Effect of Multishell Diffusion MRI Acquisition Strategy and Parcellation Scale on Rich-Club Organization of Human Brain Structural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Processing Pipeline
2.2. Imaging Data and Preprocessing
2.3. Structural Connectome Reconstruction
2.3.1. Network Construction
2.3.2. Topological Properties
2.3.3. Rich-Club Coefficient for Unweighted Networks
2.4. Statistical Test
3. Results
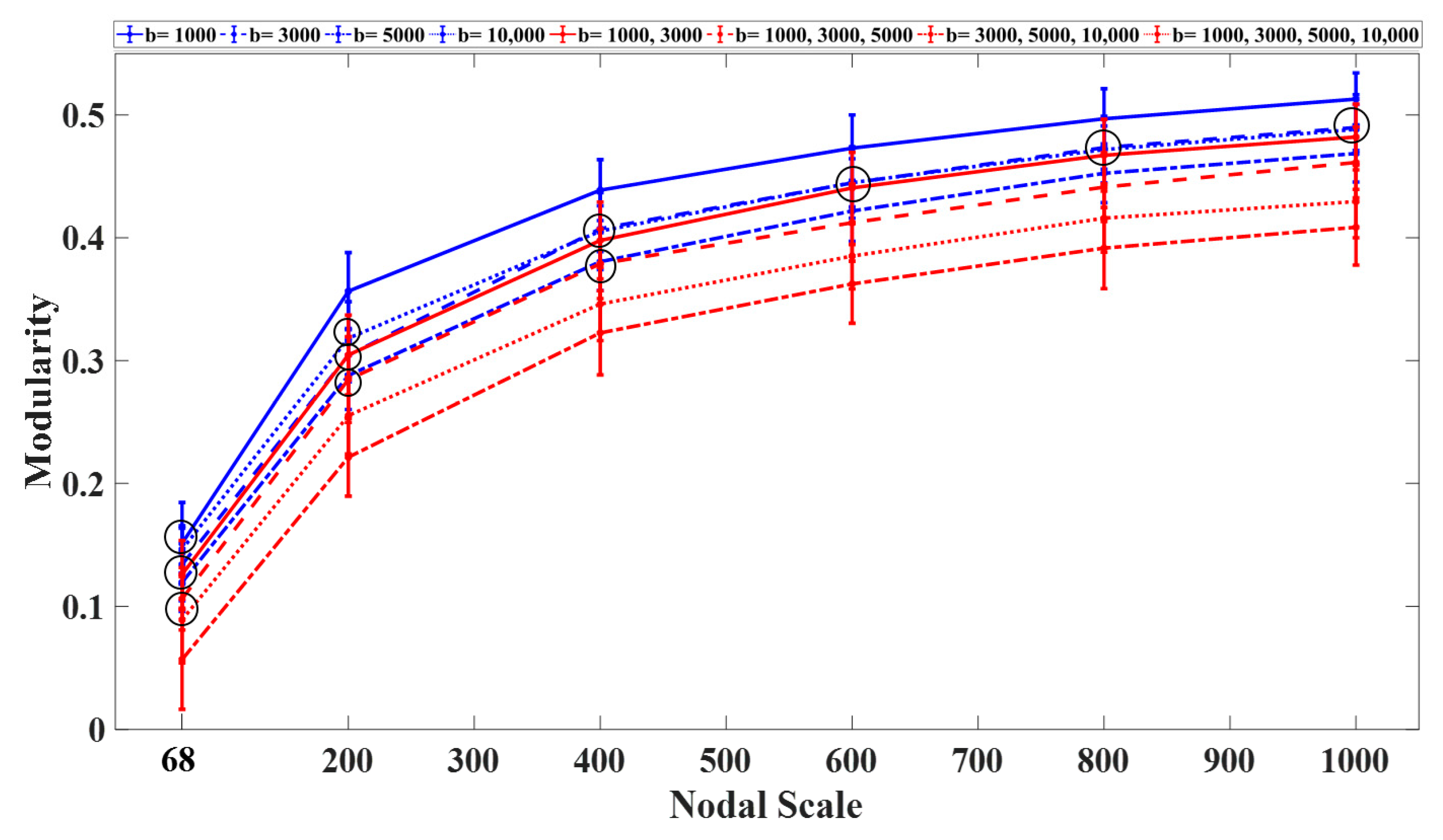
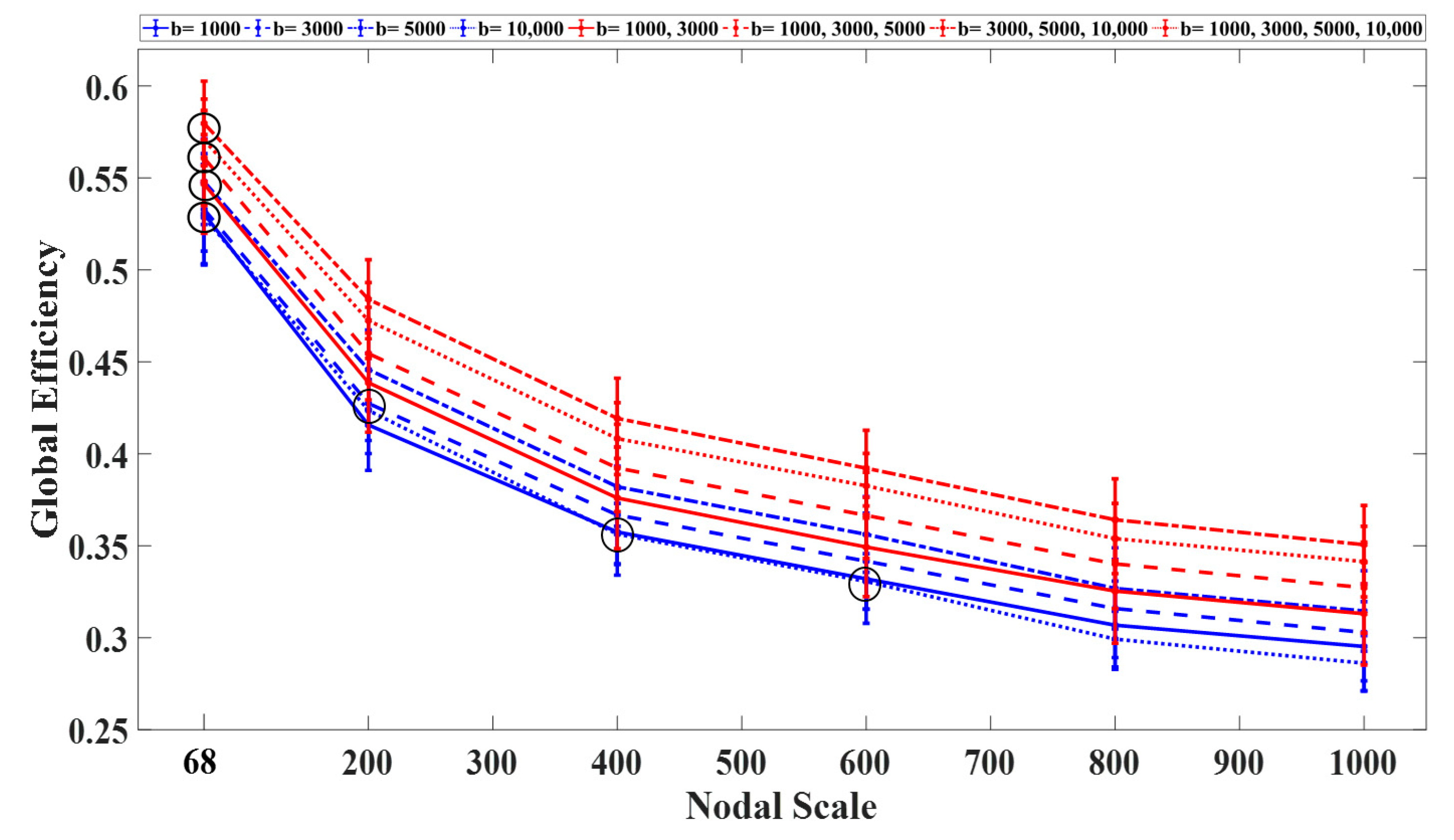
3.1. Graph Measures
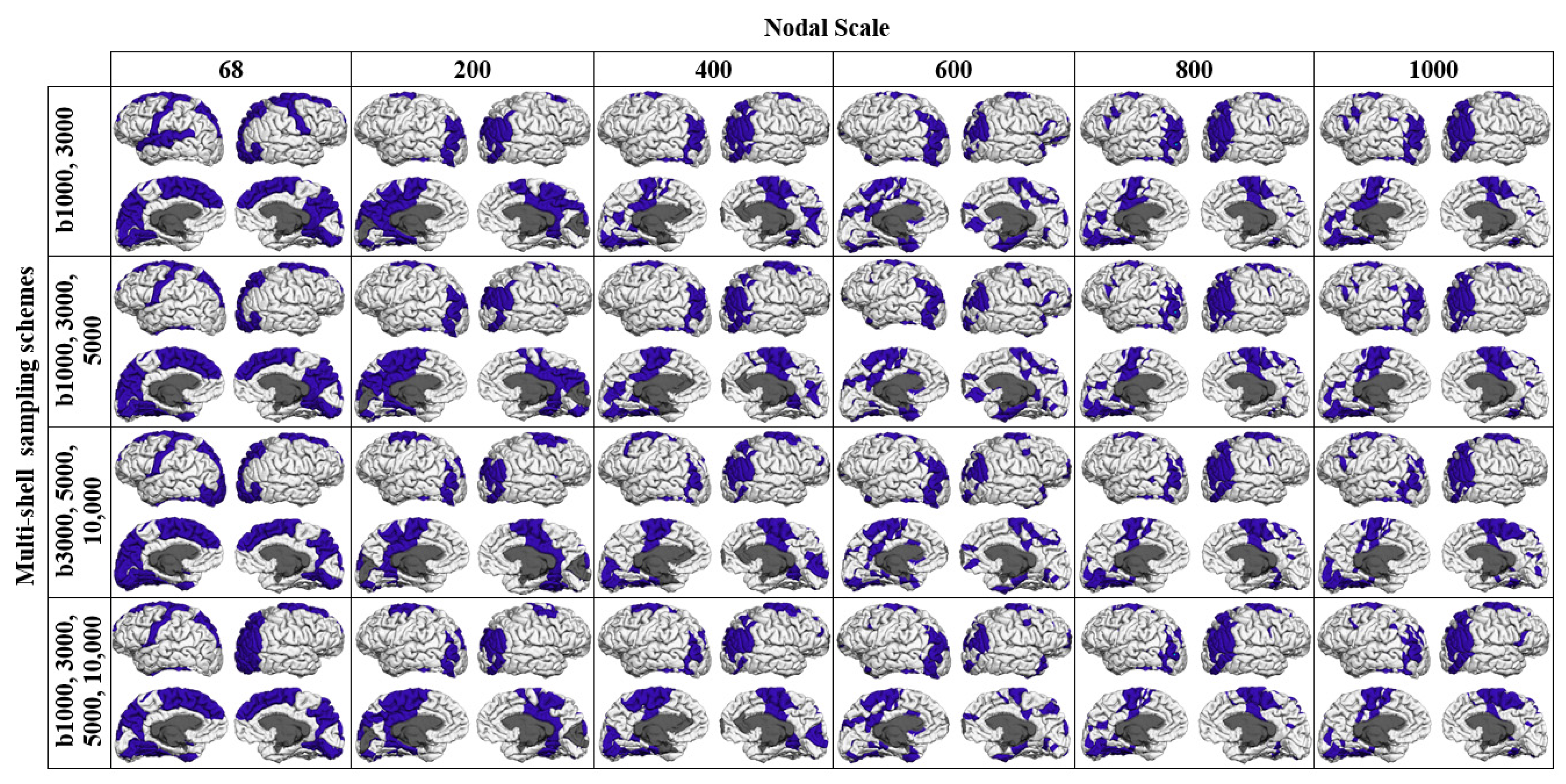
3.2. Rich-Club Organization of Structural Brain Networks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heuvel, M.P.V.D.; Sporns, O. An Anatomical Substrate for Integration among Functional Networks in Human Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 14489–14500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalesky, A.; Fornito, A.; Harding, I.H.; Cocchi, L.; Yücel, M.; Pantelis, C.; Bullmore, E.T. Whole-brain anatomical networks: Does the choice of nodes matter? NeuroImage 2010, 50, 970–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammoun, L.; Gigandet, X.; Meskaldji, D.; Thiran, J.P.; Sporns, O.; Do, K.Q.; Maeder, P.; Meuli, R.; Hagmann, P. Mapping the human connectome at multiple scales with diffusion spectrum MRI. J. Neurosci. Methods 2012, 203, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, O.; Tononi, G.; Kötter, R. The Human Connectome: A Structural Description of the Human Brain. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2005, 1, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reus, M.A.; Heuvel, M.P.V.D. Rich Club Organization and Intermodule Communication in the Cat Connectome. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 12929–12939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, H.; Fias, W.; Caeyenberghs, K.; Marinazzo, D. Brain networks under attack: Robustness properties and the impact of lesions. Brain 2016, 139 Pt 12, 3063–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, C.; Nomura, E.M.; Pérez, F.; D’Esposito, M. Focal Brain Lesions to Critical Locations Cause Widespread Disruption of the Modular Organization of the Brain. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2012, 24, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-J.; Min, B.-K. Rich-club in the brain’s macrostructure: Insights from graph theoretical analysis. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1761–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.; Wang, W.; Yang, L.; Chen, K.; Chen, R.; Han, Y. Rich club disturbances of the human connectome from subjective cognitive decline to Alzheimer’s disease. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3237–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullmore, E.T.; Sporns, O. Complex brain networks: Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzel, R.F.; Bassett, D.S. Multi-scale brain networks. NeuroImage 2017, 160, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosey, T.; Williams, G.; Ansorge, R. Inference of multiple fiber orientations in high angular resolution diffusion imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 54, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, L.R. Characterization of anisotropy in high angular resolution diffusion-weighted MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2002, 47, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.; Witzel, T.; Nummenmaa, A.; Van Dijk, K.R.; Van Horn, J.D.; Drews, M.K.; Somerville, L.H.; Sheridan, M.A.; Santillana, R.M.; Snyder, J.; et al. MGH–USC Human Connectome Project datasets with ultra-high b-value diffusion MRI. NeuroImage 2016, 124 Pt B, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuvel, M.P.V.D.; Kahn, R.S.; Goñi, J.; Sporns, O. High-cost, high-capacity backbone for global brain communication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11372–11377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.L.; Skare, S. A Model-Based Method for Retrospective Correction of Geometric Distortions in Diffusion-Weighted EPI. NeuroImage 2002, 16, 177–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, D.N.; Fischl, B. Accurate and robust brain image alignment using boundary-based registration. NeuroImage 2009, 48, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, F.-C.; Wedeen, V.J.; Tseng, W.-Y.I. Generalized q-Sampling Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, F.-C.; Verstynen, T.D.; Wang, Y.; Fernández-Miranda, J.C.; Tseng, W.-Y.I. Deterministic Diffusion Fiber Tracking Improved by Quantitative Anisotropy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffei, C.; Sarubbo, S.; Jovicich, J. Diffusion-based tractography atlas of the human acoustic radiation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, F.-C.; Zaydan, I.M.; Suski, V.R.; Lacomis, D.; Richardson, R.M.; Maroon, J.C.; Barrios-Martinez, J. Differential tractography as a track-based biomarker for neuronal injury. NeuroImage 2019, 202, 116131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, F.-C.; Panesar, S.; Barrios, J.; Fernandes, D.; Abhinav, K.; Meola, A.; Fernandez-Miranda, J.C. Automatic Removal of False Connections in Diffusion MRI Tractography Using Topology-Informed Pruning (TIP). Neurotherapeutics 2019, 16, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desikan, R.S.; Ségonne, F.; Fischl, B.; Quinn, B.T.; Dickerson, B.C.; Blacker, D.; Buckner, R.L.; Dale, A.M.; Maguire, R.P.; Hyman, B.T.; et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Bannister, P.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Improved Optimization for the Robust and Accurate Linear Registration and Motion Correction of Brain Images. NeuroImage 2002, 17, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuvel, M.P.V.D.; Sporns, O. Rich-Club Organization of the Human Connectome. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 15775–15786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinov, M.; Sporns, O. Complex network measures of brain connectivity: Uses and interpretations. NeuroImage 2010, 52, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. Modularity and community structure in networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8577–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, D.S.; Bullmore, E.T. Human brain networks in health and disease. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2009, 22, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Bao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zheng, X.; Long, S.; Wang, Y. Differences between generalized Q-sampling imaging and diffusion tensor imaging in visualization of crossing neural fibers in the brain. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2019, 41, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Cieslak, M.; Greene, C.; Grafton, S.T.; Carlson, J.M. Sensitivity analysis of human brain structural network construction. Netw. Neurosci. 2017, 1, 446–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Zuo, N.; Shang, L.; Song, M.; Fan, L.; Jiang, T. How Does B-Value Affect HARDI Reconstruction Using Clinical Diffusion MRI Data? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.; Prats-Galino, A.; Gallardo-Pujol, D.; Villoslada, P.; Falcón, C.; Prčkovska, V. Evaluating Structural Connectomics in Relation to Different Q-space Sampling Techniques. MICCAI Int. Conf. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv. 2013, 16 Pt 1, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullmore, E.T.; Sporns, O. The economy of brain network organization. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffa, A.; Heuvel, M.P.V.D. Rich-club neurocircuitry: Function, evolution, and vulnerability. Dialog Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 121–132. [Google Scholar]
- Sarwar, T.; Ramamohanarao, K.; Zalesky, A. Mapping connectomes with diffusion MRI: Deterministic or probabilistic tractography? Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 1368–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalesky, A.; Fornito, A.; Cocchi, L.; Gollo, L.L.; Heuvel, M.P.V.D.; Breakspear, M. Connectome sensitivity or specificity: Which is more important? NeuroImage 2016, 142, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calamante, F. The Seven Deadly Sins of Measuring Brain Structural Connectivity Using Diffusion MRI Streamlines Fibre-Tracking. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.S.; Bowtell, R.W.; McIntyre, D.J.; Worthington, B.S. Correction of spatial distortion in EPI due to inhomo-geneous static magnetic fields using the reversed gradient method. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2004, 19, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheryauka, A.B.; Lee, J.N.; Samsonov, A.A.; Defrise, M.; Gullberg, G.T. MRI diffusion tensor reconstruction with PROPELLER data acquisition. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2004, 22, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

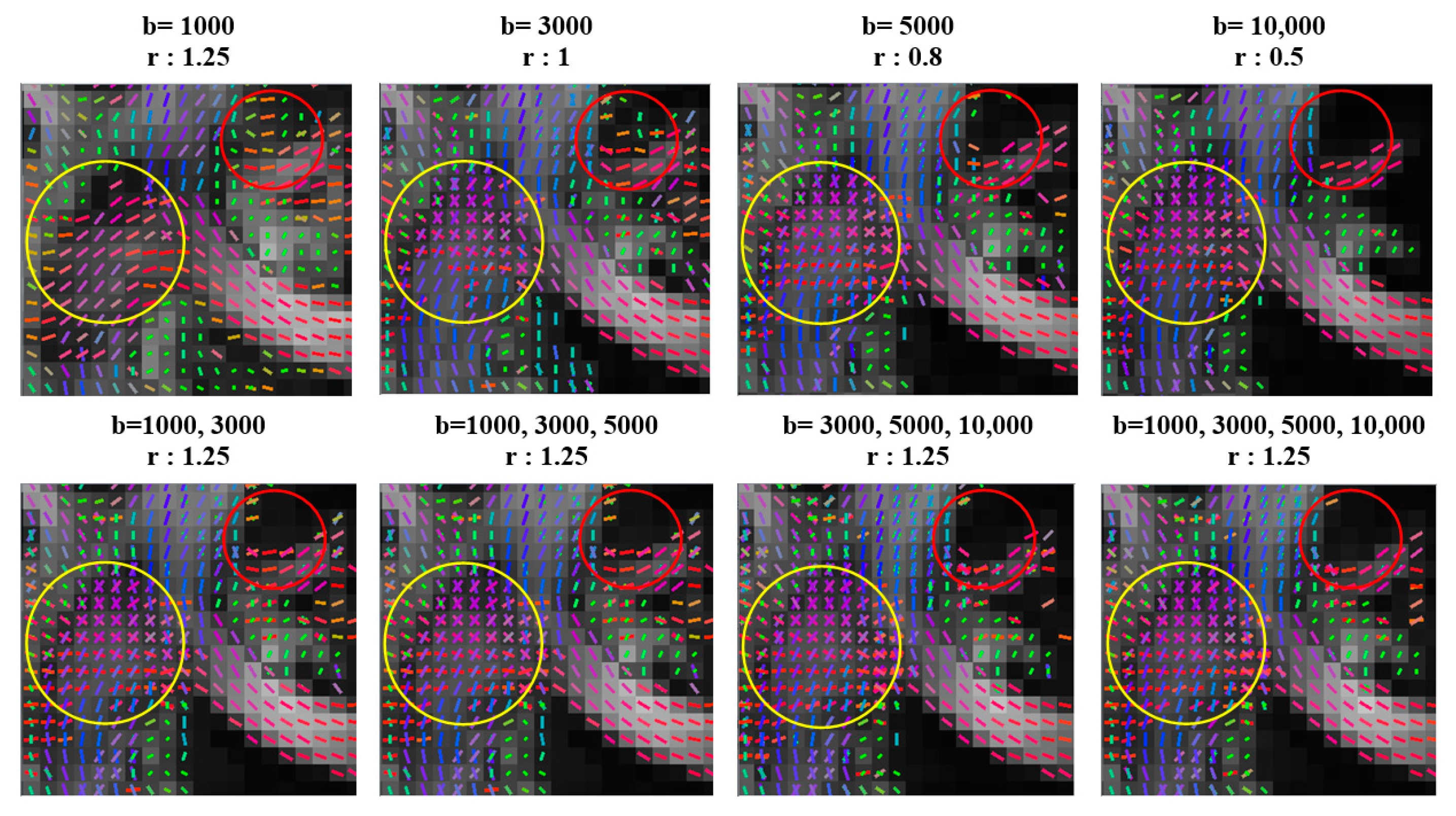




| Single-Shell Sampling Schemes | Multishell Sampling Schemes | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b = 1000 | b = 3000 | b = 5000 | b = 10,000 | b = 1000, 3000 | b = 1000, 3000, 5000 | b = 3000, 5000, 10,000 | b = 1000, 3000, 5000, 10,000 | |
| SL (mm) (mean ± S.D.) | 65.6 ± 2.9 | 66.9 ± 2.6 | 69.2 ± 2.8 | 69.9 ± 1.9 | 66.9 ± 2.9 | 68.6 ± 2.7 | 70.1 ± 2.8 | 69.5 ± 2.6 |
| nQA (a.u.) (mean ± S.D.) | 0.142 ± 0.028 | 0.123 ± 0.017 | 0.112 ± 0.011 | 0.104 ± 0.022 | 0.125 ± 0.019 | 0.116 ± 0.013 | 0.106 ± 0.009 | 0.109 ± 0.009 |
| Nodal Scale | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 68 | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 | |||
| Single-shell sampling schemes | b = 1000 | k level | 12 | 12 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 15 |
| RC | 15.2 | 17.2 | 25.6 | 29.9 | 35.9 | 40.4 | ||
| FC | 48.1 | 39.2 | 33.6 | 29.2 | 26.6 | 22.8 | ||
| LC | 36.7 | 43.6 | 40.8 | 40.9 | 37.4 | 36.8 | ||
| b = 3000 | k level | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 17 | |
| RC | 15.9 | 20.2 | 25.2 | 28.2 | 34.3 | 36.8 | ||
| FC | 45.3 | 33.6 | 32.2 | 31.9 | 27.1 | 26.5 | ||
| LC | 38.9 | 46.2 | 42.5 | 39.8 | 38.6 | 36.6 | ||
| b = 5000 | k level | 15 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 17 | |
| RC | 13.3 | 19.6 | 24.5 | 26.7 | 31.4 | 35.1 | ||
| FC | 50 | 33.9 | 32.1 | 33.2 | 30.8 | 26.9 | ||
| LC | 36.6 | 46.5 | 43.4 | 40.1 | 37.8 | 37.9 | ||
| b = 10,000 | k level | 14 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 14 | 14 | |
| RC | 18.5 | 19.2 | 25.4 | 27.9 | 34.7 | 37.9 | ||
| FC | 40.6 | 35.7 | 34.3 | 33.5 | 29.9 | 27.9 | ||
| LC | 40.9 | 45.1 | 40.3 | 38.5 | 35.4 | 34.1 | ||
| Multishell sampling schemes | b = 1000, | k level | 14 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| 3000 | RC | 14.5 | 19.6 | 23.7 | 28 | 33.3 | 36.9 | |
| FC | 45.2 | 33.9 | 33 | 31.6 | 28.3 | 26.2 | ||
| LC | 40.3 | 46.5 | 43.3 | 40.4 | 38.4 | 36.9 | ||
| b = 1000, 3000, | k level | 15 | 16 | 17 | 17 | 18 | 19 | |
| 5000 | RC | 14.7 | 17.8 | 22.6 | 25.1 | 30.7 | 34.2 | |
| FC | 45.2 | 36.8 | 34.1 | 34.1 | 30 | 27.5 | ||
| LC | 40.1 | 45.3 | 43.3 | 40.8 | 39.3 | 38.3 | ||
| b = 3000, 5000, | k level | 15 | 18 | 18 | 19 | 21 | 22 | |
| 10,000 | RC | 13.3 | 16.8 | 21.4 | 25.4 | 30.5 | 32.8 | |
| FC | 45.8 | 38.3 | 35.1 | 32.6 | 28.9 | 28 | ||
| LC | 40.9 | 44.9 | 43.5 | 42 | 40.6 | 39.2 | ||
| b = 1000, 3000, | k level | 15 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 19 | 20 | |
| 5000, 10,000 | RC | 12.9 | 17.4 | 22.5 | 24.3 | 30.4 | 33.3 | |
| FC | 46.9 | 35.5 | 32.7 | 34.7 | 29.3 | 27.9 | ||
| LC | 40.2 | 47.1 | 44.7 | 41.1 | 40.4 | 38.8 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalilian, M.; Kazemi, K.; Fouladivanda, M.; Makki, M.; Helfroush, M.S.; Aarabi, A. Effect of Multishell Diffusion MRI Acquisition Strategy and Parcellation Scale on Rich-Club Organization of Human Brain Structural Networks. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11060970
Khalilian M, Kazemi K, Fouladivanda M, Makki M, Helfroush MS, Aarabi A. Effect of Multishell Diffusion MRI Acquisition Strategy and Parcellation Scale on Rich-Club Organization of Human Brain Structural Networks. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(6):970. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11060970
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalilian, Maedeh, Kamran Kazemi, Mahshid Fouladivanda, Malek Makki, Mohammad Sadegh Helfroush, and Ardalan Aarabi. 2021. "Effect of Multishell Diffusion MRI Acquisition Strategy and Parcellation Scale on Rich-Club Organization of Human Brain Structural Networks" Diagnostics 11, no. 6: 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11060970
APA StyleKhalilian, M., Kazemi, K., Fouladivanda, M., Makki, M., Helfroush, M. S., & Aarabi, A. (2021). Effect of Multishell Diffusion MRI Acquisition Strategy and Parcellation Scale on Rich-Club Organization of Human Brain Structural Networks. Diagnostics, 11(6), 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11060970








