Optimal Insertion Depth for Nasal Mid-Turbinate and Nasopharyngeal Swabs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasell, J.; Mathieu, E.; Beltekian, D.; Macdonald, B.; Giattino, C.; Ortiz-Ospina, E.; Roser, M.; Ritchie, H. A cross-country database of COVID-19 testing. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 345. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus-testing#how-many-tests-are-performed-each-day (accessed on 23 March 2021). [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.A.; Herigon, J.C.; Benedetti, A.; Pollock, N.R.; Denkinger, C.M. Performance of Saliva, Oropharyngeal Swabs, and Nasal Swabs for SARS-CoV-2 Molecular Detection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e02881-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, N.N.Y.; So, H.C.; Ng, K.Y.; Cowling, B.J.; Leung, G.M.; Ming, D.K. Diagnostic performance of different sampling approaches for SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR testing: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Diseases 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, K.; Jensen, J.S.; Todsen, T.; Tolsaard, M.G.; Kirkby, N.; Lippert, F.; Vangsted, A.; Martel, C.J.; Klokker, M.; von Buchwald, C. Accuracy and cost description of rapid antigen test compared with reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for SARS-CoV-2 detection. Dan. Med. J. 2021, 68, A03210217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hiebert, N.M.; Chen, B.A.; Sowerby, L.J. Variability in instructions for performance of nasopharyngeal swabs across Canada in the era of COVID-19—What type of swab is actually being performed? J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 50, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, T.S.; Wu, A.W.; Ting, J.Y. SARS-CoV-2 Nasopharyngeal Swab Testing—False-Negative Results from a Pervasive Anatomical Misconception. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 146, 993–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Website with Testing Guide. Available online: https://www.albertahealthservices.ca/assets/wf/plab/wf-provlab-collection-of-nasopharyngeal-and-throat-swab.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Website with Testing Guide. Available online: https://www.amboss.com/us/knowledge/COVID-19_(coronavirus_disease_2019) (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Website with Testing Guide. Available online: https://www.ottawapublichealth.ca/en/professionals-and-partners/how-to-collect-a-nasopharyngeal--np--swab.aspx (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Interim Guidelines for Collecting and Handling of Clinical Specimens for COVID-19 Testing. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated 26 February 2021. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/guidelines-clinical-specimens.html (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Lindner, A.K.; Nikolai, O.; Kausch, F.; Wintel, M.; Hommes, F.; Gertler, M.; Krüger, L.J.; Gaeddert, M.; Tobian, F.; Lainati, F.; et al. Head-to-head comparison of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detecting rapid test with self-collected nasal swab versus professional-collected nasopharyngeal swab. Eur. Respir. J. 2021. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, C.P.; Montori, V.M.; Sampathkumar, P. COVID-19 Testing: The Threat of False-Negative Results. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020, 95, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arevalo-Rodriguez, I.; Buitrago-Garcia, D.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Zambrano-Achig, P.; Del Campo, R.; Ciapponi, A.; Sued, O.; Martinez-García, L.; Rutjes, A.W.; Low, N.; et al. False-negative results of initial RT-PCR assays for COVID-19: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- İşlek, A.; Balcı, M.K. Analysis of Factors Causing False-Negative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Results in Oropharyngeal and Nasopharyngeal Swabs of Patients With COVID-19. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Lim, H.; Lee, J.H.; Son, K.K.; Han, Y.J.; Ko, S. A method for optimal depth of the nasopharyngeal temperature probe: The philtrum to tragus distance. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2014, 66, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marty, F.M.; Chen, K.; Verrill, K.A. How to Obtain a Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimen. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piras, A.; Rizzo, D.; Longoni, E.; Turra, N.; Urru, S.; Saba, P.P.; Musumano, L.; Bussu, F. Nasopharyngeal swab collection in the suspicion of Covid-19. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2020, 41, 102551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koskinen, A.; Tolvi, M.; Jauhiainen, M.; Kekäläinen, E.; Laulajainen-Hongisto, A.; Lamminmäki, S. Complications of COVID-19 Nasopharyngeal Swab Test. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 147, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smieja, M.; Castriciano, S.; Carruthers, S.; So, G.; Chong, S.; Luinstra, K.; Mahony, J.B.; Petrich, A.; Chernesky, M.; Savarese, M.; et al. Development and evaluation of a flocked nasal midturbinate swab for self-collection in respiratory virus infection diagnostic testing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 3340–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramos, K.J.; Kapnadak, S.G.; Collins, B.F.; Pottinger, P.S.; Wall, R.; Mays, J.A.; Perchetti, G.A.; Jerome, K.R.; Khot, S.; Limaye, A.P.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 by bronchoscopy after negative nasopharyngeal testing: Stay vigilant for COVID-19. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 30, 101120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazerian, P.; Sacco, R.M.; Solbiati, M.; Targetti, E.; Marta, C.; Blasi, F.; Casazza, G.; Colao, M.G.; Tomassetti, S.; Grifoni, S.; et al. Laryngotracheal aspiration test reduce the false negative rate in patients with suspected SARS-COV-2 pneumonia despite a negative nasopharyngeal swab. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
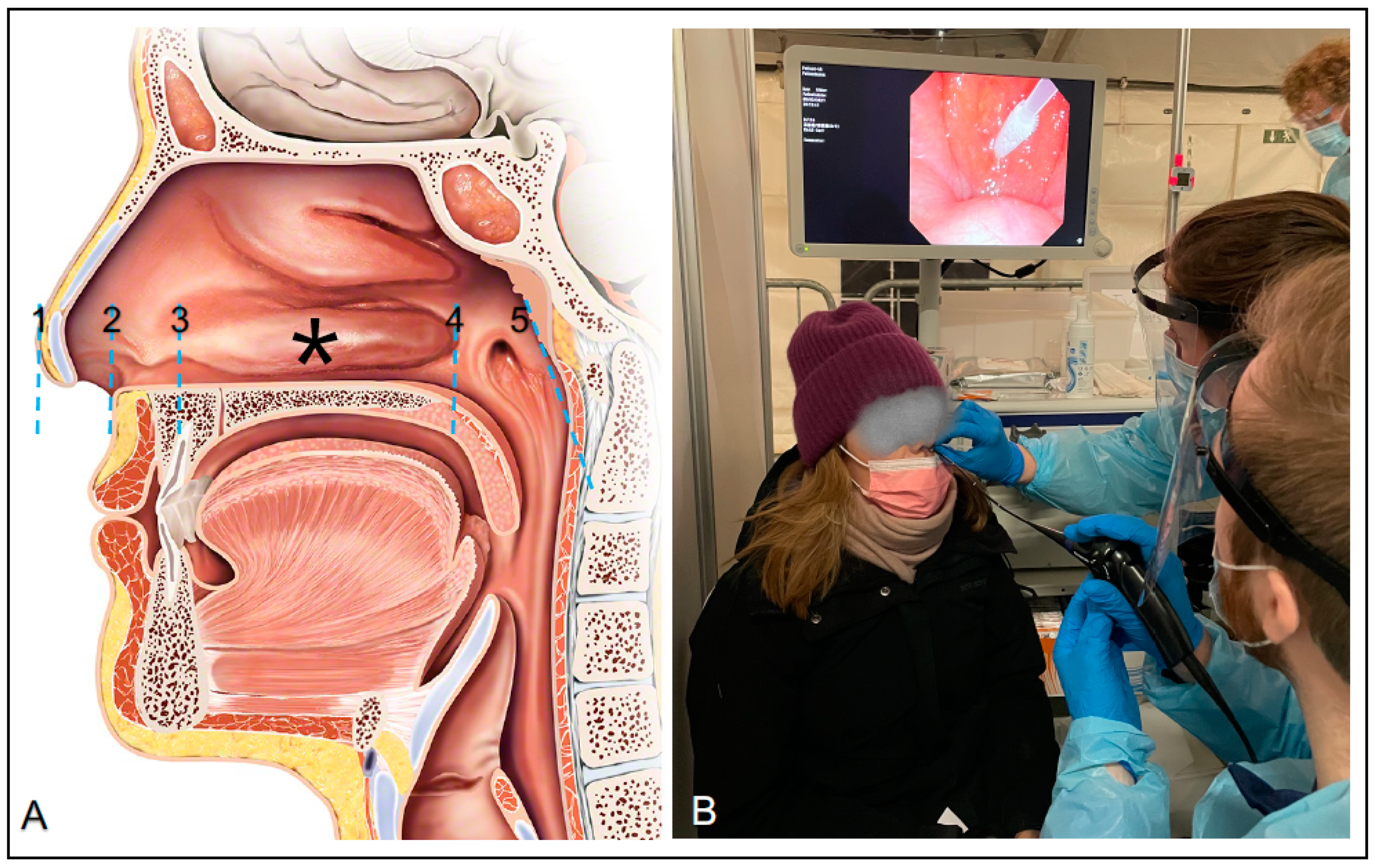
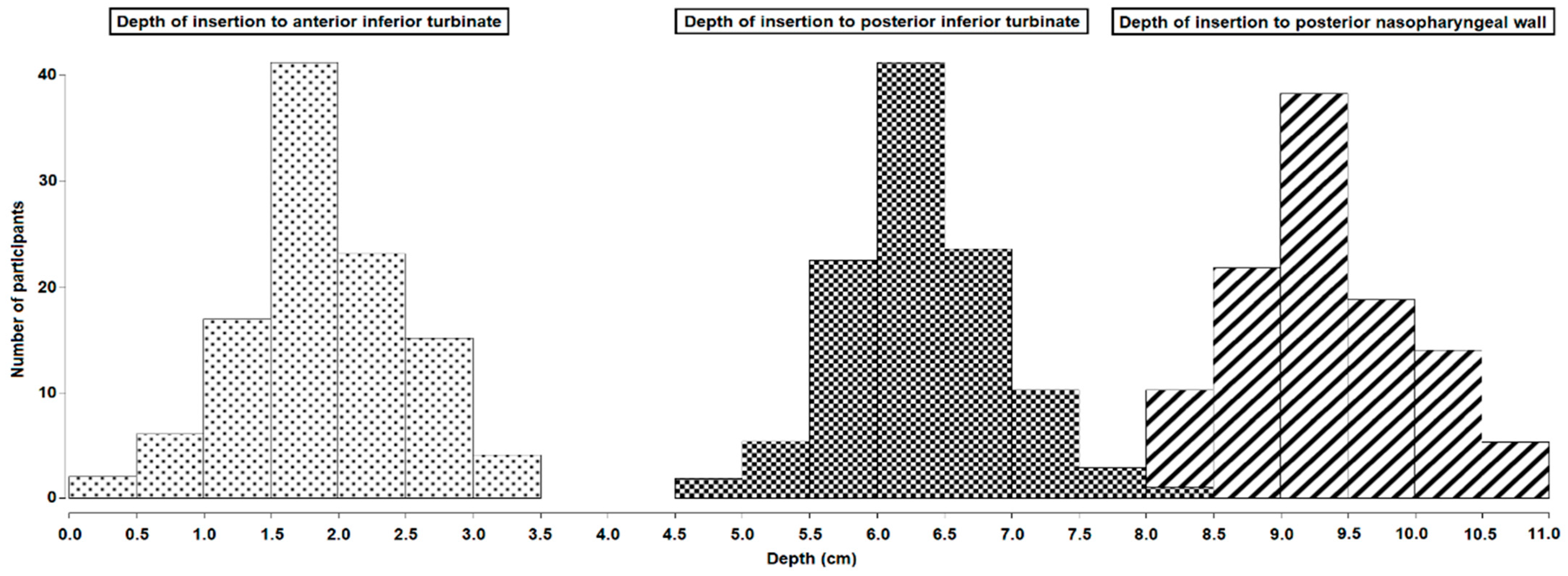
| Mean Insertion Depth (SD) to the Posterior Nasopharyngeal Wall | Mean Insertion Depth (SD) to the Anterior Part of the Inferior Turbinate | Mean Insertion Depth (SD) to the Posterior Part of the Inferior Turbinate | Mean Insertion Depth (SD) to the Nasal Mid-Turbinate | Mean Length (SD) from the Nose Tip to Vestibulum Nasi | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 9.40 (0.64) | 1.95 (0.61) | 6.39 (0.62) | 4.17 (0.48) | 1.42 (0.36) |
| Women | 9.04 (0.55) | 1.79 (0.47) | 6.13 (0.50) | 3.96 (0.39) | 1.27 (0.29) |
| Men | 9.75 (0.53) | 2.09 (0.68) | 6.63 (0.61) | 4.36 (0.47) | 1.56 (0.36) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Callesen, R.E.; Kiel, C.M.; Hovgaard, L.H.; Jakobsen, K.K.; Papesch, M.; von Buchwald, C.; Todsen, T. Optimal Insertion Depth for Nasal Mid-Turbinate and Nasopharyngeal Swabs. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11071257
Callesen RE, Kiel CM, Hovgaard LH, Jakobsen KK, Papesch M, von Buchwald C, Todsen T. Optimal Insertion Depth for Nasal Mid-Turbinate and Nasopharyngeal Swabs. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(7):1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11071257
Chicago/Turabian StyleCallesen, Rasmus Eið, Cecilie Mullerup Kiel, Lisette Hvid Hovgaard, Kathrine Kronberg Jakobsen, Michael Papesch, Christian von Buchwald, and Tobias Todsen. 2021. "Optimal Insertion Depth for Nasal Mid-Turbinate and Nasopharyngeal Swabs" Diagnostics 11, no. 7: 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11071257
APA StyleCallesen, R. E., Kiel, C. M., Hovgaard, L. H., Jakobsen, K. K., Papesch, M., von Buchwald, C., & Todsen, T. (2021). Optimal Insertion Depth for Nasal Mid-Turbinate and Nasopharyngeal Swabs. Diagnostics, 11(7), 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11071257