Quantitative Muscle MRI in Patients with Neuromuscular Diseases—Association of Muscle Proton Density Fat Fraction with Semi-Quantitative Grading of Fatty Infiltration and Muscle Strength at the Thigh Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Study Setup
2.2. Clinical Examination
2.3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
2.3.1. Image Acquisition
2.3.2. Postprocessing
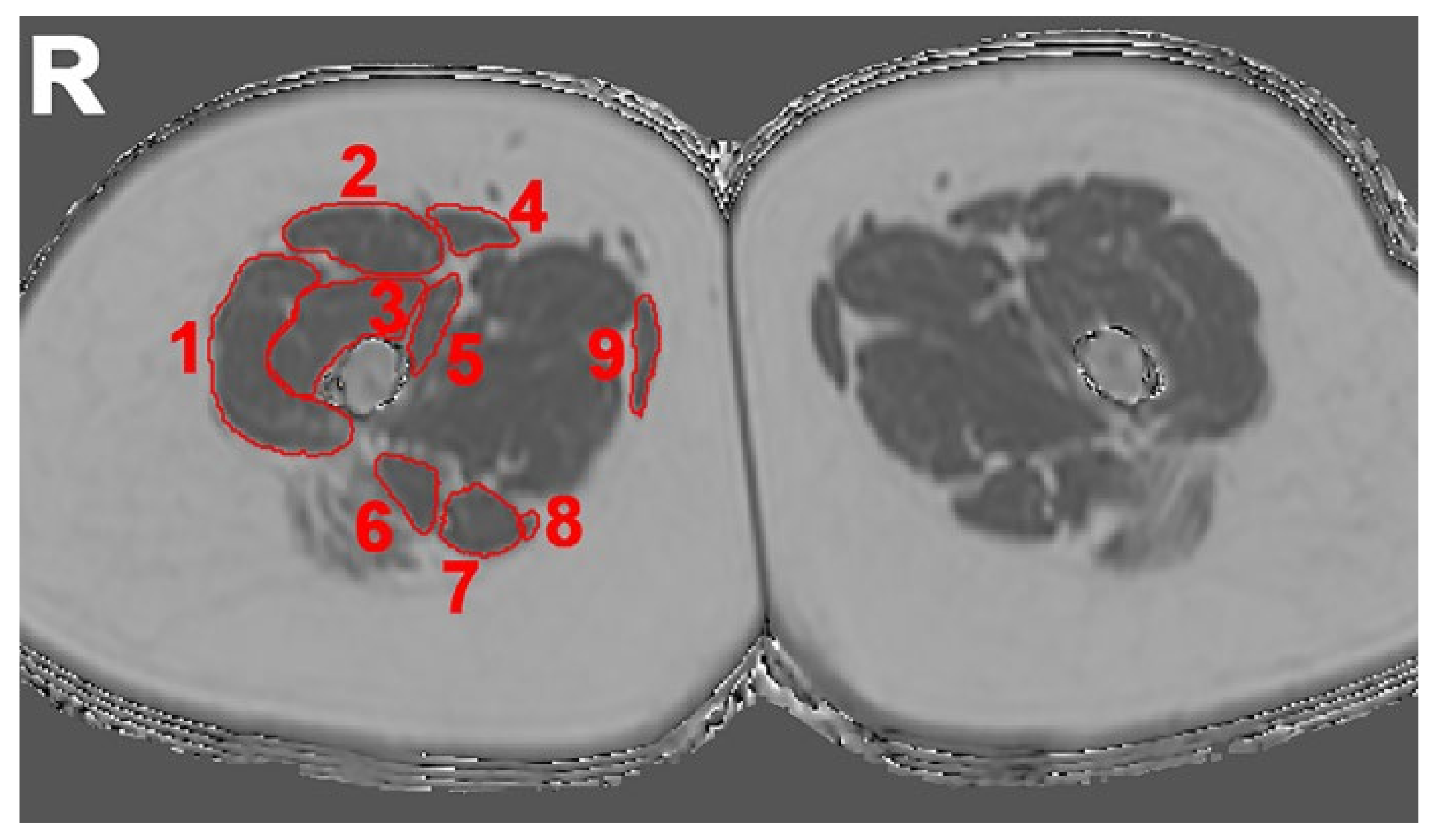
2.4. Evaluation of Imaging Data
2.4.1. Semi-Quantitative Assessment
2.4.2. Quantitative Assessment
2.5. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Study Cohort
3.2. Semi-Quantitative Mercuri Grading
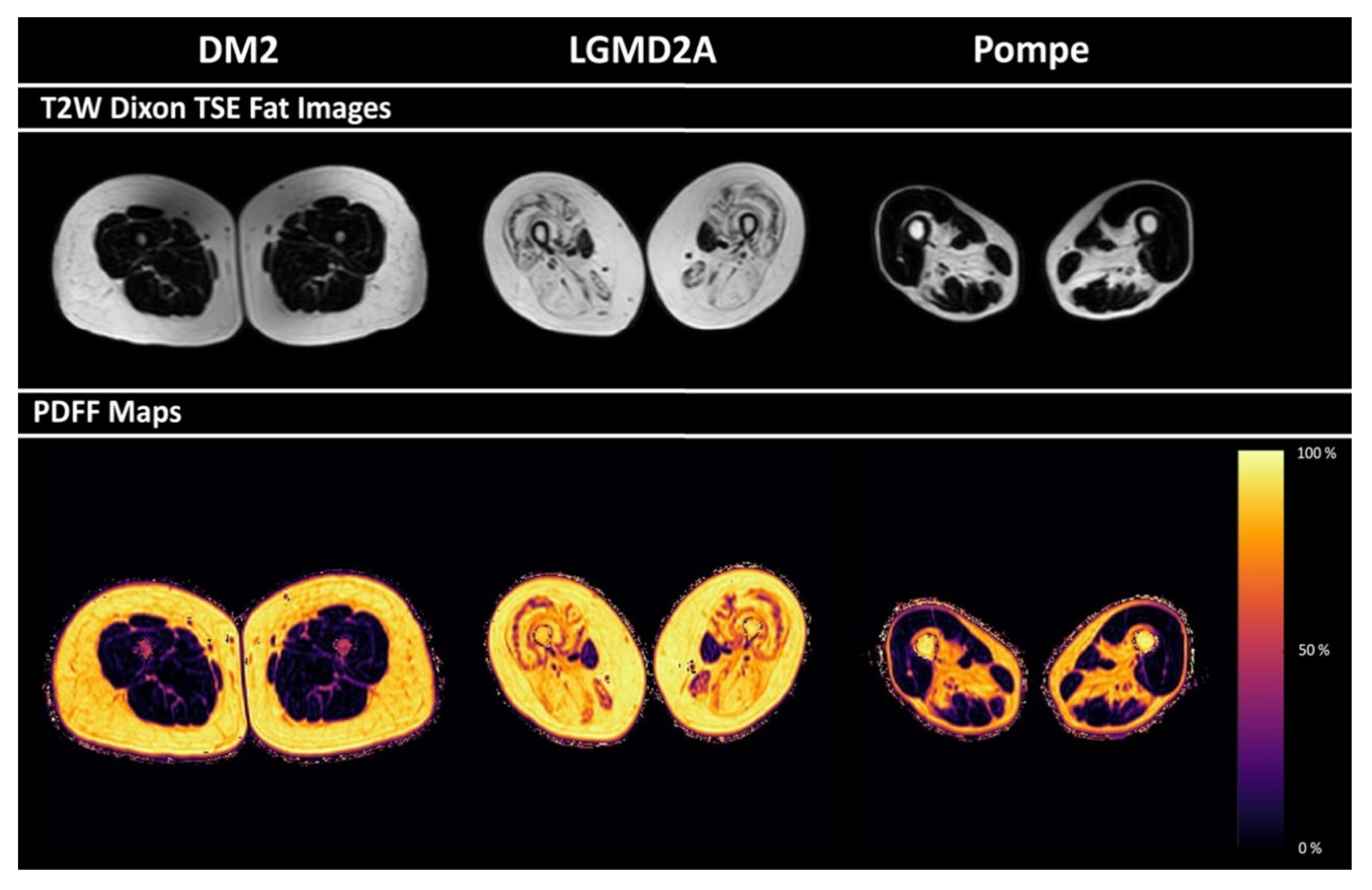
3.3. PDFF of Thigh Muscles
3.4. Correlations between PDFF and Semi-Quantitative Mercuri Grading
3.5. Correlations between PDFF and Muscle Strength
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2D | Two-dimensional |
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
| BMRC | British Medical Research Council |
| DM1 | Myotonic dystrophy type 1 |
| DM2 | Myotonic dystrophy type 2 |
| FOV | Field of view |
| FSHD | Facioscapulohumeral dystrophy |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| LGMD2A | Limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| NMD | Neuromuscular diseases |
| PACS | Picture Archiving and Communication System |
| PDFF | Proton density fat fraction |
| rs | Spearman correlation coefficient |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| SENSE | Sensitivity encoding |
| T2w | Water T2 |
| TE | Echo time |
| TR | Repetition time |
| TSE | Turbo spin echo |
References
- Morrison, B.M. Neuromuscular Diseases. Semin. Neurol. 2016, 36, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, A.E. The muscular dystrophies. BMJ 1998, 317, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, J.; Thomas, P.K. Classification of neuromuscular diseases. J. Neurol. Sci. 1988, 86, 333–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlier, P.G.; Marty, B.; Scheidegger, O.; de Sousa, P.L.; Baudin, P.Y.; Snezhko, E.; Vlodavets, D. Skeletal Muscle Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy as an Outcome Measure for Clinical Trials. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2016, 3, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattjes, M.P.; Kley, R.A.; Fischer, D. Neuromuscular imaging in inherited muscle diseases. Eur. Radiol. 2010, 20, 2447–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlier, P.G.; Azzabou, N.; de Sousa, P.L.; Hicks, A.; Boisserie, J.M.; Amadon, A.; Carlier, R.Y.; Wary, C.; Orlikowski, D.; Laforet, P. Skeletal muscle quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance imaging follow-up of adult Pompe patients. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2015, 38, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, S.C.; Willcocks, R.J.; Triplett, W.T.; Rooney, W.D.; Lott, D.J.; Wang, D.J.; Pollaro, J.; Senesac, C.R.; Daniels, M.J.; Finkel, R.S.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy assessment of lower extremity skeletal muscles in boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy: A multicenter cross sectional study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Laor, T.; Horn, P.S.; Racadio, J.M.; Wong, B.; Dardzinski, B.J. T2 mapping in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: Distribution of disease activity and correlation with clinical assessments. Radiology 2010, 255, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Grande, F.; Carrino, J.A.; Del Grande, M.; Mammen, A.L.; Christopher Stine, L. Magnetic resonance imaging of inflammatory myopathies. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 22, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, G.; Damian, M.S.; Koch, M.; Schilling, G.; Fach, B.; Stoppler, S. The clinical and genetic correlates of MRI findings in myotonic dystrophy. Neuroradiology 1996, 38, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.; Pumar, J.M.; Rodriguez, J.R.; Prieto, J.M.; Arrojo, L.; Martinez, F.; Noya, M. Magnetic resonance imaging of muscles in myotonic dystrophy. Eur. J. Radiol. 1993, 17, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damian, M.S.; Bachmann, G.; Herrmann, D.; Dorndorf, W. Magnetic resonance imaging of muscle and brain in myotonic dystrophy. J. Neurol. 1993, 240, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornblum, C.; Lutterbey, G.; Bogdanow, M.; Kesper, K.; Schild, H.; Schroder, R.; Wattjes, M.P. Distinct neuromuscular phenotypes in myotonic dystrophy types 1 and 2: A whole body highfield MRI study. J. Neurol. 2006, 253, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schedel, H.; Reimers, C.D.; Nagele, M.; Witt, T.N.; Pongratz, D.E.; Vogl, T. Imaging techniques in myotonic dystrophy. A comparative study of ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of skeletal muscles. Eur. J. Radiol. 1992, 15, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramare, R.; Beltrame, V.; Dal Borgo, R.; Gallimberti, L.; Frigo, A.C.; Pegoraro, E.; Angelini, C.; Rubaltelli, L.; Feltrin, G.P. MRI in the assessment of muscular pathology: A comparison between limb-girdle muscular dystrophies, hyaline body myopathies and myotonic dystrophies. La Radiol. Med. 2010, 115, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, D.; Walter, M.C.; Kesper, K.; Petersen, J.A.; Aurino, S.; Nigro, V.; Kubisch, C.; Meindl, T.; Lochmuller, H.; Wilhelm, K.; et al. Diagnostic value of muscle MRI in differentiating LGMD2I from other LGMDs. J. Neurol. 2005, 252, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, E.; Bushby, K.; Ricci, E.; Birchall, D.; Pane, M.; Kinali, M.; Allsop, J.; Nigro, V.; Saenz, A.; Nascimbeni, A.; et al. Muscle MRI findings in patients with limb girdle muscular dystrophy with calpain 3 deficiency (LGMD2A) and early contractures. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2005, 15, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaizo, A.; Banerjee, S.; Terk, M. Adult onset glycogen storage disease type II (adult onset Pompe disease): Report and magnetic resonance images of two cases. Skelet. Radiol. 2009, 38, 1205–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, N.; Jan, W.; Norwood, F.; Sheehan, J.; Spahr, R.; Al-Sarraj, S.; Anthony Hulse, J.; Hughes, D.; Champion, M.P.; Jungbluth, H. Muscle MRI findings in siblings with juvenile-onset acid maltase deficiency (Pompe disease). Neuromuscul. Disord. 2008, 18, 408–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichiecchio, A.; Uggetti, C.; Ravaglia, S.; Egitto, M.G.; Rossi, M.; Sandrini, G.; Danesino, C. Muscle MRI in adult-onset acid maltase deficiency. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2004, 14, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaglia, S.; Pichiecchio, A.; Ponzio, M.; Danesino, C.; Saeidi Garaghani, K.; Poloni, G.U.; Toscano, A.; Moglia, A.; Carlucci, A.; Bini, P.; et al. Changes in skeletal muscle qualities during enzyme replacement therapy in late-onset type II glycogenosis: Temporal and spatial pattern of mass vs. strength response. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2010, 33, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollingsworth, K.G.; de Sousa, P.L.; Straub, V.; Carlier, P.G. Towards harmonization of protocols for MRI outcome measures in skeletal muscle studies: Consensus recommendations from two TREAT-NMD NMR workshops, 2 May 2010, Stockholm, Sweden, 1–2 October 2009, Paris, France. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2012, 22 (Suppl. 2), S54–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.G. Magnetic resonance imaging patterns of muscle involvement in genetic muscle diseases: A systematic review. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 1320–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercuri, E.; Pichiecchio, A.; Allsop, J.; Messina, S.; Pane, M.; Muntoni, F. Muscle MRI in inherited neuromuscular disorders: Past, present, and future. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 25, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliachik, S.L.; Friedman, S.D.; Carter, G.T.; Parnell, S.E.; Shaw, D.W. Skeletal muscle edema in muscular dystrophy: Clinical and diagnostic implications. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 23, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, V.; Carlier, P.G.; Mercuri, E. TREAT-NMD workshop: Pattern recognition in genetic muscle diseases using muscle MRI: 25–26 February 2011, Rome, Italy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2012, 22 (Suppl. 2), S42–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridian-Aragh, N.; Wagner, K.R.; Leung, D.G.; Carrino, J.A. Magnetic resonance imaging phenotyping of Becker muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 2014, 50, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Dam, L.; van der Kooi, A.J.; Verhamme, C.; Wattjes, M.P.; de Visser, M. Muscle imaging in inherited and acquired muscle diseases. Eur. J. Neurol. 2016, 23, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinali, M.; Arechavala-Gomeza, V.; Cirak, S.; Glover, A.; Guglieri, M.; Feng, L.; Hollingsworth, K.G.; Hunt, D.; Jungbluth, H.; Roper, H.P.; et al. Muscle histology vs MRI in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neurology 2011, 76, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggers, H.; Brendel, B.; Duijndam, A.; Herigault, G. Dual-echo Dixon imaging with flexible choice of echo times. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 65, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeder, S.B.; Pineda, A.R.; Wen, Z.; Shimakawa, A.; Yu, H.; Brittain, J.H.; Gold, G.E.; Beaulieu, C.H.; Pelc, N.J. Iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least-squares estimation (IDEAL): Application with fast spin-echo imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 54, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaeger, S.; Klupp, E.; Weidlich, D.; Cervantes, B.; Foreman, S.C.; Deschauer, M.; Schoser, B.; Katemann, C.; Kooijman, H.; Rummeny, E.J.; et al. T2-Weighted Dixon Turbo Spin Echo for Accelerated Simultaneous Grading of Whole-Body Skeletal Muscle Fat Infiltration and Edema in Patients With Neuromuscular Diseases. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2018, 42, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, T.; Burian, E.; Zoffl, A.; Feuerriegel, G.; Schlaeger, S.; Dieckmeyer, M.; Sollmann, N.; Klupp, E.; Weidlich, D.; Inhuber, S.; et al. Regional variation of thigh muscle fat infiltration in patients with neuromuscular diseases compared to healthy controls. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 2610–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.M.; Matthews, E.; Raja Rayan, D.L.; Fischmann, A.; Sinclair, C.D.; Reilly, M.M.; Thornton, J.S.; Hanna, M.G.; Yousry, T.A. Muscle MRI reveals distinct abnormalities in genetically proven non-dystrophic myotonias. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2013, 23, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeder, S.B.; Hu, H.H.; Sirlin, C.B. Proton density fat-fraction: A standardized MR-based biomarker of tissue fat concentration. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 36, 1011–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burakiewicz, J.; Sinclair, C.D.J.; Fischer, D.; Walter, G.A.; Kan, H.E.; Hollingsworth, K.G. Quantifying fat replacement of muscle by quantitative MRI in muscular dystrophy. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 2053–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaeger, S.; Inhuber, S.; Rohrmeier, A.; Dieckmeyer, M.; Freitag, F.; Klupp, E.; Weidlich, D.; Feuerriegel, G.; Kreuzpointner, F.; Schwirtz, A.; et al. Association of paraspinal muscle water-fat MRI-based measurements with isometric strength measurements. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inhuber, S.; Sollmann, N.; Schlaeger, S.; Dieckmeyer, M.; Burian, E.; Kohlmeyer, C.; Karampinos, D.C.; Kirschke, J.S.; Baum, T.; Kreuzpointner, F.; et al. Associations of thigh muscle fat infiltration with isometric strength measurements based on chemical shift encoding-based water-fat magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2019, 3, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampinos, D.C.; Yu, H.; Shimakawa, A.; Link, T.M.; Majumdar, S. T₁-corrected fat quantification using chemical shift-based water/fat separation: Application to skeletal muscle. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heskamp, L.; van Nimwegen, M.; Ploegmakers, M.J.; Bassez, G.; Deux, J.F.; Cumming, S.A.; Monckton, D.G.; van Engelen, B.G.M.; Heerschap, A. Lower extremity muscle pathology in myotonic dystrophy type 1 assessed by quantitative MRI. Neurology 2019, 92, e2803–e2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paternostro-Sluga, T.; Grim-Stieger, M.; Posch, M.; Schuhfried, O.; Vacariu, G.; Mittermaier, C.; Bittner, C.; Fialka-Moser, V. Reliability and validity of the Medical Research Council (MRC) scale and a modified scale for testing muscle strength in patients with radial palsy. J. Rehabil. Med. 2008, 40, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; McKenzie, C.A.; Yu, H.; Brittain, J.H.; Reeder, S.B. Fat quantification with IDEAL gradient echo imaging: Correction of bias from T(1) and noise. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 58, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigoni, F.; De Luca, A.; Velardo, D.; Magri, F.; Gandossini, S.; Russo, A.; Froeling, M.; Bertoldo, A.; Leemans, A.; Bresolin, N.; et al. Multiparametric quantitative MRI assessment of thigh muscles in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2A and 2B. Muscle Nerve 2018, 58, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, T.A.; Hollingsworth, K.G.; Coombs, A.; Sveen, M.L.; Andersen, S.; Stojkovic, T.; Eagle, M.; Mayhew, A.; de Sousa, P.L.; Dewar, L.; et al. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2I: A multinational cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, C.A. Myotonic dystrophy. Neurol. Clin. 2014, 32, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Scan Parameters | T2-Weighted 2D DIXON TSE | Six-Echo 3D Spoiled Gradient Echo |
|---|---|---|
| TR/TE/ΔTE (ms) | 3725/100/1.0 | 10/1.17/0.9 |
| FOV (mm3) | 330 × 450 × 306 | 260 × 420 × 120 |
| Acquisition voxel size (mm3) | 2.5 × 2.7 × 6.0 | 3.2 × 2 × 4 |
| Number of slices | 26 | 30 |
| Slice thickness (mm) | 6.0 | 8.0 |
| Slice gap (mm) | 6.0 | 0.0 |
| TSE factor | 45 | |
| Number of signal averages | 2 | 1 |
| Receiver bandwidth (Hz/pixel) | 2325 | |
| Frequency direction | A/P | |
| SENSE direction | L/R | |
| SENSE reduction factor | 2 | |
| Scan time per stack (s) | 127 | 20 |
| PATIENT ID | SEX | AGE | DISEASE | YEARS SINCE DIAGNOSIS | GENE MUTATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | m | 52 | DM2 | 1 | ZNF9/CNBP gene: Tetranucleotide (CCTG) repeat |
| 02 | f | 54 | DM2 | 1 | ZNF9/CNBP gene: Tetranucleotide (CCTG) repeat |
| 03 | f | 61 | DM2 | 4 | ZNF9/CNBP gene: Tetranucleotide (CCTG) repeat |
| 04 | f | 63 | DM2 | 12 | ZNF9/CNBP gene: Tetranucleotide (CCTG) repeat |
| 05 | f | 66 | DM2 | 11 | ZNF9/CNBP gene: Tetranucleotide (CCTG) repeat |
| 06 | m | 26 | LGMD2A | 2 | c.1043delG c.1318C > T |
| 07 | f | 45 | LGMD2A | 32 | CAPN3 gene: c.801 + 1G > A, c.1468C > G |
| 08 | f | 47 | LGMD2A | 3 | CAPN3 gene: Exon 4: c598_612del Intron 13: c.1476-20C > G |
| 09 | f | 49 | LGMD2A | 11 | CAPN3 gene: c.1099G > A, c.1322delG |
| 10 | f | 52 | LGMD2A | 5 | CPN3 gene: c.759_761_del_GAA, c.1746-20C > G |
| 11 | m | 48 | Adult Pompe disease | 7 | GAA gene: c.-45T > G, c.1438-1G > C |
| 12 | f | 76 | Adult Pompe disease | 26 | GAA gene: c.-45T > G, c.1942G > A |
| 13 | m | 84 | Adult Pompe disease | 8 | GAA gene: c.-32-13T > G, c.1655T > C |
| DM2 | LGMD2A | Pompe | p-Value (DM2 vs. LGMD2A vs. Pompe) | Adjustedp-Value (DM2 vs. LGMD2A) | Adjustedp-Value (DM2 vs. Pompe) | Adjustedp-Value (LGMD2A vs. Pompe) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (in years) | 59.8 ± 6.1 | 44.3 ± 10.6 | 69.8 ± 19.2 | 0.02 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Muscle strength (according to BMRC scale) | Hip flexion | 4.2 ± 0.5 | 3.2 ± 1.1 | 3.7 ± 0.6 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| Hip extension | 4.2 ± 0.5 | 3.4 ± 0.6 | 3.7 ± 0.6 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Knee flexion | 4.6 ± 0.6 | 3.8 ± 0.5 | 5.0 ± 0.0 | 0.02 | n.s. | n.s. | 0.03 | |
| Knee extension | 4.8 ± 0.5 | 4.4 ± 0.9 | 4.7 ± 0.6 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| DM2 | LGMD2A | Pompe | p-Value (DM2 vs. LGMD2A vs. Pompe) | Adjustedp-Value (DM2 vs. LGMD2A) | Adjustedp-Value (DM2 vs. Pompe) | Adjustedp-Value (LGMD2A vs. Pompe) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mercuri grading score | Biceps femoris | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 2.2 ± 1.3 | 2.2 ± 1.3 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| Gracilis | 1.4 ± 0.9 | 2.0 ± 1.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Rectus femoris | 1.6 ± 0.9 | 2.1 ± 1.5 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Sartorius | 1.8 ± 1.3 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Semimembranosus | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 4.0 ± 0.0 | 2.7 ± 0.6 | <0.01 | <0.01 | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Semitendinosus | 1.9 ± 1.2 | 4.0 ± 0.0 | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 0.02 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Vastus intermedius | 1.5 ± 1.1 | 2.8 ± 1.6 | 2.0 ± 1.0 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Vastus lateralis | 1.7 ± 1.3 | 2.2 ± 1.3 | 1.8 ± 0.3 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Vastus medialis | 1.8 ± 1.2 | 2.2 ± 1.3 | 2.5 ± 1.3 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| DM2 | LGMD2A | Pompe | p-Value (DM2 vs. LGMD2A vs. Pompe) | Adjustedp-Value (DM2 vs. LGMD2A) | Adjustedp-Value (DM2 vs. Pompe) | Adjustedp-Value (LGMD2A vs. Pompe) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDFF (in %) | Biceps femoris | 15.5 ± 8.3 13.9; 12.2 | 67.6 ± 11.7 66.6; 22.8 | 18.7 ± 11.4 14.7; - | <0.01 | 0.01 | n.s. | n.s. |
| Gracilis | 20.7 ± 14.2 15.2; 18,5 | 32.0 ± 21.1 35.6; 41.6 | 8.8 ± 1.6 8.7; - | 0.04 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Rectus femoris | 17.7 ± 14.7 12.3; 20.5 | 28.5 ± 25.0 12.2; 45.0 | 12.6 ± 4.9 12.3; - | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Sartorius | 24.4 ± 17.3 17.3; 21.8 | 19.4 ± 7.2 19.0; 10.92 | 11.2 ± 2.9 10.1; - | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Semimembranosus | 16.9 ± 8.5 15.6; 13.4 | 78.8 ± 3.8 79.7; 6.0 | 32.1 ± 17.9 22.6; - | <0.01 | <0.01 | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Semitendinosus | 18.6 ± 15.6 12.1; 22.9 | 76.6 ± 9.4 74.7; 17.9 | 9.1 ± 3.7 8.8; - | <0.01 | n.s. | n.s. | 0.02 | |
| Vastus intermedius | 17.2 ± 14.1 11.3; 18.2 | 30.1 ± 25.1 23.4; 46.2 | 23.0 ± 18.7 20.8; - | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Vastus lateralis | 21.7 ± 18.6 14.0; 26.2 | 26.8 ± 27.8 9.3; 45.0 | 9.6 ± 2.7 8.2; - | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Vastus medialis | 18.9 ± 17.9 10.5; 24.6 | 28.9 ± 24.4 25.8; 46.5 | 35.5 ± 32.8 31.1; - | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| PDFF–Mercuri | ||
|---|---|---|
| rs | p-Value | |
| Biceps femoris | 0.38 | 0.19 |
| Gracilis | 0.81 | <0.01* |
| Rectus femoris | 0.87 | <0.01* |
| Sartorius | 0.71 | 0.01* |
| Semimembranosus | 0.94 | <0.01* |
| Semitendinosus | 0.83 | <0.01* |
| Vastus intermedius | 0.86 | <0.01* |
| Vastus lateralis | 0.34 | 0.25 |
| Vastus medialis | 0.87 | <0.01* |
| PDFF–BMRC | ||
|---|---|---|
| rs | p-Value | |
| Hip flexion | −0.33 | 0.28 |
| Hip extension | −0.36 | 0.23 |
| Knee flexion | −0.80 | <0.01* |
| Knee extension | −0.18 | 0.58 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schlaeger, S.; Sollmann, N.; Zoffl, A.; Becherucci, E.A.; Weidlich, D.; Kottmaier, E.; Riederer, I.; Greve, T.; Montagnese, F.; Deschauer, M.; et al. Quantitative Muscle MRI in Patients with Neuromuscular Diseases—Association of Muscle Proton Density Fat Fraction with Semi-Quantitative Grading of Fatty Infiltration and Muscle Strength at the Thigh Region. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061056
Schlaeger S, Sollmann N, Zoffl A, Becherucci EA, Weidlich D, Kottmaier E, Riederer I, Greve T, Montagnese F, Deschauer M, et al. Quantitative Muscle MRI in Patients with Neuromuscular Diseases—Association of Muscle Proton Density Fat Fraction with Semi-Quantitative Grading of Fatty Infiltration and Muscle Strength at the Thigh Region. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(6):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061056
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchlaeger, Sarah, Nico Sollmann, Agnes Zoffl, Edoardo Aitala Becherucci, Dominik Weidlich, Elisabeth Kottmaier, Isabelle Riederer, Tobias Greve, Federica Montagnese, Marcus Deschauer, and et al. 2021. "Quantitative Muscle MRI in Patients with Neuromuscular Diseases—Association of Muscle Proton Density Fat Fraction with Semi-Quantitative Grading of Fatty Infiltration and Muscle Strength at the Thigh Region" Diagnostics 11, no. 6: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061056
APA StyleSchlaeger, S., Sollmann, N., Zoffl, A., Becherucci, E. A., Weidlich, D., Kottmaier, E., Riederer, I., Greve, T., Montagnese, F., Deschauer, M., Schoser, B., Zimmer, C., Karampinos, D. C., Kirschke, J. S., & Baum, T. (2021). Quantitative Muscle MRI in Patients with Neuromuscular Diseases—Association of Muscle Proton Density Fat Fraction with Semi-Quantitative Grading of Fatty Infiltration and Muscle Strength at the Thigh Region. Diagnostics, 11(6), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061056








