Radiomics Score Combined with ACR TI-RADS in Discriminating Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules Based on Ultrasound Images: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. TN Ultrasound Images
2.3. TNs Segmentation
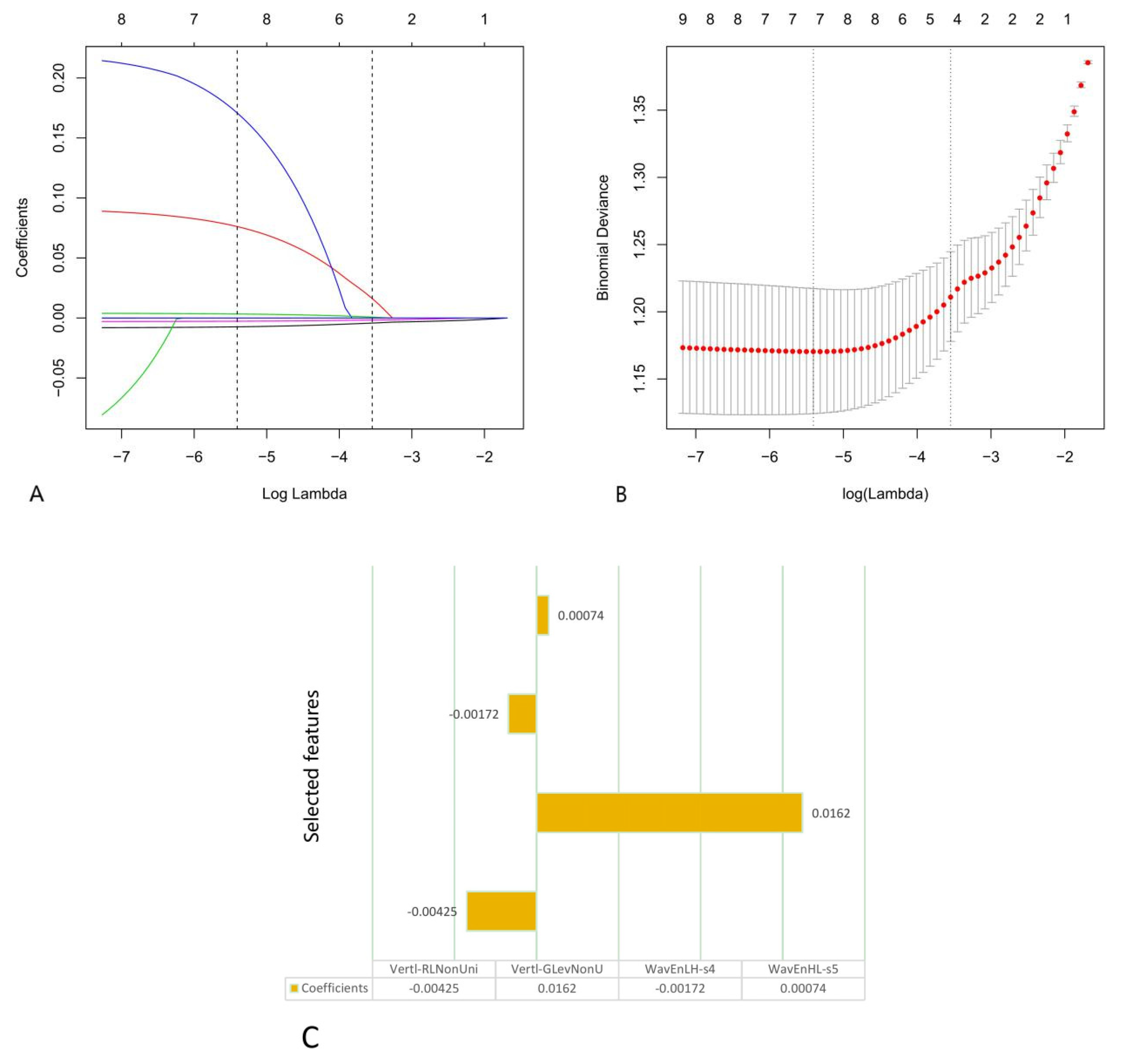
2.4. Radiomics Feature Extraction, Dimension Reduction and Calculation of the Radiomics Score
2.5. Models
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Factors of the Patients and the Model Based on ACR TI-RADS
3.2. Feature Selection and Rad-Score Calculation
3.3. DCA and the Construction of a Nomogram Based on the Rad-Score and the Five Parameters of ACR TI-RADS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hegedus, L. Clinical practice. The thyroid nodule. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1764–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guth, S.; Theune, U.; Aberle, J.; Galach, A.; Bamberger, C.M. Very high prevalence of thyroid nodules detected by high frequency (13 MHz) ultra-sound examination. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 39, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Tian, Y.; Yan, W.; Kong, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, A.; Dou, J.; Liang, P.; Mu, Y. The Prevalence of Thyroid Nodules and an Analysis of Related Lifestyle Factors in Beijing Communities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Essa, M.E.A. Potential of epigenetic events in human thyroid cancer. Cancer Genet. 2019, 239, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, L.; Welch, H.G. Current Thyroid Cancer Trends in the United States. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 140, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessler, F.N.; Middleton, W.D.; Grant, E.G. Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS): A User’s Guide. Radiology 2018, 287, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessler, F.N.; Middleton, W.D.; Grant, E.G.; Hoang, J.K.; Berland, L.L.; Teefey, S.A.; Cronan, J.J.; Beland, M.D.; Desser, T.S.; Frates, M.C.; et al. ACR Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS): White Paper of the ACR TI-RADS Committee. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2017, 14, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wettasinghe, M.C.; Rosairo, S.; Ratnatunga, N.; Wickramasinghe, N.D. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound characteristics in the identification of malignant thyroid nodules. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Rios-Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar, R.; Carvalho, S.; Van Stiphout, R.G.; Granton, P.; Zegers, C.M.; Gillies, R.; Boellard, R.; Dekker, A.; et al. Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using ad-vanced feature analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; De Jong, E.E.; Van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; LaRue, R.T.; Even, A.J.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderson, P.O.; Summers, R.M. The Evolving Status of Radiomics. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2020, 112, 869–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdim, C.; Yardimci, A.H.; Bektas, C.T.; Kocak, B.; Koca, S.B.; Demir, H.; Kilickesmez, O. Prediction of Benign and Malignant Solid Renal Masses: Machine Learn-ing-Based CT Texture Analysis. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 1422–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davnall, F.; Yip, C.S.P.; Ljungqvist, G.; Selmi, M.; Ng, F.; Sanghera, B.; Ganeshan, B.; Miles, K.A.; Cook, G.; Goh, V. Assessment of tumor heterogeneity: An emerging imaging tool for clinical practice? Insights Imaging 2012, 3, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthoff, J.; Nagpal, P.; Sanchez, R.; Gross, T.J.; Lee, C.; Sieren, J.C. Differentiation of non-small cell lung cancer and histoplasmosis pulmonary nodules: Insights from radiomics model performance compared with clinician observers. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; She, Y.; Deng, J.; Wang, T.; Ren, Y.; Su, H.; Wu, J.; Sun, X.; Jiang, G.; Fei, K.; et al. CT-based radiomics signature for the stratification of N2 disease risk in clinical stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Huang, M.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Qin, N.; Huang, D.; Shu, J. Radiomics model of magnetic resonance imaging for predicting pathological grading and lymph node metastases of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2020, 470, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.W.; Gao, Y.J.; Zhang, R.Y.; Zhou, X.X.; Chen, S.L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J.R.; Ge, Z.Z. Personalized CT-based radiomics nomogram preoperative predicting Ki-67 expres-sion in gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A multicenter development and validation cohort. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardakani, A.A.; Gharbali, A.; Mohammadi, A. Application of texture analysis method for classification of benign and malignant thyroid nodules in ultrasound images. Iran. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 8, 116–124. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, E.G.; Tessler, F.N.; Hoang, J.K.; Langer, J.E.; Beland, M.D.; Berland, L.L.; Cronan, J.J.; Desser, T.S.; Frates, M.C.; Hamper, U.M.; et al. Thyroid Ultrasound Reporting Lexicon: White Paper of the ACR Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System (TIRADS) Committee. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2015, 12, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczypiński, P.M.; Strzelecki, M.; Materka, A.; Klepaczko, A. MaZda—A software package for image texture analysis. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2009, 94, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Jin, L.; Gao, P.; Zhao, W.; Ma, W.; Tan, M.; Wu, W.; Duan, S.; Shan, Y.; et al. Radiomics for lung adenocarcinoma manifesting as pure ground-glass nodules: Invasive prediction. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 3650–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.H.; Liu, L.Z.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Shi, J.Y.; Dong, L.Q.; Tian, L.Y.; Ding, Z.B.; Ji, Y.; Rao, S.X.; Zhou, J.; et al. Radiomics score: A potential prognostic imaging feature for postoperative survival of solitary HCC patients. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.T.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.W.; Chen, S.L.; Zheng, X.; Ruan, S.M.; Xie, X.Y.; Yu, J.; Tian, J.; Liang, P.; et al. Ultrasound-based radiomics score: A potential biomarker for the prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 2890–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, P.; Yang, G.; Guo, J.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Ji, Q.; Wu, J.; Cui, J.; Xu, W. A CT-based radiomics nomogram for differentiation of focal nodular hyperplasia from hepa-tocellular carcinoma in the non-cirrhotic liver. Cancer Imaging 2020, 20, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Li, R.; Zeng, R.; Wu, C.-Q.; Chen, Y.; Chen, T.-W.; Zhang, X.-M.; Wu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, J.-Q.; et al. CT radiomic features for predicting resectability of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma as given by feature analysis: A case control study. Cancer Imaging 2019, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Luo, J. Radiomics With Attribute Bagging for Breast Tumor Classification Using Multimodal Ultra-sound Images. J Ultrasound Med. 2019, 39, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, Y.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, E.K.; Kim, S. A Radiomics Approach for the Classification of Fibroepithelial Lesions on Breast Ultrasonog-raphy. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Jin, Y.; Dai, L.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, Y.; Tian, J.; Zheng, J. Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules Using Deep Learning Ra-diomics of Thyroid Ultrasound Images. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 127, 108992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Huang, X.; Hu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, Q.; Wang, W.; Liu, B.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Predicting Malignancy in Thyroid Nodules: Radiomics Score Versus 2017 American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System. Thyroid 2018, 28, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildman-Tobriner, B.; Buda, M.; Hoang, J.K.; Middleton, W.D.; Thayer, D.; Short, R.G.; Tessler, F.N.; Mazurowski, M.A. Using Artificial Intelligence to Revise ACR TI-RADS Risk Stratification of Thyroid Nodules: Diagnostic Accuracy and Utility. Radiology 2019, 292, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xie, F.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, X.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Y.; Cao, J. Ultrasound Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) Based on the Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS) to Distinguish Benign from Malignant Thyroid Nodules and the Diagnostic Performance of Radiologists with Different Diagnostic Experience. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2020, 26, e918452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellana, M.; Piccardo, A.; Virili, C.; Scappaticcio, L.; Grani, G.; Durante, C.; Giovanella, L.; Trimboli, P. Can ultrasound systems for risk stratification of thyroid nodules identify follicular carcinoma? Cancer Cytopathol. 2020, 128, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellana, M.; Virili, C.; Paone, G.; Scappaticcio, L.; Piccardo, A.; Giovanella, L.; Trimboli, P. Ultrasound systems for risk stratification of thyroid nodules prompt inappropriate biopsy in autonomously functioning thyroid nodules. Clin. Endocrinol. 2020, 93, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Training Group | Verification Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign (196) | Malignant (198) | Benign (78) | Malignant (72) |
| 44 | 43 | 14 | 15 |
| 152 | 155 | 64 | 57 |
| 50.1 (20–80) | 42.2 (20–83) | 49.1 (20–80) | 42.4 (20–79) |
| Parameters | Training Group (394) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign (196) | Malignant (198) | ||
| Age (yr) | 49.0 (43.3, 56.0) | 42.0 (31.8, 51.0) | <0.001 * |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 44 | 43 | 0.861 |
| Female | 152 | 155 | |
| Composition | |||
| Cystic, dominantly cystic or spongiform | 0 | 0 | - |
| Cystic-solid mixture | 53 | 1 | <0.001 * |
| Solid, dominantly solid | 143 | 197 | |
| Echogenicity | <0.001 * | ||
| Anechoic | |||
| Hyperechoic or isoechoic | 148 | 45 | |
| Hypoechoic | 45 | 138 | |
| Very hypoechoic | 3 | 15 | |
| Shape | |||
| Wider-than-tall | 176 | 97 | <0.001 * |
| Taller-than-wide | 20 | 101 | |
| Margins | <0.001 * | ||
| Smooth or blurry | 179 | 106 | |
| Lobed or irregular | 17 | 69 | |
| Extrathyroid extension | 0 | 23 | |
| Echogenic foci † | <0.001 * | ||
| 0 | 173 | 124 | |
| 1 | 4 | 16 | |
| 2 | 2 | 4 | |
| 3 | 17 | 48 | |
| ≥4 | 0 | 6 | |
| Training Group | Verification Group | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | SEN (%) | SPE (%) | ACC (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) | F1-Score | AUC | SEN (%) | SPE (%) | ACC (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) | F1-Score | |
| Method1 | 0.898 | 80.30 | 83.16 | 81.73 | 82.81 | 80.69 | 0.82 | 0.870 | 75.00 | 87.18 | 81.33 | 84.38 | 79.07 | 0.79 |
| Method2 | 0.750 | 73.74 | 61.22 | 67.51 | 65.77 | 69.77 | 0.70 | 0.750 | 68.06 | 67.95 | 68.00 | 66.22 | 69.74 | 0.67 |
| Method3 | 0.913 | 87.37 | 84.18 | 85.79 | 84.80 | 86.84 | 0.86 | 0.899 | 80.56 | 88.46 | 84.67 | 86.57 | 83.13 | 0.83 |
| Method3 with ages | 0.923 | 85.86 | 84.69 | 85.28 | 85.00 | 85.57 | 0.85 | 0.912 | 83.33 | 87.18 | 85.33 | 85.71 | 85.00 | 0.85 |
| Training Group | Verification Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Difference between Areas | p Value | Difference between Areas | p Value | |
| Method1 vs. Method2 | 0.148 | <0.001 | 0.120 | 0.0059 |
| Method1 vs. Method3 | 0.015 | 0.0346 | 0.029 | 0.0202 |
| Method2 vs. Method3 | 0.163 | <0.001 | 0.149 | <0.001 |
| Method3 vs. Method3 with age | 0.010 | 0.0675 | 0.013 | 0.1761 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, P.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Su, L.; Wang, Z.; Ren, J. Radiomics Score Combined with ACR TI-RADS in Discriminating Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules Based on Ultrasound Images: A Retrospective Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061011
Luo P, Fang Z, Zhang P, Yang Y, Zhang H, Su L, Wang Z, Ren J. Radiomics Score Combined with ACR TI-RADS in Discriminating Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules Based on Ultrasound Images: A Retrospective Study. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(6):1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061011
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Peng, Zheng Fang, Ping Zhang, Yang Yang, Hua Zhang, Lei Su, Zhigang Wang, and Jianli Ren. 2021. "Radiomics Score Combined with ACR TI-RADS in Discriminating Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules Based on Ultrasound Images: A Retrospective Study" Diagnostics 11, no. 6: 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061011
APA StyleLuo, P., Fang, Z., Zhang, P., Yang, Y., Zhang, H., Su, L., Wang, Z., & Ren, J. (2021). Radiomics Score Combined with ACR TI-RADS in Discriminating Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules Based on Ultrasound Images: A Retrospective Study. Diagnostics, 11(6), 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061011






