Immunohistochemical Expression Patterns of CD45RO, p105/p50, JAK3, TOX, and IL-17 in Early-Stage Mycosis Fungoides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Group
2.2. Morphologic Examination
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristic of Patients
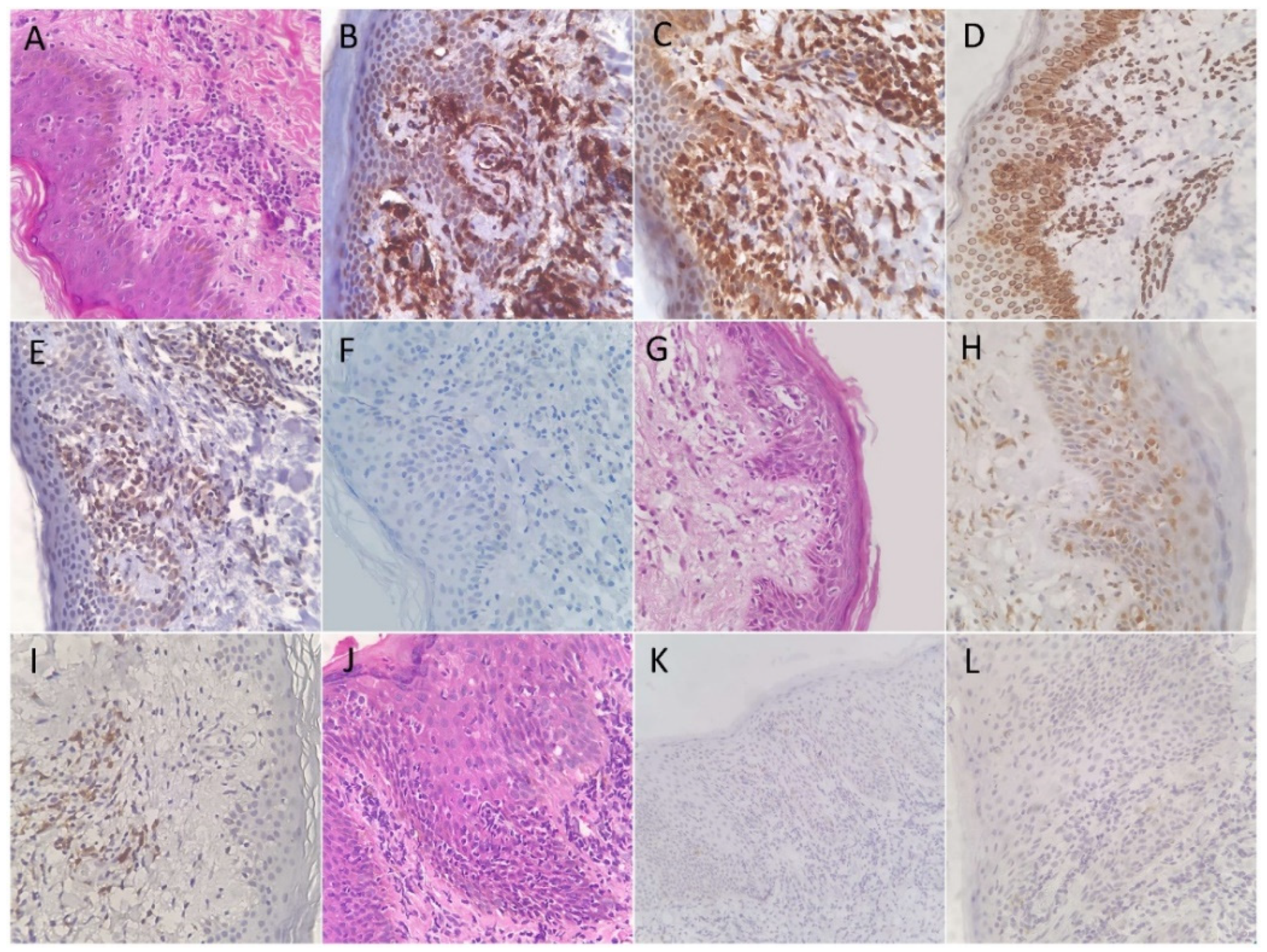
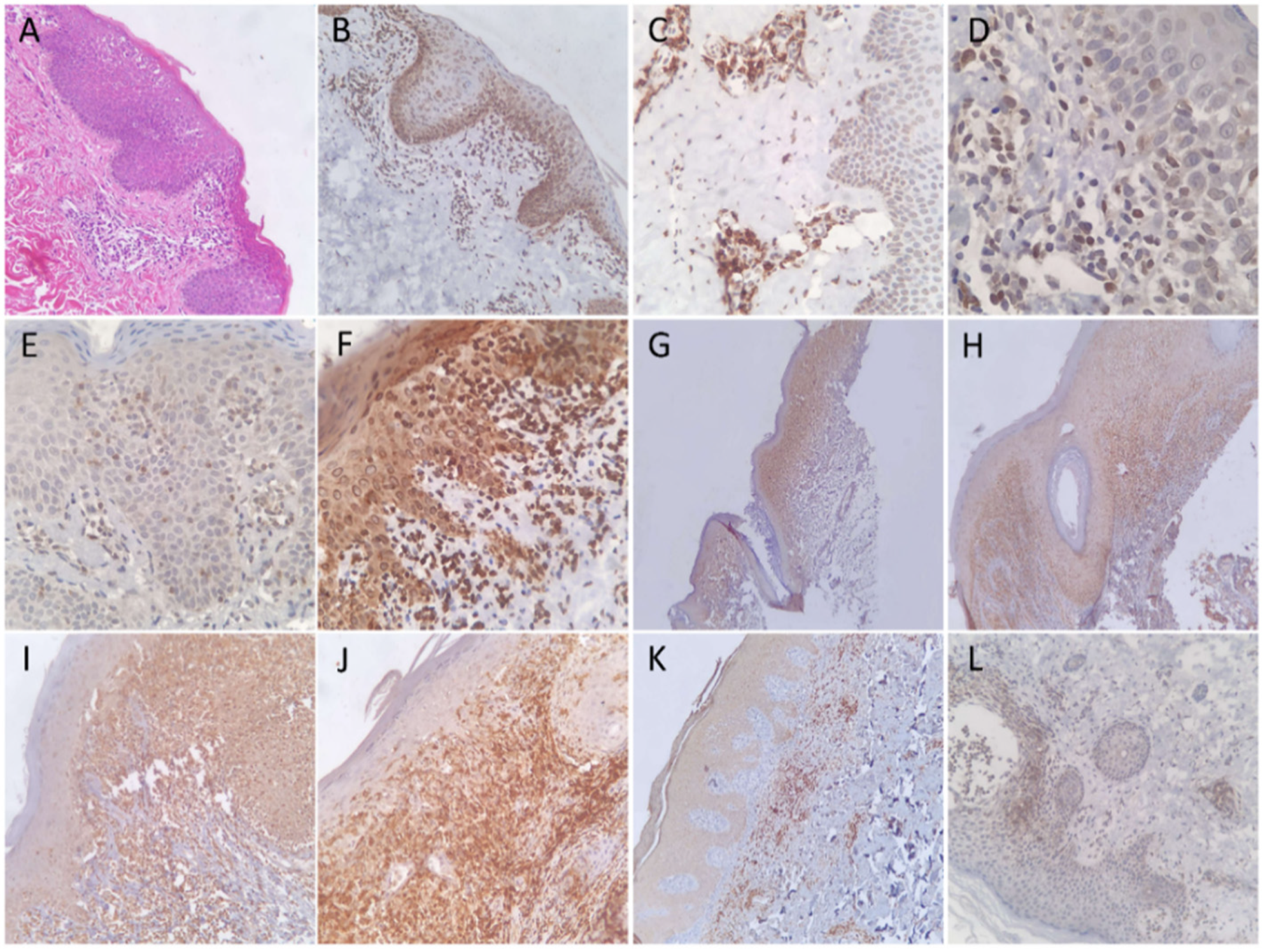
3.2. Expression Patterns of Immunohistochemical Stains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Criscione, V.D.; Weinstock, M.A. Incidence of Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma in the United States, 1973–2002. Arch. Dermatol. 2007, 143, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladily, T.N.; Khreisat, W.; Ashukhaibi, O.; Alkhatib, S.M.; Annab, H.; Tarawneh, M.S.; Salman, T.S.; Abu Farsakh, H.; Mahgoub, R.; Bustami, N.; et al. The Epidemiology of Lymphoma in Jordan: A Nationwide Population Study of 4189 Cases According to World Health Organization Classification System. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Ther. 2021, 14, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- McGirt, L.Y.; Jia, P.; Baerenwald, D.A.; Duszynski, R.J.; Dahlman, K.B.; Zic, J.A.; Zwerner, J.P.; Hucks, D.; Dave, U.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals Oncogenic Mutations in Mycosis Fungoides. Blood 2015, 126, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olsen, E.; Vonderheid, E.; Pimpinelli, N.; Willemze, R.; Kim, Y.; Knobler, R.; Zackheim, H.; Duvic, M.; Estrach, T.; Lamberg, S.; et al. Revisions to the Staging and Classification of Mycosis Fungoides and Sézary Syndrome: A Proposal of the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas (ISCL) and the Cutaneous Lymphoma Task Force of the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Blood 2007, 110, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho-Vega, J.H.; Tschen, J.A.; Duvic, M.; Vega, F. Early-Stage Mycosis Fungoides Variants: Case-Based Review. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2010, 14, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagaki, T. Diagnosis of Early Mycosis Fungoides. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, M.D.; Way, S.S.; Abbas, A.K. Regulatory T Cell Memory. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 16, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, N.J.; McQuaid, A.J.; Sobande, T.; Kissane, S.; Agius, E.; Jackson, S.E.; Salmon, M.; Falciani, F.; Yong, K.; Rustin, M.H.; et al. Different Proliferative Potential and Migratory Characteristics of Human CD4+ Regulatory T Cells That Express Either CD45RA or CD45RO. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 4317–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vade Mecum. Available online: http://e-immunohistochemistry.info/web/histopathology_help.htm#Mycosis_fungoides_Sezary_s_syndrome.htm (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Ismail, S.A.; Han, R.; Sanborn, S.L.; Stevens, S.R.; Cooper, K.D.; Wood, G.S.; Gilliam, A.C. Immunohistochemical Staining for CD45R Isoforms in Paraffin Sections to Diagnose Mycosis Fungoides–Type Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 56, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izban, K. Constitutive Expression of NF-ΚB Is a Characteristic Feature of Mycosis Fungoides: Implications for Apoptosis Resistance and Pathogenesis. Hum. Pathol. 2000, 31, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packham, G. The Role of NF-ΚB in Lymphoid Malignancies. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 143, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, C.; Mondéjar, R.; García-Díaz, N.; Cereceda, L.; León, A.; Montes, S.; Durán Vian, C.; Pérez Paredes, M.G.; González-Morán, A.; Miguel, V.; et al. Advanced-Stage Mycosis Fungoides: Role of the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3, Nuclear Factor-ΚB and Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells Pathways. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 182, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibbesen, N.A.; Kopp, K.L.; Litvinov, I.V.; Jønson, L.; Willerslev-Olsen, A.; Fredholm, S.; Petersen, D.L.; Nastasi, C.; Krejsgaard, T.; Lindahl, L.M.; et al. Jak3, STAT3, and STAT5 Inhibit Expression of MiR-22, a Novel Tumor Suppressor MicroRNA, in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20555–20569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vadivel, C.K.; Gluud, M.; Torres-Rusillo, S.; Boding, L.; Willerslev-Olsen, A.; Buus, T.B.; Nielsen, T.K.; Persson, J.L.; Bonefeld, C.M.; Geisler, C.; et al. JAK3 Is Expressed in the Nucleus of Malignant T Cells in Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma (CTCL). Cancers 2021, 13, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, V.H.; Clemmensen, O.J.; Nielsen, O.; Wasik, M.; Lovato, P.; Brender, C.; Eriksen, K.W.; Woetmann, A.; Kaestel, C.G.; Nissen, M.H.; et al. In Vivo Activation of STAT3 in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. Evidence for an Antiapoptotic Function of STAT3. Leukemia 2004, 18, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, C.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, Y. TOX as a Potential Target for Immunotherapy in Lymphocytic Malignancies. Biomark. Res. 2021, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre, L.; García-García, J.F.; Jiménez, S.; Reyes-García, A.I.; García-González, Á.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Arribas, A.J.; González-García, P.; Caleiras, E.; Banham, A.H.; et al. High-Mobility Group Box (TOX) Antibody a Useful Tool for the Identification of B and T Cell Subpopulations. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimura, S.; Sugaya, M.; Suga, H.; Miyagaki, T.; Ohmatsu, H.; Fujita, H.; Asano, Y.; Tada, Y.; Kadono, T.; Sato, S. TOX Expression in Different Subtypes of Cutaneous Lymphoma. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2014, 306, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Q. TOX Acts an Oncological Role in Mycosis Fungoides. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGirt, L.Y.; Degesys, C.A.; Johnson, V.E.; Zic, J.A.; Zwerner, J.P.; Eischen, C.M. TOX Expression and Role in CTCL. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferretti, S.; Bonneau, O.; Dubois, G.R.; Jones, C.E.; Trifilieff, A. IL-17, Produced by Lymphocytes and Neutrophils, Is Necessary for Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Airway Neutrophilia: IL-15 as a Possible Trigger. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 2106–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, A.W.; Gaffen, S.L. IL-17RC: A Partner in IL-17 Signaling and Beyond. Semin. Immunopathol. 2009, 32, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cirée, A.; Michel, L.; Camilleri-Bröet, S.; Jean Louis, F.; Oster, M.; Flageul, B.; Senet, P.; Fossiez, F.; Fridman, W.H.; Bachelez, H.; et al. Expression and Activity of IL-17 in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas (Mycosis Fungoides and Sezary Syndrome). Int. J. Cancer 2004, 112, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krejsgaard, T.; Litvinov, I.V.; Wang, Y.; Xia, L.; Willerslev-Olsen, A.; Koralov, S.B.; Kopp, K.L.; Bonefeld, C.M.; Wasik, M.A.; Geisler, C.; et al. Elucidating the Role of Interleukin-17F in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2013, 122, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krejsgaard, T.; Ralfkiaer, U.; Clasen-Linde, E.; Eriksen, K.W.; Kopp, K.L.; Bonefeld, C.M.; Geisler, C.; Dabelsteen, S.; Wasik, M.A.; Ralfkiaer, E.; et al. Malignant Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma Cells Express IL-17 Utilizing the Jak3/Stat3 Signaling Pathway. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Diagnostic Test | Sensitivity | 95% CI | Specificity | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD45RO | 100% | 83.89–100% | 0% | 0–100% | 1 |
| NFkB-p105/p50 | 0% | 0.00–16.11% | 100.00% | 82.35–100% | 1 |
| JAK3 | 14.29% | 3.05–36.34% | 10.53% | 1.30–33.14% | 0.003 |
| TOX | 90.48% | 69.62–98.83% | 31.58% | 12.58–56.55% | 0.120 |
| IL-17 | 65.00% | 40.78–84.61% | 68.42% | 43.45–87.42% | 0.056 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aladily, T.N.; Abushunar, T.; Alhesa, A.; Alrawi, R.; Almaani, N.; Abdaljaleel, M. Immunohistochemical Expression Patterns of CD45RO, p105/p50, JAK3, TOX, and IL-17 in Early-Stage Mycosis Fungoides. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010220
Aladily TN, Abushunar T, Alhesa A, Alrawi R, Almaani N, Abdaljaleel M. Immunohistochemical Expression Patterns of CD45RO, p105/p50, JAK3, TOX, and IL-17 in Early-Stage Mycosis Fungoides. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(1):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010220
Chicago/Turabian StyleAladily, Tariq N., Tasnim Abushunar, Ahmad Alhesa, Raneen Alrawi, Noor Almaani, and Maram Abdaljaleel. 2022. "Immunohistochemical Expression Patterns of CD45RO, p105/p50, JAK3, TOX, and IL-17 in Early-Stage Mycosis Fungoides" Diagnostics 12, no. 1: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010220
APA StyleAladily, T. N., Abushunar, T., Alhesa, A., Alrawi, R., Almaani, N., & Abdaljaleel, M. (2022). Immunohistochemical Expression Patterns of CD45RO, p105/p50, JAK3, TOX, and IL-17 in Early-Stage Mycosis Fungoides. Diagnostics, 12(1), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010220






