Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 Spike Antibody Response in COVID-19 Patients Using Three Fully Automated Immunoassays and a Surrogate Virus Neutralization Test
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Serum Samples
2.2. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Assays
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
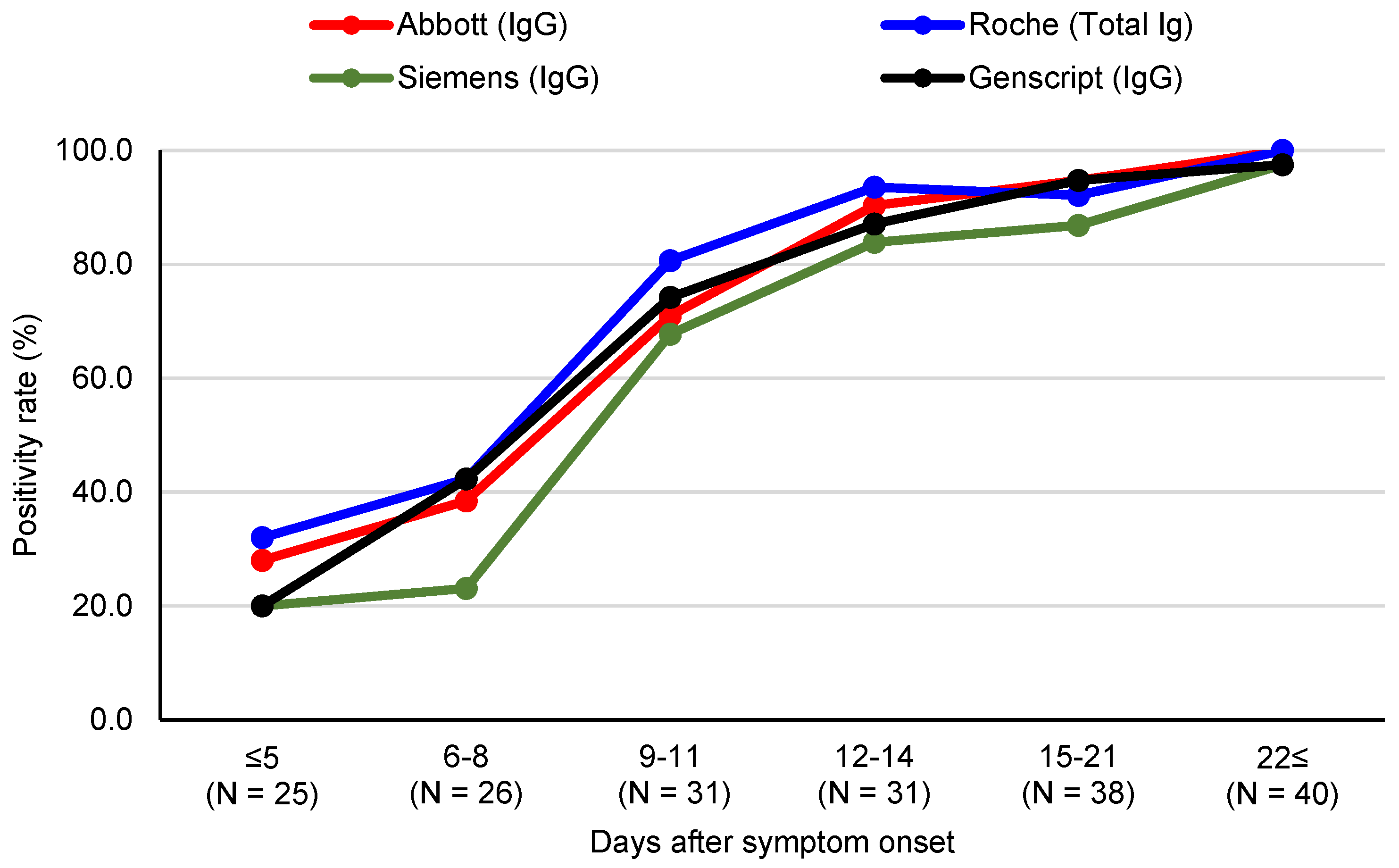
3.1. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Assay Positivity Rates
3.2. Agreement between SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Assay Results
3.3. Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Levels Related to Days after Symptom Onset and Disease Severity
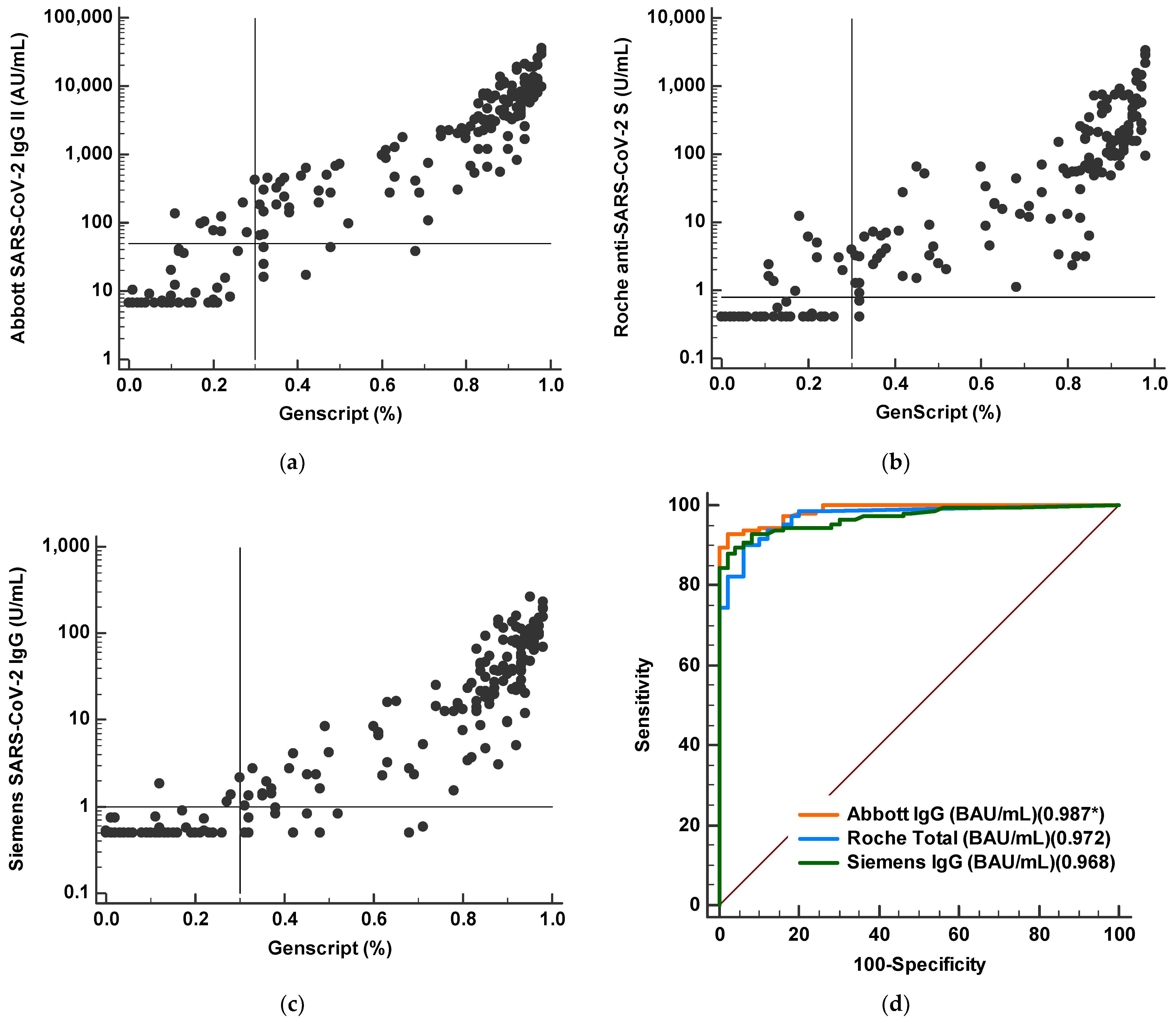
3.4. Correlations between Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 S Protein Antibody Levels from Three Chemiluminescent Immunoassays
3.5. Correlation between Binding Antibody Values and Neutralizing Antibody Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, C.H.; Cai, J.P.; Dissanayake, T.K.; Chen, L.L.; Choi, C.Y.; Wong, L.H.; Ng, A.C.; Pang, P.K.P.; Ho, D.T.; Poon, R.W.; et al. Improved Detection of Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 by Microsphere-Based Antibody Assay. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Horvath, A.R.; Adeli, K. Editorial and Executive Summary: IFCC Interim Guidelines on Clinical Laboratory testing during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 1965–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, J.J.; Dinnes, J.; Takwoingi, Y.; Davenport, C.; Spijker, R.; Taylor-Phillips, S.; Adriano, A.; Beese, S.; Dretzke, J.; Ferrante di Ruffano, L.; et al. Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 6, Cd013652. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.J.; Sung, H.; Ki, C.-S.; Hur, M. Response of Clinical Laboratories to the Ongoing COVID-19 Pandemic. Ann. Lab. Med. 2021, 41, 519–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Takai, K.; Nagasawa, T.; Kashiwagi, K.; Mori, N.; Matsubayashi, K.; Satake, M.; Tanaka, I.; Kodama, N.; Shimodaira, T.; et al. Combination of a SARS-CoV-2 IgG Assay and RT-PCR for Improved COVID-19 Diagnosis. Ann. Lab. Med. 2021, 41, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabaud, M.A.; Icard, V.; Milon, M.P.; Bal, A.; Lina, B.; Escuret, V. Comparison of eight commercial, high-throughput, automated or ELISA assays detecting SARS-CoV-2 IgG or total antibody. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 132, 104613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilla, M.; Wheeler, B.J.; Keetch, C.; Mitchell, G.; McBreen, J.; Wells, A.; Shurin, M.R.; Peck-Palmer, O.; Wheeler, S.E. Variable Performance in 6 Commercial SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Assays May Affect Convalescent Plasma and Seroprevalence Screening. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 155, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.; Ryu, J.H.; Jang, J.H.; Bae, H.; Yoo, S.H.; Choi, A.R.; Jo, S.J.; Lim, J.; Lee, J.; Ryu, H.; et al. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses and Seroconversion in COVID-19 Patients Using Twelve Commercial Immunoassays. Ann. Lab. Med. 2021, 41, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.S.; Saw, S.; Chew, K.L.; Wang, C.; Pajarillaga, A.; Khoo, C.; Wang, W.; Mohamed Ali, Z.; Yang, Z.; Huak, C.Y.; et al. Comparative Clinical Evaluation of the Roche Elecsys and Abbott SARS-CoV-2 Serology assays for COVID-19. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 145, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Petitjean, S.J.L.; Koehler, M.; Zhang, Q.; Dumitru, A.C.; Chen, W.; Derclaye, S.; Vincent, S.P.; Soumillion, P.; Alsteens, D. Molecular interaction and inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 receptor. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.S.; Case, J.B.; Franks, C.E.; Chen, R.E.; Anderson, N.W.; Henderson, J.P.; Diamond, M.S.; Gronowski, A.M.; Farnsworth, C.W. Association between SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies and Commercial Serological Assays. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Chia, W.N.; Qin, X.; Liu, P.; Chen, M.I.; Tiu, C.; Hu, Z.; Chen, V.C.; Young, B.E.; Sia, W.R.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test based on antibody-mediated blockage of ACE2-spike protein-protein interaction. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, V.; Profaizer, T.; Lozier, B.K.; Elgort, M.G.; Larragoite, E.T.; Williams, E.S.C.P.; Solis-Leal, A.; Lopez, J.B.; Berges, B.K.; Planelles, V.; et al. Evaluation of a Surrogate ELISA-Based Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) cPass Neutralization Antibody Detection Assay and Correlation with IgG Commercial Serology Assays. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2021. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irsara, C.; Egger, A.E.; Prokop, W.; Nairz, M.; Loacker, L.; Sahanic, S.; Pizzini, A.; Sonnweber, T.; Holzer, B.; Mayer, W.; et al. Clinical validation of the Siemens quantitative SARS-CoV-2 spike IgG assay (sCOVG) reveals improved sensitivity and a good correlation with virus neutralization titers. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2021, 59, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huh, H.J.; Hong, K.H.; Kim, T.S.; Song, S.H.; Roh, K.H.; Lee, H.; Kwon, G.C. Surveillance of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Testing in Clinical Laboratories in Korea. Ann. Lab. Med. 2021, 41, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, V.; Fabros, A.; Kulasingam, V. Quantitative measurement of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies: Analytical and clinical evaluation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e03149-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irsara, C.; Egger, A.E.; Prokop, W.; Nairz, M.; Loacker, L.; Sahanic, S.; Pizzini, A.; Sonnweber, T.; Mayer, W.; Schennach, H.; et al. Evaluation of four commercial, fully automated SARS-CoV-2 antibody tests suggests a revision of the Siemens SARS-CoV-2 IgG assay. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2021, 59, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittadi, R.; Afshar, H.; Carraro, P. Two SARS-CoV-2 IgG immunoassays comparison and time-course profile of antibodies response. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 99, 115297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, J.; Pelleau, S.; Cockram, C.; Merkling, S.H.; Nekkab, N.; Demeret, C.; Meola, A.; Kerneis, S.; Terrier, B.; Fafi-Kremer, S.; et al. Multiplex assays for the identification of serological signatures of SARS-CoV-2 infection: An antibody-based diagnostic and machine learning study. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e60–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacker, D.H.; Bashleben, C.; Long, T.C.; Theel, E.S.; Knight, V.; Kadkhoda, K.; Rhoads, D.D.; Linden, M.A.; Fink, S.L. Interlaboratory Agreement of Anti–Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Serologic Assays in the Expedited College of American Pathologists Proficiency Testing Program. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2021, 145, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebinger, J.E.; Fert-Bober, J.; Printsev, I.; Wu, M.; Sun, N.; Prostko, J.C.; Frias, E.C.; Stewart, J.L.; Van Eyk, J.E.; Braun, J.G.; et al. Antibody responses to the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in individuals previously infected with SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvagno, G.L.; Henry, B.M.; di Piazza, G.; Pighi, L.; De Nitto, S.; Bragantini, D.; Gianfilippi, G.L.; Lippi, G. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Receptor-Binding Domain Total Antibodies Response in Seropositive and Seronegative Healthcare Workers Undergoing COVID-19 mRNA BNT162b2 Vaccination. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.X.; Liu, B.Z.; Deng, H.J.; Wu, G.C.; Deng, K.; Chen, Y.K.; Liao, P.; Qiu, J.F.; Lin, Y.; Cai, X.F.; et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Liao, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, T.; Li, J.; et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients of novel coronavirus disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okba, N.M.A.; Müller, M.A.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Corman, V.M.; Lamers, M.M.; Sikkema, R.S.; de Bruin, E.; Chandler, F.D.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2-Specific Antibody Responses in Coronavirus Disease Patients. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, P.A.; Page, M.; Bernasconi, V.; Mattiuzzo, G.; Dull, P.; Makar, K.; Plotkin, S.; Knezevic, I. WHO International Standard for anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulin. Lancet 2021, 397, 1347–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Okba, N.M.A.; Igloi, Z.; Bogers, S.; Embregts, C.W.E.; Laksono, B.M.; Leijten, L.; Rokx, C.; Rijnders, B.; Rahamat-Langendoen, J.; et al. An evaluation of COVID-19 serological assays informs future diagnostics and exposure assessment. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bošnjak, B.; Stein, S.C.; Willenzon, S.; Cordes, A.K.; Puppe, W.; Bernhardt, G.; Ravens, I.; Ritter, C.; Schultze-Florey, C.R.; Gödecke, N.; et al. Low serum neutralizing anti-SARS-CoV-2 S antibody levels in mildly affected COVID-19 convalescent patients revealed by two different detection methods. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 18, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| SARS-CoV-2 IgG II Quant | Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S | SARS-CoV-2 IgG (sCOVG) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Abbott Diagnostics | Roche Diagnostics | Siemens |
| Target antigen | S RBD | S RBD | S1 RBD |
| Isotype | IgG | Total Ab | IgG |
| Principle | chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (CMIA) | electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA) | Chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) |
| Used analyzer | Architect i2000 | Cobas e801 | Atellica IM |
| Calibration | 4 parameter logistic curve fit data reduction | 2-point calibration | 2-point calibration |
| Specimen | Serum, Dipotassium EDTA Tripotassium EDTA Lithium heparin, Sodium heparin ACD, Sodium citrate | Serum, Li-heparin, EDTA and sodium citrate plasma. | Serum and plasma (lithium heparin) |
| Required sample volume | 75 μL | 12 μL | 40 µL |
| Interpretation of results | Positive: ≥50.0 AU/mL | Positive: ≥0.80 U/mL | Reactive: ≥1.00 index (U/mL) |
| Analytical measuring interval | 21.0–40,000 AU/mL | 0.40–250 U/mL | 0.50–150.00 index |
| reportable range | 6.8–80,000 AU/mL | Not suggested | Not suggested |
| Limit of blank | 5.7 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| Limit of detection | 6.8 | 0.35 | 0.5 |
| Limit of quantitation | 21 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| automated dilution protocol | 1:2 | 1:10 | 1:5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Ko, G.Y.; Ryu, J.H.; Jang, J.H.; Bae, H.; Yoo, S.-H.; Choi, A.-R.; Jung, J.; Lee, J.; et al. Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 Spike Antibody Response in COVID-19 Patients Using Three Fully Automated Immunoassays and a Surrogate Virus Neutralization Test. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081496
Kim Y, Lee JH, Ko GY, Ryu JH, Jang JH, Bae H, Yoo S-H, Choi A-R, Jung J, Lee J, et al. Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 Spike Antibody Response in COVID-19 Patients Using Three Fully Automated Immunoassays and a Surrogate Virus Neutralization Test. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(8):1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081496
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yoonjoo, Ji Hyun Lee, Geon Young Ko, Ji Hyeong Ryu, Joo Hee Jang, Hyunjoo Bae, Seung-Hyo Yoo, Ae-Ran Choi, Jin Jung, Jongmin Lee, and et al. 2021. "Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 Spike Antibody Response in COVID-19 Patients Using Three Fully Automated Immunoassays and a Surrogate Virus Neutralization Test" Diagnostics 11, no. 8: 1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081496
APA StyleKim, Y., Lee, J. H., Ko, G. Y., Ryu, J. H., Jang, J. H., Bae, H., Yoo, S.-H., Choi, A.-R., Jung, J., Lee, J., & Oh, E.-J. (2021). Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 Spike Antibody Response in COVID-19 Patients Using Three Fully Automated Immunoassays and a Surrogate Virus Neutralization Test. Diagnostics, 11(8), 1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081496







