A Positive Dermcidin Expression Is an Unfavorable Prognostic Marker for Extramammary Paget’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Immunostaining for Dermcidin
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.4. Microarray Data Analysis
2.5. Study Approval
3. Results
3.1. The Finding of Dermcidin-Positive Extramammary Paget’s Disease
3.2. The Different Characteristics of Extramammary Paget’s Disease Depending on the Expression Degree of Dermcidin
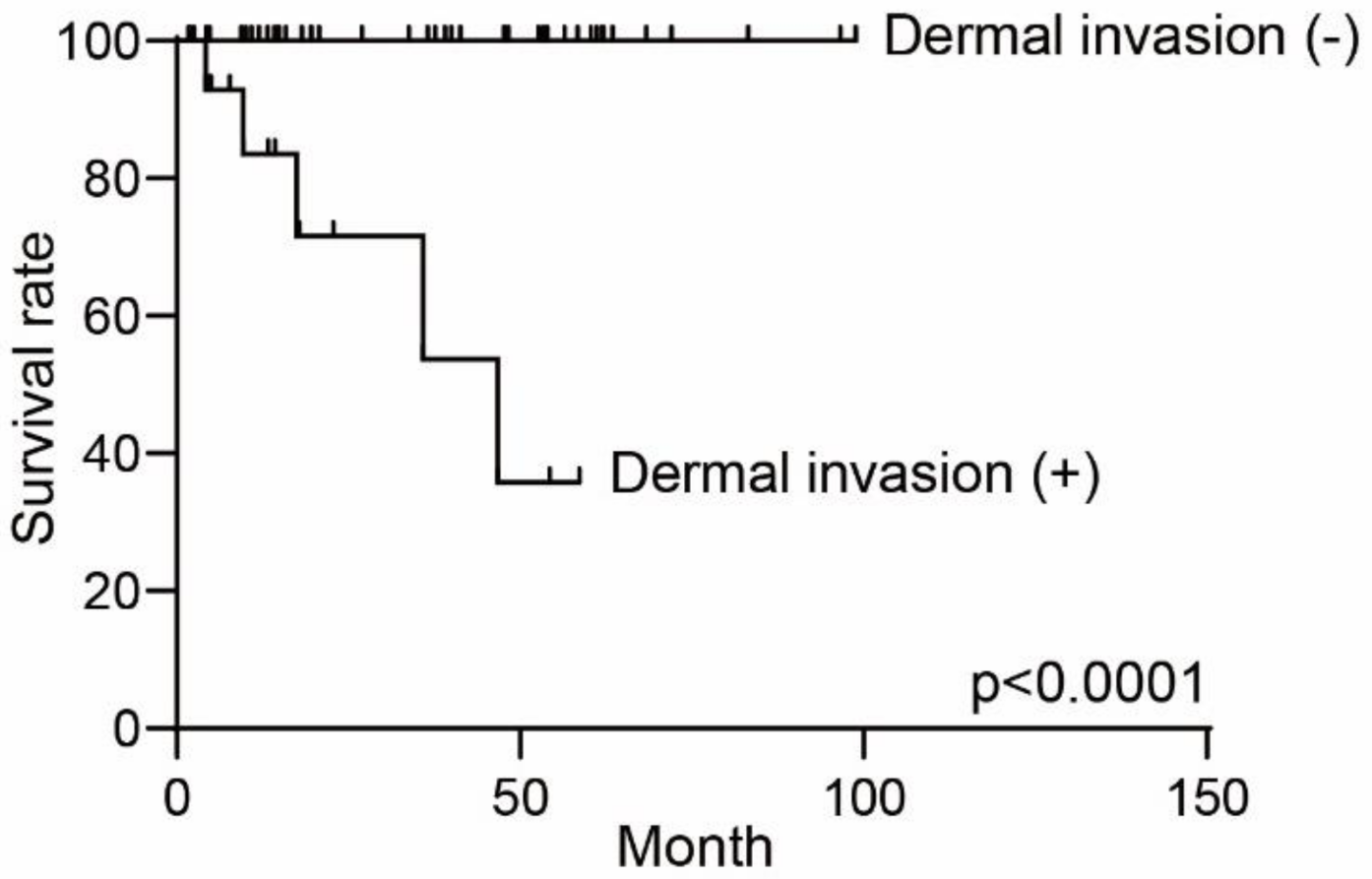
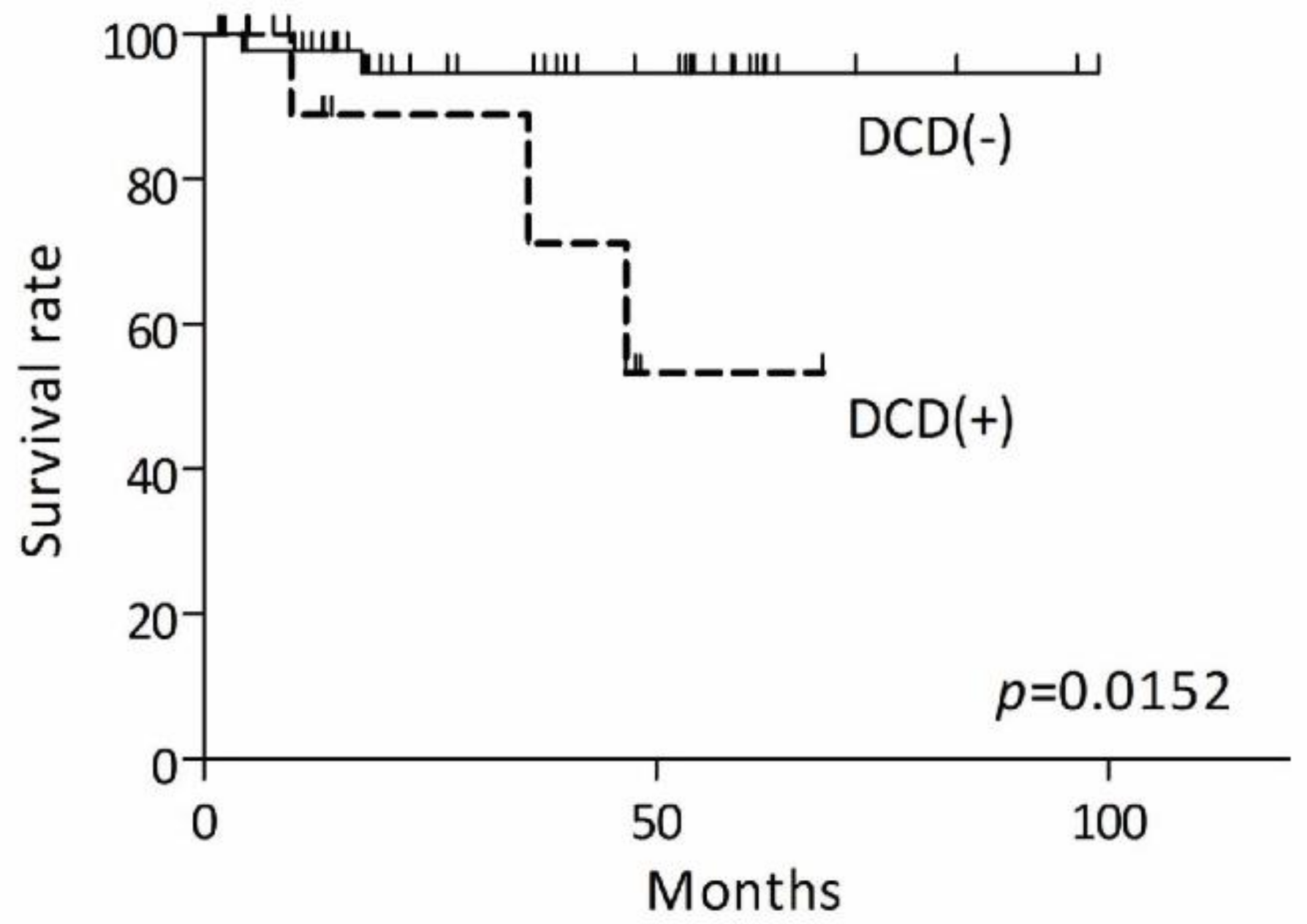
3.3. The Different Prognosis in Extramammary Paget’s Disease
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dainichi, T.; Kitoh, A.; Otsuka, A.; Nakajima, S.; Nomura, T.; Kaplan, D.H.; Kabashima, K. The epithelial immune microenvironment (EIME) in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabashima, K.; Honda, T.; Ginhoux, F.; Egawa, G. The immunological anatomy of the skin. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, Y.; Gallo, R.L. Role of Epigenetics in the Regulation of Immune Functions of the Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, C.R.; Hurst, E.A. Extramammary Paget’s Disease: A Review of the Literature Part II: Treatment and Prognosis. Dermatol. Surg. 2020, 46, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, T.J.; Ridge, J.A. Management of Squamous Cancer Metastatic to Cervical Nodes With an Unknown Primary Site. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3328–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarhini, A.A. The current state of adjuvant therapy of melanoma. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1394–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, Y.; Bito, T.; Kabashima, R.; Yoshiki, R.; Hino, R.; Nakamura, M.; Shiraishi, M.; Tokura, Y. Ectopic extramammary Paget’s disease: Case report and literature review. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2010, 90, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazoujian, G.; Pinkus, G.S.; Haagensen, D.E., Jr. Extramammary Paget’s disease–evidence for an apocrine origin. An immunoperoxidase study of gross cystic disease fluid protein-15, carcinoembryonic antigen, and keratin proteins. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1984, 8, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, N.; Yamada, M.; Hirano, T.; Fujimoto, A.; Morita, R. Extramammary Paget’s disease: Treatment, prognostic factors and outcome in 76 patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 158, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Igawa, S.; Ohishi, Y.; Uehara, J.; Yamamoto, A.I.; Iizuka, H. Prognostic indicators in 35 patients with extramammary Paget’s disease. Dermatol. Surg. 2012, 38, 1938–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zwan, J.M.; Siesling, S.; Blokx, W.A.; Pierie, J.P.; Capocaccia, R. Invasive extramammary Paget’s disease and the risk for secondary tumours in Europe. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 38, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.E., Jr.; Austin, C.; Ackerman, A.B. Extramammary Paget’s disease. A critical reexamination. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 1979, 1, 101–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schittek, B.; Hipfel, R.; Sauer, B.; Bauer, J.; Kalbacher, H.; Stevanovic, S.; Schirle, M.; Schroeder, K.; Blin, N.; Meier, F.; et al. Dermcidin: A novel human antibiotic peptide secreted by sweat glands. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellino, M.; Gargano, G.; Tinelli, R.; Carriero, C.; Minoia, C.; Tetania, S.; Silvestris, E.; Loizzi, V.; Paradiso, A.; Casamassima, P.; et al. A strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE): Are HE4 and CA 125 suitable to detect a Paget disease of the vulva? Medicine 2021, 100, e24485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito-Sasaki, N.; Sawada, Y.; Okada, E.; Nakamura, M. Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 (CADM1) Is an Independent Prognostic Factor in Patients with Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashima, E.; Sawada, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yoshioka, H.; Ohmori, S.; Haruyama, S.; Yoshioka, M.; Okada, E.; Nakamura, M. A high expression of cell adhesion molecule 1 (CADM1) is an unfavorable prognostic factor in mycosis fungoides. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 193, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, X.; Rohl, C.A.; Castle, J.C.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Johnson, J.M.; Chen, R. Definition, conservation and epigenetics of housekeeping and tissue-enriched genes. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minami, Y.; Uede, K.; Sagawa, K.; Kimura, A.; Tsuji, T.; Furukawa, F. Immunohistochemical staining of cutaneous tumours with G-81, a monoclonal antibody to dermcidin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2004, 151, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Kaku, Y.; Nagae, K.; Nakano-Nakamura, M.; Nakahara, T.; Oda, Y.; Hagihara, A.; Furue, M.; Uchi, H. Tumor thickness as a prognostic factor in extramammary Paget’s disease. J. Dermatol. 2015, 42, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, W.; Kuai, X.; Ji, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Mao, Z.; Wang, Z. Dermcidin as a novel binding protein of lncRNA STCAT3 and its effect on prognosis in gastric cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 2854–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bancovik, J.; Moreira, D.F.; Carrasco, D.; Yao, J.; Porter, D.; Moura, R.; Camargo, A.; Fontes-Oliveira, C.C.; Malpartida, M.G.; Carambula, S.; et al. Dermcidin exerts its oncogenic effects in breast cancer via modulation of ERBB signaling. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slamon, D.J.; Clark, G.M.; Wong, S.G.; Levin, W.J.; Ullrich, A.; McGuire, W.L. Human breast cancer: Correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 1987, 235, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanskanen, M.; Jahkola, T.; Asko-Seljavaara, S.; Jalkanen, J.; Isola, J. HER2 oncogene amplification in extramammary Paget’s disease. Histopathology 2003, 42, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.; Weremowicz, S.; Chin, K.; Seth, P.; Keshaviah, A.; Lahti-Domenici, J.; Bae, Y.K.; Monitto, C.L.; Merlos-Suarez, A.; Chan, J.; et al. A neural survival factor is a candidate oncogene in breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10931–10936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, F.; Qiu, F.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Huang, X. The Role of Dermcidin in the Diagnosis and Staging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2018, 22, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Núñez-Naveira, L.; Mariñas-Pardo, L.A.; Montero-Martínez, C. Mass Spectrometry Analysis of the Exhaled Breath Condensate and Proposal of Dermcidin and S100A9 as Possible Markers for Lung Cancer Prognosis. Lung 2019, 197, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, F.; Lage, S.; Rasero, J.; Díaz-Ramón, J.L.; Apraiz, A.; Pérez-Yarza, G.; Ezkurra, P.A.; Penas, C.; Sánchez-Diez, A.; García-Vazquez, M.D.; et al. Serum markers improve current prediction of metastasis development in early-stage melanoma patients: A machine learning-based study. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 1705–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Martínez, I.; Gardeazabal, J.; Erramuzpe, A.; Sanchez-Diez, A.; Cortés, J.; García-Vázquez, M.D.; Pérez-Yarza, G.; Izu, R.; Luís Díaz-Ramón, J.; de la Fuente, I.M.; et al. Vitronectin and dermcidin serum levels predict the metastatic progression of AJCC I-II early-stage melanoma. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.; Jeong, H.; Baek, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Han, S.H.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, H.; Hong, H.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Yi, E.C.; et al. PiB-PET Imaging-Based Serum Proteome Profiles Predict Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 53, 1563–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloemen, K.; Van Den Heuvel, R.; Govarts, E.; Hooyberghs, J.; Nelen, V.; Witters, E.; Desager, K.; Schoeters, G. A new approach to study exhaled proteins as potential biomarkers for asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2011, 41, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatas, E.T.; Kara Polat, A.; Kalayci, M.; Dogan, G.; Akin Belli, A. Plasma dermcidin levels in acne patients, and the effect of isotretinoin treatment on dermcidin levels. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e13044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Aziz Ragab, M.A.; Omar, S.S.; Collier, A.; El-Wafa, R.; Gomaa, N. The effect of continuous high versus low dose oral isotretinoin regimens on dermcidin expression in patients with moderate to severe acne vulgaris. Dermatol. Ther. 2018, 31, e12715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, M.; Sharma, S.K.; Upadhyay, V.; Varshney, S.; Sengupta, S.; Basak, T.; Sreenivas, V. Urinary EPCR and dermcidin as potential novel biomarkers for severe adult OSA patients. Sleep Med. 2019, 64, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corasolla Carregari, V.; Monforte, M.; Di Maio, G.; Pieroni, L.; Urbani, A.; Ricci, E.; Tasca, G. Proteomics of Muscle Microdialysates Identifies Potential Circulating Biomarkers in Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Kimura, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Uede, K.; Furukawa, F. Expression of histo-blood group A type 1, 2 and 3 antigens in normal skin and extramammary Paget’s disease. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2008, 41, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
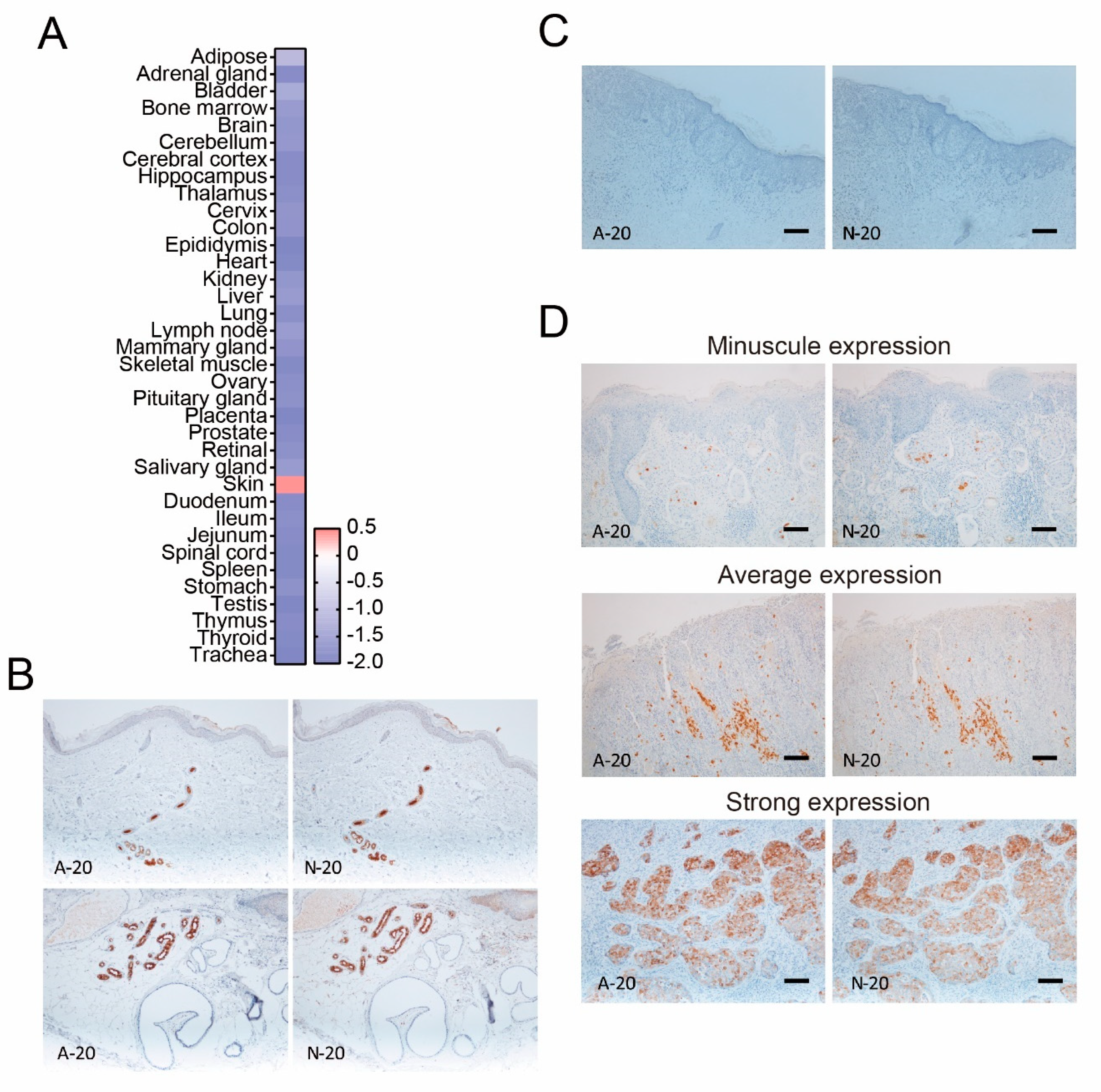
| Variable | Patients Number | |
|---|---|---|
| Total | 60 | |
| Age | ||
| <60 | 3 | |
| 60–69 | 13 | |
| 70–79 | 28 | |
| 80–89 | 13 | |
| ≥90 | 3 | |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 34 | |
| Female | 26 | |
| Primary site | ||
| Genital | 54 | |
| Genital and axillary | 1 | |
| Genital, axillary, and navel | 1 | |
| Perianal | 2 | |
| Axillary | 1 | |
| Back | 1 | |
| Clinical manifestations | ||
| Nodule | 9 | |
| Erosion | 33 | |
| Depigmentation | 21 | |
| Dermal invasion | ||
| Absent | 44 | |
| Present | 16 | |
| Lymph node metastases | ||
| Absent | 52 | |
| Present | 8 | |
| Variable | Total | Dermcidin (+) | Dermcidin (-) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 60 | 14 | 46 | ||
| Age | 0.314 | ||||
| <70 | 16 | 2 | 14 | ||
| ≥70 | 44 | 12 | 32 | ||
| Sex | 1.000 | ||||
| Male | 34 | 8 | 26 | ||
| Female | 26 | 6 | 20 | ||
| Nodule | 0.003 | ||||
| Absent | 51 | 8 | 43 | ||
| Present | 9 | 6 | 3 | ||
| Erosion | 0.013 | ||||
| Absent | 27 | 2 | 25 | ||
| Present | 33 | 12 | 21 | ||
| Depigmentation | 1.000 | ||||
| Absent | 39 | 9 | 30 | ||
| Present | 21 | 5 | 16 | ||
| Dermal invasion | 0.006 | ||||
| Absent | 44 | 6 | 38 | ||
| Present | 16 | 8 | 8 | ||
| Lymph node metastases | 0.013 | ||||
| Absent | 52 | 9 | 43 | ||
| Present | 8 | 5 | 3 | ||
| Variable | HR | 95% CI | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.234 | |||
| <70 | 1 | |||
| ≥70 | 0.3262 | 0.05144–2.068 | ||
| Sex | 0.709 | |||
| Male | 1 | |||
| Female | 1.398 | 0.2406–8.117 | ||
| Nodule | <0.0001 | |||
| Absent | 1 | |||
| Present | 7561 | 338.7–168,800 | ||
| Erosion | 0.275 | |||
| Absent | 1 | |||
| Present | 2.671 | 0.4570–15.60 | ||
| Depigmentation | 0.432 | |||
| Absent | 1 | |||
| Present | 0.4823 | 0.07834–2.969 | ||
| Dermal invasion | <0.0001 | |||
| Absent | 1 | |||
| Present | 240.8 | 24.80–2338 | ||
| Lymph node metastases | <0.0001 | |||
| Absent | 1 | |||
| Present | 442,600 | 16,480–11,880,000 | ||
| dermcidin expression | 0.015 | |||
| Absent | 1 | |||
| Present | 16.79 | 1.721–163.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ohmori, S.; Sawada, Y.; Saito-Sasaki, N.; Sato, S.; Minokawa, Y.; Sugino, H.; Nanamori, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Okada, E.; Nakamura, M. A Positive Dermcidin Expression Is an Unfavorable Prognostic Marker for Extramammary Paget’s Disease. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061086
Ohmori S, Sawada Y, Saito-Sasaki N, Sato S, Minokawa Y, Sugino H, Nanamori H, Yamamoto K, Okada E, Nakamura M. A Positive Dermcidin Expression Is an Unfavorable Prognostic Marker for Extramammary Paget’s Disease. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(6):1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061086
Chicago/Turabian StyleOhmori, Shun, Yu Sawada, Natsuko Saito-Sasaki, Sayaka Sato, Yoko Minokawa, Hitomi Sugino, Hikaru Nanamori, Kayo Yamamoto, Etsuko Okada, and Motonobu Nakamura. 2021. "A Positive Dermcidin Expression Is an Unfavorable Prognostic Marker for Extramammary Paget’s Disease" Diagnostics 11, no. 6: 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061086
APA StyleOhmori, S., Sawada, Y., Saito-Sasaki, N., Sato, S., Minokawa, Y., Sugino, H., Nanamori, H., Yamamoto, K., Okada, E., & Nakamura, M. (2021). A Positive Dermcidin Expression Is an Unfavorable Prognostic Marker for Extramammary Paget’s Disease. Diagnostics, 11(6), 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061086






