in Escherichia coli Cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996, 60, 1899–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, P.G.; Hardin, C.D.; Sturek, M. Examining glucose transport in single vascular smooth muscle cells with a fluorescent glucose analog. Physiol. Res. 1999, 48, 401–410. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, K.; Nakata, M.; Horimoto, N.; Saito, M.; Matsuoka, H.; Inagaki, N. Measurement of Glucose Uptake and Intracellular Calcium Concentration in Single, Living Pancreatic β-Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 22278–22283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, R.A.; Josephson, L.; Mahmood, U. Evaluation and clinically relevant applications of a fluorescent imaging analog to fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 064014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, M.C.; Javier, D.J.; Richards-Kortum, R. Optical contrast agents and imaging systems for detection and diagnosis of cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommen F van der Curvers, W.L.; Nagengast, W.B. Novel Developments in Endoscopic Mucosal Imaging. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1876–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Sommen, F.; Zinger, S.; Curvers, W.L.; Bisschops, R.; Pech, O.; Weusten, B.L.; Bergman, J.J.; Schoon, E.J. Computer-aided detection of early neoplastic lesions in Barrett’s esophagus. Endoscopy 2016, 48, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Sivak, M.V., Jr.; Wilson, D.L.; Rollins, A.M. Computer-aided diagnosis of dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus using endoscopic optical coherence tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006, 11, 044010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struyvenberg, M.R.; de Groof, A.J.; Fonollà, R.; van der Sommen, F.; de With, P.H.; Schoon, E.J.; Weusten, B.L.; Leggett, C.L.; Kahn, A.; Trindade, A.J.; et al. Prospective development and validation of a volumetric laser endomicroscopy computer algorithm for detection of Barrett’s neoplasia. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uno, K.; Koike, T.; Hatta, W.; Saito, M.; Tanabe, M.; Masamune, A. Development of Advanced Imaging and Molecular Imaging for Barrett’s Neoplasia. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102437
Uno K, Koike T, Hatta W, Saito M, Tanabe M, Masamune A. Development of Advanced Imaging and Molecular Imaging for Barrett’s Neoplasia. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(10):2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102437
Chicago/Turabian StyleUno, Kaname, Tomoyuki Koike, Waku Hatta, Masahiro Saito, Mizuki Tanabe, and Atsushi Masamune. 2022. "Development of Advanced Imaging and Molecular Imaging for Barrett’s Neoplasia" Diagnostics 12, no. 10: 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102437
APA StyleUno, K., Koike, T., Hatta, W., Saito, M., Tanabe, M., & Masamune, A. (2022). Development of Advanced Imaging and Molecular Imaging for Barrett’s Neoplasia. Diagnostics, 12(10), 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102437







