Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology and Definition
3. Clinical Features
4. Pulmonary Function Tests
5. Imaging
5.1. Chest Radiography
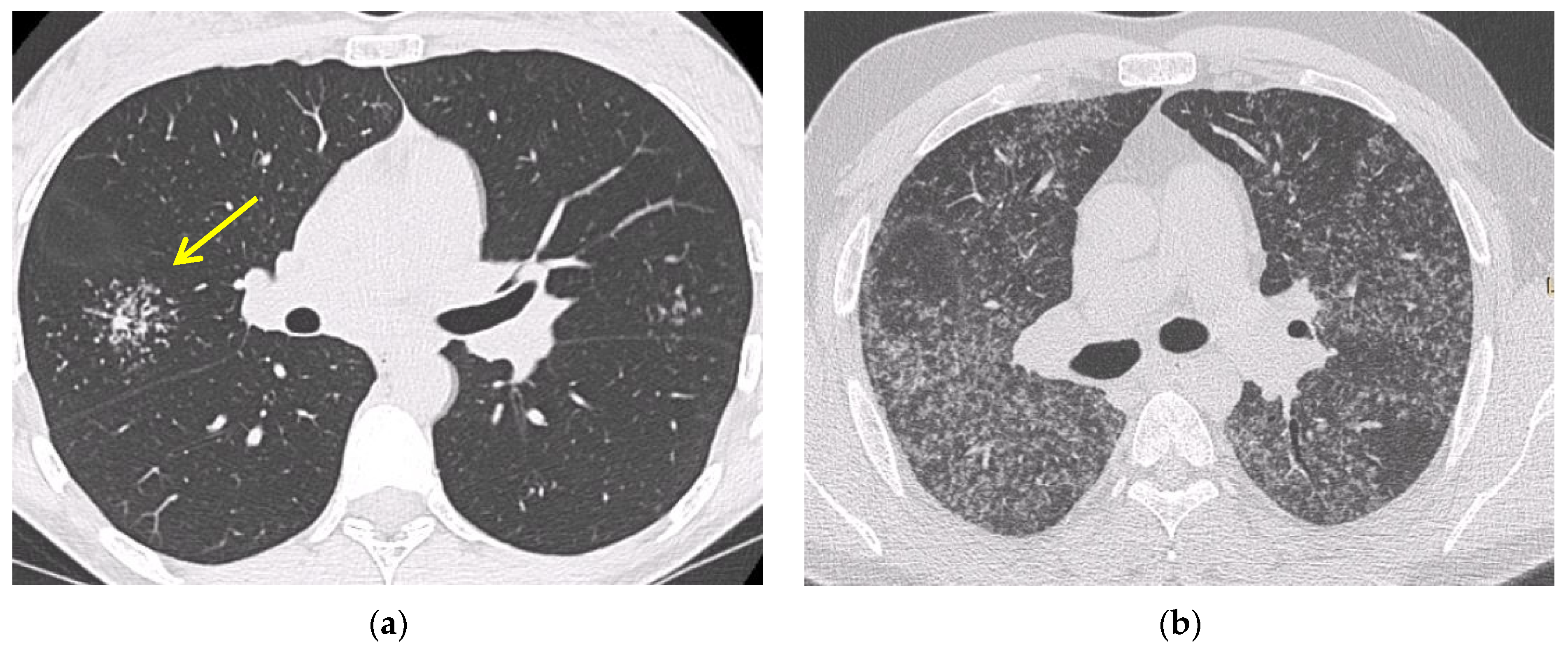
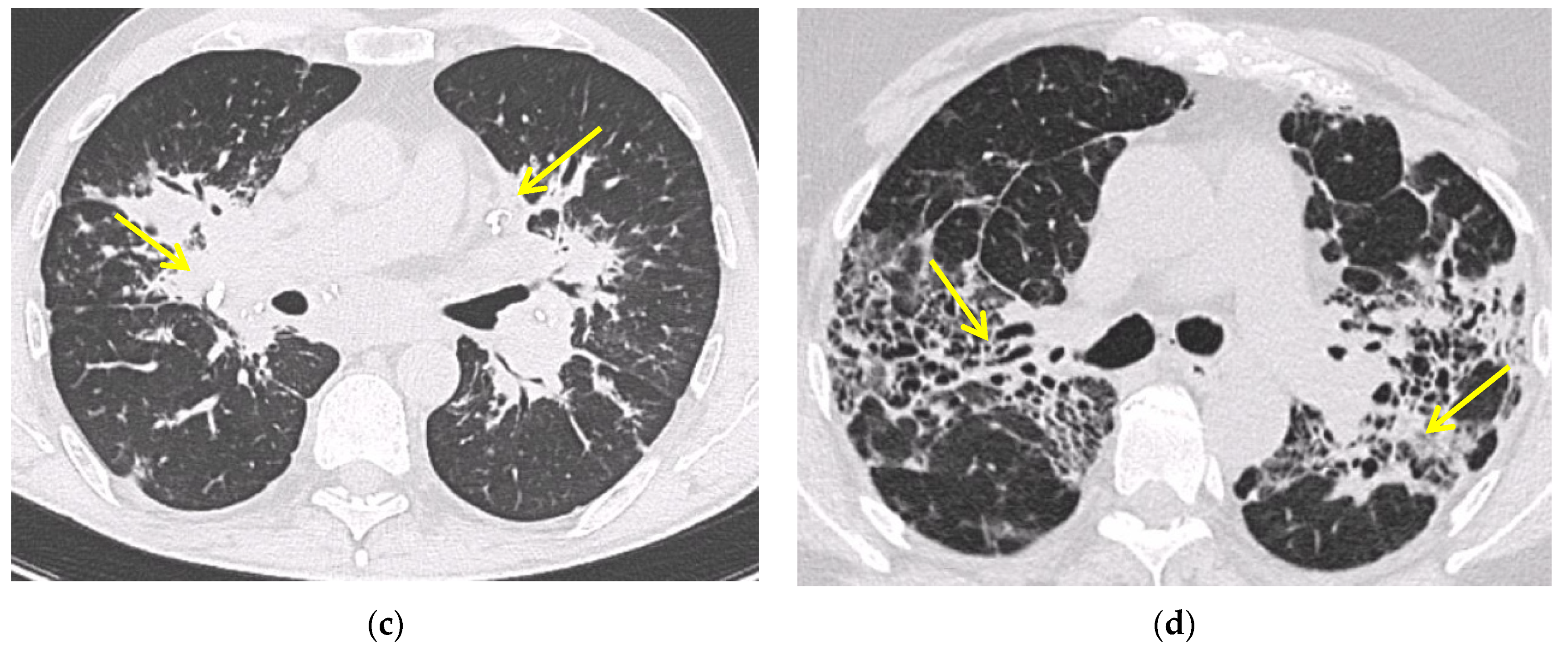
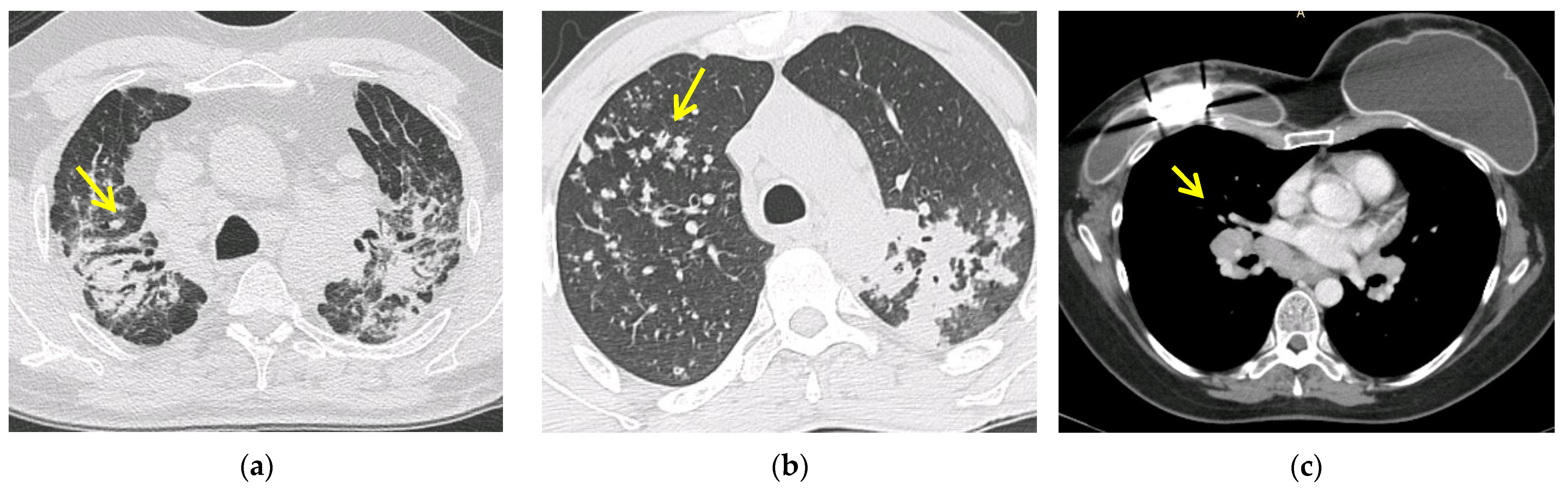
5.2. Computed Tomography (CT Scan)
5.3. Positron Emission Tomography (FDG PET/CT)
6. Confirmation of the Diagnosis
6.1. Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy
6.2. Bronchoalveolar Lavage
6.3. EBUS-TBNA
6.4. Transbronchial Lung Biopsy (TBLB)
6.5. Mediastinoscopy
6.6. Serological Biomarkers
7. Differential Diagnosis
7.1. Tuberculosis and Other Infectious Diseases
7.2. Occupational and Environmental Exposure: Chronic Beryllium Disease and Silicosis
7.3. Lymphoma, Cancer and Drug: The Sarcoid-like Reaction
7.4. Common Variable Immunodeficiency
7.5. Autoimmune Disorders
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grunewald, J.; Spagnolo, P.; Wahlström, J.; Eklund, A. Immunogenetics of disease-causing inflammation in Sarcoidosis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 49, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Thoracic Society. Statement on sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 736–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunewald, J.; Grutters, J.C.; Arkema, E.V.; Saketkoo, L.A.; Moller, D.R.; Müller-Quernheim, J. Sarcoidosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouser, E.D.; Maier, L.A.; Wilson, K.C.; Bonham, C.A.; Morgenthau, A.S.; Patterson, K.C.; Abston, E.; Bernstein, R.C.; Blankstein, R.; Chen, E.S.; et al. Diagnosis and detection of Sarcoidosis. An official American Thoracic Society clinical practice guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, e26–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neville, E.; Walker, A.N.; James, D.G. Prognostic factors predicting the outcome of Sarcoidosis: An analysis of 818 patients. Q. J. Med. 1983, 52, 525–533. [Google Scholar]
- Gerke, A.K.; Judson, M.A.; Cozier, Y.C.; Culver, D.A.; Koth, L.L. Disease burden and variability in Sarcoidosis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2017, 14, S421–S428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerke, A.K. Morbidity and mortality in Sarcoidosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2014, 20, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.P.; Barriuso, R.; Beyer, K.; Boyd, J.; Hochreiter, J.; Knoet, C.; Martone, F.; Quadder, B.; Richardson, J.; Spitzer, G.; et al. Sarcoidosis: Patient treatment priorities. ERJ Open Res. 2018, 4, 00141-2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.P.; Judson, M.A.; Wells, A. The indications for the treatment of Sarcoidosis: Wells law. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2017, 34, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomeer, M.J.; Costabel, U.; Rizzato, G.; Poletti, V.; Demedts, M. Comparison of registries of interstitial lung diseases in three European countries. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 18, 114s–118s. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, L.S.; Rose, C.S.; Maier, L.A. Sarcoidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkema, E.V.; Cozier, Y.C. Epidemiology of Sarcoidosis: Current findings and future directions. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2018, 9, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamilloux, Y.; Bonnefoy, M.; Valeyre, D.; Varron, L.; Broussolle, C.; Seve, P. Elderly-onset Sarcoidosis: Prevalence, clinical course, and treatment. Drugs Aging 2013, 30, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baughman, R.P.; Teirstein, A.S.; Judson, M.; Rossman, M.D.; Yeager, H.; Bresnitz, E.A.; DePalo, L.; Hunninghake, G.W.; Iannuzzi, M.C.; Johns, C.J.; et al. Clinical characteristics of patients in a case control study of Sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1885–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polverino, F.; Balestro, E.; Spagnolo, P. Clinical presentations, pathogenesis, and therapy of Sarcoidosis: State of the art. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacomis, D. Neurosarcoidosis. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2011, 9, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivieri, M.G.; Spagnolo, P.; Birnie, D.; Liu, P.; Drake, W.; Kovacic, J.C.; Baughman, R.; Fayad, Z.A.; Judson, M.A. Challenges in Cardiac and Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1878–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judson, M.A. Small fiber neuropathy in sarcoidosis: Something beneath the surface. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Voortman, M.; Hendriks, C.M.R.; Elfferich, M.D.P.; Bonella, F.; Møller, J.; De Vries, J.; Costabel, U.; Drent, M. The Burden of Sarcoidosis symptoms from a patient perspective. Lung 2019, 197, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mañá, J.; Gómez-Vaquero, C.; Montero, A.; Salazar, A.; Marcoval, J.; Valverde, J.; Manresa, F.; Pujol, R. Löfgren’s syndrome revisited: A study of 186 patients. Am. J. Med. 1999, 107, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, A.; Manadan, A. Heerfordt’s syndrome, or uveoparotid fever. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danila, E.; Jurgauskienė, L.; Malickaite, R. BAL fluid cells and pulmonary function in different radiographic stages of newly diagnosed sarcoidosi. Adv. Med. Sci. 2008, 53, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calaras, D.; Munteanu, O.; Scaletchi, V.; Simionica, I.; Botnaru, V. Ventilatory disturbances in patients with intrathoracic Sarcoidosis—A study from a functional and histological perspective. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2017, 34, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, J.P.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Gay, S.E. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Clin. Chest Med. 1997, 18, 755–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scadding, J.G. Prognosis of intrathoracic Sarcoidosis in England. A review of 136 cases after five years’ observation. Br. Med. J. 1961, 2, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.H.; Rosado-De-Christenson, M.L.; McAdams, H.P.; Fishback, N.F. Thoracic sarcoidosis: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. RadioGraphics 1995, 15, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judson, M.A. Sarcoidosis: Clinical presentation, diagnosis, and approach to treatment. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2008, 335, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, P.; Sverzellati, N.; Wells, A.U.; Hansell, D.M. Imaging aspects of the diagnosis of sarcoidosis. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, E.; Sánchez, M.; Ramirez, J.; Arguis, P.; De Caralt, T.M.; Perea, R.J.; Xaubet, A. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: Typical and atypical manifestations at high-resolution CT with pathologic correlation. RadioGraphics 2010, 30, 1567–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.P.; Ma, Y.L.; Koss, M.N.; White, E. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 28, 053–074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, K.C.; Strek, M.E. Pulmonary Fibrosis in Sarcoidosis. Clinical features and outcomes. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2013, 10, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abehsera, M.; Valeyre, D.; Grenier, P.; Jaillet, H.; Battesti, J.P.; Brauner, M.W. Sarcoidosis with pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 174, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeyre, D.; Nunes, H.; Bernaudin, J.-F. Advanced pulmonary sarcoidosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2014, 20, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijsers, R.G.; Grutters, J.C. In which patients with Sarcoidosis is FDG PET/CT indicated? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccarone, M.T. FDG-PET scan in Sarcoidosis: Clinical and imaging indications. Curr. Med. Imaging 2018, 15, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostard, R.; Vöö, S.; van Kroonenburgh, M.; Verschakelen, J.; Wijnen, P.; Nelemans, P.; Erckens, R.; Drent, M. Inflammatory activity assessment by F18 FDG-PET/CT in persistent symptomatic sarcoidosis. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 1917–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soussan, M.; Augier, A.; Brillet, P.-Y.; Weinmann, P.; Valeyre, D. Functional imaging in extrapulmonary Sarcoidosis. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2014, 39, e146–e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisolini, R.; Baughman, R.P.; Spagnolo, P.; Culver, D.A. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in sarcoidosis: Beyond the diagnostic yield. Respirology 2019, 24, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorr, A.F.; Torrington, K.G.; Hnatiuk, O.W. Endobronchial biopsy for Sarcoidosis. Chest 2001, 120, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danila, E.; Jurgauskienė, L.; Norkūnienė, J.; Malickaitė, R. BAL fluid cells in newly diagnosed pulmonary sarcoidosis with different clinical activity. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2009, 114, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Winterbauer, R.H.; Lammert, J.; Sellami, M.; Wu, R.; Corley, D.; Springmeyer, S.C. Bronchoalveolar lavage cell populations in the diagnosis of Sarcoidosis. Chest 1993, 104, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Welker, L.; Jörres, R.; Costabel, U.; Magnussen, H. Predictive value of BAL cell differentials in the diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 24, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heron, M.; Slieker, W.A.; Zanen, P.; Van Lochem, E.G.; Hooijkaas, H.; Bosch, J.M.V.D.; Van Velzen-Blad, H. Evaluation of CD103 as a cellular marker for the diagnosis of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drent, M.; Jacobs, J.A.; De Vries, J.; Lamers, R.J.S.; Liem, I.H.; Wouters, E.F.M. Does the cellular bronchoalveolar lavage fluid profile reflect the severity of sarcoidosis? Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 13, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chee, A.; Khalil, M.; Stather, D.R.; MacEachern, P.; Field, S.; Tremblay, A. Cytologic assessment of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspirates in Sarcoidosis. J. Bronc.-Interv. Pulmonol. 2012, 19, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, A.; Takiguchi, Y.; Kurosu, K.; Takigawa, N.; Saegusa, F.; Hiroshima, K.; Nakajima, T.; Tanabe, N.; Nakatani, Y.; Yoshino, I.; et al. Feasibility of cytological diagnosis of sarcoidosis with endobronchial US-guided transbronchial aspiration. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Llung Dis. Off. J. WASOG 2012, 29, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Yasufuku, K.; Chiyo, M.; Sekine, Y.; Chhajed, P.N.; Shibuya, K.; Iizasa, T.; Fujisawa, T. Real-time endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration of mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes. Chest 2004, 126, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bartheld, M.B.; Dekkers, O.; Szlubowski, A.; Eberhardt, R.; Herth, F.; Veen, J.C.C.M.I.; De Jong, Y.P.; van der Heijden, E.; Tournoy, K.G.; Claussen, M.; et al. Endosonography vs. conventional bronchoscopy for the diagnosis of Sarcoidosis. JAMA 2013, 309, 2457–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, P.; Rossi, G.; Trisolini, R.; Sverzellati, N.; Baughman, R.P.; Wells, A.U. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhooria, S.; Agarwal, R.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Bal, A.; Gupta, N.; Gupta, D. Differentiating tuberculosis from sarcoidosis by sonographic characteristics of lymph nodes on endobronchial ultrasonography: A study of 165 patients. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisolini, R.; Tinelli, C.; Cancellieri, A.; Paioli, D.; Alifano, M.; Boaron, M.; Patelli, M. Transbronchial needle aspiration in Sarcoidosis: Yield and predictors of a positive aspirate. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2008, 135, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Gupta, D. Efficacy and safety of conventional TBNA in Sarcoidosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir. Care 2012, 58, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Dadhwal, D.S.; Agarwal, R.; Gupta, N.; Bal, A.; Aggarwal, A.N. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration vs conventional transbronchial needle aspiration in the diagnosis of Sarcoidosis. Chest 2014, 146, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navani, N.; Booth, H.L.; Kocjan, G.; Falzon, M.; Capitanio, A.; Brown, J.M.; Porter, J.C.; Janes, S.M. Combination of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration with standard bronchoscopic techniques for the diagnosis of stage I and stage II pulmonary sarcoidosis. Respirology 2011, 16, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, I.S.; Bal, A.; Dhooria, S.; Gupta, N.; Ram, B.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Behera, D.; Agarwal, R. Predictors of successful yield of transbronchial lung biopsy in patients with Sarcoidosis. J. Bronc.-Interv. Pulmonol. 2018, 25, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plit, M.; Pearson, R.; Havryk, A.; Da Costa, J.; Chang, C.; Glanville, A.R. Diagnostic utility of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration compared with transbronchial and endobronchial biopsy for suspected sarcoidosis. Intern. Med. J. 2012, 42, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, M.; Bastos, H.N.; Mota, P.C.; Melo, N.; Cunha, R.; Pereira, J.M.; Guimarães, S.; Moura, C.S.; Morais, A. Diagnostic yield and safety of transbronchial cryobiopsy in Sarcoidosis. ERJ Open Res. 2019, 5, 00203-2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhail, J.R.; Shepherd, M.; Mitchell, D.N. Mediastinal lymph node biopsy in Sarcoidosis. Laryngo-Rhino-Otologie 1979, 11, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, J.M.; Brouns, M.C.; O’Connor, E.A.; Edwards, M.J. Mediastinoscopy in patients with presumptive stage I Sarcoidosis. Chest 1998, 113, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oki, M.; Saka, H.; Kitagawa, C.; Kogure, Y.; Murata, N.; Ichihara, S.; Moritani, S. Prospective study of endobronchial ultrasound–guided transbronchial needle aspiration of lymph nodes versus transbronchial lung biopsy of lung tissue for diagnosis of sarcoidosis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 143, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costabel, U.; Bonella, F.; Ohshimo, S.; Guzman, J. Diagnostic modalities in Sarcoidosis: BAL, EBUS, and PET. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 31, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyil, F.T.; Agca, M.; Ozturk, H.; Sonkaya, E.; Erdem, I.; Bulbul, E.U.; Ozbaki, F.; Yildiz, R.; Bekir, S.A.; Sevim, T. Correlation between the diagnostic yield from the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid analysis and clinicoradiological findings in Sarcoidosis. Turk. Thorac. J. 2020, 21, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheffield, E.A. Pathology of Sarcoidosis. Clin. Chest Med. 1997, 18, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraaijvanger, R.; Janssen Bonás, M.; Vorselaars, A.D.M.; Veltkamp, M. Biomarkers in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Sarcoidosis: Current Use and Future Prospects. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.K. A review of angiotensin converting enzyme in health and disease. Sarcoidosis 1991, 8, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Studdy, P.R.; Lapworth, R.; Bird, R. Angiotensin-converting enzyme and its clinical significance—A review. J. Clin. Pathol. 1983, 36, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigat, B.; Hubert, C.; Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Cambien, F.; Corvol, P.; Soubrier, F. An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene accounting for half the variance of serum enzyme levels. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 1343–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.; Kambe, N.; Kishimoto, I.; Ueda-Hayakawa, I.; Okamoto, H. Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor level is more sensitive than angiotensin-converting enzyme or lysozyme for diagnosis of sarcoidosis and may be a marker of multiple organ involvement. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmelpennink, M.; Quanjel, M.; Vorselaars, A.; Wiertz, I.; Veltkamp, M.; Van Moorsel, C.; Grutters, J. Value of serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor as a diagnostic and predictive biomarker in sarcoidosis. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2020, 14, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eurelings, L.E.M.; Miedema, J.R.; Dalm, V.A.S.H.; Van Daele, P.L.A.; Van Hagen, P.M.; Van Laar, J.A.M.; Dik, W.A. Sensitivity and specificity of serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor for diagnosing sarcoidosis in a population of patients suspected of sarcoidosis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, N.; Iannuzzi, M. Sarcoidosis: Pitfalls and challenging mimickers. Front. Med. 2021, 7, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopala, S.; Sankari, S.; Kancherla, R.; Ramanathan, R.P.; Balalakshmoji, D. Miliary Sarcoidosis: Does it exist? A case series and systematic review of literature. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2020, 37, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chung, C.; Huang, T.; Tsai, W.; Peng, C.; Huang, K.; Perng, W.; Chian, C.; Chien, W.; Shen, C. Bidirectional association between tuberculosis and sarcoidosis. Respirology 2019, 24, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller-Quernheim, J.; Gaede, K.I.; Fireman, E.; Zissel, G. Diagnoses of chronic beryllium disease within cohorts of sarcoidosis patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, L.S.; Mroz, M.M.; Balkissoon, R.; Maier, L.A. Beryllium sensitization progresses to chronic Beryllium disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barna, B.P.; Culver, D.A.; Yen-Lieberman, B.; Dweik, R.A.; Thomassen, M.J. Clinical application of Beryllium lymphocyte proliferation testing. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2003, 10, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marchiori, E.; Ferreira, A.; Saez, F.; Gabetto, J.M.; Souza, A.S.; Escuissato, D.L.; Gasparetto, E.L. Conglomerated masses of silicosis in sandblasters: High-resolution CT findings. Eur. J. Radiol. 2006, 59, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafnsson, V.; Ingimarsson, O.; Hjalmarsson, I.; Gunnarsdottir, H. Association between exposure to crystalline silica and risk of sarcoidosis. Occup. Environ. Med. 1998, 55, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vihlborg, P.; Bryngelsson, I.-L.; Andersson, L.; Graff, P. Risk of sarcoidosis and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis from occupational silica exposure in Swedish iron foundries: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beijer, E.; Meek, B.; Kromhout, H.; Van Es, H.W.; Seldenrijk, K.; Drent, M.; Rooijackers, J.M.; Veltkamp, M. Sarcoidosis in a patient clinically diagnosed with silicosis; is silica associated sarcoidosis a new phenotype? Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2019, 28, 100906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thillai, M.; Atkins, C.P.; Crawshaw, A.; Hart, S.P.; Ho, L.-P.; Kouranos, V.; Patterson, K.C.; Screaton, N.J.; Whight, J.; Wells, A.U. BTS clinical statement on pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Thorax 2020, 76, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastré, J.; Bouvry, D.; Juvin, K.; Benattia, A.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Valeyre, D.; Nunes, H.; Israël-Biet, D. Sarcoidosis-like cancer-associated granulomatosis: Characteristics and a case-control comparison with Sarcoidosis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brincker, H. Sarcoid reactions in malignant tumours. Cancer Treat. Rev. 1986, 13, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthi, M.; Yoshioka, K.; Cho, J.H.; Arias, S.; Danna, E.; Zaw, M.; Holt, G.; Tatsumi, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Mirsaeidi, M. Presence of concurrent sarcoid-like granulomas indicates better survival in cancer patients: A retrospective cohort study. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 00061–02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubart, F.C.; Lhote, R.; Amoura, A.; Valeyre, D.; Haroche, J.; Amoura, Z.; Lebrun-Vignes, B. Drug-induced sarcoidosis: An overview of the WHO pharmacovigilance database. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 288, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.; Sahni, S.; Vulisha, A.K.; Gumpeni, R.; Shah, R.; Talwar, A. Pulmonary manifestations of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Respir. Med. 2017, 128, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Rivas, M.; Moreira, C.; Marcoval, J. Sarcoidosis related to checkpoint and BRAF/MEK inhibitors in melanoma. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keukeleire, S.D.; Schwarze, J.; Awada, G.; Everaert, H.; Van Binst, A.M.; Cras, L.; Neyns, B.; Aspeslagh, S. An atypical Sarcoid-like reaction during anti-protein death 1 treatment in a patient with metastatic melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2020, 30, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousuf, H.; Mekki, R.; Khan, K.; Hussain, A. Pembrolizumab-induced Sarcoid-like reaction in a patient with lung cancer. Cureus 2020, 12, e12395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danlos, F.-X.; Pagès, C.; Baroudjian, B.; Vercellino, L.; Battistella, M.; Mimoun, M.; Jebali, M.; Bagot, M.; Tazi, A.; Lebbé, C. Nivolumab-induced Sarcoid-like granulomatous reaction in a patient with advanced melanoma. Chest 2016, 149, e133–e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.; Nautiyal, A.; Kalkanis, A.; Judson, M.A. Drug-induced Sarcoidosis-like reactions. Chest 2018, 154, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, S.; Perlman, D.; Allen, T.; Ritter, J.; Bhargava, M. Adalimumab induced pulmonary sarcoid reaction. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2013, 10, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gîlcă, G.-E.; Diaconescu, S.; Bălan, G.G.; Timofte, O.; Ştefănescu, G. Sarcoidosis associated with infliximab therapy in ulcerative colitis: A case report. Medicine 2017, 96, e6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciardi, B.F.; Nocon, A.A.; Jerabek, S.A.; Wilner, G.; Kaplowitz, E.; Goldring, S.R.; Purdue, P.E.; Perino, G. Histopathological characterization of corrosion product associated adverse local tissue reaction in hip implants: A study of 285 cases. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2016, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.H.; Siar, C.H.; Ganesapillai, T. Sarcoid-like foreign body reaction in body piercing. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontology 1997, 84, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patuzzo, G.; Barbieri, A.; Tinazzi, E.; Veneri, D.; Argentino, G.; Moretta, F.; Puccetti, A.; Lunardi, C. Autoimmunity and infection in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID). Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Levinson, A.I. Granulomatous-lymphocytic interstitial lung disease (GLILD) in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID). Clin. Immunol. 2010, 134, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korsten, P.; Tampe, B.; Konig, M.F.; Nikiphorou, E. Sarcoidosis and autoimmune diseases: Differences, similarities and overlaps. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2018, 24, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-H.; Chung, P.-I.; Wu, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T.; Chiu, Y.-W.; Chang, Y.-T.; Liu, H.-N. Comorbid autoimmune diseases in patients with sarcoidosis: A nationwide case-control study in Taiwan. J. Dermatol. 2016, 44, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.H.; Cox, C.W.; Montner, S.M.; Adegunsoye, A.; Oldham, J.M.; Husain, A.N.; Vij, R.; Noth, I.; Lynch, D.A.; Strek, M.E. CT features of the usual interstitial Pneumonia pattern: Differentiating connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 210, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sensitivity | Specificity | Diagnostic Yield | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBB | 46.2% | 85.7% | 30–70% | [39] |
| TBLB | 37% | 100% | 50–75% | [52,60] |
| EBUS/TBNA | 83–93% | 100% | 77–84% | [48,61] |
| Mediastinoscopy | 100% | 100% | 82–100% | [58] |
| BAL (CD4/CD8 ≥ 3.5) | 53–59% | 93–96% | 56% | [41,62] |
| Sarcoidosis | Tuberculosis | CBD and Silicosis | Sarcoid-like Reactions (SLRs) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical presentation | Often asymptomatic May be an occasional diagnosis Dry cough, dyspnea Weight loss Fever | Weight loss Cough Purulent sputum Hemoptysis Fever | Dry cough and dyspnea | Often Asymptomatic |
| Exposure history | Undefined | Recent travel to endemic countries, contact with TB patient | History of work/environment exposure to beryllium or silica | Drugs, malignancy or medical device implantation |
| Radiological findings or localizations | Bilateral and symmetrical hilar lymphadenopathy Perilymphatic and peribronchovascular nodules Cavitation (rare) | Hilar lymphadenopathy (often asymmetrical) Cavitation (frequent) Randomly distributed nodules | Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy (CBD); lymph nodes may have an egg-shell appearance (silicosis) | It depends on the underlying cause (i.e., lymph nodes near solid tumors) |
| Laboratory | Hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria Elevated serum levels of ACE Elevated levels of sIL-2R Peripheral lymphopenia Mantoux test: anergic | Mantoux test: positive IGRA: positive ACE levels may be elevated | Mantoux test: negative ACE levels may be elevated | It depends on the underlying cause ACE may occasionally be elevated Mantoux test: negative |
| Histopathology | Nonnecrotizing granulomas | Necrotizing granulomas | Nonnecrotizing granulomas Sclerotic nodules Silica particles | Indistinguishable from sarcoid granulomas |
| Bronchoscopy and BALF | Lymphocytosis CD4+/CD8+ ratio generally > 3.5 | Culture positive for mycobacterium tuberculosis | Lymphocytosis Positive BeLPT (CBD) | Variable based on the underlying cause |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernardinello, N.; Petrarulo, S.; Balestro, E.; Cocconcelli, E.; Veltkamp, M.; Spagnolo, P. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091558
Bernardinello N, Petrarulo S, Balestro E, Cocconcelli E, Veltkamp M, Spagnolo P. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(9):1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091558
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernardinello, Nicol, Simone Petrarulo, Elisabetta Balestro, Elisabetta Cocconcelli, Marcel Veltkamp, and Paolo Spagnolo. 2021. "Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis" Diagnostics 11, no. 9: 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091558
APA StyleBernardinello, N., Petrarulo, S., Balestro, E., Cocconcelli, E., Veltkamp, M., & Spagnolo, P. (2021). Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis. Diagnostics, 11(9), 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091558






