The Importance of Multimodality Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Patients with Infiltrative Cardiomyopathies: An Update
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Conventional Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE)
2.1. Left Ventricular Wall Thickness and Cavity Size
2.1.1. Left Ventricular Wall Thickness and Cavity Size in Amyloidosis
2.1.2. Left Ventricular Wall Thickness and Cavity Size in Sarcoidosis
2.1.3. Left Ventricular Wall Thickness and Cavity Size in Hemochromatosis
2.2. Diastolic Dysfunction
2.2.1. Diastolic Dysfunction in Amyloidosis
2.2.2. Diastolic Dysfunction in Sarcoidosis and Hemochromatosis
2.3. Systolic Function
2.3.1. Systolic Function in Amyloidosis
2.3.2. Systolic Function in Sarcoidosis
2.3.3. Systolic Function in Hemochromatosis
2.4. Right Heart Involvement
2.4.1. Right Heart Involvement in Amyloidosis
2.4.2. Right Heart Involvement in Sarcoidosis
2.4.3. Right Heart Involvement in Hemochromatosis
2.5. Other Echocardiographic Findings
2.5.1. Other Echocardiographic Findings in Amyloidosis
2.5.2. Other Echocardiographic Findings in Sarcoidosis
2.5.3. Other Echocardiographic Findings in Hemochromatosis
3. Advanced Echocardiographic Techniques
3.1. Advanced Echocardiographic Techniques in Amyloidosis
3.2. Advanced Echocardiographic Techniques in Sarcoidosis
3.3. Advanced Echocardiographic Techniques in Hemochromatosis
4. Computed Tomography Imaging
4.1. Computed Tomography Imaging in Amyloidosis
4.2. Computed Tomography Imaging in Sarcoidosis
4.3. Computed Tomography Imaging in Hemochromatosis
5. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
5.1. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Amyloidosis
5.2. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Sarcoidosis
5.3. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Hemochromatosis
6. Nuclear Imaging
6.1. Nuclear Imaging in Amyloidosis
6.2. Nuclear Imaging in Sarcoidosis
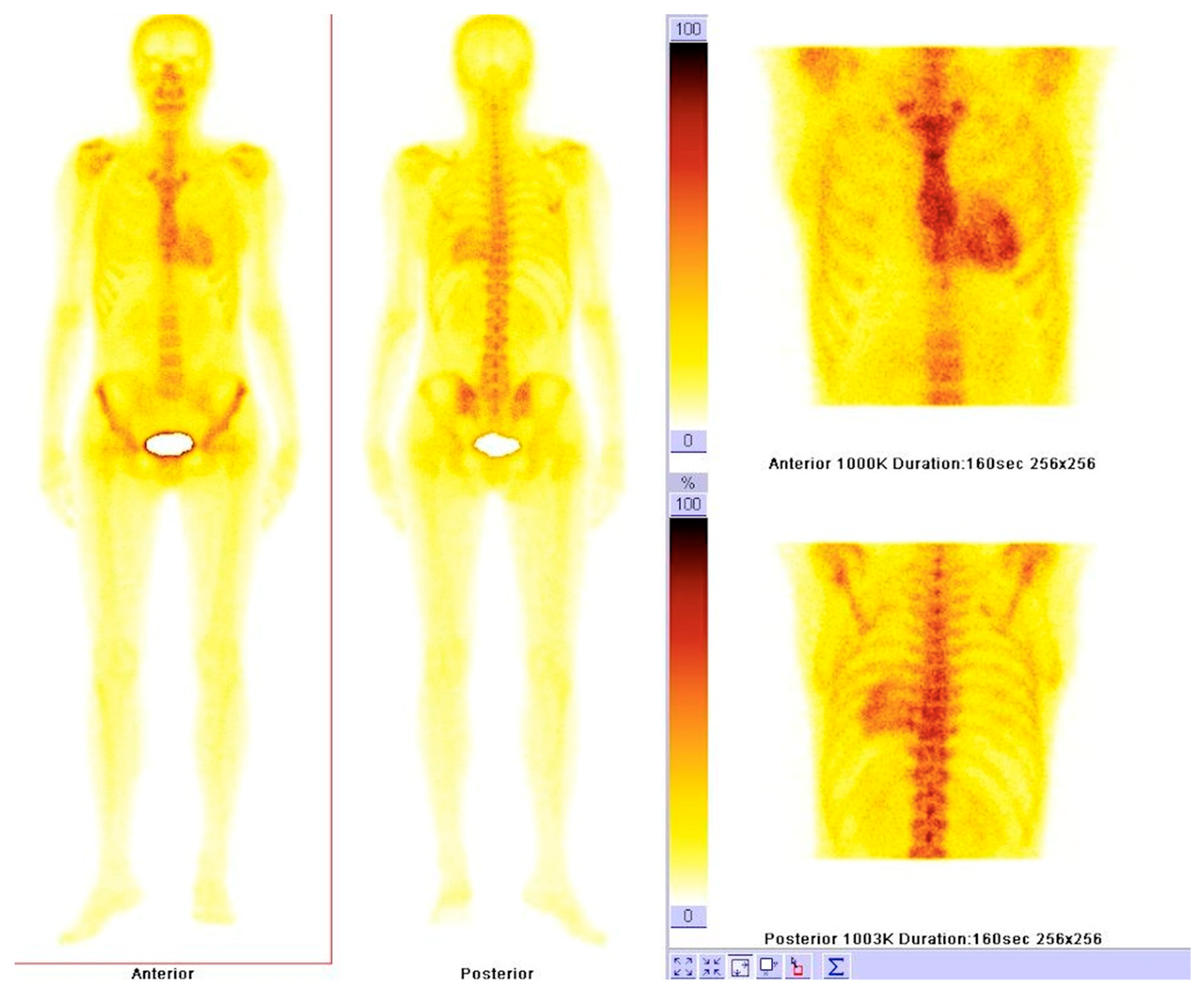
6.3. Nuclear Imaging in Hemochromatosis
7. Implications of Multimodality Imaging in Monitoring Disease Progression and Treatment Response in Infiltrative Cardiomyopathies
7.1. Implications of Multimodality Imaging in Amyloidosis
7.2. Implications of Multimodality Imaging in Sarcoidosis
7.3. Implications of Multimodality Imaging in Hemochromatosis
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seferović, P.M.; Polovina, M.; Bauersachs, J.; Arad, M.; Gal, T.B.; Lund, L.H.; Felix, S.B.; Arbustini, E.; Caforio, A.L.P.; Farmakis, D.; et al. Heart failure in cardiomyopathies: A position paper from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 553–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, N.L.; Grogan, M.; Dec, G.W. Spectrum of Restrictive and Infiltrative Cardiomyopathies: Part 1 of a 2-Part Series. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1130–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejar, D.; Colombo, P.C.; Latif, F.; Yuzefpolskaya, M. Infiltrative Cardiomyopathies. Clin. Med. Insights Cardiol. 2015, 9, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Naharro, A.; Baksi, A.J.; Hawkins, P.N.; Fontana, M. Diagnostic imaging of cardiac amyloidosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergaro, G.; Aimo, A.; Barison, A.; Genovesi, D.; Buda, G.; Passino, C.; Emdin, M. Keys to early diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis: Red flags from clinical, laboratory and imaging findings. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 1806–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nienhuis, H.L.; Bijzet, J.; Hazenberg, B.P. The Prevalence and Management of Systemic Amyloidosis in Western Countries. Kidney Dis. 2016, 2, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammos, A.; Meladinis, V.; Vovas, G.; Patsouras, D. Restrictive Cardiomyopathies: The Importance of Noninvasive Cardiac Imaging Modalities in Diagnosis and Treatment—A Systematic Review. Radiol. Res. Pract. 2017, 2017, 2874902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greulich, S.; Deluigi, C.C.; Gloekler, S.; Wahl, A.; Zürn, C.; Kramer, U.; Nothnagel, D.; Bültel, H.; Schumm, J.; Grün, S.; et al. CMR imaging predicts death and other adverse events in suspected cardiac sarcoidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre-Louis, B.; Prasad, A.; Frishman, W.H. Cardiac manifestations of sarcoidosis and therapeutic options. Cardiol. Rev. 2009, 17, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.; Selvanayagam, J.B. Echocardiography in Infiltrative Cardiomyopathy. Heart Lung Circ. 2019, 28, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtagh, G.; Laffin, L.J.; Beshai, J.F.; Maffessanti, F.; Bonham, C.A.; Patel, A.V.; Yu, Z.; Addetia, K.; Mor-Avi, V.; Moss, J.D.; et al. Prognosis of Myocardial Damage in Sarcoidosis Patients with Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction: Risk Stratification Using Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, e003738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, N.L.; Grogan, M.; Dec, G.W. Spectrum of Restrictive and Infiltrative Cardiomyopathies: Part 2 of a 2-Part Series. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1149–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seward, J.B.; Casaclang-Verzosa, G. Infiltrative cardiovascular diseases: Cardiomyopathies that look alike. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muchtar, E.; Blauwet, L.A.; Gertz, M.A. Restrictive Cardiomyopathy: Genetics, Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 819–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, G.; Bucciarelli-Ducci, C.; Caforio, A.L.P.; Cardim, N.; Charron, P.; Cosyns, B.; Dehaene, A.; Derumeaux, G.; Donal, E.; Dweck, M.R.; et al. Multimodality Imaging in Restrictive Cardiomyopathies: An EACVI expert consensus document In collaboration with the “Working Group on myocardial and pericardial diseases” of the European Society of Cardiology Endorsed by The Indian Academy of Echocardiography. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 18, 1090–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, R.H. Diagnosis and management of the cardiac amyloidoses. Circulation 2005, 112, 2047–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrini, M.; Cappelli, F.; Chacko, L.; Restrepo-Cordoba, M.A.; Lopez-Sainz, A.; Giannoni, A.; Aimo, A.; Baggiano, A.; Martinez-Naharro, A.; Whelan, C.; et al. Multiparametric Echocardiography Scores for the Diagnosis of Cardiac Amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Judson, M.A.; Donnino, R.; Gold, M.; Cooper, L.T., Jr.; Prystowsky, E.N.; Prystowsky, S. Cardiac sarcoidosis. Am. Heart J. 2009, 157, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumis, A.; Berdoukas, V.; Gotsis, E.; Aessopos, A. Comparison of echocardiographic (US) volumetry with cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging in transfusion dependent thalassemia major (TM). Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2007, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennell, D.J.; Udelson, J.E.; Arai, A.E.; Bozkurt, B.; Cohen, A.R.; Galanello, R.; Hoffman, T.M.; Kiernan, M.S.; Lerakis, S.; Piga, A.; et al. Cardiovascular function and treatment in β-thalassemia major: A consensus statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2013, 128, 281–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.S.; Elliott, P.; Comenzo, R.; Semigran, M.; Rapezzi, C. Addressing Common Questions Encountered in the Diagnosis and Management of Cardiac Amyloidosis. Circulation 2017, 135, 1357–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorbala, S.; Cuddy, S.; Falk, R.H. How to Image Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Practical Approach. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 1368–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, L.; Martone, R.; Cappelli, F.; Fontana, M. Cardiac Amyloidosis: Updates in Imaging. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2019, 21, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmann, R.; Mankad, S.V.; Mankad, R. Echocardiography in Sarcoidosis. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2018, 20, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyala, U.S.; Nair, A.P.; Padilla, M.L. Cardiac sarcoidosis. Clin. Chest Med. 2008, 29, 493–508, ix. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez-López, C.; Comín-Colet, J.; González-Costello, J. Iron overload cardiomyopathy: From diagnosis to management. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2018, 33, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozwadowska, K.; Raczak, G.; Sikorska, K.; Fijałkowski, M.; Kozłowski, D.; Daniłowicz-Szymanowicz, L. Influence of hereditary haemochromatosis on left ventricular wall thickness: Does iron overload exacerbate cardiac hypertrophy? Folia Morphol. 2019, 78, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.L.; Hatle, L.K.; Taliercio, C.P.; Oh, J.K.; Kyle, R.A.; Gertz, M.A.; Bailey, K.R.; Seward, J.B.; Tajik, A.J. Prognostic significance of Doppler measures of diastolic function in cardiac amyloidosis. A Doppler echocardiography study. Circulation 1991, 83, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Edwards, W.D.; Oh, J.K.; Chandrasekaran, K.; Grogan, M.; Martinez, M.W.; Syed, I.S.; Hughes, D.A.; Lust, J.A.; Jaffe, A.S.; et al. Intracardiac thrombosis and embolism in patients with cardiac amyloidosis. Circulation 2007, 116, 2420–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nunzio, D.; Recupero, A.; de Gregorio, C.; Zito, C.; Carerj, S.; Di Bella, G. Echocardiographic Findings in Cardiac Amyloidosis: Inside Two-Dimensional, Doppler, and Strain Imaging. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2019, 21, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakou, P.; Mouselimis, D.; Tsarouchas, A.; Rigopoulos, A.; Bakogiannis, C.; Noutsias, M.; Vassilikos, V. Diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis: A systematic review on the role of imaging and biomarkers. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2018, 18, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiano-Lomoriello, V.; Galderisi, M.; Mele, D.; Esposito, R.; Cerciello, G.; Buonauro, A.; Della Pepa, R.; Picardi, M.; Catalano, L.; Trimarco, B.; et al. Longitudinal strain of left ventricular basal segments and E/e’ ratio differentiate primary cardiac amyloidosis at presentation from hypertensive hypertrophy: An automated function imaging study. Echocardiography 2016, 33, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tei, C.; Dujardin, K.S.; Hodge, D.O.; Kyle, R.A.; Tajik, A.J.; Seward, J.B. Doppler index combining systolic and diastolic myocardial performance: Clinical value in cardiac amyloidosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1996, 28, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, D.H.; Nery, P.B.; Ha, A.C.; Beanlands, R.S. Cardiac Sarcoidosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazaki, Y.; Isobe, M.; Hiroe, M.; Morimoto, S.; Hiramitsu, S.; Nakano, T.; Izumi, T.; Sekiguchi, M. Prognostic determinants of long-term survival in Japanese patients with cardiac sarcoidosis treated with prednisone. Am. J. Cardiol. 2001, 88, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremastinos, D.T.; Farmakis, D. Iron overload cardiomyopathy in clinical practice. Circulation 2011, 124, 2253–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, Y.M.; Cuddy, S.; Falk, R.H.; Dorbala, S. Multimodality Imaging in the Evaluation and Management of Cardiac Amyloidosis. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2020, 50, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodez, D.; Ternacle, J.; Guellich, A.; Galat, A.; Lim, P.; Radu, C.; Guendouz, S.; Bergoend, E.; Couetil, J.P.; Hittinger, L.; et al. Prognostic value of right ventricular systolic function in cardiac amyloidosis. Amyloid 2016, 23, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicco, S.; Solimando, A.G.; Buono, R.; Susca, N.; Inglese, G.; Melaccio, A.; Prete, M.; Ria, R.; Racanelli, V.; Vacca, A. Right heart changes impact on clinical phenotype of amyloid cardiac involvement: A single centre study. Life 2020, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvidsson, S.; Henein, M.Y.; Wikström, G.; Suhr, O.B.; Lindqvist, P. Right ventricular involvement in transthyretin amyloidosis. Amyloid 2018, 25, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedema, J.P.; van Geuns, R.J.; Ainslie, G.; Ector, J.; Heidbuchel, H.; Crijns, H. Right ventricular involvement in cardiac sarcoidosis demonstrated with cardiac magnetic resonance. ESC Heart Fail. 2017, 4, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.B.; Mor-Avi, V.; Murtagh, G.; Bonham, C.A.; Laffin, L.J.; Hogarth, D.K.; Medvedofsky, D.; Lang, R.M.; Patel, A.R. Right Heart Involvement in Patients with Sarcoidosis. Echocardiography 2016, 33, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huitema, M.P.; Grutters, J.C.; Rensing, B.; Reesink, H.J.; Post, M.C. Pulmonary hypertension complicating pulmonary sarcoidosis. Neth. Heart J. 2016, 24, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Philips, B.; Madhavan, S.; James, C.A.; Riele, A.S.T.; Murray, B.; Tichnell, C.; Bhonsale, A.; Nazarian, S.; Judge, D.P.; Calkins, H.; et al. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy and cardiac sarcoidosis: Distinguishing features when the diagnosis is unclear. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2014, 7, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velangi, P.S.; Chen, K.A.; Kazmirczak, F.; Okasha, O.; von Wald, L.; Roukoz, H.; Farzaneh-Far, A.; Markowitz, J.; Nijjar, P.S.; Bhargava, M.; et al. Right Ventricular Abnormalities on Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Sarcoidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagioka, Y.; Yasuda, M.; Okune, M.; Kakehi, K.; Kawamura, T.; Kobuke, K.; Miyazaki, S.; Iwanaga, Y. Right ventricular involvement is an important prognostic factor and risk stratification tool in suspected cardiac sarcoidosis: Analysis by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2020, 109, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Tian, Z.; Fang, Q. Risk Factors and Prognostic Role of Left Atrial Enlargement in Patients with Cardiac Light-Chain Amyloidosis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 351, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, R.H.; Plehn, J.F.; Deering, T.; Schick, E.C., Jr.; Boinay, P.; Rubinow, A.; Skinner, M.; Cohen, A.S. Sensitivity and specificity of the echocardiographic features of cardiac amyloidosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 1987, 59, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurcuţ, R.; Onciul, S.; Adam, R.; Stan, C.; Coriu, D.; Rapezzi, C.; Popescu, B.A. Multimodality imaging in cardiac amyloidosis: A primer for cardiologists. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 21, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohty, D.; Pradel, S.; Magne, J.; Fadel, B.; Boulogne, C.; Petitalot, V.; Raboukhi, S.; Darodes, N.; Damy, T.; Aboyans, V.; et al. Prevalence and prognostic impact of left-sided valve thickening in systemic light-chain amyloidosis. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2017, 106, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damy, T.; Jaccard, A.; Guellich, A.; Lavergne, D.; Galat, A.; Deux, J.F.; Hittinger, L.; Dupuis, J.; Frenkel, V.; Rigaud, C.; et al. Identification of prognostic markers in transthyretin and AL cardiac amyloidosis. Amyloid 2016, 23, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escher, F.; Senoner, M.; Doerler, J.; Zaruba, M.M.; Messner, M.; Mussner-Seeber, C.; Ebert, M.; Ensinger, C.; Mair, A.; Kroiss, A.; et al. When and how do patients with cardiac amyloidosis die? Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2020, 109, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Garcia, J.I.; Shaikh, S.J.; Villacis-Nunez, D.S.; Gurram, M.K. Pericardial Effusion in Systemic Sarcoidosis: A Rare Manifestation of Cardiac Sarcoid. Hear. Views 2019, 20, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarta, C.C.; Solomon, S.D.; Uraizee, I.; Kruger, J.; Longhi, S.; Ferlito, M.; Gagliardi, C.; Milandri, A.; Rapezzi, C.; Falk, R.H. Left ventricular structure and function in transthyretin-related versus light-chain cardiac amyloidosis. Circulation 2014, 129, 1840–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagourelias, E.D.; Duchenne, J.; Mirea, O.; Vovas, G.; Van Cleemput, J.; Delforge, M.; Kuznetsova, T.; Bogaert, J.; Voigt, J.U. The Relation of Ejection Fraction and Global Longitudinal Strain in Amyloidosis: Implications for Differential Diagnosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, 1358–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, N.M.; White, J.A.; Jimenez-Zepeda, V.; Howlett, J.G. Determinants and prognostic significance of serial right heart function changes in patients with cardiac amyloidosis. Can. J. Cardiol. 2020, 36, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausch, K.; Scalia, G.M.; Sato, K.; Edwards, N.; Lam, A.K.; Platts, D.G.; Chan, J. Left atrial strain imaging differentiates cardiac amyloidosis and hypertensive heart disease. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nochioka, K.; Quarta, C.C.; Claggett, B.; Roca, G.Q.; Rapezzi, C.; Falk, R.H.; Solomon, S.D. Left atrial structure and function in cardiac amyloidosis. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 18, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohty, D.; Petitalot, V.; Magne, J.; Fadel, B.M.; Boulogne, C.; Rouabhia, D.; ElHamel, C.; Lavergne, D.; Damy, T.; Aboyans, V.; et al. Left atrial function in patients with light chain amyloidosis: A transthoracic 3D speckle tracking imaging study. J. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, C.; Bruno, G.; Arciniegas Calle, M.C.; Acharya, G.A.; Fussner, L.M.; Ungprasert, P.; Cooper, L.T., Jr.; Blauwet, L.A.; Ryu, J.H.; Pellikka, P.A.; et al. Diagnostic and predictive value of speckle tracking echocardiography in cardiac sarcoidosis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusunose, K.; Fujiwara, M.; Yamada, H.; Nishio, S.; Saijo, Y.; Yamada, N.; Hirata, Y.; Torii, Y.; Ise, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; et al. Deterioration of biventricular strain is an early marker of cardiac involvement in confirmed sarcoidosis. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 21, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barssoum, K.; Altibi, A.M.; Rai, D.; Kumar, A.; Kharsa, A.; Chowdhury, M.; Thakkar, S.; Shahid, S.; Abdelazeem, M.; Abuzaid, A.S.; et al. Speckle tracking echocardiography can predict subclinical myocardial involvement in patients with sarcoidosis: A meta-analysis. Echocardiography 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orii, M.; Hirata, K.; Tanimoto, T.; Shiono, Y.; Shimamura, K.; Yamano, T.; Ino, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kubo, T.; Tanaka, A.; et al. Myocardial Damage Detected by Two-Dimensional Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography in Patients with Extracardiac Sarcoidosis: Comparison with Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palka, P.; Lange, A.; Atherton, J.; Stafford, W.J.; Burstow, D.J. Biventricular diastolic behaviour in patients with hypertrophic and hereditary hemochromatosis cardiomyopathies. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2004, 5, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shizukuda, Y.; Bolan, C.D.; Tripodi, D.J.; Sachdev, V.; Nguyen, T.T.; Botello, G.; Yau, Y.Y.; Sidenko, S.; Inez, E.; Ali, M.I.; et al. Does oxidative stress modulate left ventricular diastolic function in asymptomatic subjects with hereditary hemochromatosis? Echocardiography 2009, 26, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozwadowska, K.; Daniłowicz-Szymanowicz, L.; Fijałkowski, M.; Sikorska, K.; Gałąska, R.; Kozłowski, D.; Gruchała, M.; Raczak, G. Can two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography be useful for left ventricular assessment in the early stages of hereditary haemochromatosis? Echocardiography 2018, 35, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, D.; Walsh, J.P.; Daly, C.; McKiernan, S.; Norris, S.; Murphy, R.T.; King, G. Improvements in cardiac function detected using echocardiography in patients with hereditary haemochromatosis. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 189, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, S.; Kidoh, M.; Nagayama, Y.; Takashio, S.; Usuku, H.; Ueda, M.; Yamashita, T.; Ando, Y.; Tsujita, K.; Yamashita, Y. Trends in Diagnostic Imaging of Cardiac Amyloidosis: Emerging Knowledge and Concepts. Radiographics 2020, 40, 961–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treibel, T.A.; Bandula, S.; Fontana, M.; White, S.K.; Gilbertson, J.A.; Herrey, A.S.; Gillmore, J.D.; Punwani, S.; Hawkins, P.N.; Taylor, S.A.; et al. Extracellular volume quantification by dynamic equilibrium cardiac computed tomography in cardiac amyloidosis. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2015, 9, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternacle, J.; Krapf, L.; Mohty, D.; Magne, J.; Nguyen, A.; Galat, A.; Gallet, R.; Teiger, E.; Côté, N.; Clavel, M.A.; et al. Aortic Stenosis and Cardiac Amyloidosis: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 2638–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, S.; Takashio, S.; Nagamatsu, S.; Yamashita, T.; Uchimura, R.; Kidoh, M.; Utsunomiya, D.; Nakaura, T.; Tsujita, K.; Yamashita, Y. Myocardial extracellular volume quantification using CT for the identification of occult cardiac amyloidosis in patients with severe aortic stenosis referred for transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Amyloid 2019, 26, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, P.; Basset, M.; Russo, F.; Foli, A.; Palladini, G.; Merlini, G. The lung in amyloidosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, F.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Kha, L.C.; Jimenez-Juan, L.; Cool, C.; Vargas, D.; Oikonomou, A. Pathological entities that may affect the lungs and the myocardium. Evaluation with chest CT and cardiac MR. Clin. Imaging 2020, 70, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondi, P.M.; Lisker, J.; Rini, J.N.; Vitkovski, T.; Rahmani, N.; Kuvin, J.T.; Saba, S.G. Myocardial hypoattenuation in cardiac sarcoidosis: CT correlation with CMR, PET and SPECT. Clin. Imaging 2020, 67, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, A.; Lee, T.Y.; Tzemos, N. Myocardial Perfusion and Scar Assessment in Cardiac Sarcoidosis With Functional Computed Tomography Imaging. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, e010046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosyns, B.; Plein, S.; Nihoyanopoulos, P.; Smiseth, O.; Achenbach, S.; Andrade, M.J.; Pepi, M.; Ristic, A.; Imazio, M.; Paelinck, B.; et al. European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI) position paper: Multimodality imaging in pericardial disease. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 16, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, M.; Pica, S.; Reant, P.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Treibel, T.A.; Banypersad, S.M.; Maestrini, V.; Barcella, W.; Rosmini, S.; Bulluck, H.; et al. Prognostic Value of Late Gadolinium Enhancement Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Cardiac Amyloidosis. Circulation 2015, 132, 1570–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamitsos, T.D.; Piechnik, S.K.; Banypersad, S.M.; Fontana, M.; Ntusi, N.B.; Ferreira, V.M.; Whelan, C.J.; Myerson, S.G.; Robson, M.D.; Hawkins, P.N.; et al. Noncontrast T1 mapping for the diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapezzi, C.; Arbustini, E.; Caforio, A.L.; Charron, P.; Gimeno-Blanes, J.; Heliö, T.; Linhart, A.; Mogensen, J.; Pinto, Y.; Ristic, A.; et al. Diagnostic work-up in cardiomyopathies: Bridging the gap between clinical phenotypes and final diagnosis. A position statement from the ESC Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 1448–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhao, S.; Jiang, S.; Lu, M.; Yan, C.; Ling, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ma, N.; Yin, G.; et al. The relative atrial volume ratio and late gadolinium enhancement provide additive information to differentiate constrictive pericarditis from restrictive cardiomyopathy. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2011, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muehlberg, F.; Toepper, A.; Fritschi, S.; Prothmann, M.; Schulz-Menger, J. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Applications on Infiltrative Cardiomyopathies. J. Thorac. Imaging 2016, 31, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boynton, S.J.; Geske, J.B.; Dispenzieri, A.; Syed, I.S.; Hanson, T.J.; Grogan, M.; Araoz, P.A. LGE Provides Incremental Prognostic Information Over Serum Biomarkers in AL Cardiac Amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Naharro, A.; Treibel, T.A.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Bulluck, H.; Zumbo, G.; Knight, D.S.; Kotecha, T.; Francis, R.; Hutt, D.F.; Rezk, T.; et al. Magnetic Resonance in Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, D.S.; Zumbo, G.; Barcella, W.; Steeden, J.A.; Muthurangu, V.; Martinez-Naharro, A.; Treibel, T.A.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Bulluck, H.; Kotecha, T.; et al. Cardiac Structural and Functional Consequences of Amyloid Deposition by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance and Echocardiography and Their Prognostic Roles. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, G.; Minutoli, F.; Mazzeo, A.; Vita, G.; Oreto, G.; Carerj, S.; Anfuso, C.; Russo, M.; Gaeta, M. MRI of cardiac involvement in transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, W394–W399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, S.; Lensing, S.Y.; Nairooz, R.S.; Pothineni, N.V.; Hakeem, A.; Bhatti, S.; Pandey, T. Prognostic Value of Late Gadolinium Enhancement CMR in Systemic Amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungu, J.N.; Valencia, O.; Pinney, J.H.; Gibbs, S.D.; Rowczenio, D.; Gilbertson, J.A.; Lachmann, H.J.; Wechalekar, A.; Gillmore, J.D.; Whelan, C.J.; et al. CMR-based differentiation of AL and ATTR cardiac amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banypersad, S.M.; Fontana, M.; Maestrini, V.; Sado, D.M.; Captur, G.; Petrie, A.; Piechnik, S.K.; Whelan, C.J.; Herrey, A.S.; Gillmore, J.D.; et al. T1 mapping and survival in systemic light-chain amyloidosis. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Naharro, A.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Treibel, T.A.; Zumbo, G.; Knight, D.S.; Rosmini, S.; Lane, T.; Mahmood, S.; Sachchithanantham, S.; Whelan, C.J.; et al. CMR-Verified Regression of Cardiac AL Amyloid After Chemotherapy. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, M.; Banypersad, S.M.; Treibel, T.A.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Maestrini, V.; Lane, T.; Gilbertson, J.A.; Hutt, D.F.; Lachmann, H.J.; Whelan, C.J.; et al. Differential Myocyte Responses in Patients with Cardiac Transthyretin Amyloidosis and Light-Chain Amyloidosis: A Cardiac MR Imaging Study. Radiology 2015, 277, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, T.; Martinez-Naharro, A.; Treibel, T.A.; Francis, R.; Nordin, S.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Knight, D.S.; Zumbo, G.; Rosmini, S.; Maestrini, V.; et al. Myocardial Edema and Prognosis in Amyloidosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2919–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.R.; Cawley, P.J.; Heitner, J.F.; Klem, I.; Parker, M.A.; Jaroudi, W.A.; Meine, T.J.; White, J.B.; Elliott, M.D.; Kim, H.W.; et al. Detection of myocardial damage in patients with sarcoidosis. Circulation 2009, 120, 1969–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, R.; Trivieri, M.; Fayad, Z.A.; Ahmadi, A.; Narula, J.; Argulian, E. Advanced Imaging in Cardiac Sarcoidosis. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puntmann, V.O.; Isted, A.; Hinojar, R.; Foote, L.; Carr-White, G.; Nagel, E. T1 and T2 Mapping in Recognition of Early Cardiac Involvement in Systemic Sarcoidosis. Radiology 2017, 285, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, D.H.; Sauer, W.H.; Bogun, F.; Cooper, J.M.; Culver, D.A.; Duvernoy, C.S.; Judson, M.A.; Kron, J.; Mehta, D.; Cosedis Nielsen, J.; et al. HRS expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and management of arrhythmias associated with cardiac sarcoidosis. Heart Rhythm 2014, 11, 1305–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouranos, V.; Tzelepis, G.E.; Rapti, A.; Mavrogeni, S.; Aggeli, K.; Douskou, M.; Prasad, S.; Koulouris, N.; Sfikakis, P.; Wells, A.; et al. Complementary Role of CMR to Conventional Screening in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cardiac Sarcoidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, I.E.; Garcia, M.J.; Taub, C.C. Multimodality Imaging in Cardiac Sarcoidosis: Is There a Winner? Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2016, 12, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, A.; Pawar, S.; Govender, P.; Berman, J.; Ruberg, F.L.; Miller, E.J. The response of FDG uptake to immunosuppressive treatment on FDG PET/CT imaging for cardiac sarcoidosis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2017, 24, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.S.; Bokhari, S.; Damy, T.; Dorbala, S.; Drachman, B.M.; Fontana, M.; Grogan, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Lousada, I.; Nativi-Nicolau, J.; et al. Expert Consensus Recommendations for the Suspicion and Diagnosis of Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis. Circ. Heart Fail. 2019, 12, e006075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljaroudi, W.A.; Desai, M.Y.; Tang, W.H.; Phelan, D.; Cerqueira, M.D.; Jaber, W.A. Role of imaging in the diagnosis and management of patients with cardiac amyloidosis: State of the art review and focus on emerging nuclear techniques. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2014, 21, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperry, B.W.; Reyes, B.A.; Ikram, A.; Donnelly, J.P.; Phelan, D.; Jaber, W.A.; Shapiro, D.; Evans, P.J.; Maschke, S.; Kilpatrick, S.E.; et al. Tenosynovial and Cardiac Amyloidosis in Patients Undergoing Carpal Tunnel Release. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2040–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhi, S.; Guidalotti, P.L.; Quarta, C.C.; Gagliardi, C.; Milandri, A.; Lorenzini, M.; Potena, L.; Leone, O.; Bartolomei, I.; Pastorelli, F.; et al. Identification of TTR-related subclinical amyloidosis with 99mTc-DPD scintigraphy. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 531–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed-Salem, L.; Santos-Mateo, J.J.; Sanchez-Serna, J.; Hernández-Vicente, Á.; Reyes-Marle, R.; Castellón Sánchez, M.I.; Claver-Valderas, M.A.; Gonzalez-Vioque, E.; Haro-Del Moral, F.J.; García-Pavía, P.; et al. Prevalence of wild type ATTR assessed as myocardial uptake in bone scan in the elderly population. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 270, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhari, S.; Shahzad, R.; Castaño, A.; Maurer, M.S. Nuclear imaging modalities for cardiac amyloidosis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2014, 21, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano, A.; Haq, M.; Narotsky, D.L.; Goldsmith, J.; Weinberg, R.L.; Morgenstern, R.; Pozniakoff, T.; Ruberg, F.L.; Miller, E.J.; Berk, J.L.; et al. Multicenter Study of Planar Technetium 99m Pyrophosphate Cardiac Imaging: Predicting Survival for Patients With ATTR Cardiac Amyloidosis. JAMA Cardiol. 2016, 1, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillmore, J.D.; Maurer, M.S.; Falk, R.H.; Merlini, G.; Damy, T.; Dispenzieri, A.; Wechalekar, A.D.; Berk, J.L.; Quarta, C.C.; Grogan, M.; et al. Nonbiopsy Diagnosis of Cardiac Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Circulation 2016, 133, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Yokochi, T. Transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis: An update on diagnosis and treatment. ESC Heart Fail. 2019, 6, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorbala, S.; Vangala, D.; Semer, J.; Strader, C.; Bruyere, J.R., Jr.; Di Carli, M.F.; Moore, S.C.; Falk, R.H. Imaging cardiac amyloidosis: A pilot study using ¹⁸F-florbetapir positron emission tomography. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 1652–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, D.R.; Acuff, S.N.; Stuckey, A.; Wall, J.S. A Routine PET/CT Protocol with Streamlined Calculations for Assessing Cardiac Amyloidosis Using (18)F-Florbetapir. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2015, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, W.P.; Wang, W.Y.; Moore, P.T.; Mollee, P.N.; Ng, A.C. Cardiac Amyloid Imaging with 18F-Florbetaben PET: A Pilot Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijsers, R.G.; Grutters, J.C.; Thomeer, M.; Du Bois, R.M.; Van Buul, M.M.; Lavalaye, J.; Van Den Bosch, J.M.; Verzijlbergen, F.J. Imaging the inflammatory activity of sarcoidosis: Sensitivity and inter observer agreement of (67)Ga imaging and (18)F-FDG PET. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 55, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, G.; Leung, E.; Mylonas, I.; Nery, P.; Williams, K.; Wisenberg, G.; Gulenchyn, K.Y.; Dekemp, R.A.; Dasilva, J.; Birnie, D.; et al. The use of 18F-FDG PET in the diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis including the Ontario experience. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Wang, J.T.; Wang, L.; Le, K.; Huang, Y.; Hickey, A.J.; Emmett, L. Impact of Patient Preparation on the Diagnostic Performance of 18F-FDG PET in Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2016, 41, e327–e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, M.T.; Hulten, E.A.; Singh, A.; Waller, A.H.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Stewart, G.C.; Hainer, J.; Murthy, V.L.; Skali, H.; Dorbala, S.; et al. Reduction in ¹⁸F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake on serial cardiac positron emission tomography is associated with improved left ventricular ejection fraction in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2014, 21, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohira, H.; Birnie, D.H.; Pena, E.; Bernick, J.; Mc Ardle, B.; Leung, E.; Wells, G.A.; Yoshinaga, K.; Tsujino, I.; Sato, T.; et al. Comparison of (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG PET) and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) in corticosteroid-naive patients with conduction system disease due to cardiac sarcoidosis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante, J.R.; Moreno, M.; Rayo, J.I.; Serrano, J.; Dominguez, M.L.; Garcia, L. High liver FDG uptake on PET/CT in patient with lymphoma diagnosed with hereditary hemochromatosis. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2015, 40, 538–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Minamimoto, R.; Morooka, M.; Kubota, K. A case of secondary hemochromatosis with high uptake of liver in F-18 FDG PET/CT imaging. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2011, 36, 606–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinney, J.H.; Whelan, C.J.; Petrie, A.; Dungu, J.; Banypersad, S.M.; Sattianayagam, P.; Wechalekar, A.; Gibbs, S.D.; Venner, C.P.; Wassef, N.; et al. Senile systemic amyloidosis: Clinical features at presentation and outcome. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e000098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownrigg, J.; Lorenzini, M.; Lumley, M.; Elliott, P. Diagnostic performance of imaging investigations in detecting and differentiating cardiac amyloidosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. ESC Heart Fail. 2019, 6, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertz, M.A.; Dispenzieri, A. Systemic Amyloidosis Recognition, Prognosis, and Therapy: A Systematic Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittleson, M.M.; Maurer, M.S.; Ambardekar, A.V.; Bullock-Palmer, R.P.; Chang, P.P.; Eisen, H.J.; Nair, A.P.; Nativi-Nicolau, J.; Ruberg, F.L. Cardiac Amyloidosis: Evolving Diagnosis and Management: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 142, e7–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, N.R.; Rissing, S.M.; Smith, J.; Jung, J.; Benson, M.D. Inotersen therapy of transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy. Amyloid 2020, 27, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yafasova, A.; Fosbøl, E.L.; Schou, M.; Gustafsson, F.; Rossing, K.; Bundgaard, H.; Lauridsen, M.D.; Kristensen, S.L.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Gislason, G.H.; et al. Long-Term Adverse Cardiac Outcomes in Patients With Sarcoidosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, D.; Lubitz, S.A.; Frankel, Z.; Wisnivesky, J.P.; Einstein, A.J.; Goldman, M.; Machac, J.; Teirstein, A. Cardiac involvement in patients with sarcoidosis: Diagnostic and prognostic value of outpatient testing. Chest 2008, 133, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, D.H.; Kandolin, R.; Nery, P.B.; Kupari, M. Cardiac manifestations of sarcoidosis: Diagnosis and management. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2663–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, H.; Sarai, M.; Kato, Y.; Naruse, H.; Watanabe, A.; Matsuyama, T.; Takahashi, H.; Motoyama, S.; Ishii, J.; Morimoto, S.I.; et al. Diagnosis of isolated cardiac sarcoidosis based on new guidelines. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 2662–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro Neto, M.L.; Jellis, C.; Hachamovitch, R.; Wimer, A.; Highland, K.B.; Sahoo, D.; Khabbaza, J.E.; Pande, A.; Bindra, A.; Southern, B.D.; et al. Performance of diagnostic criteria in patients clinically judged to have cardiac sarcoidosis: Is it time to regroup? Am. Heart J. 2020, 223, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacoub, P.; Chapelon-Abric, C.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Saadoun, D.; Desbois, A.C.; Biard, L. Cardiac sarcoidosis: A long term follow up study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederau, C.; Fischer, R.; Pürschel, A.; Stremmel, W.; Häussinger, D.; Strohmeyer, G. Long-term survival in patients with hereditary hemochromatosis. Gastroenterology 1996, 110, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
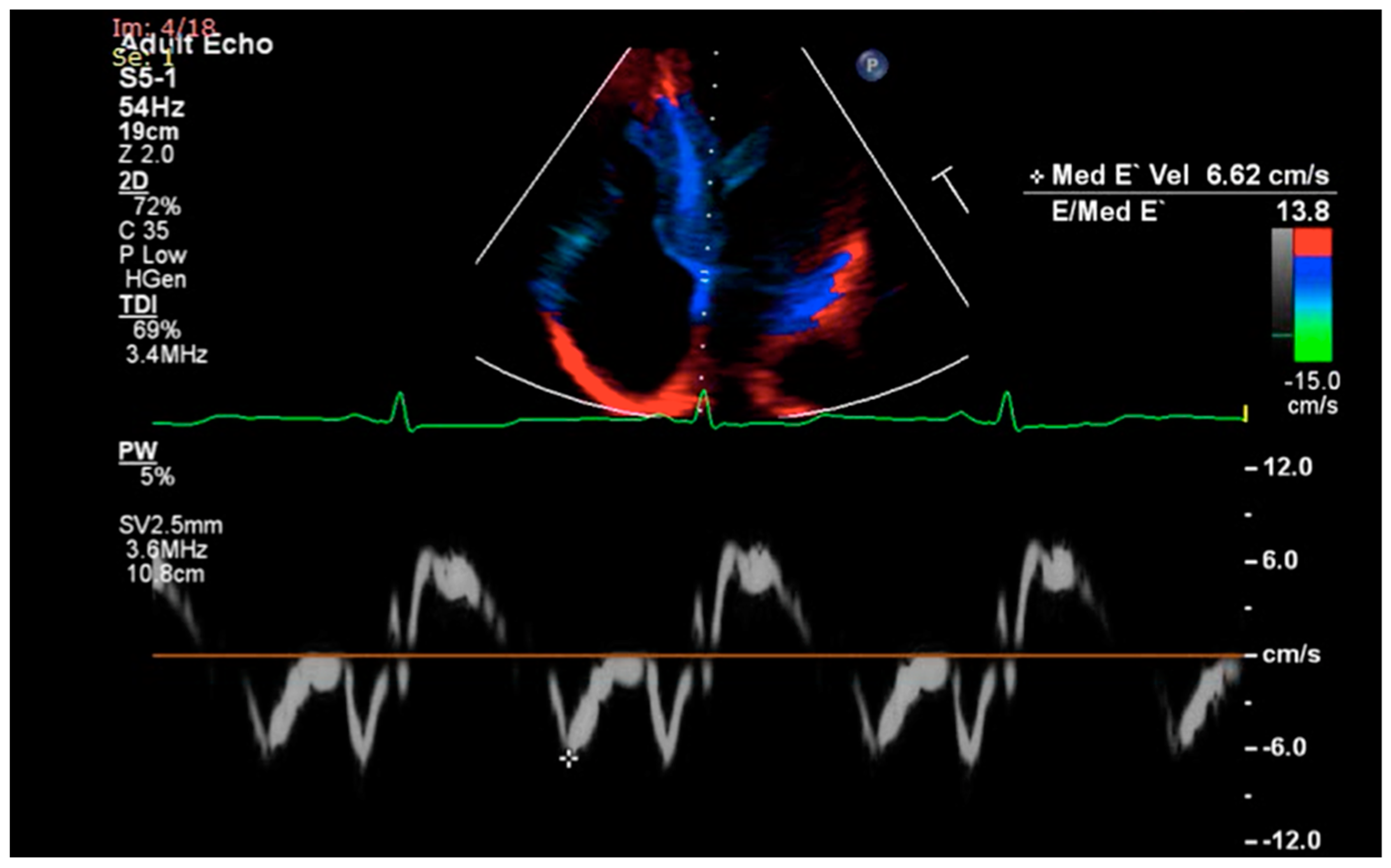

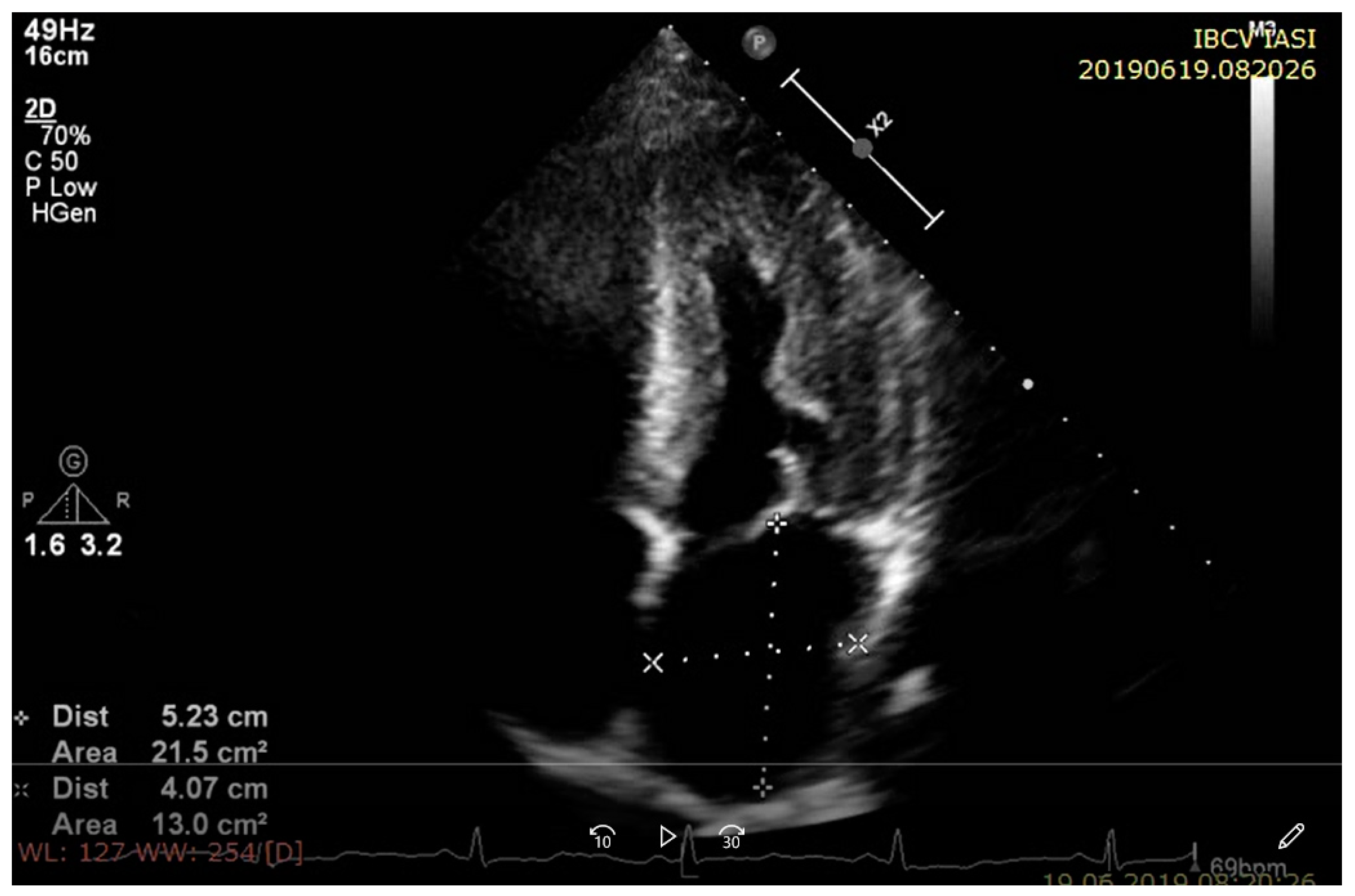
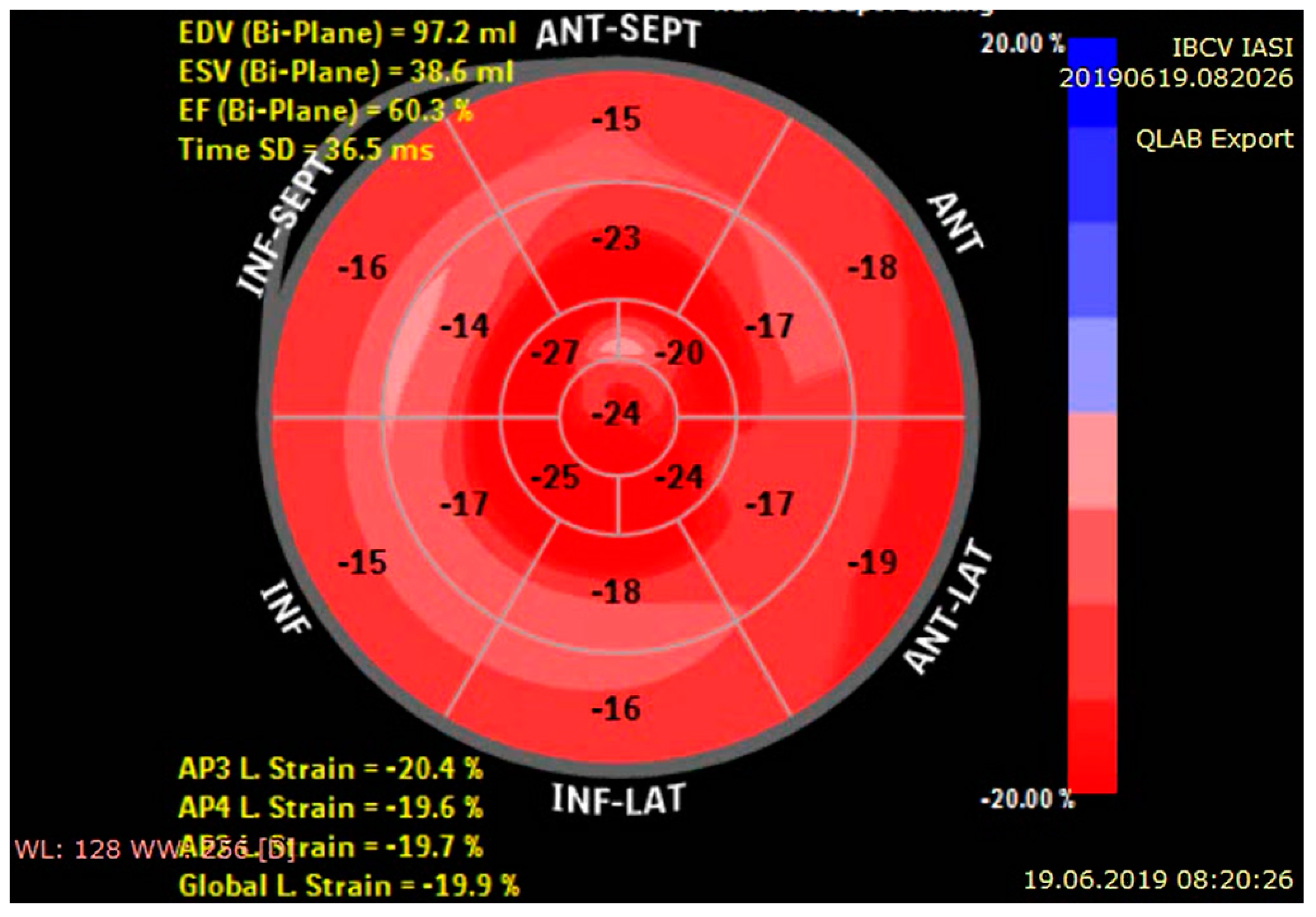
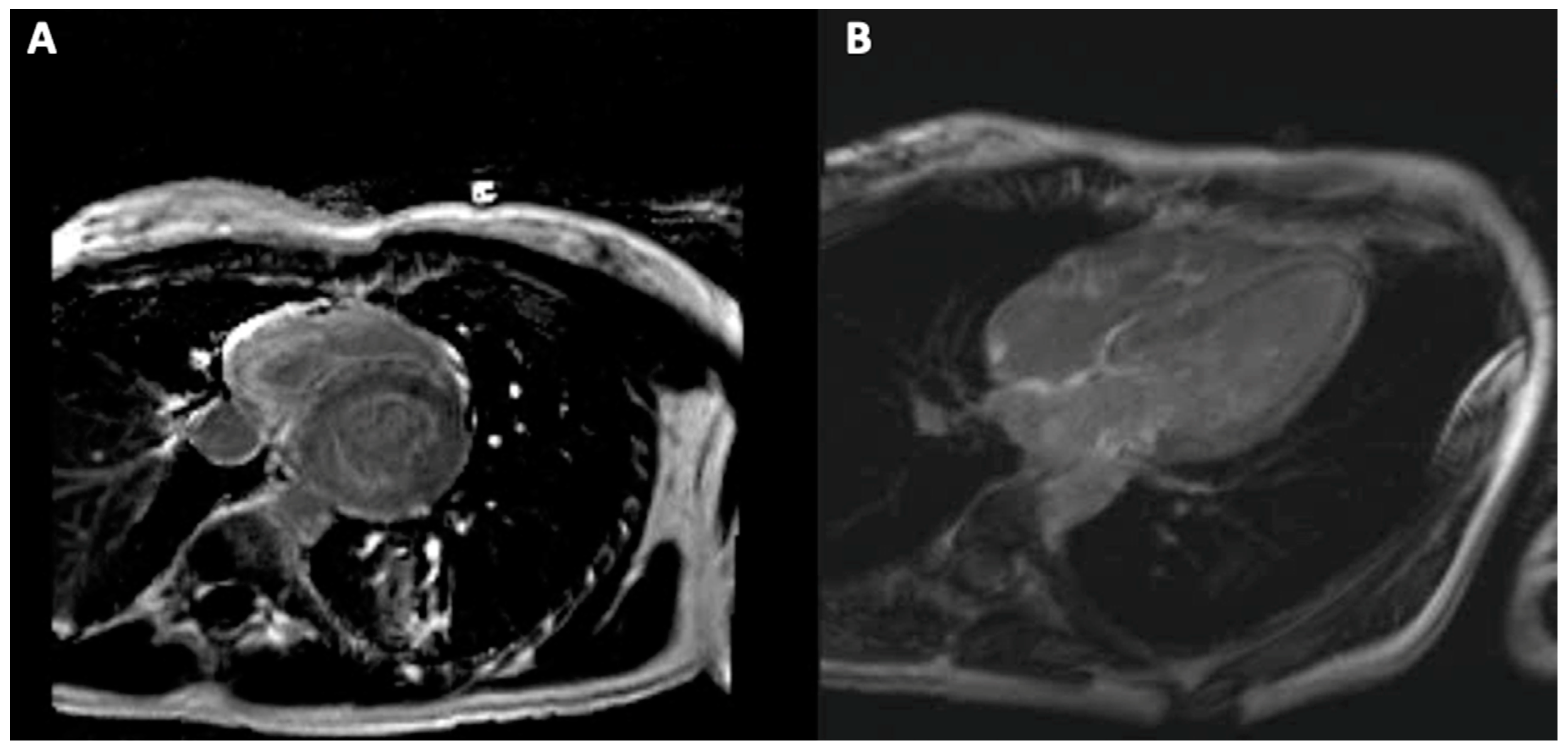
| Multimo-dality Imaging | Cardiac Amyloidosis | Sarcoidosis | Hemochromatosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Echocardio-graphy | Strength: widely available, LVH with bull’s eye pattern on strain imaging is a well-known red flag for CA. Weakness: lack of sensitivity and specificity. | Strength: first imaging screening method for CS. Weakness: lack of sensitivity in identifying early cardiac involvement and high variability of echocardiographic findings. | Strength: useful in screening and regular follow-up. Weakness: second-line imaging method, after CMR for the evaluation of cardiac hemochromatosis. |
| Cardiac magnetic resonance | Strength: able to establish the diagnosis of CA. Weakness: not capable of distinguishing between ATTR and AL amyloidosis. | Strength: allows an early identification of active inflammation and myocardial scarring. Weakness: there is no distinctive feature of CS on CMR. | Strength: CMR imaging (particularly T2 relaxation times) is the method of choice for assessing cardiac hemochromatosis, evaluating myocardial fibrosis and edema. Weakness: risk of gadolinium toxicity. |
| Computed tomography | Strength: enables myocardial characterization via LIE imaging as well as cardiac amyloid burden assessment via ECV quantification. Weakness: use of ionizing radiation and iodinated contrast. | Strength: useful in recognizing both cardiac and lung involvement, especially in subjects with metallic implants. Weakness: radiation-related risk and complications. | Strength: limited literature information available; might help evaluate cardiac function. Weakness: radiation exposure; provides static images, precluding dynamic analyses of left ventricular hemodynamics, filing or relaxation. |
| Nuclear imaging | Strength: useful in diagnosing ATTR cardiomyopathy beginning with early stages, eliminating the need of histological confirmation. Weakness: its diagnostic accuracy highly depends on the used radiotracers. | Strength: useful in monitoring disease activity and response to immunosuppressive therapy as well as in guiding biopsy. Weakness: less specific than CMR imaging, being recommended in subjects with contraindications to CMR. | No evidence available regarding the role of nuclear imaging in diagnosing, guiding therapy or monitoring disease evolution in cardiac hemochromatosis. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sascău, R.; Anghel, L.; Clement, A.; Bostan, M.; Radu, R.; Stătescu, C. The Importance of Multimodality Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Patients with Infiltrative Cardiomyopathies: An Update. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020256
Sascău R, Anghel L, Clement A, Bostan M, Radu R, Stătescu C. The Importance of Multimodality Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Patients with Infiltrative Cardiomyopathies: An Update. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(2):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020256
Chicago/Turabian StyleSascău, Radu, Larisa Anghel, Alexandra Clement, Mădălina Bostan, Rodica Radu, and Cristian Stătescu. 2021. "The Importance of Multimodality Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Patients with Infiltrative Cardiomyopathies: An Update" Diagnostics 11, no. 2: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020256
APA StyleSascău, R., Anghel, L., Clement, A., Bostan, M., Radu, R., & Stătescu, C. (2021). The Importance of Multimodality Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Patients with Infiltrative Cardiomyopathies: An Update. Diagnostics, 11(2), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020256








