Abstract
The unusual cases of pneumonia outbreak were reported from Wuhan city in late December 2019. Serological testing provides a powerful tool for the identification of prior infection and for epidemiological studies. Pseudotype virus neutralization assays are widely used for many viruses and applications in the fields of serology. The accuracy of pseudotype neutralizing assay allows for its use in low biosafety lab and provides a safe and effective alternative to the use of wild-type viruses. In this study, we evaluated the performance of this assay compared to the standard microneutralization assay as a reference. The lentiviral pseudotype particles were generated harboring the Spike gene of SARS-CoV-2. The generated pseudotype particles assay was used to evaluate the activity of neutralizing antibodies in 300 human serum samples from a COVID-19 sero-epidemiological study. Testing of these samples resulted in 55 positive samples and 245 negative samples by pseudotype viral particles assay while microneutralization assay resulted in 64 positive and 236 negative by MN assay. Compared to the MN, the pseudotyped viral particles assay showed a sensitivity of 85.94% and a specificity of 100%. Based on the data generated from this study, the pseudotype-based neutralization assay showed a reliable performance for the detection of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and can be used safely and efficiently as a diagnostic tool in a biosafety level 2 laboratory.
1. Introduction
The first case of unusual pneumonia was reported from Wuhan, China in late December 2019 and designated as COVID-19. The causative agent was identified similar to SARS-CoV reported in 2003 falling under the betacoronavirus group [1,2,3]. The spread of the virus caused a pandemic as declared by the WHO resulting in border closer between countries and lockdown in many parts of the world [4]. The humoral and cellular response is induced by S protein and thereby the Spike protein is being used as a significant target for vaccine and antiviral therapeutics [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. The immunogenic responses to the viral diseases against S glycoprotein can be distinguished by using multiple tools including virus microneutralization (MN) assays or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and ELISA variants, such as lateral flow assay (LFA) and chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) [13,14,15]. The high throughput detection of antibodies can be applied by using the ELISA with high safety and sensitivity. The major drawback of these assays is that they are not capable of detecting the neutralization ability of the positive samples [16,17,18,19]. Despite the usefulness of SARS-CoV-2 MN assays and their ability to detect neutralizing antibodies and continue to be the gold standard method, the MN assay needs a biosafety-level-3 facility and well-trained personnel with specialized skills [20].
Currently, there are different types of pseudotyping assays against SARS-CoV-2 that have now been developed using HIV-based lentiviral [21], MLV-based retroviral [22,23], and vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) [24]. The correlation of measurements performed using these assays was significantly similar with microneutralization assays using live SARS-CoV-2 [23,25]. The currently developed system such as lentiviral pseudotype has been efficiently adopted and used against emerging and re-emerging viruses and has been proven as a safe and versatile tool to study the efficacy of antiviral therapies and vaccines [26,27,28]. The use of SARS-Co-2 Spike protein based pseudotypes virus particles provides a useful tool for the detection of antibodies as well as for the evaluation of neutralization capacity of antibodies in serum samples of COVID-19 patients [29,30].
In this study, we have evaluated the performance of pseudotype lentiviral particles using the Spike gene of SARS-CoV-2 and to validate the efficacy of pseudotype particles assay in detecting neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in serum samples collected in a sero-epidemiological study from Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. The results of the assay were compared to microneutralization assay.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture of Cell Lines
Vero E6 (ATCC CRL-1586) and HEK 293 T/17 cells (ATCC–CRL 1573) were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). HEK 293T cells with human ACE2 expression (NR-52511) were kindly provided from the BEI resources, NIAD, and NIH. All the cell lines were grown in standard DMEM with 10% FBS at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
2.2. Virus Isolate
A SARS-CoV-2 clinical human isolate (GenBank accession number: MT630432) was used in all experiments at the Special Infectious Agents Unit (SIAU), King Fahd Medical Research Center, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
2.3. Serum Samples
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee (REC), Unit of Biomedical Ethics, Faculty of Medicine, King Abdulaziz University (KAU) (Reference No 35–21). Written consent forms were obtained from participants. Serum samples used in this study were received in SIAU as a part of a seroprevalence study of SARS-CoV-2 (n = 300). Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 were originally tested using micro-neutralization (MN) assay conducted in the BSL-3 facility of SIAU. These sera were further examined with SARS-CoV-2 pseudotypes to evaluate the performance of the assay against the live virus assay in assessing the neutralization titer of the serum samples.
2.4. Microneutralization (MN) Assay
The collected serum samples were verified for neutralizing antibodies (nAbs) using published protocol [31]. Briefly, sera were heat inactivated and diluted to an initial dilution of 1:20 followed by a serial dilution of 1:2 in DMEM supplemented with 2% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and antibiotics. The diluted samples were co-incubated for 1 h at 37 °C with SARS-CoV-2 isolate (100 TCID50) in a 1:1 ratio (v/v). The mixture was then added to a monolayer of Vero E6 cells in a 96-well plate and incubated at 37 °C in 5% CO2 for three days and observed daily for any cytopathic effect (CPE). All the experiments were performed quadruplicates and samples with CPE in all wells were considered as positive, and titer was defined as the first dilution showing CPE in all wells.
2.5. Generation of Pseudotyped Lentiviral Particles
The plasmids used were supplied from BEI Resources [32]. The HEK 293T/17 cells (2 × 105 cells/mL) were seeded into six-well plates in DMEM with 10% FBS till they have a 50–70% confluency. At 16–24 h, the cells were transfected with the plasmid DNA for lentiviral production. The transfection was performed using Lipofectamine TM 2000 following the manufacturer’s instructions. The complex mixture was made by adding the lentiviral backbone DNA (1 µg-Luciferase-IRES-ZsGreen) and 0.22 µg of each plasmid DNA (HDM-Hgpm2, pRC-CMV-Rev1b, HDM-tat1b) while 0.34 µg plasmid DNA of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein was used as viral entry protein. Lentiviral virus was used as positive control and cell only wells were used as negative control. The cells were replenished with fresh DMEM containing 10% FBS after 18–24 h post transfection and further incubated for 48 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. After 48 h, the supernatants were collected, filtered, and finally stored at −80 °C for further use.
2.6. SARS-CoV-2 Pseudotypes Titration
In a 96-well white opaque culture plate, 100 ul of supernatant contain SARS-CoV-2 pseudotype virus particles were added, positive control lentiviral virus, and negative control cell only, followed by a 1:2 serial dilutions. HEK293-ACE2 cells from the 75 cm2 tissue culture flask were harvested, and the cells were counted to 2 × 105 cells/mL. Finally, 50 μL of cells on 50 μL of diluted pseudotype virus particles were added, and the plate was centrifuged for 1 min at 500× g and incubated for 48 h at 37 °C, 5% CO2. After incubation, a Bright-Glo assay system is used (E2610, Promega, Madison, WI, USA) for luminescence generation. Then, luminescence is measured in Relative Luminescence Units (RLUs) using a plate reader (Synergy 2, BioTeck). RLUs are then plotted against virus dilution. In calculating the virus titer, the wells that showed >1000-fold signal above a virus-only background were selected, and the titration curve was plotted which showed a linear relationship between virus titer and RLU (Figure 1).
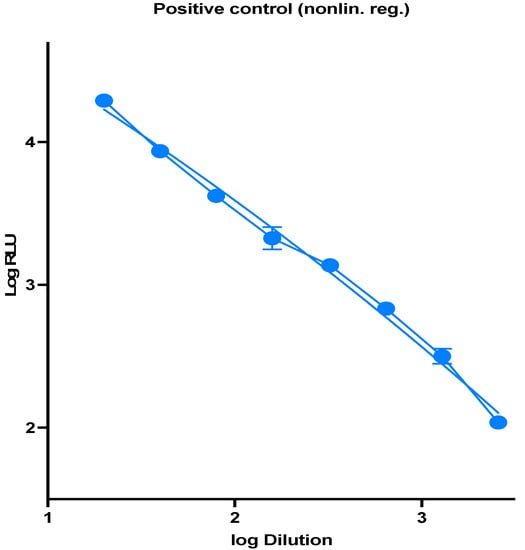
Figure 1.
RLU values observed at each serial dilution, virus dilution vs. RLU readout was plotted to select the needed amount of virus.
2.7. Pseudotype-Based Neutralization Assays
The pseudotype-based neutralization assays were performed following the published protocol [33] with minor modifications. In brief, the serum samples were initially diluted to a 1:20 dilution followed by a 1:1 serial dilution. Diluted serum samples were mixed with SARS-CoV-2 pseudotypes in a 1:1 v/v ratio and then incubated for 1 h at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. After 1 h, the transfected cell suspensions were mixed into each well of cell culture plate and further incubated for 48–72 h at 37 °C and the neutralizing antibodies were characterized based on luciferase activity reading.
2.8. Calculation of SARS-CoV-2 Pseudotype Titers
The neutralization titers of samples were calculated by first normalizing the neutralization titer for each dilution relative to the positive control; then, the IC50 was calculated through a nonlinear regression model of log10 inhibitor dilution vs. normalized response with a variable slope using GraphPad Prism version 9.0 package (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). Titers were then expressed as the range of sample dilution in which the IC50 value lay and the dilution closest to the IC50 value was chosen as the antibody titer.
2.9. Sensitivity and Specificity of the Assay
The sensitivity of the assay compared to the MNT assay as the reference assay was calculated according to the following equation:
while the specificity of the assay compared to the MNT assay as the reference assay was calculated according to the following equation:
Sensitivity = (number of positive samples/(number of positive samples + number of false negative samples)) × 100,
Specificity = (number of negative samples/(number of negative samples + number of false positive samples)) × 100
3. Results
3.1. Sero-Status of Sample
The samples were tested using SARS-CoV-2 MN assay as the reference standard with a MN titer of >1:20 used as the cut-off for positive samples. The MN assay showed that 64 samples were positive while 236 samples were negative.
3.2. Titration of the Generated SARS-2-S-Luciferase Pseudoviruses
To measure the titers of lentiviral pseudotyped particles, we produced viral particles with SARS-CoV-2 spike gene, and quantification was performed using a luminescence signal of the expressed luciferase. Based on the RLU values observed at each serial dilution, virus dilution vs. RLU readout was plotted to select the needed amount of virus for further experiments (Figure 1), and the signal for the needed amount of virus was found to be the quantity producing a luminescence of 104 RLUs per mL in 96-well plate infections.
3.3. Neutralization Assays with Spike-Pseudotyped Lentiviral Particles
The assay was conducted by using the confirmed positive and negative samples with MN assay. A serial dilution of serum samples was made in a 96-well plate and incubated with pseudotyped lentiviral particles for sixty minutes to achieve 2 × 104 RLUs. Finally, the mixture was added to a pre-seeded plate of 293T-ACE2 cells, and the luciferase activity was measured 48 h post-infection. Dilution-dependent reduction in luciferase activity was observed with a tested seropositive sample, in contrast to the seronegative sera that did not show significant changes in the luciferase activity with dilution. Neutralizing Ab titer was computed as IC50 using a 4PL logistic curve fitting in Prism 9 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA).
3.4. Correlation between Live Virus MN and Pseudotype-Based Neutralization Assays
Out of 300 serum samples analyzed, we found that only 55 positive samples and 245 negative samples by pseudotyped viral particles assay, while 64 were positive and 236 were negative by MN assay (Table 1) (Figure 2). Therefore, only nine serum samples were found to be false negative when compared with MN results as shown in (Table 2). Compared to the microneutralization assay, the pseudotyped viral particles assay showed a sensitivity of 85.94% and a specificity of 100%. A simple linear regression was made to predict the log2 PNT based on the log2 MNT data (Figure 3).

Table 1.
Total number of serum samples by MN and PNT.
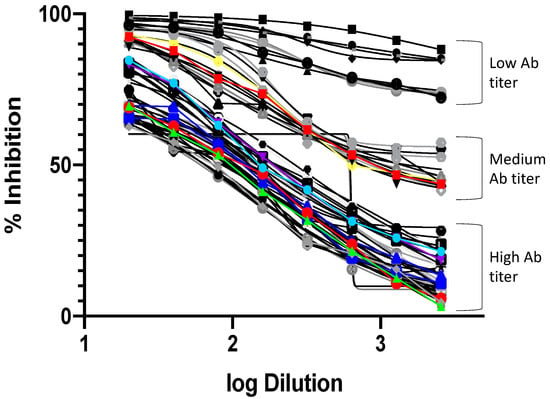
Figure 2.
Dilution curves for the positive samples included in the study. The curves are plots of the log sample dilution vs. the percent normalized inhibition for each dilution compared to the positive control. The curves show samples with high, medium, and low titers.

Table 2.
Sensitivity and specificity of the pseudotyped viral particles assay.
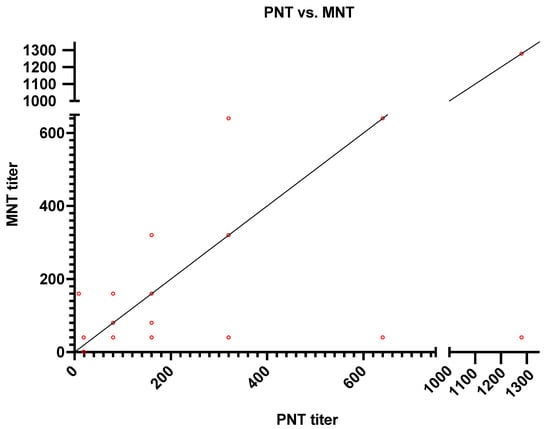
Figure 3.
Correlation of SARS-CoV-2 Ab titers as detected by PNT (x-axis) vs. MNT (y-axis).
Results show the concordance of antibody titers between MNT and PNT in 16 samples as follows: 4 samples had a titer of 1:80, 7 samples with a titer of 1:160, 3 with a titer of 1:320, and 1 each with a titer of 1:640 and 1:1280. PNT was constantly showing at least one dilution higher than MNT except for two samples, where it showed one dilution lower than MNT.
4. Discussion
The pseudotyped viral particles assays offer the advantage of evaluating the titer of the antibodies without the need for the laboratory intensive and the biohazard safety measures needed for the microneutralization assays, especially for highly contagious pathogens like SARS-CoV-2. The assay also offers a more quantitative measure based on the RLU reading rather than relying on the visual evaluation of the observer under the microscope.
The emergence of COVID-19 led to a global pandemic, exposing a serious threat to human health. SARS-CoV-2 infection results in the induction and elicitation of specific antibodies that bind to SARS-CoV-2 in infected patients. Recent publications have shown that effective protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection (or re-infection) is achieved through several factors including cellular immunity and the level of neutralizing antibodies in the sera of cases [33]. Currently, the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection is being performed by many standard assays [16,17,18,19]. However, the demand for serological assay is always valuable and very high. This demand is needed for sero-epidemiological studies and the screening of a large number of samples including symptomatic, non-symptomatic, vaccinated individuals as well as recovered patients. Additionally, serological assays are also a very valuable, low-cost tool as well as being available in laboratories with limited facilities. Detection of antibodies using ELISA provides a qualitative measure of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and does not show the neutralizing ability of the detected antibodies. The standard method for the detection of neutralizing antibodies is the MNT, which requires the use of a live SARS-CoV-2 virus and the availability of a BSL-3 laboratory. These limitations of the ELISA and MNT have encouraged us to evaluate the pseudotyped viral particles assay using the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 for the detection of neutralizing antibodies in serum samples. The developed assay was evaluated using human serum samples and further validated by comparison with the MN assay.
The assay was setup as previously described by Crawford et al. [26], and the neutralization titer was estimated by serially diluting the samples and evaluating the range of dilution where the IC50 falls between. The signal generated by the amount of lentivirus generated was found to be 104 RLUs per mL in 96-well plates, which is in accordance with the data reported by Crawford et al. [26]. The assay showed a robust performance with an inter-run assay variability of <10% and an intra-run assay variability of <3%.
Our data showed an 85.9% sensitivity and 100% specificity of the assay when compared to the standard MN assay. The reduction in assay sensitivity was because of nine samples that showed false negative results by PNT and showed a low titer in MN assay (1:40) [33]. These data are in accordance with the data reported by Hyseni et al. [33], where they compared the performance of PNT compared to MN assay by testing 65 human serum samples, 28 samples were positive by MN, while 24 samples were positive by PNT. On other hand, 37 negative samples by MN and 41 samples were negative by PNT. Comparable to our study, they reported a sensitivity of 85.7% and the specificity of 100% [33].
5. Conclusions
Based on the data generated from this study, the assay can be used with confidence in the sensitivity and specificity for the evaluation of the titer of neutralizing antibodies against the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 in infected and vaccinated cases. This assay has the advantage of being used in a BSL-2 facility and does not require a high-level biocontainment facility because the pseudotype is devoid of virulent viral components.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M.K.T. and E.I.A.; methodology, A.M.K.T., A.M.H., and S.S.S.; formal analysis, S.A.E.-K., K.M.K.T. and S.S.S. investigation, A.M.K.T., A.M.H., and S.A.E.-K. data curation, A.M.K.T. and S.S.S.; writing—original draft preparation, K.M.K.T., S.A.E.-K. and S.S.S.; writing—review and editing, All authors; supervision, A.M.K.T., S.S.S. and E.I.A.; project administration, A.M.K.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper contains studies, results, and recommendations of the research titled “Evaluation of a pseudovirus neutralization assay for SARS-CoV-2 and correlation with live virus-based Micro Neutralization Assay” has been supported by the Ministry of Health, project number 915 and date. 1 May 2020.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee (REC), Unit of Biomedical Ethics, Faculty of Medicine, King Abdulaziz University (KAU) (Reference No 35–21). Written consent forms were obtained from participants.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
All data that support the findings of this study are included in this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by the Ministry of Health to King Abdulaziz University to implement this work through the fast-track program for COVID-19 research, project no. 915. The authors would also like to thank BEI Resources for providing a panel of plasmids used for SARS-CoV-2 pseudotype production.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbalenya, A.E. Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus–The species and its viruses, a statement of the Coronavirus Study Group. BioRxiv 2020, 937862v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Chan, J.F.-W.; Kok, K.-H.; Zhu, Z.; Chu, H.; To, K.K.-W.; Yuan, S.; Yuen, K.-Y. Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Guo, D. Emerging coronaviruses: Genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Peng, Y.; Huang, B.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Niu, P.; Meng, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. Genome composition and divergence of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) originating in China. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Penninger, J.M.; Li, Y.; Zhong, N.; Slutsky, A.S. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS-CoV-2 receptor: Molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic target. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; He, Y.; Liu, S. SARS vaccine development. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; He, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Zheng, B.-J.; Jiang, S. The spike protein of SARS-CoV—A target for vaccine and therapeutic development. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, R.L.; Rehm, K.E. SARS vaccines: Where are we? Expert Rev. Vaccines 2009, 8, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enjuanes, L.; Zuñiga, S.; Castano-Rodriguez, C.; Gutierrez-Alvarez, J.; Canton, J.; Sola, I. Molecular basis of coronavirus virulence and vaccine development. Adv. Virus Res. 2016, 96, 245–286. [Google Scholar]
- Amanat, F.; Stadlbauer, D.; Strohmeier, S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Chromikova, V.; McMahon, M.; Jiang, K.; Arunkumar, G.A.; Jurczyszak, D.; Polanco, J. A serological assay to detect SARS-CoV-2 seroconversion in humans. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruana, G.; Croxatto, A.; Coste, A.T.; Opota, O.; Lamoth, F.; Jaton, K.; Greub, G. Diagnostic strategies for SARS-CoV-2 infection and interpretation of microbiological results. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Kou, G.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Ni, W.; Wang, Q.; Tan, L.; Wu, W.; Tang, S. Evaluation of nucleocapsid and spike protein-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for detecting antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenti, A.; Maggetti, M.; Casa, E.; Martinuzzi, D.; Torelli, A.; Trombetta, C.M.; Marchi, S.; Montomoli, E. Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies using of a CPE-based Colorimetric live virus micro-neutralization assay in human serum samples. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2096–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, R.A.; Mok, C.K.; Tsang, O.T.; Lv, H.; Ko, R.L.; Wu, N.C.; Yuan, M.; Leung, W.S.; Chan, J.M.; Chik, T.S. Serological assays for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), March 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, M.K.; Lippi, G.; Horvath, A.; Sethi, S.; Koch, D.; Ferrari, M.; Wang, C.-B.; Mancini, N.; Steele, S.; Adeli, K. Molecular, serological, and biochemical diagnosis and monitoring of COVID-19: IFCC taskforce evaluation of the latest evidence. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. CCLM 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özçürümez, M.K.; Ambrosch, A.; Frey, O.; Haselmann, V.; Holdenrieder, S.; Kiehntopf, M.; Neumaier, M.; Walter, M.; Wenzel, F.; Wölfel, R. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Testing–Questions to be asked. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zettl, F.; Meister, T.L.; Vollmer, T.; Fischer, B.; Steinmann, J.; Krawczyk, A.; V’kovski, P.; Todt, D.; Steinmann, E.; Pfaender, S. Rapid quantification of SARS-CoV-2-neutralizing antibodies using propagation-defective vesicular stomatitis virus pseudotypes. Vaccines 2020, 8, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Wang, A.; Liu, M.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Xia, S.; Ling, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xun, J.; Lu, L. Neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in a COVID-19 recovered patient cohort and their implications. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, B.; Mou, H.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; He, W.; Ojha, A.; Parcells, M.; Luo, G.; Li, W.; Zhong, G. The SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain elicits a potent neutralizing response without antibody-dependent enhancement. BioRxiv 2020, ppbiorxiv-036418. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, D.; Park, Y.-J.; Beltramello, M.; Walls, A.C.; Tortorici, M.A.; Bianchi, S.; Jaconi, S.; Culap, K.; Zatta, F.; De Marco, A. Structural and functional analysis of a potent sarbecovirus neutralizing antibody. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahboub, S.A.; Algaissi, A.; Alfaleh, M.A.; El Assouli, M.; Hashem, A.M. Evaluation of neutralizing antibodies against highly pathogenic coronaviruses: A detailed protocol for a rapid evaluation of neutralizing antibodies using vesicular stomatitis virus pseudovirus-based assay. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, R.; Pan, Z.; Qian, C.; Yang, Y.; You, R.; Zhao, J.; Liu, P.; Gao, L.; Li, Z. Human monoclonal antibodies block the binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, K.H.; Eguia, R.; Dingens, A.S.; Loes, A.N.; Malone, K.D.; Wolf, C.R.; Chu, H.Y.; Tortorici, M.A.; Veesler, D.; Murphy, M. Protocol and reagents for pseudotyping lentiviral particles with SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein for neutralization assays. Viruses 2020, 12, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, J.K.; Tang, T.; Nathan, L.; Jaimes, J.A.; Hsu, H.-L.; Daniel, S.; Whittaker, G.R. Production of pseudotyped particles to study highly pathogenic coronaviruses in a biosafety level 2 setting. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 145, e59010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhao, C.; Hao, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Nie, L.; Qin, H.; Wang, M. Establishment and validation of a pseudovirus neutralization assay for SARS-CoV-2. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, B.; Zhang, Q.; Ge, X.; Wang, R.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, B.; Song, S.; Tang, X.; Yu, J.; et al. Human neutralizing antibodies elicited by SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nature 2020, 584, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trombetta, C.M.; Remarque, E.J.; Mortier, D.; Montomoli, E. Comparison of hemagglutination inhibition, single radial hemolysis, virus neutralization assays, and ELISA to detect antibody levels against seasonal influenza viruses. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2018, 12, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alandijany, T.A.; El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Tolah, A.M.; Sohrab, S.S.; Faizo, A.A.; Hassan, A.M.; Alsubhi, T.L.; Othman, N.A.; Azhar, E.I. Development and optimization of in-house ELISA for detection of human IgG antibody to SARS-CoV-2 full length spike protein. Pathogens 2020, 9, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.beiresources.org/ (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Hyseni, I.; Molesti, E.; Benincasa, L.; Piu, P.; Casa, E.; Temperton, N.J.; Manenti, A.; Montomoli, E. Characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 Lentiviral Pseudotypes and Correlation between Pseudotype-Based Neutralisation Assays and Live Virus-Based Micro Neutralisation Assays. Viruses 2020, 12, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).